1. Introduction
Familial Mediterranean fever (FMF) is a genetically determined autoinflammatory disease transmitted by an autosomal recessive mechanism. The cause of the nosology is point mutations of the
MEFV (Mediterranean FeVer) gene coding for pyrin protein. The
MEFV gene is located on the short arm of the 16th chromosome (16p13.3) and is composed of 10 exons. Most pathogenic mutations of the
MEFV gene are located in exons 2, 3, 5 and 10 with about 85% of those located in the 2
nd and 10
th exons [
1,
2]. According to the current data, more than 300 mutations have been registered [
3]. Despite being considered as an autosomal recessive disorder, there are some clinical cases with the involvement of only one
MEFV heterozygous mutation and even those with any apparent
MEFV mutation [
4,
5].
Pyrin is a regulator of inflammation and mainly expressed in the cells of the innate immune system, namely, granulocytes, eosinophils, monocytes, dendritic cells, and synovial fibroblasts [
2]. Several alternatively spliced transcripts of pyrin encoding
MEFV gene have been identified. While some transcripts (FL, 2a, 2D, 8ext, 9ext) can produce different functional isoforms of
MEFV, others are degraded by nonsense-mediated decay [
6]. The first described alternatively spliced isoform, namely MEFV-d2, is lacking exon 2 and found in a higher ratio compared to the full-length MEFV isoform (MEFV-f l) in mononuclear cells than polymorphonuclear cells [
7]. The full-length isoform actually represents the sum of MEFV-d2 and MEFV-f l isoforms [
8]. In monocytes, the expression of
MEFV is variable and upregulated by proinflammatory cytokines, interferon-γ (IFN-γ), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and interleukin 1 (IL-1) [
9].
The
MEFV gene mutations might lead to changes in pyrin activity, altering various reactions of innate and adaptive immunity [
10]. Thus, several lines of evidence suggested also impact on inflammasome activity [
11]. Inflammasomes are molecular platforms responsible for the activation of caspase-1, a cysteine protease mediating proteolytic processing and activation of the proinflammatory cytokines IL-1β and IL-18 [
11,
12,
13]. Usually, inflammasomes are formed as result of oligomerization of a nucleotide-binding domain-like receptor (NLR) after sensing different pathogenic or endogenous sterile dangerous signals. The NLR family forms the main group of proteins considered as inflammasome sensors [
10]. However, other proteins such as absent in melanoma 2 (AIM-2), retinoic acid-inducible gene I, or pyrin could also form inflammasome platforms and that the activation of caspase-1 (Casp-1) in different physiological conditions can be due to the activation of different inflammasomes such as the NLRP1-inflammasome, the NLRP3-inflammasome, the NLRC4-inflammasome, and AIM2-inflammasome [
11]. Dysfunction of inflammasomes leads to spontaneous triggering of the inflammatory cascade and hyperactivation of the innate immune system [
11].
Being a part of pyrin inflammasome, pyrin acts as a pattern recognition receptor sensing pathogen modification and inactivation of Rho GTPases and also by directing the inflammasome components NLRP1, NLRP3, and pro-caspase 1. Through N-terminal PYD domain pyrin modulates Casp-1 and IL-1β activation exerting proinflammatory or anti-inflammatory regulatory effects [
10,
14]. Several studies indicated the implication of both pyrin and NALP3 inflammasomes in the pathogenesis of autoinflammatory disease including FMF [
7,
10,
11,
14].
The aim of this study was to evaluate the expression of inflammasome genes (p65, Casp-1, MEFV-d2, MEFV-I, NLRP3) in patients with FMF compared to healthy subjects (a reference control group) to understand the changes that may play a key role in disease development. These findings might complement the existing data on functional changes of inflammasome comprising genes in FMF and underline the major alterations in immunity present in patients with FMF. The results obtained might find further use in the development of more accurate diagnostic and prognostic approaches for this disease.
2. Results
This study was aimed to evaluate the expression of inflammasome genes in patients with FMF compared to healthy subjects (a reference control group) to underline the changes implicated in disease pathogenesis.
In total, 29 FMF patients (male/female: 10/19) and 20 healthy controls (male/female: 7/13) participated in inflammasome gene expression analysis using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR).
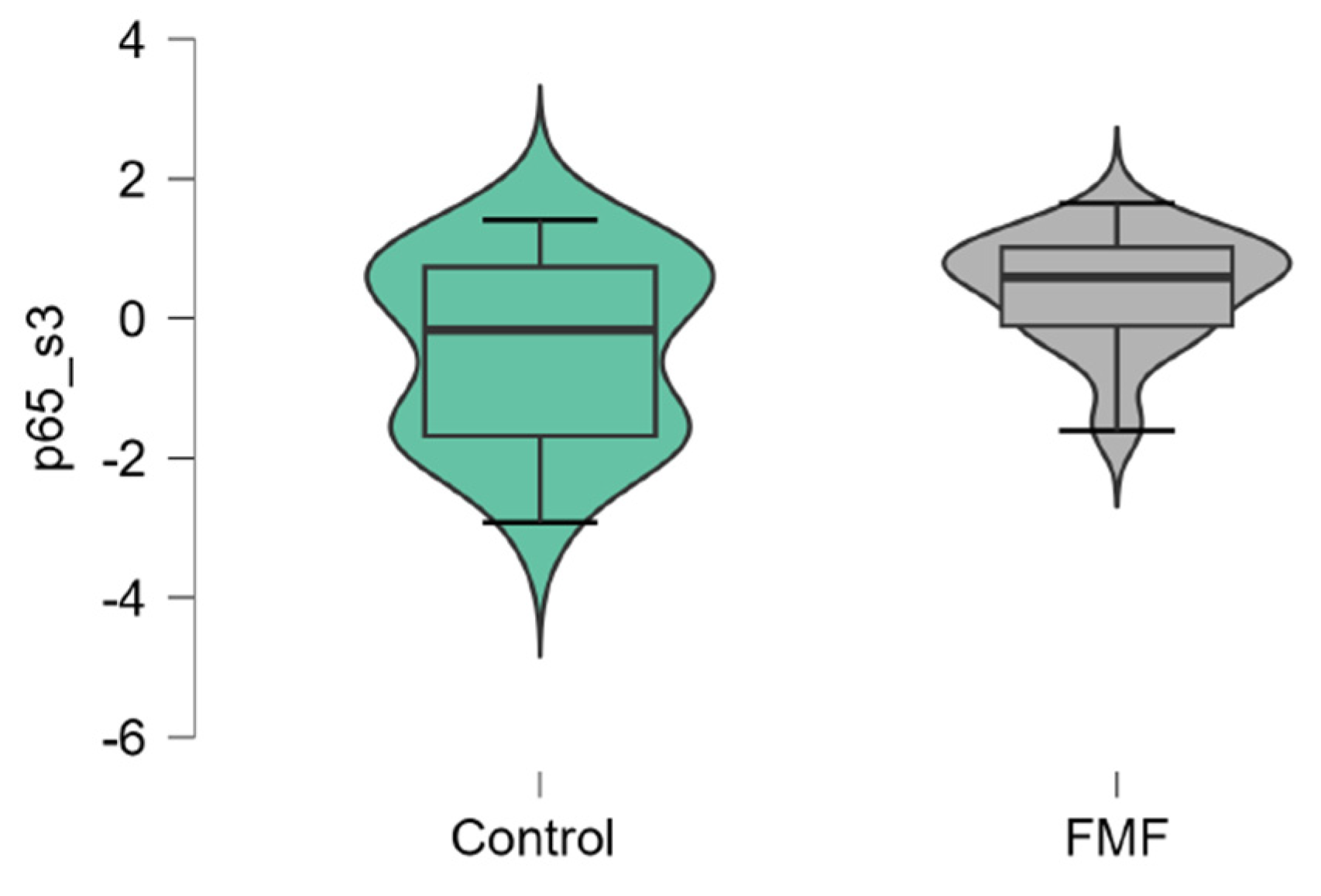
The mean mRNA expression levels for p65, Casp1, MEFV isoforms, NLRP3 were calculated as logarithm of fold change. The mean expression levels for p65 were significantly higher in FMF patients than in controls (patients vs. controls, mean±SD, -0.45±1.29 vs. 0.42±0.79, p=0.02) (
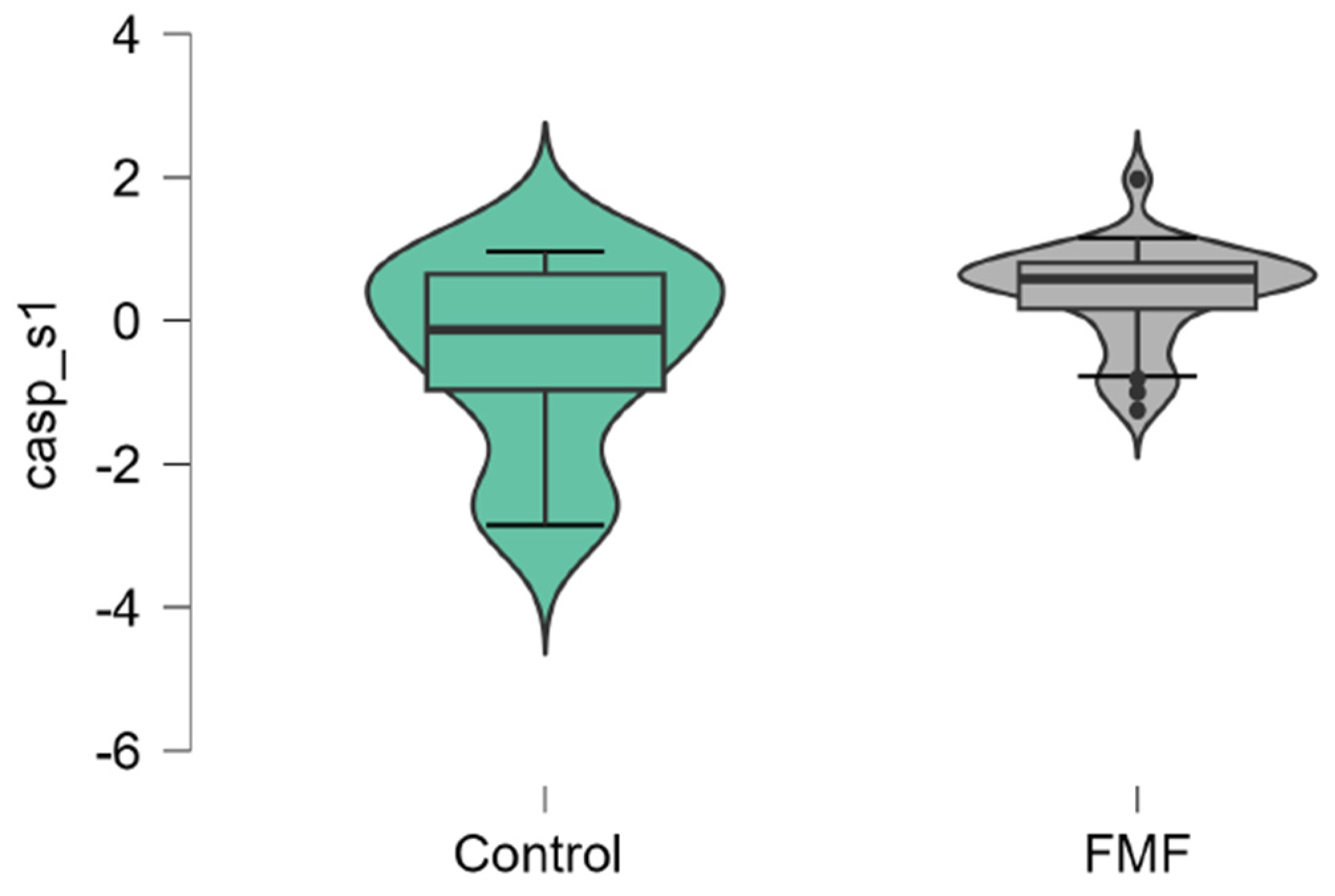
Figure 1). The difference in the expression of Casp1 also reached statistical significance between the groups (patients vs. controls, mean±SD, -0.44±1.31 vs. 0.39±0.71, p=0.048,
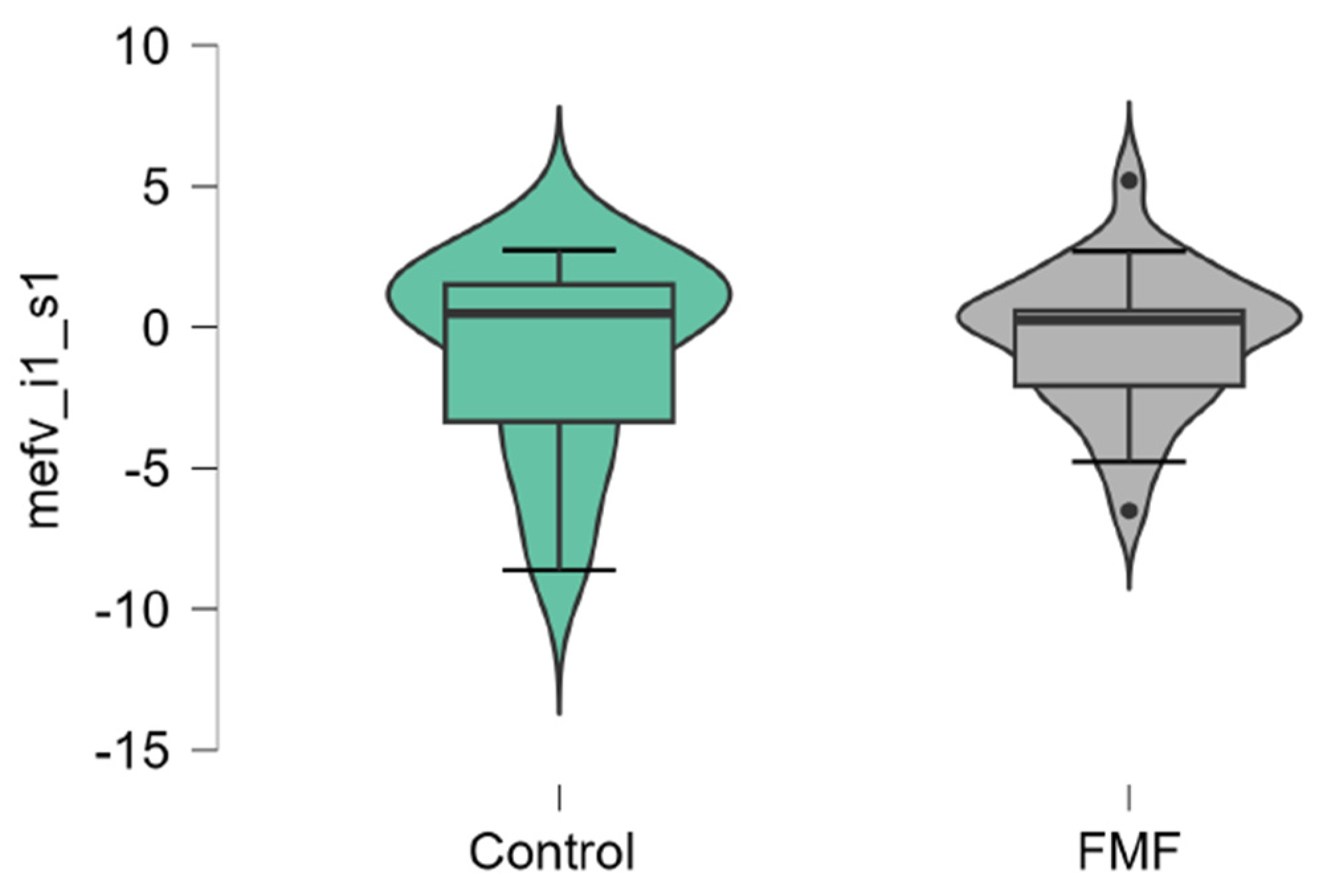
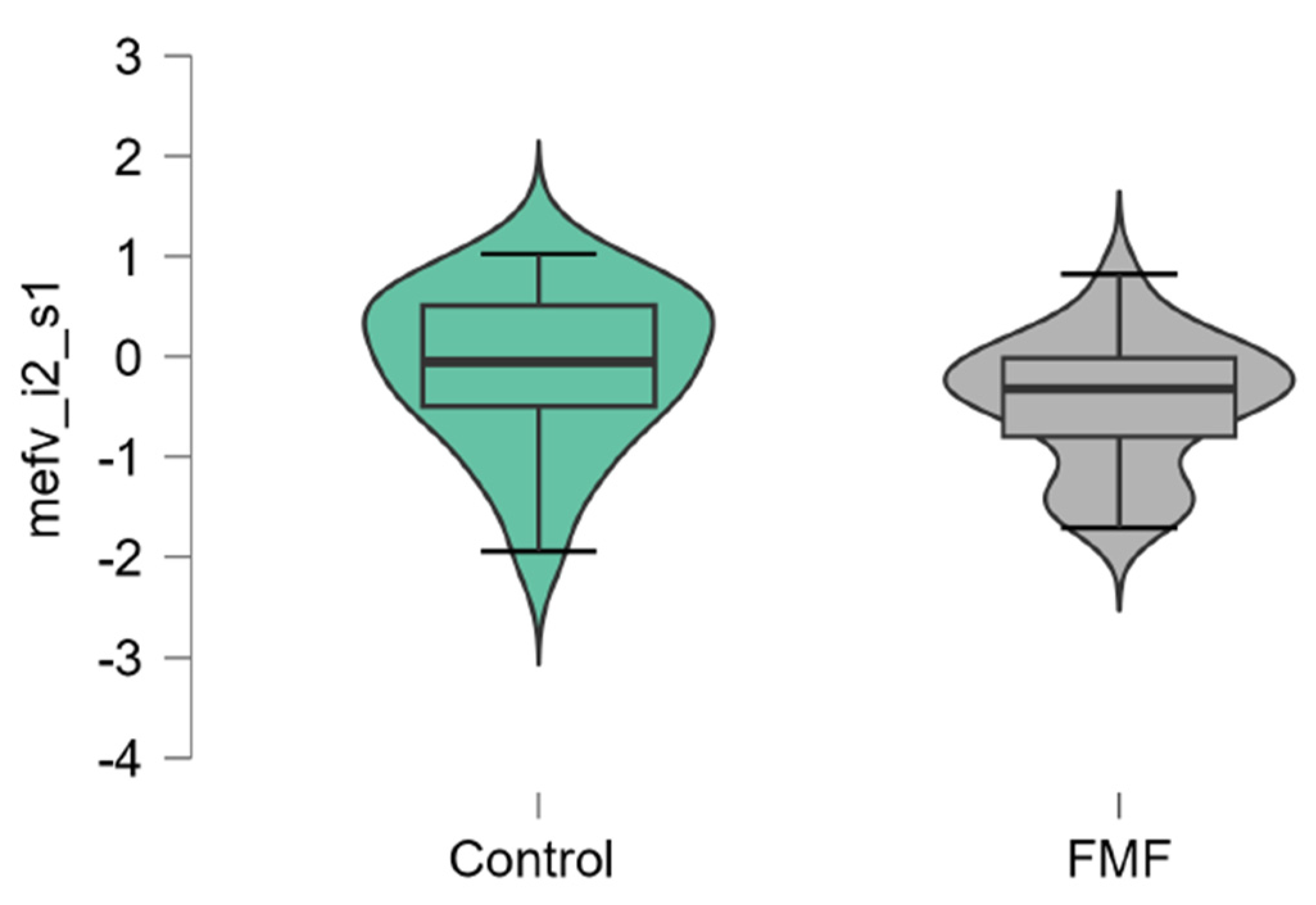
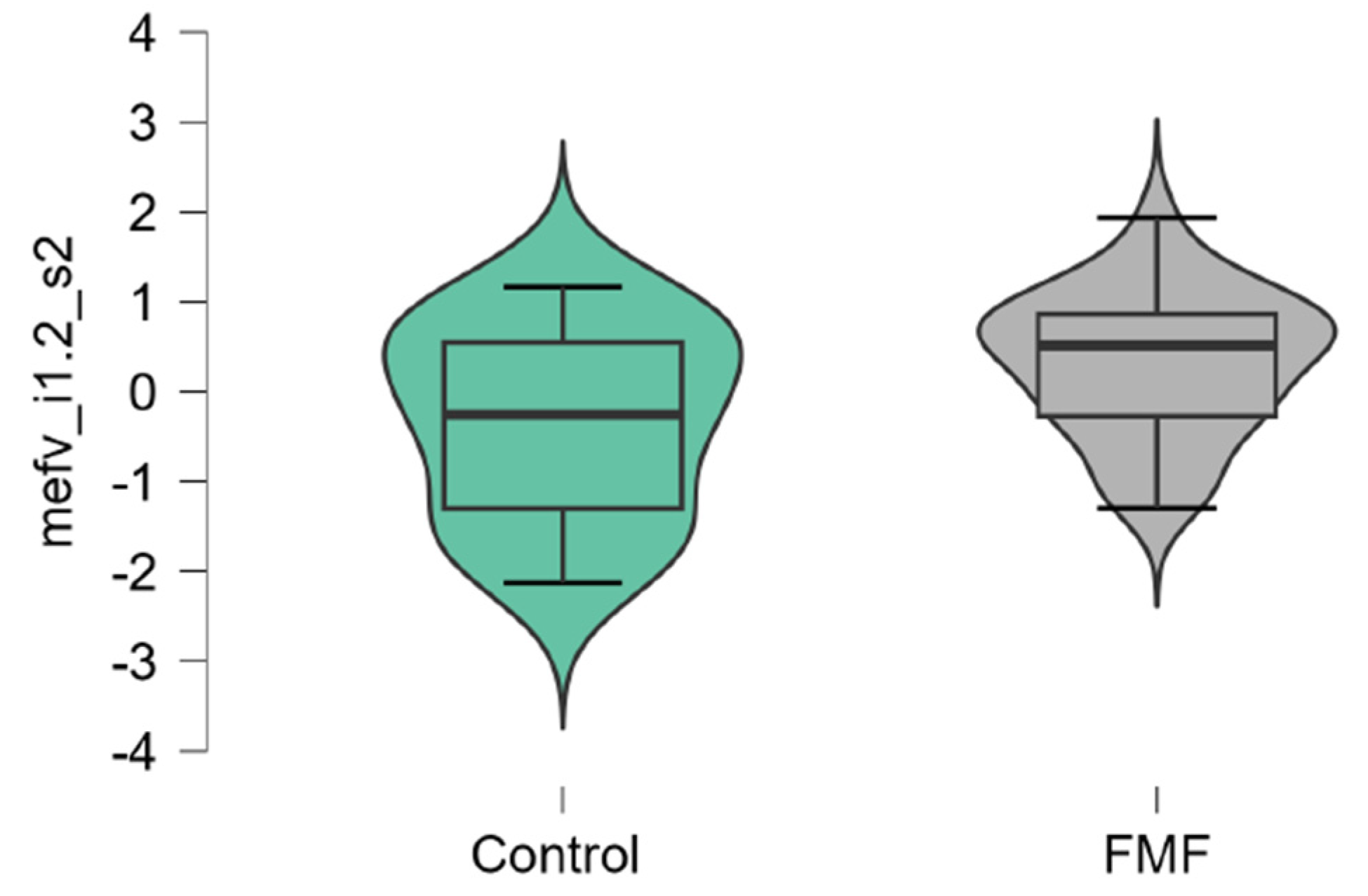
Figure 2). Among three isoforms, only the expression of the full-length transcript was borderline significant (patients vs. controls, mean±SD, -0.34±1.1 vs. 0.32±0.79, p=0.049) while for the transcript lacking exon 2 p-values exceed the significance threshold (patients vs. controls, mean±SD, -0.1±0.79 vs. -0.45±0.65, p=0.08,
Figure 3,
Figure 4 and
Figure 5).
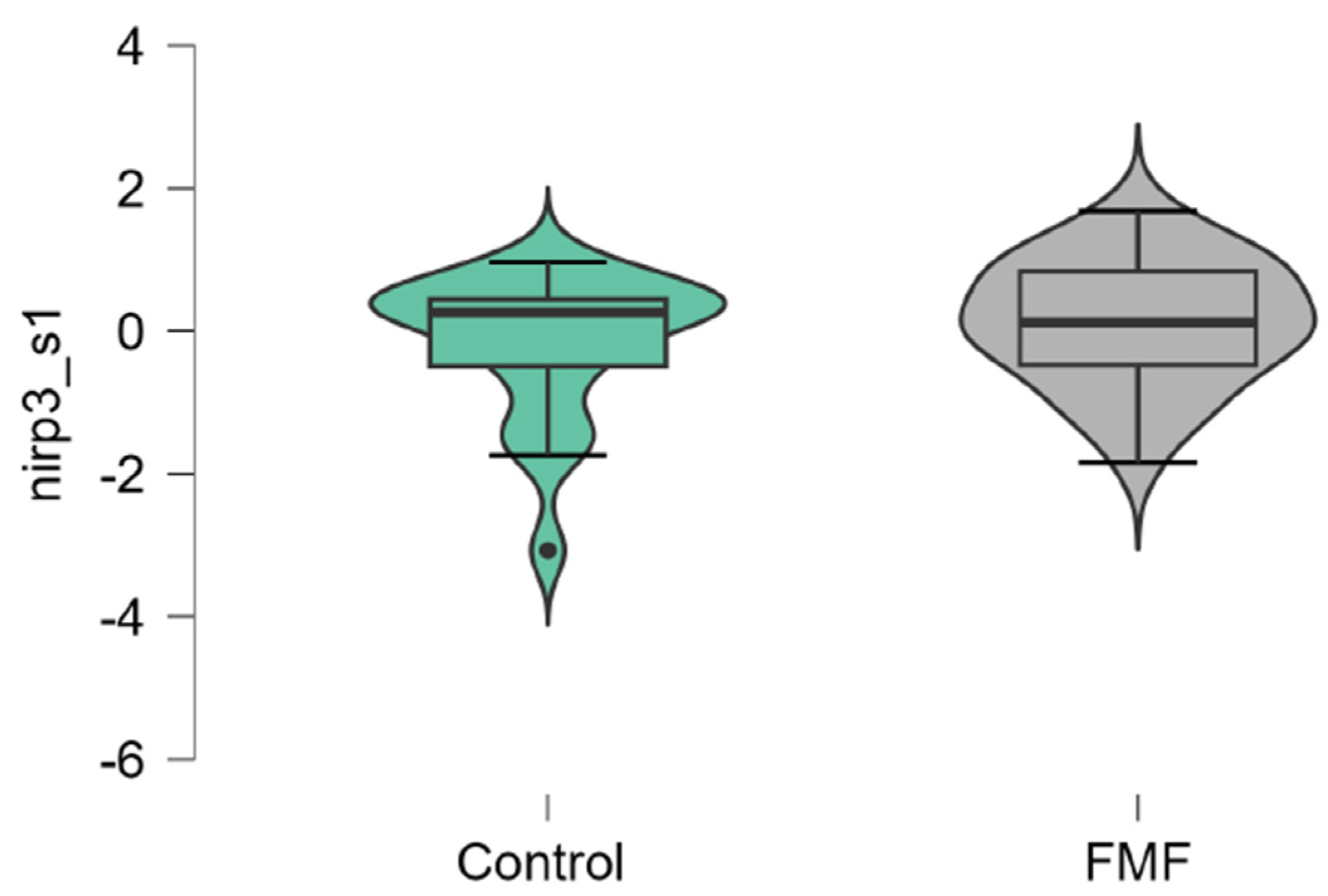
Concerning NLRP3, it was differentially expressed in the groups of patients compared to controls, however, this difference does not reach statistical significance (patients vs. controls, mean±SD, -0.18 ±1.00 vs. 0.006±1.16, p=0.33,
Figure 6). In general, the results obtained indicated different tendencies of alterations for all studied genes with notable changes in terms of MEFV, Casp1, and p65.
3. Discussion
In physiologic conditions, RhoA GTPase activates the serine-threonine kinases; PKN1 and PKN2 that bind and phosphorylate pyrin [
14]. Phosphorylated pyrin binds to inhibitory 14-3-3 proteins and this process retains pyrin in an inactive state that prevents formation of the pyrin inflammasome. In FMF, mutations in MEFV gene impair interaction of pyrin with microtubules, PKN and 14-3-3 proteins facilitating formation of a proinflammatory pyrin inflammasome. When the pyrin inflammasome is assembled, it activates caspase-1 to process pro-IL-1β and pro-IL-18 to their mature forms IL-1β and IL-18, respectively, and cells undergo an inflammatory death termed pyroptosis [
15]. The genes involved in the formation of the pyrin inflammasome include NLRP3, CASP1, GAPDH, and p65. Excessive activation of the pyrin inflammasome leads to the inflammation that characterizes the febrile inflammatory episodes seen in FMF [
15].
Repa et al. found that LPS/ATP activation of NLRP3 resulted in lower levels of IL-1β in FMF patients compared to healthy individuals. Similarly, the overexpression of the M694V mutated pyrin in THP-1 cells decreased the release of IL-1β mediated by NLRP3 [
16]. Previous findings by Chae et al. (2006) revealed the tendency of increased levels of Casp1 in three common FMF-associated B30.2 mutations [
17]. It must be noted that mutations in pyrin also result in heightened activation of the NF-κB (P65) gene [
18,
19]. However, the way MEFV mutations in FMF patients affect inflammasome activity is still unclear and needs further investigation. Furthermore, the specific impact of MEFV sequence variations on the pyrin inflammasome response remains largely unexplored. Jamilloux et al. (2018) reported that FMF severity is tightly linked to the nature of the MEFV mutation and to the number of mutated alleles [
20].
A few limitations related to our study must be considered. A limitation of our study is the relatively small sample size in each group, therefore, the results obtained can be considered as preliminary. Moreover, because of the first limitation we did not explore the potential relationship between the presence of pathogenic variants of MEFV and inflammasome gene expression levels that we plan to do in the near future. Moreover, it is planned to evaluate the inflammasome expression levels in FMF patient-specific induced pluripotent stem cell lines depending on the presence of genetic variants.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Population and Selection Criteria
In total, 29 patients with FMF and 20 healthy subjects were enrolled. Mutations in the MEFV gene in the FMF patient was determined by commercially available qPCR assay for the 26 most common mutations with FMF Multiplex real-time PCR kit (SNP Biotechnology RnD Ltd., Turkey). This qPCR kit determines 20 mutations, which have been identified in exon 1 (E84K), in exon 2 (L110P, E148Q, E148V, E167D, E230K/Q, T267I, P283L, G304R), in exon 3 (P369S), in exon 5 (F479L), and in exon 10 (M680I (G/C-A), M694I, M694V, K695R, V726A, A744S, R761H) covering 99.2% of the mutation rate of FMF in the Anatolian, Middle East and many other countries. Patients having at least 1 functional mutation in the MEFV gene and appearance of clinical symptoms of FMF were enrolled in this study.
All subjects gave their informed consents to participate in the study, which was approved by the Ethical Committee of the Institute of Molecular Biology of the National Academy of Sciences RA (IRB #00004079, Protocol N3 from 23.08.2021).
4.2. RNA Extraction and cDNA Synthesis
Five ml of morning fasting blood was collected in EDTA-containing tubes. The extraction was performed using Quick-DNA/RNA Miniprep Plus Kit (Zymo Research, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. For all extracted RNA samples measurements of concentrations and purity were performed using nano spectrophotometer (DeNovix DS-11+, USA) and Qubit 4 Fluorometer with Qubit RNA HS Assay Kit (ThermoFisher Scientific, USA). Only highly purified samples with A260/A230 ratio within the 1.7-2.2 range and concentration within 10-47 ng/μl range were used. Extracted RNA samples were stored at -80°C until further use at the Center of Excellence for Genetic engineering, genome editing and third generation sequencing at the Russian-Armenian University (Yerevan, Armenia).
cDNA synthesis was performed by reverse transcription (8 μl total RNA, total volume of cDNA 10 μl) using LunaScriptTM RT SuperMix Kit (New England Biolabs, USA) primer annealing for 2 min at 25°C, cDNA synthesis for 10 min at 55°C and heat inactivation for 1 min at 95°C. cDNA samples were stored at -20°C until further use.
4.3. Evaluation of Inflammasome Gene Expression
To assess the expression of inflammasome genes, primers targeting the genes MEFV, p65, CASP1, NF-kB, NLRP3, and GAPDH as a housekeeping gene were used. They were measured by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) on the Rotor-Gene™ Q machine (Qiagen, Germany).
Three μl of cDNA was added to 20 μl of PCR-mix. The final reaction mix contained 4 μl of 5x HOT FIREPol® EvaGreen® qPCR Mix Plus (Solis BioDyne, Estonia, content: HOT FIREPol® DNA Polymerase, 5x EvaGreen® qPCR buffer, 12,5 mM MgCl2 (1x PCR solution - 2.5 mM MgCl2), dNTPs, EvaGreen® dye), 0,5 μl of reverse and forward primers (for housekeeping gene, 0,375 μl of both forward and reverse primers were used), and a nuclease-free water to adjust the final volume to 20 μl.
The reaction of qPCR was performed using the following thermal cycling conditions: initial activation for 12 minutes at 95°C; 40 cycles of denaturation for 15 seconds at 95°C, annealing for 30 seconds at 60°C and extension (acquiring on green) for 30 seconds at 72°C.
The primers and fluorescently-labeled probes were selected using the PrimerQuest tool (Integrated DNA Technologies) as described in the
Table 1.
4.4. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis of expression data was analyzed using Mann-Whitney and Welch by JASP software.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, our study revealed altered gene expression of Casp1, MEFV, p65 in patients with FMF compared to healthy subjects supporting the previous findings on activation of pyrin inflammasome in autoinflammatory diseases including FMF. Lack of significant differences in NLRP3 expression between the comparison groups might reflect the more significant contribution of pyrin inflammasome than NLRP3 inflammasome in our terms. However, additional studies with larger sample sizes are needed to clarify this issue.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on
Preprints.org.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.A. and R.Z.; methodology, L.Gh., L.K., V.H., A.A., and R.Z.; validation, L.Gh., L.K., V.H., V.V., V.M.; formal analysis, L.Gh., L.K., V.H., S.A., H.Gh., and A.A.; investigation, L.Gh., L.K., V.H., S.A., and H.Gh.; resources, A.A., R.Z.; data curation, A.A. and R.Z.; interpretation of data, L.Gh., L.K., V.H., V.V., V.M., A.A., R.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, L.Gh., L.K., R.Z.; writing—review and editing, R.Z. and A.A.; visualization, L.Gh., L.K., V.H., A.A., and R.Z.; supervision, A.A., and R.Z.; project administration, A.A., and R.Z.; funding acquisition, L.Gh., A.A., and R.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Science Committee of the MESCS of Armenia (21SCG-1F010 to R.Z., and 23AA-1F035 to L.Gh.) and a research grant provided by the Armenian Engineers and Scientists of America (AESA) to RZ.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee of the Institute of Molecular Biology NAS RA (IRB 00004079, Protocol N3 from 23.08.2021.
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available at …
Acknowledgments
Authors would like to express their gratitude to the colleagues from the laboratory of Human Genomics of the Institute of Molecular Biology NAS RA who significantly contributed to sample collection and processing. Also, we are thankful to the research staff of the Center of Excellence on “Genome editing and third generation sequencing of the Institute of Biomedicine and Pharmacy at the Russian-Armenian University.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Touitou, I. The spectrum of Familial Mediterranean Fever (FMF) mutations. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2001, 9, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnappauf, O.; Chae, J.J., Kastner; Kastner, D.L.; Aksentijevich, I. The pyrin inflammasome in health and disease. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milhavet, F.; Cuisset, L.; Hoffman, H.M.; Slim, R.; El-Shanti, H.; Aksentijevich, I.; Lesage, S.; Waterham, H.; Wise, C.; Menthiere, C.S.; Touitou, I. The infevers autoinflammatory mutation online registry: Update with new genes and functions. Hum. Mutat. 2008, 29, 803–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Zvi, I.; Herskovizh, C.; Kukuy, O.; et al. Familial Mediterranean fever without MEFV mutations: A case–control study. Orphanet J Rare Dis 2015, 10, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marek-Yagel, D.; Berkun, Y.; Padeh Sh Abu, A.; Reznik-Wolf, H.; Livneh, A.; Pras, M.; Pras, E. Clinical disease among patients heterozygous for familial Mediterranean fever. Arthritis. Rheum. 2009, 60, 1862–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandemange, S.; Soler, S.; Touitou, I. Expression of the familial Mediterranean fever gene is regulated by nonsense-mediated decay. Human molecular genetics 2009, 18, 4746–4755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papin, S.; Duquesnoy, P.; Cazeneuve, C.; Pantel, J.; Coppey-Moisan, M.; Dargemont, C.; Amselem, S. Alternative splicing at the MEFV locus involved in familial Mediterranean fever regulates translocation of the marenostrin/pyrin protein to the nucleus. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2000, 9, 3001–3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdem, G.C.; Erdemir, S.; Abaci, I.; Aydin, A.K.K.; Everest, E.; Turanli, E.T. Alternatively spliced MEFV transcript lacking exon 2 and its protein isoform pyrin-2d implies an epigenetic regulation of the gene in inflammatory cell culture models. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2017, 40, 688–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matzner, Y.; Abedat, S.; Shapiro, E.; Eisenberg, S.; Bar-Gil-Shitrit, A.; Stepensky, P.; Calco, S.; Azar, Y.; Urieli-Shoval, S. Expression of the familial Mediterranean fever gene and activity of the C5a inhibitor in human primary fibroblast cultures. Blood 2000, 96, 727–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Torre-Minguela, C.; Del Castillo, P.M.; Pelegrín, P. The NLRP3 and pyrin inflammasomes: Implications in the pathophysiology of autoinflammatory diseases. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkurede, V.U.; Franchi, L. Immunology in clinic review series; focus on autoinflammatory diseases: Role of inflammasomes in autoinflammatory syndromes. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2012, 167, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franchi, L.; Eigenbrod, T.; Munoz-Planillo, R.; Nunez, G. The inflammasome: A caspase-1-activation platform that regulates immune responses and disease pathogenesis. Nat. Immunol. 2009, 10, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauernfeind, F.; Ablasser, A.; Bartok, E.; et al. Inflammasomes: Current understanding and open questions. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2011, 68, 765–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manukyan, G.; Aminov, R. Update on pyrin functions and mechanisms of Familial Mediterranean fever. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heilig, R.; Broz, P. Function and mechanism of the pyrin inflammasome. Eur. J. Immunol. 2018, 48, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Repa, A.; Bertsias, G.K.; Petraki, E.; Choulaki, C.; Vassou, D.; Kambas, K.; Sidiropoulos, P. Dysregulated production of interleukin-1β upon activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome in patients with familial Mediterranean fever. Human Immunol. 2015, 76, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, J.J.; Wood, G.; Masters, S.L.; Richard, K.; Park, G.; Smith, B.J.; Kastner, D.L. The B30. 2 domain of pyrin, the familial Mediterranean fever protein, interacts directly with caspase-1 to modulate IL-1β production. PNAS 2006, 103, 9982–9987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, J.J.; Wood, G.; Richard, K.; Jaffe, H.; Colburn, N.T.; Masters, S.L.; Kastner, D.L. The familial Mediterranean fever protein, pyrin, is cleaved by caspase-1 and activates NF-κB through its N-terminal fragment. Blood 2008, 112, 1794–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-David, H.; Livneh, A.; Lidar, M.; Feld, O.; Yahia, S.H.; Grossman, C.; Ben-Zvi, I. Toll-like receptor 2 is overexpressed in Familial Mediterranean fever patients and is inhibited by colchicine treatment. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2018, 32, 651–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamilloux, Y.; Lefeuvre, L.; Magnotti, F.; Martin, A.; Benezech, S.; Allatif, O.; Henry, T. Familial Mediterranean fever mutations are hypermorphic mutations that specifically decrease the activation threshold of the pyrin inflammasome. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2018, 57, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).