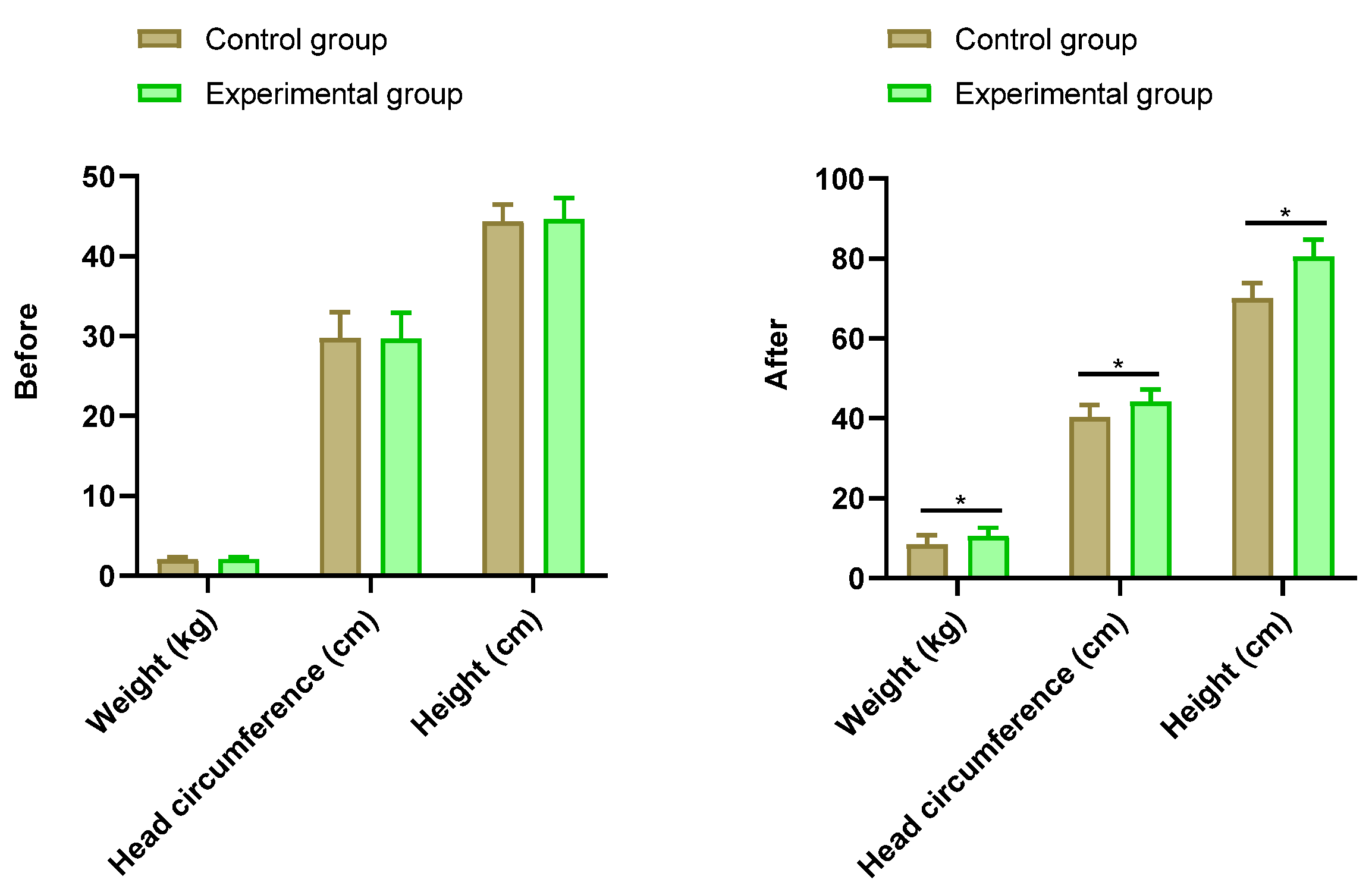Introduction
Preterm infants are defined as infants born before 37 weeks of gestation and those born earlier than the expected due date. The normal gestation period is 40 weeks, so preterm infants may be born in the early stages of physiological development and may not have fully matured. The birth of preterm infants is often accompanied by a range of physiological and developmental issues, as their organs and systems may not have fully developed and require specialized medical care and support. Late preterm infants, born in the later stages of pregnancy, between 32 and 36 weeks of gestation, face particular challenges in growth and development [
1,
2]. Compared to earlier preterm infants, they generally have better survival and developmental outcomes due to spending more time in the maternal environment, allowing for more opportunities for physiological development. However, they may still face health problems and developmental delays, requiring special attention and medical support. Their morbidity and mortality rates are nearly three times higher than those of full-term infants, classifying them as high-risk newborns [
3,
4]. Medical teams develop appropriate care plans based on the specific circumstances of preterm infants to promote their growth, development, and adaptation to the external environment.
In this context, early rehabilitation training based on developmental sequencing has become a highly regarded intervention. The concept of developmental sequencing emphasizes the gradual progression of infants in their developmental process, from basic survival functions to more complex motor and cognitive abilities. In the case of preterm infants, where the premature birth leads to underdeveloped nervous systems, developmental sequencing rehabilitation training aims to systematically promote the development of preterm infants in various aspects following the normal sequence of infant development [
5,
6]. This rehabilitation concept provides comprehensive and systematic support for the growth and development of late preterm infants. Previous research has often focused on extremely preterm and very low birth weight infants, with limited studies on the growth, development, and prognosis of late preterm infants. This article will delve into the impact of this rehabilitation training on the growth and development of late preterm infants and discuss its potential value in clinical practice. Through research on this topic, we hope to provide more effective strategies and methods to improve the quality of life and developmental potential of late preterm infants.
1. Objectives and Methods
This study was approved by the ethics committee of Qinhuangdao of Traditional Chinese Medicine, (NO.011; Date: June 02, 2021). Informed consent was obtained from all study participants. All the methods were carried out in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
1.1. Research Object
This study focused on all late preterm infants admitted to our hospital from June 2021 to November 2021. After strict screening according to comprehensive inclusion criteria, a total of 54 cases were registered and enrolled, and clinical data for each subject were collected. Based on different intervention protocols, the subjects were divided into a control group and an experimental group, with 27 cases in each group. The experimental group of preterm infants received early rehabilitation intervention based on developmental sequencing in addition to routine care, while the control group received only routine care. The study adhered to the principles of the Helsinki Declaration.
1.2. Inclusion Criteria
Inclusion criteria: All preterm infants with a gestational age between 34-36 weeks, meeting the diagnostic criteria for late preterm infants in “Practical Neonatology.” Clinical data were complete, and gender was not restricted. Vital signs were stable, and routine follow-up examinations were conducted in the preterm infant outpatient clinic.
Exclusion criteria: These included but were not limited to congenital malformations, hypoxia and asphyxia during delivery, critically ill infants, genetic metabolic diseases, and situations where the maternal consciousness and cognition were unclear. Presence of congenital heart disease, pneumonia, and others were also excluded.
1.3. Intervention Methods
During the hospitalization period, both groups received routine care to ensure the stability of their vital signs. After discharge, the preterm infants in the control group received traditional routine care, including guidance for feeding and care, with regular follow-up visits to the outpatient clinic.
The experimental group, in addition to routine care, underwent early rehabilitation training based on developmental sequencing. Trained rehabilitation therapists provided training, covering complications and reasons for late preterm infants, standardized learning of the early rehabilitation process, and practical exercises. This was achieved through lectures and classes to ensure that rehabilitation caregivers could proficiently and safely perform early rehabilitation procedures. Early rehabilitation methods included physical therapy, conducted when the infant’s physical condition was good. It involved age-appropriate rehabilitation content to promote the normal development of the infant’s motor function. The training focused on corresponding exercises such as lifting the head, rolling over, sitting, crawling, standing, and walking, following the sequence of growth. For infants aged 1 to 2 months, training was conducted on a treatment bed or therapy ball, with the infant in a prone position to develop head and neck control. Training for infants aged 3 to 4 months focused on finger grasping ability and rolling over. Infants aged 5 to 7 months underwent training to exercise their waist, providing a foundation for crawling, standing, and walking. Infants at 10 months of age were encouraged to attempt standing, and for those unable to stand independently, corresponding assistive training was provided. Infants aged 11 to 12 months began assisted walking. Additionally, to enhance knowledge and skills, caregivers regularly reminded each other of feeding and other considerations to avoid overfeeding and ensure standardized training to prevent injuries. In terms of care, customized complementary feeding was provided based on the different growth conditions of preterm infants. Family members were educated on the awareness of complications in preterm infants, and systematic learning of late preterm infant care knowledge and growth development patterns was emphasized.
1.4. Observation Indicators
Physical Indicators: Detailed records of physiological data, including the height, weight, and head circumference of the infants, are maintained. Regular analysis and organization of the records are conducted. In the case of abnormal data, prompt investigation is carried out, and data comparisons are performed to ensure data accuracy.
Intellectual-Motor Skills: After intervention, the Chinese standardized CDCC scale is employed to assess the cognitive development index (MDI) and motor development index (PDI) of preterm infants. The scores for these indices range from 0 to 100, with higher scores indicating higher levels of cognitive and motor development in preterm infants.
Neurobehavioral Assessment: Following intervention, the Newborn Behavioral Neurological Assessment (NBNA) scale is used to score infants. This scale comprises five dimensions, including passive muscle tone, active muscle tone, behavioral capacity, general conditions, and primitive reflexes. The scores are positively correlated with the neurobehavioral development of preterm infants.
Developmental Monitoring: After intervention, the Gesell Developmental Diagnosis Scale is employed for comprehensive developmental monitoring. The scale includes five areas of ability: gross motor skills, fine motor skills, adaptive skills, language skills, and personal-social skills. Developmental Quotients (DQ) are calculated for each area, with the scores positively correlating with the overall developmental level of preterm infants.
1.5. Data Statistics
Data analysis is performed using SPSS 22.0, and image processing is conducted using GraphPad Prism 8. Statistical analysis is performed using descriptive statistics. Continuous data are presented as mean ± standard deviation (±s) and analyzed using the t-test. Categorical data are presented as percentages (%) and analyzed using the chi-square test. A significance level of P < 0.05 indicates statistically significant differences.
2. Results
2.1. Clinical Data
In the control group of 27 cases, there were 16 males and 11 females, with an average weight of (2.15±0.53) kg and an average gestational age of (35.81±0.42) weeks. In the experimental group of 27 cases, there were 20 males and 7 females, with an average weight of (2.20±0.61) kg and an average gestational age of (35.40±0.49) weeks. There were no significant differences in clinical data between the two groups, indicating comparability (P > 0.05). Refer to
Table 1.
2.2. Physical Indicators
There was no statistically significant difference in physical indicator data between the two groups of preterm infants before intervention (P > 0.05). After intervention, the control group’s preterm infants had a weight of (8.44±2.34) kg, head circumference of (40.26±3.07) cm, and height of (70.14±3.70) cm. The experimental group’s preterm infants had a weight of (10.55±2.06) kg, head circumference of (44.15±3.12) cm, and height of (80.49±4.30) cm. After intervention, the physical indicator data, including weight, head circumference, and height, were higher in the experimental group than in the control group (P < 0.05). See
Figure 1.
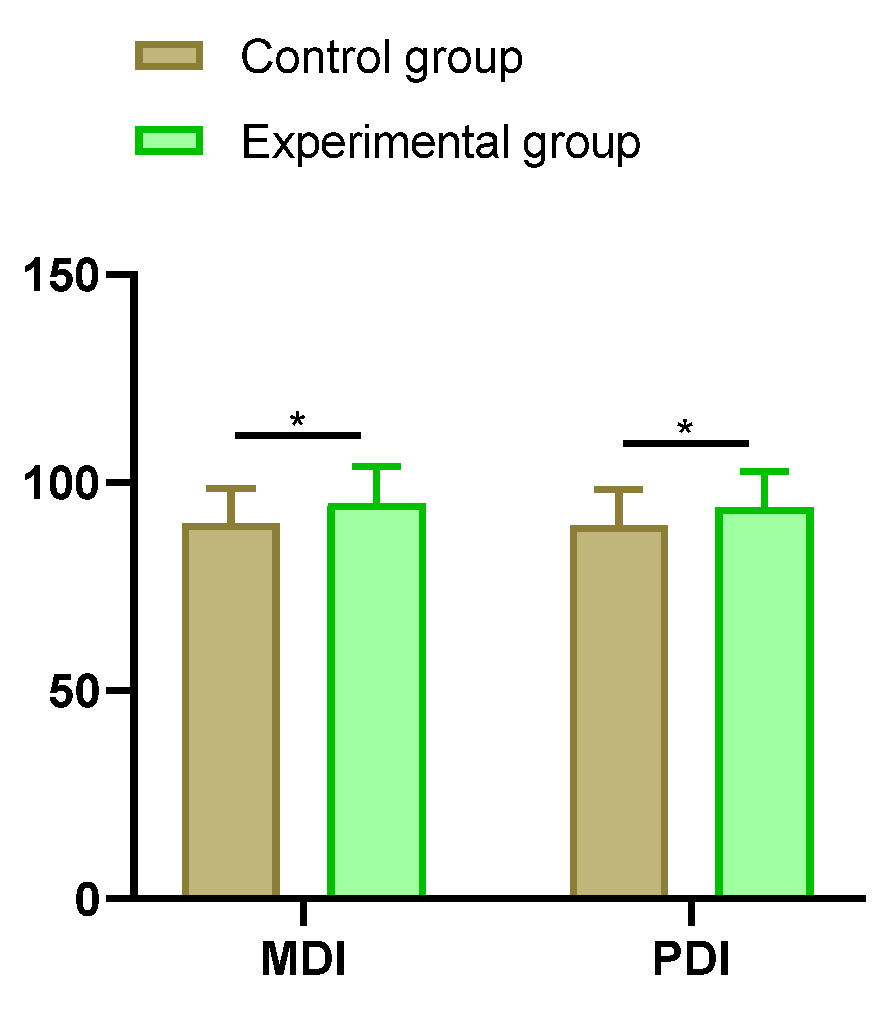
2.3. Intellectual-Motor Skills
After intervention, the MDI score (90.17±8.32) and PDI score (89.72±8.65) of preterm infants in the control group were compared with the MDI score (95.06±8.87) and PDI score (94.02±8.69) of preterm infants in the experimental group. The intellectual-motor skill indices, namely MDI and PDI scores, were higher in the experimental group than in the control group (P < 0.05). See
Figure 2.
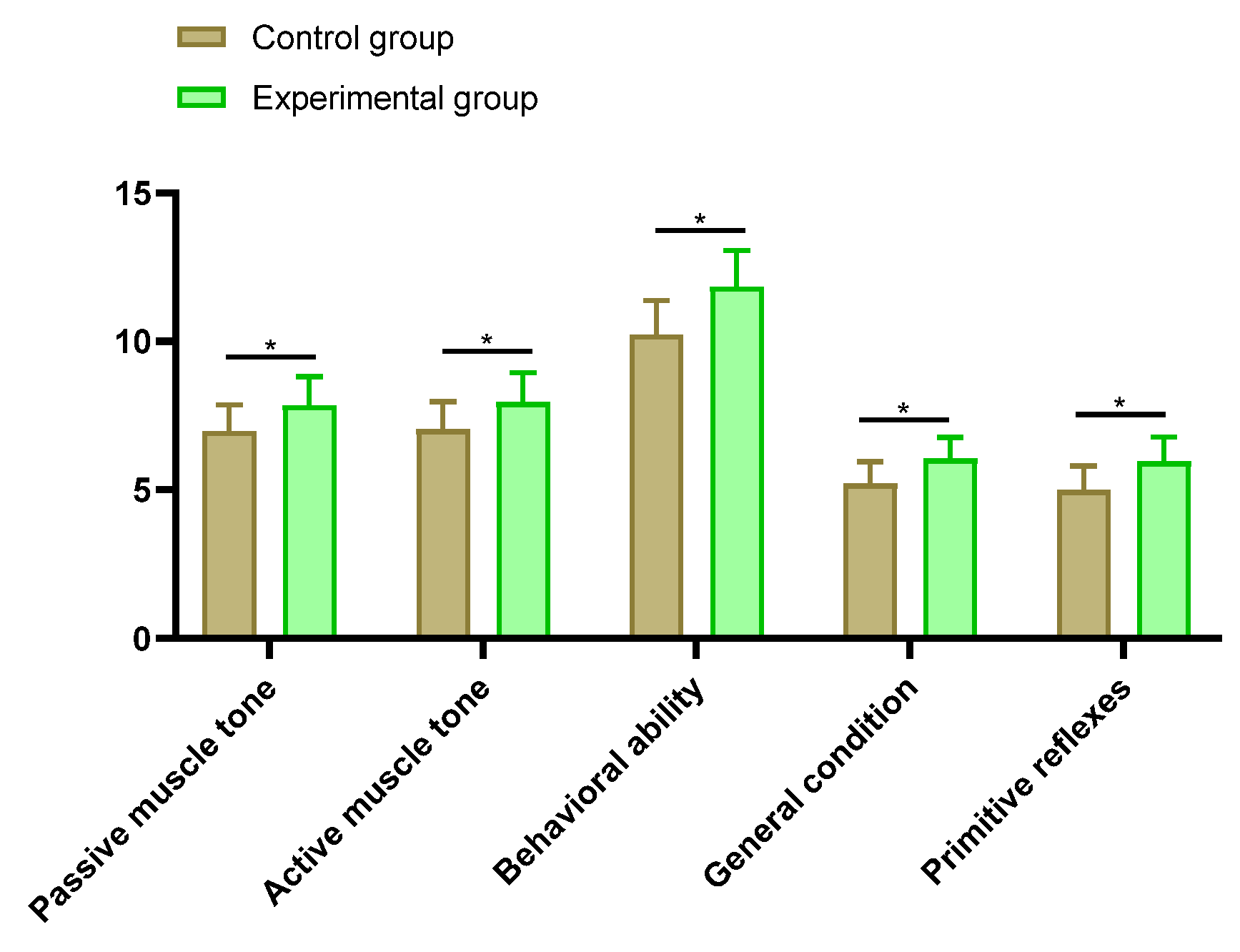
2.4. Neurobehavioral Assessment
The control group’s preterm infants had scores for passive muscle tone (6.98±0.89), active muscle tone (7.03±0.94), behavioral capacity (10.23±1.14), general conditions (5.21±0.74), and primitive reflexes (4.99±0.81). The experimental group’s preterm infants had scores for passive muscle tone (7.85±0.97), active muscle tone (7.96±0.98), behavioral capacity (11.84±1.23), general conditions (6.04±0.73), and primitive reflexes (5.96±0.82). The NBNA scale scores for each dimension were higher in the experimental group than in the control group (P < 0.05). See
Figure 3.
2.5. Developmental Monitoring
The control group’s preterm infants had scores for gross motor skills (93.56±3.51), fine motor skills (87.94±5.11), adaptive skills (91.65±4.88), language skills (89.23±5.03), personal-social skills (91.01±5.35), and DQ value (90.48±3.22). The experimental group’s preterm infants had scores for gross motor skills (99.56±6.17), fine motor skills (89.32±5.34), adaptive skills (96.23±5.11), language skills (91.23±4.65), personal-social skills (96.56±5.23), and DQ value (95.56±5.28). The DQ value was higher in the experimental group than in the control group (P < 0.05). See
Figure 4.
3. Discussion
Early rehabilitation training is an intervention strategy aimed at infants and young children, with the goal of enhancing overall functional levels by promoting normal physiological, cognitive, and motor development. This type of training is typically applied to preterm infants or infants at risk of developmental delays, helping them overcome potential physiological and neurodevelopmental challenges. Early rehabilitation training is characterized by individualized intervention plans tailored to the specific conditions and developmental stages of the child, incorporating systematic training based on developmental sequences to ensure the targeted and effective nature of rehabilitation measures [
7,
8]. This training is often conducted by professional rehabilitation therapists or medical teams, covering multiple domains such as physical fitness, neurobehavioral aspects, cognition, and social skills, with the aim of maximizing the comprehensive development of the child. Late preterm infants, in comparison to full-term infants, spend a shorter time in the womb, leading to potential physiological developmental differences and incomplete maturation of the nervous system, making them susceptible to a range of neurodevelopmental issues [
9,
10]. Some studies suggest that early intervention can help bridge this gap, promoting the normal development of organs and systems, and reducing the risk of developmental delays through rehabilitative training focused on neurobehavioral aspects.
Through the use of developmental sequence-based early rehabilitation training for preterm infants, we conducted a comprehensive assessment of physical indicators, cognitive and motor development, neurobehavior, and overall development. In discussing the results in these aspects, several observations and conclusions can be drawn. First, in terms of physical indicators, infants in the experimental group may show a better developmental trend in terms of height, weight, and head circumference. Scholars argue that late preterm infants have significant growth potential after birth, and through proper feeding and nutritional interventions, their physical development can be significantly improved [
11,
12]. The developmental sequence-based early rehabilitation training used in this study, which focuses on the rational feeding of preterm infants, emphasizes daily feeding reminders for mothers based on the infant’s daily dietary intake, and observes the infant’s excretion volume and frequency. As the preterm infants grow, appropriate complementary feeding is gradually added. Simultaneously, clinical attention is given to educating mothers on neonatal feeding methods, feeding amounts, etc., to achieve scientific feeding, ensuring that the preterm infants’ growth and development meet nutritional needs [
13,
14]. This comprehensive approach has positively contributed to their overall growth and development, resulting in significant progress in weight, head circumference, and height levels in the experimental group compared to the control group. This indicates that the developmental sequence-based early rehabilitation program has a promoting effect on the physical development of late preterm infants, consistent with previous research results.
Late preterm infants may face delays in motor and cognitive development, impacting their daily life and learning abilities. The use of the Chinese standardized CDC scale in this study indicates that rehabilitative training based on developmental sequences helps improve the cognitive and motor development levels of preterm infants. It facilitates the targeted development of motor skills and cognitive abilities, enhancing the quality of life for these infants. Developmental sequence-based early rehabilitation training is a specialized rehabilitation intervention strategy for infants and young children, aiming to conduct systematic training based on the normal developmental stages and sequences of children. This approach emphasizes the targeted arrangement of rehabilitation content based on the infant’s age and developmental stage, including but not limited to milestone training such as lifting the head, rolling over, sitting, crawling, standing, and walking. Through early rehabilitation training, the goal is to improve the functional level of infants and young children, prevent or alleviate various physiological and neurodevelopmental issues that may arise from developmental delays, and create an environment that supports their comprehensive development [
15,
16]. In terms of neurobehavior, this study observed higher scores in passive muscle tone, active muscle tone, and behavioral capacity in the experimental group of preterm infants using the Neonatal Behavioral Neurological Assessment (NBNA) scale. This indicates that early rehabilitation training may have a positive impact on their neurobehavioral development, providing further evidence of the crucial role of developmental sequence-based early rehabilitation training in the growth and development of late preterm infants.
In addition, based on a comprehensive review of domestic and international research, late preterm infants may face challenges in psychological and social aspects, such as anxiety and attention deficits. Early psychological and social interventions can assist them in establishing healthy social relationships and cultivating positive psychological states. This not only benefits the development of the affected children but also provides more comprehensive support to their families. Providing relevant education and guidance to parents helps them better cope with and support the growth of preterm infants. Overall, early intervention for late preterm infants is a comprehensive measure that helps minimize potential developmental delays and health issues, thereby improving their quality of life [
17,
18]. This aligns with the results of this study, where the Gesell Developmental Diagnosis Scale assessment showed a higher developmental quotient (DQ) in the experimental group, indicating a promoting effect of developmental sequence-based early rehabilitation training on overall development.
Early rehabilitation intervention is a specialized care method specifically designed for preterm infants. This care plan is tailored to the clinical needs of preterm infants, aiming to facilitate optimal growth and development, thereby raising the developmental level of preterm infants and reducing the occurrence of death and complications. During implementation, caregivers and rehabilitation therapists need to ensure effective protection and exercise for the infants, employing specific and standardized rehabilitative stimulation interventions to prevent sequelae issues. Late preterm infants are at a higher risk of various neonatal developmental disorders due to reasons such as incomplete uterine development, intrauterine infections, and advanced maternal age. Therefore, early rehabilitation intervention for late preterm infants is particularly important [
19,
20]. The results of this study demonstrate that the application of the developmental sequence-based early rehabilitation intervention care model can normalize the physical development of affected children. Hence, this early rehabilitation intervention care model has the potential for wide application and promotion in the clinical practice of late preterm infants.
In conclusion, the results of this study indicate that developmental sequence-based early rehabilitation training has a positive impact on the growth and development of late preterm infants, providing an effective intervention strategy for clinical practice. However, further research is needed to validate these observational results and gain a deeper understanding of the mechanisms by which rehabilitation training affects preterm infants at different ages and developmental stages.
4. Challenges
While developmental sequence-based early rehabilitation training holds theoretical appeal, it still faces some challenges in clinical practice. Firstly, individual differences require adjustments to rehabilitation plans based on the specific circumstances of each infant. Secondly, long-term follow-up studies are still limited, making it challenging to comprehensively assess the long-term impact of rehabilitation training on the growth and development of late preterm infants. Nevertheless, as research advances and medical technology progresses, developmental sequence-based early rehabilitation training is poised to become a crucial means of improving the growth and development of late preterm infants. Through more refined and personalized rehabilitation plans, coupled with advanced monitoring technologies, we can better understand the effectiveness of rehabilitation training for late preterm infants and provide more effective support for their growth and development.
5. Conclusion
Developmental sequence-based early rehabilitation training plays a crucial and positively influential role in the growth and development of late preterm infants. Through systematic and sequenced rehabilitative interventions, various aspects of development in late preterm infants can be promoted, providing support for their adaptation to the external environment. This intervention effectively improves the physical development of late preterm infants while enhancing cognitive, motor, and neurobehavioral development levels. The results are significant and worthy of widespread application. Future research and practice should continually refine rehabilitation plans to better meet the individualized needs of late preterm infants, creating more favorable conditions for their healthy growth.
Funding
This study was supported by Qinhuangdao Science and Technology Bureau Project, 201902A065.
References
- Snyers, D.; et al. [Late preterm : High risk newborns despite appearances]. Rev Med Liege 2020, 75, 105–110. [Google Scholar]
- Delnord, M.; Zeitlin, J. Epidemiology of late preterm and early term births—An international perspective. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med 2019, 24, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; et al. Late preterm: A new high risk group in neonatology. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2021, 34, 2717–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huff, K.; Rose, R.S.; Engle, W.A. Late Preterm Infants: Morbidities, Mortality, and Management Recommendations. Pediatr Clin North Am 2019, 66, 387–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, C.; et al. Effects of early intervention on feeding behavior in preterm infants: A randomized controlled trial. Early Hum Dev 2018, 121, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neel, M.L.; et al. Randomized controlled trial protocol to improve multisensory neural processing, language and motor outcomes in preterm infants. BMC Pediatr 2019, 19, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberg, G.K.; et al. Study protocol: An early intervention program to improve motor outcome in preterm infants: A randomized controlled trial and a qualitative study of physiotherapy performance and parental experiences. BMC Pediatr 2012, 12, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dusing, S.C.; et al. Supporting play exploration and early developmental intervention versus usual care to enhance development outcomes during the transition from the neonatal intensive care unit to home: A pilot randomized controlled trial. BMC Pediatr 2018, 18, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.E.; Pugh, Y. The Late Preterm: A Population at Risk. Crit Care Nurs Clin North Am 2018, 30, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medically Indicated Late-Preterm and Early-Term Deliveries: ACOG Committee Opinion, Number 831. Obstet Gynecol 2021, 138, e35–e39. [CrossRef]
- Gutzeit, O.; et al. Late preterm delivery has a distinctive second-stage duration and characteristics. Am J Obstet Gynecol MFM 2023, 5, 100845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vohr, B. Long-term outcomes of moderately preterm, late preterm, and early term infants. Clin Perinatol 2013, 40, 739–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; et al. Early combined rehabilitation intervention to improve the short-term prognosis of premature infants. BMC Pediatr 2021, 21, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelc, K.; et al. Multicentre prospective randomised single-blind controlled study protocol of the effect of an additional parent-administered sensorimotor stimulation on neurological development of preterm infants: Primebrain. BMJ Open 2017, 7, e018084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivas Jois, R. Neurodevelopmental outcome of late-preterm infants: A pragmatic review. Aust J Gen Pract 2018, 47, 776–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnati, S.; Kollikonda, S.; Abu-Shaweesh, J. Late preterm infants—Changing trends and continuing challenges. Int J Pediatr Adolesc Med 2020, 7, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flanagan, D.; et al. Addressing disparities among children with cerebral palsy: Optimizing enablement, functioning, and participation. J Pediatr Rehabil Med 2021, 14, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gire, C.; et al. Neurobehavioral Phenotype and Dysexecutive Syndrome of Preterm Children: Comorbidity or Trigger? An Update. Children (Basel) 2022, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizzari, G.; et al. Postnatal growth of small for gestational age late preterm infants: Determinants of catch-up growth. Pediatr Res 2023, 94, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iams, J.D.; Donovan, E.F. Spontaneous late preterm births: What can be done to improve outcomes? Semin Perinatol 2011, 35, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).