Submitted:
01 October 2024
Posted:
02 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Global Heritage Stone Resources
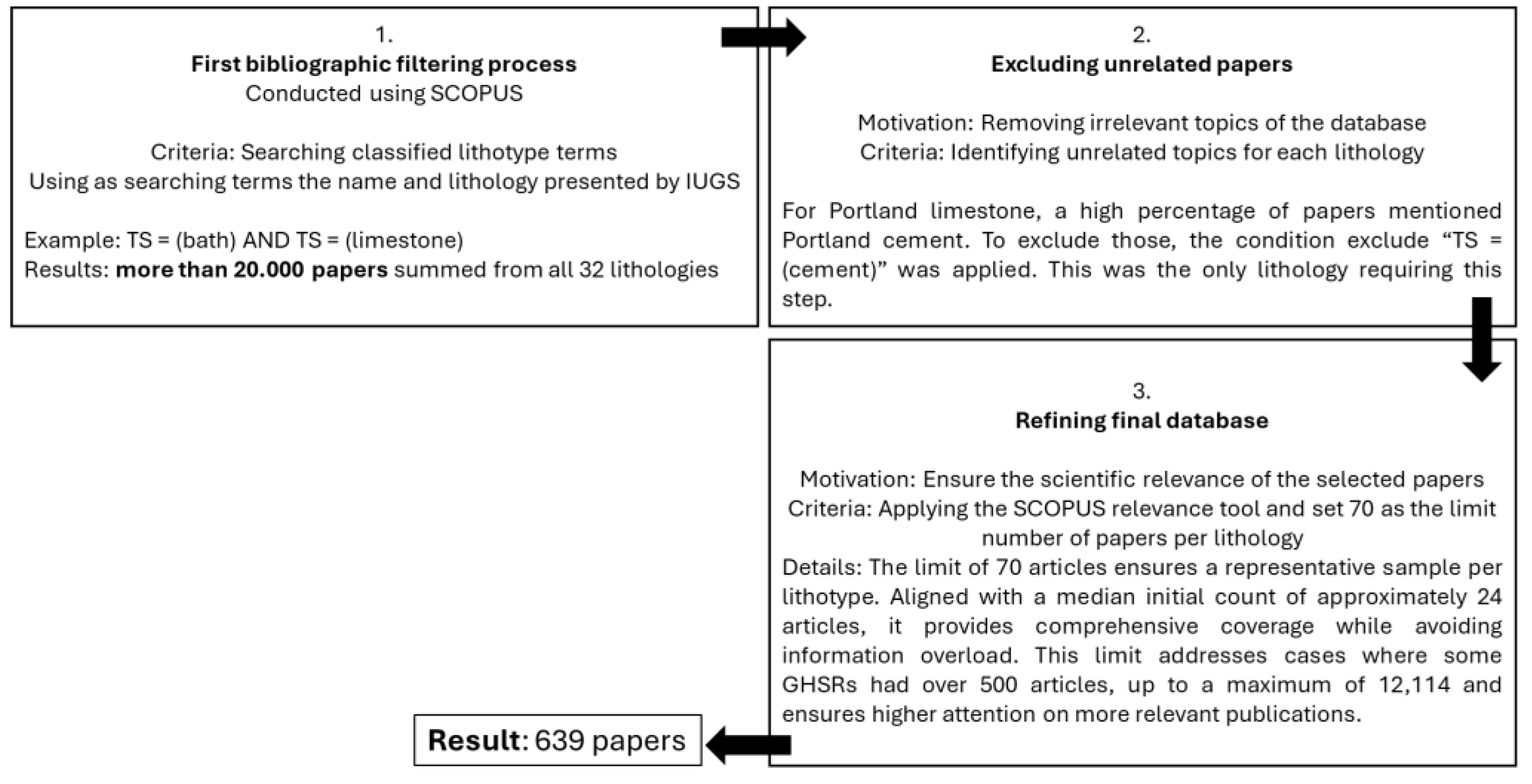
3. Methods
3.1. Selection of Database
3.2. Database Analyses Criteria
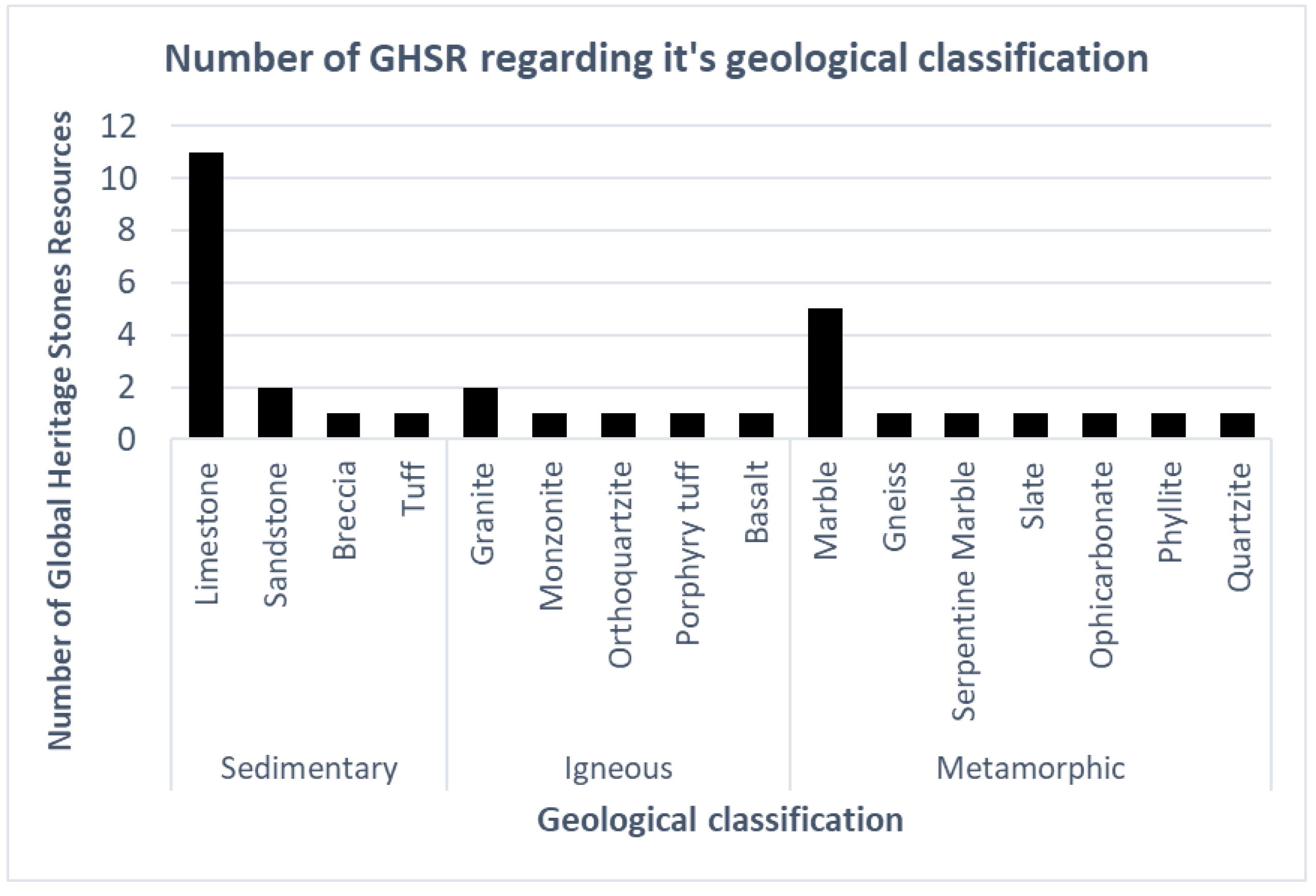
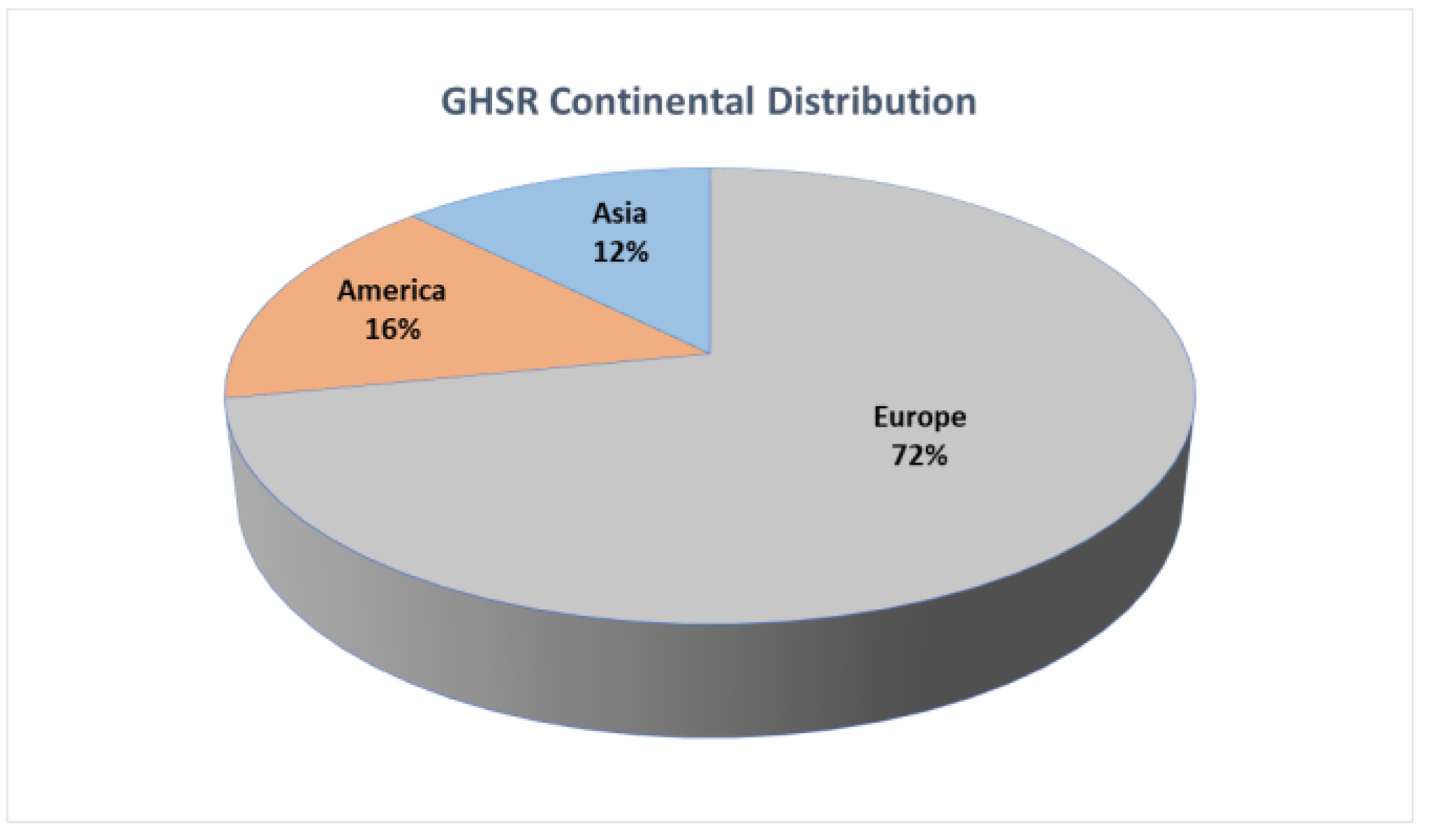
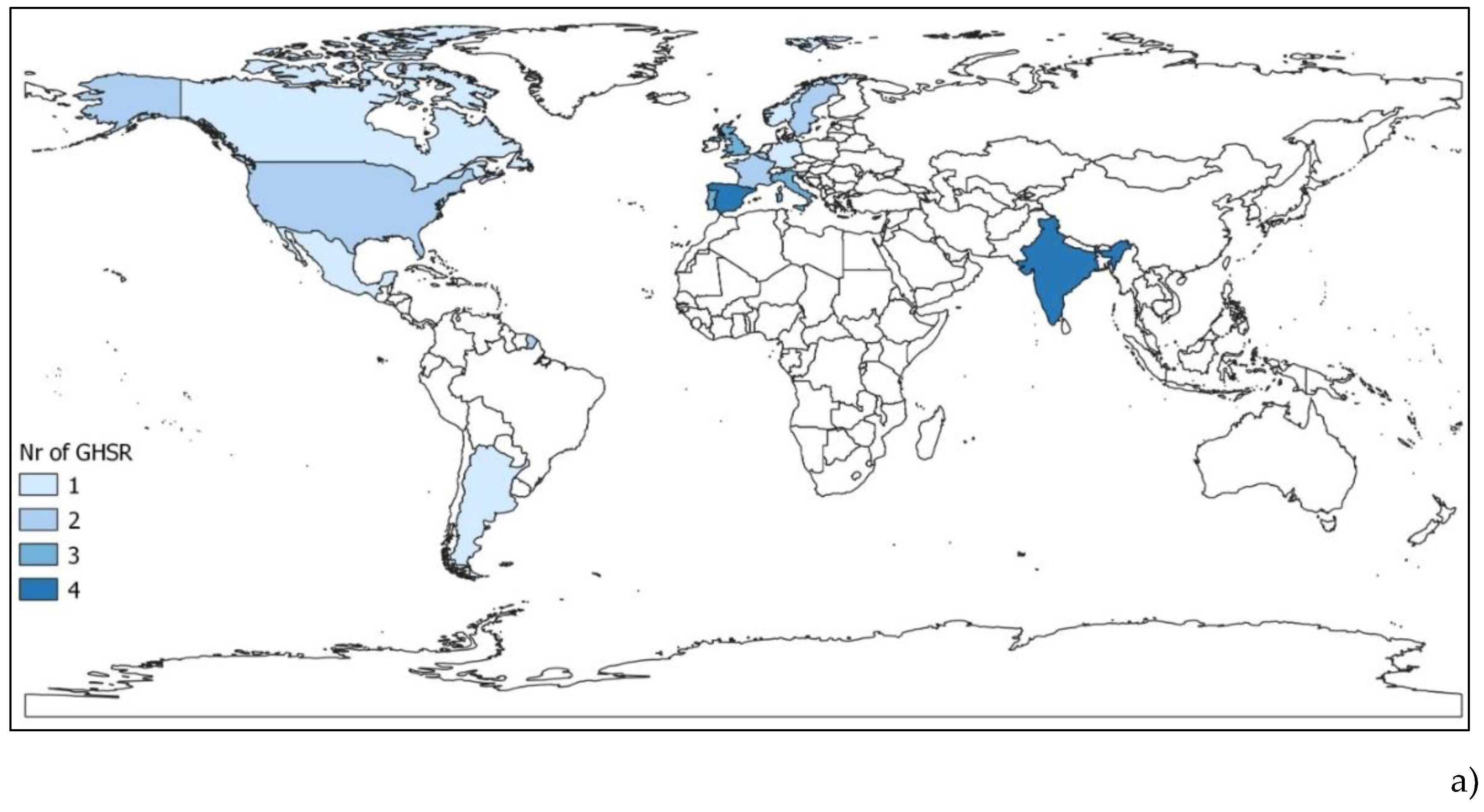
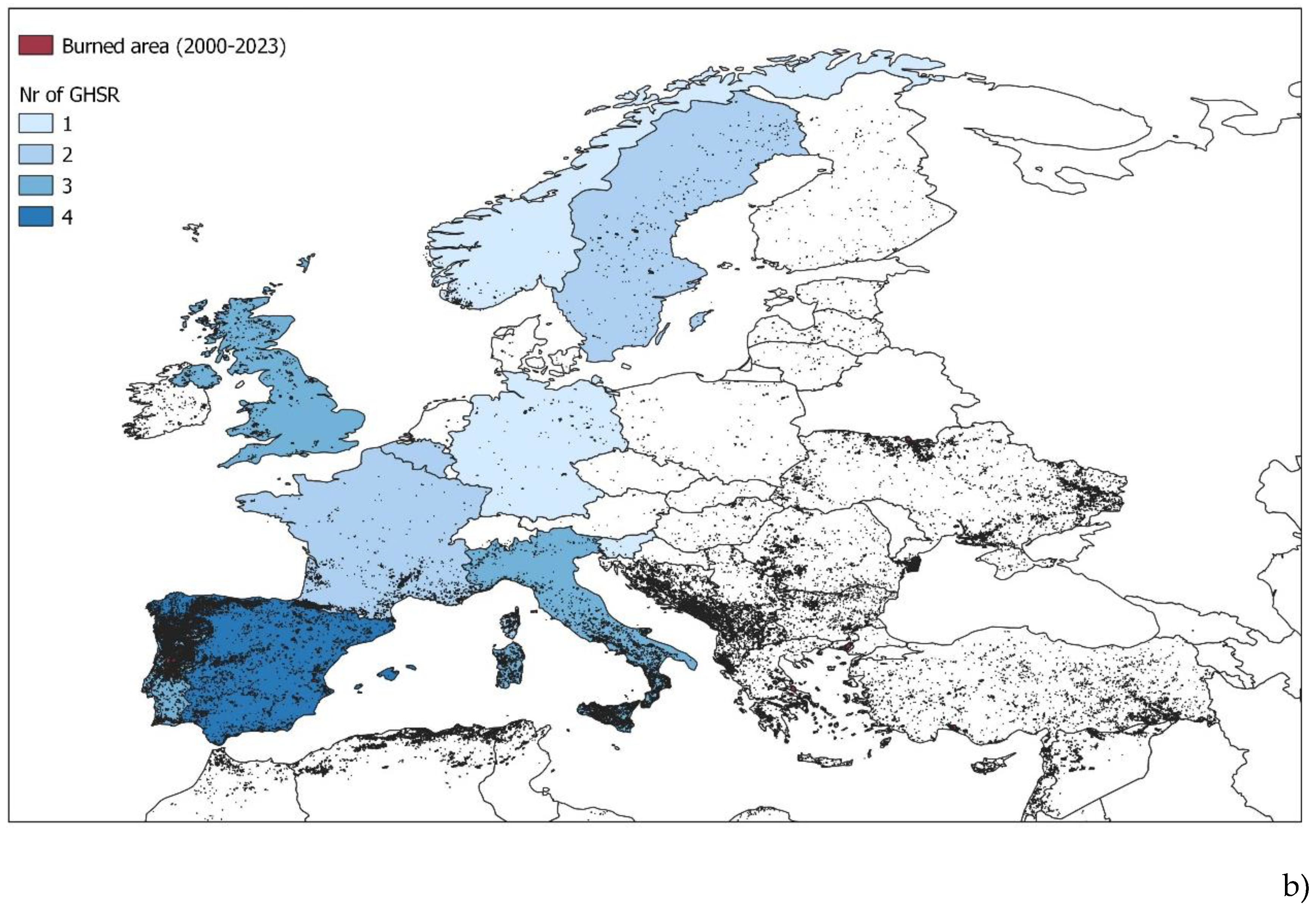
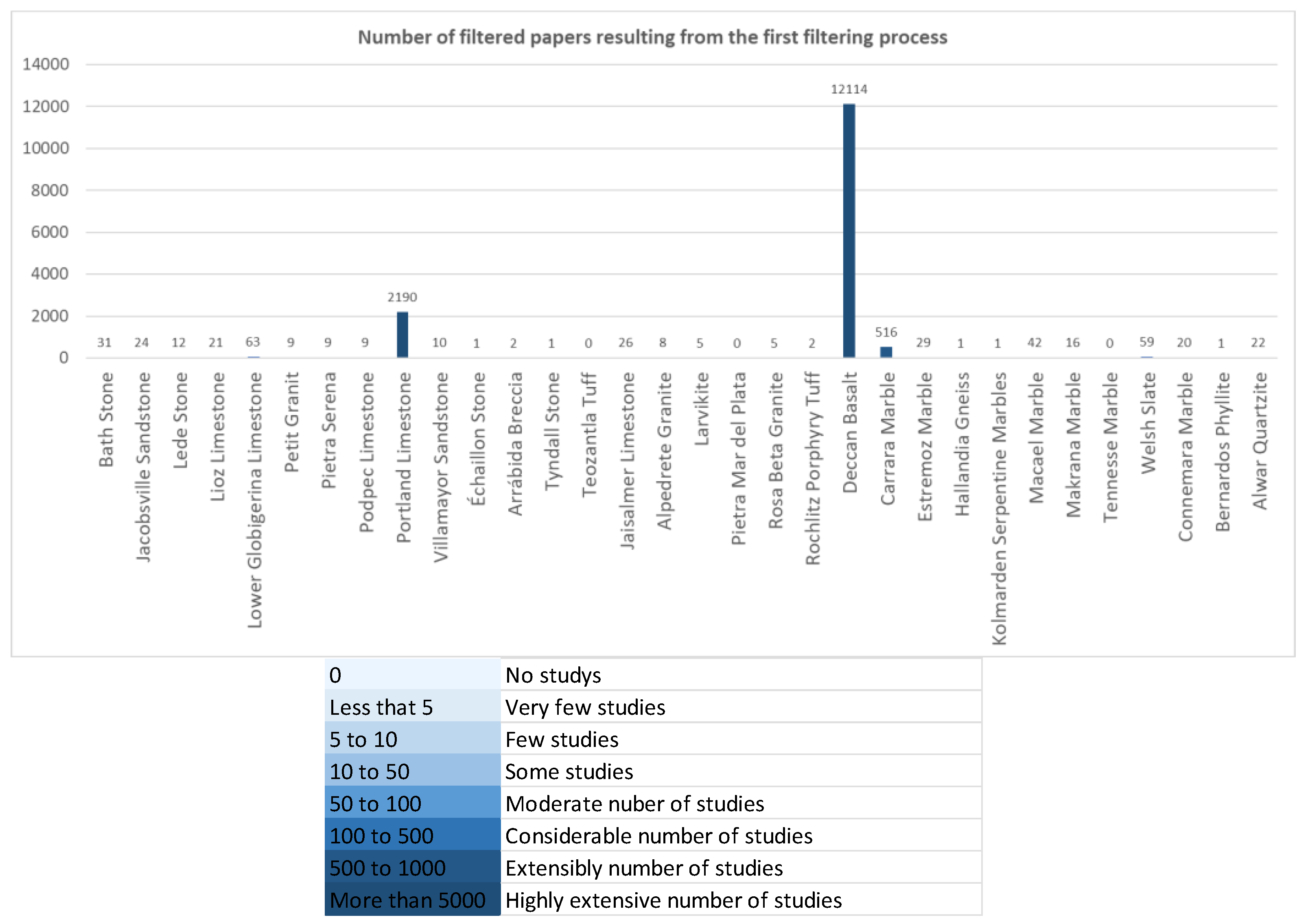
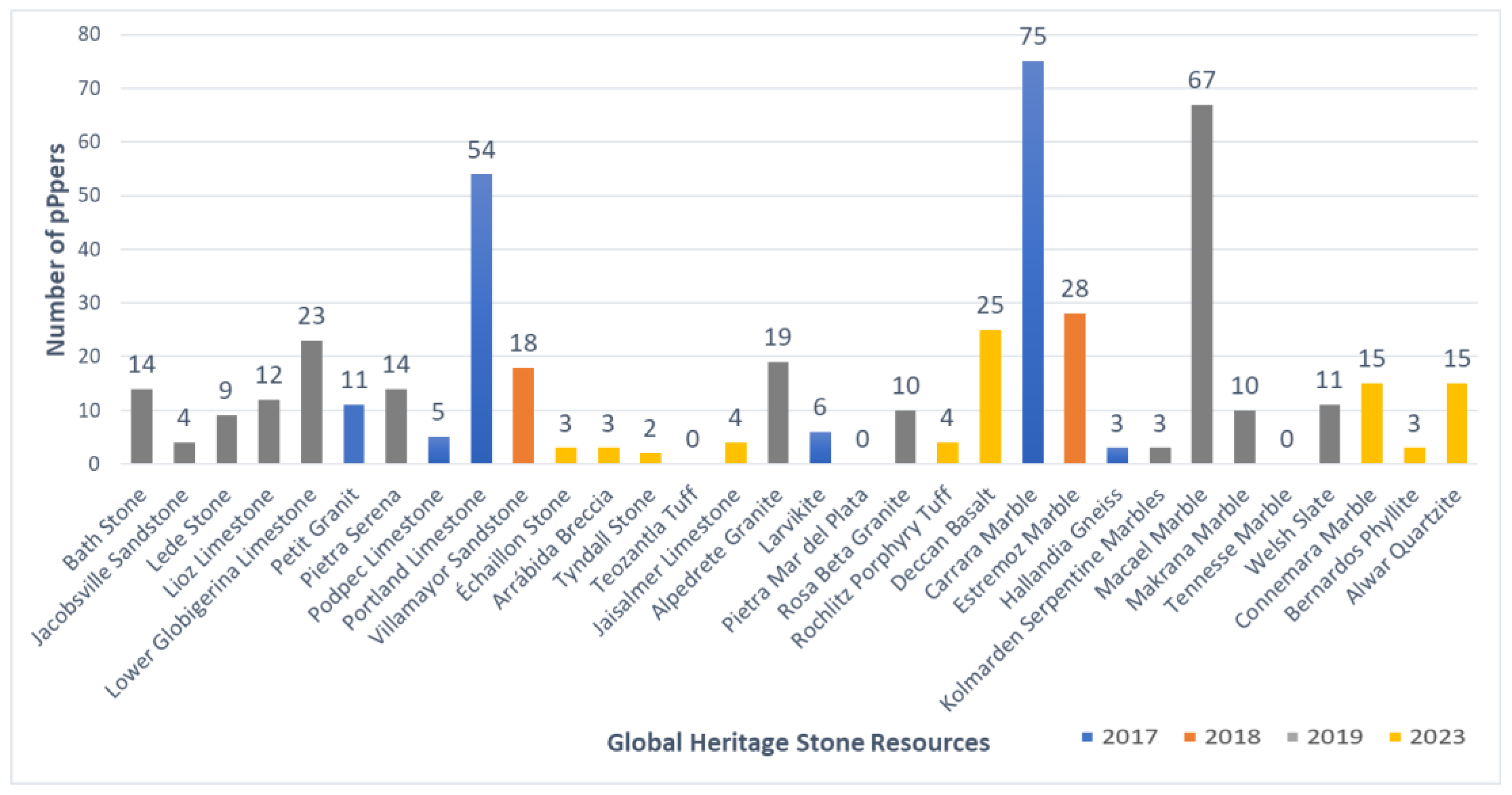
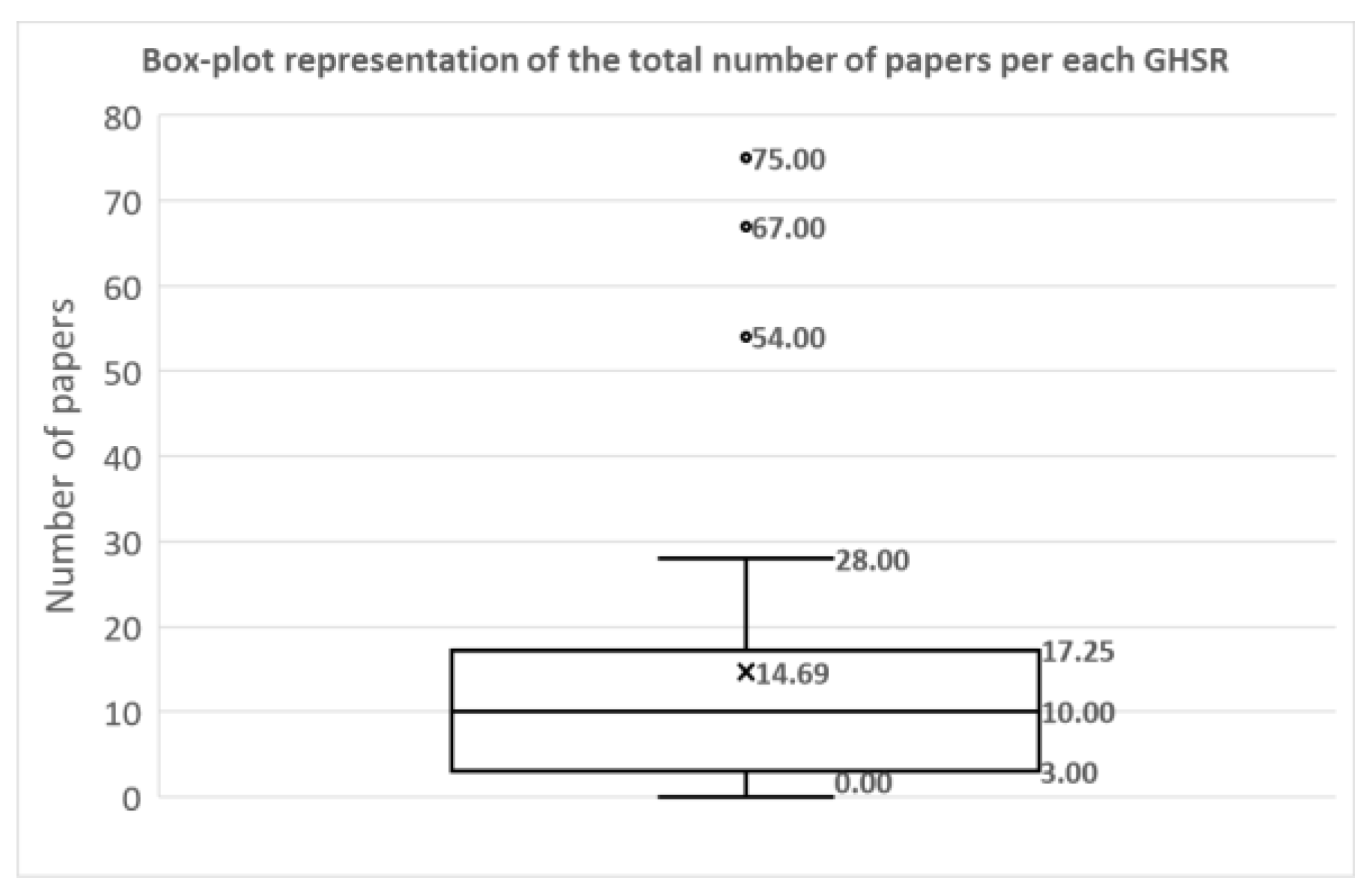
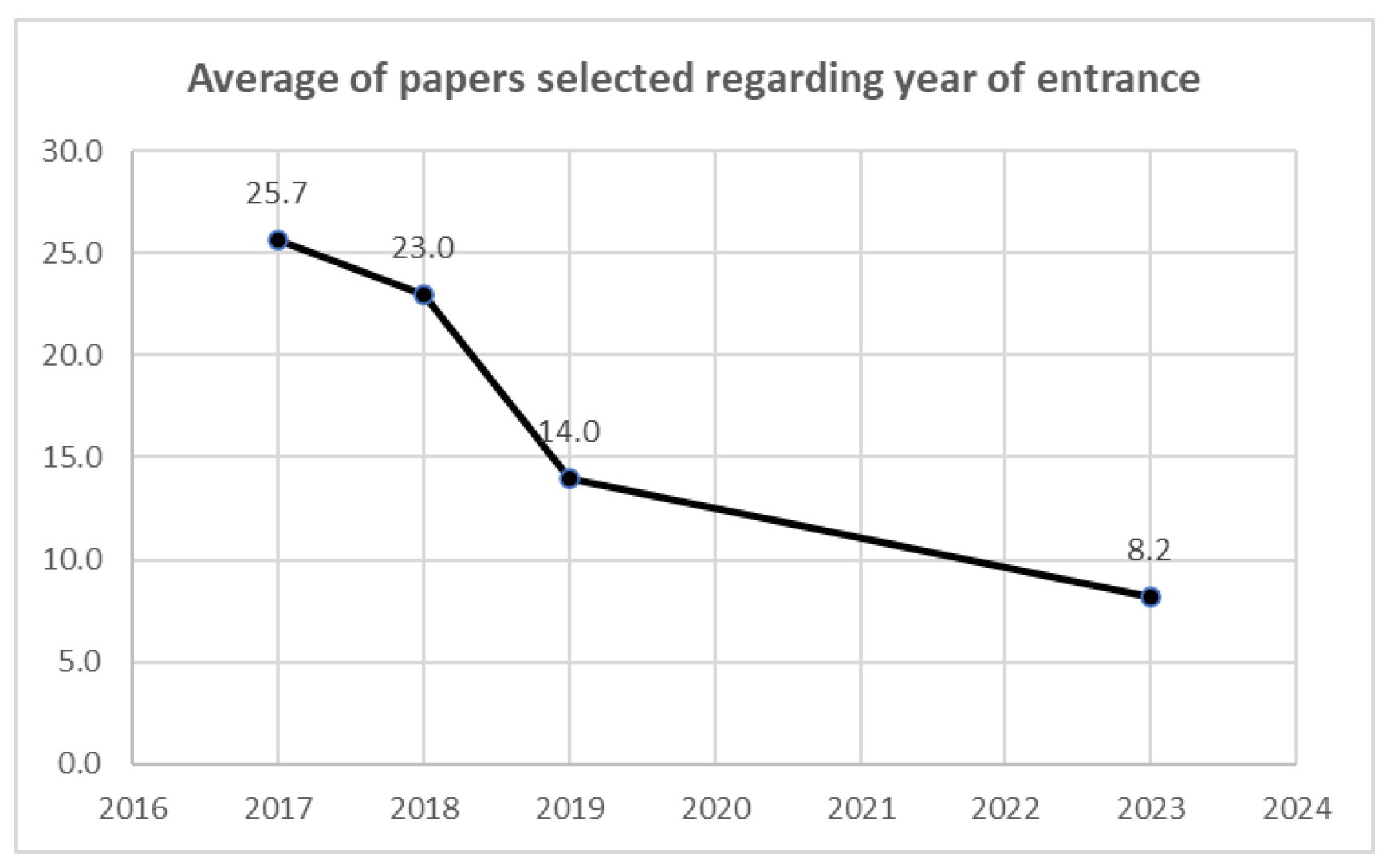
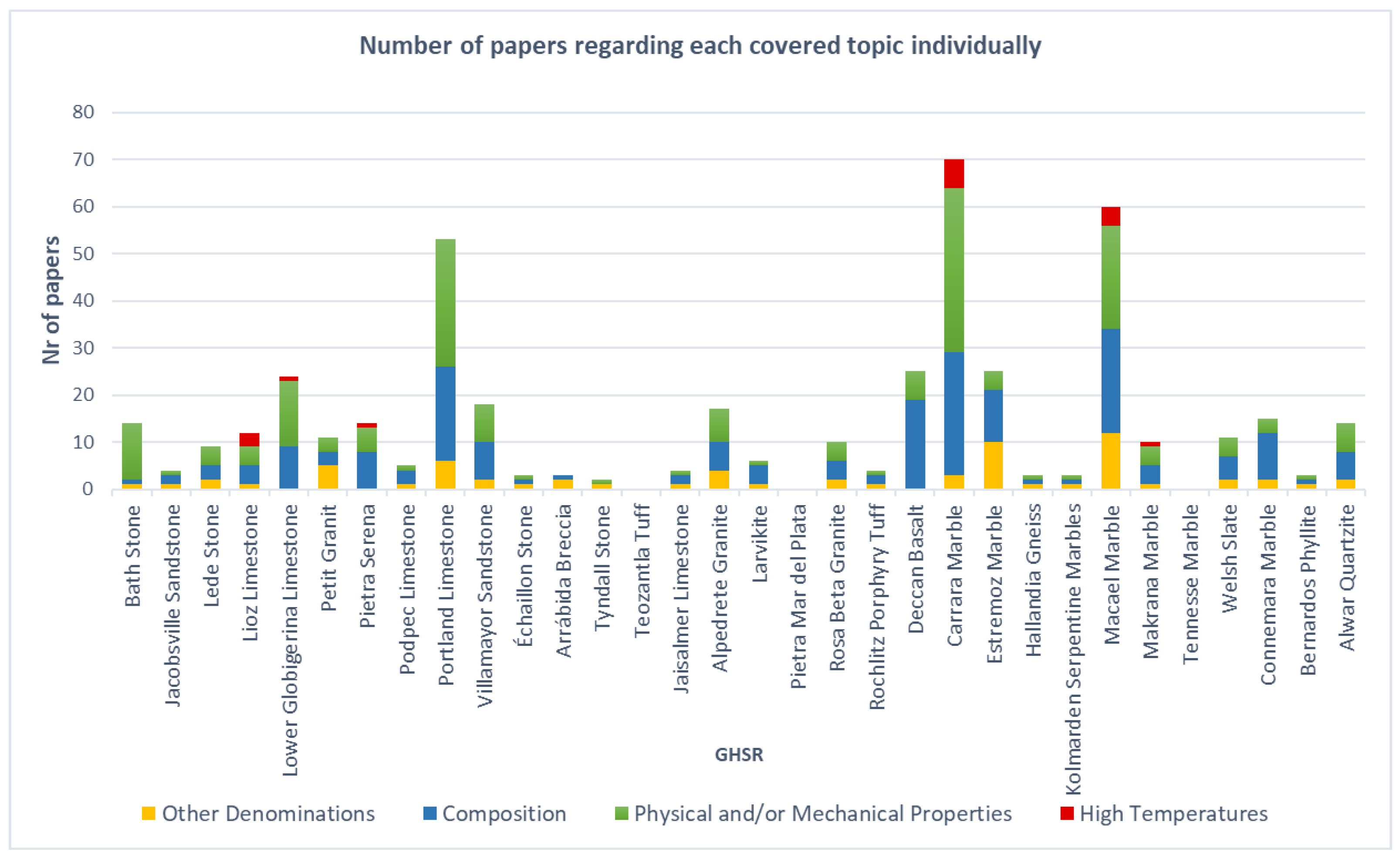
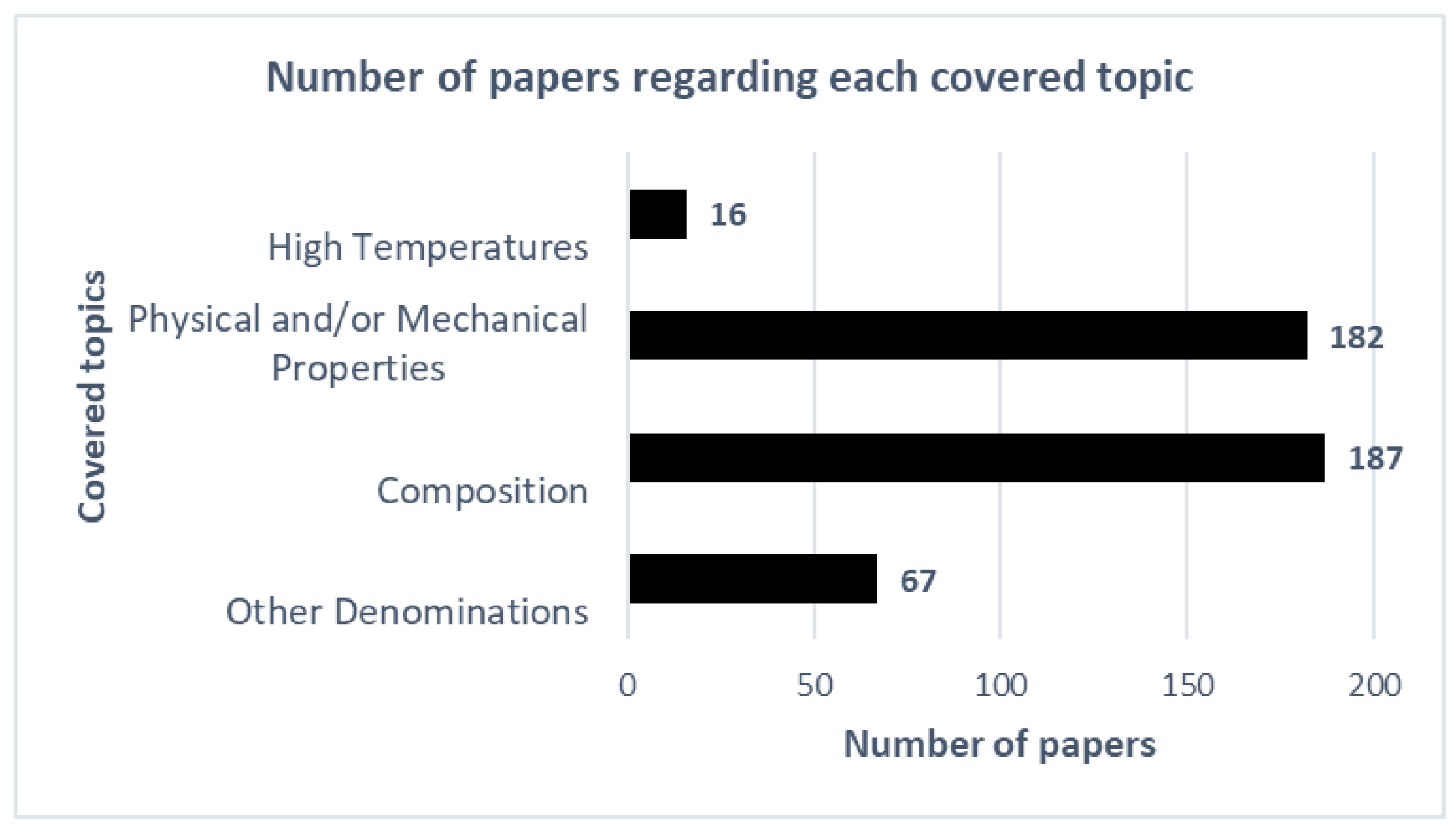
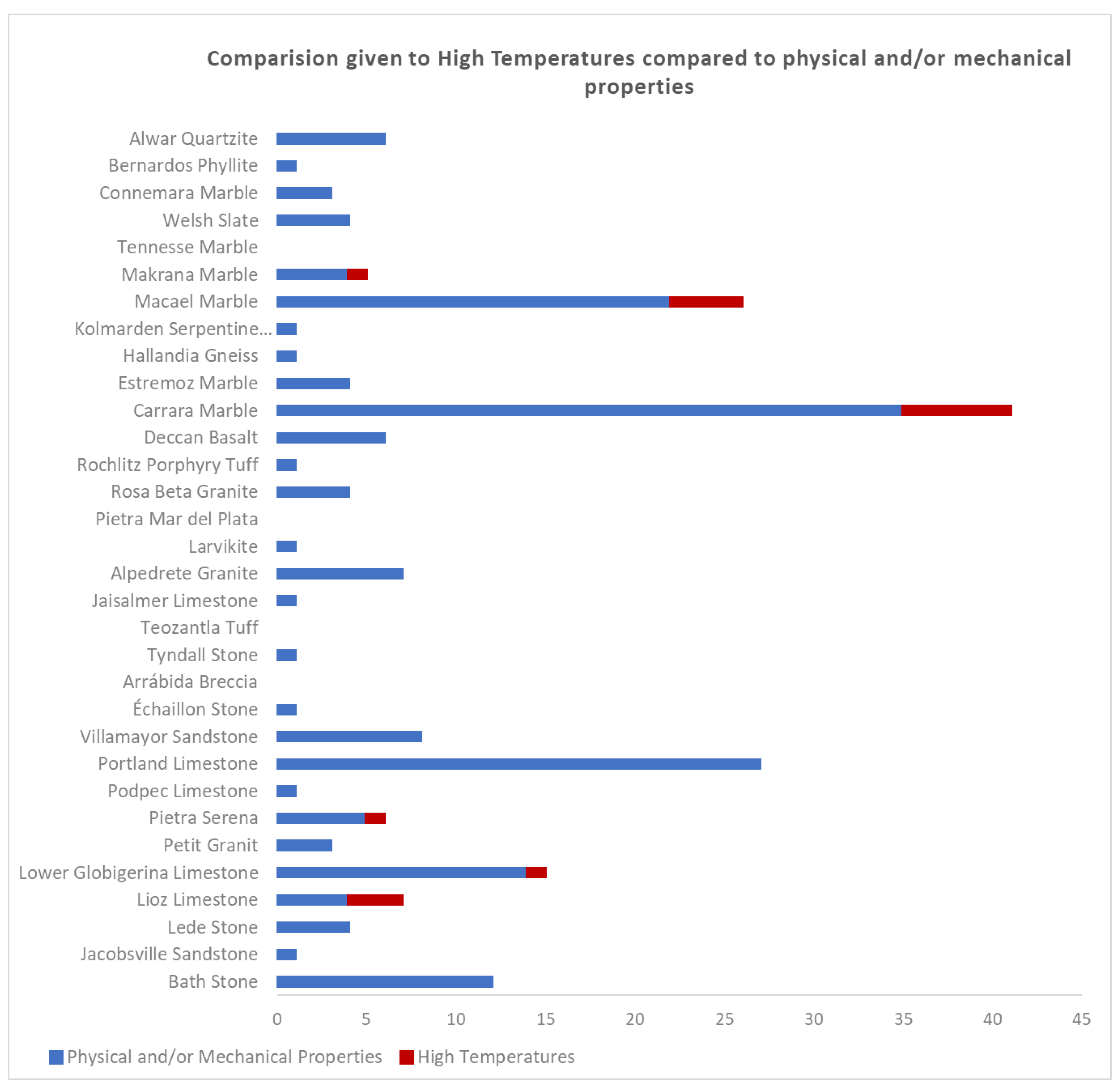
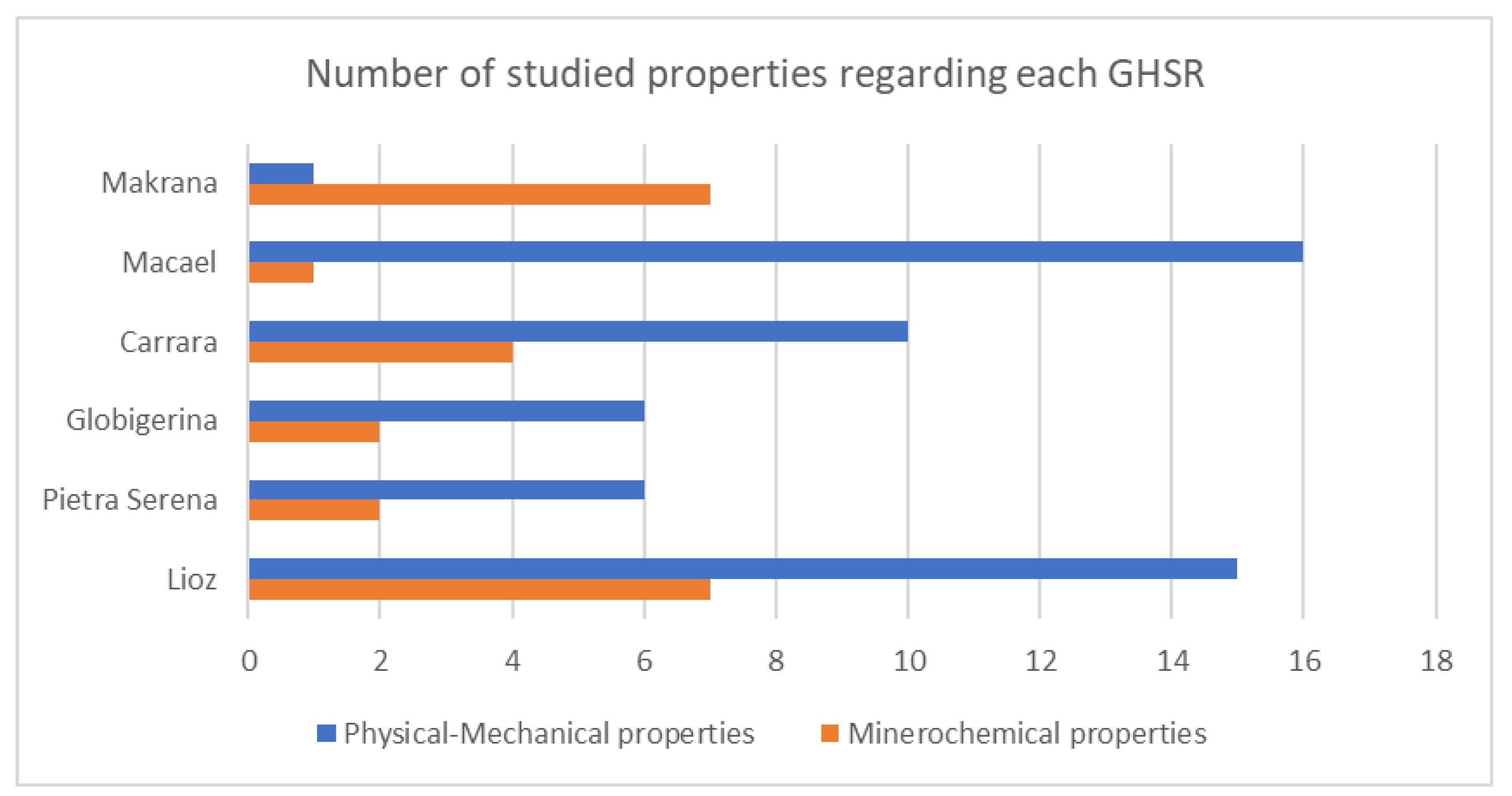
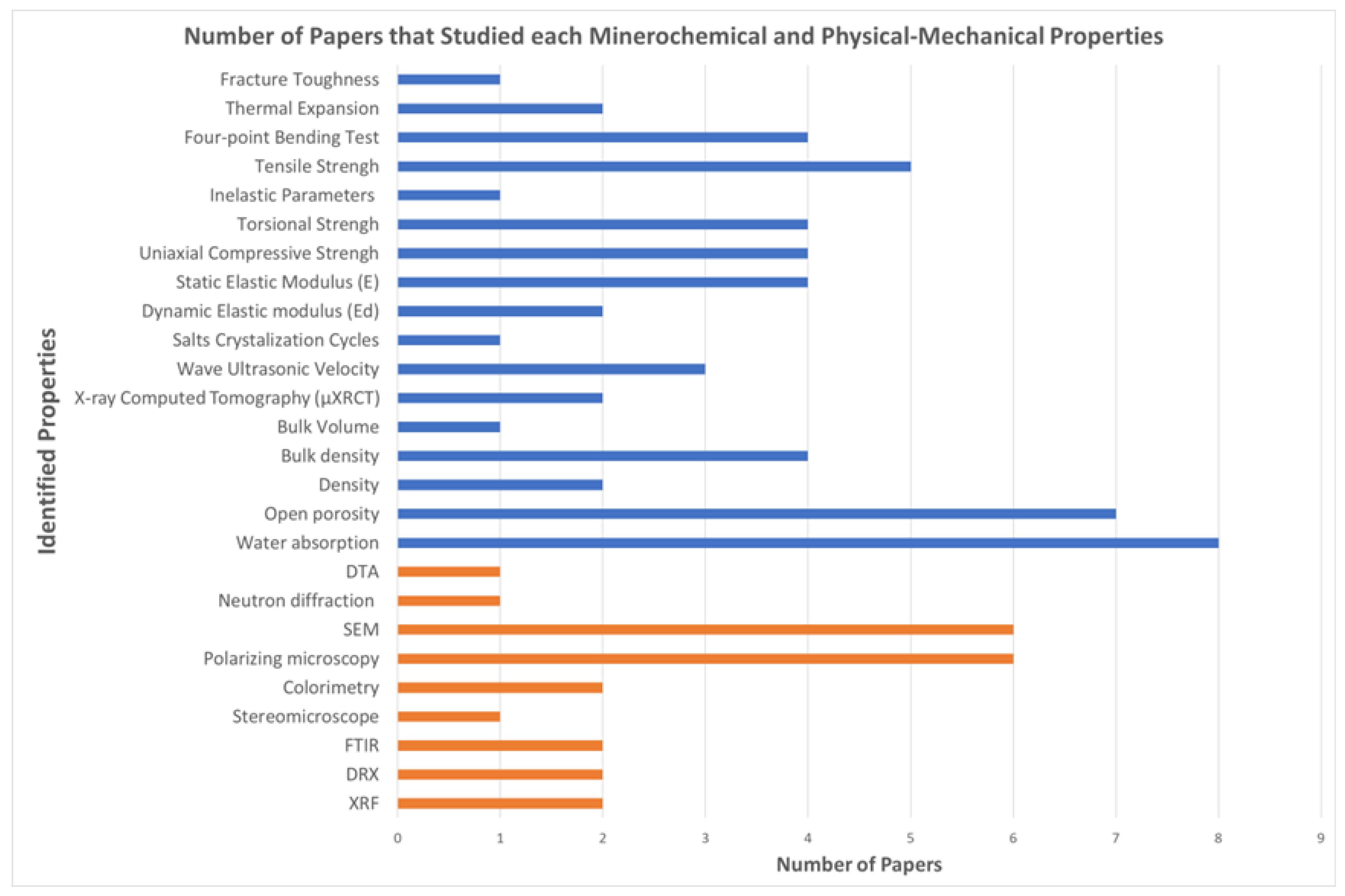
4. Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Name and Visual Aspect | Lithology | Place of Origin | Year of entrance | Reference for application | Total nr of papers found | Search words | Other nomenclatures | Composition | Physical and/or Mechanical Properties | High Temperatures | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sedimentary stones |  |
Limestone | Bath, United Kingdom | July 2019 | Marker, 2015 | 31 | Bath stone + Limestone | 1 [63] | 1 [64] | 12 [48,49,54,63–71] | 0 |
 |
Sandstone | Michigan, USA | January 2019 | Rose et al. 2017 | 24 | Jacobsville + Sandstone | 1 [72] | 2 [73,74] | 1 [72] | 0 | |
 |
Sandy Limestone | Brusssels, Belgium | January 2019 | De Kock et al. 2015 | 9 | Lede Stone + Limestone | 2 [75,76] | 3 [76,77,78] | 4 [76,77,78,79] | 0 | |
 |
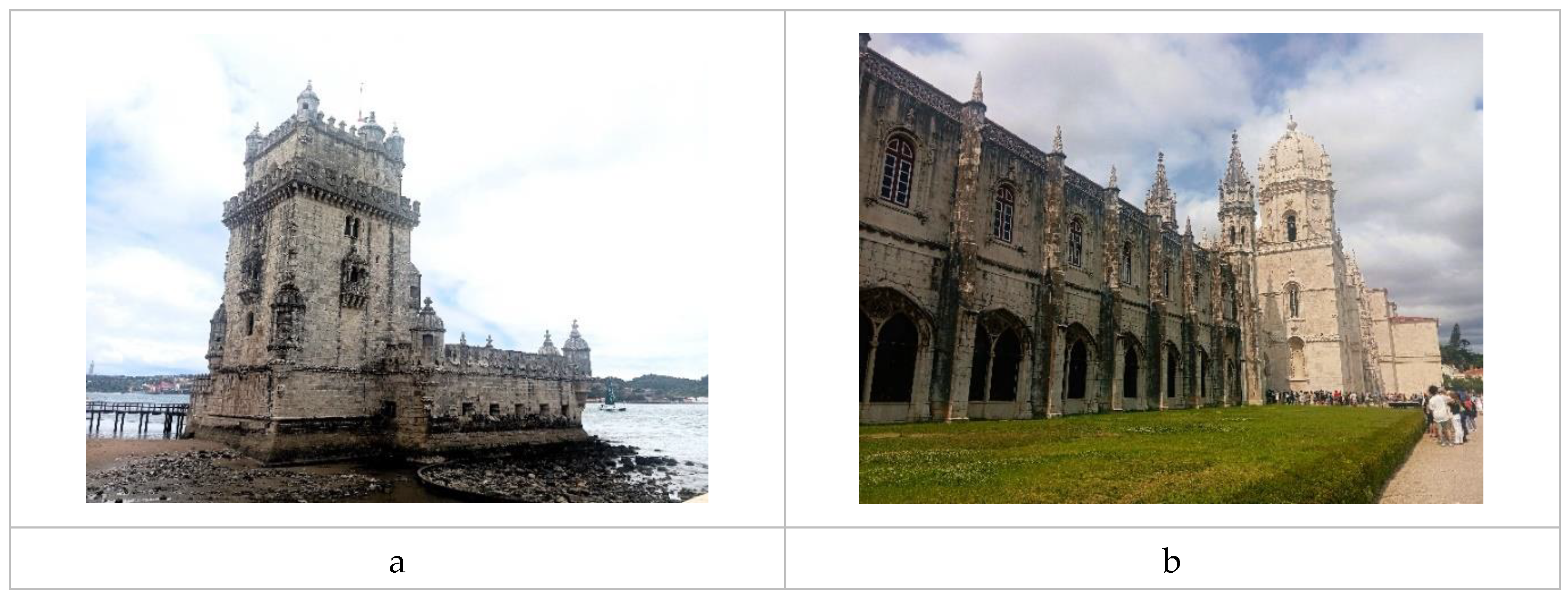
Limestone | Lisbon, Portugal | July 2019 | Silva, 2019 | 21 | Lioz + Limestone | 1 [80] | 4 [81,82,83,84] | 4 [47,80,81,85] | 3 [36,47,86] | |
 |
Limestone | Malta | January 2019 | Cassar et al. 2017 | 63 | Globigerina + Limestone | 0 | 9 [87,88,89,90,91,92,93,94,95] | 14 [50,51,87,88,90–99] | 1 [41] | |
 |
Limestone | Namur, Belgium | December 2017 | Pereira et al. 2015 | 9 | Petit Granit + Limestone | 5 [100,101,102,103,104] | 3 [100,101,105] | 3 [101,103,105] | 0 | |
 |
Sandy limestone / Sandstone | Florence, Italy | July 2019 | Fratini et al. 20115 | 9 | Pietra Serena + Limestone | 0 | 8 [41,106–112] | 5 [41,106,108,109,113] | 1 [41] | |
 |
Limestone | Podpeč, Slovenia | December 2017 | Kramar et al. 2015 | 9 | Podpeč + Limestone | 1 [114] | 3 [114,115,116] | 1 [114] | 0 | |
 |
Limestone | Portland, United Kingdom | December 2017 | Hughes et al. 2013 | 2 190 | Portland + Limestone | 6 [52,117–121] | 20 [55,117–120,122–136] | 27 [52,55,118,120–123,125,126,128–145] | 0 | |
 |
Sandstone | Salamanca, Spain | February 2018 | Garcia-Talegon et al. 2015 | 10 | Villamayor + Sandstone | 2 [146,147] | 8 [147,148,149,150,151,152,153,154] | 8 [146–148,150,152–155] | 0 | |
 |
Limestone | Alps, France | April, 2023 | Dumont, 2020 | 1 | Echaillon Stone + Limestone | 1 [156] | 1 [156] | 1 [156] | 0 | |
 |
Breccia | Arrábida, Portugal | April, 2023 | 2 | Arrábida + Breccia | 2 [157,158] | 1 [159] | 0 | 0 | ||
 |
Dolomitic limestone | Manitoba, Canada | April, 2023 | 1 | Tyndall Stone + Limestone | 1 [160] | 0 | 1 [160] | 0 | ||
| (not found) | Tuff | Mexico | April, 2023 | 0 | Teozantla + Tuff | - | - | - | - | ||
| Igneous stones |  |
Limestone | Jaisalmer, India | April, 2023 | [161] | 26 | Jaisalmer + Limestone | 1 [162] | 2 [162,163] | 1 [162] | 0 |
 |
Granite | Alpedrete Province, Madrid, Spain | July 2019 | Freire-Lista et al. 2015 | 8 | Alpedrete + Granite | 4 [164,165,166,167] | 6 [53,164–168] | 7 [53,164–169] | 0 | |
 |
Monzonite | Larvik, Norway | December 2017 | Heldal et al. 2015 | 5 | Larvikite + Monzonite | 1 [170] | 4 [170,171,172,173] | 1 [170] | 0 | |
 |
Orthoquartzite | Mar del Plata, Argentina | January 2019 | Cravero et al.2015 | 0 | Piedra Mar del Plata + | - | - | - | - | |
 |
Granite | Italy | July 2019 | Careddu et al. 2015 | 5 | Rosa Beta + Granite | 2 [174,175] | 4 [174,176–178] | 4 [174,176–178] | 0 | |
 |
Porphyry tuff | Rochlitz, Germany | April 2023 | [179] | 2 | Rochlitz + Porphyry Tuff | 1 [180] | 2 [180,181] | 1 [180] | 0 | |
| Metamorphic stones |  |
Deccan | Deccan, India | April 2023 | 12114 | Deccan + Basalt | 0 | 19 [182,183,184,185,186,187,188,189,190,191,192,193,194,195,196,197,198,199,200] | 6 [182,183,190,201–203] | 0 | |
 |
Marble | Tuscany, Italy | December 2017 | Primavori, 2015 | 560 | Carrara + Marble | 3 [38,87,204] | 26 [37,87,205–228] | 35 [37,38,205–211,213–219,221–239] | 6 [37,38,208,218,222,240] | |
 |
Marble | Estremoz, Portugal | February 2018 | Lopes & Martins, 2015 | 29 | Estremoz + Marble | 10 [241,242,243,244,245,246,247,248,249,250] | 10 [241,242,243,244,245,246,247,248,249,250,251] | 4 [242–244,249] | 0 | |
 |
Gneiss | Getinge, Sweden | December 2017 | Schouenborg et al. 2015 | 1 | Hallandia + Gneiss | 1 [252] | 1 [252] | 1 [252] | 0 | |
 |
Serpentine Marble | Kolmarden, Sweden | January 2019 | Wikstrom & Pereira, 2015 | 1 | Kolmarden Serpentine + Marble | 1 [253] | 1 [253] | 1 [253] | 0 | |
 |
Marble | Almeria, Spain | July 2019 | Navarro et al. 2015 | 42 | Macael + Marble | 12 [18,248,254–263] | 22 [15,18–20,248,254–256,258–262,264–272] | 22 [15,18,19,44,46,255–262,265–267,270–275] | 4 [19,20,46,273] | |
 |
Marble | Makrana, India | July 2019 | Garg et al. 2019 | 16 | Makrana + Marble | 1 [276] | 4 [23,276–278] | 4 [23,276,279,280] | 1 [23] | |
 |
Marble | Tennessee, USA | July 2019 | Byerly & Knowles, 2017 | 0 | Tennesse + Marble | - | - | - | - | |
 |
Slate | Wales, United Kingdom | January 2019 | Hughes et al. 2016 | 59 | Welsh + Slate | 2 [281,282] | 5 [281,282,283,284,285] | 4 [281,284–286] | 0 | |
 |
Sillimanite-grade ophicarbonate | Connemara, Ireland | April, 2023 | [287] | 20 | Connemara + Marble | 2 [288,289] | 10 [55,288–296] | 3 [289,290,293] | 0 | |
 |
Phyllite | Lugo, Spain | April, 2023 | [297] | 1 | Bernardos + Phyllite | 1 [298] | 1 [298] | 1 [298] | 0 | |
 |
Quartzite | Delhi, India | April, 2023 | [299] | 22 | Alwar + Quartzite | 2 [300,301] | 6 [300,302–306] | 6 [300,301,303,304,307,308] | 0 |
References
- Sims, I. Natural stone: sustaining the future of the world’s oldest construction material. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. Civ. Eng. 2015, 166, 149–157. https://doi.org/10.1680/CIEN.2013.166.4.149. [CrossRef]
- Cooper, B.J. Sustainable Development: An Opportunity for Dimension Stone. Roc Maquina 2004, 54, 12–17.
- Cooper, B.J. Toward establishing a “Global Heritage Stone Resource” designation. Proc. Geol. Soc. Am. 2010.
- Adorni, E.; Venturelli, G. Mortars and stones of the Damascus Citadel (Syria). Int. J. Archit. Herit. 2010, 4, 337–350. https://doi.org/10.1080/15583050903121851. [CrossRef]
- Pinho, F.F.S.; Lúcio, V.J.G. Rubble Stone Masonry Walls in Portugal: Material Properties, Carbonation Depth and Mechanical Characterization. Int. J. Archit. Herit. 2017, 11, 685–702. https://doi.org/10.1080/15583058.2017.1289424. [CrossRef]
- Winkler, E. Stone in Architecture: Properties, Durability; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1997.
- Martinho, E.; Dionísio, A. Assessment Techniques for Studying the Effects of Fire on Stone Materials: A Literature Review. Int. J. Archit. Herit. 2018, 14, 275–299. https://doi.org/10.1080/15583058.2018.1535008. [CrossRef]
- United Nations. Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2015.
- Ross, S.M. Saving heritage is key to sustainable development. Herit. Can. Found. J. 2006, Spring. Available online: https://archive.nationaltrustcanada.ca (accessed on 13 September 2024).
- Carter, B.; Grimwade, G. Balancing use and preservation in cultural heritage management. Int. J. Herit. Stud. 1997, 3, 45–53. https://doi.org/10.1080/13527259708722186. [CrossRef]
- Hannibal, J.T.; Kramar, S.; Cooper, B.J. Worldwide examples of global heritage stones: An introduction. Geol. Soc. Spec. Publ. 2020, 486, 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1144/SP486-2020-84. [CrossRef]
- Cooper, B.J. Recognition of a “World Heritage Stone Resource": A proposal. Presented at the International Conference on Heritage Stone Designation, 2008.
- Pereira, D. The value of Global Heritage Stone Resource Designation in enhancing and recovering our legacy and culture. Proc. Geol. Assoc. 2015.
- Cooper, B.J.; Marker, B.R.; Thomas, I.A. Towards international designation of a heritage dimension stone. Proc. Int. Assoc. Eng. Geol. 2013.
- Rodríguez Gordillo, J.; Sáez Pérez, M.P. Performance of Spanish white Macael marble exposed to narrow- and medium-range temperature cycling. Mater. Constr. 2010, 60, 127–141. https://doi.org/10.3989/mc.2010.44107. [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.M.; Falcão, P.; Paneiro, G. Finishing Surface Influence on Stone Thermal Behaviour. Hydrogeol. Eng. Geol. Geotech. 2015.
- Andriani, G.F.; Germinario, L. Thermal decay of carbonate dimension stones: fabric, physical and mechanical changes. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3160-6. [CrossRef]
- Navarro, R.; Pereira, D.; Cruz, A.S.; Carrillo, G. The Significance of “White Macael” Marble Since Ancient Times: Characteristics of a Candidate as Global Heritage Stone Resource. Geoheritage 2019, 11, 113–123. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12371-017-0264-x. [CrossRef]
- Justo, J.; Lagüera, A.; Castro, J.; Miranda, M.; Sagaseta, C. Influence of temperature on the tensile strength of a limestone and a marble. In Proceedings of the 17th European Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, ECSMGE 2019, Reykjavík, Iceland, 1–6 September 2019.
- Justo, J.; Castro, J.; Cicero, S.; Sánchez-Carro, M.A. Influence of temperature on the fracture toughness of several rocks. Proc. ECSMGE 2019, Reykjavík, Iceland, 1–6 September 2019.
- Justo, J.; Castro, J. Mechanical properties of 4 rocks at different temperatures and fracture assessment using the strain energy density criterion. Geomech. Energy Environ. 2021, 25, 100212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gete.2020.100212. [CrossRef]
- Justo, J.; Castro, J.; Cicero, S.; Sánchez-Carro, M.A.; Husillos, R. Notch effect on the fracture of several rocks: Application of the Theory of Critical Distances. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 2017, 90, 251–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tafmec.2017.05.025. [CrossRef]
- Gautam, P.K.; Jha, M.K.; Verma, A.K.; Singh, T.N. Experimental study of thermal damage under compression and tension of Makrana marble. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2020, 139, 609–627. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08403-5. [CrossRef]
- Dionísio, A.; Martinho, E.; Pozo-António, J.S.; Sequeira Braga, M.A.; Mendes, M. Evaluation of combined effects of real-fire and natural environment in a building granite. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 277, 122327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.122327. [CrossRef]
- Dionísio, A. Stone decay induced by fire on historic buildings: the case of the cloister of Lisbon Cathedral (Portugal). Geol. Soc. Lond., Spec. Publ. 2007, 271, 87–98. https://doi.org/10.1144/GSL.SP.2007.271.01.10. [CrossRef]
- Pozo-Antonio, J.S.; Sanmartín, P.; Serrano, M.; De la Rosa, J.M.; Miller, A.Z.; Sanjurjo-Sánchez, J. Impact of wildfire on granite outcrops in archaeological sites surrounded by different types of vegetation. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 747, 141143. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2020.141143. [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarti, B.; Yates, T.; Lewry, A. Effect of fire damage on natural stonework in buildings. Constr. Build. Mater. 1996, 10, 539–544. https://doi.org/10.1016/0950-0618(95)00076-3. [CrossRef]
- Gillhuber, S.; Lehrberger, G.; Göske, J. Fire damage of trachyte: investigations of the Teplá monastery building stones. Geol. Soc. Lond., Spec. Publ. 2010, 333, 73–79. https://doi.org/10.1144/SP333.8. [CrossRef]
- Hajpál, M. Changes in sandstones of historical monuments exposed to fire or high temperature. Fire Technol. 2002, 38, 373–382. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020174500861. [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Heras, M.; McCabe, S.; Smith, B.J.; Fort, R. Impacts of fire on stone-built heritage: An overview. J. Archit. Conserv. 2009, 15, 47–58. https://doi.org/10.1080/13556207.2009.10785047. [CrossRef]
- Franzen, C.; Krause, D.; Siedel, H.; Ullrich, B. Temperature impact on Cotta sandstone. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/257304809_Impact_of_temperature_on_Cotta_sandstone (accessed on 13 Sept 2024).
- Sanjurjo-Sanchez, J.; Gomez-Heras, M.; Fort, R. Dating fires and estimating the temperature attained on stone surfaces: The case of Ciudad de Vascos (Spain). Microchem. J. 2016, 124, 247–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2015.09.014. [CrossRef]
- McCabe, S.; Smith, B.J.; Warke, P.A. Exploitation of inherited weakness in fire-damaged building sandstone: The “fatiguing” of “shocked” stone. Eng. Geol. 2010, 115, 217–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2009.06.003. [CrossRef]
- Heidari, M.; Torabi-Kaveh, M.; Mohseni, H. Artificial weathering assessment of Persepolis stone due to heating to elucidate the effects of the burning of Persepolis. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2016, 75, 979–992. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-016-0887-1. [CrossRef]
- Koca, M.Y.; Ozden, G.; Yavuz, A.B.; Kincal, C.; Onargan, T.; Kucuk, K. Changes in the engineering properties of marble in fire-exposed columns. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2006, 43, 520–530. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2005.09.007. [CrossRef]
- Martinho, E.; Mendes, M.; Dionísio, A. 3D imaging of P-waves velocity as a tool for evaluation of heat induced limestone decay. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 135, 119–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.12.192. [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Jackson, I. Seismic-frequency laboratory measurements of shear mode viscoelasticity in crustal rocks I: Competition between cracking and plastic flow in thermally cycled Carrara marble. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 1996, 94, 105–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/0031-9201(95)03079-4. [CrossRef]
- Ruf, M.; Steeb, H. Effects of thermal treatment on acoustic waves in Carrara marble. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2022, 159, 105205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2022.105205. [CrossRef]
- Casey, M.; Rutter, E.H.; Schmid, S.M.; Siddans, A.W.B.; Whalley, J.S. Texture development in experimentally deformed calcite rocks. Presented at the Conference on Deformation Mechanisms in Rocks, London, UK, 1978.
- Hacker, B.R. High-pressure deformation of calcite marble and its transformation to aragonite under non-hydrostatic conditions. J. Struct. Geol. 1993, 15, 1207–1222. https://doi.org/10.1016/0191-8141(93)90158-R. [CrossRef]
- Franzoni, E.; Sassoni, E.; Scherer, G.W.; Naidu, S. Artificial weathering of stone by heating. J. Cult. Herit. 2013, 14, 0–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.culher.2012.11.026. [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.; Kang, Y.; Meng, T.; Hu, Y.Q.; Li, X.H. The Influence of Temperature on Mode I Fracture Toughness and Fracture Characteristics of Sandstone. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2017, 50, 2007–2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-017-1226-y. [CrossRef]
- Al-Shayea, N. Comparing reservoir and outcrop specimens for mixed mode I–II fracture toughness of a limestone rock formation at various conditions. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2002, 35, 271–297. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-002-0027-z. [CrossRef]
- Justo, J.; Castro, J.; Cicero, S. Notch effect and fracture load predictions of rock beams at different temperatures using the Theory of Critical Distances. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2020, 125, 104161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2019.104161. [CrossRef]
- Justo, J.; Castro, J. Application of the TCD for the fracture prediction of rocks with U-shaped notches at different temperatures. In Proceedings of the 14th International Congress on Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, ISRM 2019; Fuenmayor, F., Eds.; Springer: London, UK, 2020; pp. 1242–1249.
- Justo, J.; Castro, J. Mechanical properties of 4 rocks at different temperatures and fracture assessment using the strain energy density criterion. Geomech. Energy Environ. 2021, 25, 100212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gete.2020.100212. [CrossRef]
- Martinho, E.; Dionísio, A.; Mendes, M. Simulation of a Portuguese limestone masonry structure submitted to fire: 3D ultrasonic tomography approach. Int. J. Conserv. Sci. 2017, 8, 565–580.
- Channon, D. Feral pigeon excrement on heritage stonework. Constr. Build. Mater. 2004, 1, 24–28.
- Viles, H.A.; Goudie, A.S. Rapid salt weathering in the coastal Namib desert: Implications for landscape development. Geomorphology 2007, 85, 49–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2006.03.025. [CrossRef]
- Roussel, E.; Vautier, F.; Voldoire, O.; André, M.-F.; Cassar, J.; Fronteau, G.; Phalip, B.; Thomachot-Schneider, C.; Toumazet, J.-P. Quantifying 450 years of limestone weathering induced by salt crystallization on fortifications in Malta and Gozo. Geomorphology 2021, 378, 107614. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2021.107614. [CrossRef]
- Graziani, G.; Sassoni, E.; Scherer, G.W.; Franzoni, E. Phosphate-based treatments for consolidation of salt-bearing Globigerina limestone. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2018; pp. 1–7.
- Wilhelm, K.; Viles, H.; Burke, Ò. The Influence of Salt on Handheld Electrical Moisture Meters: Can They Be Used to Detect Salt Problems in Porous Stone? Int. J. Archit. Herit. 2016, 10, 735–748. https://doi.org/10.1080/15583058.2015.1109733. [CrossRef]
- López-Arce, P.; Varas-Muriel, M.J.; Fernández-Revuelta, B.; Álvarez de Buergo, M.; Fort, R.; Pérez-Soba, C. Artificial weathering of Spanish granites subjected to salt crystallization tests: Surface roughness quantification. Catena 2010, 83, 170–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2010.08.009. [CrossRef]
- Thornbush, M.J.; Viles, H.A. Simulation of the dissolution of weathered versus unweathered limestone in carbonic acid solutions of varying strength. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2007, 32, 841–852. https://doi.org/10.1002/esp.1441. [CrossRef]
- Compton, R.G.; Walker, C.T.; Unwin, P.R.; House, W.A. Dissolution kinetics of Carrera marble, Portland stone and several limestones in acid waters. J. Chem. Soc., Faraday Trans. 1990, 86, 849–854. https://doi.org/10.1039/FT9908600849. [CrossRef]
- Giunchi, D.; Baldaccini, N.E.; Sbragia, G.; Soldatini, C. Feral pigeons: problems, dynamics and control methods. In: Brooks, S. (Ed.), Pest Control Solutions for Urban Environments; Springer: New York, 2012; pp. 23–46.
- Viles, H.A.; Taylor, M.P.; Yates, T.J.S.; Massey, S.W. Soiling and decay of N.M.E.P. limestone tablets. Sci. Total Environ. 2002, 292, 215–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(01)01124-X. [CrossRef]
- Giunchi, D.; Baldaccini, N.E.; Sbragia, G.; Soldatini, C. Feral pigeons: problems, dynamics and control methods. In: Brooks, S. (Ed.), Pest Control Solutions for Urban Environments; Springer: New York, 2012; pp. 23–46.
- Laue, S. Salt Weathering of Porous Structures Related to Climate Changes/Klimaabhängige Salzverwitterung poröser Strukturen. Restor. Build. Monum. 2005, 11, 381–390.
- Godts, S.; Hayen, R.; De Clercq, H. Investigating salt decay of stone materials related to the environment: A case study in the St. James Church in Liège, Belgium. Stud. Conserv. 2017, 62, 329–342. https://doi.org/10.1080/00393630.2016.1236997. [CrossRef]
- Davies, T.D.; Kelly, P.M.; Brimblecombe, P.; Farmer, G.; Barthelmie, R.J. Acidity of Scottish rainfall influenced by climatic change. Nature 1986, 322, 359–361.
- White, J.; Wagner, W.; Beal, C. Global Climate Change Linkages: Acid Rain, Air Quality, and Stratospheric Ozone; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, 1989.
- Allen, G.C.; El-Turki, A.; Hallam, K.R.; McLaughlin, D.; Stacey, M. Role of NO2 and SO2 in degradation of limestone. Br. Corros. J. 2000, 35, 35–38. https://doi.org/10.1179/000705900101501047. [CrossRef]
- Marker, B.R. Bath Stone and Purbeck Stone: A comparison in terms of criteria for Global Heritage Stone Resource designation. Episodes 2015, 38, 118–123. https://doi.org/10.18814/epiiugs/2015/v38i2/008. [CrossRef]
- Viles, H.A.; Gorbushina, A.A. Soiling and microbial colonisation on urban roadside limestone: A three-year study in Oxford, England. Build. Environ. 2003, 38, 1217–1224. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0360-1323(03)00078-7. [CrossRef]
- Pesce, G.L.; Morgan, D.; Odgers, D.; Henry, A.; Allen, M.; Ball, R.J. Consolidation of weathered limestone using nanolime. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. Constr. Mater. 2013, 166, 213–228. https://doi.org/10.1680/coma.12.00051. [CrossRef]
- Thornbush, M.J.; Viles, H. Changing patterns of soiling and microbial growth on building stone in Oxford, England after implementation of a major traffic scheme. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 367, 203–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2005.11.022. [CrossRef]
- Laycock, E.A.; Spence, K.; Jefferson, D.P.; Hetherington, S.; Martin, B.; Wood, C. Testing the durability of limestone for Cathedral façade restoration. Environ. Geol. 2008, 56, 521–528. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-008-1333-x. [CrossRef]
- Elliott, G.M.; Brown, E.T. Yield of a soft, high porosity rock. Geotechnique 1985, 35, 413–423. https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.1985.35.4.413. [CrossRef]
- Nuño, M.; Pesce, G.L.; Bowen, C.R.; Xenophontos, P.; Ball, R.J. Environmental performance of nano-structured Ca(OH)2/TiO2 photocatalytic coatings for buildings. Build. Environ. 2015, 92, 734–742. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2015.05.028. [CrossRef]
- Forrest, M. Secure Heritage; Heritage Council of New South Wales: Sydney, 2007.
- Sherman, H.M.; Gierke, J.S.; Anderson, C.P. Controls on spatial variability of uranium in sandstone aquifers. Ground Water Monit. Remediat. 2007, 27, 106–118. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6592.2007.00142.x. [CrossRef]
- Kerfoot, W.C.; Hobmeier, M.M.; Green, S.A.; Yousef, F.; Brooks, C.N.; Shuchman, R.; Sayers, M.; Lin, L.; Luong, P.; Hayter, E.; Reif, M. Coastal ecosystem investigations with LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) and bottom reflectance: Lake Superior reef threatened by migrating tailings. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1076. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11091076. [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, R.L.; Sheldon, N.D. Sedimentary provenance and weathering processes in the 1.1Ga Midcontinental Rift of the Keweenaw Peninsula, Michigan, USA. Precambrian Res. 2016, 275, 225–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precamres.2016.01.017. [CrossRef]
- De Kock, T.; Turmel, A.; Fronteau, G.; Cnudde, V. Rock fabric heterogeneity and its influence on the petrophysical properties of a building limestone: Lede stone (Belgium) as an example. Eng. Geol. 2017, 216, 31–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2016.11.007. [CrossRef]
- Dewanckele, J.; Boone, M.A.; De Kock, T.; De Boever, W.; Brabant, L.; Boone, M.N.; Fronteau, G.; Dils, J.; Van Hoorebeke, L.; Jacobs, P.; Cnudde, V. Holistic approach of pre-existing flaws on the decay of two limestones. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 447, 403–414. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.12.094. [CrossRef]
- De Kock, T.; Van Stappen, J.; Fronteau, G.; Boone, M.; De Boever, W.; Dagrain, F.; Silversmit, G.; Vincze, L.; Cnudde, V. Laminar gypsum crust on lede stone: Microspatial characterization and laboratory acid weathering. Talanta 2017, 162, 193–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2016.10.025. [CrossRef]
- De Kock, T.; Turmel, A.; Fronteau, G.; Cnudde, V. Rock fabric heterogeneity and its influence on the petrophysical properties of a building limestone: Lede stone (Belgium) as an example. Eng. Geol. 2017, 216, 31–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2016.11.007. [CrossRef]
- Schröer, L.; De Kock, T.; Cnudde, V.; Boon, N. Differential colonization of microbial communities inhabiting Lede stone in the urban and rural environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 733, 139339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139339. [CrossRef]
- Mozer, A.G.S.; Castro, N.F.; Mansur, K.L.; Ribeiro, R.C.C. Mapping Lioz Limestone in Monuments at Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Geoheritage 2022, 14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12371-022-00682-z. [CrossRef]
- Da Conceição Ribeiro, R.C.; Marques Ferreira de Figueiredo, P.; Silva Barbutti, D. Multi-analytical investigation of stains on dimension stones in master Valentim’s fountain, Brazil. Minerals 2018, 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/min8100465. [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.; Dionísio, A.; Macedo, M.F. Primary bioreceptivity: A comparative study of different Portuguese lithotypes. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2006, 57, 136–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2006.01.003. [CrossRef]
- Polck, M.A.R.; Siqueira, L.M.P.; Barreto, A.M. An urban geotourism route in the city of Recife (PE), based on fossiliferous stones | Um roteiro geoturístico urbano na cidade do Recife (PE), com base em rochas fossilíferas. Anuário do Instituto de Geociências 2020, 43, 425–435. https://doi.org/10.11137/2020_3_425_435. [CrossRef]
- Silva, Z.C.G. Lioz—a Royal Stone in Portugal and a Monumental Stone in Colonial Brazil. Geoheritage 2019, 11, 165–175. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12371-017-0267-7. [CrossRef]
- Pozo-Antonio, J.S.; López, L.; Dionísio, A.; Rivas, T. A study on the suitability of mechanical soft-abrasive blasting methods to extract graffiti paints on ornamental stones. Coatings 2018, 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings8100335. [CrossRef]
- Pozo-Antonio, J.S.; Otero, J.; Alonso, P.; Mas i Barberà, X. Nanolime- and nanosilica-based consolidants applied on heated granite and limestone: Effectiveness and durability. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 201, 852–870. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.12.213. [CrossRef]
- Eichert, D.; Vergès-Belmin, V.E.; Kahn, O. Electronic paramagnetic resonance as a tool for studying the blackening of Carrara marble due to irradiation by a Q-switched YAG laser. J. Cult. Herit. 2000, 1. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1296-2074(00)00151-5. [CrossRef]
- Bianco, L. Geochemistry, mineralogy and textural properties of the lower globigerina limestone used in the built heritage. Minerals 2021, 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11070740. [CrossRef]
- Bianco, L. Petrological, mineralogical and geochemical characteristics of the globigerina limestone outcropping at Fomm IR-RI¯ H¯, Malta. Comptes Rendus de L’Academie Bulgare des Sciences 2020, 73, 985–991. https://doi.org/10.7546/CRABS.2020.07.12. [CrossRef]
- Briffa, S.M.; Vella, D.A. The behaviour of as-applied and artificially weathered silica–epoxy consolidants on a typical Mediterranean porous limestone: A comparison with TEOS. Herit. Sci. 2019, 7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40494-019-0270-1. [CrossRef]
- Cataldo, A.; De Benedetto, E.; Cannazza, G.; D’Amico, S.; Farrugia, L.; Misfud, G.; Dimech, E.; Sammut, C.V.; Persico, R.; Leucci, G.; De Giorgi, L. TDR-based water content estimation on globigerina limestone through permittivity measurements. In: IMEKO International Conference on Metrology for Archaeology and Cultural Heritage, MetroArchaeo 2017; pp. 528–533, 2019.
- Andreotti, S.; Franzoni, E.; Ruiz-Agudo, E.; Scherer, G.W.; Fabbri, P.; Sassoni, E.; Rodriguez-Navarro, C. New polymer-based treatments for the prevention of damage by salt crystallization in stone. Mater. Struct./Mater. Constr. 2019, 52. https://doi.org/10.1617/s11527-018-1309-6. [CrossRef]
- Cataldo, A.; De Benedetto, E.; Cannazza, G.; D’Amico, S.; Farrugia, L.; Mifsud, G.; Dimech, E.; Sammut, C.V.; Persico, R.; Leucci, G.; De Giorgi, L. Dielectric permittivity diagnostics as a tool for cultural heritage preservation: Application on degradable globigerina limestone. Measurement (Lond.) 2018, 123, 270–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2018.03.078. [CrossRef]
- Bianco, L. Petrological characteristics of blue lenticular patches occurring in the lower globigerina building limestone of Malta | Caracteristicile petrografice ale intercalațiilor lenticulare albastre care apar în nivelul inferior al calcarului cu globigerine pent. Rev. Romana Mater. 2018, 48, 115–120.
- Cassar, J.; Torpiano, A.; Zammit, T.; Micallef, A. Proposal for the nomination of lower globigerina limestone of the Maltese Islands as a “global Heritage Stone Resource.” Episodes 2017, 40, 221–231. https://doi.org/10.18814/epiiugs/2017/v40i3/017025. [CrossRef]
- Grøntoft, T.; Cassar, J.A. An assessment of the contribution of air pollution to the weathering of limestone heritage in Malta. Environ. Earth Sci. 2020, 79. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-020-09027-x. [CrossRef]
- Dreyfuss, T. Artificially induced calcium oxalate on limestone in urban environments – New findings. J. Cult. Herit. 2020, 42, 56–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.culher.2019.06.011. [CrossRef]
- Camilleri, D.H. Malta’s heritage in stone: From temple builders to Eurocodes 6/8. Masonry Int. 2019, 31, 49–65.
- Cabello-Briones, C.; Viles, H.A. Evaluating the effects of open shelters on limestone deterioration at archaeological sites in different climatic locations. Int. J. Archit. Herit. 2017, 11, 816–828. https://doi.org/10.1080/15583058.2017.1300710. [CrossRef]
- Hibo, D. The “petit granit’’ from the Meuse Valley and Soignies Basin mines: a sedimentological examination and comparison | Le ‘petit-granit’’ de la vallee de la Meuse et du bassin carrier de Soignies: approche du contexte sedimentologique et comparaison.’” Bull. - Soc. Belge Geol. 1993, 102, 359–378.
- Pereira, D., Tourneur, F., Bernáldez, L., Blázquez, A.G. Petit Granit: A Belgian limestone used in heritage, construction and sculpture. Episodes 2015, 38, 85–90. https://doi.org/10.18814/epiiugs/2015/v38i2/003. [CrossRef]
- Groessens, E. The origin and evolution of the expression “Petit Granit” | L’origine et l’evolution de l’expression ‘Petit Granit’.’ Bulletin - Societe Belge de Geologie 1993, 102, 271–276.
- Netels, V., Doyen, L. Geoelectrical and electromagnetic mapping of a faulted and karstified limestone deposit under a thick Tertiary overburden. Resolution of a hydrological problem at Carrierres du Hainaut (Soignies, Belgium) | Cartographie geoelectrique et electromagnetique. Bulletin - Societe Belge de Geologie 1997, 105, 15–28.
- Pereira, D., Perez-Castro, P. Art Museums: a Good Context for Outreach Activities on Natural Stones and Heritage. Geoheritage 2019, 11, 125–132. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12371-017-0265-9. [CrossRef]
- Dubois, C., Quinif, Y., Baele, J.-M., Dagrain, F., Deceuster, J., Kaufmann, O. The evolution of the mineralogical and petrophysical properties of a weathered limestone in southern Belgium. Geologica Belgica 2014, 17, 1–8.
- Coli, M., Livi, E., Pandeli, E., Tanini, Ch. Pietra Serena mining in Fiesole. Part II: Geological situation. J. Min. Sci. 2003, 39, 56–63. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025761227284. [CrossRef]
- Clausi, M., Magnani, L.L., Occhipinti, R., Riccardi, M.P., Zema, M., Tarantino, S.C. Interaction of metakaolin-based geopolymers with natural and artificial stones and implications on their use in cultural heritage. Int. J. Conserv. Sci. 2016, 7, 871–884.
- Santo, A.P., Centauro, I., Pecchioni, E. Walking Through Florence to Discover the Stone-Built Cultural Heritage. (2022).
- Sorace, S. Long-term tensile and bending strength of natural building stones. Mater. Struct./Mater. Constr. 1996, 29, 426–435. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02485993. [CrossRef]
- Coli, M., Ciuffreda, A.L., Donigaglia, T., Tanganelli, M. The Building Stones of Prato’s Cathedral and Bell Tower, Italy. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/app121910132. [CrossRef]
- Sassoni, E., Franzoni, E., Pigino, B., Scherer, G.W., Naidu, S. Consolidation of calcareous and siliceous sandstones by hydroxyapatite: Comparison with a TEOS-based consolidant. J. Cult. Herit. 2013, 14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.culher.2012.11.029. [CrossRef]
- Fratini, F., Cantisani, E., Pecchioni, E., Pandeli, E., Vettori, S. Pietra Alberese: Building material and stone for lime in the Florentine territory (Tuscany, Italy). Heritage 2020, 3, 1520–1538. https://doi.org/10.3390/heritage3040084. [CrossRef]
- Bargossi, G.M., Gamberini, F., Gasparotto, G., Grillini, G.C., Marocchi, M. Dimension and ornamental stones from the Tosco-Romagnolo and Bolognese Apennine. Period. Mineral. 2004, 73, 171–195.
- Kramar, S., Bedjanič, M., Mirtič, B., Mladenović, A., Rožič, B., Skaberne, D., Gutman, M., Zupančič, N., Cooper, B. Podpeč limestone: A heritage stone from Slovenia. (2015).
- Rožič, B., Gale, L., Brajković, R., Popit, T., Žvab Rožič, P. Lower Jurassic succession at the site of potential Roman quarry Staje near Ig (central Slovenia). Geologija 2018, 61, 49–71. https://doi.org/10.5474/geologija.2018.004. [CrossRef]
- Gale, L. Lower Jurassic foraminiferal biostratigraphy of Podpeč Limestone (External Dinarides, Slovenia). Geologija 2014, 57, 119–146. https://doi.org/10.5474/geologija.2014.011. [CrossRef]
- Marinelli, A., Stewart, M.R. Comparative experimental study of the mechanical and fracture properties of Portland limestone and Corsehill sandstone. Frattura ed Integrita Strutturale 2019, 13, 438–450. https://doi.org/10.3221/IGF-ESIS.50.37. [CrossRef]
- Hughes, T., Lott, G.K., Poultney, M.J., Cooper, B.J. Portland stone: A nomination for “global heritage stone resource” from the United Kingdom. Episodes 2013, 36, 221–226. https://doi.org/10.18814/epiiugs/2013/v36i3/004. [CrossRef]
- Falcon-Lang, H. The isle of Portland, Dorset, England, (2011).
- Butler-Warke, A., Warke, M.R. Foundation stone of empire: The role of Portland stone in ‘heritage’, commemoration, and identity. Trans. Inst. Br. Geogr. 2021, 46, 958–972. https://doi.org/10.1111/tran.12462. [CrossRef]
- Eklund, J.A., Zhang, H., Viles, H.A., Curteis, T. Using handheld moisture meters on limestone: Factors affecting performance and guidelines for best practice. Int. J. Archit. Herit. 2013, 7, 207–224. https://doi.org/10.1080/15583058.2011.626491. [CrossRef]
- Dubelaar, C.W., Engering, S., Van Hees, R.P.J., Koch, R., Lorenz, H.-G. Lithofacies and petrophysical properties of Portland Base Bed and Portland Whit Bed limestone as related to durability. Heron 2003, 48, 221–229.
- Kirkitsos, P., Sikiotis, D. Deterioration of pentelic marble, Portland limestone and baumberger sandstone in laboratory exposures to gaseous nitric acid. Atmos. Environ. 1995, 29, 77–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/1352-2310(94)00230-I. [CrossRef]
- Kirkitsos, P., Sikiotis, D. Deterioration of Pentelic marble, Portland limestone and Baumberger sandstone in laboratory exposures to NO₂: A comparison with exposures to gaseous HNO₃. Atmos. Environ. 1996, 30, 941–950. https://doi.org/10.1016/1352-2310(95)00297-9. [CrossRef]
- Allison, R.J. A non-destructive method of determining rock strength. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 1988, 13, 729–736. https://doi.org/10.1002/esp.3290130807. [CrossRef]
- Searle, D.E., Mitchell, D.J. The effect of coal and diesel particulates on the weathering loss of Portland Limestone in an urban environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 370, 207–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2006.07.005. [CrossRef]
- Viles, H.A. The early stages of building stone decay in an urban environment. Atmos. Environ. Part A Gen. Top. 1990, 24, 229–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/0960-1686(90)90459-Z. [CrossRef]
- Cabello Briones, C., Viles, H. An Assessment of the Role of an Open Shelter in Reducing Soiling and Microbial Growth on the Archaeological Site of the Bishop’s Palace, Witney, England. Conserv. Manag. Archaeol. Sites 2018, 20, 2–17. https://doi.org/10.1080/13505033.2018.1430437. [CrossRef]
- Allison, R.J., Kimber, O.G. Modelling failure mechanisms to explain rock slope change along the Isle of Purbeck coast, UK. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 1998, 23, 731–750. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1096-9837(199808)23:8<731::AID-ESP885>3.0.CO;2-F. [CrossRef]
- Bijeljic, B., Mostaghimi, P., Blunt, M.J. Signature of non-fickian solute transport in complex heterogeneous porous media. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 107. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.107.204502. [CrossRef]
- Cooper, T.P., O’Brien, P.F., Jeffrey, D.W. Rates of deterioration of portland limestone in an urban environment. Stud. Conserv. 1992, 37, 228–238. https://doi.org/10.1179/sic.1992.37.4.228. [CrossRef]
- Alyafei, N., Blunt, M.J. The effect of wettability on capillary trapping in carbonates. Adv. Water Resour. 2016, 90, 36–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2016.02.001. [CrossRef]
- Perry, S.H., Duffy, A.P. The short-term effects of mortar joints on salt movement in stone. Atmos. Environ. 1997, 31, 1297–1305. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1352-2310(96)00290-7. [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, A.J., Johnson, J.B., Thompson, G.E., Wood, G.C., Sage, P.W., Cooke, M.J. The role of fly-ash particulate material and oxide catalysts in stone degradation. Atmos. Environ. Part A Gen. Top. 1992, 26, 2795–2803. https://doi.org/10.1016/0960-1686(92)90017-F. [CrossRef]
- Roots, O. ICP materials: Long-term studies at the Lahemaa monitoring station, Estonia. Proc. Est. Acad. Sci. 2015, 64, 43–52. https://doi.org/10.3176/proc.2015.1.06. [CrossRef]
- Carmona-Quiroga, P.M., Martínez-Ramírez, S., Viles, H.A. Efficiency and durability of a self-cleaning coating on concrete and stones under both natural and artificial ageing trials. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 433, 312–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.10.052. [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.B., Montgomery, M., Thompson, G.E., Wood, G.C., Sage, P.W., Cooke, M.J. The influence of combustion-derived pollutants on limestone deterioration: 2. The wet deposition of pollutant species. Corros. Sci. 1996, 38, 267–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/0010-938X(96)00118-7. [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm, K., Viles, H., Burke, O., Mayaud, J. Surface hardness as a proxy for weathering behaviour of limestone heritage: a case study on dated headstones on the Isle of Portland, UK. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5661-y. [CrossRef]
- Hennah, S.J., Astin, T.R., Sothcott, J., McCann, C. Relationships between rock heterogeneity, attenuation and velocity dispersion at ultrasonic and sonic frequencies. (2003).
- Cabello Briones, C. Effects of open shelters on limestone decay: The case-study of the bishop’s palace archaeological site in Witney (England). In: Science, Technology and Cultural Heritage - Proceedings of the 2nd International Congress on Science and Technology for the Conservation of Cultural Heritage, 2014, pp. 41–46.
- Grossi, C.M., Esbert, R.M., Díaz-Pache, F. Decay and durability of building stones in urban environments | Degradación y durabilidad de materiales rocosos de edificación en ambientes urbanos. Materiales de Construccion 1998, 5–25. https://doi.org/10.3989/mc.1998.v48.i252.461. [CrossRef]
- Daengprathum, N., Onchang, R., Nakhapakorn, K., Robert, O., Tipayarom, A., Sturm, P.J. Estimation of Effects of Air Pollution on the Corrosion of Historical Buildings in Bangkok. Environ Nat Resour J. 2022, 20, 505–514. https://doi.org/10.32526/ennrj/20/202200071. [CrossRef]
- Inkpen, R. Errors in measuring the percentage dry weight change of stone tablets. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 1995, 20, 783–793. https://doi.org/10.1002/esp.3290200904. [CrossRef]
- Inkpen, R., Viles, H., Moses, C., Baily, B. Modelling the impact of changing atmospheric pollution levels on limestone erosion rates in central London, 1980-2010. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 61, 476–481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2012.07.042. [CrossRef]
- Roots, O.O., Roose, A., Eerme, K. Remote sensing of climate change, long-term monitoring of air pollution and stone material corrosion in Estonia. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 9691–9705. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431161.2011.574163. [CrossRef]
- García-Talegon, J., Vicente, M.A., Vicente-Tavera, S., Molina-Ballesteros, E. Assessment of chromatic changes due to artificial ageing and/or conservation treatments of sandstones. Color Res. Appl. 1998, 23, 46–51. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1520-6378(199802)23:1<46::AID-COL7>3.0.CO;2-3. [CrossRef]
- Ordaz, J., Alonso, F.J. Caracteristicas del sistema poroso de la arenisca de Villamayor (Salamanca). Trabajos de Geologia, Universidad de Oviedo 1983, 13, 83–92.
- Martin Patino, M.T., Madruga, F., Saavedra, J. The internal structure of the Villamayor sandstone as it affects its use as a construction material. Appl. Clay Sci. 1993, 8, 61–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/0169-1317(93)90026-W. [CrossRef]
- Marcos Laso, B. Biodiversity and lichenic growth on some monuments in Salamanca City | Biodiversidad y colonización liquénica de algunos monumentos en la ciudad de Salamanca (España). Bot. Complut. 2001, 93–102.
- Vielba Cuerpo, C., Hernández Olivares, F. Tests to characterize the behaviour of natural stone in contact with water | Ensayos de caracterización del comportamiento frente al agua de la piedra natural. Materiales de Construccion 2002, 43–54. https://doi.org/10.3989/mc.2002.v52.i267.325. [CrossRef]
- Schleicher, N., Hernández, C.R. Source identification of sulphate forming salts on sandstones from monuments in Salamanca, Spain-a stable isotope approach. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2010, 17, 770–778. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-009-0196-3. [CrossRef]
- Grondona, I., Monte, E., Rives, V., Vicente, M.A. Lichenized association between Septonema tormes sp. nov., a coccoid cyanobacterium, and a green alga with an unforeseen biopreservation effect of Villamayor sandstone at “Casa lis” of Salamanca, Spain. Mycol. Res. 1997, 101, 1489–1495. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0953756297004309. [CrossRef]
- Arco, M.D., Carballo, A.M., Holgado, M.J., Martín, C., Rives, V. A microporosity study of Villamayor Sandstone (Salamanca, Spain). Appl. Clay Sci. 1987, 2, 375–383. https://doi.org/10.1016/0169-1317(87)90043-3. [CrossRef]
- Vicente, M.A., Brufau, A. Weathering of the Villamayor arkosic sandstone used in buildings, under a continental semi-arid climate. Appl. Clay Sci. 1986, 1, 265–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/0169-1317(86)90003-7. [CrossRef]
- Saavedra, J., Madruga, F., Martin Patino, M.T. Classification of Villamayor sandstone (Salamanca) from technological characteristics and internal structure | Clasificacion de la arenisca de Villamayor (Salamanca) por sus caracteristicas tecnologicas y estructura interna. Boletin Geologico y Minero 1993, 104, 655–663.
- Dumont, T. Échaillon stone from France: a global heritage stone resource proposal. (2020).
- Kullberg, J.C., Coelho, C., Prego, A. Geological and Cultural Routes of the Arrábida Breccia: A Contribution to the Nomination of Arrábida for UNESCO’s Mixed World Heritage List. (2014).
- Kullberg, J.C., Prego, A. The Historical Importance and Architectonic Relevance of the “Extinct” Arrábida Breccia. Geoheritage 2019, 11, 87–111. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12371-017-0272-x. [CrossRef]
- Kullberg, J.C., Prego, A. The Historical Importance and Architectonic Relevance of the “Extinct” Arrábida Breccia. Geoheritage 2019, 11, 87–111. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12371-017-0272-x. [CrossRef]
- Brisbin, W.C., Young, G., Young, J. Geology of the parliament buildings 5: Geology of the Manitoba legislative building. Geoscience Canada 2005, 32, 177–193.
- Kaur, G., Kaur, P., Ahuja, A., Singh, A., Saini, J., Agarwal, P., Bhargava, O.N., Pandit, M., Goswami, R.G., Acharya, K., Garg, S. Jaisalmer Golden Limestone: A Heritage Stone Resource from the Desert of Western India. Geoheritage 2020, 12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12371-020-00475-2. [CrossRef]
- Kaur, G., Kaur, P., Ahuja, A., Singh, A., Saini, J., Agarwal, P., Bhargava, O.N., Pandit, M., Goswami, R.G., Acharya, K., Garg, S. Jaisalmer Golden Limestone: A Heritage Stone Resource from the Desert of Western India. Geoheritage 2020, 12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12371-020-00475-2. [CrossRef]
- Sen, P., Ghosh, J., Prabhulingaiah, G., Sekhar, D.M.R. Internal morphology of SMS grade limestone samples. Trans. Inst. Min. Metall., Sect. C: Mineral Process. Extract. Metall. 2006, 115, 127–131. https://doi.org/10.1179/174328506X99952. [CrossRef]
- Freire-Lista, D.M., Fort, R. Exfoliation microcracks in building granite. Implications for anisotropy. Eng. Geol. 2017, 220, 85–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.01.027. [CrossRef]
- Freire-Lista, D.M., Fort, R., Varas-Muriel, M.J. Thermal stress-induced microcracking in building granite. Eng. Geol. 2016, 206, 83–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2016.03.005. [CrossRef]
- Freire-Lista, D.M., Fort, R. Heritage stone 4. The piedra berroqueña region: Candidacy for global heritage stone province status. Geoscience Canada 2016, 43, 43–52. https://doi.org/10.12789/geocanj.2015.42.076. [CrossRef]
- Freire-Lista, D.M., Fort, R., Varas-Muriel, M.J. Alpedrete granite (Spain). A nomination for the “Global Heritage Stone Resource” designation. Episodes 2015, 38, 106–113. https://doi.org/10.18814/epiiugs/2015/v38i2/006. [CrossRef]
- Sanz, M., Oujja, M., Ascaso, C., Pérez-Ortega, S., Souza-Egipsy, V., Fort, R., de los Rios, A., Wierzchos, J., Cañamares, M.V., Castillejo, M. Influence of wavelength on the laser removal of lichens colonizing heritage stone. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 399, 758–768. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.12.032. [CrossRef]
- Fort, R., de Buergo, M.A., Perez-Monserrat, E.M., Gomez-Heras, M., Jose Varas-Muriel, M., Freire, D.M. Evolution in the use of natural building stone in Madrid, Spain. Quarterly Journal of Engineering Geology and Hydrogeology 2013, 46, 421–429. https://doi.org/10.1144/qjegh2012-041. [CrossRef]
- Heldal, T., Meyer, G.B., Dahl, R. Global stone heritage: Larvikite, Norway. (2015).
- Andersen, T. Crystallization history of a Permian composite monzonite-alkali syenite pluton in the Sande cauldron, Oslo rift, southern Norway. Lithos 1984, 17, 153–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/0024-4937(84)90016-1. [CrossRef]
- Ramberg, I.B. Braid perthite in nepheline syenite pegmatite, Langesundsfjorden, Oslo Region (Norway). Lithos 1972, 5, 281–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/0024-4937(72)90085-0. [CrossRef]
- Andersen, T., Erambert, M., Larsen, A.O., Selbekk, R.S. Petrology of nepheline syenite pegmatites in the Oslo Rift, Norway: Zirconium silicate mineral assemblages as indicators of alkalinity and volatile fugacity in mildly agpaitic magma. Journal of Petrology 2010, 51, 2303–2325. https://doi.org/10.1093/petrology/egq058. [CrossRef]
- Careddu, N., Grillo, S. Rosa Beta granite (Sardinian Pink Granite): A heritage stone of international significance from Italy. (2015).
- Del Lama, E.A., Costa, A.G. Global Heritage Stones in Brazil. Geoheritage 2022, 14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12371-022-00661-4. [CrossRef]
- Cuccuru, S., Puccini, A. Petrographic, physical–mechanical and radiological characterisation of the rosa beta granite (Corsica-sardinia batholith). (2015).
- Cuccuru, S., Cherchi, G.P. The Bassacutena district: Quarrying aspects and physicomechanical characterization of “Rosa Beta” granite | Il Polo Estrattivo di Bassacutena: aspetti giacimentologici e caratterizzazione fisico-meccanica del granito “Rosa Beta.” Rendiconti Online Societa Geologica Italiana 2008, 3, 282–283.
- Puccini, A., Xhixha, G., Cuccuru, S., Oggiano, G., Xhixha, M.K., Mantovani, F., Alvarez, C.R., Casini, L. Radiological characterization of granitoid outcrops and dimension stones of the Variscan Corsica-Sardinia Batholith. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 71, 393–405. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2442-8. [CrossRef]
- Siedel, H., Rust, M., Goth, K., Krüger, A., Heidenfelder, W. Rochlitz porphyry tuff (“Rochlitzer Porphyrtuff”): A candidate for “global Heritage Stone Resource” designation from Germany. Episodes 2019, 42, 81–91. https://doi.org/10.18814/epiiugs/2019/019007. [CrossRef]
- Siedel, H., Rust, M., Goth, K., Krüger, A., Heidenfelder, W. Rochlitz porphyry tuff (“Rochlitzer Porphyrtuff”): A candidate for “global Heritage Stone Resource” designation from Germany. Episodes 2019, 42, 81–91. https://doi.org/10.18814/epiiugs/2019/019007. [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, Y. Some topics in English newsmagazines in 2019, with special reference to mineral resources, building stones, and a revised classification of igneous rocks | 2019 年の地質鉱物関連英文ニュース誌の話題 「鉱物資源,石材および火成岩記載法」. Japanese Magazine of Mineralogical and Petrological Sciences 2020, 48, 133–141. https://doi.org/10.2465/GKK.200221. [CrossRef]
- Vedanti, N., Malkoti, A., Pandey, O.P., Shrivastava, J.P. Ultrasonic P- and S-Wave Attenuation and Petrophysical Properties of Deccan Flood Basalts, India, as Revealed by Borehole Studies. Pure Appl Geophys. 2018, 175, 2905–2930. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-018-1817-x. [CrossRef]
- Prasanna Lakshmi, K.J., Senthil Kumar, P., Vijayakumar, K., Ravinder, S., Seshunarayana, T., Sen, M.K. Petrophysical properties of the Deccan basalts exposed in the Western Ghats escarpment around Mahabaleshwar and Koyna, India. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2014, 84, 176–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.08.028. [CrossRef]
- Das, A., Krishnaswami, S. Barium in Deccan Basalt Rivers: Its abundance, relative mobility and flux. Aquat Geochem. 2006, 12, 221–238. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10498-005-5856-4. [CrossRef]
- Sukheswala, R.N., Poldervaart, A. Deccan basalts of the Bombay area, India. Bull. Geol. Soc. Am. 1958, 69, 1473–1494. https://doi.org/10.1130/0016-7606(1958)69[1473:DBOTBA]2.0.CO;2. [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, H., Deolankar, S.B., Lalwani, A., Joseph, B., Pawar, S. Hydrogeological framework of the Deccan basalt groundwater systems, west-central India. Hydrogeol J. 2000, 8, 368–378. https://doi.org/10.1007/s100400000079. [CrossRef]
- Salil, M.S., Shrivastava, J.P., Pattanayak, S.K. Similarities in the mineralogical and geochemical attributes of detrital clays of Maastrichtian Lameta Beds and weathered Deccan basalt, Central India. Chem. Geol. 1997, 136, 25–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0009-2541(96)00128-3. [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekharam, D., Vaselli, O., Sheth, H.C., Keshav, S. Petrogenetic significance of ferro-enstatite orthopyroxene in basaltic dikes from the Tapi rift, Deccan flood basalt province, India. Earth Planet Sci Lett. 2000, 179, 469–476. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0012-821X(00)00131-X. [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, Y.R., Sangode, S.J., Meshram, D.C., Patil, S.K., Dutt, Y. Mineral magnetic characterization of the Godavari river sediments: Implications to Deccan basalt weathering. J. Geol. Soc. India 2014, 83, 376–384. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-014-0054-x. [CrossRef]
- Malik, A., Chakraborty, T., Rao, K.S., Kumar, D., Chandel, P., Sharma, P. Dynamic Response of Deccan Trap Basalt under Hopkinson Bar Test. In: Procedia Engineering 2017, pp. 647–654.
- Kumar, A., Shrivastava, J.P. Carbon capture induced changes in Deccan basalt: a mass-balance approach. Greenhouse Gases: Science and Technology 2019, 9, 1158–1180. https://doi.org/10.1002/ghg.1923. [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, S.K., Ma, G.S.-K., Matsuhisa, Y. Oxygen isotope evidence for crustal contamination in Deccan Basalts. Chemie der Erde 2013, 73, 105–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemer.2012.11.007. [CrossRef]
- Sano, T., Fujii, T., Deshmukh, S.S., Fukuoka, T., Aramaki, S. Differentiation processes of Deccan Trap basalts: Contribution from geochemistry and experimental petrology. Journal of Petrology 2001, 42, 2175–2195. https://doi.org/10.1093/petrology/42.12.2175. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A., Shrivastava, J.P. Thermodynamic Modelling and Experimental Validation of CO<inf>2</inf> Mineral Sequestration in Mandla Basalt of the Eastern Deccan Volcanic Province, India. J. Geol. Soc. India 2019, 93, 269–277. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-019-1173-1. [CrossRef]
- Santosh, M., Hari, K.R., Chatterjee, A.C. Fluid inclusions in Deccan basalt. (1988).
- Choubey, V.D. Long-Distance correlation of deccan basalt flows, Central India. Bull. Geol. Soc. Am. 1973, 84, 2785–2790. https://doi.org/10.1130/0016-7606(1973)84<2785>2.0.CO;2. [CrossRef]
- Das, A., Krishnaswami, S. Elemental geochemistry of river sediments from the Deccan Traps, India: Implications to sources of elements and their mobility during basalt-water interaction. Chem. Geol. 2007, 242, 232–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2007.03.023. [CrossRef]
- Keays, R.R., Lightfoot, P.C. Crustal sulfur is required to form magmatic Ni-Cu sulfide deposits: Evidence from chalcophile element signatures of Siberian and Deccan Trap basalts. Miner Depos. 2010, 45, 241–257. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00126-009-0271-1. [CrossRef]
- Sayyed, M.R.G., Hundekari, S.M. Preliminary comparison of ancient bole beds and modern soils developed upon the Deccan volcanic basalts around Pune (India): Potential for palaeoenvironmental reconstruction. Quaternary International 2006, 156–157, 189–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.QUAINT.2006.05.030. [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S., Misra, S., Vyas, D., Nikalje, D., Warhade, A., Roy, S. A 1251m-thick Deccan flood basalt pile recovered by scientific drilling in the Koyna region, western India. J. Geol. Soc. India 2017, 90, 788–794. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-017-0792-7. [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, M., Sharma, R., Kapoor, D., Sadiq, M. Formation evaluation of Deccan (basalt) trap basement of Kutch Offshore basin, Gulf of Kutch, India. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2022.110854. [CrossRef]
- Liu, D., Agarwal, R., Liu, F., Yang, S., Li, Y. Modeling and assessment of CO<inf>2</inf> geological storage in the Eastern Deccan Basalt of India. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 85465–85481. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21757-y. [CrossRef]
- Deolankar, S.B. The Deccan basalts of Maharashtra, India - their potential as aquifers. Ground Water 1980.
- Coli, M., Criscuolo, A. The Carrara Marble: Geology, geomechanics and quarrying. In: IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science 2021.
- Borla, O., Lacidogna, G., Carpinteri, A. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy on fracture surfaces of Carrara marble specimens crushed in compression. In: 19th European Conference on Fracture: Fracture Mechanics for Durability, Reliability and Safety, ECF 2012 2012.
- Carpinteri, A., Lacidogna, G., Borla, O. Alpha particle emissions from Carrara marble specimens crushed in compression and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy of correlated nuclear transmutations. 2016.
- Cheng, Y., Wong, L.N.Y., Maruvanchery, V. Transgranular Crack Nucleation in Carrara Marble of Brittle Failure. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2016, 49, 3069–3082. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-016-0976-2. [CrossRef]
- Bruijn, R.H.C., Kunze, K., Mainprice, D., Burlini, L. Mechanical and microstructural development of Carrara marble with pre-existing strain variation. Tectonophysics 2011, 503, 75–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2010.09.029. [CrossRef]
- Kandula, N., Cordonnier, B., Boller, E., Weiss, J., Dysthe, D.K., Renard, F. Dynamics of Microscale Precursors During Brittle Compressive Failure in Carrara Marble. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2019, 124, 6121–6139. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019JB017381. [CrossRef]
- Ree, J.-H., Ando, J.-I., Han, R., Shimamoto, T. Coseismic microstructures of experimental fault zones in Carrara marble. J. Struct. Geol. 2014, 66, 75–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsg.2014.05.012. [CrossRef]
- Vaselli, L., Cortecci, G., Tonarini, S., Ottria, G., Mussi, M. Conditions for veining and origin of mineralizing fluids in the Alpi Apuane (NW Tuscany, Italy): Evidence from structural and geochemical analyses on calcite veins hosted in Carrara marbles. J. Struct. Geol. 2012, 44, 76–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsg.2012.09.016. [CrossRef]
- Giresse, P., Bromblet, P., de Barrau, C. Carrara marble in the 11th century Romanesque works of Roussillion (lintel of Saint-Genis-des-Fontaines, lintel and altar table of Saint-André-de-Sorède, Eastern Pyrénées). Textural and isotopic analysis. ArcheoSciences 2020, 44, 71–79. https://doi.org/10.4000/archeosciences.7332. [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y., Wong, L.N.Y., Zou, C. Experimental study on the formation of faults from en-echelon fractures in Carrara Marble. Eng. Geol. 2015, 195, 312–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2015.06.004. [CrossRef]
- Luzin, V., Nikolayev, D., Siegesmund, S. Temperature induced internal stress in Carrara marble. 2014.
- Molli, G., Cortecci, G., Vaselli, L., Ottria, G. Fault zone structure and fluid-rock interaction of a high angle normal fault in the Carrara marble (NW Tuscany, Italy). Rendiconti Online Societa Geologica Italiana 2009, 5, 142–143.
- Aidun, J.B., Gupta, Y.M. Shear wave measurements for improved characterization of shock-Induced phase transformations in Carrara marble. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1989, 16, 191–194. https://doi.org/10.1029/GL016i002p00191. [CrossRef]
- Tal, Y., Evans, B., Mok, U. Direct observations of damage during unconfined brittle failure of Carrara marble. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2016, 121, 1584–1609. https://doi.org/10.1002/2015JB012749. [CrossRef]
- Nardini, L., Rybacki, E., Döhmann, M.J.E.A., Morales, L.F.G., Brune, S., Dresen, G. High-temperature shear zone formation in Carrara marble: The effect of loading conditions. Tectonophysics 2018, 749, 120–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2018.10.022. [CrossRef]
- Doan, M.-L., Billi, A. High strain rate damage of Carrara marble. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38. https://doi.org/10.1029/2011GL049169. [CrossRef]
- Bruni, S., Cariati, F., Bianchi, C.L., Zanardini, E., Sorlini, C. Spectroscopic investigation of red stains affecting the Carrara marble façade of the Certosa of Pavia. Archaeometry 1995, 37, 249–255. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1475-4754.1995.tb00741.x. [CrossRef]
- Schubnel, A., Walker, E., Thompson, B.D., Fortin, J., Guéguen, Y., Young, R.P. Transient creep, aseismic damage and slow failure in Carrara marble deformed across the brittle-ductile transition. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33. https://doi.org/10.1029/2006GL026619. [CrossRef]
- Covey-Crump, S.J. The application of Hart’s state variable description of inelastic deformation to Carrara marble at T < 450°C. J. Geophys. Res. 1994, 99. https://doi.org/10.1029/94jb01797. [CrossRef]
- Bonazza, A., Sabbioni, C., Messina, P., Guaraldi, C., De Nuntiis, P. Climate change impact: Mapping thermal stress on Carrara marble in Europe. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 4506–4512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.04.008. [CrossRef]
- Wong, L.N.Y., Xiong, Q. A Method for Multiscale Interpretation of Fracture Processes in Carrara Marble Specimen Containing a Single Flaw Under Uniaxial Compression. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2018, 123, 6459–6490. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018JB015447. [CrossRef]
- Covey-Crump, S.J. The high temperature static recovery and recrystallization behaviour of cold-worked Carrara marble. J. Struct. Geol. 1997, 19, 225–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0191-8141(96)00088-0. [CrossRef]
- Zou, C., Cheng, Y., Li, J. Strain rate and size effects on the brittleness indexes of Carrara marble. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2021, 146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2021.104860. [CrossRef]
- Wielgosz-Rondolino, D., Antonelli, F., Bojanowski, M.J., Gładki, M., Göncüoğlu, M.C., Lazzarini, L. Improved methodology for identification of Göktepe white marble and the understanding of its use: A comparison with Carrara marble. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2020, 113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jas.2019.105059. [CrossRef]
- Molli, G., Cortecci, G., Vaselli, L., Ottria, G., Cortopassi, A., Dinelli, E., Mussi, M., Barbieri, M. Fault zone structure and fluid-rock interaction of a high angle normal fault in Carrara marble (NW Tuscany, Italy). J. Struct. Geol. 2010, 32, 1334–1348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsg.2009.04.021. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-H., Zhou, Y.-S., Yao, W.-M., He, C.-R., Dang, J.-X. Experimental Study on the Effect of Water on the Strength and Deformation Mechanism of Carrara Marble at High Temperature. Dizhen Dizhi 2017, 39, 54–66. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2017.01.004. [CrossRef]
- Affuso, A.M.G., Garzonio, C.A. Analysis of the correlation between bending phenomena and physical-mechanical and petrographic parameters of Carrara marble slabs. In: 10th ISRM Congress, 2003, pp. 1–6.
- Coli, M., Livi, E., Baldi, M., Coli, N. Studies for rockburst prediction in the Carrara Marble – II: Geostructural/geomechanical revisitation and 2D FEM modeling of a large underground quarry. In: ISRM International Symposium - EUROCK 2012, 2012.
- Scheffzük, Ch., Siegesmund, S., Hoffmann, A., Nikolayev, D.I. Texture and residual strain in Carrara marbles measured by TOF neutron diffraction. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Heritage, Weathering and Conservation, HWC 2006, 2006, pp. 547–553.
- Song, J., Zhou, Y., Dang, J., Yao, W. An experimental study on pressure solution creep and micro-crack healing of Carrara marble. Zhongguo Shiyou Daxue Xuebao (Ziran Kexue Ban)/Journal of China University of Petroleum (Edition of Natural Science) 2017, 41, 52–60. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1673-5005.2017.05.006. [CrossRef]
- Royer-Carfagni, G., Salvatore, W. Localized fatigue damage of Carrara marble. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Damage and Fracture Mechanics, 1998, pp. 65–76.
- Chaye D’albissin, M., Yokoyama, Y., Massot, J.-C. Effect of experimental deformation on ESR spectrum of Carrara Marble: application to tectonized marbles. Comptes Rendus - Académie des Sciences, Série II: Sciences de la Terre et des Planètes 1994, 318, 405–410.
- Zhang, G., Song, M., Li, J., Shao, T., Ji, S., Wang, H. Microstructural Characteristics and Deformation Mechanism of Carrara Marble in Axial Compression Experiments. Geotectonica et Metallogenia 2018, 42, 786–797. https://doi.org/10.16539/j.ddgzyckx.2018.05.001. [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.T., Einstein, H.H. Crack coalescence tests on granite. In: 42nd U.S. Rock Mechanics - 2nd U.S.-Canada Rock Mechanics Symposium, 2008.
- Zou, C., Wong, L.N.Y. Size and Geometry Effects on the Mechanical Properties of Carrara Marble Under Dynamic Loadings. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2016, 49, 1695–1708. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-015-0899-3. [CrossRef]
- Lissa, S., Ruf, M., Steeb, H., Quintal, B. Effects of crack roughness on attenuation caused by squirt flow in Carrara marble. In: SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts, 2020, pp. 2439–2443.
- de Raadt, W.S., Burlini, L., Kunze, K., Spiers, C.J. Effect of pre-existing crystallographic preferred orientation on the rheology of Carrara marble. J. Struct. Geol. 2014, 68, 44–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsg.2014.07.011. [CrossRef]
- Soutelo, S.G., Garcia-M, A.G., Bordas, H.G., Savin, M.-C. Epigraphic and archaeometric study of the roman funerary plaque of Cela (Mos, Pontevedra): New approach to its interpretation. Estudos do Quaternario 2019, 71–84. https://doi.org/10.30893/eq.v0i20.193. [CrossRef]
- Lopes, L., Martins, R. Global Heritage Stone: Estremoz Marbles, Portugal. 2015.
- Lapuente Mercadal, P., Savin, M.-C., González Soutelo, S., Gutiérrez Garcia-M, A., Chapoulie, R., Laborde Marqueze, A., Pérez García, P.P. Marble Pieces in the Romanesque Portal of Glory of the Santiago de Compostela Cathedral. New Data through a Multi-Analytical Approach. Int. J. Archit. Herit. 2020, 14, 1239–1251. https://doi.org/10.1080/15583058.2019.1602683. [CrossRef]
- Menningen, J., Siegesmund, S., Lopes, L., Martins, R., Sousa, L. The Estremoz marbles: an updated summary on the geological, mineralogical and rock physical characteristics. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7328-3. [CrossRef]
- Moreira, N., Pedro, J., Santos, J.F., Araújo, A., Dias, R., Ribeiro, S., Romão, J., Mirão, J. 87 Sr/ 86 Sr applied to age discrimination of the Palaeozoic carbonates of the Ossa-Morena zone (SW Iberia Variscides). Int. J. Earth Sci. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00531-019-01688-9. [CrossRef]
- Moreira, N., Pedro, J., Lopes, L., Carneiro, A., Mourinha, N., Araújo, A., Santos, J.F. The Ossa-Morena marbles used in classical antiquity: Review of their petrographic features and isotopic data. Comunicacoes Geologicas 2020, 107, 81–89.
- Ochoa, C.F., Galán, M.B., García-Entero, V., Álvarez, S.V. Cover of the sarcophagus with the cycle of Jonah found in Carranque (Toledo). Archivo Español de Arqueología 2011, 84, 231–242. https://doi.org/10.3989/aespa.084.011.009. [CrossRef]
- Origlia, F., Gliozzo, E., Meccheri, M., Spangenberg, J.E., Memmi, I.T., Papi, E. Mineralogical, petrographic and geochemical characterisation of white and coloured Iberian marbles in the context of the provenancing of some artifacts from Thamusida (Kenitra, Morocco). Eur. J. Mineral. 2011, 23, 857–869. https://doi.org/10.1127/0935-1221/2011/0023-2145. [CrossRef]
- Siegesmund, S., Ruedrich, J., Koch, A. Marble bowing: Comparative studies of three different public building facades. Environ. Geol. 2008, 56, 473–494. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-008-1307-z. [CrossRef]
- Taelman, D., Elburg, M., Smet, I., De Paepe, P., Vanhaecke, F., Vermeulen, F. White, veined marble from Roman Ammaia (Portugal): Provenance and use. Archaeometry 2013, 55, 370–390. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1475-4754.2012.00691.x. [CrossRef]
- Taelman, D., Elburg, M., Smet, I., De Paepe, P., Lopes, L., Vanhaecke, F., Vermeulen, F. Roman marble from Lusitania: petrographic and geochemical characterisation. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2013, 40, 2227–2236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jas.2012.12.030. [CrossRef]
- Schouenborg, B., Andersson, J., Göransson, M., Inger, L. The Hallandia gneiss, a Swedish heritage stone resource. 2015.
- Wikström, Pereira, D. The Kolmården serpentine marble in Sweden: A stone found both in castles and people’s homes. 2015.
- Lapuente, P., Rodà, I., Gutiérrez Garcia-M, A., Brilli, M. Addressing the controversial origin of the marble source used in the Phoenician anthropoid sarcophagi of Gadir (Cadiz, Spain). Archaeometry 2021, 63, 467–480. https://doi.org/10.1111/arcm.12623. [CrossRef]
- Navarro, R., Pereira, D., Gimeno, A., Del Barrio, S. Influence of natural carbonation process in serpentinites used as construction and building materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 170, 537–546. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.03.100. [CrossRef]
- Navarro, R., Cruz, A.S., Arriaga, L., Baltuille, J.M. Characterization of the main types of marble extracted in the area of Macael (Almeria, southeastern Spain) and its historical importance. Boletin Geologico y Minero 2017, 128, 345–361. https://doi.org/10.21701/bolgeomin.128.2.005. [CrossRef]
- Rey, J., Martínez, J., Vera, P., Ruiz, N., Cañadas, F., Montiel, V. Ground-penetrating radar method used for the characterisation of ornamental stone quarries. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 77, 439–447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2014.12.076. [CrossRef]
- Navarro, R., Pereira, D., Gimeno, A., Del Barrio, S. Characterization of the natural variability of Macael serpentinite (Verde Macael) (Almería, south of Spain) for their appropriate use in the building industry. 2015.
- Navarro, R., Pereira, D., Gimeno, A., Del Barrio, S. Verde Macael: A serpentinite wrongly referred to as a marble. Geosciences 2013, 3, 102–113. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences3010102. [CrossRef]
- Luque, A., Ruiz-Agudo, E., Cultrone, G., Sebastián, E., Siegesmund, S. Direct observation of microcrack development in marble caused by thermal weathering. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 62, 1375–1386. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-010-0624-1. [CrossRef]
- Sáez-Pérez, M.P., Rodríguez-Gordillo, J. Structural and compositional anisotropy in Macael marble (Spain) by ultrasonic, XRD and optical microscopy methods. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 2121–2126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2008.10.013. [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Gordillo, J., Sáez-Pérez, M.P. Effects of thermal changes on Macael marble: Experimental study. Constr. Build. Mater. 2006, 20, 355–365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2005.01.061. [CrossRef]
- Mehiri, K., Vieville, P., Lipinski, P., Tidu, A., Tijeras, V. Initiation and coalescence of local damages on blanco de Macael marble. In: Fracture of Nano and Engineering Materials and Structures - Proceedings of the 16th European Conference of Fracture. 2006, pp. 545–546.
- Cámara, B., de Buergo, M.Á., Bethencourt, M., Fernández-Montblanc, T., La Russa, M.F., Ricca, M., Fort, R. Biodeterioration of marble in an underwater environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 609, 109–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.07.103. [CrossRef]
- Martínez, J., Montiel, V., Rey, J., Cañadas, F., Vera, P. Utilization of integrated geophysical techniques to delineate the extraction of mining bench of ornamental rocks (marble). Remote Sens. (Basel) 2017, 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9121322. [CrossRef]
- Burgos-Cara, A., Ruiz-Agudo, E., Rodriguez-Navarro, C. Effectiveness of oxalic acid treatments for the protection of marble surfaces. Mater. Des. 2017, 115, 82–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2016.11.037. [CrossRef]
- Luque, A., Cultrone, G., Mosch, S., Siegesmund, S., Sebastian, E., Leiss, B. Anisotropic behaviour of White Macael marble used in the Alhambra of Granada (Spain). The role of thermohydric expansion in stone durability. Eng. Geol. 2010, 115, 209–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2009.06.015. [CrossRef]
- Tucci, P., Marrese, G., Polvorinos, A., Azzaro, E. Italica (Seville, Spain): Use of local marble in Augustan age. Periodico di Mineralogia 2010, 79, 113–129. https://doi.org/10.2451/2010PM0025. [CrossRef]
- Morbidelli, P., Tucci, P., Imperatori, C., Polvorinos, A., Preite Martinez, M., Azzaro, E., Hernandez, M.J. Roman quarries of the Iberian peninsula: “Anasol” and “anasol”-type. Eur. J. Mineral. 2007, 19, 125–135. https://doi.org/10.1127/0935-1221/2007/0019-0125. [CrossRef]
- Benavente, D., Martínez-Verdú, F., Bernabeu, A., Viqueira, V., Fort, R., García del Cura, M.A., Illueca, C., Ordóñez, S. Influence of Surface Roughness on Color Changes in Building Stones. Color Res. Appl. 2003, 28, 343–351. https://doi.org/10.1002/col.10178. [CrossRef]
- Bello, M.A., Martin, L., Martin, A. Decay and treatment of Macael white marble. Studies in Conservation 1992, 37, 193–200. https://doi.org/10.1179/sic.1992.37.3.193. [CrossRef]
- Bello, M.A., Martin, L., Martin, A. Scanning electron microscopy to establish the marble weathering mechanism in the Alhambra of Granada (Spain). Scanning Microsc. 1991, 5, 645–652.
- Justo, J., Castro, J., Miranda, M., Gatica, D., Cicero, S. The theory of critical distances applied to fracture of rocks with circular cavities. Theoretical and Applied Fracture Mechanics 2022, 121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tafmec.2022.103530. [CrossRef]
- Acampa, G., Grasso, M. Integrated Evaluation Methods to HBIM for the Management of Cultural Heritage: The case study of the Colonnade of Patio de los Leones, Alhambra-Granada. Valori e Valutazioni 2021, 133–153.
- Garcia-Guinea, J., Crespo-Feo, E., Correcher, V., Iordanidis, A., Charalampides, G., Karamitou-Mentessidi, G. New data on the cathodoluminescence of white marbles: Interpretation of peaks and relationships to weathering. Mediterranean Archaeology and Archaeometry 2010, 10, 107–114.
- Garg, S., Kaur, P., Pandit, M., Fareeduddin, Kaur, G., Kamboj, A., Thakur, S.N. Makrana Marble: a Popular Heritage Stone Resource from NW India. Geoheritage 2019, 11, 909–925. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12371-018-00343-0. [CrossRef]
- Pappu, A., Chaturvedi, R., Tyagi, P. Sustainable approach towards utilizing Makrana marble waste for making water resistant green composite materials. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-020-2133-5. [CrossRef]
- Bhadra, B.K., Gupta, A.K., Sharma, J.R., Choudhary, B.R. Mining activity and its impact on the environment: Study from Makrana marble and Jodhpur sandstone mining areas of Rajasthan. J. Geol. Soc. India 2007, 70, 557–570.
- Dwivedi, R.D., Singh, P.K., Singh, T.N., Singh, D.P. Compressive strength and tensile strength of rocks at sub-zero temperature. Indian J. Eng. Mater. Sci. 1998, 5, 43–48.
- Kaul, B.K., Chattopadhyay, B.C. Effect of the volume of the specimen on the flexural strength of Makrana marble. 1973, 200–203.
- Hughes, T., Horak, J., Lott, G., Roberts, D. Cambrian age Welsh Slate: A global heritage stone resource from the United Kingdom. Episodes 2016, 39, 45–51. https://doi.org/10.18814/epiiugs/2016/v39i1/89236. [CrossRef]
- Attewell, P.B., Taylor, R.K. A microtextural interpretation of a Welsh slate. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 1969, 6. https://doi.org/10.1016/0148-9062(69)90011-4. [CrossRef]
- Price, W.R., Ronck, C.L. Quarrying for World Heritage Designation: Slate Tourism in North Wales. Geoheritage 2019, 11, 1839–1854. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12371-019-00402-0. [CrossRef]
- Girdler, R.W. Some Preliminary Measurements of Anisotropy of Magnetic Susceptibility of Rocks. Geophys. J. R. Astron. Soc. 1961, 5, 197–206. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246X.1961.tb00427.x. [CrossRef]
- Fuller, M.D. Anisotropy of susceptibility and the natural remanent magnetization of some Welsh slates. Nature 1960, 186, 791–792. https://doi.org/10.1038/186791a0. [CrossRef]
- Rathore, J.S., Henry, B. Comparison of strain and magnetic fabrics in Dalradian rocks from the southwest Highlands of Scotland. J. Struct. Geol. 1982, 4, 373–384. https://doi.org/10.1016/0191-8141(82)90020-7. [CrossRef]
- Wyse Jackson, P.N., Caulfield, L., Feely, M., Joyce, A., Parkes, M.A. Connemara marble, Co. Galway, Ireland: A global heritage stone resource proposal. Geol. Soc. Spec. Publ. 2020, 486, 251–268. https://doi.org/10.1144/SP486.6. [CrossRef]
- Kollar, A.D., Feely, M., Joyce, A., Fedosick, R., Hughes, K., Costanzo, A. Carnegie Institute Extension Connemara Marble: Cross-Atlantic connections between western Ireland and gilded age architecture in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. Ann. Carnegie Mus. 2020, 86, 207–253. https://doi.org/10.2992/007.086.0301. [CrossRef]
- Wyse Jackson, P.N., Caulfield, L., Feely, M., Joyce, A., Parkes, M.A. Connemara marble, Co. Galway, Ireland: A global heritage stone resource proposal. 2020.
- Yardley, B.W.D., Lloyd, G.E. An application of cathodoluminescence microscopy to the study of textures and reactions in high-grade marbles from Connemara, Ireland. Geol. Mag. 1989, 126, 333–337. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0016756800006531. [CrossRef]
- Max, M.D. Connemara Marble and the industry based upon it. Report Series - Geological Survey of Ireland. 1985.
- Feely, M., Wilton, D.H., Costanzo, A., Kollar, A.D., Goudie, D.J., Joyce, A. Mineral Liberation Analysis and Scanning Electron Microscopy of Connemara Marble: New mineral distribution maps of an iconic Irish gem material. J. Gemmology 2019, 36, 456–466. https://doi.org/10.15506/JoG.2019.36.5.456. [CrossRef]
- McCaffrey, K.J.W., Feely, M., Hennessy, R., Thompson, J. Visualization of folding in marble outcrops, Connemara, western Ireland: An application of virtual outcrop technology. Geosphere 2008, 4, 588–599. https://doi.org/10.1130/GES00147.1. [CrossRef]
- Leake, B.E., Tanner, P.W.G., Senior, A. The composition and origin of the Connemara dolomitic marbles and ophicalcites, Ireland. J. Petrology 1975, 16, 237–257. https://doi.org/10.1093/petrology/16.1.237. [CrossRef]
- Cliff, R.A., Yardley, B.W.D., Bussy, F. U–Pb isotopic dating of fluid infiltration and metasomatism during Dalradian regional metamorphism in Connemara, western Ireland. J. Metamorphic Geol. 1993, 11, 185–191. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1525-1314.1993.tb00141.x. [CrossRef]
- Senior, A., Leake, B.E. Regional metasomatism and the geochemistry of the Dalradian metasediments of Connemara, Western Ireland. J. Petrology 1978, 19, 585–625. https://doi.org/10.1093/petrology/19.3.585. [CrossRef]
- Cárdenes, V., López-Piñeiro, S., Ruiz de Argandoña, V.G. The relevance of the green phyllites of Lugo (Spain) in the architectural heritage: An exceptional roofing slate resource. Geoheritage 2021. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12371-021-00537-z. [CrossRef]
- Cárdenes, V., Rubio, A., Ruiz de Argandoña, V.G. Roofing slate from Bernardos, Spain: A potential candidate for global heritage stone. Episodes 2021, 44, 3–9. https://doi.org/10.18814/EPIIUGS/2020/0200S07. [CrossRef]
- Kaur, G., Agarwal, P., Garg, S., Kaur, P., Saini, J., Singh, A. The Alwar Quartzite Built Architectural Heritage of North India: A case for global heritage stone resource designation. 2021.
- Kaur, G., Agarwal, P., Garg, S., Kaur, P., Saini, J., Singh, A., Pandit, M., Acharya, K., Rooprai, V.S., Bhargava, O.N., Kumar, M., Ahuja, A. The Alwar Quartzite Built Architectural Heritage of North India: A case for global heritage stone resource designation. Geoheritage 2021. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12371-021-00574-8. [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, A.K., Shukla, A.K., Pandey, A., Chauhan, M., Chauhan, N., Rai, N. Shear wave velocity investigation for ten representative sites of national capital territory, New Delhi, India. Int. J. Geotech. Earthquake Eng. 2011, 2, 29–43. https://doi.org/10.4018/jgee.2011010103. [CrossRef]
- Pathak, A.K., Tripathi, S., Maurya, A.K., Das, P., Ranjan, J., Patel, A.K., Misra, P., Kumar, A. High resolution heliborne magnetic, radiometric and time domain electromagnetic data interpretation of Chomun-Alwar tract of Alwar sub-basin, North Delhi Fold Belt, Northern India as an aid to uranium exploration. Explor. Res. Atomic Minerals 2020, 28, 24–35.
- Muthamilselvan, A. Application of supervised classification and Crosta technique for lithological discrimination in parts of South Khetri Belt, Sikar District, Rajasthan. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2017, 45, 377–383. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-016-0589-y. [CrossRef]
- Kaur, P., Zeh, A., Chaudhri, N., Gerdes, A., Okrusch, M. Archaean to Palaeoproterozoic crustal evolution of the Aravalli mountain range, NW India, and its hinterland: The U-Pb and Hf isotope record of detrital zircon. Precambrian Res. 2011, 187, 155–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precamres.2011.03.005. [CrossRef]
- Kaur, G., Mehta, P.K. Geochemistry and petrogenesis of Jasrapura granitoid, north Khetri Copper Belt, Rajasthan: Evidence for island arc magmatism. J. Geol. Soc. India 2007, 69, 319–330.
- Powar, M.M., Mathur, A.B. Geology and geochemistry of amphibolites from Ghataser area, Mahendragarh District, Haryana. Indian Minerals 2004, 58, 27–34.
- Verma, V.K. Ripple marks in Alwar quartzites east of Mera ka Gurha near Udaipur, Rajasthan. Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. - Sect. A 1964, 59, 313–317. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03046445. [CrossRef]
- Zaheeruddin, Khurshid, S. Aquifer geometry and hydrochemical framework of the shallow alluvial aquifers in the western part of the Yamuna River Basin, India. Water Qual. Res. J. Canada 2004, 39, 129–139. https://doi.org/10.2166/wqrj.2004.020. [CrossRef]
- Layers sources: OpenDataSource (2023) World countries layer – QGIS EFFIS (2023) - https://forest-fire.emergency.copernicus.eu.

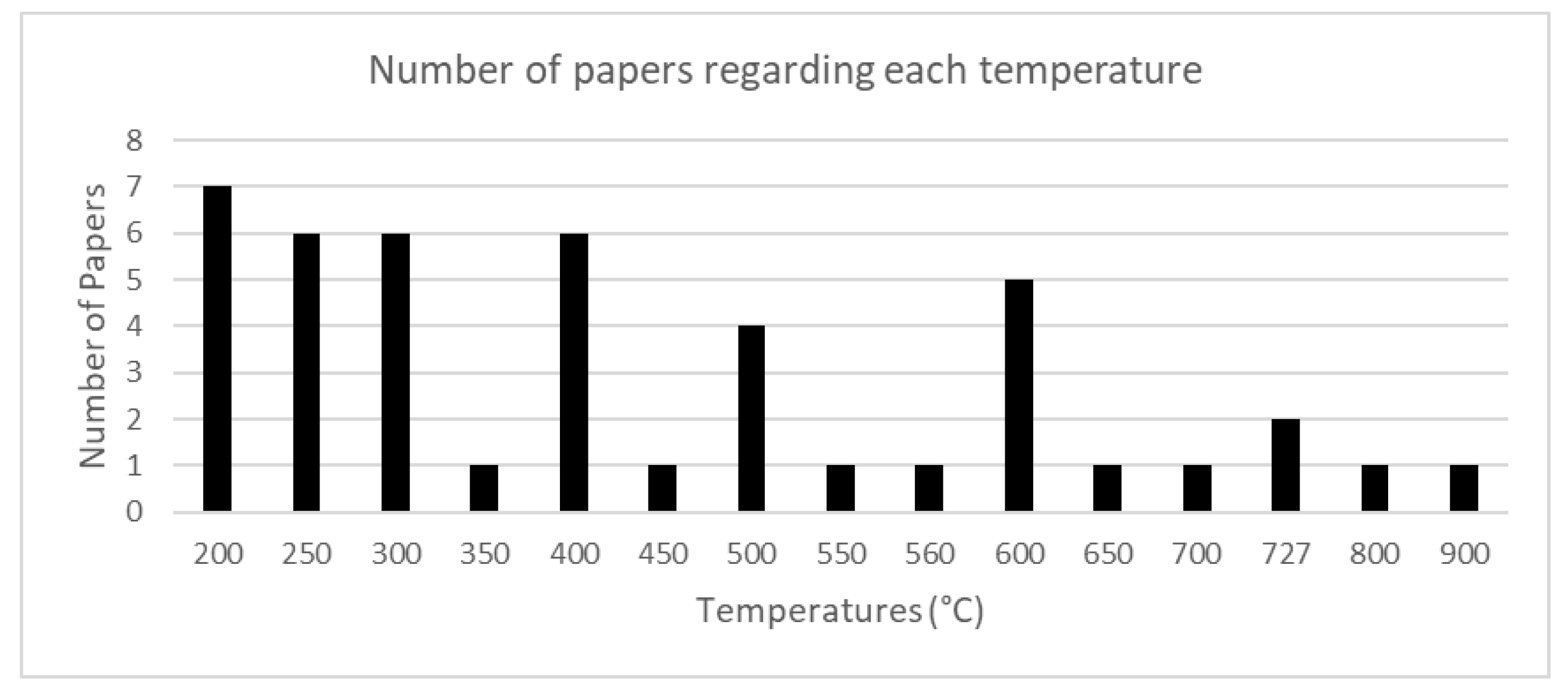
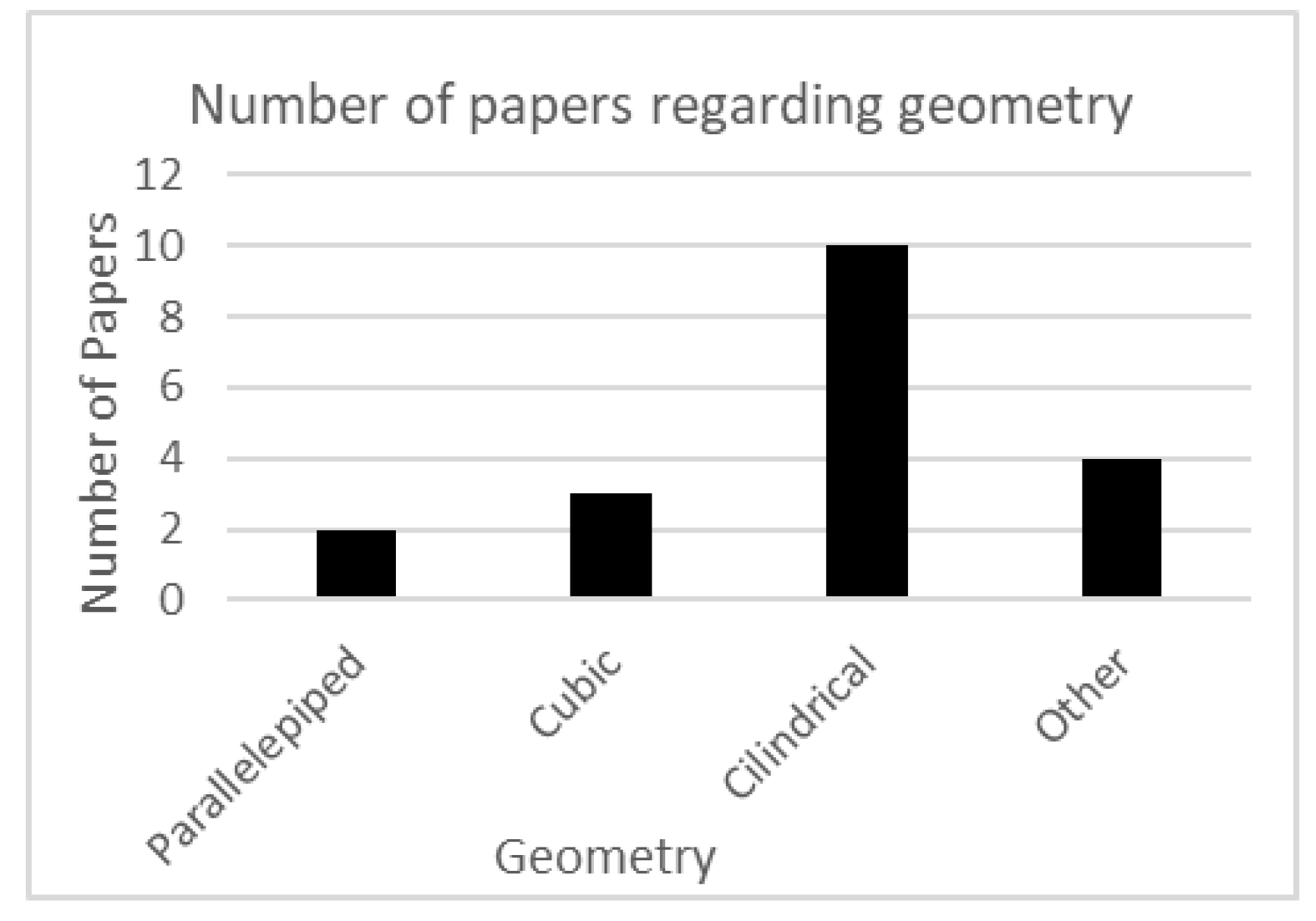
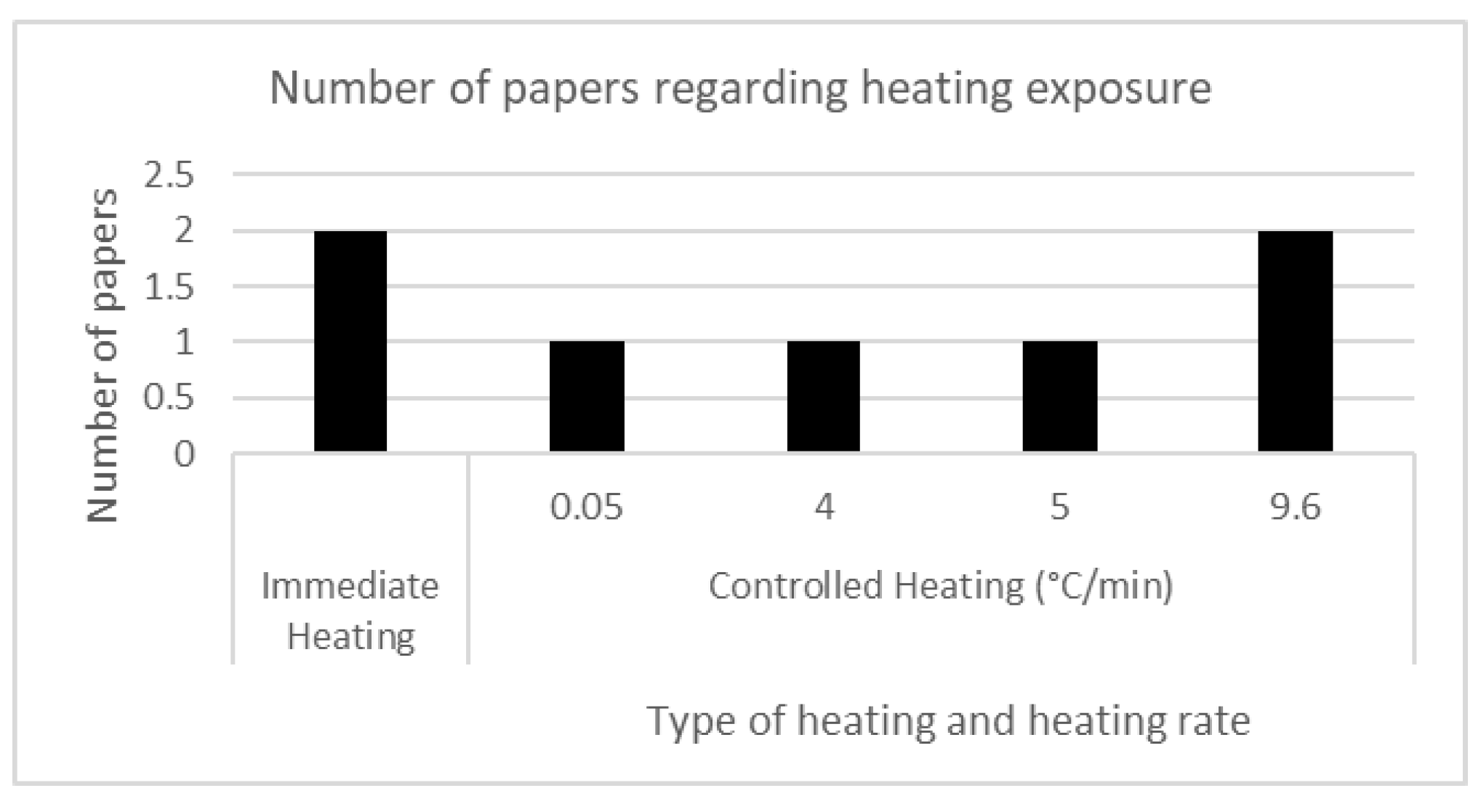
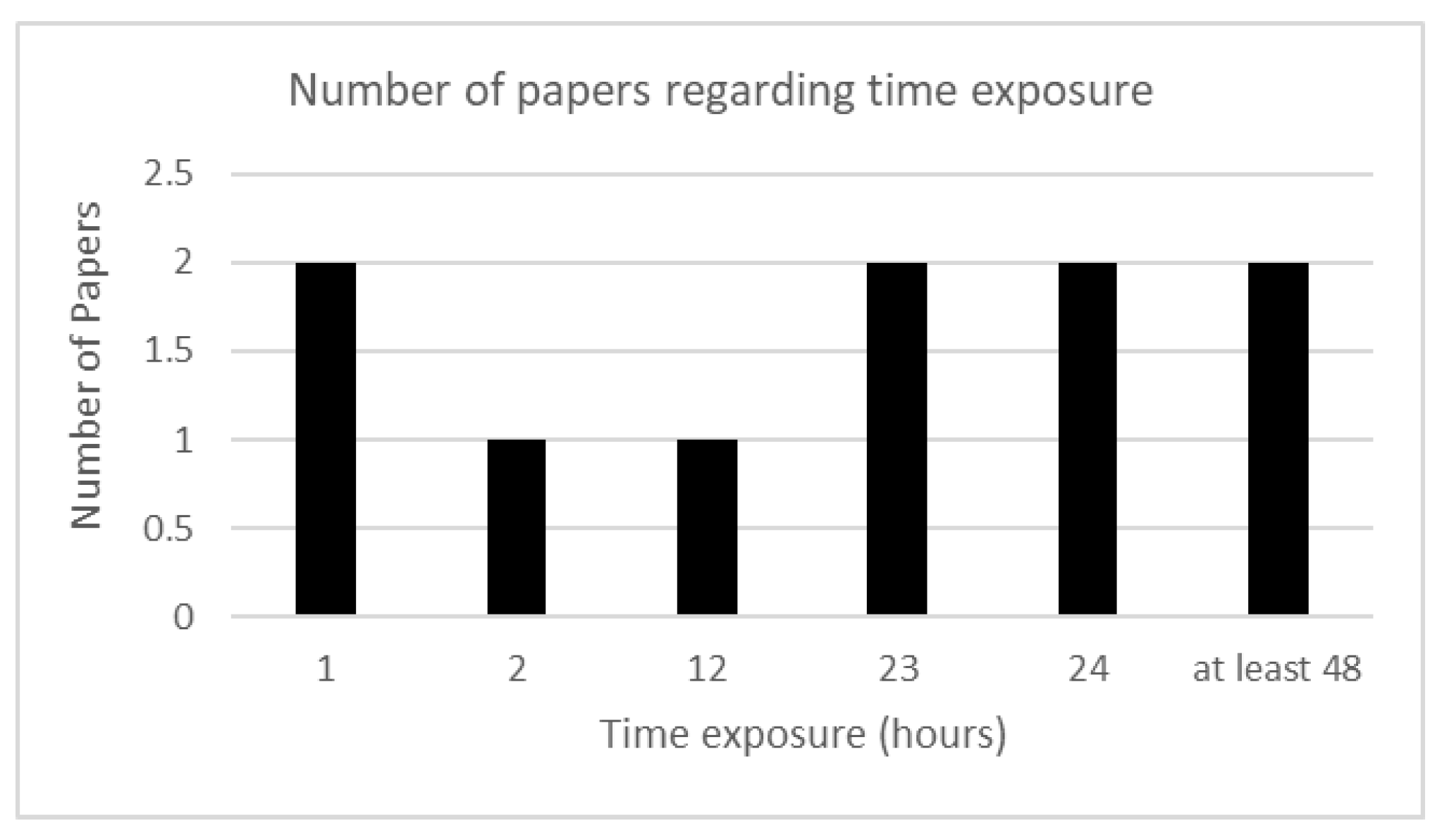
| Categories | Identified information for selection / Topic detected for selection |
|---|---|
| Other nomenclatures | References to other facies of the same lithotype |
| Different commercial names for the same lithotypedata | |
| Composition | Mineralogic and petrographic composition |
| Chemical composition | |
| Physical and/or Mechanical Properties | Properties that characterize the stone as a material, some examples found: porosity, capillarity, structure properties, color measurements, gloss. |
| High Temperatures | Exposition of stone to temperatures above 120º Celsiusdata |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





