Submitted:
02 October 2024
Posted:
03 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
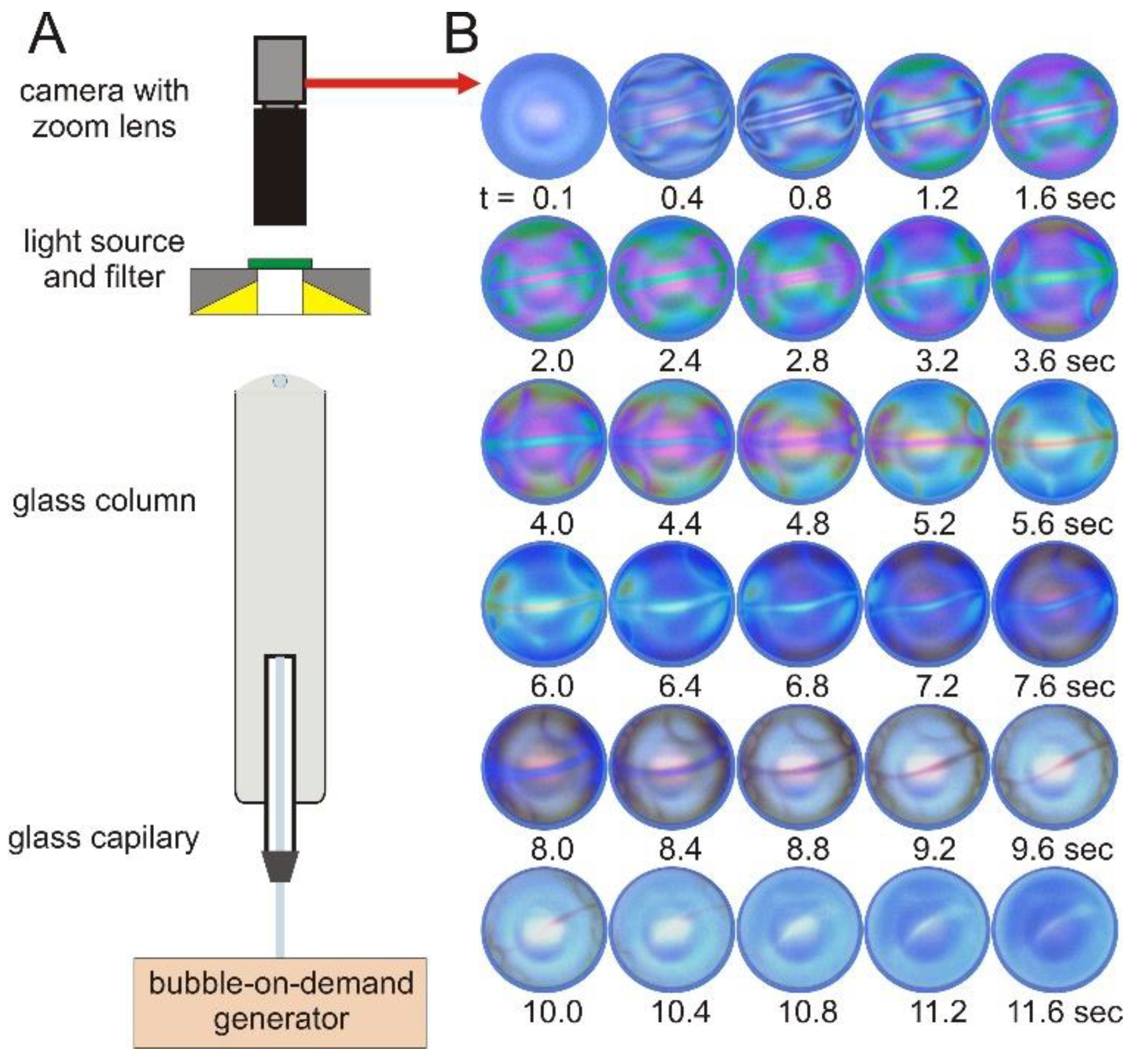
2.2. Methods
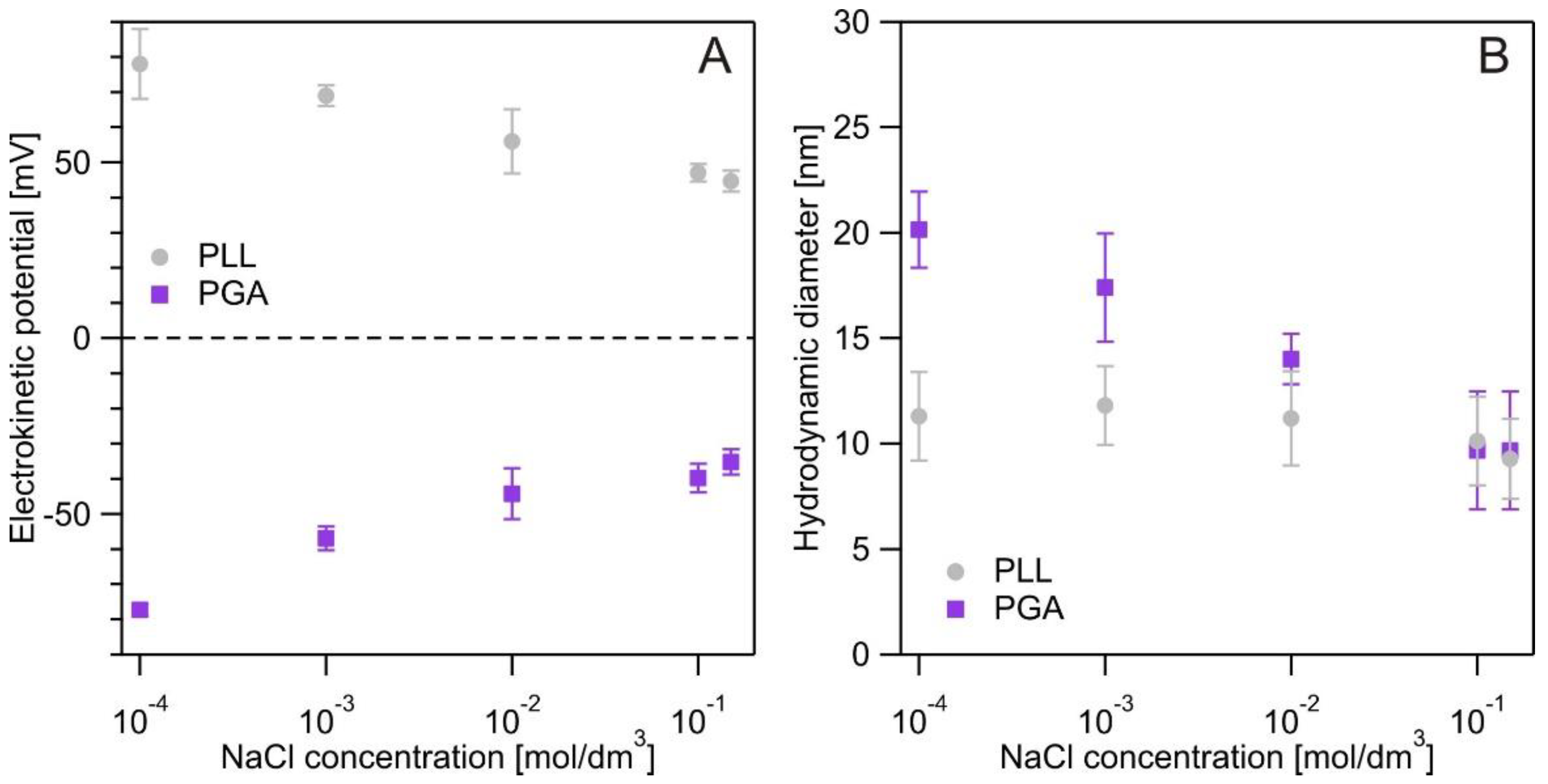
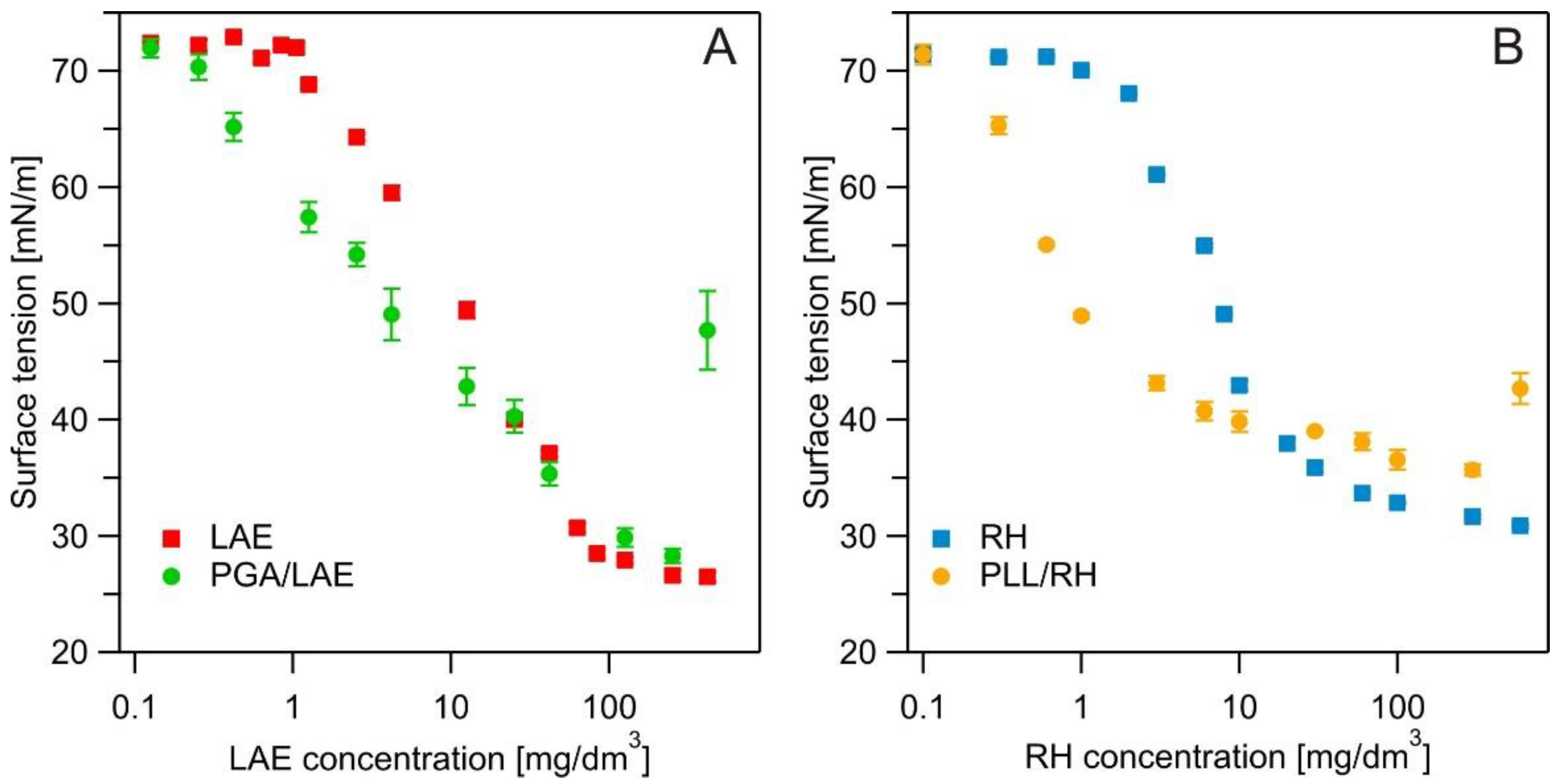
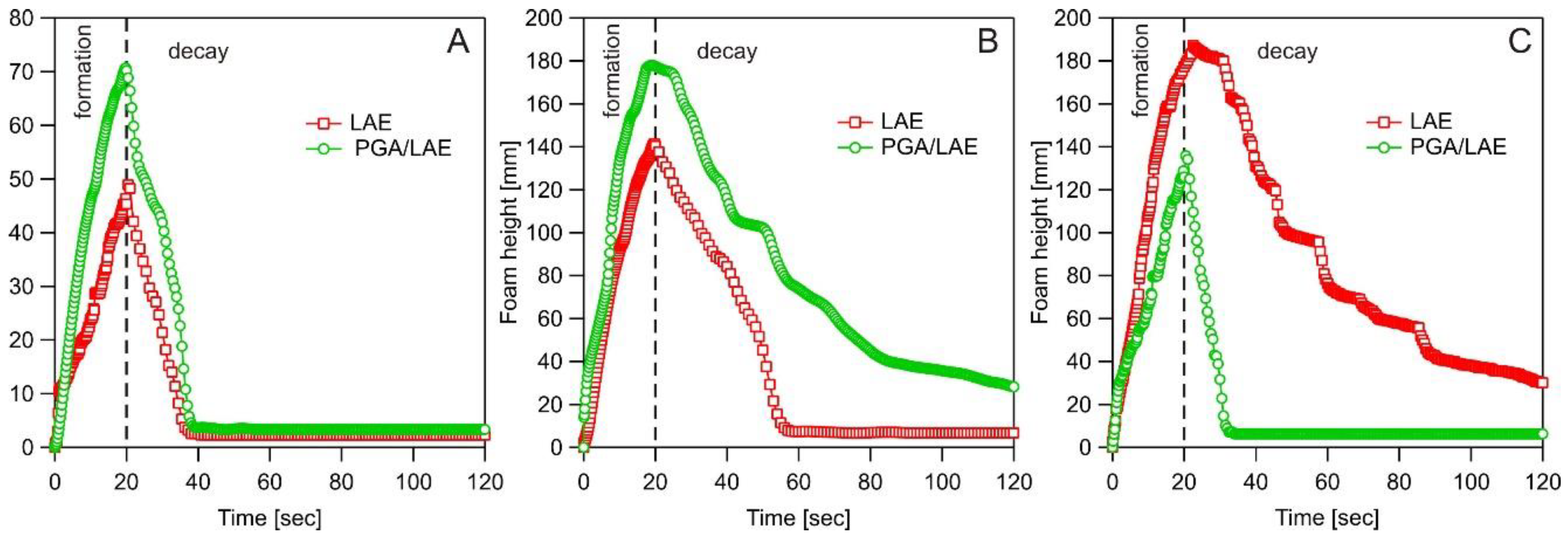
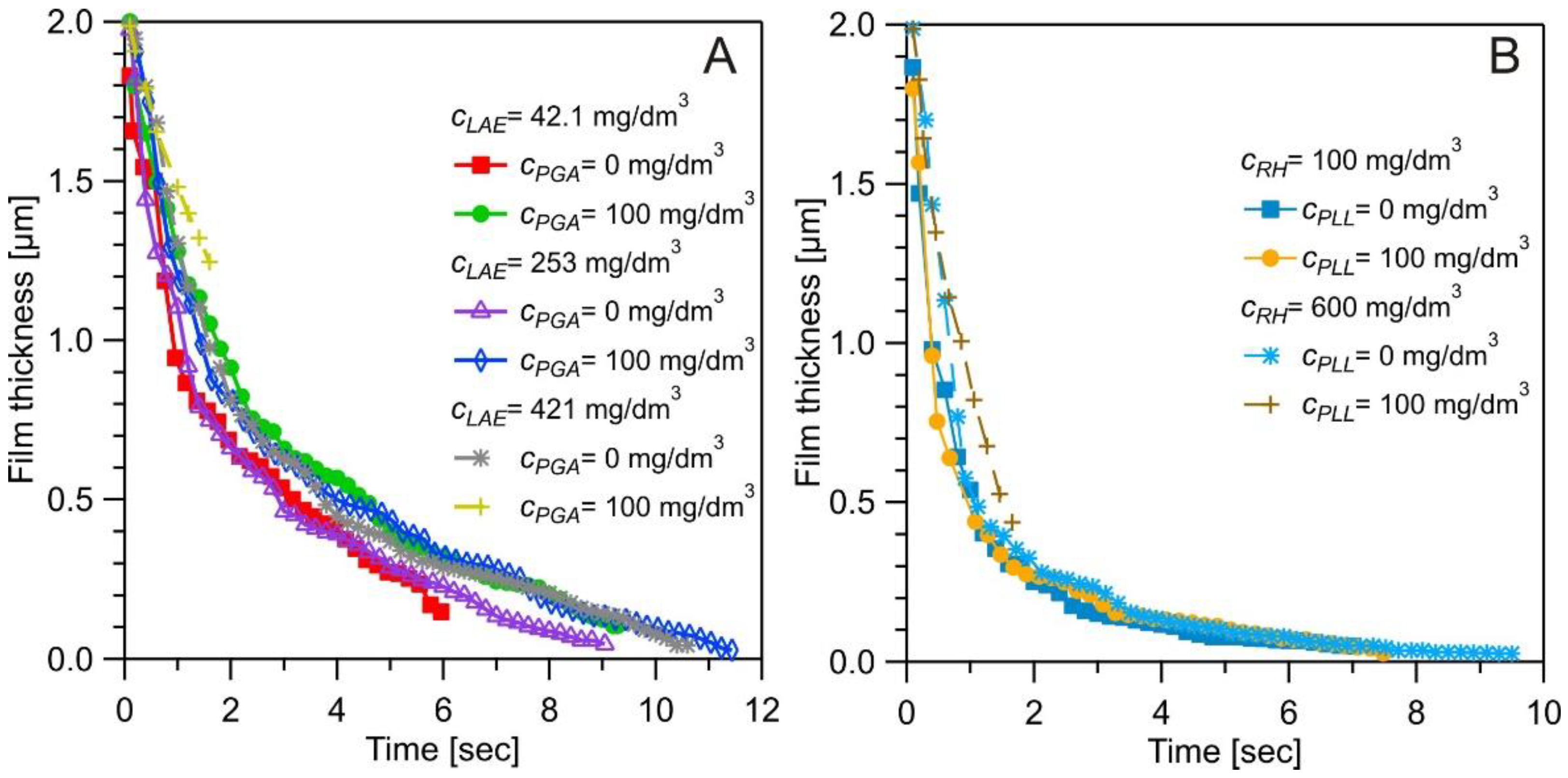
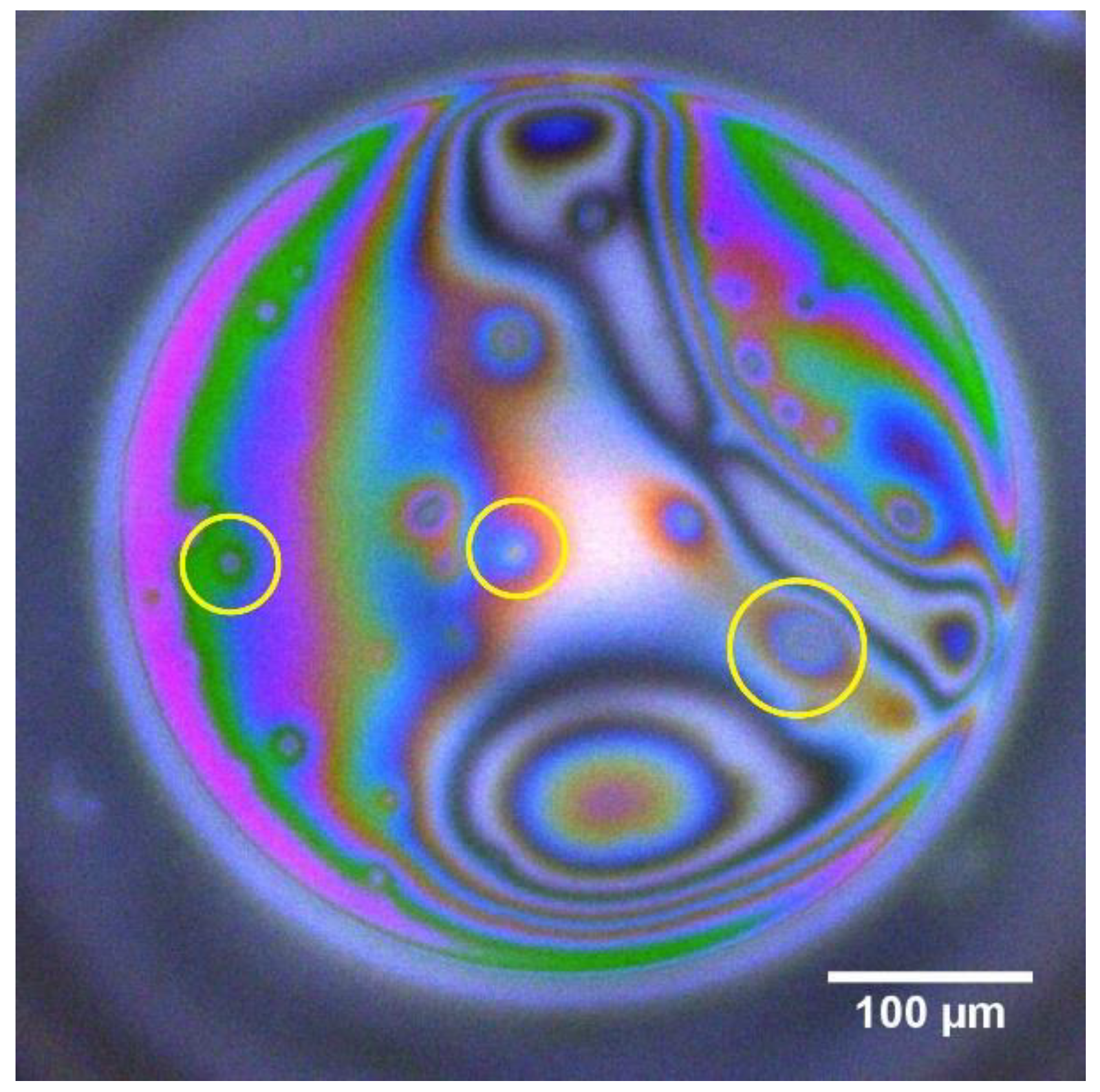
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cho, Y.S.; Laskowski, J.S. Effect of Flotation Frothers on Bubble Size and Foam Stability. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2002, 64, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakashev, S.I.; Grozev, N.A.; Ozdemir, O.; Batjargal, K.; Guven, O.; Ata, S.; Bournival, G.; Boylu, F.; Sabri Çelik, M. On the Frother’s Strength and Its Performance. Miner. Eng. 2021, 171, 107093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, B.S. Recent Developments in Food Foams. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 50, 101394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y.; Xue, M.; Ma, L.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Q.; Liu, X. Environmentally Friendly Firefighting Foams Used to Fight Flammable Liquid Fire. Fire Technol. 2021, 57, 2079–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schad, T.; Preisig, N.; Drenckhan, W.; Stubenrauch, C. Foam-Based Cleaning of Surfaces Contaminated with Mixtures of Oil and Soot. J. Surfactants Deterg. 2022, 25, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arzhavitina, A.; Steckel, H. Foams for Pharmaceutical and Cosmetic Application. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 394, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fameau, A.-L.; Fujii, S. Stimuli-Responsive Liquid Foams: From Design to Applications. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 50, 101380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritacco, H.A. Polyelectrolyte/Surfactant Mixtures: A Pathway to Smart Foams. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 36117–36136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinelli, H.; Domínguez, C.; Leyes, M.F.; Moya, S.; Ritacco, H. A pH-Responsive Foam Formulated with PAA/Gemini 12-2-12 Complexes. Colloids Interfaces 2021, 5, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaev, M.S.; Lobov, A.N.; Shishlov, N.M.; Kolesov, S.V. pH-Sensitive Particles of Polymer-Surfactant Complexes Based on a Copolymer of N,N′-Diallyl-N,N′-Dimethylammonium Chloride with Maleic Acid and Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate. React. Funct. Polym. 2022, 178, 105359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benhur, A.M.; Diaz, J.; Amin, S. Impact of Polyelectrolyte-Surfactant Interactions on the Rheology and Wet Lubrication Performance of Conditioning Shampoo. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2021, 43, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnurbus, M.; Hardt, M.; Steinforth, P.; Carrascosa-Tejedor, J.; Winnall, S.; Gutfreund, P.; Schönhoff, M.; Campbell, R.A.; Braunschweig, B. Responsive Material and Interfacial Properties through Remote Control of Polyelectrolyte–Surfactant Mixtures. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 4656–4667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alter, H. The Recovery of Plastics from Waste with Reference to Froth Flotation. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2005, 43, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peleka, E.N.; Gallios, G.P.; Matis, K.A. A Perspective on Flotation: A Review. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2018, 93, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barany, S.; Szepesszentgyörgyi, A. Flocculation of Cellular Suspensions by Polyelectrolytes. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 111, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bournival, G.; Du, Z.; Ata, S.; Jameson, G.J. Foaming and Gas Dispersion Properties of Non-Ionic Frothers in the Presence of Hydrophobized Submicron Particles. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2014, 133, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eftekhari, M.; Schwarzenberger, K.; Karakashev, S.I.; Grozev, N.A.; Eckert, K. Oppositely Charged Surfactants and Nanoparticles at the Air-Water Interface: Influence of Surfactant to Nanoparticle Ratio. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2024, 653, 1388–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristen, N.; Klitzing, R. von Effect of Polyelectrolyte/Surfactant Combinations on the Stability of Foam Films. Soft Matter 2010, 6, 849–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chronakis, I.S.; Alexandridis, P. Rheological Properties of Oppositely Charged Polyelectrolyte−Surfactant Mixtures: Effect of Polymer Molecular Weight and Surfactant Architecture. Macromolecules 2001, 34, 5005–5018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langevin, D. Polyelectrolyte and Surfactant Mixed Solutions. Behavior at Surfaces and in Thin Films. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2001, 89–90, 467–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinschmidt, F.; Stubenrauch, C.; Delacotte, J.; von Klitzing, R.; Langevin, D. Stratification of Foam Films Containing Polyelectrolytes. Influence of the Polymer Backbone’s Rigidity. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 3972–3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petkova, R.; Tcholakova, S.; Denkov, N.D. Foaming and Foam Stability for Mixed Polymer–Surfactant Solutions: Effects of Surfactant Type and Polymer Charge. Langmuir 2012, 28, 4996–5009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, L.; von Klitzing, R. When Bulk Matters: Disentanglement of the Role of Polyelectrolyte/Surfactant Complexes at Surfaces and in the Bulk of Foam Films. Langmuir 2023, 39, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, J.L.; Vidal, T.; Gonçalves, F.J.M.; Gabriel, R.G.; Costa, R.; Rasteiro, M.G. Is the Aquatic Toxicity of Cationic Polyelectrolytes Predictable from Selected Physical Properties? Chemosphere 2018, 202, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, J.; Ranjan, A.; Chauhan, A.; Biswas, R.; Rajput, V.D.; Sushkova, S.; Mandzhieva, S.; Minkina, T.; Jindal, T. Surfactant Pollution, an Emerging Threat to Ecosystem: Approaches for Effective Bacterial Degradation. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 133, 1229–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drzymala, J.; Kowalczuk, P.B. Classification of Flotation Frothers. Minerals 2018, 8, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawliszak, P.; Bradshaw-Hajek, B.H.; Skinner, W.; Beattie, D.A.; Krasowska, M. Frothers in Flotation: A Review of Performance and Function in the Context of Chemical Classification. Miner. Eng. 2024, 207, 108567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, F.; Liu, Q. Froth Treatment in Athabasca Oil Sands Bitumen Recovery Process: A Review. Energy Fuels 2013, 27, 7199–7207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Li, Z.; Li, S.; Jiang, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, P. Utilization of Surfactant-Stabilized Foam for Enhanced Oil Recovery by Adding Nanoparticles. Energy Fuels 2014, 28, 2384–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiappisi, L.; Hoffmann, I.; Gradzielski, M. Complexes of Oppositely Charged Polyelectrolytes and Surfactants – Recent Developments in the Field of Biologically Derived Polyelectrolytes. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 3896–3909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagtode, V.S.; Cardoza, C.; Yasin, H.K.A.; Mali, S.N.; Tambe, S.M.; Roy, P.; Singh, K.; Goel, A.; Amin, P.D.; Thorat, B.R.; et al. Green Surfactants (Biosurfactants): A Petroleum-Free Substitute for Sustainability─Comparison, Applications, Market, and Future Prospects. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 11674–11699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deming, T.J. Synthetic Polypeptides for Biomedical Applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2007, 32, 858–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, I.; Singhal, R. Poly (Glutamic Acid) – An Emerging Biopolymer of Commercial Interest. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 5551–5561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán, E.; Ortega, F.; Rubio, R.G. Exploring the World of Rhamnolipids: A Critical Review of Their Production, Interfacial Properties, and Potential Application. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2024, 69, 101780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özdemir, G.; Peker, S.; Helvaci, S.S. Effect of pH on the Surface and Interfacial Behavior of Rhamnolipids R1 and R2. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2004, 234, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legawiec, K.J.; Kruszelnicki, M.; Zawadzka, M.; Basařová, P.; Zawala, J.; Polowczyk, I. Towards Green Flotation: Investigating the Effect of Rhamnolipid Biosurfactant on Single Bubble Adhesion Dynamics. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 388, 122759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshdast, H.; Abbasi, H.; Sam, A.; Noghabi, K.A. Frothability and Surface Behavior of a Rhamnolipid Biosurfactant Produced by Pseudomonas Aeruginosa MA01. Biochem. Eng. J. 2012, 60, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amani, H.; Müller, M.M.; Syldatk, C.; Hausmann, R. Production of Microbial Rhamnolipid by Pseudomonas Aeruginosa MM1011 for Ex Situ Enhanced Oil Recovery. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2013, 170, 1080–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Infante, R.; Dominguez, J.G.; Erra, P.; Julia, R.; Prats, M. Surface Active Molecules: Preparation and Properties of Long Chain Nα-Acyl-l-α-Amino-ω-Guanidine Alkyl Acid Derivatives. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 1984, 6, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becerril, R.; Manso, S.; Nerin, C.; Gómez-Lus, R. Antimicrobial Activity of Lauroyl Arginate Ethyl (LAE), against Selected Food-Borne Bacteria. Food Control 2013, 32, 404–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, K.; Catchmark, J.M. Crystalline Nanocellulose/Lauric Arginate Complexes. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 175, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czakaj, A.; Chatzigiannakis, E.; Vermant, J.; Krzan, M.; Warszyński, P. The Influence of the Surface Chemistry of Cellulose Nanocrystals on Ethyl Lauroyl Arginate Foam Stability. Polymers 2022, 14, 5402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czakaj, A.; Jarek, E.; Krzan, M.; Warszyński, P. Ethyl Lauroyl Arginate, an Inherently Multicomponent Surfactant System. Molecules 2021, 26, 5894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russel, W.B.; Saville, D.A.; Schowalter, W.R. Colloidal Dispersions; Cambridge Monographs on Mechanics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, 1989; ISBN 978-0-521-42600-8. [Google Scholar]
- Batjargal, K.; Guven, O.; Ozdemir, O.; Karakashev, S.I.; Grozev, N.A.; Boylu, F.; Çelik, M.S. Frothing Performance of Frother-Collector Mixtures as Determined by Dynamic Foam Analyzer and Its Implications in Flotation. Minerals 2023, 13, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikerman, J.J. The Unit of Foaminess. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1938, 34, 634–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakashev, S.I.; Georgiev, P.; Balashev, K. Foam Production – Ratio between Foaminess and Rate of Foam Decay. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 379, 144–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawala, J.; Niecikowska, A. “Bubble-on-Demand” Generator with Precise Adsorption Time Control. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2017, 88, 095106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitagawa, K. Thin-Film Thickness Profile Measurement by Three-Wavelength Interference Color Analysis. Appl. Opt. 2013, 52, 1998–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandran Suja, V.; Sentmanat, J.; Hofmann, G.; Scales, C.; Fuller, G.G. Hyperspectral Imaging for Dynamic Thin Film Interferometry. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamczyk, Z.; Morga, M.; Kosior, D.; Batys, P. Conformations of Poly-l-Lysine Molecules in Electrolyte Solutions: Modeling and Experimental Measurements. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 23180–23190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morga, M.; Batys, P.; Kosior, D.; Bonarek, P.; Adamczyk, Z. Poly-L-Arginine Molecule Properties in Simple Electrolytes: Molecular Dynamic Modeling and Experiments. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 3588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckingham, J.H.; Lucassen, J.; Hollway, F. Surface Properties of Mixed Solutions of Poly-l-Lysine and Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate: I. Equilibrium Surface Properties. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1978, 67, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okubo, T.; Kobayashi, K. Surface Tension of Biological Polyelectrolyte Solutions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1998, 205, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staples, E.; Tucker, I.; Penfold, J.; Warren, N.; Thomas, R.K. Organization of Polymer−Surfactant Mixtures at the Air−Water Interface: Poly(Dimethyldiallylammonium Chloride), Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate, and Hexaethylene Glycol Monododecyl Ether. Langmuir 2002, 18, 5139–5146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteux, C.; Williams, C.E.; Meunier, J.; Anthony, O.; Bergeron, V. Adsorption of Oppositely Charged Polyelectrolyte/Surfactant Complexes at the Air/Water Interface: Formation of Interfacial Gels. Langmuir 2004, 20, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penfold, J.; Thomas, R.K.; Taylor, D.J.F. Polyelectrolyte/Surfactant Mixtures at the Air–Solution Interface. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 11, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, R.A.; Angus-Smyth, A.; Yanez Arteta, M.; Tonigold, K.; Nylander, T.; Varga, I. New Perspective on the Cliff Edge Peak in the Surface Tension of Oppositely Charged Polyelectrolyte/Surfactant Mixtures. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2010, 1, 3021–3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawala, J.; Kosior, D.; Malysa, K. Formation and Influence of the Dynamic Adsorption Layer on Kinetics of the Rising Bubble Collisions with Solution/Gas and Solution/Solid Interfaces. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 222, 765–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dukhin, S.S.; Kovalchuk, V.I.; Gochev, G.G.; Lotfi, M.; Krzan, M.; Malysa, K.; Miller, R. Dynamics of Rear Stagnant Cap Formation at the Surface of Spherical Bubbles Rising in Surfactant Solutions at Large Reynolds Numbers under Conditions of Small Marangoni Number and Slow Sorption Kinetics. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 222, 260–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosior, D.; Zawala, J. Initial Degree of Detaching Bubble Adsorption Coverage and the Kinetics of Dynamic Adsorption Layer Formation. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 2403–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




