Submitted:
02 October 2024
Posted:
04 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
- a)
- Relevance and recent publications are required to ensure the review reflects the most current research and knowledge.
- b)
- Focus and scope of the study: Limiting the timeframe helps maintain focus on recent developments and trends within a manageable scope.
- c)
- Manageability of the reviewing process to make the task more feasible in terms of time and effort.
3. Discussion
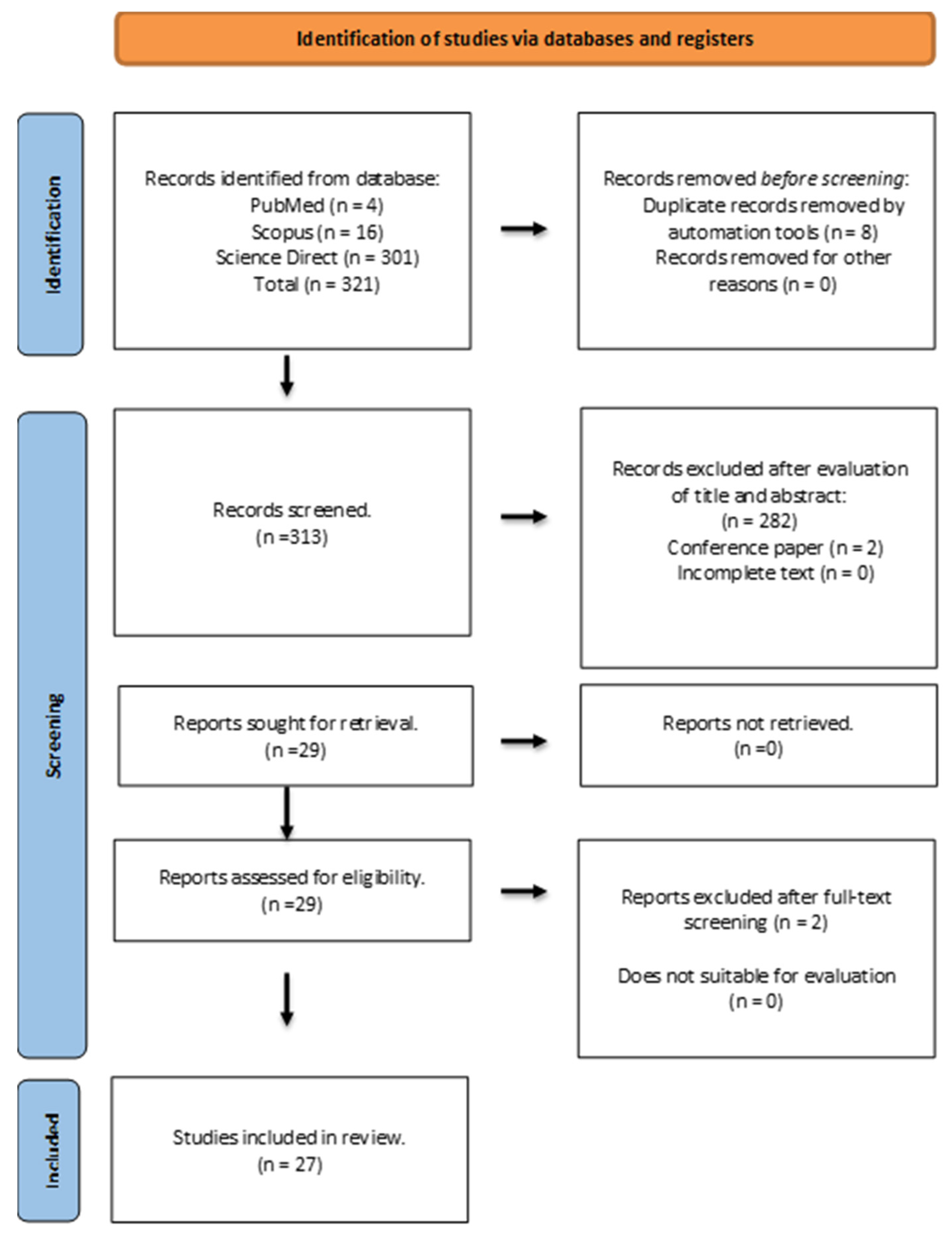
4. Materials and Methods
5. Limitations of The Study
6. Conclusions
7. Future Perspective
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jensen, A. Domestication of Aquilaria spp. and rural poverty—socio-economic and genetic aspects of the planting boom in the. In Proceedings of the Wood of the Gods “,” in Poverty Reduction and Shifting Cultivation Stabilization in the Uplands of Lao PDR: Technologies, Approaches and Methods for Improving Upland Livelihoods—Proceedings of a Workshop held in Luang Prabang, Lao PDR, 2004; pp. 233-239.
- Oldfield, S.; Lusty, C.; MacKinven, A. The world list of threatened trees; 1998.
- de Alwis, W.N.H.; Subasinghe, S.M.C.U.P.; Hettiarachchi, D.S. Characterisation and variation of agarwood resins from Gyrinops walla. Journal of Tropical Forest Science (JTFS) 2019, 31, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyn, L.T.; Anak, N.A. Wood for trees: A review of the agarwood (gaharu) trade in Malaysia; Petaling Jaya, Selangor, Malaysia, 2010.
- Batubara, R.; Hanum, T.I.; Surjanto. Phytochemical and tannin content in two species of agarwood leaves from Mandailing Natal Regency North Sumatera Province. AIP Conference Proceedings 2018, 2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajuddin, S.N.; Yusoff, M.M. Chemical composition of volatile oils of Aquilaria malaccensis (Thymelaeaceae) from Malaysia. Nat Prod Commun 2010, 5, 1965–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamil, J.M.R.; Paudel, K.R.; Chan, Y.; Xenaki, D.; Panneerselvam, J.; Singh, S.K.; Gulati, M.; Jha, N.K.; Kumar, D.; Prasher, P.; et al. Rediscovering the Therapeutic Potential of Agarwood in the Management of Chronic Inflammatory Diseases. Molecules 2022, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yu, Z.; Wang, C.; Wu, C.; Guo, P.; Wei, J. Chemical Constituents and Pharmacological Activity of Agarwood and Aquilaria Plants. Molecules 2018, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurmiati Nurmiati; Periadnadi Periadnadi; Rosadi, Z. F. Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Potential of Some Agarwood Plant Extracts (Aquilaria malaccensis Lamk.) Against Escherichia coli ATCC 25922, Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213 and Candida albicans (C.P Robin) Berkhout 1923. International Journal of Progressive Sciences and Technologies 2024, 43. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, M.; Wei, J.; Chen, H.; Gao, Z.; Sui, C.; Luo, H.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.; et al. Identification of genes related to agarwood formation: transcriptome analysis of healthy and wounded tissues of Aquilaria sinensis. BMC Genomics 2013, 14, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Mohler, J.; Mahajan, S.D.; Schwartz, S.A.; Bruggemann, L.; Aalinkeel, R. Microbial Biofilm: A Review on Formation, Infection, Antibiotic Resistance, Control Measures, and Innovative Treatment. Microorganisms 2023, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rubis, G.; Paudel, K.R.; Manandhar, B.; Singh, S.K.; Gupta, G.; Malik, R.; Shen, J.; Chami, A.; MacLoughlin, R.; Chellappan, D.K.; et al. Agarwood Oil Nanoemulsion Attenuates Cigarette Smoke-Induced Inflammation and Oxidative Stress Markers in BCi-NS1.1 Airway Epithelial Cells. Nutrients 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.R.; Li, W.; Luo, S.; Zhao, X.; Ma, C.H.; Liu, S.X. GC-MS Study of the Chemical Components of Different Aquilaria sinensis (Lour.) Gilgorgans and Agarwood from Different Asian Countries. Molecules 2018, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canlı, K.; Yetgin, A.; Akata, I.; Altuner, E.M. In vitro antimicrobial screening of aquilaria agallocha roots. Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med 2016, 13, 178–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, R.; Kristian, F.; Fajriaty, I. Uji aktivitas antibakteri ekstrak etanol daun gaharu (Aquilaria microcarpa Baill.) terhadap bakteri Salmonella typhi dan Bacillus subtilis secara in vitro. Jurnal Komunitas Farmasi Nasional 2021, 1, 139–154. [Google Scholar]
- Batubara, R.; Wirjosentono, B.; Siregar, A.H.; Harahap, U.; Tamrin, T. Bioactive compounds of ethanol extract from agarwood leaves (Aquilaria malaccensis) and antimicrobial activity against bacteria and fungi growing on the skin. Biodiversitas Journal of Biological Diversity 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamonwannasit, S.; Nantapong, N.; Kumkrai, P.; Luecha, P.; Kupittayanant, S.; Chudapongse, N. Antibacterial activity of Aquilaria crassna leaf extract against Staphylococcus epidermidis by disruption of cell wall. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob 2013, 12, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jihadi, N.I.M.; Maifiah, M.H.M.; Rahim, N.A.; Sani, M.S.A.; Hashim, Y.Z.H.-Y.; Kamal, K.M. Combination of polymyxin B and Aquilaria malaccensis extract enhanced the killing and inhibited the growth of Acinetobacter baumannii and Klebsiella pneumoniae. Malaysian Journal of Microbiology 2022, 18. [Google Scholar]
- Valan, S.L.; Cruz, A.; De Jacob, P.; Djearamane, S. Sustainable synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles using Aquilaria Malaccensis (Agarwood) leaf extract as reducing agent. Int J Technol 2022, 13, 1115–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van, Y.T.; Dinh, D.; Tran, D.M.; Tran, T.N.; Nguyen, H.; Duong, T.T.; Doan, T.Q.; Nguyen, H.T.; Ogunwande, I.A. The antimicrobial activity and essential oil constituents of the leaves and trunks of Aquilaria banaensis P.H.Hô (Thymelaeceae) from Vietnam. Nat Prod Res 2024, 38, 744–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anugrah, R.; Mumtaz, R.K.; Suryasaputra, D. Study In-Silico Oleanane Triterpenoids in Aquilaria spp. as a Covid-19 Antiviral. IOP Conference Series. Earth and Environmental Science 2022, 1104, 012027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurminah, M.; Batubara, R.; Ismanelly, T.; Albert. Taking essential oil by water distillation and antibacterial activity test of refined water from agarwood plant parts (Aquilaria malaccensis Lamk). IOP Conference Series. Earth and Environmental Science 2021, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahham, S.S.; Tabana, Y.M.; Iqbal, M.A.; Ahamed, M.B.; Ezzat, M.O.; Majid, A.S.; Majid, A.M. The Anticancer, Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Properties of the Sesquiterpene β-Caryophyllene from the Essential Oil of Aquilaria crassna. Molecules 2015, 20, 11808–11829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasetya, Y.A. Aktivitas nanoemulsi minyak agarwood bouya (Aquilaria agallocha) terhadap bakteri multidrug resistant (MDR). Berita Biologi 2022, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ga’al, H.; Fouad, H.; Mao, G.; Tian, J.; Jianchu, M. Larvicidal and pupicidal evaluation of silver nanoparticles synthesized using Aquilaria sinensis and Pogostemon cablin essential oils against dengue and zika viruses vector Aedes albopictus mosquito and its histopathological analysis. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 2018, 46, 1171–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yang, Y.; Xue, J.; Wei, J.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, H. Comparison of compositions and antimicrobial activities of essential oils from chemically stimulated agarwood, wild agarwood and healthy Aquilaria sinensis (Lour.) gilg trees. Molecules 2011, 16, 4884–4896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Han, X.-m.; Wei, J.-h.; Xue, J.; Yang, Y.; Liang, L.; Li, X.-j.; Guo, Q.-m.; Xu, Y.-h.; Gao, Z.-h. Compositions and antifungal activities of essential oils from agarwood of Aquilaria sinensis (Lour.) Gilg induced by Lasiodiplodia theobromae (Pat.) Griffon. & Maubl. Journal of the Brazilian Chemical Society 2014, 25. [Google Scholar]
- Hidayati, E.; Handayani, Y.; Sudarma, I.M. Antibacterial Activity of Gyrinops versteegii Fruit Extracts against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli and GC-MS Analysis. Journal of Mathematical and Fundamental Sciences 2022, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Wang, C.; Zheng, W.; Chen, D.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wei, J. Anti-inflammatory 5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-2-(2-phenylethyl)chromones from agarwood of Aquilaria sinensis. Bioorg Chem 2020, 99, 103789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.X.; Wang, C.H.; Chen, D.L.; Liu, Y.Y.; Wei, J.H. Anti-inflammatory sesquiterpenes from agarwood produced via whole-tree agarwood-inducing technique of Aquilaria sinensis. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2019, 44, 4196–4202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.C.; Wang, S.L.; Wu, M.Y.; Liao, C.H.; Lin, C.H.; Chen, J.J.; Fu, S.L. Pilloin, A Flavonoid Isolated from Aquilaria sinensis, Exhibits Anti-Inflammatory Activity In Vitro and In Vivo. Molecules 2018, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, H.X.; Gu, Y.F.; Zhu, Z.X.; Zhang, Y.F.; Chen, X.N.; Guan, P.W.; Shi, S.P.; Song, Y.L.; Zhao, Y.F.; Tu, P.F.; et al. LC-MS-guided isolation of anti-inflammatory 2-(2-phenylethyl)chromone dimers from Chinese agarwood (Aquilaria sinensis). Phytochemistry 2019, 158, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.L.; Tsai, Y.C.; Fu, S.L.; Cheng, M.J.; Chung, M.I.; Chen, J.J. 2-(2-Phenylethyl)-4H-chromen-4-one Derivatives from the Resinous Wood of Aquilaria sinensis with Anti-Inflammatory Effects in LPS-Induced Macrophages. Molecules 2018, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, H.X.; Zhu, Z.X.; Song, Y.L.; Shi, S.P.; Sun, J.; Sun, H.; Zhao, Y.F.; Zheng, J.; Ferreira, D.; Zjawiony, J.K.; et al. Anti-inflammatory Dimeric 2-(2-Phenylethyl)chromones from the Resinous Wood of Aquilaria sinensis. J Nat Prod 2018, 81, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.L.; Liao, H.R.; Cheng, M.J.; Shu, C.W.; Chen, C.L.; Chung, M.I.; Chen, J.J. Four New 2-(2-Phenylethyl)-4H-chromen-4-one Derivatives from the Resinous Wood of Aquilaria sinensis and Their Inhibitory Activities on Neutrophil Pro-Inflammatory Responses. Planta Med 2018, 84, 1340–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.L.; Hwang, T.L.; Chung, M.I.; Sung, P.J.; Shu, C.W.; Cheng, M.J.; Chen, J.J. New Flavones, a 2-(2-Phenylethyl)-4H-chromen-4-one Derivative, and Anti-Inflammatory Constituents from the Stem Barks of Aquilaria sinensis. Molecules 2015, 20, 20912–20925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, H.X.; Gu, Y.F.; Sun, H.; Zhang, Y.F.; Liu, W.J.; Zhu, Z.X.; Shi, S.P.; Song, Y.L.; Jin, H.W.; Zhao, Y.F.; et al. Anti-inflammatory 2-(2-phenylethyl)chromone derivatives from Chinese agarwood. Fitoterapia 2017, 118, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattayasai, J.; Bantadkit, J.; Aromdee, C.; Lattmann, E.; Airarat, W. Antipyretic, analgesic and anti-oxidative activities of Aquilaria crassna leaves extract in rodents. J Ayurveda Integr Med 2012, 3, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.-Q.; Yu, Z.-X.; Wang, C.-H.; Gong, B.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Wei, J.-H. Chemical Constituents and Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Incense Smoke from Agarwood Determined by GC-MS. International Journal of Analytical Chemistry 2020, 2020, 4575030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, K.P.; Hung, D.T. Targeting LPS biosynthesis and transport in gram-negative bacteria in the era of multi-drug resistance. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res 2023, 1870, 119407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, B.; Mathur, P.; Das, A.; Kapil, A.; Gupta, B.; Bhoi, S.; Farooque, K.; Sharma, V.; Misra, M.C. Evaluation of susceptibility testing methods for polymyxin. Int J Infect Dis 2010, 14, e596–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Wang, H.; Suolangjiba; Kou, J. ; Yu, B. Antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory activities of Aquilaria sinensis (Lour.) Gilg. Leaves extract. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 2008, 117, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Yang, X.W.; Wang, R.F. Bio-assay guided isolation and identification of α-glucosidase inhibitors from the leaves of Aquilaria sinensis. Phytochemistry 2011, 72, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| No | Reference | Objective | Method | Findings | Conclusion/Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | [13] |
|
|
|
|
| 2 | [14] |
|
|
|
|
| 3 | [15] |
|
|
|
|
| 4 | [16] |
|
|
|
|
| 5 | [17] |
|
|
|
|
| 6 | [18] |
|
|
|
|
| 7 | [19] |
|
|
|
|
| 8 | [20] |
|
|
|
|
| 9 | [21] |
|
|
|
|
| 10 | [22] |
|
|
|
|
| 11 | [23] |
|
|
|
|
| 12 | [24] |
|
|
|
|
| 13 | [25] |
|
|
|
|
| 14 | [26] |
|
|
|
|
| 15 | [27] |
|
|
|
|
| 16 | [28] |
|
|
|
|
| 17 | [29] |
|
|
|
|
| 18 | [30] |
|
|
|
|
| 19 | [31] |
|
|
|
|
| 20 | [32] |
|
|
|
|
| 21 | [33] |
|
|
|
|
| 22 | [34] |
|
|
|
|
| 23 | [35] |
|
|
|
|
| 24 | [36] |
|
|
|
|
| 25 | [37] |
|
|
|
|
| 26 | [38] |
|
|
|
|
| 27 | [39] |
|
|
|
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





