Submitted:
03 October 2024
Posted:
04 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
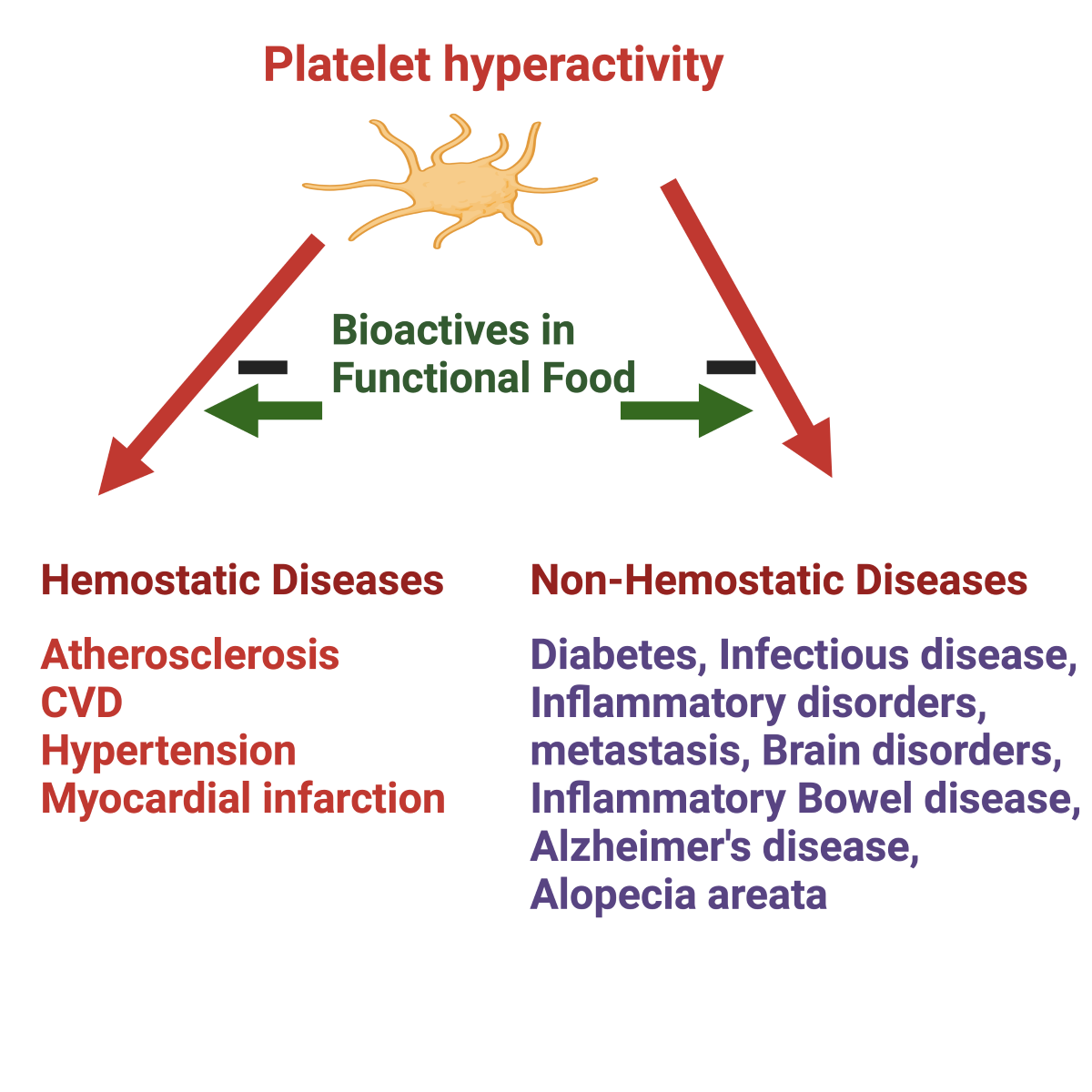
Keywords:
Introduction
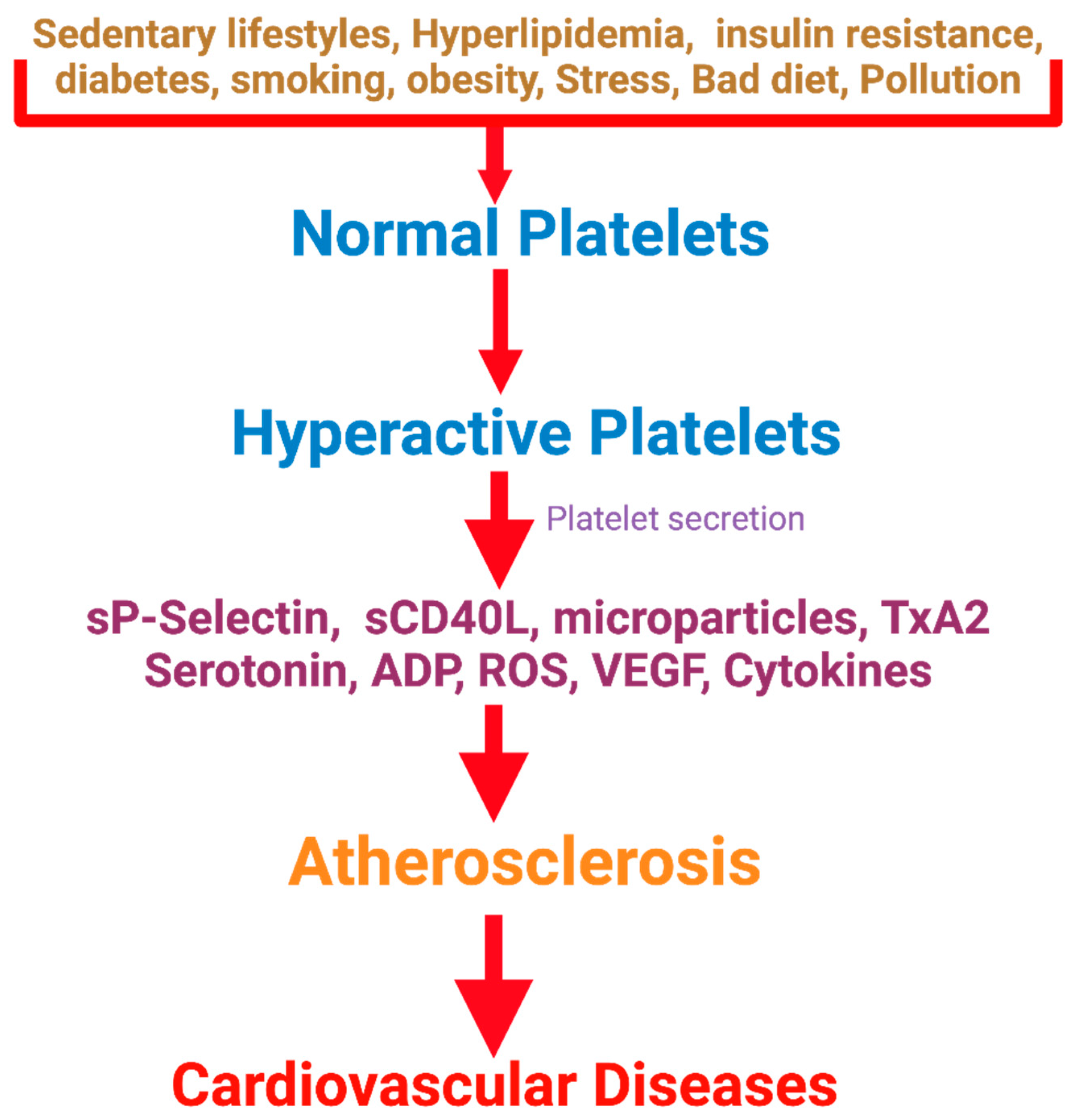
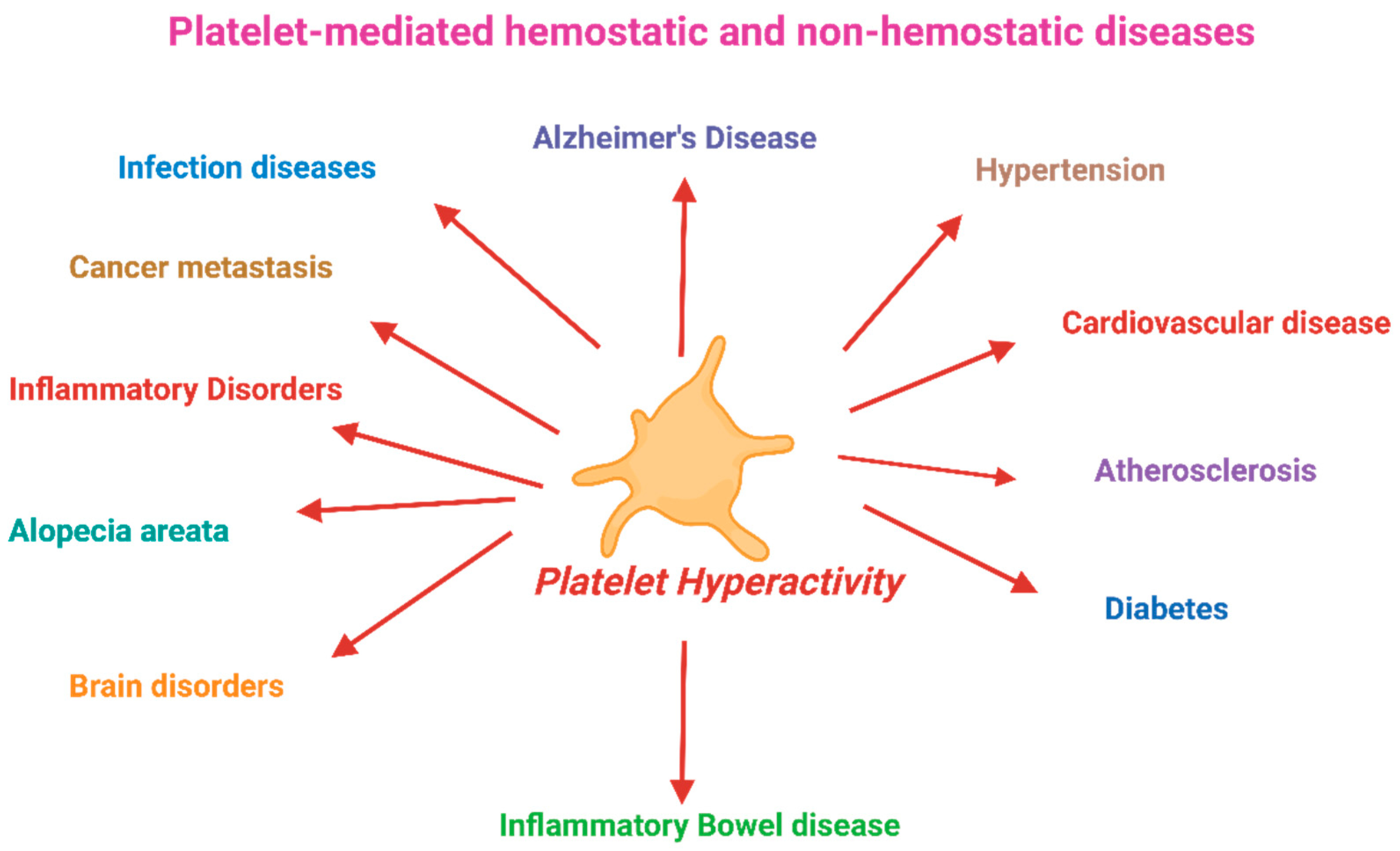
Platelet Hyperactivity in Many Pathological Conditions
Pathological Conditions Such as Metabolic Syndrome, Insulin Resistance, Obesity, Hypertension and Tumors Enhance Platelet Hyperactivity
Modulation of Platelet Activity by Bioactive Compounds of Dietary Origin
N-3 Fatty Acids
Plant Polyphenols
Water-Soluble Extracts from Tomato and Kiwifruit: The Latest Dietary Antiplatelet Regimes
Tomato
Human Trials and Animal Experiments Using Fruitflow®
Kiwifruit and Its Anti-Platelet Factors
Human Trials
Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ho-Tin-Noe, B.; Boulaftali, Y.; Camerer, E. Platelets and vascular integrity: How platelets prevent bleeding in inflammation. Blood 2018, 131, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davi, G.; Patrono, C. Platelet activation and atherothrombosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 2482–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.R.; Zhang, D.; Oswald, B.E.; Carrim, N.; Wang, X.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Lavalle, C.; McKeown, T.; Marshall, A.H.; et al. Platelets are versatile cells: New discoveries in hemostasis, thrombosis, immune responses, tumor metastasis and beyond. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2016, 53, 409–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D.; Adhikary, S.; Das, R.K.; Banerjee, A.; Radhakrishnan, A.K.; Paul, S.; Pathak, S.; Duttaroy, A.K. Bioactive food components and their inhibitory actions in multiple platelet pathways. J. Food Biochem. 2022, 46, e14476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O'Kennedy, N.; Duss, R.; Duttaroy, A.K. Dietary Antiplatelets: A New Perspective on the Health Benefits of the Water-Soluble Tomato Concentrate Fruitflow((R)). Nutrients 2021, 13, 2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D.; Shruthi, N.R.; Banerjee, A.; Jothimani, G.; Duttaroy, A.K.; Pathak, S. Endothelial dysfunction, platelet hyperactivity, hypertension, and the metabolic syndrome: Molecular insights and combating strategies. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1221438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.R.; Yousef, G.M.; Ni, H. Cancer and platelet crosstalk: Opportunities and challenges for aspirin and other antiplatelet agents. Blood 2018, 131, 1777–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koupenova, M.; Corkrey, H.A.; Vitseva, O.; Manni, G.; Pang, C.J.; Clancy, L.; Yao, C.; Rade, J.; Levy, D.; Wang, J.P.; et al. The role of platelets in mediating a response to human influenza infection. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puurunen, M.K.; Hwang, S.J.; Larson, M.G.; Vasan, R.S.; O'Donnell, C.J.; Tofler, G.; Johnson, A.D. ADP Platelet Hyperreactivity Predicts Cardiovascular Disease in the FHS (Framingham Heart Study). J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2018, 7, 8522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, A.; Zaman, A.G.; Marshall, S.M. Platelet hyperactivity in type 2 diabetes: Role of antiplatelet agents. Diab Vasc. Dis. Res. 2008, 5, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massberg, S.; Brand, K.; Gruner, S.; Page, S.; Muller, E.; Muller, I.; Bergmeier, W.; Richter, T.; Lorenz, M.; Konrad, I.; et al. A critical role of platelet adhesion in the initiation of atherosclerotic lesion formation. J. Exp. Med. 2002, 196, 887–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, Z.S.; Jackson, S.P. The role of platelets in atherothrombosis. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program. 2011, 2011, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagadinou, M.; Onisor, M.O.; Rigas, A.; Musetescu, D.V.; Gkentzi, D.; Assimakopoulos, S.F.; Panos, G.; Marangos, M. Antimicrobial Properties on Non-Antibiotic Drugs in the Era of Increased Bacterial Resistance. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, B.; Dunbar, M. Platelets and Intravascular Immunity: Guardians of the Vascular Space During Bloodstream Infections and Sepsis. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koupenova, M.; Clancy, L.; Corkrey, H.A.; Freedman, J.E. Circulating Platelets as Mediators of Immunity, Inflammation, and Thrombosis. Circ. Res. 2018, 122, 337–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.R.; Storey, R.F. The role of platelets in inflammation. Thromb. Haemost. 2015, 114, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varon, D.; Shai, E. Platelets and their microparticles as key players in pathophysiological responses. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2015, 13 (Suppl. S1), S40–S46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Blanc, J.; Lordkipanidze, M. Platelet Function in Aging. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2019, 6, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenhardt, S.U.; Habersberger, J.; Peter, K. Monomeric C-reactive protein generation on activated platelets: The missing link between inflammation and atherothrombotic risk. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2009, 19, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, I.; Massberg, S.; Zierhut, W.; Binz, C.; Schuster, A.; Rudiger-von Hoch, S.; Braun, S.; Gawaz, M. Effects of aspirin and clopidogrel versus oral anticoagulation on platelet function and on coagulation in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation (CLAFIB). Pathophysiol. Haemost. Thromb. 2002, 32, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, G.; Zhou, W.; Lu, Y.; Chen, P.; Lu, Z.; Fu, Y. Aspirin resistance and other aspirin-related concerns. Neurol. Sci. 2016, 37, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piepoli, M.F.; Hoes, A.W.; Agewall, S.; Albus, C.; Brotons, C.; Catapano, A.L.; Cooney, M.T.; Corra, U.; Cosyns, B.; Deaton, C.; et al. 2016 European Guidelines on cardiovascular disease prevention in clinical practice: The Sixth Joint Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and Other Societies on Cardiovascular Disease Prevention in Clinical Practice (constituted by representatives of 10 societies and by invited experts)Developed with the special contribution of the European Association for Cardiovascular Prevention & Rehabilitation (EACPR). Eur. Heart J. 2016, 37, 2315–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta-Roy, A.K. Dietary components and human platelet activity. Platelets 2002, 13, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O'Kennedy, N.; Raederstorff, D.; Duttaroy, A.K. Fruitflow((R)): The first European Food Safety Authority-approved natural cardio-protective functional ingredient. Eur. J. Nutr. 2017, 56, 461–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duttaroy, A.K.; Jorgensen, A. Effects of kiwi fruit consumption on platelet aggregation and plasma lipids in healthy human volunteers. Platelets 2004, 15, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta-Roy, A.K.; Gordon, M.J.; Kelly, C.; Hunter, K.; Crosbie, L.; Knight-Carpentar, T.; Williams, B.C. Inhibitory effect of Ginkgo biloba extract on human platelet aggregation. Platelets 1999, 10, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta-Roy, A.K.; Crosbie, L.; Gordon, M.J. Effects of tomato extract on human platelet aggregation in vitro. Platelets 2001, 12, 218–227. [Google Scholar]
- Lowery, C.L., 3rd; Elliott, C.; Cooper, A.; Hadden, C.; Sonon, R.N.; Azadi, P.; Williams, D.K.; Marsh, J.D.; Woulfe, D.S.; Kilic, F. Cigarette Smoking-Associated Alterations in Serotonin/Adrenalin Signaling Pathways of Platelets. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6, 5465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, M.; Sakai, C.; Kobayashi, Y.; Ishida, T. Cigarette Smoking and Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2024, 31, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, S.; Miller, M.R. Ambient air pollution and thrombosis. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2018, 15, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; McGeoch, S.C.; Johnstone, A.M.; Holtrop, G.; Sneddon, A.A.; MacRury, S.M.; Megson, I.L.; Pearson, D.W.; Abraham, P.; De Roos, B.; et al. Platelet-derived microparticle count and surface molecule expression differ between subjects with and without type 2 diabetes, independently of obesity status. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2014, 37, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huskens, D.; Roest, M.; Remijn, J.A.; Konings, J.; Kremers, R.M.; Bloemen, S.; Schurgers, E.; Selmeczi, A.; Kelchtermans, H.; van Meel, R.; et al. Strenuous exercise induces a hyperreactive rebalanced haemostatic state that is more pronounced in men. Thromb. Haemost. 2016, 115, 1109–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, P.K.; Kim, S.; Kim, S. An Insight into Recent Advances on Platelet Function in Health and Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podrez, E.A.; Byzova, T.V.; Febbraio, M.; Salomon, R.G.; Ma, Y.; Valiyaveettil, M.; Poliakov, E.; Sun, M.; Finton, P.J.; Curtis, B.R.; et al. Platelet CD36 links hyperlipidemia, oxidant stress and a prothrombotic phenotype. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 1086–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Febbraio, M.; Li, W.; Silverstein, R.L. A specific CD36-dependent signaling pathway is required for platelet activation by oxidized low-density lipoprotein. Circ. Res. 2008, 102, 1512–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennings, L.K. Mechanisms of platelet activation: Need for new strategies to protect against platelet-mediated atherothrombosis. Thromb. Haemost. 2009, 102, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, J.; Li, W.; Holinstat, M. Platelet Signaling and Disease: Targeted Therapy for Thrombosis and Other Related Diseases. Pharmacol. Rev. 2018, 70, 526–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiter, O.; Walker, T.L. Platelets in Neurodegenerative Conditions-Friend or Foe? Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendu, F.; Brohard-Bohn, B. The platelet release reaction: granules' constituents, secretion and functions. Platelets 2001, 12, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janowska-Wieczorek, A.; Majka, M.; Kijowski, J.; Baj-Krzyworzeka, M.; Reca, R.; Turner, A.R.; Ratajczak, J.; Emerson, S.G.; Kowalska, M.A.; Ratajczak, M.Z. Platelet-derived microparticles bind to hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells and enhance their engraftment. Blood 2001, 98, 3143–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heijnen, H.F.; Schiel, A.E.; Fijnheer, R.; Geuze, H.J.; Sixma, J.J. Activated platelets release two types of membrane vesicles: Microvesicles by surface shedding and exosomes derived from exocytosis of multivesicular bodies and alpha-granules. Blood 1999, 94, 3791–3799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frossard, M.; Fuchs, I.; Leitner, J.M.; Hsieh, K.; Vlcek, M.; Losert, H.; Domanovits, H.; Schreiber, W.; Laggner, A.N.; Jilma, B. Platelet function predicts myocardial damage in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Circulation 2004, 110, 1392–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tantry, U.S.; Bonello, L.; Aradi, D.; Price, M.J.; Jeong, Y.H.; Angiolillo, D.J.; Stone, G.W.; Curzen, N.; Geisler, T.; Ten Berg, J.; et al. Consensus and update on the definition of on-treatment platelet reactivity to adenosine diphosphate associated with ischemia and bleeding. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 62, 2261–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnoldussen, I.A.C.; Witkamp, R.F. Effects of Nutrients on Platelet Function: A Modifiable Link between Metabolic Syndrome and Neurodegeneration? Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barale, C.; Russo, I. Influence of Cardiometabolic Risk Factors on Platelet Function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, I. The prothrombotic tendency in metabolic syndrome: Focus on the potential mechanisms involved in impaired haemostasis and fibrinolytic balance. Scientifica 2012, 2012, 525374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Kholmukhamedov, A. Platelet reactivity in dyslipidemia: Atherothrombotic signaling and therapeutic implications. Rev. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 22, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta-Roy, A.K.; Gordon, M.J.; Campbell, F.M.; Crosbie, L.C. Arachidonic acid uptake by human platelets is mediated by CD36. Platelets 1996, 7, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N. Platelets as an inter-player between hyperlipidaemia and atherosclerosis. J. Intern. Med. 2024, 296, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbatarny, H.S.; Maurice, D.H. Leptin-mediated activation of human platelets: Involvement of a leptin receptor and phosphodiesterase 3A-containing cellular signaling complex. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 289, E695–E702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinides, S.; Schafer, K.; Koschnick, S.; Loskutoff, D.J. Leptin-dependent platelet aggregation and arterial thrombosis suggests a mechanism for atherothrombotic disease in obesity. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 108, 1533–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bladowski, M.; Gawrys, J.; Gajecki, D.; Szahidewicz-Krupska, E.; Sawicz-Bladowska, A.; Doroszko, A. Role of the Platelets and Nitric Oxide Biotransformation in Ischemic Stroke: A Translative Review from Bench to Bedside. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2020, 2020, 2979260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zennadi, R. Oxidative Stress and Thrombosis during Aging: The Roles of Oxidative Stress in RBCs in Venous Thrombosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedman, J.E. Oxidative stress and platelets. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2008, 28, s11–s16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceriello, A. Postprandial hyperglycemia and diabetes complications: Is it time to treat? Diabetes 2005, 54, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andre, P.; Nannizzi-Alaimo, L.; Prasad, S.K.; Phillips, D.R. Platelet-derived CD40L: The switch-hitting player of cardiovascular disease. Circulation 2002, 106, 896–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henn, V.; Steinbach, S.; Buchner, K.; Presek, P.; Kroczek, R.A. The inflammatory action of CD40 ligand (CD154) expressed on activated human platelets is temporally limited by coexpressed CD40. Blood 2001, 98, 1047–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miceli, G.; Basso, M.G.; Rizzo, G.; Pintus, C.; Tuttolomondo, A. The Role of the Coagulation System in Peripheral Arterial Disease: Interactions with the Arterial Wall and Its Vascular Microenvironment and Implications for Rational Therapies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azimova, K.; San Juan, Z.; Mukherjee, D. Cardiovascular safety profile of currently available diabetic drugs. Ochsner J. 2014, 14, 616–632. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, M.; Harrison, H.E.; Raftery, A.T.; Elder, J.B. Vascular prostacyclin may be reduced in diabetes in man. Lancet 1979, 1, 325–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabini, R.A.; Staffolani, R.; Fumelli, P.; Mutus, B.; Curatola, G.; Mazzanti, L. Decreased nitric oxide synthase activity in platelets from IDDM and NIDDM patients. Diabetologia 1998, 41, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blann, A.D.; Nadar, S.; Lip, G.Y. Pharmacological modulation of platelet function in hypertension. Hypertension 2003, 42, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pravenec, M.; Kunes, J.; Zicha, J.; Kren, V.; Klir, P. Platelet aggregation in spontaneous hypertension: Genetic determination and correlation analysis. J. Hypertens. 1992, 10, 1453–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breddin, H.K.; Lippold, R.; Bittner, M.; Kirchmaier, C.M.; Krzywanek, H.J.; Michaelis, J. Spontaneous platelet aggregation as a predictive risk factor for vascular occlusions in healthy volunteers? Results of the HAPARG Study. Haemostatic parameters as risk factors in healthy volunteers. Atherosclerosis 1999, 144, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torsellini, A.; Becucci, A.; Citi, S.; Cozzolino, F.; Guidi, G.; Lombardi, V.; Vercelli, D.; Veloci, M. Effects of pressure excursions on human platelets. In vitro studies on betathromboglobulin (beta-TG) and platelet factor 4 (PF4) release and on platelet sensitivity to ADP-aggregation. Haematologica 1982, 67, 860–866. [Google Scholar]
- Lip, G.Y.; Blann, A.D.; Farooqi, I.S.; Zarifis, J.; Sagar, G.; Beevers, D.G. Sequential alterations in haemorheology, endothelial dysfunction, platelet activation and thrombogenesis in relation to prognosis following acute stroke: The West Birmingham Stroke Project. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2002, 13, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blann, A.D.; Naqvi, T.; Waite, M.; McCollum, C.N. von Willebrand factor and endothelial damage in essential hypertension. J. Hum. Hypertens. 1993, 7, 107–111. [Google Scholar]
- Nityanand, S.; Pande, I.; Bajpai, V.K.; Singh, L.; Chandra, M.; Singh, B.N. Platelets in essential hypertension. Thromb. Res. 1993, 72, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjeldsen, S.E.; Gjesdal, K.; Eide, I.; Aakesson, I.; Amundsen, R.; Foss, O.P.; Leren, P. Increased beta-thromboglobulin in essential hypertension: Interactions between arterial plasma adrenaline, platelet function and blood lipids. Acta Med. Scand. 1983, 213, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, C.G.; Gurney, D.; Blann, A.D.; Beevers, D.G.; Lip, G.Y.; Ascot Steering Committee, A.-S.C.O.T. Von Willebrand factor, soluble P-selectin, and target organ damage in hypertension: A substudy of the Anglo-Scandinavian Cardiac Outcomes Trial (ASCOT). Hypertension 2002, 40, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechi, C.; Sinigaglia, D.; Delva, P.; Guzzo, P.; Arosio, E.; Steele, A.; Lechi, A. Platelet intracellular free Ca2+ after incubation with plasma from hypertensive patients. J. Hum. Hypertens. 1989, 3, 45–48. [Google Scholar]
- Yamanishi, J.; Sano, H.; Saito, K.; Furuta, Y.; Fukuzaki, H. Plasma concentrations of platelet-specific proteins in different stages of essential hypertension: Interactions between platelet aggregation, blood lipids and age. Thromb. Haemost. 1985, 54, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forte, P.; Copland, M.; Smith, L.M.; Milne, E.; Sutherland, J.; Benjamin, N. Basal nitric oxide synthesis in essential hypertension. Lancet 1997, 349, 837–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camilletti, A.; Moretti, N.; Giacchetti, G.; Faloia, E.; Martarelli, D.; Mantero, F.; Mazzanti, L. Decreased nitric oxide levels and increased calcium content in platelets of hypertensive patients. Am. J. Hypertens. 2001, 14, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dockrell, M.E.; Walker, B.R.; Noon, J.P.; Watt, G.C.; Williams, B.C.; Webb, D.J. Platelet aggregation in young men with contrasting predisposition to high blood pressure. Am. J. Hypertens. 1999, 12, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Lu, Z.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, M.; Chu, T.; Wang, P.; Qi, F.; Anderson, G.J.; Jiang, E.; et al. Monitoring circulating platelet activity to predict cancer-associated thrombosis. Cell Rep. Methods 2023, 3, 100513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gussoni, G.; Frasson, S.; La Regina, M.; Di Micco, P.; Monreal, M.; Investigators, R. Three-month mortality rate and clinical predictors in patients with venous thromboembolism and cancer. Findings from the RIETE registry. Thromb. Res. 2013, 131, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O'Kennedy, N.; Crosbie, L.; van Lieshout, M.; Broom, J.I.; Webb, D.J.; Duttaroy, A.K. Effects of antiplatelet components of tomato extract on platelet function in vitro and ex vivo: A time-course cannulation study in healthy humans. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 84, 570–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisman, S.M.; Graham, D.Y. Evaluation of the benefits and risks of low-dose aspirin in the secondary prevention of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events. Arch. Intern. Med. 2002, 162, 2197–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schror, K. Aspirin and platelets: The antiplatelet action of aspirin and its role in thrombosis treatment and prophylaxis. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 1997, 23, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaragoza, C.; Monserrat, J.; Mantecon, C.; Villaescusa, L.; Zaragoza, F.; Alvarez-Mon, M. Antiplatelet activity of flavonoid and coumarin drugs. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2016, 87, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Harris, W.S.; Chung, M.; Lichtenstein, A.H.; Balk, E.M.; Kupelnick, B.; Jordan, H.S.; Lau, J. n-3 Fatty acids from fish or fish-oil supplements, but not alpha-linolenic acid, benefit cardiovascular disease outcomes in primary- and secondary-prevention studies: A systematic review. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 84, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrioli, G.; Carletto, A.; Guarini, P.; Galvani, S.; Biasi, D.; Bellavite, P.; Corrocher, R. Differential effects of dietary supplementation with fish oil or soy lecithin on human platelet adhesion. Thromb. Haemost. 1999, 82, 1522–1527. [Google Scholar]
- Golanski, J.; Szymanska, P.; Rozalski, M. Effects of Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and Their Metabolites on Haemostasis-Current Perspectives in Cardiovascular Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parent, C.A.; Lagarde, M.; Venton, D.L.; Le Breton, G.C. Selective modulation of the human platelet thromboxane A2/prostaglandin H2 receptor by eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acids in intact platelets and solubilized platelet membranes. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 6541–6547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta-Roy, A.K. Insulin mediated processes in platelets, erythrocytes and monocytes/macrophages: Effects of essential fatty acid metabolism. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 1994, 51, 385–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Schacky, C. Prophylaxis of atherosclerosis with marine omega-3 fatty acids. A comprehensive strategy. Ann. Intern. Med. 1987, 107, 890–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.G.; Cao, J.; Mao, Q.X.; Lu, X.C.; Zhou, X.L.; Fan, L. Influence of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid-supplementation on platelet aggregation in humans: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Atherosclerosis 2013, 226, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, M.; Hossain, S.; Shido, O. Docosahexaenoic acid but not eicosapentaenoic acid withstands dietary cholesterol-induced decreases in platelet membrane fluidity. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2006, 293, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, M.K.; Tormoen, G.W.; Weaver, L.J.; Luepke, K.J.; Patel, I.A.; Hjelmen, C.E.; Ensz, N.M.; McComas, L.S.; McCarty, O.J. Exogenous modification of platelet membranes with the omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA reduces platelet procoagulant activity and thrombus formation. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2013, 304, C273–C279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEwen, B.J.; Morel-Kopp, M.C.; Tofler, G.H.; Ward, C.M. The effect of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on fibrin and thrombin generation in healthy subjects and subjects with cardiovascular disease. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2015, 41, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dona, M.; Fredman, G.; Schwab, J.M.; Chiang, N.; Arita, M.; Goodarzi, A.; Cheng, G.; von Andrian, U.H.; Serhan, C.N. Resolvin E1, an EPA-derived mediator in whole blood, selectively counterregulates leukocytes and platelets. Blood 2008, 112, 848–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, A.; Stanger, L.; Freedman, C.J.; Standley, M.; Hoang, T.; Adili, R.; Tsai, W.C.; van Hoorebeke, C.; Holman, T.R.; Holinstat, M. DHA 12-LOX-derived oxylipins regulate platelet activation and thrombus formation through a PKA-dependent signaling pathway. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2021, 19, 839–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, S.; Weber, P.C. Thromboxane A3 (TXA3) is formed in human platelets after dietary eicosapentaenoic acid (C20:5 omega 3). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1983, 116, 1091–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibney, M.J.; Bolton-Smith, C. The effect of a dietary supplement of n-3 polyunsaturated fat on platelet lipid composition, platelet function and platelet plasma membrane fluidity in healthy volunteers. Br. J. Nutr. 1988, 60, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.L.; Steiner, M. Dose response of dietary fish oil supplementations on platelet adhesion. Arterioscler. Thromb. 1991, 11, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirich, C.; Gaszo, A.; Granegger, S.; Sinzinger, H. Effects of fish oil supplementation on platelet survival and ex vivo platelet function in hypercholesterolemic patients. Thromb. Res. 1999, 96, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svaneborg, N.; Kristensen, S.D.; Hansen, L.M.; Bullow, I.; Husted, S.E.; Schmidt, E.B. The acute and short-time effect of supplementation with the combination of n-3 fatty acids and acetylsalicylic acid on platelet function and plasma lipids. Thromb. Res. 2002, 105, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eschen, O.; Christensen, J.H.; De Caterina, R.; Schmidt, E.B. Soluble adhesion molecules in healthy subjects: A dose-response study using n-3 fatty acids. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2004, 14, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanschoonbeek, K.; Feijge, M.A.; Paquay, M.; Rosing, J.; Saris, W.; Kluft, C.; Giesen, P.L.; de Maat, M.P.; Heemskerk, J.W. Variable hypocoagulant effect of fish oil intake in humans: Modulation of fibrinogen level and thrombin generation. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2004, 24, 1734–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Din, J.N.; Harding, S.A.; Valerio, C.J.; Sarma, J.; Lyall, K.; Riemersma, R.A.; Newby, D.E.; Flapan, A.D. Dietary intervention with oil rich fish reduces platelet-monocyte aggregation in man. Atherosclerosis 2008, 197, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, M.K.; Shearer, G.C.; Ashmore, J.H.; Anderson-Daniels, J.M.; Graslie, E.L.; Tholen, J.T.; Vogelaar, J.L.; Korth, A.J.; Nareddy, V.; Sprehe, M.; et al. Omega-3 fatty acids modulate collagen signaling in human platelets. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2011, 84, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vericel, E.; Calzada, C.; Chapuy, P.; Lagarde, M. The influence of low intake of n-3 fatty acids on platelets in elderly people. Atherosclerosis 1999, 147, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croset, M.; Vericel, E.; Rigaud, M.; Hanss, M.; Courpron, P.; Dechavanne, M.; Lagarde, M. Functions and tocopherol content of blood platelets from elderly people after low intake of purified eicosapentaenoic acid. Thromb. Res. 1990, 57, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driss, F.; Vericel, E.; Lagarde, M.; Dechavanne, M.; Darcet, P. Inhibition of platelet aggregation and thromboxane synthesis after intake of small amount of icosapentaenoic acid. Thromb. Res. 1984, 36, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillot, N.; Caillet, E.; Laville, M.; Calzada, C.; Lagarde, M.; Vericel, E. Increasing intakes of the long-chain omega-3 docosahexaenoic acid: Effects on platelet functions and redox status in healthy men. FASEB J. 2009, 23, 2909–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, S.; Kanazawa, S.; Fukuhara, S. Effects of eicosapentaenoic acid on platelet activation markers and cell adhesion molecules in hyperlipidemic patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2003, 17, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Qian, Z.M.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Vaughn, M.G.; Aaron, H.E.; Wang, C.; Lip, G.Y.; Lin, H. Regular use of fish oil supplements and course of cardiovascular diseases: Prospective cohort study. BMJ Med. 2024, 3, e000451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dael, P. Role of n-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids in human nutrition and health: Review of recent studies and recommendations. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2021, 15, 137–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.T.; Dai, J.H.; Gao, Q. Effects of Omega-3 fatty acid on major cardiovascular events and mortality in patients with coronary heart disease: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2014, 24, 470–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, S.M.; Myung, S.K.; Lee, Y.J.; Seo, H.G.; Korean Meta-analysis Study, G. Efficacy of omega-3 fatty acid supplements (eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid) in the secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease: A meta-analysis of randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials. Arch. Intern. Med. 2012, 172, 686–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nestel, P.; Clifton, P.; Colquhoun, D.; Noakes, M.; Mori, T.A.; Sullivan, D.; Thomas, B. Indications for Omega-3 Long Chain Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid in the Prevention and Treatment of Cardiovascular Disease. Heart Lung Circ. 2015, 24, 769–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, B.J.; Groot, R.H.M. Effects of Omega-3 Long Chain Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Supplementation on Cardiovascular Mortality: The Importance of the Dose of DHA. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozaffarian, D.; Wu, J.H. Omega-3 fatty acids and cardiovascular disease: Effects on risk factors, molecular pathways, and clinical events. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011, 58, 2047–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kris-Etherton, P.M.; Harris, W.S.; Appel, L.J.; American Heart Association. Nutrition, C. Fish consumption, fish oil, omega-3 fatty acids, and cardiovascular disease. Circulation 2002, 106, 2747–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siscovick, D.S.; Barringer, T.A.; Fretts, A.M.; Wu, J.H.; Lichtenstein, A.H.; Costello, R.B.; Kris-Etherton, P.M.; Jacobson, T.A.; Engler, M.B.; Alger, H.M.; et al. Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid (Fish Oil) Supplementation and the Prevention of Clinical Cardiovascular Disease: A Science Advisory From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2017, 135, e867–e884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skulas-Ray, A.C.; Wilson, P.W.F.; Harris, W.S.; Brinton, E.A.; Kris-Etherton, P.M.; Richter, C.K.; Jacobson, T.A.; Engler, M.B.; Miller, M.; Robinson, J.G.; et al. Omega-3 Fatty Acids for the Management of Hypertriglyceridemia: A Science Advisory From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2019, 140, e673–e691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aung, T.; Halsey, J.; Kromhout, D.; Gerstein, H.C.; Marchioli, R.; Tavazzi, L.; Geleijnse, J.M.; Rauch, B.; Ness, A.; Galan, P.; et al. Associations of Omega-3 Fatty Acid Supplement Use With Cardiovascular Disease Risks: Meta-analysis of 10 Trials Involving 77 917 Individuals. JAMA Cardiol. 2018, 3, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhamid, A.S.; Brown, T.J.; Brainard, J.S.; Biswas, P.; Thorpe, G.C.; Moore, H.J.; Deane, K.H.; AlAbdulghafoor, F.K.; Summerbell, C.D.; Worthington, H.V.; et al. Omega-3 fatty acids for the primary and secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 7, CD003177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimm, E.B.; Appel, L.J.; Chiuve, S.E.; Djousse, L.; Engler, M.B.; Kris-Etherton, P.M.; Mozaffarian, D.; Siscovick, D.S.; Lichtenstein, A.H.; American Heart Association Nutrition Committee of the Council on, L. ; et al. Seafood Long-Chain n-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and Cardiovascular Disease: A Science Advisory From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2018, 138, e35–e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ed Nignpense, B.; Chinkwo, K.A.; Blanchard, C.L.; Santhakumar, A.B. Polyphenols: Modulators of Platelet Function and Platelet Microparticle Generation? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 21, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goszcz, K.; Duthie, G.G.; Stewart, D.; Leslie, S.J.; Megson, I.L. Bioactive polyphenols and cardiovascular disease: Chemical antagonists, pharmacological agents or xenobiotics that drive an adaptive response? Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 1209–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arts, I.C.; Hollman, P.C. Polyphenols and disease risk in epidemiologic studies. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 81, 317S–325S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.; Jawad, M.; Kamal, M.A.; Baldi, A.; Xiao, J.; Nabavi, S.M.; Daglia, M. Evidence and prospective of plant derived flavonoids as antiplatelet agents: Strong candidates to be drugs of future. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 119, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludovici, V.; Barthelmes, J.; Nagele, M.P.; Flammer, A.J.; Sudano, I. Polyphenols: Anti-Platelet Nutraceutical? Curr. Pharm. Des. 2018, 24, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heptinstall, S.; May, J.; Fox, S.; Kwik-Uribe, C.; Zhao, L. Cocoa flavanols and platelet and leukocyte function: Recent in vitro and ex vivo studies in healthy adults. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2006, 47 (Suppl. S2), S197–S205, discussion S206–S199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, R.R.; Actis-Goretta, L.; Momma, T.Y.; Keen, C.L. Dietary flavanols and platelet reactivity. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2006, 47 (Suppl. S2), S187–S196, discussion S206-S189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, M.S.; Gambert, S.; Bliden, K.P.; Bailon, O.; Singla, A.; Antonino, M.J.; Hamed, F.; Tantry, U.S.; Gurbel, P.A. Dark chocolate effect on platelet activity, C-reactive protein and lipid profile: A pilot study. South. Med. J. 2008, 101, 1203–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, D.A.; Holt, R.R.; Rein, D.; Paglieroni, T.; Schmitz, H.H.; Keen, C.L. Flavanols and platelet reactivity. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2005, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, E.L.; Hutfless, S.M.; Ding, X.; Girotra, S. Chocolate and prevention of cardiovascular disease: A systematic review. Nutr. Metab. (Lond) 2006, 3, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermann, F.; Spieker, L.E.; Ruschitzka, F.; Sudano, I.; Hermann, M.; Binggeli, C.; Luscher, T.F.; Riesen, W.; Noll, G.; Corti, R. Dark chocolate improves endothelial and platelet function. Heart 2006, 92, 119–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, B.; Moraes, L.A.; Kemp, C.F.; Mullen, W.; Crozier, A.; Lovegrove, J.A.; Gibbins, J.M. A structural basis for the inhibition of collagen-stimulated platelet function by quercetin and structurally related flavonoids. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 159, 1312–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojic, M.; Debeljak, Z.; Tomicic, M.; Medic-Saric, M.; Tomic, S. Evaluation of antiaggregatory activity of flavonoid aglycone series. Nutr. J. 2011, 10, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rein, D.; Paglieroni, T.G.; Pearson, D.A.; Wun, T.; Schmitz, H.H.; Gosselin, R.; Keen, C.L. Cocoa and wine polyphenols modulate platelet activation and function. J. Nutr. 2000, 130, 2120S–2126S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innes, A.J.; Kennedy, G.; McLaren, M.; Bancroft, A.J.; Belch, J.J. Dark chocolate inhibits platelet aggregation in healthy volunteers. Platelets 2003, 14, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manach, C.; Williamson, G.; Morand, C.; Scalbert, A.; Remesy, C. Bioavailability and bioefficacy of polyphenols in humans. I. Review of 97 bioavailability studies. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 81, 230S–242S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D.; Adhikary, S.; Das, R.K.; Banerjee, A.; Radhakrishnan, A.K.; Paul, S.; Pathak, S.; Duttaroy, A.K. Bioactive food components and their inhibitory actions in multiple platelet pathways. J. Food Biochem. 2022, 46, e14476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta-Roy, A.K.; Crosbie, L.C.; Gordon, M.J.; Campbell, F.M. Platelet membrane glycoprotein IV (CD36) is involved in arachidonic acid induced-platelet aggregation. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 1996, 24, 167S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierre, S.; Crosbie, L.; Duttaroy, A.K. Inhibitory effect of aqueous extracts of some herbs on human platelet aggregation in vitro. Platelets 2005, 16, 469–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimbach, G.; Melchin, M.; Moehring, J.; Wagner, A.E. Polyphenols from cocoa and vascular health-a critical review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 4290–4309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostertag, L.M.; O'Kennedy, N.; Kroon, P.A.; Duthie, G.G.; de Roos, B. Impact of dietary polyphenols on human platelet function--a critical review of controlled dietary intervention studies. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2010, 54, 60–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, I.; Mok, M.; Christensen, A.M.; Turner, A.H.; Hawley, J.A. The effects of polyphenols in olive leaves on platelet function. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2008, 18, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, I.; Quinn, H.; Mok, M.; Southgate, R.J.; Turner, A.H.; Li, D.; Sinclair, A.J.; Hawley, J.A. The effect of exercise and training status on platelet activation: Do cocoa polyphenols play a role? Platelets 2006, 17, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, E.; Caballero, J.; Alarcon, M.; Rojas, A.; Palomo, I. Chlorogenic acid inhibits human platelet activation and thrombus formation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.H.; Deng, X.J.; Chen, Y.Q.; Ya, F.L.; Zhang, X.D.; Song, F.; Li, D.; Yang, Y. Anthocyanin Cyanidin-3-Glucoside Attenuates Platelet Granule Release in Mice Fed High-Fat Diets. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. (Tokyo) 2017, 63, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Adili, R.; McKeown, T.; Chen, P.; Zhu, G.; Li, D.; Ling, W.; Ni, H.; Yang, Y. Plant-based Food Cyanidin-3-Glucoside Modulates Human Platelet Glycoprotein VI Signaling and Inhibits Platelet Activation and Thrombus Formation. J. Nutr. 2017, 147, 1917–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Torre, R. Bioavailability of olive oil phenolic compounds in humans. Inflammopharmacology 2008, 16, 245–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, J.A.; Lopez-Villodres, J.A.; Asensi, R.; Espartero, J.L.; Rodriguez-Gutierez, G.; De La Cruz, J.P. Virgin olive oil polyphenol hydroxytyrosol acetate inhibits in vitro platelet aggregation in human whole blood: Comparison with hydroxytyrosol and acetylsalicylic acid. Br. J. Nutr. 2009, 101, 1157–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojic, M.; Antolic, A.; Tomicic, M.; Debeljak, Z.; Males, Z. Propolis ethanolic extracts reduce adenosine diphosphate induced platelet aggregation determined on whole blood. Nutr. J. 2018, 17, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faggio, C.; Sureda, A.; Morabito, S.; Sanches-Silva, A.; Mocan, A.; Nabavi, S.F.; Nabavi, S.M. Flavonoids and platelet aggregation: A brief review. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 807, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.S.; Lee, V.S.; Tseng, Y.L.; Chang, K.C.; Chen, K.B.; Chen, Y.L.; Li, C.Y. Gallic Acid Attenuates Platelet Activation and Platelet-Leukocyte Aggregation: Involving Pathways of Akt and GSK3beta. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 2012, 683872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olas, B.; Wachowicz, B.; Stochmal, A.; Oleszek, W. The polyphenol-rich extract from grape seeds inhibits platelet signaling pathways triggered by both proteolytic and non-proteolytic agonists. Platelets 2012, 23, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Yu, J.; Pohorly, J.E.; Kakuda, Y. Polyphenolics in grape seeds-biochemistry and functionality. J. Med. Food 2003, 6, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Zou, J.; Cao, K.; Xu, Y.; Wu, J.M. Effects of red wine and wine polyphenol resveratrol on platelet aggregation in vivo and in vitro. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2002, 9, 77–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijak, M.; Saluk-Bijak, J. Flavonolignans inhibit the arachidonic acid pathway in blood platelets. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duttaroy, A.K. Role of Gut Microbiota and Their Metabolites on Atherosclerosis, Hypertension and Human Blood Platelet Function: A Review. Nutrients 2021, 13, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Gregory, J.C.; Org, E.; Buffa, J.A.; Gupta, N.; Wang, Z.; Li, L.; Fu, X.; Wu, Y.; Mehrabian, M.; et al. Gut Microbial Metabolite TMAO Enhances Platelet Hyperreactivity and Thrombosis Risk. Cell 2016, 165, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Klipfell, E.; Bennett, B.J.; Koeth, R.; Levison, B.S.; Dugar, B.; Feldstein, A.E.; Britt, E.B.; Fu, X.; Chung, Y.M.; et al. Gut flora metabolism of phosphatidylcholine promotes cardiovascular disease. Nature 2011, 472, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drosos, I.; Tavridou, A.; Kolios, G. New aspects on the metabolic role of intestinal microbiota in the development of atherosclerosis. Metabolism 2015, 64, 476–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, J.C.; Buffa, J.A.; Org, E.; Wang, Z.; Levison, B.S.; Zhu, W.; Wagner, M.A.; Bennett, B.J.; Li, L.; DiDonato, J.A.; et al. Transmission of atherosclerosis susceptibility with gut microbial transplantation. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 5647–5660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, Z.; Xia, H.; Zhong, S.L.; Feng, Q.; Li, S.; Liang, S.; Zhong, H.; Liu, Z.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, H.; et al. The gut microbiome in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, F.H.; Fak, F.; Nookaew, I.; Tremaroli, V.; Fagerberg, B.; Petranovic, D.; Backhed, F.; Nielsen, J. Symptomatic atherosclerosis is associated with an altered gut metagenome. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, K.; Srivatsav, V.; Rizwan, A.; Nashed, A.; Liu, R.; Shen, R.; Akhtar, M. Bridging the Gap between Gut Microbial Dysbiosis and Cardiovascular Diseases. Nutrients 2017, 9, 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santisteban, M.M.; Qi, Y.; Zubcevic, J.; Kim, S.; Yang, T.; Shenoy, V.; Cole-Jeffrey, C.T.; Lobaton, G.O.; Stewart, D.C.; Rubiano, A.; et al. Hypertension-Linked Pathophysiological Alterations in the Gut. Circ. Res. 2017, 120, 312–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.L.; Yi, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Ran, L.; Yang, J.; Zhu, J.D.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Mi, M.T. Resveratrol Attenuates Trimethylamine-N-Oxide (TMAO)-Induced Atherosclerosis by Regulating TMAO Synthesis and Bile Acid Metabolism via Remodeling of the Gut Microbiota. mBio 2016, 7, e02210–e02215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, T.; Ryu, J.; Lee, K.; Park, S.Y.; Hwang, K.T. Protective Effects of Black Raspberry (Rubus occidentalis) Extract against Hypercholesterolemia and Hepatic Inflammation in Rats Fed High-Fat and High-Choline Diets. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annunziata, G.; Maisto, M.; Schisano, C.; Ciampaglia, R.; Narciso, V.; Tenore, G.C.; Novellino, E. Effects of Grape Pomace Polyphenolic Extract (Taurisolo((R))) in Reducing TMAO Serum Levels in Humans: Preliminary Results from a Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Cross-Over Study. Nutrients 2019, 11, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, A.; Tyree, S.M.; Fehlbaum, S.; DunnGalvin, G.; Panagos, C.G.; Guy, B.; Patel, S.; Dinan, T.G.; Duttaroy, A.K.; Duss, R.; et al. A water-soluble tomato extract rich in secondary plant metabolites lowers trimethylamine-n-oxide and modulates gut microbiota: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled cross-over study in overweight and obese adults. J. Nutr. 2023, 153, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundy, S.M.; Cleeman, J.I.; Daniels, S.R.; Donato, K.A.; Eckel, R.H.; Franklin, B.A.; Gordon, D.J.; Krauss, R.M.; Savage, P.J.; Smith, S.C., Jr.; et al. Diagnosis and management of the metabolic syndrome: An American Heart Association/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Scientific Statement. Circulation 2005, 112, 2735–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimodaira, M.; Niwa, T.; Nakajima, K.; Kobayashi, M.; Hanyu, N.; Nakayama, T. Correlation between mean platelet volume and fasting plasma glucose levels in prediabetic and normoglycemic individuals. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2013, 12, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamukcu, B.; Lip, G.Y.; Snezhitskiy, V.; Shantsila, E. The CD40-CD40L system in cardiovascular disease. Ann. Med. 2011, 43, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferroni, P.; Basili, S.; Falco, A.; Davi, G. Platelet activation in type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Thromb. Haemost. JTH 2004, 2, 1282–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferroni, P.; Martini, F.; D'Alessandro, R.; Magnapera, A.; Raparelli, V.; Scarno, A.; Davi, G.; Basili, S.; Guadagni, F. In vivo platelet activation is responsible for enhanced vascular endothelial growth factor levels in hypertensive patients. Clin. Chim. Acta 2008, 388, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Ye, Z.; Li, Q.; Wen, J.; Tao, X.; Chen, L.; He, M.; Wang, X.; Lu, B.; et al. Lipocalin-2, glucose metabolism and chronic low-grade systemic inflammation in Chinese people. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2012, 11, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davi, G.; Patrono, C. Platelet activation and atherothrombosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 2482–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, Z.S.; Jackson, S.P. The role of platelets in atherothrombosis. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program. 2011, 2011, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slavin, J.L.; Lloyd, B. Health benefits of fruits and vegetables. Adv. Nutr. 2012, 3, 506–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaziano, J.M.; Manson, J.E.; Branch, L.G.; Colditz, G.A.; Willett, W.C.; Buring, J.E. A prospective study of consumption of carotenoids in fruits and vegetables and decreased cardiovascular mortality in the elderly. Ann. Epidemiol. 1995, 5, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshipura, K.J.; Ascherio, A.; Manson, J.E.; Stampfer, M.J.; Rimm, E.B.; Speizer, F.E.; Hennekens, C.H.; Spiegelman, D.; Willett, W.C. Fruit and vegetable intake in relation to risk of ischemic stroke. JAMA 1999, 282, 1233–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta-Roy, A.K.; Crosbie, L.; Gordon, M.J. Effects of tomato extract on human platelet aggregation in vitro. Platelets 2001, 12, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obarzanek, E.; Sacks, F.M.; Vollmer, W.M.; Bray, G.A.; Miller, E.R., 3rd; Lin, P.H.; Karanja, N.M.; Most-Windhauser, M.M.; Moore, T.J.; Swain, J.F.; et al. Effects on blood lipids of a blood pressure-lowering diet: The Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) Trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2001, 74, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dizdarevic, L.L.; Biswas, D.; Uddin, M.D.; Jorgenesen, A.; Falch, E.; Bastani, N.E.; Duttaroy, A.K. Inhibitory effects of kiwifruit extract on human platelet aggregation and plasma angiotensin-converting enzyme activity. Platelets 2014, 25, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barin, A.; Das, R.K.; Bastani, N.E.; Iversen, P.O.; Duttaroy, A.K. Extracts of tamarillo, horned melon, and raspberry, but not extract of pear, inhibit human blood platelet aggregation: Investigating the underlying factors for their differential mechanisms. J. Funct. Foods 2023, 110, 105847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovannucci, E. Tomatoes, tomato-based products, lycopene, and cancer: Review of the epidemiologic literature. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1999, 91, 317–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovannucci, E. A review of epidemiologic studies of tomatoes, lycopene, and prostate cancer. Exp. Biol. Med. 2002, 227, 852–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovannucci, E.; Rimm, E.B.; Liu, Y.; Stampfer, M.J.; Willett, W.C. A prospective study of tomato products, lycopene, and prostate cancer risk. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2002, 94, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O'Kennedy, N.; Crosbie, L.; van Lieshout, M.; Broom, J.I.; Webb, D.J.; Duttaroy, A.K. Effects of antiplatelet components of tomato extract on platelet function in vitro and ex vivo: A time-course cannulation study in healthy humans. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 84, 570–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, E.; Castro, R.; Astudillo, L.; Carrasco, G.; Alarcon, M.; Gutierrez, M.; Palomo, I. Bioassay-Guided Isolation and HPLC Determination of Bioactive Compound That Relate to the Antiplatelet Activity (Adhesion, Secretion, and Aggregation) from Solanum lycopersicum. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 2012, 147031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, S.; Wang, H.; Bao, L.; Wu, W.; Qi, R. Fruitflow inhibits platelet function by suppressing Akt/GSK3beta, Syk/PLCgamma2 and p38 MAPK phosphorylation in collagen-stimulated platelets. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2022, 22, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwager, J.; Richard, N.; Mussler, B.; Raederstorff, D. Tomato Aqueous Extract Modulates the Inflammatory Profile of Immune Cells and Endothelial Cells. Molecules 2016, 21, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Chen, H.; Li, C.; Chen, B.; Gong, H.; Zhao, Y.; Qi, R. Water-Soluble Tomato Extract Fruitflow Alters the Phosphoproteomic Profile of Collagen-Stimulated Platelets. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 746107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J. Protein disulfide isomerase in thrombosis and vascular inflammation. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2013, 11, 2084–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manickam, N.; Sun, X.; Li, M.; Gazitt, Y.; Essex, D.W. Protein disulphide isomerase in platelet function. Br. J. Haematol. 2008, 140, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasuja, R.; Passam, F.H.; Kennedy, D.R.; Kim, S.H.; van Hessem, L.; Lin, L.; Bowley, S.R.; Joshi, S.S.; Dilks, J.R.; Furie, B.; et al. Protein disulfide isomerase inhibitors constitute a new class of antithrombotic agents. J. Clin. Invest. 2012, 122, 2104–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheu, J.R.; Hsiao, G.; Chou, P.H.; Shen, M.Y.; Chou, D.S. Mechanisms involved in the antiplatelet activity of rutin, a glycoside of the flavonol quercetin, in human platelets. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 4414–4418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O'Kennedy, N.; Crosbie, L.; Whelan, S.; Luther, V.; Horgan, G.; Broom, J.I.; Webb, D.J.; Duttaroy, A.K. Effects of tomato extract on platelet function: A double-blinded crossover study in healthy humans. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 84, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O'Kennedy, N.; Crosbie, L.; Whelan, S.; Luther, V.; Horgan, G.; Broom, J.I.; Webb, D.J.; Duttaroy, A.K. Effects of tomato extract on platelet function: A double-blinded crossover study in healthy humans. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 84, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, R.K.; Datta, T.; Biswas, D.; Duss, R.; O'Kennedy, N.; Duttaroy, A.K. Evaluation of the equivalence of different intakes of Fruitflow in affecting platelet aggregation and thrombin generation capacity in a randomized, double-blinded pilot study in male subjects. BMC Nutr. 2021, 7, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O'Kennedy, N.; Crosbie, L.; Song, H.J.; Zhang, X.; Horgan, G.; Duttaroy, A.K. A randomised controlled trial comparing a dietary antiplatelet, the water-soluble tomato extract Fruitflow, with 75 mg aspirin in healthy subjects. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 71, 723–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Fan, D.; Li, K.; Zhao, D.; Liang, Y.; Ji, Q.; Gao, X.; Ma, X.; Zhao, Y.; Mao, Y.; et al. Four-Week Supplementation of Water-Soluble Tomato Extract Attenuates Platelet Function in Chinese Healthy Middle-Aged and Older Individuals: A Randomized, Double-Blinded, and Crossover Clinical Trial. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 891241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasinska, B.; Osinska, A.; Osinski, M.; Krasinska, A.; Rzymski, P.; Tykarski, A.; Krasinski, Z. Standardised tomato extract as an alternative to acetylsalicylic acid in patients with primary hypertension and high cardiovascular risk - a randomised, controlled trial. Arch. Med. Sci. 2018, 14, 773–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Xiao, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Yin, X.; Liao, F.; You, Y.; et al. Water-soluble tomato concentrate modulates shear-induced platelet aggregation and blood flow in vitro and in vivo. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 961301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorentino, A.; D'Abrosca, B.; Pacifico, S.; Mastellone, C.; Scognamiglio, M.; Monaco, P. Identification and assessment of antioxidant capacity of phytochemicals from kiwi fruits. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 4148–4155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsen, A.; Svendsen, M.; Seljeflot, I.; Laake, P.; Duttaroy, A.K.; Drevon, C.A.; Arnesen, H.; Tonstad, S.; Blomhoff, R. Kiwifruit decreases blood pressure and whole-blood platelet aggregation in male smokers. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2012, 27, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brevik, A.; Gaivao, I.; Medin, T.; Jorgenesen, A.; Piasek, A.; Elilasson, J.; Karlsen, A.; Blomhoff, R.; Veggan, T.; Duttaroy, A.K.; et al. Supplementation of a western diet with golden kiwifruits (Actinidia chinensis var.'Hort 16A':) effects on biomarkers of oxidation damage and antioxidant protection. Nutr. J. 2011, 10, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.H.; Liu, J.F. Effects of kiwifruit consumption on serum lipid profiles and antioxidative status in hyperlipidemic subjects. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2009, 60, 709–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, K.A.; Song, T.C.; Han, D.; Kim, I.H.; Kim, Y.E.; Lee, C.H. Cardiovascular protective properties of kiwifruit extracts in vitro. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2005, 28, 1782–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroll, M.H.; Schafer, A.I. Biochemical mechanisms of platelet activation. Blood 1989, 74, 1181–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brevik, A.; Gaivao, I.; Medin, T.; Jorgenesen, A.; Piasek, A.; Elilasson, J.; Karlsen, A.; Blomhoff, R.; Veggan, T.; Duttaroy, A.K.; et al. Supplementation of a western diet with golden kiwifruits (Actinidia chinensis var.'Hort 16A':) effects on biomarkers of oxidation damage and antioxidant protection. Nutr. J. 2011, 10, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.H.; Liu, J.F. Effects of kiwifruit consumption on serum lipid profiles and antioxidative status in hyperlipidemic subjects. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2009, 60, 709–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsen, A.; Svendsen, M.; Seljeflot, I.; Laake, P.; Duttaroy, A.K.; Drevon, C.A.; Arnesen, H.; Tonstad, S.; Blomhoff, R. Kiwifruit decreases blood pressure and whole-blood platelet aggregation in male smokers. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2013, 27, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferroni, P.; Santilli, F.; Guadagni, F.; Basili, S.; Davi, G. Contribution of platelet-derived CD40 ligand to inflammation, thrombosis and neoangiogenesis. Curr. Med. Chem. 2007, 14, 2170–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, E.J.; Astudillo, L.A.; Gutierrez, M.I.; Contreras, S.O.; Bustamante, L.O.; Rubio, P.I.; Moore-Carrasco, R.; Alarcon, M.A.; Fuentes, J.A.; Gonzalez, D.E.; et al. Fractions of aqueous and methanolic extracts from tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) present platelet antiaggregant activity. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis Int. J. Haemost. Thromb. 2012, 23, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hankey, G.J.; Eikelboom, J.W. Aspirin resistance. Lancet 2006, 367, 606–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravishankar, D.; Albadawi, D.A.I.; Chaggar, V.; Patra, P.H.; Williams, H.F.; Salamah, M.; Vaiyapuri, R.; Dash, P.R.; Patel, K.; Watson, K.A.; et al. Isorhapontigenin, a resveratrol analogue selectively inhibits ADP-stimulated platelet activation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 862, 172627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumacher, E.; Vigh, E.; Molnar, V.; Kenyeres, P.; Feher, G.; Kesmarky, G.; Toth, K.; Garai, J. Thrombosis preventive potential of chicory coffee consumption: A clinical study. Phytother. Res. 2011, 25, 744–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickel, T.; Lackermair, K.; Scherr, J.; Calatzis, A.; Vogeser, M.; Hanssen, H.; Waidhauser, G.; Schonermark, U.; Methe, H.; Horster, S.; et al. Influence of High Polyphenol Beverage on Stress-Induced Platelet Activation. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2016, 20, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draijer, R.; de Graaf, Y.; Slettenaar, M.; de Groot, E.; Wright, C.I. Consumption of a polyphenol-rich grape-wine extract lowers ambulatory blood pressure in mildly hypertensive subjects. Nutrients 2015, 7, 3138–3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ras, R.T.; Zock, P.L.; Zebregs, Y.E.; Johnston, N.R.; Webb, D.J.; Draijer, R. Effect of polyphenol-rich grape seed extract on ambulatory blood pressure in subjects with pre- and stage I hypertension. Br. J. Nutr. 2013, 110, 2234–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flammer, A.J.; Sudano, I.; Wolfrum, M.; Thomas, R.; Enseleit, F.; Periat, D.; Kaiser, P.; Hirt, A.; Hermann, M.; Serafini, M.; et al. Cardiovascular effects of flavanol-rich chocolate in patients with heart failure. Eur. Heart J. 2012, 33, 2172–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loo, B.M.; Erlund, I.; Koli, R.; Puukka, P.; Hellstrom, J.; Wahala, K.; Mattila, P.; Jula, A. Consumption of chokeberry (Aronia mitschurinii) products modestly lowered blood pressure and reduced low-grade inflammation in patients with mildly elevated blood pressure. Nutr. Res. 2016, 36, 1222–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; McGeoch, S.C.; Megson, I.L.; MacRury, S.M.; Johnstone, A.M.; Abraham, P.; Pearson, D.W.; de Roos, B.; Holtrop, G.; O'Kennedy, N.; et al. Oat-enriched diet reduces inflammatory status assessed by circulating cell-derived microparticle concentrations in type 2 diabetes. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2014, 58, 1322–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Source | Models | Experimental conditions | Conclusions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chlorogenic acid | Mice (n=18) | Inhibition of in vivo thrombus formation | Inhibited thrombus formation[144] |
| Anthocyanin cyaniding-3-glucoside from purified black rice | Mice (n=60) | Mice randomly assigned to 3 groups (n=20): control group, high-fat diet, or a high-fat diet+ Anthocyanin cyaniding-3-glucoside | Decreased platelet activation, and inhibited platelet ATP release [145] |
| Red wine polyphenols (Provinols™) | Rats (n= 149) | Rats were randomly grouped as treated with or without aldosterone-salt, with or without Provinols (20 mg/kg/day) or spironolactone (30 mg/kg/day) for 4 weeks | Provinols decreased circulating levels microparticles [215]. |
| Cocoa | Healthy males (n=16) | Double-blind, crossover study. Placebo-controlled. Eight subjects in two groups (trains and untrained) randomly received placebo or cocoa polyphenol (236 mg/day) for a week and then afterwards subjected to one hour of exercise | No change in collagen induced platelet aggregation post exercise. ATP release higher post exercise in both groups. Cocoa supplementation did not normalize platelet activity after exercise[143] . |
| Chicory coffee | Healthy subjects (n=27) | Chicory coffee (300 mL) consumed every day for 1 week | Effect on platelet aggregation is variable depending on the agonists used [216]. |
| High polyphenol beverage | Healthy Athletes (n = 103) | Group 1 received a polyphenol-rich beverage, Group 2 a placebo in a randomized, double-blind study. Samples were collected three weeks before, one day before, immediately, as well as 24 h and 72 h, after a marathon run | Control group demonstrated a 2.2-fold increase in platelet aggregation after marathon completion. But there was no increase in platelet aggregation in polyphenol-rich beverage group [217]. |
| Polyphenol-rich grape wine | Untreated, mildly hypertensive subjects (n =60) | Grape juice extract; grape and wine extract each for 4 weeks including a 2-week run-in period in a double-blind placebo-controlled crossover study. | There was no effect on ADP, collagen, or epinephrine induced platelet aggregation[218]. |
| Polyphenol-rich grape seed extract | Untreated subjects with pre and stage 1 hypertension (n=35) | Double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized, parallel-group intervention with 300 mg/day grape seed extract capsule. Eight-week duration study |
Platelet aggregation was not affected [219] |
| Flavanol-rich chocolate | Patients with congestive heart failure (n =20) | 2h after after consumption of a chocolate bar and 4 weeks of consumption (two chocolate bars/day) in a double-blind, randomized placebo-controlled trial. | Platelet adhesion significantly decreased 2 h after flavanol-rich chocolate ingestion. But no effect after 2- and 4-week supplementation[220]. |
| Chokeberry (Aronia mitschurinii) products | Patients with untreated mild hypertension (n =38) | Cold-pressed 100% chokeberry juice (300 mL/day) and oven-dried chokeberry powder (3 g/day), or placebo for 8 weeks without washout in a single blinded crossover trial for 16-week. | No change in platelet aggregation response [221] |
| Oats | Type 2 diabetes subjects (n =22) | Randomized crossover involving 8-week intervention with either oat enriched diet or a standard dietary advised diet. Pre-intervention habitual intakes were used to compare responses. | Decreased in tissue factor-activated platelets (CD142) after oat rich diet than habitual or standard advised diet. Decreased in tissue factor positive PMPs and fibrinogen-positive PMPs with oat enriched diet intervention[222] |
| Anthocyanin rich beverage | Sedentary subjects (n =21) | Queen garnet plum juice (200 mL/day) were consumed for 28 days in a double-blind placebo controlled study | Reduced ADP-, collagen- and ARA-induced platelet aggregation. Reduced P-selectin expression |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





