1. Introduction
In December 2019, the Wuhan Municipal Health Commission identified and reported 27 cases of pneumonia of unknown etiology, characterized by fever, dyspnea, and bilateral pulmonary infiltrates on chest X-rays in Wuhan City, Hubei Province, China.[
1] On January 7, 2020, the causative agent was identified from oropharyngeal and nasopharyngeal swab samples conducted by the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. The pathogen was found to be a virus genetically related to the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS-CoV) outbreak of 2002-2003 and was therefore named SARS-CoV-2. [
2] By January 17, 2020, 44 cases of infection by the novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) had been confirmed, 7 of which developed severe illness. Of these, 2 elderly adults with chronic-degenerative diseases died due to multiple organ failure and Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS).[
3]
On February 11, 2020, the World Health Organization (WHO), in collaboration with the World Organization for Animal Health and the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, officially named the disease: coronavirus disease 2019 (COronaVIrus Disease 2019 [COVID-19]).[
4,
5,
6] In Mexico, the first COVID-19 case was reported on February 27, 2020; the first case of critical COVID-19 with ARDS treated in the Intensive Care Unit (ICU) of the South Central High Specialty Hospital (Health Services of Petróleos Mexicanos) was reported on March 21, 2020.[
7,
8,
9]
Pathophysiologically, the local and systemic response mechanisms are multiple, and the primary organs affected include the respiratory system (pneumonia, severe pneumonia, and acute respiratory failure syndrome), cardiovascular system (vascular inflammation, acute myocardial injury, myocarditis, arrhythmias, venous thromboembolism), and kidneys (Acute Kidney Injury [AKI]).[
10]
Several meta-analyses have confirmed that age, gender (male), cardiovascular diseases (hypertension), diabetes, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and cancer are major risk factors for critical COVID-19 and mortality.[
11,
12] Most patients (90%) with COVID-19 have developed mild symptoms such as fever and/or cough, and dyspnea, myalgia, headache, arthralgia, and/or sore throat, which resolved without specific intervention (symptomatic treatment); however, others (10%) have developed symptoms requiring hospitalization (pneumonia) and 5% experienced complications such as severe pneumonia, ARDS, sepsis/septic shock, and multiple organ failure, with high mortality.[
13,
14,
15,
16,
17]
Since the onset of the pandemic, multiple treatments have been tested for COVID-19; by late 2020, the vaccination campaign against SARS-CoV-2 began, reducing disease severity and improving survival rates in the context of critical COVID-19. [
18,
19] Currently, there is no specific treatment available for critical COVID-19 with ARDS; management involves supportive care (ventilatory support, vasopressor support, renal replacement therapy, etc.) in Intensive Care Units (ICUs).[
20,
21,
22,
23,
24,
25] Severe ARDS in critical COVID-19 occurs in at least two-thirds of cases and is associated with high mortality.[
26,
27,
28]
It has been documented that 5% of patients with COVID-19 require admission to the ICU. Studies have found an association between age, gender (male), cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, COPD, and cancer and mortality, identifying this population as at-risk. However, once critically ill, the exact survival rates of these patients and the factors that may influence survival are not fully understood. It is crucial to identify the factors associated with survival in critically ill patients with ARDS due to SARS-CoV-2 who require ICU admission.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Setting
The study was conducted in an Intensive Care Unit (ICU) adapted for the management of COVID-19 patients at a tertiary care teaching hospital in Mexico City, covering the period from March 21, 2020, to March 20, 2023.
2.2. Study Design
This was an observational, retrospective, longitudinal, and comparative study.
2.3. Population Definition
All patients admitted to the ICU who met the eligibility criteria were included in the study.
2.4. Inclusion Criteria
Patients of both sexes, aged 18 years and older, with a confirmed diagnosis of COVID-19 through a positive PCR test for SARS-CoV-2.
2.5. Exclusion Criteria
Patients with a negative PCR test were excluded.
2.6. Elimination Criteria
Patients who died within the first 24 hours of ICU admission and those who did not require invasive mechanical ventilation were eliminated from the analysis.
2.7. Primary Objective
To determine the survival of critically ill patients with ARDS due to SARS-CoV-2.
2.8. Secondary Objectives
To identify factors associated with mortality in critically ill patients with ARDS due to SARS-CoV-2.
To determine 90-day survival according to the factors associated with mortality in critically ill patients with ARDS due to SARS-CoV-2.
2.9. Variable Operationalization
Demographic variables (age, gender), anthropometric data (weight, height, BMI), comorbidities (diabetes, hypertension, among others), and admission data (PaO2/FiO2, SpO2/FiO2, and vital signs) were collected to classify the severity of respiratory failure (defined as PaO2/FiO2 <300 mmHg or SpO2/FiO2 <460 mmHg) and hemodynamic failure (defined as a mean arterial pressure [MAP] <65 mmHg or the need for vasopressor support). The confirmation of the SARS-CoV-2 diagnosis was made by nasopharyngeal PCR test (CFX96 Touch RT-PCR Detection System, USA). Indicators of renal function (urine output, serum creatinine, and urinary NGAL) were also recorded to classify acute kidney injury (AKI). The number of days on mechanical ventilation, the need and duration of prone positioning, use of neuromuscular blockade, tracheostomy, and renal support through hemodialysis were documented. Length of ICU stay and total hospital stay were also recorded. Data were obtained from the Critical Care Unit Database.
2.10. Statistical Analysis
The most prevalent mortality-associated factors were analyzed using descriptive statistics; absolute (n) and relative (%) frequencies were used for categorical variables, while means (X) and standard deviations (SD) were calculated for continuous variables. For hypothesis testing, the Student’s t-test was used to compare means, the chi-square test to compare proportions, and the Mann-Whitney U test to contrast medians. A p-value <0.05 was considered significant. These variables were included in a binary logistic regression model to calculate odds ratios (OR) with 95% confidence intervals (95% CI). Once the factors associated with mortality with statistical significance were identified, cumulative individual survival probability was estimated using the Kaplan-Meier method, and the log-rank test was used to evaluate significant differences in survival between groups defined by the identified risk factors. Data were processed using SPSS software, version 25.0 (IBM Corporation).
2.11. Ethical Considerations
This study was approved by the Research Committee and the Ethics and Research Committee under the numbers 17-21, 20-21, and 26-21, ensuring the confidentiality and protection of patient data. Since this was an observational study without intervention, informed consent was not required.
3. Results
A total of 157 patients were studied, of whom 74.5% (n=117) were male. The mean age was 62.8 ± 11.8 years. Nutritional status, evaluated using body mass index (BMI), had a mean of 30.81 ± 5.90 kg/m²; no patients presented with malnutrition at the time of admission. A total of 12.1% (n=19) were classified as having a normal weight, 38.9% (n=61) were overweight, and 49% (n=77) were obese. The most common comorbidity was hypertension, present in 54.8% (n=86) of patients, followed by type 2 diabetes, present in 43.3% (n=68).
Upon ICU admission, the mean SpO2/FiO2 ratio was 107.31 ± 40 mmHg, and the mean PaO2/FiO2 ratio was 93.83 ± 41.64 mmHg. The prevalence of severe ARDS was 68.2% (n=107), with a mean duration of mechanical ventilation of 16.34 ± 12.43 days. Prone positioning was used in 42% (n=66) of patients, 86.4% (n=57) of whom underwent early pronation, defined as within the first 48 hours of ARDS diagnosis. The mean duration of the pronation maneuver was 49.2 ± 18.77 hours, and only 6.1% required a second pronation session. Neuromuscular blockade was used in 49.7% (n=78) of cases, and tracheostomy was performed in 29.3% (n=49) of patients.
Acute kidney injury (AKI) occurred in 70.1% (n=110) of cases, classified based on urinary volumes and the presence of biochemical markers, with a higher prevalence in class 1A (34.5%, n=38). Hemodynamic failure at ICU admission was observed in 74.5% (n=117) of patients, with a mean SOFA score of 7 points (range: 2–14) and a mean serum lactate level of 1.72 ± 0.74 mmol/L.
The mean length of ICU stay was 17.70 ± 13.59 days, and the mean total hospital stay was 26.90 ± 19.91 days. Overall mortality was 58.6% (n=92), with a cumulative 90-day survival rate of 41.4%.
For logistic regression analysis, variables that showed statistical significance for mortality were included. Continuous variables such as lactate and SpO2/FiO2 were adjusted as dummy variables with cut-off points of 2 mmol/L for lactate and 160 mmHg for SpO2/FiO2, respectively. The presence of AKI (OR = 3.4, 95% CI: 1.702–7.169, p = 0.00), hemodynamic failure at ICU admission (OR = 6.5, 95% CI: 2.97–14.21, p = 0.00), and lactate level (OR = 0.201, 95% CI: 0.079–0.515, p = 0.00) were independently associated with mortality.
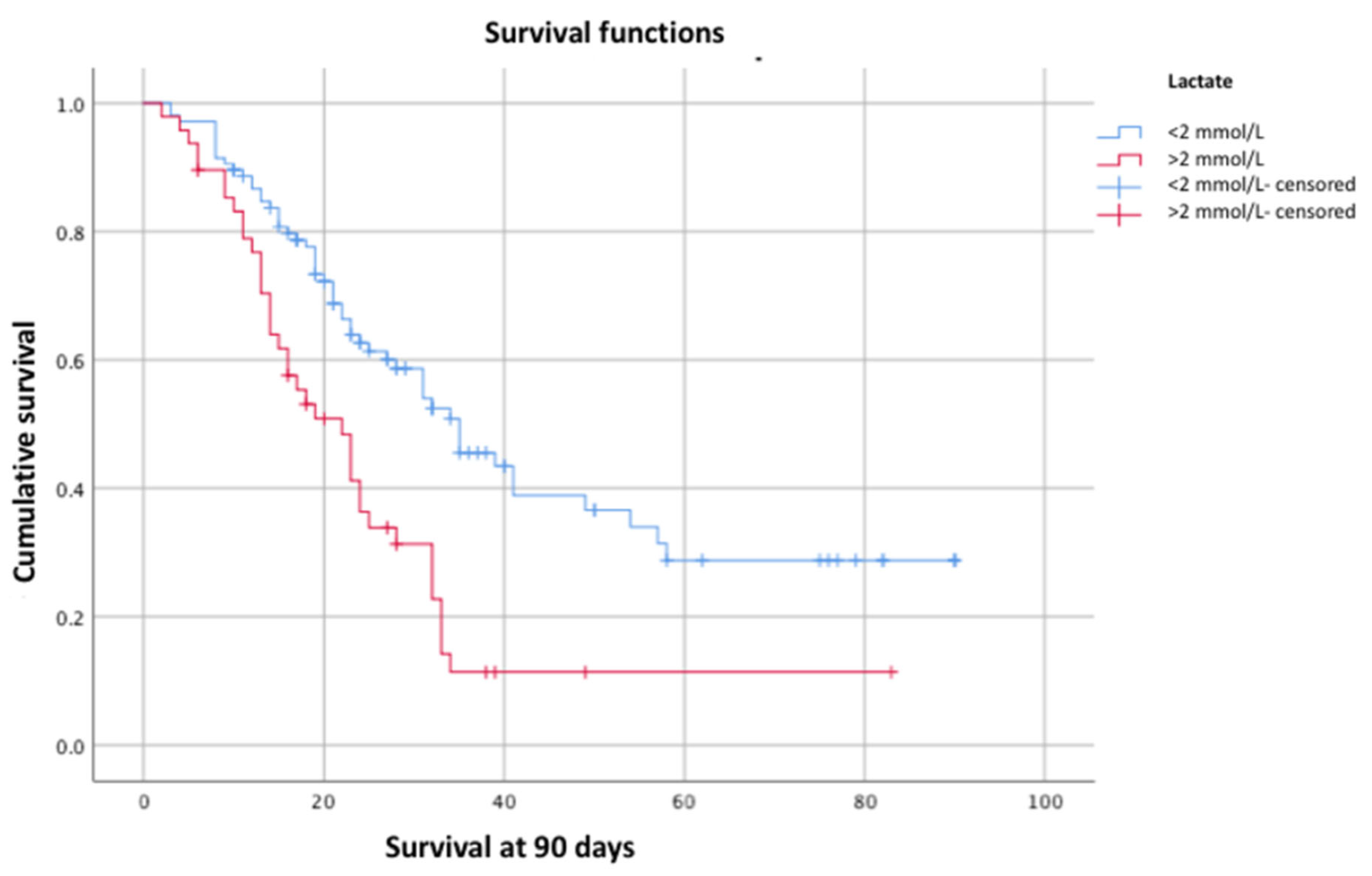
Subsequently, the log-rank test was used to evaluate these variables in relation to 90-day survival, confirming statistical significance for lactate (p = 0.00) (
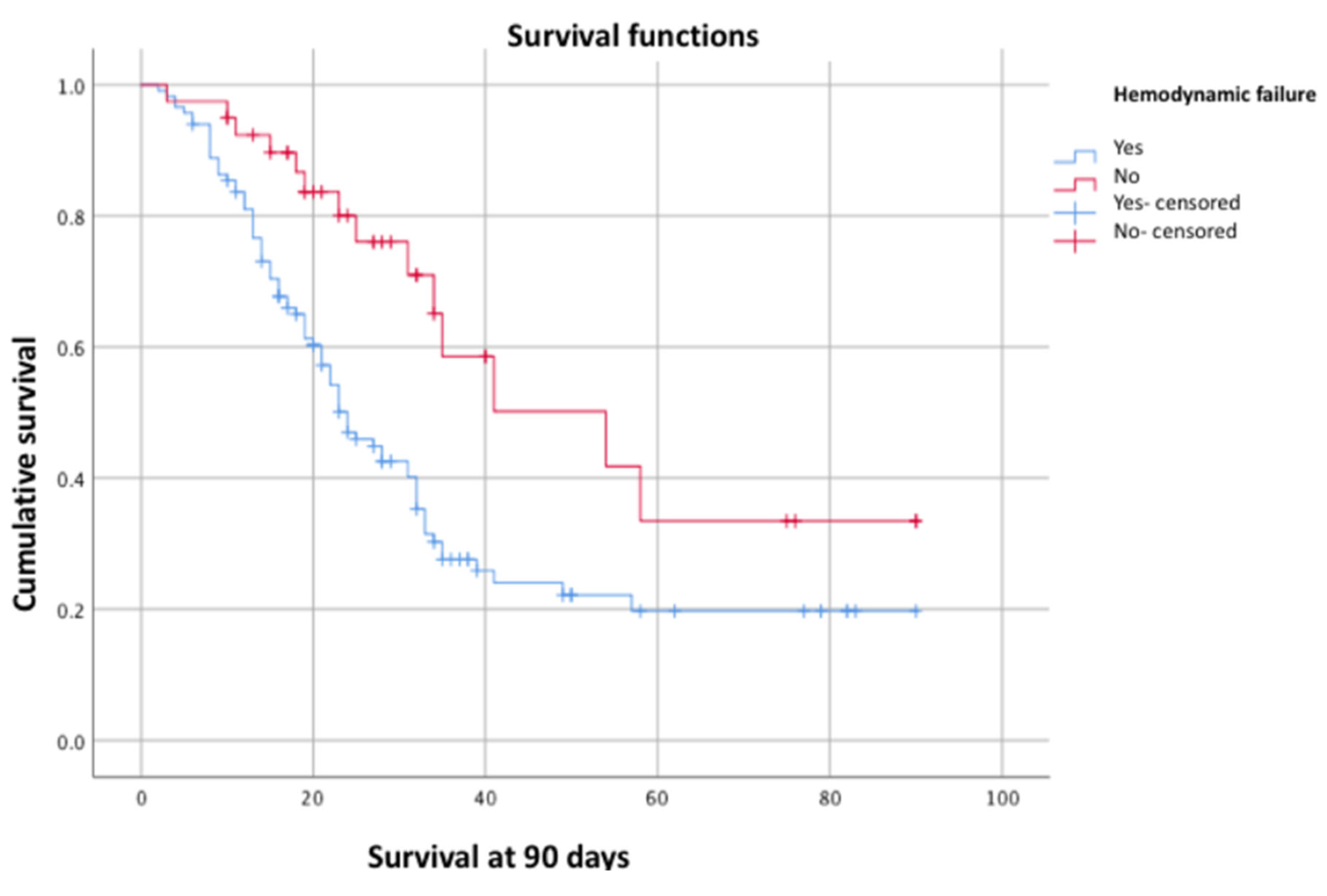
Figure 1), hemodynamic failure (p = 0.00) (
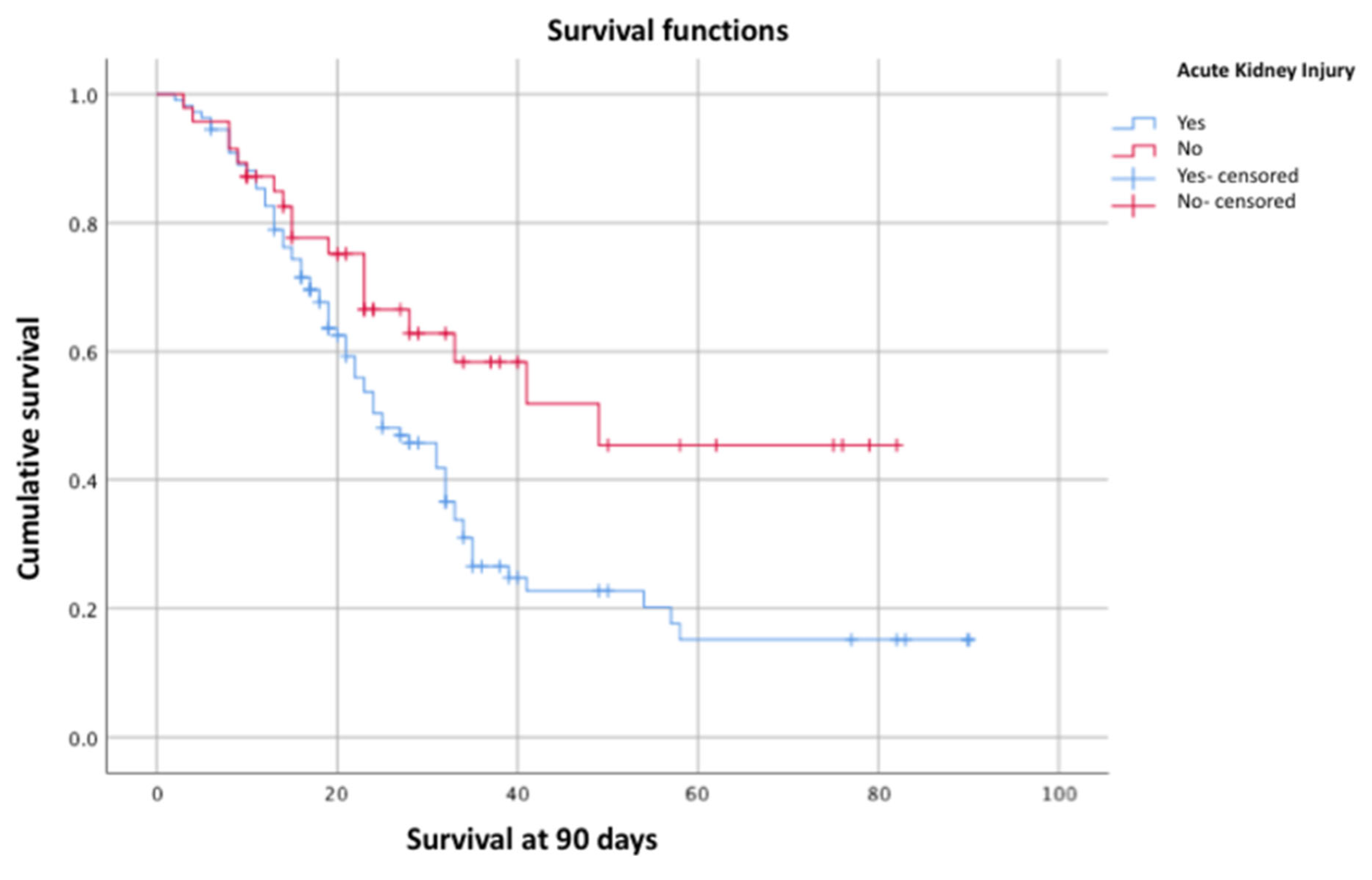
Figure 2), and AKI (p = 0.01) (
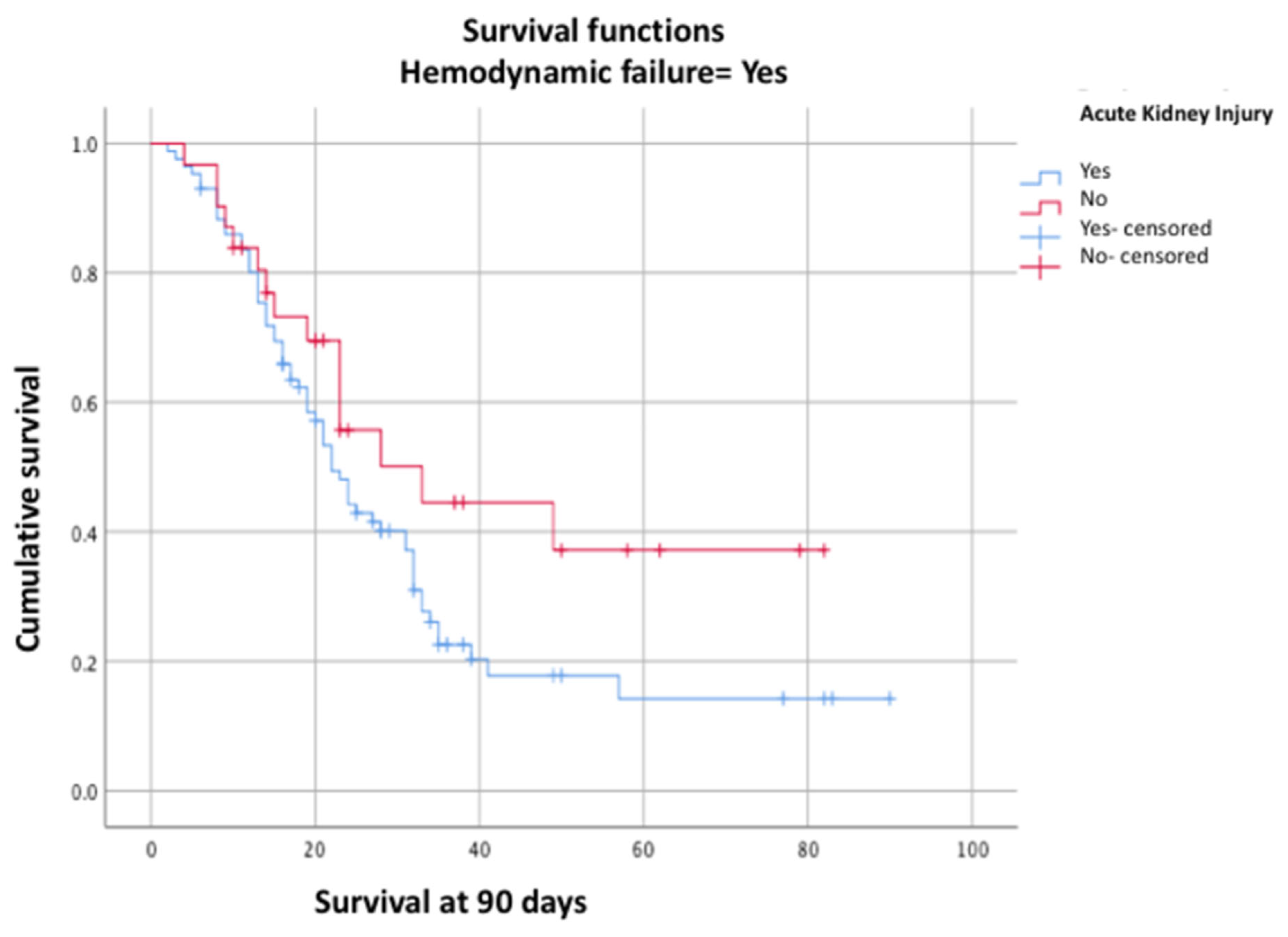
Figure 3), with a p-value < 0.05, confirming their association with survival. Moreover, a lower 90-day survival was observed in the group with AKI associated with hemodynamic failure (26.7% vs. 54.2%, p = 0.03, log-rank test) (
Figure 4).
4. Discussion
Several meta-analyses have identified factors associated with hospital mortality in COVID-19 patients. These factors include advanced age (mean difference = 13.32, 95% CI: 10.87–15.77; p < 0.00), male gender (OR = 1.66, 95% CI: 1.37–2.01; p < 0.00), comorbidities such as hypertension (OR = 2.67, 95% CI: 2.08–3.43; p < 0.00001) and type 2 diabetes (OR = 2.14, 95% CI: 1.76–2.6; p < 0.00), as well as overweight (OR = 1.4) and obesity (OR = 1.3), which are associated with higher mortality, greater need for mechanical ventilation, and development of ARDS. These factors were present in our cohort but did not show independent association with 90-day survival. The majority of our patients were classified as having severe ARDS (68.2%, n = 107) based on PaO2/FiO2 and SpO2/FiO2 values, which correlates with greater severity and risk of death. This may explain why other factors did not show significance in our population, which was more severely affected compared to other studies.
Regarding ventilatory management, all patients in our cohort were intubated, with a mean duration of mechanical ventilation longer than that reported in some meta-analyses (10.2 days, 95% CI: 7.08–13.16), which could reflect the severity of our patients compared to other studies. Prone positioning was used in 42% (n = 66) of patients, with a mean duration of 49.2 ± 18.77 hours, which has been shown to improve oxygenation parameters in patients with severe ARDS. Tracheostomy was performed in 29.3% of cases, but its relationship with survival was unclear due to the lack of a specific protocol in all cases. The current literature is inconclusive on the impact of early versus late tracheostomy or on differences between surgical and percutaneous techniques.
The prevalence of AKI in our cohort was high compared to what has been reported in the general literature for COVID-19 patients (70% vs. 10.8%). The risk factors identified for AKI include advanced age, male sex, use of mechanical ventilation, BMI greater than 30 kg/m², hypertension, and type 2 diabetes—all of which were present in our study. In a pooled analysis of more than 22 studies, the prevalence of AKI was 67% (95% CI: 57–76) with a mortality of 60.3% in patients with COVID-19-associated ARDS. In our study, AKI was an independent factor for 90-day survival, which aligns with some previous studies.
Another independent factor for 90-day survival was hemodynamic instability, already identified as a predictor of hospital mortality with an OR of 1.74 (95% CI: 1.07–2.86), along with elevated lactate levels, similar to what was observed in our study.
Survival across different studies varies depending on whether the cases occurred at the start of the pandemic or in later periods, as well as on the characteristics of the ICU population. In our study, mortality was high, which could be related to the inclusion of patients from the first reported cases up to those accumulated over the past three years.
5. Limitations
Our study has several limitations. First, the retrospective nature of the cohort may introduce biases in data collection and analysis. Additionally, the inclusion of patients from the onset of the pandemic, when treatment was not fully standardized, could affect the comparability of results. The lack of complete ventilatory data is another significant limitation, as it prevents an exhaustive evaluation of ventilatory parameters and their impact on outcomes. Furthermore, the admission of patients in extreme critical conditions could influence the high mortality observed, potentially limiting the generalizability of the findings.
However, these limitations can be mitigated by focusing on a study population consisting of patients with known risk factors for severe disease and adverse outcomes, as documented in the literature. All patients in our cohort were under mechanical ventilation, reinforcing the characterization of the sample as a group of critically ill patients, allowing for a more focused analysis of the factors associated with mortality in this specific population.
6. Conclusions
In our cohort of critically ill patients with ARDS caused by SARS-CoV-2 who required mechanical ventilation, cumulative 90-day survival was 41.4%. This survival was independently associated with the presence of AKI (p = 0.01, log-rank test), hemodynamic failure (p = 0.00, log-rank test), and elevated lactate levels (p = 0.01, log-rank test). We observed a significant decrease in 90-day survival when AKI was associated with hemodynamic failure (26.7%).
Our population presented several of the known risk factors for developing severe disease and severe ARDS. However, according to our study, in critically ill patients with mechanical ventilation secondary to COVID-19-related ARDS, AKI and hemodynamic failure are strongly associated with decreased survival.
References
- Lu H, Stratton CW, Tang Y. Outbreak of pneumonia of unknown etiology in Wuhan, China: The Mystery and the miracle. J Med Virol. 2020;92(4):401-2. [CrossRef]
- Chen L, Liu W, Zhang Q, Xu K, Ye G, Wu WC, et al. RNA-based MNGS approach identifies a novel human coronavirus from two individual pneumonia cases in 2019 Wuhan outbreak. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2020;9(1):313-9. [CrossRef]
- RTHK Hong Kong. The Center for Health Protection says that most men with pneumonia in Wuhan have not visited a market. XINHUANET News Report [Internet]. 2020. Available from: https://gbcode.rthk.hk/TuniS/news.rthk.hk/rthk/ch/component/k2/1502927-20200115.htm?spTabChangeable=0.
- World Health Organization. WHO Director-General’s remarks at the media briefing on 2019-nCoV on 11 February 2020. Available from: https://www.who.int/dg/speeches/detail/who-directorgeneral-s-remarks-at-the-media-briefing-on-2019-ncov-on-11-february-2020.
- Adhikari SP, Meng S, Wu Y, Mao Y, Ye RX, Wang QZ, et al. Epidemiology, causes, clinical manifestation and diagnosis, prevention and control of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) during the early outbreak period: A scoping review. Infect Dis Poverty. 2020;9(1). [CrossRef]
- Haberal M. COVID-19 update. Exp Clin Transplant. 2020;18(2):139-40. [CrossRef]
- COVID-19 Tablero México [Internet]. Available from: https://coronavirus.gob.mx/datos/.
- PEMEX. Health Status Report of PEMEX Workers and Beneficiaries Affected by COVID-19. Press Release 166/2021. June 2021. Available from: www.pemex.com.
- Jin Y, Yang H, Ji W, Wu W, Chen S, Zhang W, et al. Virology, epidemiology, pathogenesis, and control of COVID-19. Viruses. 2020;12(4):372. [CrossRef]
- Morty RE, Ziebuhr J. Call for papers: The pathophysiology of COVID-19 and SARS-COV-2 infection. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2020;318(5). [CrossRef]
- Parohan M, Yaghoubi S, Seraji A, Javanbakht MH, Sarraf P, Djalali M. Risk factors for mortality in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Aging Male. 2020;23(5):1416-24. [CrossRef]
- Gold M, Sehayek D, Gabrielli S, Zhang X, McCusker C, Ben-Shoshan M. COVID-19 and comorbidities: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Postgrad Med. 2020;132(8):749-55. [CrossRef]
- Zhai P, Ding Y, Wu X, Long J, Zhong Y, Li Y. The epidemiology, diagnosis and treatment of COVID-19. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2020;105955. [CrossRef]
- Cao J, Tu WJ, Cheng W, Yu L, Liu YK, Hu X, et al. Clinical features and short-term outcomes of 102 patients with coronavirus disease 2019 in Wuhan, China. Clin Infect Dis. 2020. pii: ciaa243. [CrossRef]
- Chen N, Zhou M, Dong X, Qu J, Gong F, Han Y, et al. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study. Lancet. 2020;395(10223):507-13. [CrossRef]
- Guan WJ, Ni ZY, Hu Y, Liang WH, Ou CQ, He JX, et al. Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China. N Engl J Med. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, Ren L, Zhao J, Hu Y, et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet. 2020;395(10223):497-506. [CrossRef]
- Stasi C, Fallani S, Voller F, Silvestri C. Treatment for COVID-19: An overview. Eur J Pharmacol. 2020;889:173644. [CrossRef]
- Ledford H. US authorization of first COVID vaccine marks new phase in safety monitoring. Nature. 2020;588(7838):377-8. [CrossRef]
- Reina J. Remdesivir, the antiviral hope against SARS-CoV-2. Rev Esp Quimioter. 2020. pii: reina01apr2020. [CrossRef]
- Zhou M, Zhang X, Qu J. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A clinical update. Front Med. 2020;14(2):126-35. [CrossRef]
- Ahn D, Shin HJ, Kim MH, Lee S, Kim HS, Myoung J, et al. Current status of epidemiology, diagnosis, therapeutics, and vaccines for novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020;30(3):313-24. [CrossRef]
- Nascimento IJBD, Bralić N, Abdulazeem HM, Von Groote T, Jayarajah U, Weerasekara I, et al. Novel coronavirus infection (COVID-19) in humans: A scoping review and meta-analysis. J Clin Med. 2020;9(4):941. [CrossRef]
- Ford N, Vitória M, Rangaraj A, Norris SL, Calmy A, Doherty M. Systematic review of the efficacy and safety of antiretroviral drugs against SARS, MERS or COVID-19: Initial assessment. J Int AIDS Soc. 2020;23(4). [CrossRef]
- Rismanbaf A. Potential treatments for COVID-19: A narrative literature review. PubMed. 2020;8(1). Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32232214.
- Murthy S, Gomersall CD, Fowler R. Care for critically ill patients with COVID-19. JAMA [Internet]. 2020;323(15):1499. [CrossRef]
- Alhazzani W, Møller MH, Arabi YM, Loeb M, Gong MN, Fan E, et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: Guidelines on the Management of Critically Ill Adults with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Critical Care Medicine [Internet]. 2020;48(6). [CrossRef]
- Matthay MA, Aldrich J, Gotts JE. Treatment for severe acute respiratory distress syndrome from COVID-19. The Lancet Respiratory Medicine [Internet]. 2020;8(5):433-4. [CrossRef]
- Wu Y, Li H, Zhang Z, Liang W, Zhang T, Tong Z, et al. Risk factors for mortality of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients during the early outbreak of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Annals of Palliative Medicine [Internet]. 2021;10(4):70. [CrossRef]
- Fang X, Li S, Yu H, Wang P, Zhang Y, Chen Z, et al. Epidemiological, comorbidity factors with severity and prognosis of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Aging [Internet]. 2020;12(13):12493-503. [CrossRef]
- Manolis AS, Manolis AA, Manolis TA, Apostolaki NE, Melita H. COVID-19 infection and body weight: A deleterious liaison in a J-curve relationship. Obesity Research & Clinical Practice [Internet]. 2021;15(6):523-35. [CrossRef]
- Chang R, Elhusseiny KM, Yeh YC, Sun WZ. COVID-19 ICU and mechanical ventilation patient characteristics and outcomes—A systematic review and meta-analysis. PloS One [Internet]. 2021;16(2). [CrossRef]
- Ashra F, Chen R, Kang XL, Chiang KJ, Pien LC, Jen HJ, et al. Effectiveness of prone position in acute respiratory distress syndrome and moderating factors of obesity class and treatment durations for COVID-19 patients: A meta-analysis. Intensive & Critical Care Nursing/Intensive And Critical Care Nursing [Internet]. 2022;72:103257. [CrossRef]
- Battaglini D, Premraj L, White N, Sutt AL, Robba C, Cho SM, et al. Tracheostomy outcomes in critically ill patients with COVID-19: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression. British Journal of Anaesthesia [Internet]. 2022;129(5):679-92. [CrossRef]
- Nasiri N, Rahmati S, Etminan A, Sharifi H, Bazrafshan A, Karamouzian M, et al. Kidney Complications of COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Research in Health Sciences [Internet]. 2021;21(1). [CrossRef]
- Zhang J, Pang Q, Zhou T, Meng J, Dong X, Wang Z, et al. Risk factors for acute kidney injury in COVID-19 patients: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Renal Failure [Internet]. 2023;45(1). [CrossRef]
- Alenezi FK, Almeshari MA, Mahida R, Bangash MN, Thickett DR, Patel JM. Incidence and risk factors of acute kidney injury in COVID-19 patients with and without acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) during the first wave of COVID-19: a systematic review and Meta-Analysis. Renal Failure [Internet]. 2021;43(1):1621-33. [CrossRef]
- Peltan ID, Caldwell E, Admon AJ, Attia EF, Gundel SJ, Mathews KS, et al. Characteristics and Outcomes of US Patients Hospitalized With COVID-19. American Journal of Critical Care [Internet]. 2022;31(2):146-57. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).