1.0. Introduction
The contemporary landscape of transportation infrastructure is marked by a confluence of challenges stemming from population growth, urban expansion, and the ever-increasing demands of human mobility. In response, city planners are turning to the concept of smart transportation, which integrates a suite of advanced technologies to optimize transportation networks and enhance service delivery [
1]. These technologies encompass diverse innovations, including computer vision, wireless communication, location-based services, and cloud computing, all aimed at improving mobility and efficiency [
2]. However, amidst the pursuit of efficiency, there is a pressing need for transportation technologies that are cost-effective and environmentally sustainable, ensuring the preservation of ecological biodiversity [
3]. So, the consequences of unplanned urbanization, such as pollution, accidents, and traffic congestion [
4,
5], underscore the importance of integrating renewable energy sources with contemporary technological solutions to foster a greener urban environment [
6,
7,
8].
On the other hand, the specter of climate change looms large over the transportation sector [
9,
10], with emissions from fossil fuel-powered vehicles significantly contributing to urban air pollution and exacerbating global warming [
11]. While there is a growing recognition of the need for cleaner transportation solutions, the reality of economic progress [
12] and the persistent reliance on fossil fuels pose formidable challenges [
13,
14]. For instance, the current congestion in the transportation system results from the 50-year surge in automobile demand [
15], which is now expected to rise as long as the human population and technological development continue to increase [
16,
17,
18]. However, 97% of the vehicles on the road currently are powered by combustion engines using liquid petroleum fuels [
19], which significantly increases carbon dioxide emissions [
20]. In contrast, by adopting smart transportation systems, cities can promote alternative transportation methods, acquire fuel-efficient vehicles, and implement strategies to minimize energy consumption and vehicle mileage [
21]. Thus, by transitioning from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources such as wind and solar power, cities have the potential to significantly reduce carbon dioxide emissions and create a more sustainable urban environment [
6,
17].
Literally, integrating smart transport technologies into urban infrastructures offers a promising avenue for mitigating the environmental impact of transportation systems. As for solutions, the integration of AI algorithms and IoT devices enables cities to optimize transportation systems, enhance safety, and improve environmental compliance [
22,
23]. Furthermore, the Intelligent Transport System (ITS) exemplifies the transformative potential of smart transportation, offering real-time operational information and historical traffic statistics while simultaneously reducing traffic congestion [
2]. By leveraging traffic management systems, real-time data analytics, and modern communication networks, cities can enhance transport network efficiency, reduce carbon emissions, and alleviate congestion [
24]. Moreover, the incorporation of non-transportation technologies such as blockchain, IoT, and artificial intelligence into supply chain and logistics management further enhances transportation efficiency and promotes sustainability [
25,
26]. For instance, AI algorithms play a pivotal role in smart transportation, harnessing data from IoT devices and sensors to optimize traffic flow, enhance safety measures, and improve overall system performance [
22]. Similarly, blockchain technology offers innumerable benefits for smart transportation systems, ranging from secure record-keeping to decentralized energy management [
27,
28].
Likewise, the intersection of AI, blockchain, and IoT holds immense promise for revolutionizing transportation systems driving progress towards sustainable urban mobility. These technologies optimize resource utilization, enhance operational efficiency, and improve air quality [
29,
30]. By leveraging AI algorithms, transportation systems can mitigate congestion, improve safety, and optimize route planning [
31,
32,
33]. Moreover, AI-enabled applications enhance signal control, dynamic route guidance, and traffic demand modeling, facilitating smoother traffic flow and reducing emissions [
34,
35]. For instance, several GPS-enabled applications help alert drivers on over-speeding, sharp turns, and expeditions to make the road safer [
35]. Other advances include trips, passenger regalement, and conveyance weight checking [
36], except for cyber security difficulties and privacy [
37,
38,
39]. In addition, IoT-compatible smart sensors help companies calculate their carbon footprint and flag areas that need immediate attention [
40]. Thus, depending on the situation and current ambivalence, this article aims to idealize further ecological problems and the development of future effective, safe, and intelligent transportation systems focusing on carbon emissions. Also, this study explores the possibility of enhancing environmental protection by integrating smart technology into the sustainable transportation movement.
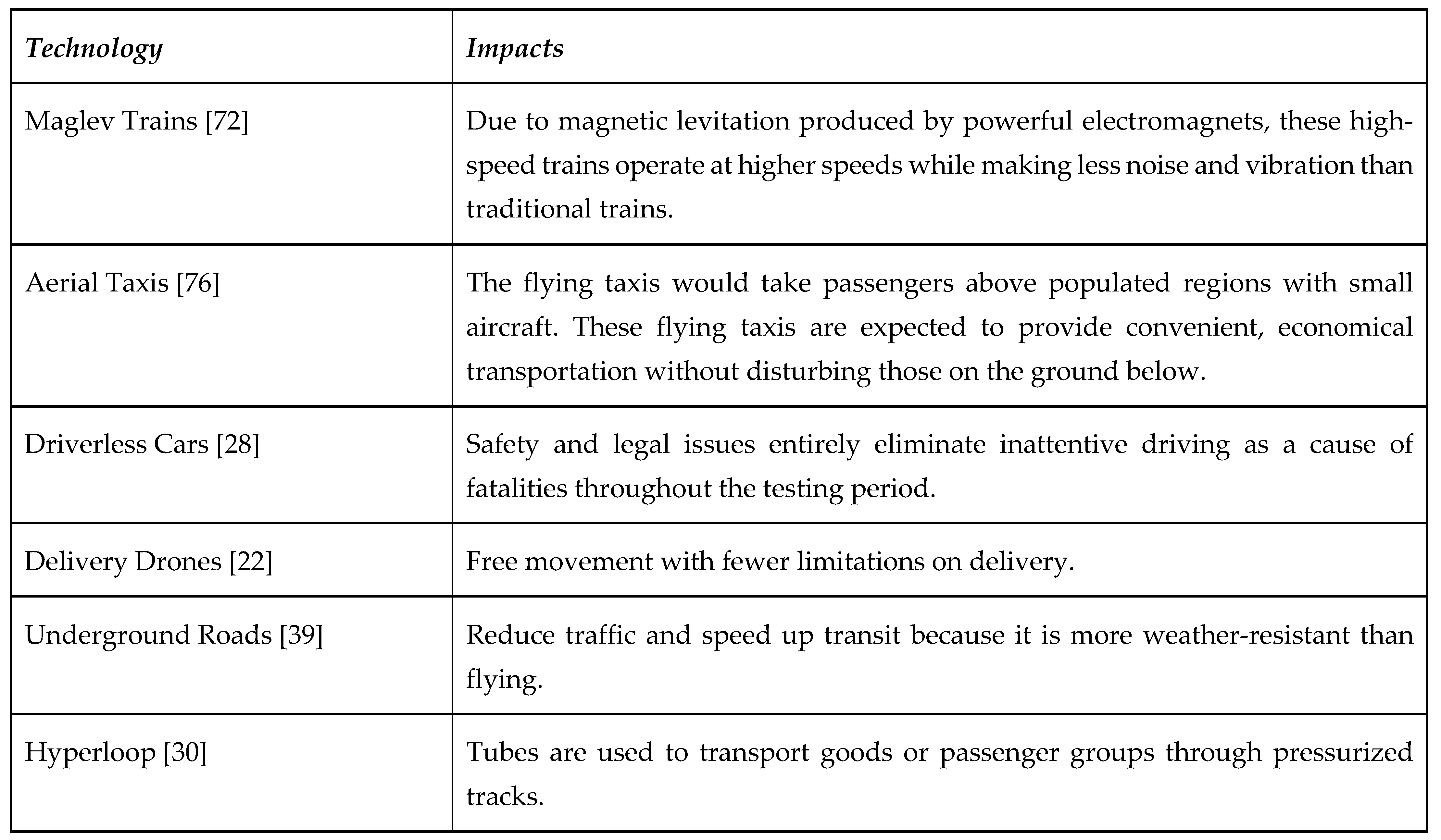
For a comprehensive literature review, in the following sections, this study focuses on evolving strategies and technologies for carbon emissions mitigation, laying the foundation for the construction of a predictive framework to guide the development of intelligent transportation systems. However, this study systematically evaluates relevant literature and conducts Bibliometric Studies to map the intellectual structure of the field for employing a robust research methodology integrated with the elements of the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) framework and a Systematic Literature Review (SLR) approach, this study systematically evaluates relevant literature and conducts Bibliometric Studies to map the intellectual structure of the field. Seemingly, this approach facilitates a nuanced understanding of the extended roles of Blockchain, AI, and IoT in reducing carbon emissions and enhancing sustainability within transportation systems. Again, this endeavour will explore the synergistic effects of these technologies in optimizing transportation networks, enhancing route planning, and facilitating real-time monitoring of vehicle emissions. This study also quantifies the potential impact of these technologies, highlighting substantial reductions in carbon emissions and traffic congestion achievable through AI, IoT, and Blockchain integration. Moreover, this research explores emerging transportation technologies such as Maglev Trains, Aerial Taxis, Driverless Cars, Delivery Drones, Underground Roads, and Hyperloop, showcasing their potential to revolutionize transportation and contribute to a more sustainable future.
2.0. Materials and Methods
The study explores how recent technological advances in transportation, particularly smart systems, can lower carbon emissions and improve efficiency, highlighting the importance of integrating sustainable practices beyond transportation. It suggests that developing smart transportation is crucial for reducing carbon emissions, enhancing real-time information efficiency, and alleviating traffic congestion, emphasizing the significance of recent technological advancements in addressing current transportation challenges [
41]. Along with a thorough literature review, a predictive framework based on the literature constructed and justified in this article under the development of the relevant technology for intelligent transportation systems. The following is the study's research question:
"What are the implications of integrating Artificial Intelligence, Internet of Things, and Blockchain technologies in smart transportation systems for mitigating carbon emissions and fostering sustainability in urban environments?"
The exploration of this research question concerning sustainable smart transportation systems and their impact on lowering carbon emissions is paramount for addressing contemporary environmental challenges. Initially, investigating the recent trends in research provides critical insights into the evolving strategies and technologies employed in mitigating carbon emissions within transportation networks. Understanding these trends not only informs current practices but also guides future research directions, fostering innovation and adaptation. Afterward, focusing on the construction of smart and sustainable transportation systems through modern technological advancements offers a pathway toward actionable solutions. By leveraging artificial intelligence, Internet of Things, and blockchain technologies, a comprehensive framework can be developed to optimize transportation efficiency, reduce emissions, and enhance overall sustainability. So, depending on the answer to the research question, this research serves as a foundational guide for policymakers, urban planners, and technologists in shaping a more sustainable future for transportation systems worldwide. These study topics are based on the limitations found in previous studies' integration of blockchain, artificial intelligence (AI), and Internet of Things (IoT) developments in highly intelligent delivery. Ultimately, this article will address these research issues by presenting citation-based trends in the conveyance system literature throughout time and by creating a thorough framework for an intelligent, sustainable conveyance system.
In this study, we employ a rigorous methodology combining elements of the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) framework and a Systematic Literature Review (SLR) approach to examine the research question comprehensively. Research methodology involves systematically identifying, selecting, and analyzing relevant literature from various academic databases and sources. Additionally, we conduct a Bibliometric Study utilizing keyword co-occurrence clustering and co-citation network analysis techniques to map the intellectual structure of the field and identify key themes, trends, and relationships among scholarly publications. By employing a multidimensional approach, we aim to provide a comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the intersection between smart transportation technologies and carbon emission reduction strategies, focusing on the role of Artificial Intelligence, Internet of Things, and Blockchain in shaping a sustainable future.
2.1. Preferred Reporting Items for Meta-Analyses and Systematic Reviews (PRISMA)
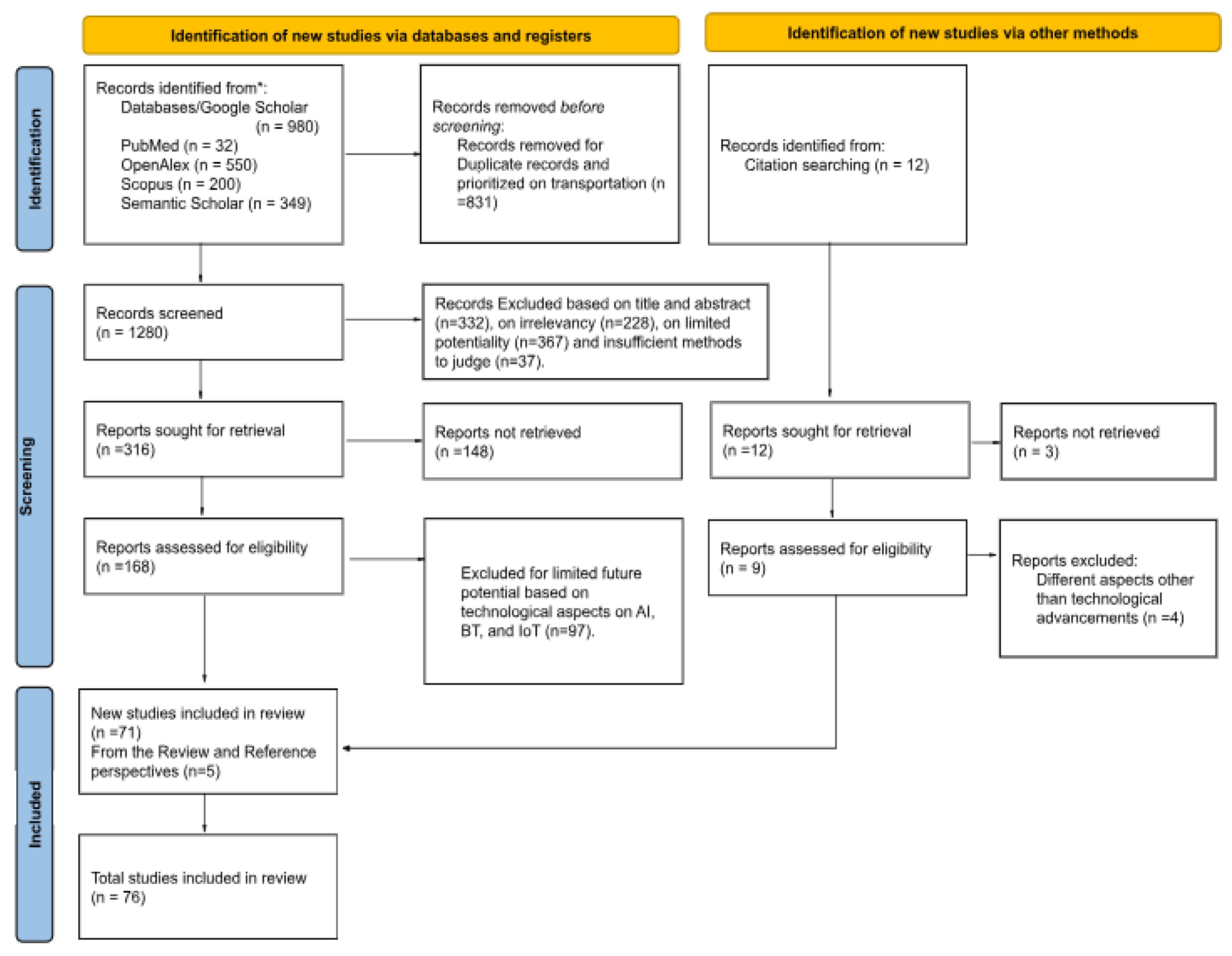
This study employs a qualitative methodology and concentrates on technology-driven platforms, particularly blockchain, IoT, and AI-based adaptations for lowering carbon emissions in the transport sector. More specifically, this study follows the PRISMA concept to review systematically with careful attention from Ross et al. [
42], Moher [
43], and Kashem et al. [
44]. The main focus of the early phases of this study was to identify and select potential and contributing publications for this review. Under the broad headings of abstracts, introduction, methodology, findings, debate, and finance, PRISMA components and key components were justified. In essence, the abstract screening is considered with underlying assumptions of the background, objectives, data sources, and other common elements. The eligibility parameters consider whether they are satisfied owing to the logical introduction, study questions, and clear goals. Specific keywords and criteria used to locate and reference research publications on intelligent transportation, including carbon emissions, technological use, and involvement. 76 publications out of 175 were selected to use the PRISMA and IMRAD techniques. The IMRAD framework (introduction, methodology, results, and discussion) improved the article's organization [
45]. Last but not least, this PRISMA feature prioritized funded studies for systematic reviews (see
Figure 1).
However, this study included the PRISMA framework over "narrative synthesis"—aside from meta-analysis—to optimize the review with the help of Endnote. In addition, this study registered the review process for record-keeping in the open Science Forum (OSF) [
46]. Correspondingly, this study's limitation is that it does not consider meta-analysis using the PRISMA framework; this research continues the narrative review.
2.1.1. Inclusion Criteria:
i. Studies must focus on aspects related to smart transportation systems, including but not limited to traffic management, vehicle optimization, route planning, and public transit.
ii. Research should directly address the impact of smart transportation technologies on carbon emission reduction or mitigation strategies.
iii. Studies must investigate the role of AI, IoT, or Blockchain technologies in addressing carbon emission challenges within the context of smart transportation.
iv. Only articles published in peer-reviewed journals, conference proceedings, or reputable scholarly sources will be considered.
v. Research published within the last 10 years will be included to ensure relevance and currency of findings.
vi. Only studies published in the English language will be included to facilitate comprehension and analysis.
vii. Both empirical studies and review articles that provide comprehensive insights into the relationship between smart transportation, carbon emission, and AI, IoT, or Blockchain technologies will be considered.
2.1.2. Exclusion Criteria:
Studies that do not specifically address smart transportation or carbon emission reduction within the context of AI, IoT, or Blockchain technologies will be excluded.
ii. Duplicate studies or redundant data will be excluded to ensure the integrity and efficiency of the review process.
iii. Research published in non-peer-reviewed sources such as blogs, opinion pieces, or news articles will be excluded due to a potential lack of rigor and reliability.
iv. Studies published in languages other than English will be excluded to maintain consistency and facilitate comprehension.
v. Studies published before 1989 will be excluded to prioritize recent advancements and insights in the field.
vi. Studies that do not provide substantial insights or contributions to understanding smart transportation and carbon emission reduction strategies will be excluded.
vi. Studies with significant methodological flaws or limitations that may compromise the validity or reliability of findings will be excluded from the review.
2.2. Systematic Literature Search and Citation Metrics
The authors primarily focused on the scholarly articles from the Google Scholar dataset because it allows convenient citation and has a broad audience for all kinds of research [
47]. Publications produced in languages other than English, exclusively technical studies, and works emphasizing legitimate factual contributions more than business are also disallowed. The author's names, publication titles, abstracts, keywords, and other information were collected and reviewed for the initial set of bibliometric data. A quick search of the Google Scholar and PubMed databases turned around 2111 papers on smart transportation. Moreover, the comprehensive review found that between 1989 and 2023, smart transportation and carbon-related papers have been included in other repositories like Scopus, OpenAlex, and Semantic Scholar. Again, the keywords were "transportation", "smart transportation", "smart transportation" AND "carbon" "smart transportation" AND "carbon emission" (
Table 1). After concentrating on keywords, abstracts, and manuscripts, 76 articles were considered (
Table 2).
Table 3 from the 1989-2023 citation study reveals that the average number of citations per document was 102.95, with 2.94 citations per paper, h-index of 254, g-index of 404 and hA-index of 60.
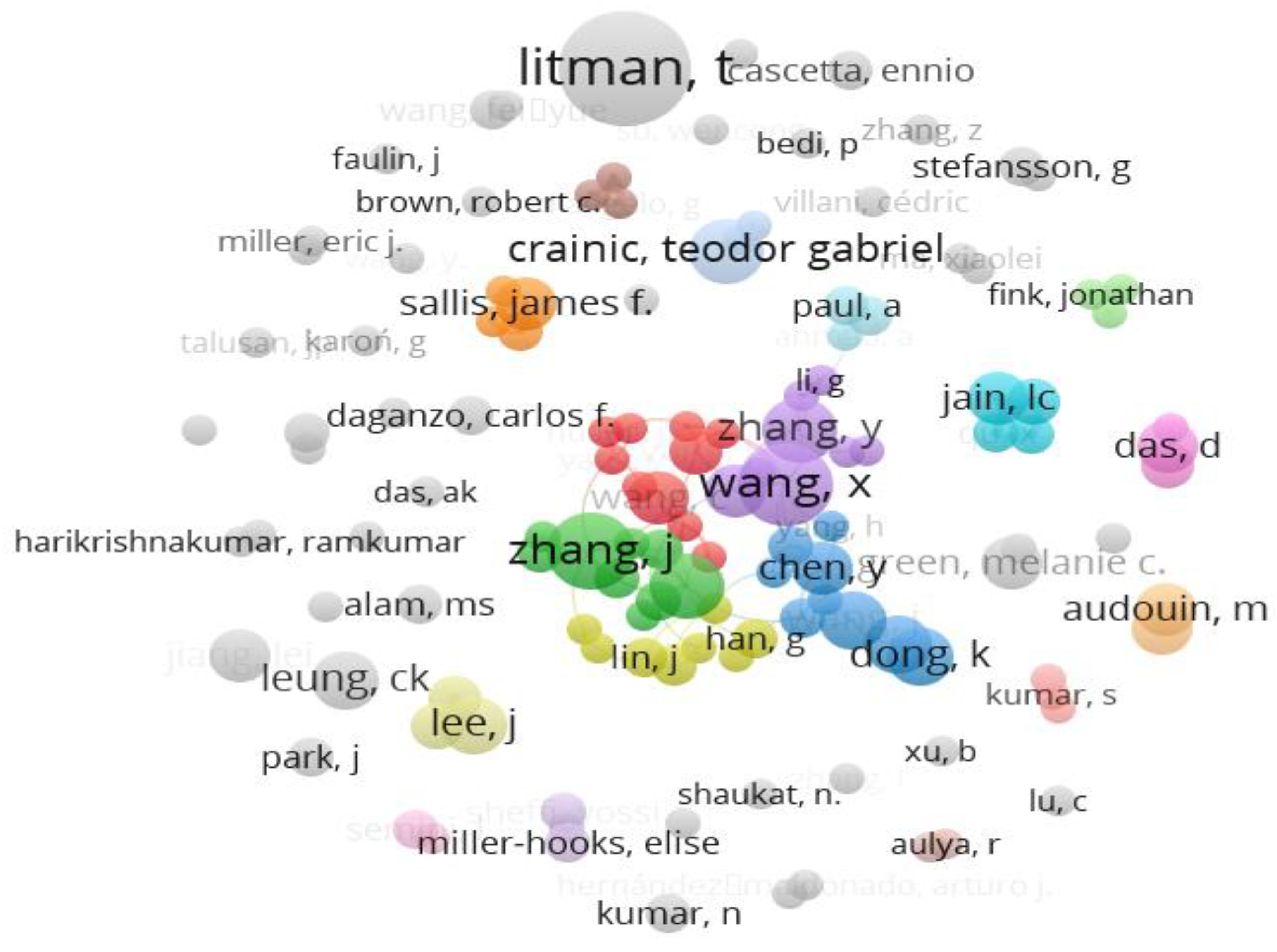
Moreover, this paper utilized this co-citation network analysis (
Table 3) to enable the mapping of the intellectual structure of a research field by identifying frequently cited works and their relationships. Usually, this approach helps to understand the foundational literature and the flow of ideas within the field. For instance, Co-citation Network Analysis in
Table 3 unveils the interconnected web of seminal works and influential authors, elucidating the intellectual lineage and the diffusion of ideas within the research ecosystem that have significantly shaped the discourse on smart transportation and carbon emission reduction.
2.4. Bibliometric Study
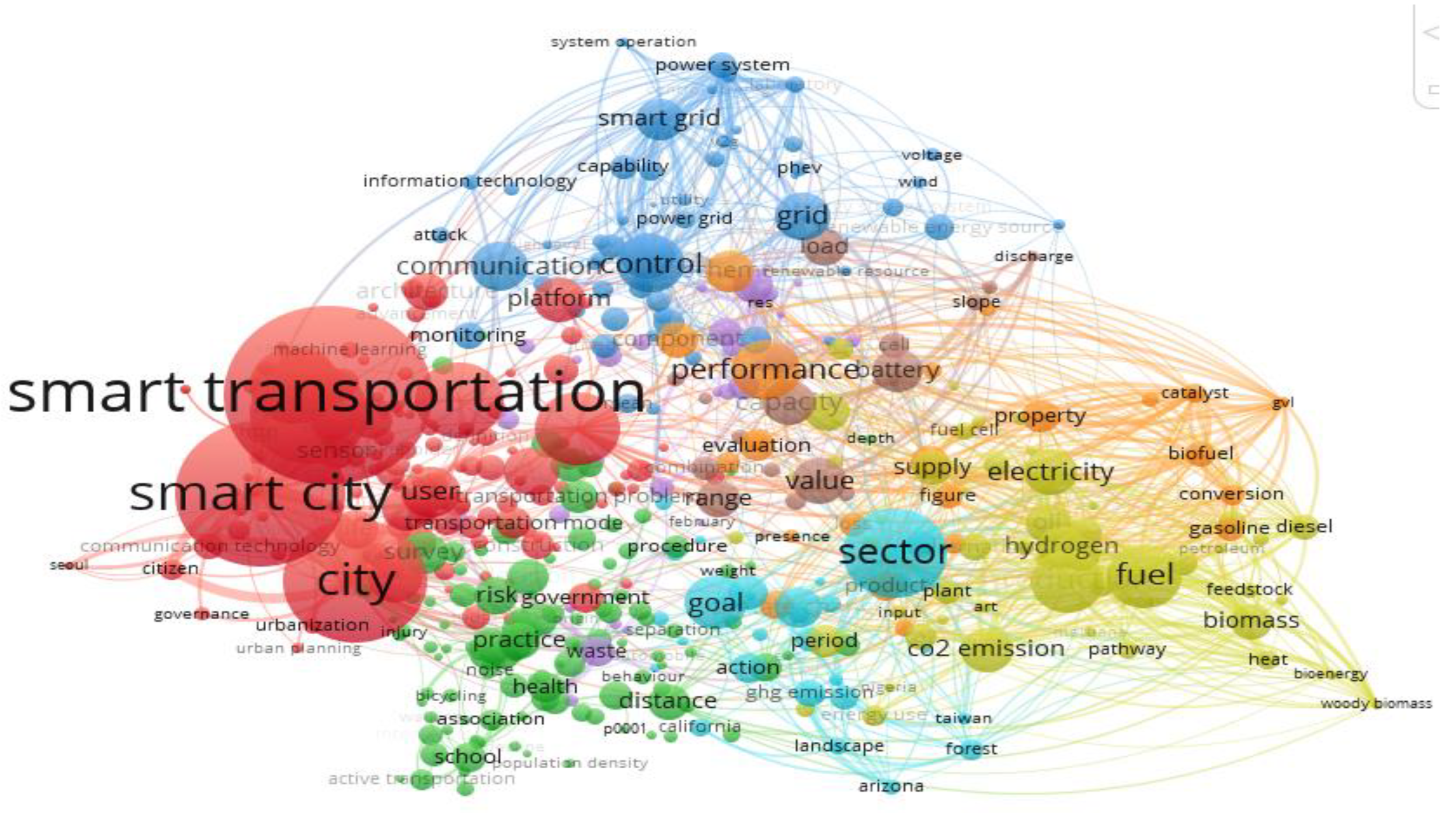
This bibliometric study aims to methodically evaluate and synthesize the existing body of information by exploring various academic publications, research papers, and conference proceedings. The main objective is to comprehend how blockchain, IoT, and AI technologies are utilized in smart transportation to reduce carbon emissions and contribute to a sustainable future (
Figure 2 and
Figure 3). These analyses make artificial intelligence essential for traffic management, predictive modeling, and route optimization in transportation system optimization [
44,
48,
49]. On the other hand, this citation analysis (in
Figure 2 and
Figure 3) delves into the many AI-driven applications—like deep neural networks and machine learning algorithms—that improve the effectiveness of smart transportation systems [
22,
28,
31,
32].
Another important participant in this paradigm is the IoT, whose sensors and networked devices provide real-time information on traffic patterns, vehicle performance, and environmental variables [
28,
37,
39]. By networking automobiles, buildings, and intelligent gadgets, the Internet of Things facilitates data-driven choices that lower carbon footprints [
36,
50,
51,
52,
53]. The evaluation also clarifies the creative way in which blockchain technology is integrated, improving transaction security, transparency, and traceability in smart transportation networks [
25,
26,
27,
28,
33,
44,
53,
54,
55,
56,
57,
58]. The evaluation offers important insights into the existing state of research, identifies new trends, and recommends prospective directions for further investigation in pursuing a technologically sophisticated and sustainable transportation environment by examining citations across different disciplines.
In essence, the Keyword Co-occurrence Cluster Analysis unveils the synergistic interplay between advanced technologies, carbon emission reduction strategies, integration challenges, and regulatory frameworks within the realm of smart transportation. By leveraging AI, IoT, and Blockchain in tandem with effective policy interventions, a sustainable future characterized by reduced carbon emissions and efficient transportation systems becomes within reach [
28]. This analysis dissects the intricate landscape of smart transportation's role in mitigating carbon emissions, revealing the distinct thematic clusters [
19]. Each cluster unveils key focal points within the research domain, offering technical insights into the convergence of these technologies, which focus on smart transportation, carbon emission reduction strategies, integration and interoperability challenges and policy and regulatory frameworks [
2,
4,
9,
16,
19,
24,
25,
29,
34,
41]. Specifically, these cluster items encompass AI-driven solutions, IoT-enabled systems, and Blockchain applications with diverse approaches to mitigate carbon footprints, ranging from electrification to sustainable mobility solutions [
28]. These items also include complexities surrounding the integration and the need for seamless interoperability, and the pivotal role of regulatory measures in shaping the trajectory of sustainable transportation initiatives [
59].
5.0. Framework for New Transportation Technology
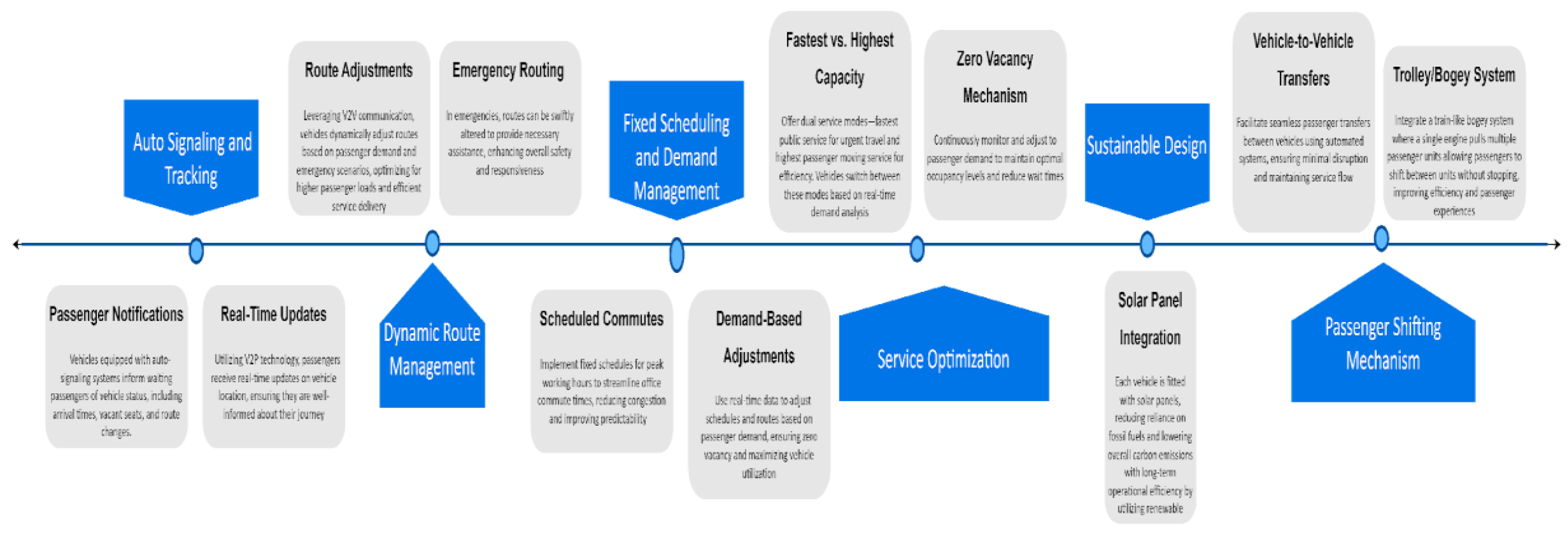
This framework outlines a new transportation technology designed to enhance efficiency, passenger convenience, and environmental sustainability. The system integrates advanced auto-signaling, vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) and vehicle-to-passenger (V2P) communication, fixed scheduling, solar-powered vehicles, and flexible passenger shifting mechanisms (as in Fig. 4).
5.1. Key Components
1. Auto Signaling and Tracking:
- Passenger Notifications: Vehicles equipped with auto-signaling systems inform waiting passengers of vehicle status, including arrival times, vacant seats, and route changes.
- Real-Time Updates: Utilizing V2P technology, passengers receive real-time updates on vehicle location, ensuring they are well-informed about their journey.
2. Dynamic Route Management:
- Route Adjustments: Leveraging V2V communication, vehicles dynamically adjust routes based on passenger demand and emergency scenarios, optimizing for higher passenger loads and efficient service delivery.
- Emergency Routing: In emergencies, routes can be swiftly altered to provide necessary assistance, enhancing overall safety and responsiveness.
3. Fixed Scheduling and Demand Management:
- Scheduled Commutes: Implement fixed schedules for peak working hours to streamline office commute times, reducing congestion and improving predictability.
- Demand-Based Adjustments: Use real-time data to adjust schedules and routes based on passenger demand, ensuring zero vacancy and maximizing vehicle utilization.
4. Service Optimization:
- Fastest vs. Highest Capacity: Offer dual service modes—fastest public service for urgent travel and highest passenger moving service for efficiency. Vehicles switch between these modes based on real-time demand analysis.
- Zero Vacancy Mechanism: Continuously monitor and adjust to passenger demand to maintain optimal occupancy levels and reduce wait times.
5. Sustainable Design:
- Solar Panel Integration: Equip each vehicle with solar panels, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and lowering overall carbon emissions. This design enhances sustainability and operational efficiency.
6. Passenger Shifting Mechanism:
- Vehicle-to-Vehicle Transfers: Facilitate seamless passenger transfers between vehicles using automated systems, ensuring minimal disruption and maintaining service flow.
- Trolley/Bogey System: Integrate a train-like bogey system where a single engine pulls multiple passenger units allowing passengers to shift between units without stopping, improving efficiency and passenger experience.
Figure 4.
Framework for New Transportation Technology.
Figure 4.
Framework for New Transportation Technology.
5.2. Implementation Strategy
1. Technology Integration:
- Develop and deploy V2V and V2P communication infrastructure.
- Implement auto-signaling and real-time tracking systems in all vehicles.
2. Operational Planning:
- Design fixed schedules for peak commuting hours and create dynamic adjustment protocols based on real-time data.
- Establish criteria for switching between fastest service and highest capacity modes.
3. Sustainability Measures:
- Retrofit existing vehicles with solar panel structures.
- Regularly monitor and optimize the energy efficiency of solar-powered systems.
4. Passenger Experience Enhancements:
- Train staff on new technologies and passenger shifting protocols.
- Implement user-friendly interfaces for passengers to receive updates and manage their commutes.
Ultimately, this comprehensive framework for new transportation technology aims to revolutionize urban mobility by integrating advanced auto-signaling, dynamic route management, fixed scheduling, sustainable design, and efficient passenger shifting mechanisms. By leveraging cutting-edge technologies and sustainable practices, this system promises to deliver an efficient, reliable, and eco-friendly transportation solution.
6.0. The Key Contributions of Emerging Technologies toward Smart Transportation
By seeing how residents react to new technologies, decision-makers in smart transportation may also learn about the variables and obstacles that prevent the adoption of various sensing technologies. More precisely, the emergence of developing technologies has transformed smart transportation as follows:
RFID, a key player in smart transportation applications, makes it possible to identify and transmit critical data and agent intelligence from any connecting object [
28,
82].
RFID has the potential to offer excellent reading rates, real-time and automatic recognition, and cost-effective operation. Such a capacity is viable for smart applications like smart parking and air pollution monitoring [
1].
As a paper-based alternative to ticketing systems, RFID tags enable vehicles to navigate to their designated parking spots [
78]. Additionally, they are increasingly being used to track the locations of various objects, including vehicles, products, buildings, and power plants.
Supporting the verticals of transportation, logistics, supply chain, construction, and energy can help shed more light on the safety benefits of these technologies in various smart transportation scenarios [
72].
The transportation sector may leverage the Internet of Things (IoT) as a vast network of embedded sensors, actuators, smart objects, and other intelligent devices [
51].
With the involvement of RFID, Smart grids enabled by the Internet of Things can automatically adjust to variations in electricity supply and demand and provide the data required to limit demand [
52]. For instance, lighting control systems (in buildings and on the street), power generation, such as smart power meters, home security systems, and industrial automation, are all examples of Zigbee applications for the Internet of Things in the energy sector [
46].
By using IoT devices like programmable devices and lighting systems to monitor a building's actual efficient energy usage techniques [
43], facility managers can change the energy use schedule by some of the electronics in a building to lower demand during peak hours [
42]. So, future connected technology will assist businesses in reducing shipping costs by enabling truckers to access information on weather, rest places, and parking lots [
73].
Analysts can also predict fuel consumption depending on driving distance and road conditions to help decide the optimal routes and types of transportation [
48]. Therefore, with the development of these technologies, smart transportation activities outperform the functionality of traditional transportation systems currently operating.
For accurate simulation of carbon emissions, sophisticated modeling tools, system dynamics, and different soft computing techniques can be used [
83,
84,
85]. These regulations will extensively support the Net Zero Scenario, the desired temperature value for space cooling, and even speed reduction [
86].
In light of artificial intelligence and blockchain development, smart transportation systems might contribute to carbon emissions using renewable energy, alternative fuels, and even electricity [
48].
The connections between blockchain, IoT, and intelligent transportation movements may improve the security, dependability, transparency, and data flow authentication in smart urban environments [
72].
Adopting policies against complex mechanisms of carbon emissions is more urgent in transportation. Because of the reliance on fossil fuels, interactions between technical and non-technical measures and carbon emissions are typically complicated and non-linear [
11,
87,
88]. Based on the current research on carbon emissions and smart transportation systems, a realistic integration is developed to solve the study's challenge. Hence, this integration may adapt the transportation system in response to new technological advancements like artificial intelligence, blockchain, and IoT.
7.0. Theoretical and Practical Implications
AI, Blockchain, and IoT, the more effective and inspirational technologies, have significant effects on corporations, governments, and society at large with their dramatic expansion of applications. Despite growing interest and its critical significance on smart urban activities, only a few focused and thorough studies of this technology-integrated research have been published [
22]. Therefore, evaluating the current state of the field and the knowledge gaps encourage the development of new research and increase worldwide scholarly production on AI, blockchain, IoT, and smart transportation. For instance, AI algorithms have the potency to forecast traffic patterns, modify traffic signals, minimize idle time at junctions, optimize delivery truck routes, minimize distance traveled, and minimize fuel consumption. However, AI works to improve electric car performance, increasing range and decreasing the need for charging stations.
On the other hand, traffic pattern monitoring, congestion reduction, safety enhancement, traffic flow monitoring, and traffic signal adjustment are all possible with the use of IoT. In order to lower the danger of collisions and breakdowns, IoT might even be put-upon to monitor vehicle performance and identify maintenance problems. Arguably, blockchain technology has the upside of reducing pollution, measuring carbon emissions securely and transparently, tracking credits for carbon reduction and enabling businesses to buy and sell credits depending on emissions. In order to make sure that the resources used in the manufacture of electric cars come from ethical and sustainable sources, blockchain technology is applied to build a system for monitoring their origin and cutting down on the number of cars on the road, lowering carbon emissions. Again, considering the effects of scale, structure, and technology in transportation, this study's findings contribute to the body of knowledge and have significant policy ramifications for advancing smart transportation and reducing carbon emissions in that industry and others [
2,
19,
41,
89,
90]. Therefore, the integration of these emerging technologies will quicken the dynamic of smart transport in the direction of carbon-free mobility.
8.0. Conclusion
The results of this review are paired with a thorough, systematic assessment of the literature and a critical analysis of the works that form the basis of this research stream to comprehend the technology properly. This paper has articulated sustainable smart transportation, environmental concerns, and future technologies. For instance, urban residents, including drivers and passengers, are expected to work together to construct and build sustainable smart cities. Ultimately, the key contribution of this paper lies in its exploration of the intersection between transportation innovation, smart technology, and environmental sustainability, such as carbon emissions, traffic congestion, and related logistical and regulatory challenges. Numerous problems, such as device incompatibility, subpar topology design, constrained network coverage and capacity, security and privacy concerns, and legislative ambiguity, could make these emerging technologies less suitable for smart mobility. Therefore, future research on digitized energy systems might be able to determine who needs energy when and where and deliver it for the least amount of money, for example, demand and potentiality for electric vehicles and renewable energy in the future. Thus, the future world will see flying cars and so many things. Still, we need to plan from now on what future strategies would be for making this transportation sector safe, environmentally friendly, and economically viable to get immense positive customer responses as sustainable transports.