1. Introduction
5G Mobile Ad-hoc Networks (5G-MANETs) are a communication paradigm that leverages dynamic mobile devices to transmit information locally while utilizing the 5G network interface for remote communications [
1,
2]. These networks are particularly suited for deploying contextual applications that exploit physical proximity between devices for direct communication. The integration of 5G enhances their capabilities, enabling seamless access to Internet-based services and cloud resources. This combination of local ad-hoc networking and global 5G connectivity allows 5G-MANETs to provide efficient, scalable, and reliable solutions for real-time applications, autonomous systems, IoT deployments, and smart city environments, offering enhanced mobility, low latency, and high data rates for both local and remote interactions [
1,
2]. As a result, there is increasing interest in providing techniques to manage and monitor these networks [
3]. However, the inherent characteristics of 5G-MANETs pose significant problems.
Effective management and monitoring are relevant challenges in 5G-MANETs [
3,
4]. One key challenge is the highly variable topology, where nodes frequently move, join, or leave the network, making it difficult to maintain stable communication paths. This dynamic environment also leads to unstable links between nodes, resulting in intermittent connections and degraded communication quality [
3]. The energy consumption of mobile devices is another critical concern, as continuous communication and dynamic routing can quickly deplete battery life, impacting network longevity [
4]. Additionally, the dynamic routing of messages introduces complexity, as routes require constant recalibration to adapt to node mobility and changing network conditions [
1]. Finally, 5G disconnections in nodes, caused by signal loss or network coverage gaps, can disrupt both local and remote communication.
Monitoring is a critical task in 5G-MANETs, enabling the evaluation of Quality of Service (QoS) and helping to identify key contextual variables that influence performance [
4,
5]. This is especially relevant in the implementation of routing protocols, where assessing performance requires continuous monitoring of network resources. Thus, metrics such as latency, delivery probability, overhead, and hop count become significant variables to collect [
4,
6]. However, monitoring 5G-MANETs poses unique challenges, particularly due to their dynamic topology and the constantly shifting interactions between nodes, which make the accurate calculation of performance metrics difficult [
6]. Additionally, the demand for ultra-low latency and precision in modern communication systems further intensifies the need for advanced monitoring tools that can provide real-time insights in challenging environments [
3]. In this context, the widespread adoption of 5G technologies has become a game-changer for communications.
5G connectivity provides high coverage availability, low-latency transmission, and advanced support for real-time data flows [
2]. As a result, 5G is particularly well-suited for Mobile Ad Hoc Networks (MANETs), especially due to its potential integration with advanced monitoring paradigms such as Digital Twins (DTs), which can further enhance monitoring accuracy and network performance [
7]. DTs are digital replicas of physical assets, mirroring their actual performance and operational conditions to achieve high accuracy [
8]. These implementations integrate ultra-low latency communication mechanisms to create virtual entities that precisely replicate the processes of physical systems [
8]. This technology has demonstrated successful applications in industrial contexts [
9], in monitoring distributed systems [
10], and even in representing complex entities in medicine [
11]. However, beyond monitoring, the principal achievement of DTs lies in their ability to simulate and predict outcomes based on variations in the virtual entity, enabling proactive optimization and informed decision-making. This allows for the assessment of the impact of changes in the system’s functioning without requiring interaction with or modification of the physical solution. Considering this, the proposed paper presents a DT over 5G to address the challenge of monitoring 5G-MANETs.
The proposed work focuses on providing a connection-aware communication architecture to monitor 5G-MANETs using a DT. This approach offers a real-time virtual representation of physical networks, updating the topology and displaying communication processes. Based on the collected network events, the proposal integrates a simulation core to estimate the impact of customized configurations on performance. For this, contextual applications may be deployed on physical nodes, which individually manage local connections within the 5G-MANET, while continuously updating the DT with network events via the 5G infrastructure. Considering the inherent challenges of MANETs, the proposal incorporates a connection-aware routing strategy to keep the DT updated during disconnection periods. Thus, when nodes lack Internet access to communicate with the DT, gateway devices are used to transmit control data.
To assess the accuracy of the proposal and its technical viability, a proof-of-concept is implemented and evaluated under multiple testing scenarios. In these tests, a physical 5G-MANET is monitored, analyzing the latency of the DT and comparing the estimated QoS results with the actual ones. As a result, experiments show that the proposal provides a reliable DT.
The paper is organized as follows: first,
Section 2 details the most relevant proposals in the DT field for 5G-MANETs; then,
Section 3 provides an overview of the proposal, including the architecture and connection-aware routing. After this,
Section 4 analyzes the QoS of the communications between the network and the DT, comparing the outcomes obtained in each. Finally,
Section 5 presents the main findings of the approach and outlines the next steps in the research.
2. Related Works
Monitorization of 5G-MANETs has motivated a large collection of works over the years [
5]. These approaches provide a set of outcomes and variables about the network, enabling a deep understanding of the communication processes and the impact of contextual events. However, most of these works focus on evaluating the performance of routing protocols, instead of monitoring the global actions of the network [
5]. Also, most of proposals are centered on providing customized virtual scenarios, mainly due to the significant reduction of time and resource investment regarding physical testbeds [
12].
In monitoring approaches, the main focus is on the performance evaluation of routing protocols, specially in simulations [
4]. This is mainly due to the significant reduction of costs and time regarding real testbeds [
4,
12]. As a result, it is possible to appreciate that most of the monitoring tools are focused on virtual contexts [
4,
6,
12,
13,
14,
15]. However, there are relevant works which aim to respond to the necessity of representing the events of the MANET [
16,
17,
17].
The work proposed in [
16] provides a communication architecture focused on monitoring real-time events from sensors, aiming to proactively detect hazards from landslides. For this, a MANET is applied to broadcast notifications to the nearby population while utilizing cellular communication to monitor the resulting topology. Thus, the approach combines the monitoring of fixed sensors with the study of MANET behavior. Following a similar approach, the proposal in [
17] analyzes the use of ad-hoc networks to monitor critical contextual variables, specifically using MANETs to notify emergencies. In both cases, the monitoring processes involve MANETs, but are not focused on providing detailed performance analysis. Additionally, disconnections between nodes are not considered in the operation, and are instead regarded as potential challenges [
17].
Other works utilize MANETs for communication and system monitoring. In the work [
18], these networks are applied to communicate to Internet of Things (IoT) systems. A connection-aware routing protocol is proposed, which monitors the global topology and active connections. This ensures the availability of communication paths, while also considering energy consumption. As a result, the protocol selects the most suitable path within the topology.
Similarly, the proposal in [
19] applies MANETs in healthcare environments. This scenario is particularly relevant due to its demands for real-time transmissions, which are addressed using a routing protocol. However, the advances in low latency are not oriented towards providing an interoperable architecture. Consequently, these monitoring approaches do not fully address global monitoring requirements and the challenges of disconnections. Nevertheless, there are some implementations that are combining DT and MANETs.
DT has become one of the most relevant research lines in recent years. Its contributions in areas such as industry [
20], healthcare [
21], autonomous mobility [
22], and communications [
23] have established DT as a disruptive paradigm to enhance the monitoring and virtual representations of physical processes and systems. In the context of communications, DT has been explored in multiple works, focusing on MANETs [
24] and Mobile Edge Computing (MEC) [
22,
25,
26].
The work proposed in [
24] explores the application of a DT to enhance routing information in a smart city context. The virtual representation of the topology is used to restrict the communication area and reduce unnecessary control traffic in the network. For this, precise monitoring of node locations is applied, utilizing individual cellular networks to transmit control data. This solution is a successful technique that aligns DT with ad-hoc networks. However, the proposal does not include any mechanisms to handle potential disconnections in the network. As a result, this study assumes constant connection availability, allowing nodes to share their location and computational resources at any time. Therefore, despite its valuable contribution, the work is not operable in contexts where coverage is unstable.
Works such as [
25,
26] explore the role of DT in offloading techniques while preserving energy consumption. In the case of [
25], the proposal focuses on calculating deviations between pre-decision configurations and the worst-case scenario. Thus, a DT is used to calculate the optimal setup to minimize latency and energy consumption. Similarly, alternatives such as [
26] apply Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) to define the optimal network configuration. In addition to research in MEC, the work proposed in [
22] introduces a DT to enhance autonomous vehicles’ ability to change lanes effectively.
Considering the addressed proposals, there is no perspective focused on providing a global architecture to monitor 5G-MANETs while enabling adaptation to the network’s changing topology. Since most works concentrate on providing contextual applications, this proposal aims to address the growing need for a global real-time monitoring tool for 5G-MANETs, tackling the well-defined challenge of their dynamic and nondeterministic behavior [
17]. The main contributions of this work are detailed next.
The proposal aims to provide a DT-based monitoring architecture focused on real-time virtual representations of 5G-MANETs. Specifically, the work proposes a solution that enables integration in multiple local contexts, utilizing 5G technology to reduce latency and empower devices with autonomous communication.
The work accounts for occasional disconnections of nodes due to mobility or lack of 5G coverage. In these cases, the proposal applies a distance-based routing protocol that enables routing control information to keep the DT updated.
The proposal has been evaluated in a proof-of-concept implementation, analyzing the impact of contextual variables such as cellular network availability and varying topologies.
Considering these claims, the next section addresses the details of the proposal, providing an overview of the system, analyzing the components involved in the architecture, and discussing the context-aware routing.
3. Connection-Aware DT for 5G-MANETs
This paper aims to provide an accurate virtual representation of 5G-MANETs deployed in physical scenarios, enabling precise monitoring of network events and resources. To achieve this, a DT is applied to represent the set of nodes, their connections, and the transmitted messages. Given the dynamic nature of the nodes and the potential variations in the availability and strength of the 5G signal, the proposal includes routing mechanisms to transmit information from disconnected nodes using connected devices such as gateways. To detail the operation of the proposal, this section addresses the overview of the system, the architecture and components behind its functioning, and the proposed routing algorithm for information transmission.
3.1. Overview
5G-MANETs are a suitable solution to support the deployment of contextual applications, relying on the physical proximity between dynamic nodes. However, the mobility of the devices and the potential variability of the topology make communication performance critical to measure. 5G technology enables the transmission of real-time information about network events, enhancing centralized monitoring of resource consumption and QoS. Considering the capabilities of these networks, this paper introduces a DT for 5G-MANETs, providing a suitable solution to study the overall productivity and enabling a real-time virtual representation of the physical devices. Furthermore, the proposal addresses potential connectivity interruptions caused by the inherent dynamic mobility of the nodes and the wide variety of contextual scenarios.
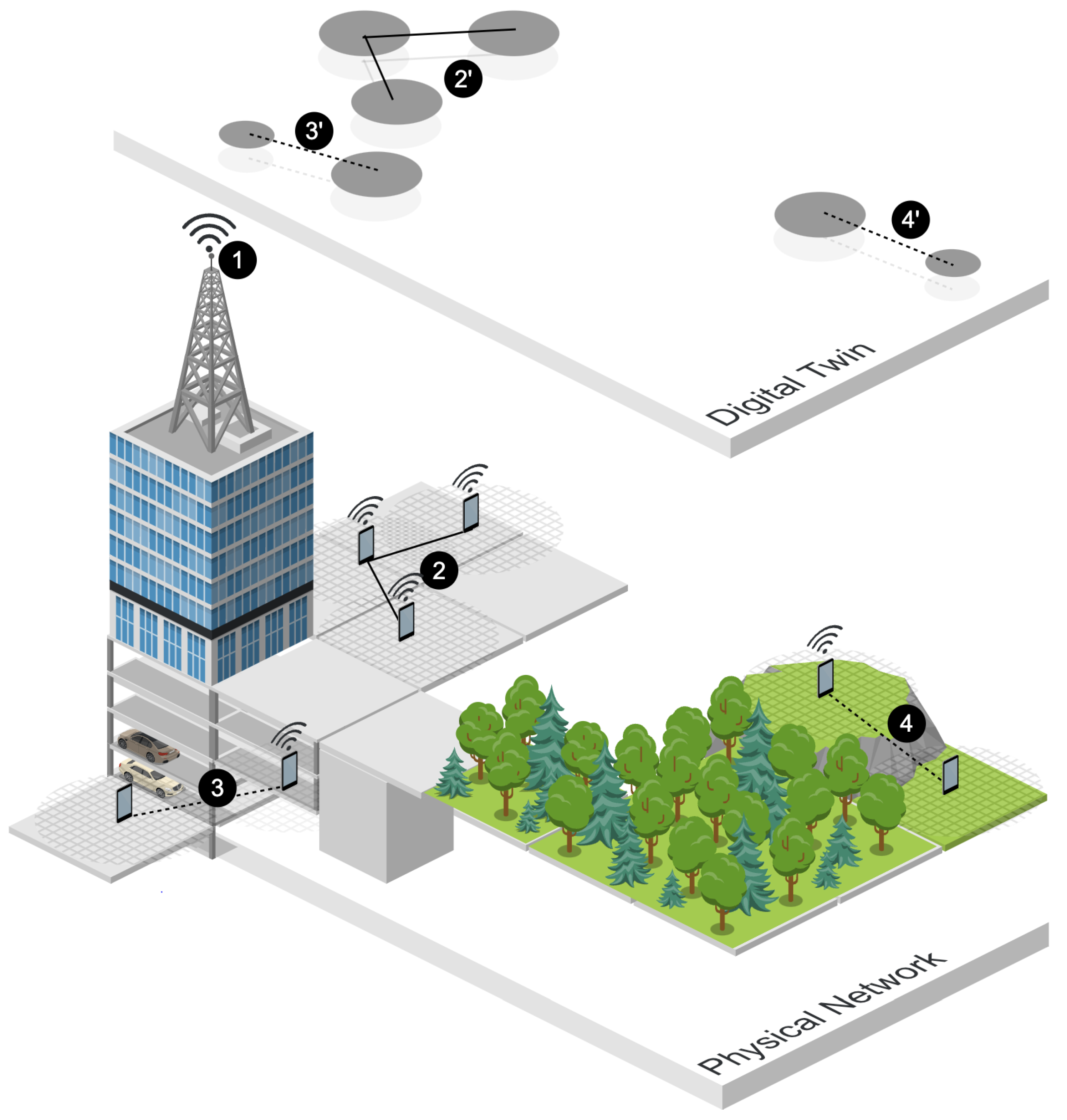
Figure 1 provides a detailed visual overview of the work, including the representation of the physical network and its virtualization in the DT.
In
Figure 1, a 5G antenna (1) provides Internet access to three different MANETs deployed in physical contexts, represented by numbers 2, 3, and 4. In the case of 2, three mobile devices are connected to the 5G network, providing real-time information about their active links, as well as contextual data such as current energy consumption, the creation of new messages, and the reception and delivery of messages. As a result, the DT is able to provide an accurate representation of the communications (2’). However, MANETs may be deployed in scenarios that challenge communication infrastructures, such as underground environments, represented by number 3, and remote rural areas, represented by number 4. In both cases (3 and 4), two devices form the network, but only one is able to connect to 5G. Thus, disconnected nodes provide their individual contextual data to the connected devices, which act as gateways to transmit the data to the DT (3’ and 4’). Consequently, the connection-aware DT is able to maintain an accurate real-time representation of the MANETs, utilizing opportunistic routing [
4].
Based on the information captured by the DT, it is possible to achieve reliable representations of the MANETs, using virtual entities (2’, 3’, and 4’ in
Figure 1). These representations enable detailed monitoring of the communications, as well as prediction of the potential impact of changes in the network. To do this, the DT allows modification of contextual variables such as the number of nodes involved in the network, their Internet availability, the network traffic, and the topology. As a result, the DT makes use of simulation features such as mobility patterns and scenario customization to provide QoS analysis of the variations, enabling the study of the impact of these changes.
Considering the proposal, the work aims to provide a solution that combines contextual communication technologies such as Bluetooth, WiFi, and 5G, while applying simulation techniques to estimate the performance of the MANETs after applying changes. To understand the integration of the different technologies, the next subsection addresses the global architecture of the proposal.
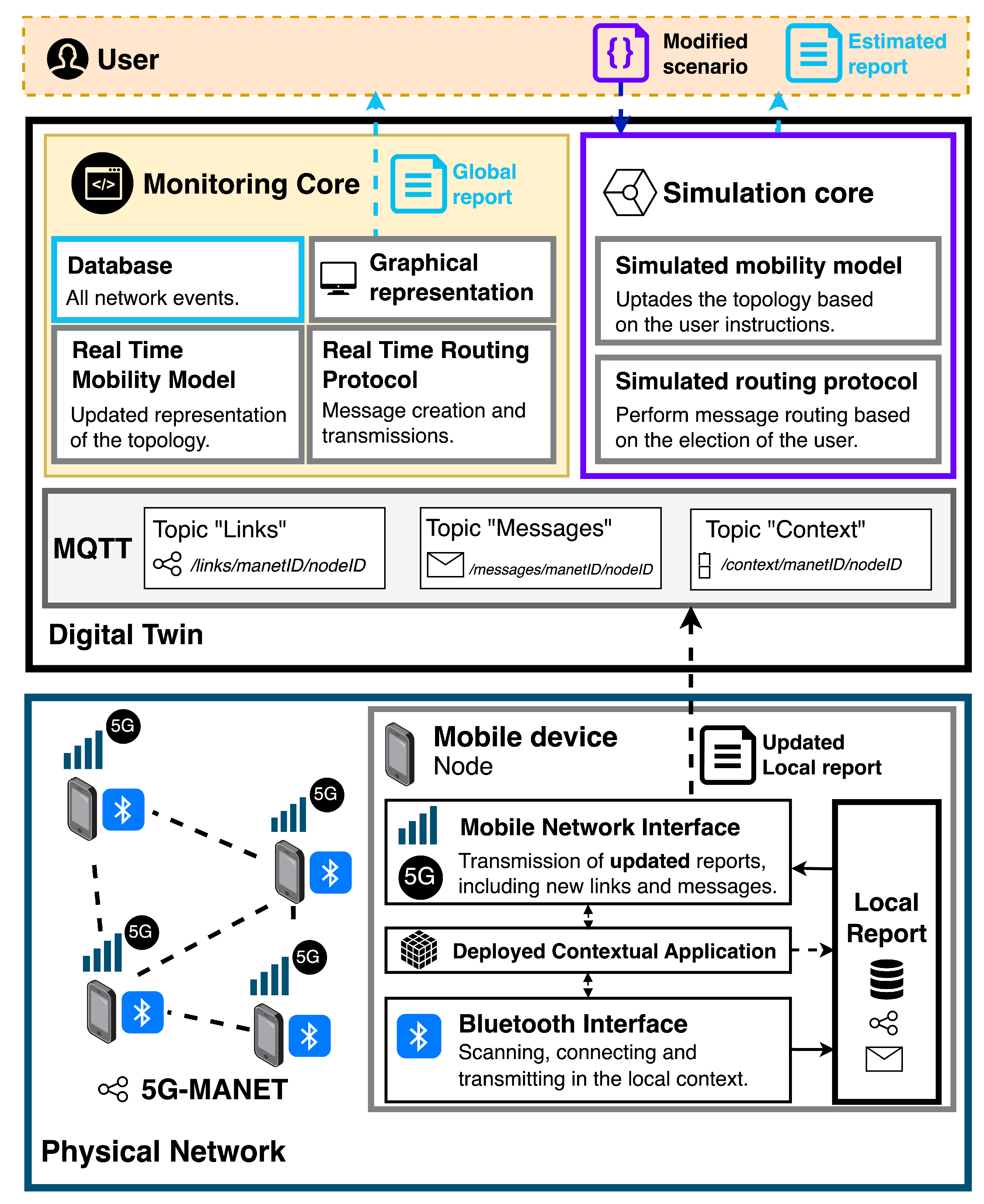
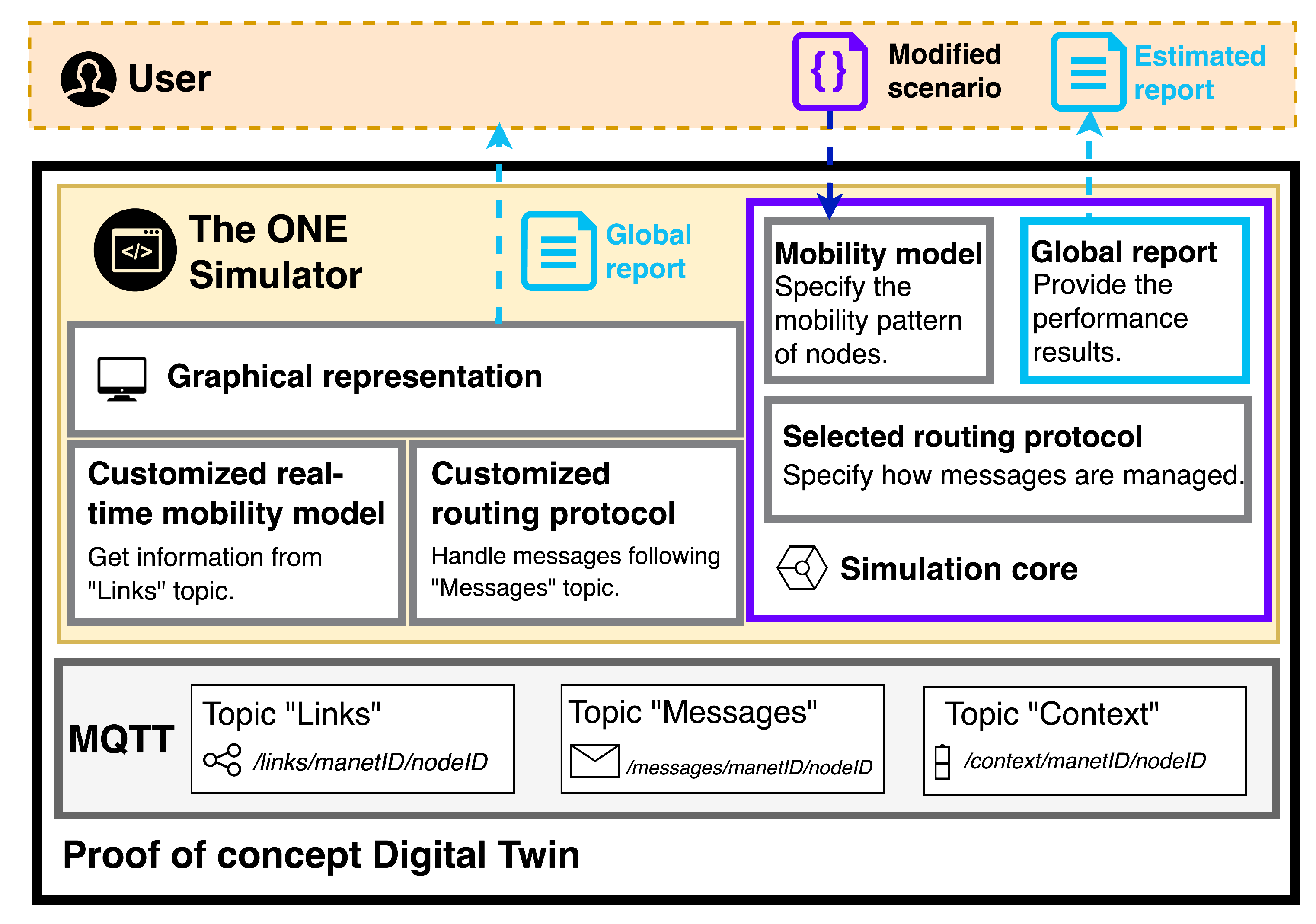
3.2. Architecture
The proposed solution requires the coordination of multiple technologies in two main contexts: the local scenario and the DT scenario. The first represents the set of components needed to form 5G-MANETs in physical scenarios, including the wireless interfaces and individual performance reports. In the case of the DT, it is necessary to obtain updated reports about network events, aiming to provide users with a real-time representation of the 5G-MANETs. At the same time, additional components are used to customize context and network variables, including estimates of their impact on QoS and performance. Considering this,
Figure 2 represents the global architecture of the proposal.
The local context is shaped by the nodes of the physical 5G-MANETs. These devices are responsible for acting as communication elements to enable the deployment of contextual applications that require both remote and local communications. Thus, monitoring the network requires node devices to use two communication interfaces: Bluetooth or WiFi for local data transmissions, and 5G for communication with the DT. Additionally, a local reporting component is required to coordinate monitoring actions. The components are described as follows:
Contextual application. Nodes in 5G-MANETs may execute applications that exploit the possibilities of contextual interactions. Thus, they can be focused on multiple purposes and serve as sources of interactions for the proposed DT.
Local wireless interface. This component is responsible for providing data transmissions in local contexts. Considering the communication requirements of MANETs, limited-range wireless interfaces are suitable for enabling the transmission of information between nodes while providing reliable contextual data. For this, options such as Bluetooth, Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), or WiFi are suitable, depending on the application’s requirements. In the architecture, this layer provides contextual information to the individual local report of the nodes, including data such as new connections and disconnections, as well as performance variables like signal strength.
Local report. This component performs two main functions: managing and monitoring the network events executed by the node, and providing structured storage for communication statistics. On the one hand, it handles the node’s interactions, including managing routing processes and the creation, reception, and delivery of messages. On the other hand, the structured storage of this information enables the identification of new interactions, allowing for early notification of events to the DT via the 5G interface. For this, a cache storage is used to keep the latest updates of the node.
5G interface. The low-latency properties of 5G enhance the potential application of DT to monitor MANETs. In this way, when the local report updates network variables, changes are transmitted to the DT, ensuring a reliable representation of the nodes.
As a result, the components integrated into the nodes foster the monitoring of 5G-MANETs, providing updated and accurate information about the events in the network to the DT. Meanwhile, the DT is executed remotely on a cloud server and consists of two main components: the monitoring core, responsible for simultaneously monitoring multiple physical 5G-MANETs, and the simulation core, which provides customized configurations of the physical networks. Next, each of these components is addressed.
-
Monitoring core. This component is responsible for managing the virtual representation of the physical 5G-MANETs, including handling incoming communications with updates in the network topology, displaying information about data traffic, generating performance reports on QoS, storing historical information, and providing real-time graphical representations. The following set of sub-components is involved:
- -
MQTT Interface. This entity is responsible for receiving incoming communications from the physical nodes of the 5G-MANETs. Several topics are provided, enabling the specification of the alive links associated with each node, the creation, sending, and reception of messages, and the transmission of contextual information about the devices. MQTT technology enhances real-time communication, providing low-latency data transmission.
- -
Real-time mobility model. Based on the information about links received by the MQTT interface, the mobility model manages the topology of the virtual 5G-MANET. In this way, it is possible to track the connections between nodes and additional contextual variables, such as signal strength.
- -
Real-time routing protocol. Using the data received by the MQTT interface, this component is responsible for representing the creation, reception, and delivery of messages between nodes in the 5G-MANET. This allows for tracking the latest data transfers, including those successfully completed and those that failed.
- -
Database. This component is responsible for storing all network interactions received by the MQTT interface. The database is implemented following a relational paradigm, considering the structured nature of the data. As a result, registering historical information about network events provides a valuable source of knowledge about network behavior, especially useful for Artificial Intelligence (AI) purposes.
- -
Global report. Based on the information stored in the database, the global reports provide an updated summary of network performance, including QoS variables such as delivery probability, latency, overhead, and hop count. Considering the variety of variables involved in the report,
Table 1 details the collection.
- -
Graphical Representation. Based on the components of the real-time mobility model and real-time routing protocol, the graphical representation provides users with a virtual depiction of the network. This function enhances the understanding of physical interactions by including the real-time topology and communication events between nodes.
-
Simulation core. This component is responsible for evaluating the impact of customized modifications on the performance and QoS of the virtual networks. Thus, the user is able to change contextual variables to explore their potential influence on the global reports, comparing the outcomes with those obtained from the physical network. As a result, those features enable a detailed simulation of variations, exploring alternative configurations of the 5G-MANET and providing the user with estimations of their impact. To achieve this, there are two main sub-components that enable this task:
- -
Modification of the scenario. This input enables the user to specify new network conditions, including variations in the topology, selection of the routing protocol, definition of additional network conditions, and modification of contextual data for each node. Considering the variety of these inputs,
Table 2 details the set of customizable variations.
- -
Estimated reports. Based on a simulation of the virtual network, executed under the provided conditions, the DT provides estimated reports on performance and QoS, following the same variables reflected in
Table 1. The collection of accurate and detailed data about historical network events enhances these estimations.
Considering the described architecture, the proposal provides accurate virtual representations of physical 5G-MANETs and offers detailed estimations for customized variations. Nevertheless, the dynamic nature of mobile nodes in the physical network may lead to significant changes in topology and 5G availability. Some contexts, such as underground scenarios and isolated rural locations, may result in Internet disconnections for nodes, preventing real-time updates of the DT. In light of this situation, the following subsection details the synchronization strategy proposed.
3.3. Connection-Aware Synchronization of the DT
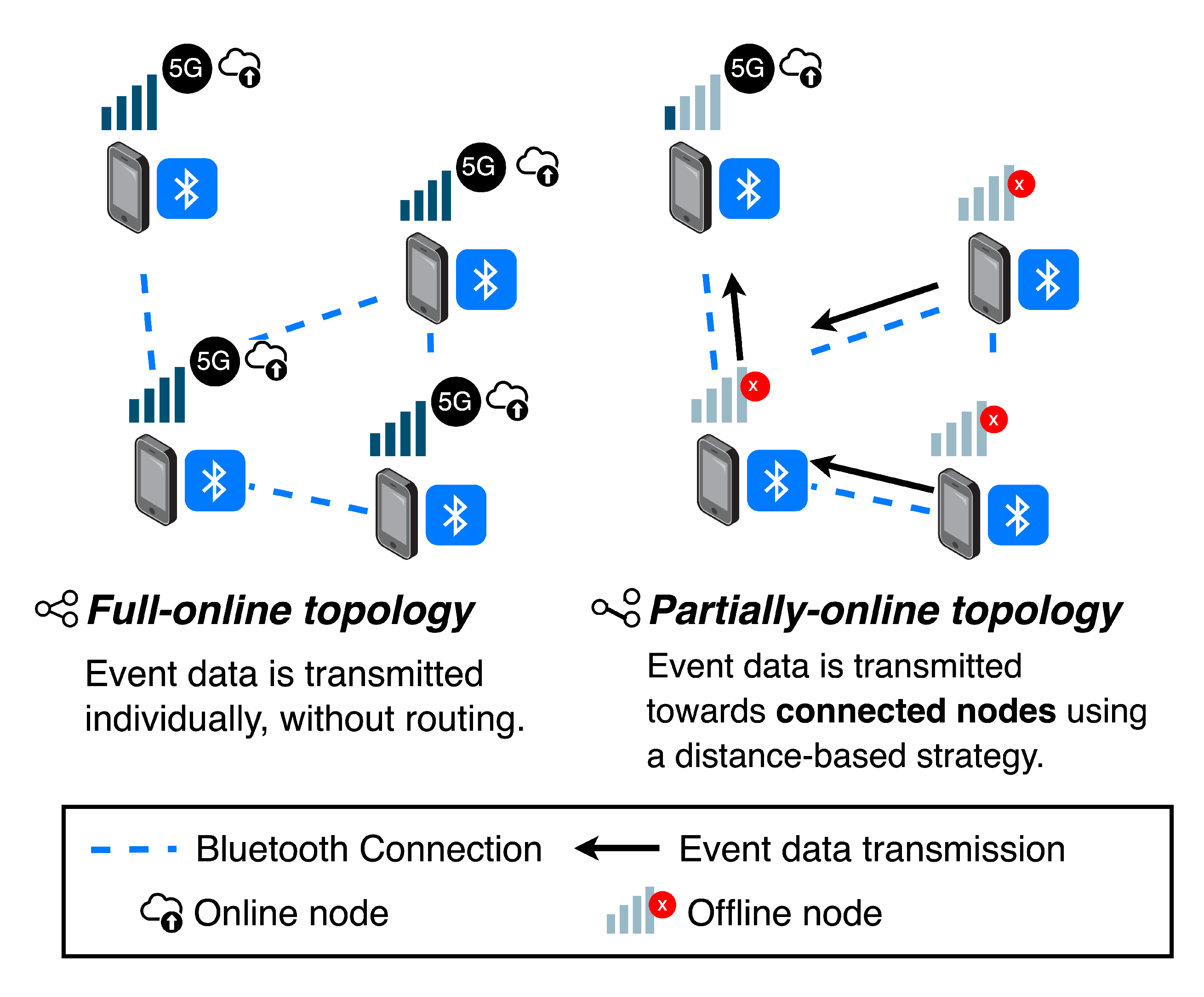
The dynamic nature of the nodes in MANETs leads to a potential scenario where some nodes lack 5G access. This context prevents the transmission of the latest updated local report entries, resulting in a decoherence that affects the accuracy and fidelity of the DT. Since variable coverage is assumed to be an inherent challenge of 5G-MANETs, it is important to address these contexts to minimize their impact on the digital representation. To this end, the proposal includes a connection-aware strategy to opportunistically synchronize the information. As
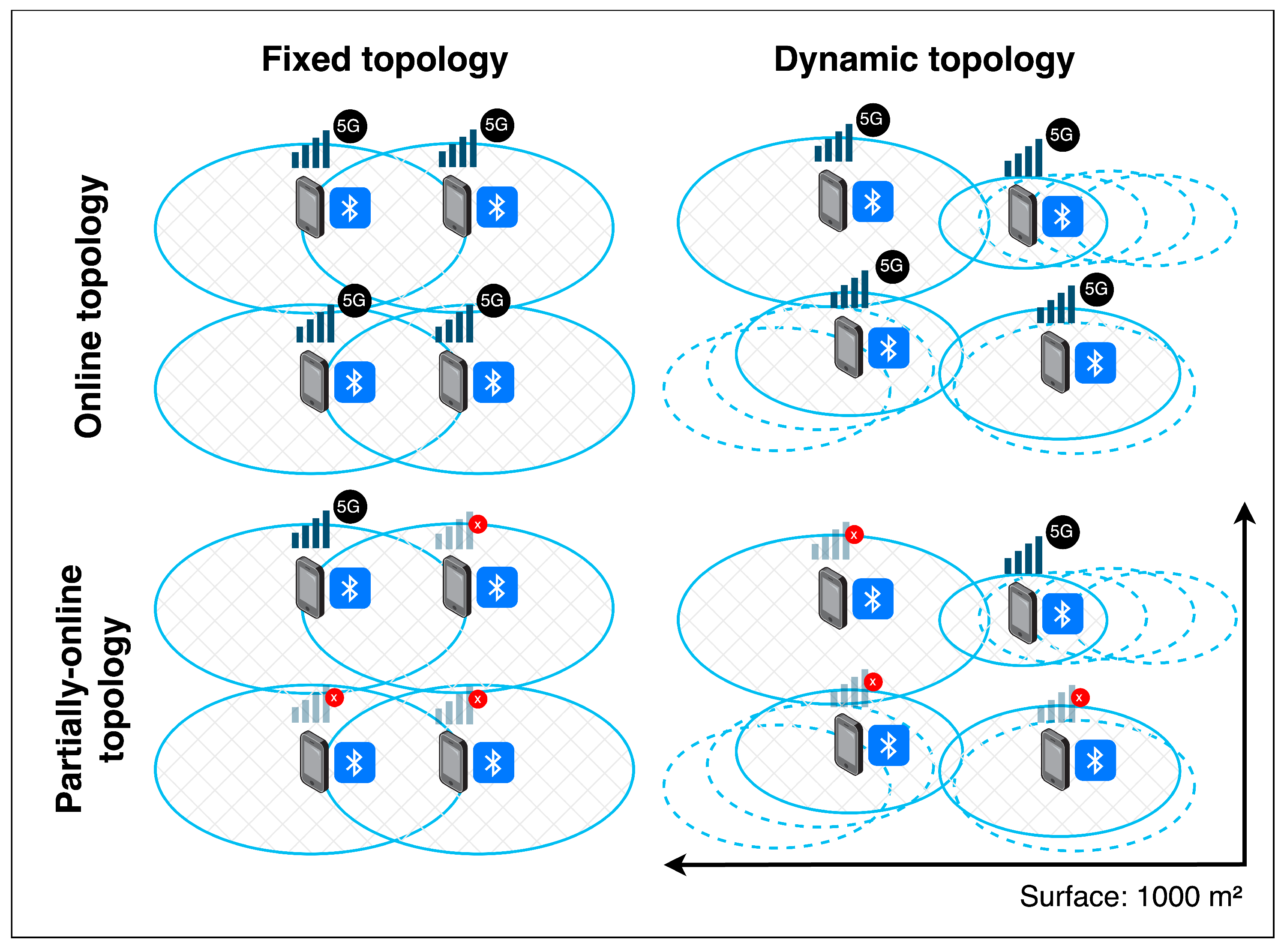
Figure 3 illustrates, two main potential topologies can be found: full-online and partially-online.
A full-online topology defines the ideal case: all nodes in the 5G-MANET are connected to the Internet, providing the DT with new events in real-time. In this case, it is not necessary to apply routing mechanisms to avoid disconnections, as nodes can individually provide their data.
In the case of a partially-online topology, the accuracy of the DT may be affected because some nodes in the MANET are unable to transmit their local events to the centralized MQTT interface. As a result, some nodes in the network remain connected to 5G, while others face disconnections. For these situations, a distance-based routing strategy is proposed, using online nodes as gateways for the local reports from offline devices, aiming to transmit the information to the nearest online node. This process is carried out in two phases: recognition of the optimal path and the transmission of the local records to the connected node.
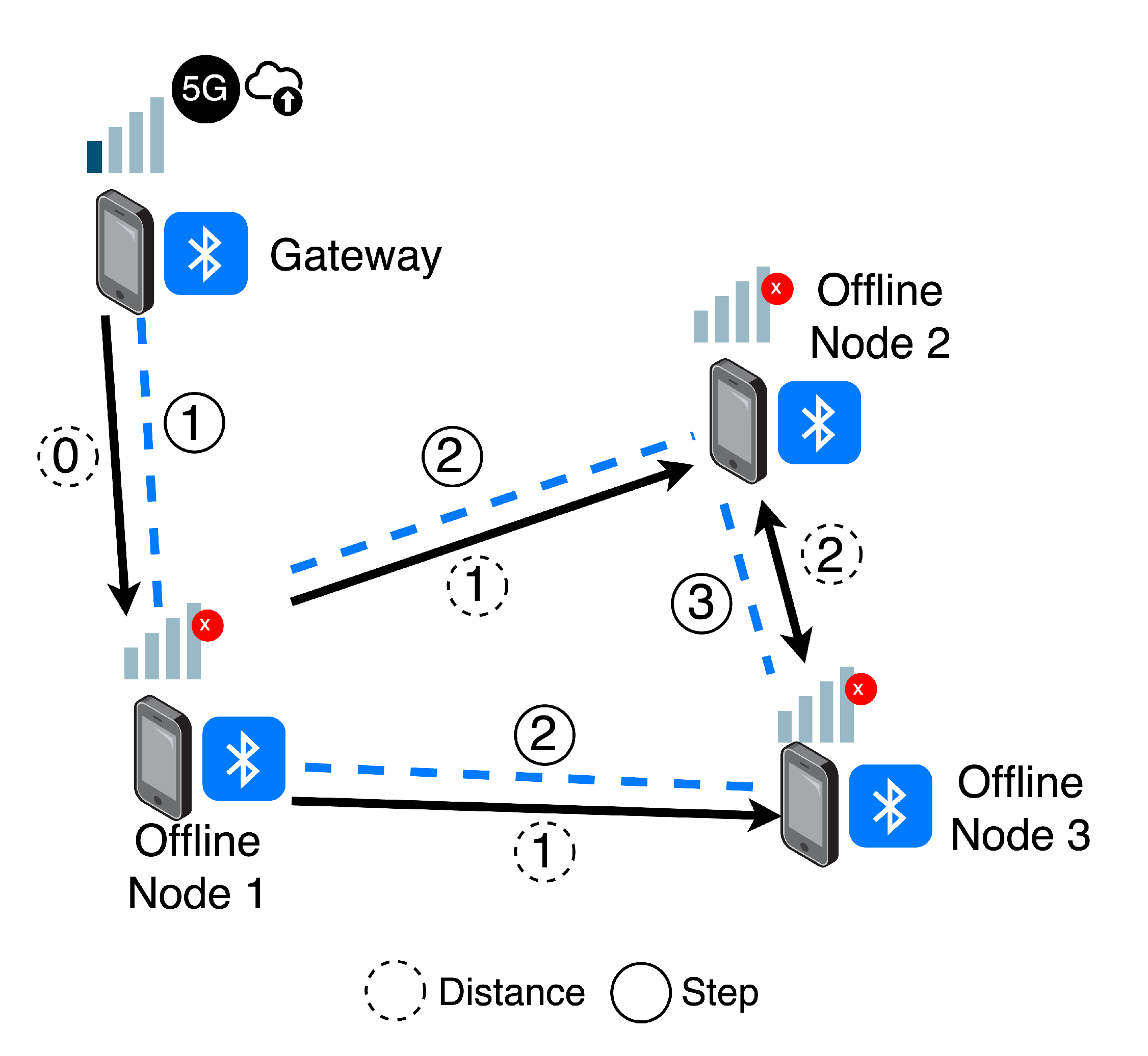
Recognition of the optimal path. Algorithm 1 proposes a routing strategy to transmit network data from offline nodes to connected devices, based on proximity.
Figure 4 illustrates a potential scenario for this approach: four nodes (Gateway and Offline Nodes 1, 2, and 3) are distributed in a context, forming a local topology. In this case, only one of the devices has a 5G connection, while the others are not connected to the Internet. To address this situation, the Gateway node communicates with connected devices to notify them of its online status (step 1). The message includes the distance to the destination, which is zero in this case. As nearby devices receive the notification, they broadcast the message to their connections, incrementing the distance by one unit (step 2). As a result, second-level nodes receive the message, identifying the connection with the shortest distance as optimal. Hence, when Offline Nodes 2 and 3 receive their mutual distances (a distance of 3), their connection with Offline Node 1 is identified as optimal (a distance of 2). Using this strategy, it is possible to define an optimal path to communicate the reports generated by offline nodes to connected devices.
Transmission of the local records. Once a path is established between offline nodes and online entities, devices are able to transmit new events from their local reports to the MQTT interface using intermediate nodes. This technique is dynamic in response to changes in topology, as it can detect disconnections and abrupt changes in links.
|
Algorithm 1: Routing strategy to provide network information in partially connected 5G-MANETs. |
|
Require: I as 5G interface, B as local wireless communication interface.
- 1:
while is true do
- 2:
- 3:
- 4:
if newDistance is 1 then
- 5:
- 6:
else
- 7:
if newDistance < currentDistance then
- 8:
- 9:
end if
- 10:
- 11:
end if
- 12:
end while
|
Alternatively, there may be contexts where all nodes in the topology become disconnected from 5G. In these cases, it is possible to route information toward the last online node; however, its eventual permanent disconnection would lead to harmful energy consumption. As a result, fully offline topologies become impractical for providing a reliable virtual representation in the DT. For such cases, it would be possible to estimate reports based on the simulation core, though this approach assumes the possibility of deviations.
Considering the description of the proposal, its architectural components, and the context-aware strategy, the next section presents the experimental results obtained from a proof-of-concept implementation of the proposal.
4. Experimental Results
Assessing the performance of the proposed work involves evaluating the accuracy of the virtual representation in relation to the physical network. Additionally, considering the connection-aware capability of the proposal, evaluation scenarios vary 5G availability to test the impact of disconnections and the effectiveness of the routing strategy. For this purpose, a proof-of-concept of the proposal has been implemented, utilizing the core of The ONE Simulator [
27] to perform visual representations of the network and execute customized scenarios. This section describes the implementation, details the evaluation setup, and analyzes the obtained results.
4.1. Proof-of-Concept Implementation
The implementation of the architecture has been carried out using two main elements: a smartphone application and a customized version of The ONE Simulator. These elements are detailed below:
Smartphone application. The proposed application is based on a modification of the tool provided in the work [
4]. For this proof-of-concept, the application manages communications in the physical 5G-MANET, acting as a simple message chat between local devices. The application generates random new messages at fixed intervals of 5 seconds, with a random destination selected among the nodes in the 5G-MANET. The selected routing algorithm is Epidemic Routing [
28], due to its intensive use of encounters and data duplication. Local communications are handled using BLE to discover surrounding devices and Bluetooth to transmit information. These technologies are applied as alternatives to WiFi, as WiFi-Direct and WiFi Ad Hoc impose challenging restrictions: WiFi-Direct requires a centralized node as a group manager, which impedes the application of dynamic and ad-hoc topologies [
29], while WiFi Ad Hoc requires root access for smartphones [
30]. As a result, Bluetooth provides a flexible wireless interface for ad-hoc transmissions [
31]. Finally, the application logs all individual events in the network, enabling the eventual performance assessment of QoS metrics. It is also responsible for communicating updates to the MQTT interface using 5G.
-
DT. As
Figure 5 shows, the proof-of-concept integrates the minimal components to provide a functional version of the DT. It has been implemented using The ONE Simulator to enable quick integration of visualization and simulation tasks into the proposal. Two main customized elements have been implemented, utilizing the real-time information received by the MQTT interface: a real-time mobility model, responsible for updating node positions, and a real-time routing protocol, which manages messages. Finally, the graphical representation enables the visualization of the scenario.
On the other hand, simulation tasks are handled by the default simulation core of The ONE Simulator. In this way, users can configure contextual variables such as the mobility model, topology, and routing protocol.
The proposed proof-of-concept represents an initial implementation to assess the platform’s capabilities and its performance in an evaluation scenario. The following section describes the evaluation setup of the proposal.
4.2. Evaluation Setup
The assessment of the proposal has been conducted in a laboratory context, using four physical smartphones to form the 5G-MANET. Additionally, a laptop is used to execute the DT. The experimental design focuses on evaluating the accuracy of the virtual representation in the DT, analyzing the update time and the accuracy of the calculated performance for the 5G-MANET. As a result, the evaluation scenario considers two main variables: the 5G connection of the nodes in the network and the QoS evaluation.
On the one hand, the first condition enables the assessment of the context-aware functions, analyzing the impact of routing on the latency of the DT. On the other hand, the comparison between the QoS report calculated by the DT and the one obtained from the physical 5G-MANET assesses the accuracy of the global reports. The considered variables are described below:
-
5G connection of nodes in the network. The variation in network topology, as well as Internet availability, negatively impacts the accuracy of the DT. Considering the connection-aware functions of the proposal, analyzing the impact of routing functions on the delivery probability and latency of the messages transmitted to the DT is significant for evaluating the real-time accuracy of the implementation. To achieve this, four different topologies are planned for the physical network (
Figure 6):
- -
Fixed Online Topology (FOT). This topology consists of a static ring where all nodes are connected to the Internet. In this case, no routing is required to keep the DT updated.
- -
Fixed Partially-Online Topology (FPOT). The topology follows a ring distribution, where four nodes lack 5G connection and only one is connected to the Internet. As a result, distance-based routing is required to keep the DT updated.
- -
Dynamic Online Topology (DOT). All nodes are connected to 5G, but the topology is not fixed. Thus, although each node can send control information to the DT, local messages in the MANET still require routing.
- -
Dynamic Partially-Online Topology (DPOT). This topology is not fixed, so nodes move within the physical context. Additionally, only one device has a 5G connection, so routing is required to keep the DT updated.
The proposed scenarios are executed using mid-range smartphones, with their positions and connections modified randomly. The movement in the context is performed in an open space of 1000 (20x50m), allowing for occasional local disconnections between nodes. Finally, the network is run for a period of 15 minutes.
Accuracy of global performance. Considering that the DT provides QoS reports based on the events reported in the network, four variables are measured for the experiment: delivery probability, latency, overhead, and hop count.
Considering the described scenario variations, the QoS metrics are analyzed for each executed scenario, comparing the results obtained from the physical network with those provided by the DT. The next subsection analyzes the different obtained statistics and discusses the results.
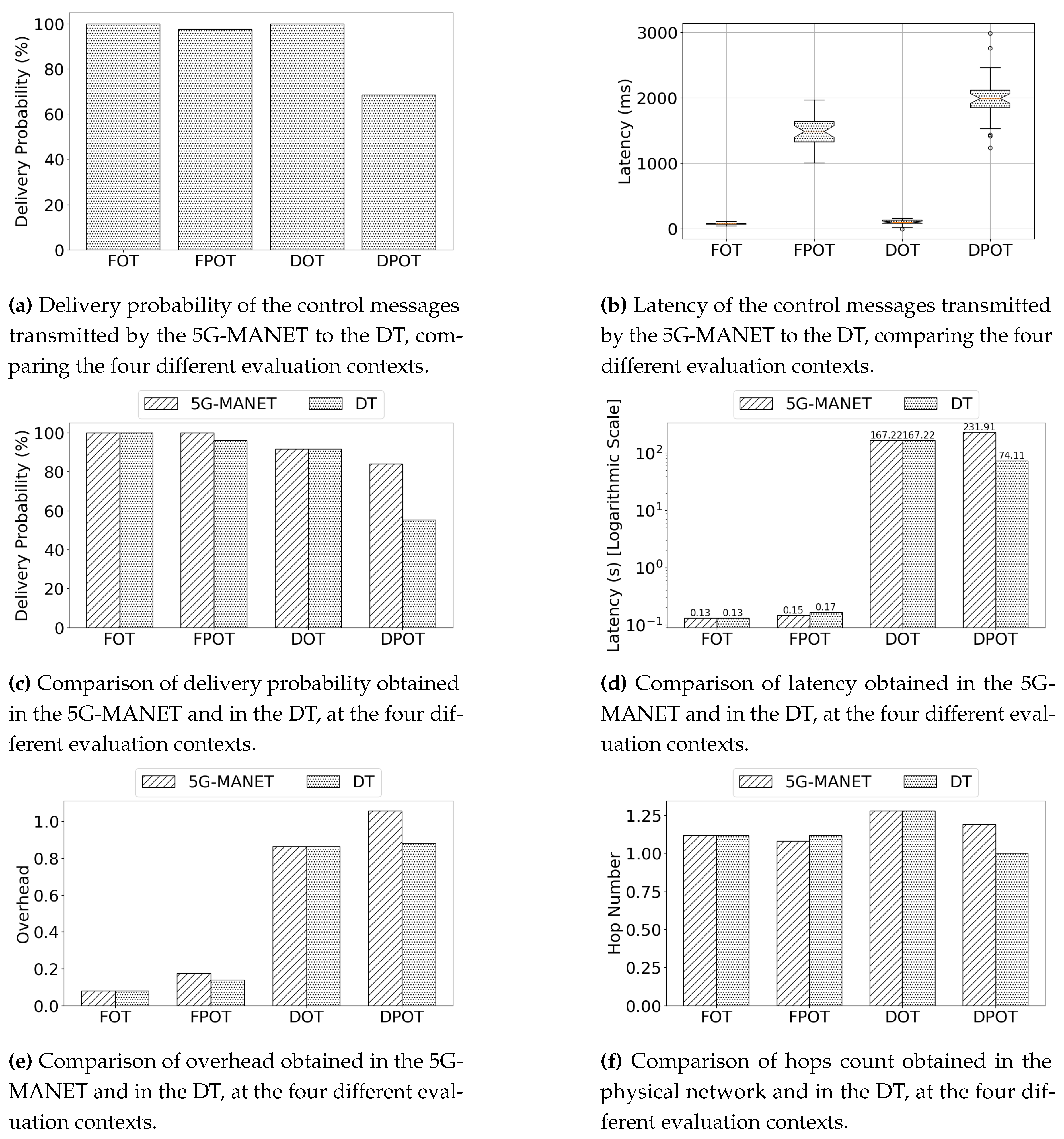
4.3. Analysis of the Results
Figure 7 presents the results obtained after executing the testing scenarios. The results are organized into two main topics: the analysis of communication quality between the 5G-MANET and the DT, shown in
Figure 7 and
Figure 7; and the comparison of QoS results obtained from the physical network with those calculated by the DT, shown in
Figure 7,
Figure 7,
Figure 7, and
Figure 7. For this, the considered variables are extracted from the QoS report of the DT (
Table 1): delivery probability, measuring the percentage of created messages that have been delivered; latency, indicating the average time elapsed since a message is created and it is delivered; overhead, representing the ratio between the messages copied and the messages delivered; and hop count, representing the average number of hops required to deliver a message. Next, the results for each value are analyzed.
Subfigure 7a displays the delivery probability of the control messages sent by the nodes in the physical network to the DT. As shown, the percentage of correctly delivered messages is high, reaching 100% for the online scenarios (FOT and DOT). On the other hand, partially-online scenarios such as FPOT and DPOT exhibit lower delivery ratios. In the case of FPOT, the connection-aware routing strategy achieves a high delivery probability; however, in DPOT, the dynamic topology reduces the algorithm’s effectiveness. As a result, it is possible to deduce a lower performance of the DT in sparse, disconnected scenarios, where synchronization becomes challenging. This factor directly influences the QoS results obtained for the DPOT scenario.
Subfigure 7b represents the average latency of the control messages received by the DT in each scenario. The standard deviation and interquartile range provide meaningful insights into the values. As shown, there is a significant gap between contexts where nodes are online and connected to 5G, and those where routing is required. It is clear that the synchronization and data quality provided by the DT are sensitive to the connection availability of the physical network. However, despite this, the average latency remains suitable to meet DT standards [
2].
The delivery probability of the messages transmitted in the network, comparing the performance calculated by the 5G-MANET and that calculated by the DT, is depicted in subfigure 7c. As shown, the DT provides accurate results, especially for the online topologies (FOT and DOT). However, the DT calculates different results for the partially-online scenarios: in the case of FPOT, the estimation is very close to the actual values; whereas in DPOT, the difference is larger, offering a result that deviates from the actual.
Subfigure 7d shows the latency of the delivered messages in the network, comparing the results obtained in the physical network with those calculated by the DT. Online scenarios provide high accuracy for the DT, enabling the estimation of nearly identical results. In the case of the partially-online contexts, the DT provides slightly different results but maintains values that are very close.
Regarding overhead, which represents the ratio of redundant copies, subfigure 7e illustrates the comparison results. As shown, the deviations between the values calculated by the DT and the actual values in the 5G-MANET are minimal. For the online topologies, the DT correctly calculates the results, while it underperforms in partially-online topologies.
Finally, subfigure 7f represents the comparison between the average hop count calculated by the physical network and the results calculated by the DT. In the case of the partially-online topologies (FPOT and DPOT), the DT provides a higher estimation, though the values remain close to the actual ones.
Considering the provided results, the proposed proof-of-concept offers a reliable virtual representation of physical 5G-MANETs. On the one hand, the results obtained in online topologies reported by the DT match those of the actual network, demonstrating successful monitoring of the events. On the other hand, partially-offline scenarios present a challenge for the DT, leading to significant deviations from the actual values, especially in dynamic topologies. These deviations are primarily due to the lack of control information, stemming from the low delivery probability of the received messages. This issue leads to a loss of information, affecting the accuracy of delivery reports and reducing the calculated latency, overhead, and hop count. Nevertheless, the application of the context-aware routing strategy proves to be a suitable response for handling disconnection periods, as it shows how the gateway node communicates control data from disconnected devices. Based on these outcomes, the next subsection discusses the main conclusions derived from the results.
4.4. Discussion
The overall results demonstrate successful outcomes for the QoS predictions of the DT, with its performance varying based on the availability of Internet connection in the topology. In the first and third scenarios, FOT and DOT, the communication between the 5G-MANET and the DT is stable, achieving low-latency transmissions. This is primarily due to the availability of Internet for each individual node, enabling real-time transmission of network events. Additionally, the movement of nodes does not directly affect the accuracy of the DT. As a result, the DT proves to be a suitable monitoring tool when Internet access is available for all nodes in the topology, regardless of their mobility model. However, the lack of 5G access can lead to a reduction in performance.
In the case of the partially-online topologies, the movement of nodes becomes a significant variable that impacts the performance of the DT. For the FPOT scenario, the lack of 5G access in certain nodes necessitates the use of the context-aware routing protocol, which employs a distance-based strategy to keep the DT updated. In this topology, the fixed mobility of the nodes leads to high success in communications between the network and the DT, resulting in high accuracy between the actual QoS values and those estimated. Consequently, the proposed routing protocol can be considered a booster for the DT in challenging contexts. However, the lack of Internet becomes more challenging when the physical network’s topology is not fixed but dynamic.
The DPOT scenario represents a context where only one node is connected to the Internet, while the others are disconnected. Additionally, the nodes are not fixed but move randomly throughout the scenario, leading to random connections. As a result, this testing context becomes the most challenging for the DT, with a reduced percentage of delivered control data and resulting deviations. Nevertheless, the differences between the actual results and the calculated ones are not critical and can be reasonably accepted by the user.
As a result, the proposed proof-of-concept provides a solid approach to implementing the architecture detailed in this work. The results demonstrate how the DT is reliable for online contexts, including dynamic topologies, and for partially-online scenarios. Finally, the lack of Internet access in dynamic MANETs leads to a loss in the accuracy of the proposal, but this is acceptable depending on the application scope.
Considering these results, next section address the conclusion and future works motivated by this approach.
5. Conclusion and Future Work
5G-MANETs are a popular and agile solution for facilitating information exchange in local contexts. These communication infrastructures are significant due to their use of 5G for remote communications and local wireless interfaces for effective data transmissions in local contexts. The relevance of these networks, and their connectivity possibilities, has led to increasing interest in their application for deploying contextual solutions, as well as in real-time monitoring of their resources. However, 5G-MANETs present unique challenges, such as highly variable topology, unstable links between nodes, energy consumption of the devices, dynamic routing of messages, and 5G disconnections in nodes. As a result, these characteristics pose significant challenges for monitoring these networks. In response, this paper introduces a communication architecture to monitor 5G-MANETs based on a DT, enabling real-time representation of physical 5G-MANETs and the estimation of their QoS in customized scenarios.
The work proposes a connection-aware solution that equips nodes with the capability to use their local wireless interface to track network events and their 5G interface to update the DT with the latest interactions. For this, a heterogeneous architecture is described, combining the computing capabilities of autonomous nodes with the low-latency transmissions of 5G. Considering the potential challenges of these networks in physical contexts, the proposal integrates a connection-aware routing protocol designed to handle intermittent Internet disconnections in network nodes. As a result, when nodes lack 5G access, control data is routed toward gateway nodes to keep the DT updated. These functionalities enable two main objectives: real-time accurate monitoring of network events in 5G-MANETs and estimation of the network’s performance under customized scenarios. For the first objective, the DT is updated with the latest changes in the topology, including contextual information about nodes, such as their energy consumption and active connections. Additionally, message transmissions are monitored, providing a real-time representation of the creation, delivery, and reception of local information. Considering these interactions, the DT maintains a historical record of network events, enabling the definition of historical data, which is relevant for AI applications.
On the other hand, the DT also provides a simulation core responsible for estimating QoS outcomes for customized variations of the networks. Users can define contextual conditions over virtual networks, allowing the estimation of their performance based on historical data. Simulated mobility models and routing protocols are provided to analyze the impact of the applied changes.
Considering the multidimensional features of the proposed work, a proof-of-concept of the architecture was developed to assess the performance of the DT’s monitoring functions. A simplified version of the proposal was implemented, integrating real-time monitoring of nodes, connection-aware routing for control messages, and virtual representation of the networks. These functions enable the analysis of the global performance of the proposal, including the accuracy of the DT and the calculated outcomes for the physical network. To evaluate the implementation, four scenarios were considered to explore the impact of 5G availability and mobility on the accuracy of the proposal. The DT performed successfully for online topologies, providing real-time information about network events and reaching 100% accuracy. In contexts where Internet is unavailable for most nodes, performance decreases but remains close to the actual values. Finally, in scenarios with limited connectivity and dynamic topology, estimated results slightly differ from the physical network.
As a result, the outcomes obtained from the proof-of-concept motivate the extension of this proposal and its improvement in future work. The research directions opened by this contribution will focus on extending the proof-of-concept toward a full version of the DT architecture. An extensive simulation core, based on historical knowledge of 5G-MANETs, may provide a reliable tool for exploring the impact of customized modifications. Additionally, the connection-aware routing strategy could be improved to enhance its performance in contexts where nodes lack Internet connectivity and experience high mobility. Implementing strategies based on historical network conditions could potentially improve the accuracy of the DT even in challenging scenarios. Considering the advances of the proposal, this approach offers a promising solution for real-time monitoring of physical 5G-MANETs, providing a reliable source for detailed analysis of network performance and QoS.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, software, validation, writing, supervision, M.J.A, Z.Z, G.B, Y.J and V.S.
Acknowledgments
V.N.G.J.S. acknowledges that this work was supported by FCT - Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia, I.P. by project reference UIDB/50008/2020, and DOI identifier https://doi.org/10.54499/UIDB/50008/2020
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Agrawal, R.; Faujdar, N.; Romero, C.A.T.; Sharma, O.; Abdulsahib, G.M.; Khalaf, O.I.; Mansoor, R.F.; Ghoneim, O.A. Classification and comparison of ad hoc networks: A review. Egyptian Informatics Journal 2023, 24, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binh, L.H.; Duong, T.V.T. An improved method of AODV routing protocol using reinforcement learning for ensuring QoS in 5G-based mobile ad-hoc networks. ICT Express 2024, 10, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.; Kumar, A. Future Trends in 5G:-Challenges, Architecture and Applications. In Converging Horizons: Excelling in English Communication, Science and Strategic Management for Professional Success; 2024; p. 55. [Google Scholar]
- Jesús-Azabal, M.; García-Alonso, J.; Galán-Jiménez, J. Evaluating the quality of service of Opportunistic Mobile Ad Hoc Network routing algorithms on real devices: A software-driven approach. Ad Hoc Networks 2024, 163, 103591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battat, N.; Makhoul, A.; Laiymani, D.; Kheddouci, H. Continuous energy-efficient monitoring model for mobile ad hoc networks. 2021 International Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing (IWCMC), 2021, pp. 1587–1592. [CrossRef]
- Jesús-Azabal, M.; García-Alonso, J.; Soares, V.N.G.J.; Galán-Jiménez, J. Improving Delivery Probability in Mobile Opportunistic Networks with Social-Based Routing. Electronics 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, Y.; Toumpis, S.; Smyrnioudis, N. Digital twin approach to estimating and utilizing the capacity region of wireless ad hoc networks. Computer Networks 2024, 241, 110213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attaran, M.; Celik, B.G. Digital Twin: Benefits, use cases, challenges, and opportunities. Decision Analytics Journal 2023, 6, 100165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, F.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, C. Advancements and challenges of digital twins in industry. Nature Computational Science 2024, 4, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuñat Negueroles, S.; Reinosa Simón, R.; Julián, M.; Belsa, A.; Lacalle, I.; S-Julián, R.; Palau, C.E. A Blockchain-based Digital Twin for IoT deployments in logistics and transportation. Future Generation Computer Systems 2024, 158, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laubenbacher, R.; Mehrad, B.; Shmulevich, I.; Trayanova, N. Digital twins in medicine. Nature Computational Science 2024, 4, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltahlawy, A.M.; Aslan, H.K.; Abdallah, E.G.; Elsayed, M.S.; Jurcut, A.D.; Azer, M.A. A Survey on Parameters Affecting MANET Performance. Electronics 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesús-Azabal, M.; Berrocal, J.; Soares, V.N.G.J.; García-Alonso, J.; Galán-Jiménez, J. A self-sustainable opportunistic solution for emergency detection in ageing people living in rural areas. Wireless Networks 2023, 29, 2353–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesús-Azabal, M.; Herrera, J.L.; Laso, S.; Galán-Jiménez, J. OPPNets and Rural Areas: An Opportunistic Solution for Remote Communications. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing 2021, 2021, 8883501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galán-Jiménez, J.; Berrocal, J.; Garcia-Alonso, J.; Azabal, M.J. A Novel Routing Scheme for Creating Opportunistic Context-Virtual Networks in IoT Scenarios. Sensors 2019, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohta, T.; Nishi, M.; Terami, T.; Kakuda, Y. Information Dissemination Using MANET for Disaster Evacuation Support. IEICE Trans. Commun. 2019, 102, 670–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, E.; Sirswal, M.; Gupta, D.; Khanna, A. A Critical Review: SANET and Other Variants of Ad Hoc Networks. International Conference on Innovative Computing and Communications; Gupta, D., Khanna, A., Bhattacharyya, S., Hassanien, A.E., Anand, S., Jaiswal, A., Eds.; Springer Singapore: Singapore, 2021; pp. 1093–1114. [Google Scholar]
- Bruzgiene, R.; Narbutaite, L.; Adomkus, T. MANET Network in Internet of Things System. In Ad Hoc Networks; Ortiz, J.H., de la Cruz, A.P., Eds.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, 2017; chapter5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, S.; Shafi, I.; Abid, S. Improving energy efficiency in MANET’s for healthcar eenvironments. 2014; arXiv:cs.NI/1407.2747. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Yin, S.; Li, K.; Luo, H.; Kaynak, O. Industrial applications of digital twins. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences 2021, 379, 20200360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsoulakis, E.; Wang, Q.; Wu, H.; Shahriyari, L.; Fletcher, R.; Liu, J.; Achenie, L.; Liu, H.; Jackson, P.; Xiao, Y.; Syeda-Mahmood, T.; Tuli, R.; Deng, J. Digital twins for health: a scoping review. npj Digital Medicine 2024, 7, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, B.; Wu, Y.; He, Z.; Chen, Y.; Quek, T.Q.; Xu, C.Z. Digital Twin Empowered Mobile Edge Computing for Intelligent Vehicular Lane-Changing. IEEE Network 2021, 35, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakiri, A.; Gokhale, A.; Yahia, S.B.; Mellouli, N. A comprehensive survey on digital twin for future networks and emerging Internet of Things industry. Computer Networks 2024, 244, 110350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, S.; Yamazaki, T.; Miyoshi, T.; Taya, A.; Nishiyama, Y.; Sezaki, K. AMoND: Area-Controlled Mobile Ad-Hoc Networking With Digital Twin. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 85224–85236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Wang, J.; Huo, D.; Guizani, N.; Hu, L.; Chen, M. Digital Twin-Assisted URLLC-Enabled Task Offloading in Mobile Edge Network via Robust Combinatorial Optimization. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications 2023, 41, 3022–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Gu, W.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Min, G. Dynamic task offloading for digital twin-empowered mobile edge computing via deep reinforcement learning. China Communications 2023, 20, 164–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keränen, A.; Ott, J.; Kärkkäinen, T. The ONE simulator for DTN protocol evaluation. Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Simulation Tools and Techniques; ICST (Institute for Computer Sciences, Social-Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering): Brussels, BEL, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Neglia, G.; Kurose, J.; Towsley, D. Performance modeling of epidemic routing. Computer Networks 2007, 51, 2867–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagos Jenschke, T.; Dias de Amorim, M.; Fdida, S. Nearby connections strategies: Features, usage, and empirical performance evaluation. Internet of Things 2023, 23, 100895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Extending Wi-Fi Direct Single-Group Network to Multi-Group Network Based on Android Smartphone. Iraqi Journal of Science 2023, 64, 419–438. [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, J.; Li, M. A Rapid Flooding Approach Based on Adaptive Delay and Low-Power Sleep for BLE Mesh Networks. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 65323–65332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).