3.1. Determination of Fatty Acid Composition
Lipid oxidation in meat products frequently results in a decline in consumer quality, affecting key attributes such as flavor, aroma, color, texture, and both nutritional and biological value, while also reducing the shelf life. Furthermore, lipid oxidation products pose significant health risks due to their mutagenic, carcinogenic, and cytotoxic effects on humans [
30]. The progression of oxidative processes in fats, influenced by the type of fat and storage conditions, can lead to a noticeable degradation in the organoleptic properties of the product. This deterioration is further exacerbated by alterations in the fats during storage, which subsequently diminishes the nutritional value of the meat. The formation of carbonyl compounds during fat oxidation also promotes carbonyl-amine reactions, altering the color of dried meat and adversely impacting overall quality. These oxidative reactions are accelerated by increased temperature, light exposure, and the presence of catalysts such as meat pigments. Lipid oxidation can proceed through both enzymatic and non-enzymatic pathways, with the rate of oxidation largely governed by the degree of unsaturation in fatty acids. This rate escalates with the number of double bonds present in the fatty acid structure, making polyunsaturated fats particularly susceptible to oxidative degradation. Given the above, the primary interest was in evaluating the total amount of fatty acids in the sausages with purslane to understand oxidation processes, taking into account the quantity of unsaturated fatty acids.
Table 1 presents the main fatty acid composition of the studied samples.
From the 36 fatty acids analyzed, only 22 could be quantified. The sausages with purslane exhibited a slightly higher proportion of saturated fatty acids compared to the control sample—29.0% versus 28.6%. Although the difference in saturated fatty acid content is marginal, at just 0.4%, it is noteworthy that the control sample contained two additional fatty acids that were absent in the sausages with purslane. Similarly, there was virtually no difference in the levels of monounsaturated fatty acids between the samples. Both the control and sausages with purslane had nearly identical amounts—38.4% and 38.3%, respectively. When examining individual monounsaturated fatty acids, no significant variations were observed, with the exception of gondoic acid, which was present at 0.5% in the sausages with purslane and 1% in the control sample, and erucic acid, which was detected at 0.3% in the control but was not detected in the sausages with purslane. The most pronounced difference between the samples emerged in the content of omega-3 fatty acids. The incorporation of purslane into the product led to a nearly 1.3-fold increase in linolenic acid levels. The levels of omega-6 fatty acids, much like the monounsaturated fatty acids, showed minimal variation between the control and experimental samples—31.6% and 30.8%, respectively. It is also important to highlight that no trans fatty acid isomers (such as elaidic and linolelaidic acids) were detected in either sample.
When analyzing the total content of unsaturated fatty acids in the control sausage sample, it was observed that their overall level was marginally, yet noticeably, higher compared to the sausages containing Portulaca oleracea (purslane). This disparity could have implications for the shelf life and the susceptibility of fats to oxidative spoilage during storage, as unsaturated fatty acids, characterized by double or triple bonds between adjacent carbon atoms, are more prone to oxidation. In contrast, the inclusion of purslane in the sausage formulation appeared to exert a stabilizing effect on the oxidation process, as evidenced by the evaluation of oxidative spoilage indices, which are detailed later in the report. Additionally, sausages with purslane exhibited higher levels of stearic acid, a saturated fatty acid. Currently, synthetic antioxidants are extensively employed in the meat industry to prevent the oxidation of lipids and proteins. However, oxidative reactions during the production, retail, and storage phases of meat and meat products induce undesirable physicochemical alterations and off-flavors, detrimentally impacting product quality. These changes often lead to consumer dissatisfaction and potential economic losses. One common strategy to address this issue has been the use of synthetic antioxidants. However, with rising consumer awareness of health concerns and a growing preference for natural additives, the demand for natural alternatives to synthetic antioxidants has intensified [
31]. The objective of this study was to assess the protective effects of Portulaca oleracea extract against lipid and protein oxidation in meat during refrigerated storage over a 10-day period. The progression of oxidative spoilage in cooked products is presented in
Table 2,
Table 3 and
Table 4.
It can be concluded that the accumulation of peroxide values occurs at a relatively fast rate, likely driven by autoxidation. Autoxidation refers to the reaction between oxygen and unsaturated lipids, leading to the formation of hydroperoxides, which subsequently undergo further transformations. Since the accumulation of hydroperoxides is measured by the peroxide value, their levels initially rise and then begin to decrease, as was observed in the sausages containing Portulaca oleracea starting from day 10 of storage. On day 8, the peroxide value in the sausages with purslane reached 10.1 meq/kg, and by day 10, it had only slightly increased to 10.9 meq/kg. This is in contrast to the control samples, where the oxidation and accumulation of peroxides were more pronounced, with values rising from 8.6 meq/kg on day 8 to 12.5 meq/kg on day 10. This difference may be attributed to the antioxidant properties of purslane, which appears to have a stabilizing effect, or possibly due to a reduction in oxidation-initiating compounds during the first six days of storage. It is worth noting that, after day 6, the rate of peroxide accumulation slowed significantly.
The extent of oxidative degradation in the fat fraction of the sausages during refrigerated storage was further assessed through the thiobarbituric acid (TBA) value. The progression and severity of oxidative changes in the fat phase of meat products are positively correlated with the TBA value, which quantifies the presence of malondialdehyde. The relative stability of malondialdehyde allows for an accurate evaluation of the accumulation of secondary oxidation products. The formation of malondialdehyde is regarded as one of the adverse outcomes of lipid peroxidation, stemming from the breakdown of polyunsaturated fatty acids under the influence of free radicals, a process often associated with the development of undesirable off-flavors [
32]. Data on the malondialdehyde content in the sausage formulations under study are presented in
Table 3.
It was determined that during sausage storage, a gradual increase in TBA values was observed across all tested sausage formulations. The accumulation of malondialdehyde, relative to its initial concentration, resulted in a fourfold increase in the control sausages by the 10th day of storage, while sausages containing Portulaca oleracea (purslane) showed a 3.7-fold increase over the same period. Despite this rise, the absolute TBA values for all tested products remained below 0.5 mg/kg, indicating that the lipid fraction remained relatively stable throughout the storage period. It is important to note that TBA concentrations exceeding 0.5 mg/kg indicate the onset of oxidation, while values surpassing 1.0 mg/kg are considered indicative of significant oxidative degradation [
32]. The accumulation dynamics of the acid value (AV) in fats demonstrated noticeable signs of oxidative changes only after 8 days of storage. However, the rate of AV increase in the experimental sausages containing purslane was lower compared to the control samples. Interestingly, until the 6th day of storage, the AV in sausages with purslane was slightly higher than in the control, but after this point, the rate of fat spoilage accelerated significantly in the samples without purslane. Based on the analysis of these experimental findings, it can be concluded that the inclusion of Portulaca oleracea extract in sausage formulations has a notable impact on both the rate and extent of lipid oxidation, demonstrating its potential as an effective antioxidant in meat products.
In addition to lipid oxidation, proteins in meat products are also vulnerable to oxidative processes. One of the most commonly employed methods for assessing protein oxidation is the measurement of carbonyl derivatives. In this study, the total content of carbonyl compounds extracted from the protein matrix of both control sausages and those supplemented with Portulaca oleracea (purslane) was evaluated. This assessment was conducted only during the initial days of storage. Unfortunately, due to the lack of extended storage studies, it was not possible to monitor the accumulation of carbonyl compounds over time to fully examine purslane's role as an antioxidant and stabilizer in mitigating protein oxidation. However, it is notable that even in the early stages of storage, the control sausages displayed higher levels of carbonyl compounds compared to those with purslane supplementation. The presence of a higher proportion of unsaturated fatty acids and sulfur-containing amino acids in animal muscles leads to an elevated susceptibility of both lipids and proteins to oxidative processes. Lipid oxidation, in particular, is a critical factor impacting the quality of meat products, as it contributes to color changes, the development of off-flavors and odors, and the formation of toxic compounds, all of which pose potential risks to human health [
33]. The oxidation of both lipids and proteins can lead to undesirable changes in meat products from both a technological and sensory standpoint, including discoloration, defects in texture, diminished nutritional value, and negative health implications [
34].
A range of essential oils is being investigated for their strong antioxidant properties as natural alternatives to synthetic antioxidants used in the meat industry. Many of these oils are classified as Generally Recognized As Safe (GRAS) and have demonstrated beneficial effects on meat products when used alone or in combination with other essential oils, ingredients, or preservation technologies. The effectiveness of these oils depends on various factors such as concentration, potential synergistic effects, and the method of extraction. While steam distillation remains the most widely used method for extracting essential oils industrially, new extraction technologies have been developed to overcome the limitations of traditional methods, enabling the production of higher-quality essential oils [
35]. Portulaca oleracea extract is known for its potent antioxidant activity, attributed to its high concentration of polyphenols, short-chain organic acids, and saccharides. As a natural antioxidant, purslane offers several advantages over synthetic antioxidants, including superior stability, non-toxicity, and medicinal properties. Additionally, it is a low-calorie food with numerous therapeutic benefits [
36,
37,
38]. The use of dried purslane further enhances its shelf life and maintains its usability, as this form retains a greater proportion of its beneficial properties compared to extracts, whether water-based or solvent-based. This makes dried purslane a valuable ingredient for improving both the nutritional and functional properties of meat products.
3.3. Analysis of the Molecular Weight Distribution of Protein Fractions in the Sample by One-Dimensional Electrophoresis
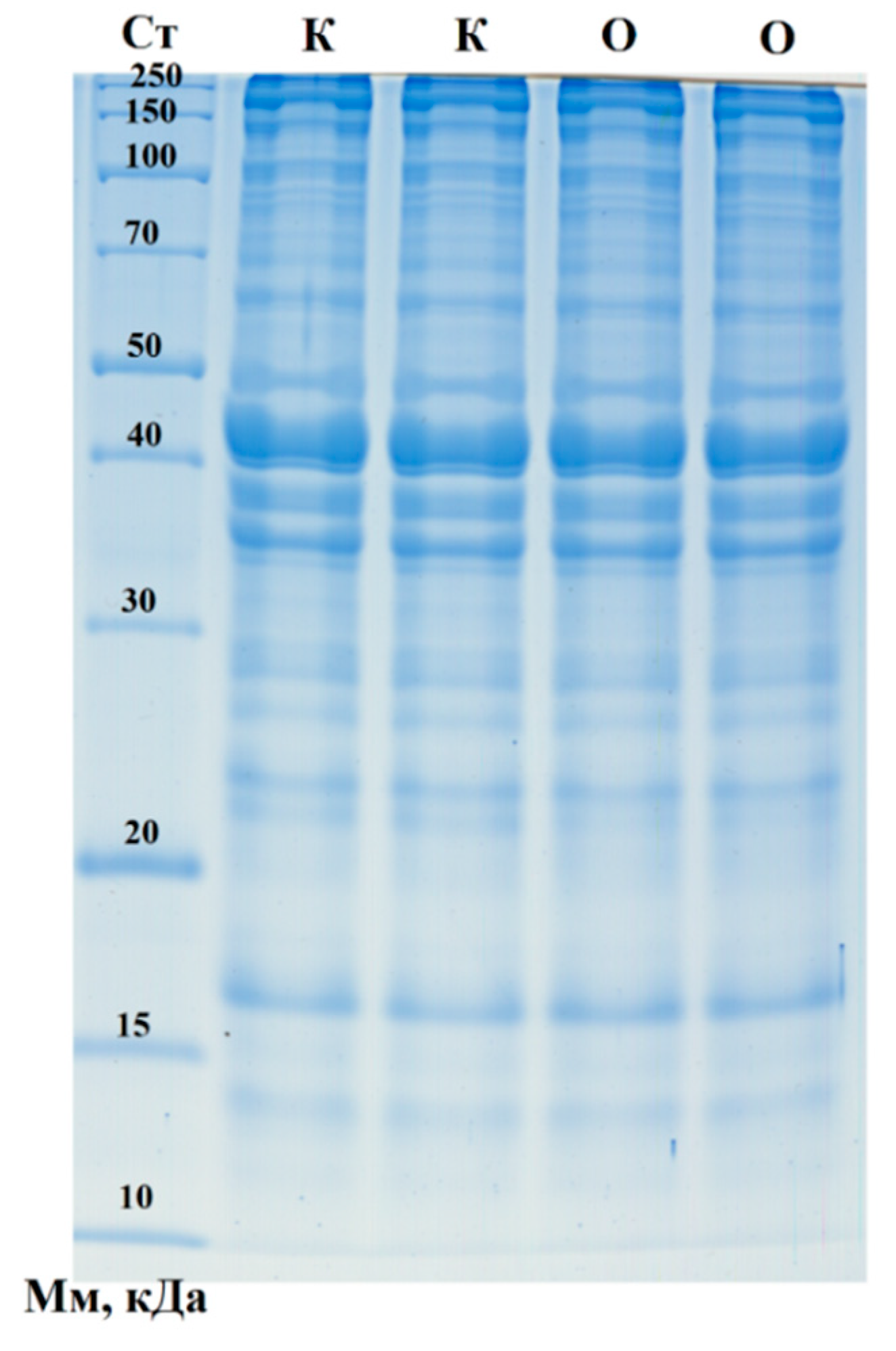
The analysis of the molecular weight distribution of protein fractions in the samples, performed via one-dimensional electrophoresis in polyacrylamide gel, yielded the results shown in
Figure 1.
A broad range of protein fractions was identified, including key structural proteins, with no significant differences observed between the control sausages and those containing Portulaca oleracea (purslane). Among the protein bands, several likely correspond to fragments of major proteins such as NADH dehydrogenase (21.7 kDa), frataxin (23.5 kDa), NADH dehydrogenase subunit K (31.1 kDa), myozenin-1 (31.6 kDa), and alpha-1D tubulin chain (50.2 kDa), which were more prominently expressed in the control sample. Additionally, other protein fractions were well-represented, including fragments of cofilin (18.5 kDa), cathepsin B (36.6 kDa), cysteine protease (39.9 kDa), RNA-binding protein (40.0 kDa), cyclin-dependent kinase (42.7 kDa), actin (42.0 kDa), serine/threonine-protein kinase (49.0 kDa), ribonuclease (64.2 kDa), heat shock protein (70.2 kDa), catenin beta-1 (85.5 kDa), spondin-1 (90.9 kDa), desmocollin 2 (100.4 kDa), histidine-rich calcium-binding protein (104.6 kDa), and supervillin (244.8 kDa). Moreover, densitometric analysis revealed two distinct proteins, unique to the purslane family, that were identified in the sausages containing purslane (
Table 6). These findings suggest the potential influence of purslane on the protein composition of the product, although the overall protein profile between the two sausage types remains largely similar.
As a result of computer-assisted densitometry, two plant-associated proteins (enzymes) were identified in the sausages containing Portulaca oleracea: 4,5-DOPA dioxygenase extradiol and Maturase K.
4,5-DOPA dioxygenase extradiol plays a crucial role in the formation of betalamic acid, which functions similarly to anthocyanins in other plants, serving as a structural, chromophoric, and bioactive component of plant betalain pigments [
39]. This enzyme catalyzes the oxidative cleavage of DOPA, producing 4,5-secodopa, which spontaneously cyclizes to form betalamic acid. Betalains not only serve as physiological pigments but also possess strong radical-scavenging activity [
40]. These water-soluble pigments are unique to plants in the Caryophyllaceae family and are simpler to synthesize and regulate compared to anthocyanins and carotenoids, beginning from tyrosine and regulated primarily by the MYB transcription factor [
41]. Functionally, betalains are analogous to anthocyanins, attracting animal pollinators and exhibiting high antioxidant and free radical-scavenging properties [
42]. In addition, betalains are used commercially as food colorants and additives, further highlighting their practical value [
43].
Maturase K (matK) is a plastid gene found in plants and is considered one of the most variable coding genes in angiosperms. It has been proposed as a molecular "barcode" for identifying terrestrial plants [
44]. Given its variability, matK could potentially serve as a marker to identify the addition of Portulaca oleracea in food products, though further research is necessary to confirm this hypothesis [
45]. While plant mitochondrial genes evolve slowly and are less effective in distinguishing between plant species, matK offers a more promising alternative for plant identification [
46].
The inclusion of purslane in meat products is thus a functionally justified approach, as it helps reduce oxidative lipid spoilage under various environmental conditions. This natural additive provides antioxidant protection without the need for synthetic stabilizers or chemical antioxidants in the product formulation, making it a valuable and sustainable ingredient.