Submitted:
05 October 2024
Posted:
07 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Variants on Genes Reported in the Literature with Association to OAD
2.2. Genes with Alternate Allele Exclusively in Cases but Not in Controls
2.2.1. Co-Occurrence of Variants on Genes and Association to OAD
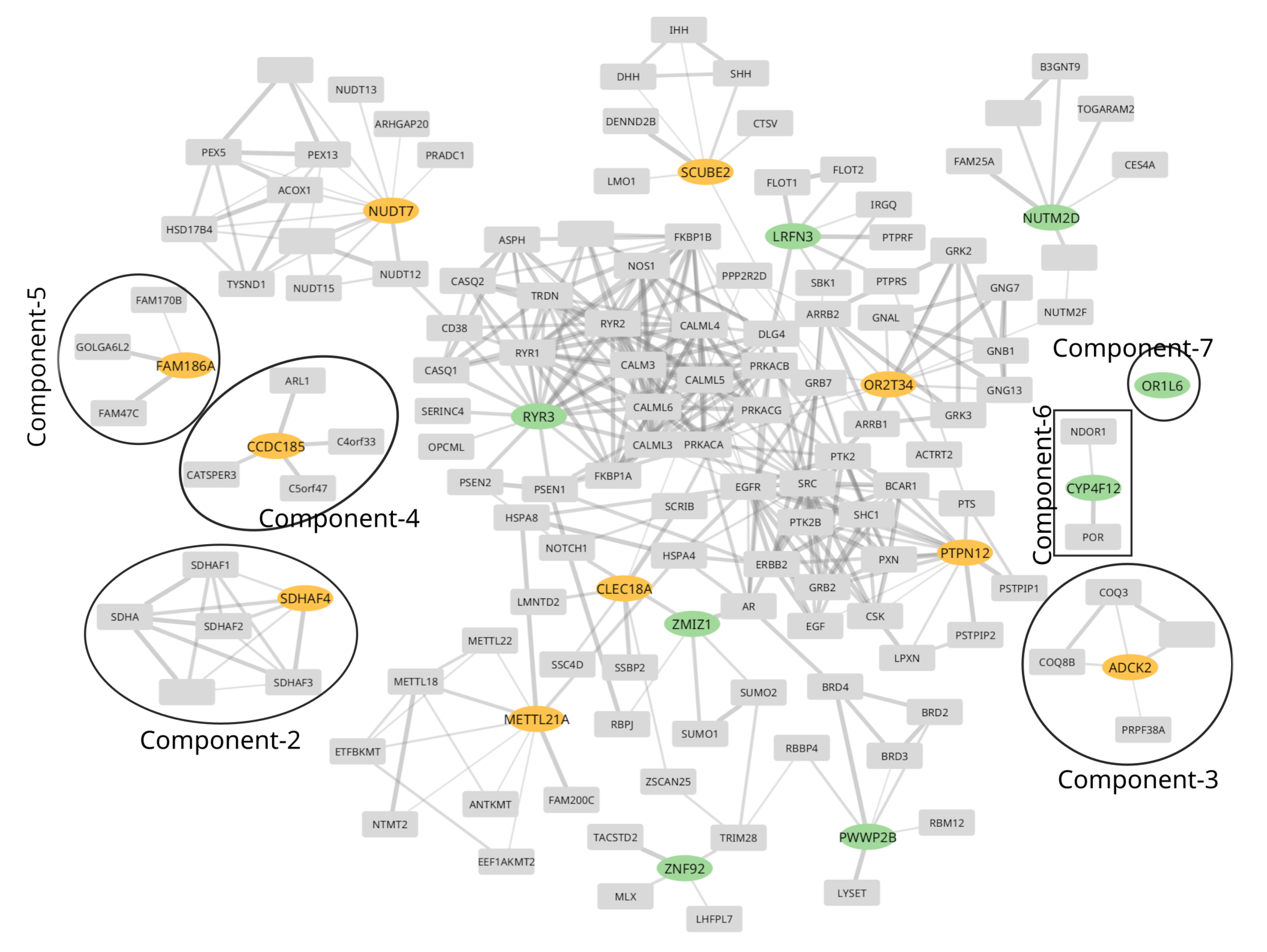
2.3. PPI Network Analysis of Genes of Interest
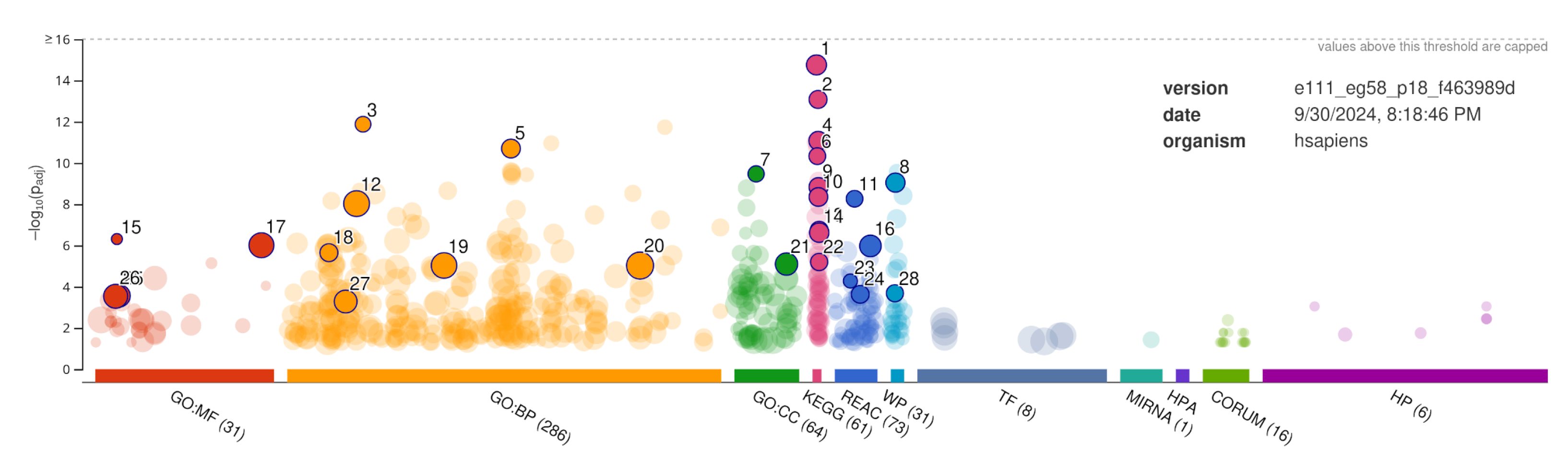
2.4. Gene Ontology and Functional Enrichment Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sample Collection
4.2. DNA Sequencing and Genotyping
4.3. Variants Filtering, Effects Prediction and Association Analysis
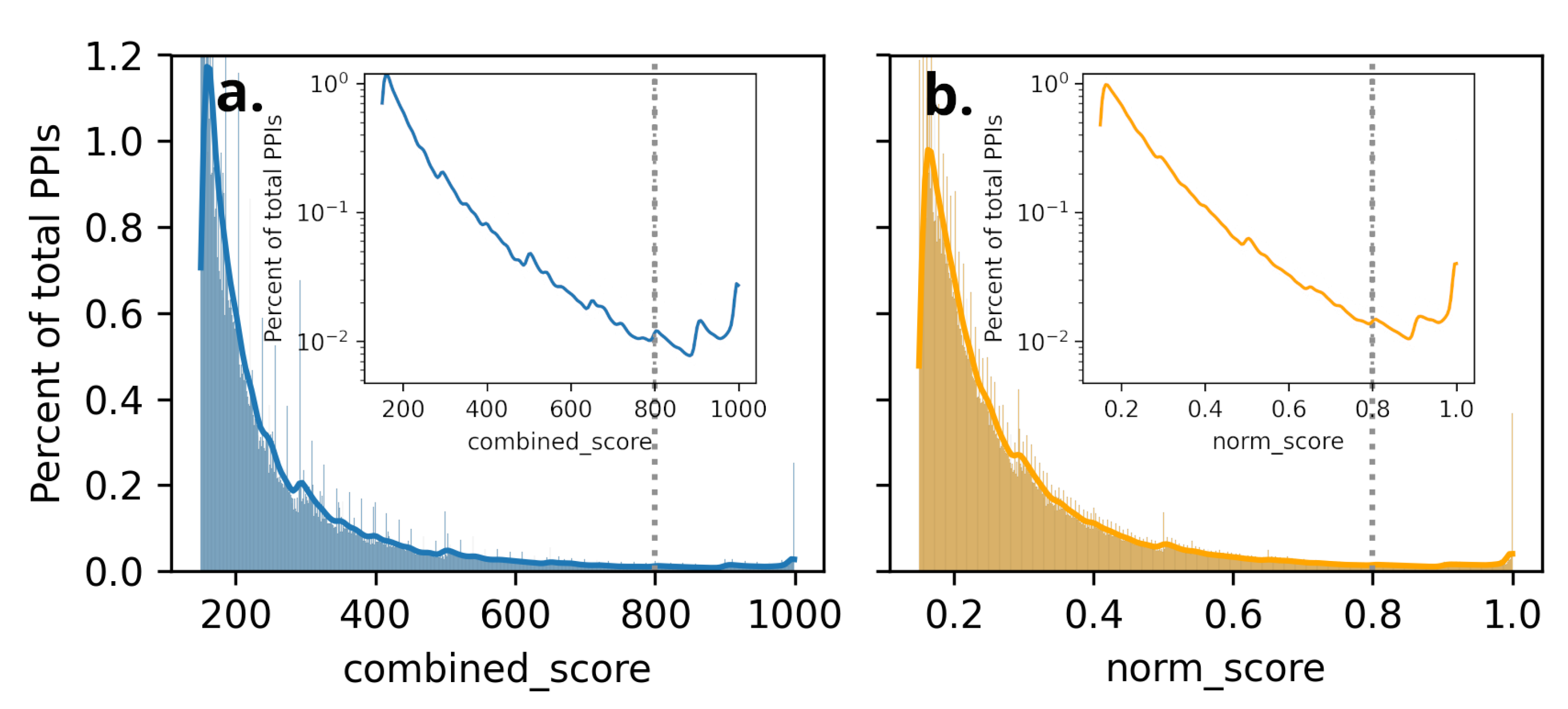
4.4. PPIs Network Construction and Analysis
4.5. Gene Ontology and Functional Enrichment
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DSM-IV | Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders 4th edition |
| GWAS | Genome-Wide Association Study |
| DSM | Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders |
| OAD | Opioid Addiction Disorder |
| GOI | Genes of Interest |
| SNP | Single Nucleotide Polymorphism |
| PPI | Protein-Protein Interaction |
| GO | Gene Ontology |
References
- Florence, C.; Luo, F.; Rice, K. The economic burden of opioid use disorder and fatal opioid overdose in the United States, 2017. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2021, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wall, R.; Rehm, J.; Fischer, B.; Brand’s, B.; Gliksman, L.; Stewart, J.; Medved, W.; Blake, J. Social costs of untreated opioid dependence. J. Urban Health 2000, 77, 688–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedegaard, H.; Miniño, A.M.; Spencer, M.R.; Warner, M. Drug overdose deaths in the United States, 1999–2020. NCHS Data Brief. 2021, 426, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florence, C.S.; Zhou, C.; Luo, F.; Xu, L. The Economic Burden of Prescription Opioid Overdose, Abuse, and Dependence in the United States, 2013. Med. Care 2016, 54, 901–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, A.; Marchand, J.; Mark, P. Loss of Life and Labor Productivity: The Canadian Opioid Crisis. Annals Am. Acad. Pol. & Soc. Sci. 2022, 703, 303–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, A.G.; Easter, M.M.; Lin, H.J.; Frisman, L.K.; Swanson, J.W.; Swartz, M.S. Associations between pharmacotherapy for opioid dependence and clinical and criminal justice outcomes among adults with co-occurring serious mental illness. J. Subst. Abuse Treat. 2018, 86, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grella, C.E.; Ostile, E.; Scott, C.K.; Dennis, M.; Carnavale, J. A Scoping Review of Barriers and Facilitators to Implementation of Medications for Treatment of Opioid Use Disorder within the Criminal Justice System. Int. J. Drug Policy 2020, 81, 102768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuang, M.T.; Lyons, M.J.; Meyer, J.M.; Doyle, T.; Eisen, S.A.; Goldberg, J.; True, W.; Lin, N.; Toomey, R.; Eaves, L. Co-occurrence of abuse of different drugs in men: the role of drug-specific and shared vulnerabilities. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1998, 55, 967–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendler, K.S.; Karkowski, L.M.; Neale, M.C.; Prescott, C.A. Illicit psychoactive substance use, heavy use, abuse, and dependence in a US population-based sample of male twins. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2000, 57, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuang, M.T.; Lyons, M.J.; Eisen, S.A.; Goldberg, J.; True, W.; Lin, N.; Meyer, J.M.; Toomey, R.; Faraone, S.V.; Eaves, L. Genetic influences on DSM-III-R drug abuse and dependence: a study of 3,372 twin pairs. Am. J. Med. Genet. 1996, 67, 473–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Foll, B.; Gallo, A.; Le Strat, Y.; Lu, L.; Gorwood, P. Genetics of dopamine receptors and drug addiction: a comprehensive review. Behav. Pharmacol. 2009, 20, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Liu, F.; Shang, Q.; Song, X.; Miao, X.; Wang, Z. Association between polymorphisms of DRD2 and DRD4 and opioid dependence: Evidence from the current studies. Am. J. Med. Genet., Part B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2011, 156, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, J.W.; Mazei-Robison, M.S.; Chaudhury, D.; Juarez, B.; LaPlant, Q.; Ferguson, D.; Feng, J.; Sun, H.; Scobie, K.N.; Damez-Werno, D.; Crumiller, M.; Ohnishi, Y.N.; Ohnishi, Y.H.; Mouzon, E.; Dietz, D.M.; Lobo, M.K.; Neve, R.L.; Russo, S.J.; Han, M.H.; Nestler, E.J. BDNF is a negative modulator of morphine action. Science 2012, 338, 124–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haerian, B.S.; Haerian, M.S. OPRM1 rs1799971 polymorphism and opioid dependence: evidence from a meta-analysis. Pharmacogenomics 2013, 14, 813–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beer, B.; Erb, R.; Pavlic, M.; Ulmer, H.; Giacomuzzi, S. Association of Polymorphisms in Pharmacogenetic Candidate Genes (OPRD1, GAL, ABCB1, OPRM1) with Opioid Dependence in European Population: A Case-Control Study. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, 75359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crist, R.; Ambrose-Lanci, L.; Vaswani, M.; Clarke, T.; Zeng, A.; Yuan, C.; Ferraro, T.; Hakonarson, H.; Kampman, K.; Dackis, C.; Pettinati, H.; O’Brien, C.; Oslin, D.; Doyle, G.; Lohoff, F.; Berrettini, W. Case–control association analysis of polymorphisms in the delta-opioid receptor, OPRD1, with cocaine and opioid addicted populations. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2013, 127, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutz, P.E.; Kieffer, B.L. The multiple facets of opioid receptor function: implications for addiction. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2013, 23, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, T.K.; Weiss, A.R.; Ferarro, T.N.; Kampman, K.M.; Dackis, C.A.; Pettinati, H.M.; O’brien, C.P.; Oslin, D.W.; Lohoff, F.W.; Berrettini, W.H. The dopamine receptor D2 (DRD2) SNP rs1076560 is associated with opioid addiction. Ann. Hum. Genet. 2014, 78, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bawor, M.; Dennis, B.B.; Tan, C.; Pare, G.; Varenbut, M.; Daiter, J.; Plater, C.; Worster, A.; Marsh, D.C.; Steiner, M.; Anglin, R.; Desai, D.; Thabane, L.; Samaan, Z. Contribution of BDNF and DRD2 genetic polymorphisms to continued opioid use in patients receiving methadone treatment for opioid use disorder: An observational study. Addict. Sci. Clin. Pract. 2015, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Rentsch, C.T.; Cheng, Z.; Kember, R.L.; Nunez, Y.Z.; Sherva, R.M.; Tate, J.P.; Dao, C.; Xu, K.; Polimanti, R.; Farrer, L.A.; Justice, A.C.; Kranzler, H.R.; Gelernter, J. Association of OPRM1 Functional Coding Variant with Opioid Use Disorder: A Genome-Wide Association Study. JAMA Psychiatry 2020, 77, 1072–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strang, J.; Volkow, N.D.; Degenhardt, L.; Hickman, M.; Johnson, K.; Koob, G.F.; Marshall, B.D.; Tyndall, M.; Walsh, S.L. Opioid use disorder. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2020, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, D.; Ji, F.; Yuferov, V.; Ho, A.; Chen, A.; Levran, O.; Ott, J.; Kreek, M. Genotype patterns that contribute to increased risk for or protection from developing heroin addiction. Mol. Psychiatry 2008, 13, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, D.A.; Ji, F.; Yuferov, V.; Ho, A.; He, C.; Ott, J.; Kreek, M.J. Genome-wide association study identifies genes that may contribute to risk for developing heroin addiction. Psychiatr. Genet. 2010, 20, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelernter, J.; Kranzler, H.R.; Sherva, R.; Koesterer, R.; Almasy, L.; Zhao, H.; Farrer, L.A. Genome-wide association study of opioid dependence: Multiple associations mapped to calcium and potassium pathways. Biol. Psychiatry 2014, 76, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Z.; Zhou, H.; Sherva, R.; Farrer, L.A.; Kranzler, H.R.; Gelernter, J. Genome-wide Association Study Identifies a Regulatory Variant of RGMA Associated With Opioid Dependence in European Americans. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 84, 762–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, E.C.; Agrawal, A.; Heath, A.C.; Bogdan, R.; Sherva, R.; Zhang, B.; Al-Hasani, R.; Bruchas, M.R.; Chou, Y.L.; Demers, C.H.; others. Evidence of CNIH3 involvement in opioid dependence. Mol. Psychiatry 2016, 21, 608–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, K.E.; Huhn, A.S.; Finan, P.H.; Mange, A.; Bergeria, C.L.; Maher, B.S.; Rabinowitz, J.A.; Strain, E.C.; Antoine, D. Polymorphisms in the A118G SNP of the OPRM1 gene produce different experiences of opioids: A human laboratory phenotype–genotype assessment. Addict. Biol. 2024, 29, e13355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, M.; Morici, J.F.; Zanoni, M.B.; Bekinschtein, P. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor: a key molecule for memory in the healthy and the pathological brain. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 472800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.R.; Walther, D.; Drgon, T.; Polesskaya, O.; Lesnick, T.G.; Strain, K.J.; De Andrade, M.; Bower, J.H.; Maraganore, D.M.; Uhl, G.R. Human brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) genes, splicing patterns, and assessments of associations with substance abuse and Parkinson’s Disease. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2005, 134, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crist, R.C.; Reiner, B.C.; Berrettini, W.H. A review of opioid addiction genetics. Curr. Opin. Psychol. 2019, 27, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaddis, N.; Mathur, R.; Marks, J.; Zhou, L.; Quach, B.; Waldrop, A.; Levran, O.; Agrawal, A.; Randesi, M.; Adelson, M.; Jeffries, P.W.; Martin, N.G.; Degenhardt, L.; Montgomery, G.W.; Wetherill, L.; Lai, D.; Bucholz, K.; Foroud, T.; Porjesz, B.; Runarsdottir, V.; Tyrfingsson, T.; Einarsson, G.; Gudbjartsson, D.F.; Webb, B.T.; Crist, R.C.; Kranzler, H.R.; Sherva, R.; Zhou, H.; Hulse, G.; Wildenauer, D.; Kelty, E.; Attia, J.; Holliday, E.G.; McEvoy, M.; Scott, R.J.; Schwab, S.G.; Maher, B.S.; Gruza, R.; Kreek, M.J.; Nelson, E.C.; Thorgeirsson, T.; Stefansson, K.; Berrettini, W.H.; Gelernter, J.; Edenberg, H.J.; Bierut, L.; Hancock, D.B.; Johnson, E.O. Multi-trait genome-wide association study of opioid addiction: OPRM1 and beyond. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gondré-Lewis, M.C.; Elman, I.; Alim, T.; Chapman, E.; Settles-Reaves, B.; Galvao, C.; Gold, M.S.; Baron, D.; Kazmi, S.; Gardner, E.; Gupta, A.; Dennen, C.; Blum, K. Frequency of the Dopamine Receptor D3 (rs6280) vs. Opioid Receptor µ1 (rs1799971) Polymorphic Risk Alleles in Patients with Opioid Use Disorder: A Preponderance of Dopaminergic Mechanisms? Biomedicines 2022, 10, 870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freiermuth, C.E.; Kisor, D.F.; Lambert, J.; Braun, R.; Frey, J.A.; Bachmann, D.J.; Bischof, J.J.; Lyons, M.S.; Pantalon, M.V.; Punches, B.E.; others. Genetic variants associated with opioid use disorder. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2023, 113, 1089–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, A.M.; Tang, N.L.; Cheung, B.K.; Stadlin, A. Dopamine receptor D4 gene -521C/T polymorphism is associated with opioid dependence through cold-pain responses. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. Blackwell Publishing Inc., 2008, Vol. 1139, pp. 20–26. [CrossRef]
- Chung, P.; Logge, W.B.; Riordan, B.C.; Haber, P.S.; Merriman, M.E.; Phipps-Green, A.; Topless, R.K.; Merriman, T.R.; Conner, T.; Morley, K.C. Genetic polymorphisms on OPRM1, DRD2, DRD4, and COMT in young adults: lack of association with alcohol consumption. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 549429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedrosa, E.; Kaushik, S.; Lachman, H.M. ChIP-chip analysis of neurexins and other candidate genes for addiction and neuropsychiatric disorders. J. Neurogenet. 2010, 24, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoltenberg, S.F.; Lehmann, M.K.; Christ, C.C.; Hersrud, S.L.; Davies, G.E. Associations among types of impulsivity, substance use problems and neurexin-3 polymorphisms. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2011, 119, e31–e38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLaren, W.; Gil, L.; Hunt, S.E.; Riat, H.S.; Ritchie, G.R.; Thormann, A.; Flicek, P.; Cunningham, F. The ensembl variant effect predictor. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, S.; Neale, B.; Todd-Brown, K.; Thomas, L.; Ferreira, M.A.; Bender, D.; Maller, J.; Sklar, P.; De Bakker, P.I.; Daly, M.J.; others. PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogari, N.M.; Al-Allaf, F.A.; Aljohani, A.; Taher, M.M.; Qutub, N.A.; Alhelfawi, S.; Alobaidi, A.; Alqudah, D.M.; Banni, H.; Dairi, G.; others. The co-existence of ADHD with autism in Saudi children: an analysis using next-generation DNA sequencing. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 548559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lie, E.; Ko, J.S.; Choi, S.Y.; Roh, J.D.; Cho, Y.S.; Noh, R.; Kim, D.; Li, Y.; Kang, H.; Choi, T.Y.; others. SALM4 suppresses excitatory synapse development by cis-inhibiting trans-synaptic SALM3–LAR adhesion. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lie, E.; Yeo, Y.; Lee, E.J.; Shin, W.; Kim, K.; Han, K.A.; Yang, E.; Choi, T.Y.; Bae, M.; Lee, S.; others. SALM4 negatively regulates NMDA receptor function and fear memory consolidation. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fill, M.; Copello, J.A. Ryanodine receptor calcium release channels. Physiol. Rev. 2002, 82, 893–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santulli, G.; Nakashima, R.; Yuan, Q.; Marks, A.R. Intracellular calcium release channels: an update. J. Physiol. 2017, 595, 3041–3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brini, M.; Calì, T.; Ottolini, D.; Carafoli, E. Neuronal calcium signaling: function and dysfunction. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2014, 71, 2787–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhu, C.; Tu, W.H.; Yang, N.; Qin, H.; Sun, Z. ZMIZ1 preferably enhances the transcriptional activity of androgen receptor with short polyglutamine tract. PLoS One 2011, 6, e25040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobiansky, D.J.; Wallin-Miller, K.G.; Floresco, S.B.; Wood, R.I.; Soma, K.K. Androgen regulation of the mesocorticolimbic system and executive function. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Kirsch, R.; Koutrouli, M.; Nastou, K.; Mehryary, F.; Hachilif, R.; Gable, A.L.; Fang, T.; Doncheva, N.T.; Pyysalo, S.; others. The STRING database in 2023: protein–protein association networks and functional enrichment analyses for any sequenced genome of interest. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D638–D646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raudvere, U.; Kolberg, L.; Kuzmin, I.; Arak, T.; Adler, P.; Peterson, H.; Vilo, J. g: Profiler: a web server for functional enrichment analysis and conversions of gene lists (2019 update). Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W191–W198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Auwera, G.A.; O’Connor, B.D. Genomics in the cloud: using Docker, GATK, and WDL in Terra; O’Reilly Media, 2020.
- Poplin, R.; Ruano-Rubio, V.; DePristo, M.A.; Fennell, T.J.; Carneiro, M.O.; Van der Auwera, G.A.; Kling, D.E.; Gauthier, L.D.; Levy-Moonshine, A.; Roazen, D. ; others. Scaling accurate genetic variant discovery to tens of thousands of samples. BioRxiv, 2011; 201178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caetano-Anolles, D. (How to) Filter variants either with VQSR or by hard-filtering. GATK [Internet], 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Danecek, P.; Bonfield, J.K.; Liddle, J.; Marshall, J.; Ohan, V.; Pollard, M.O.; Whitwham, A.; Keane, T.; McCarthy, S.A.; Davies, R.M.; Li, H. Twelve years of SAMtools and BCFtools. GigaScience 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Gene | Chra | Gene BP(beg)b | Gene BP(end)c | Variant (rsID) | Sample population | Opioid exposed controls | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OPRM1 | chr6 | 154039240 | 154132356 | rs1799971 | EuAd, AfAe | Yes | [14,15,20] |
| OPRD1 | chr1 | 28812170 | 28871267 | rs2236861 | EuA, AfA; EuA, AfA | Yes; No | [15,16] |
| DRD2 | chr11 | 113409605 | 113475398 | rs1799978 | Euf, NaAmg, Asnh, Peri | Yes | [19] |
| BDNF | chr11 | 27654893 | 27700455 | rs6265 | Euf, NaAmg, Asnh, Peri | Yes | [19] |
| APBB2 | chr4 | 40810027 | 41214542 | rs114070671 | EuAmk, AfAmm | No | [24] |
| KCNG2 | chr18 | 79797938 | 79900100 | rs62103177 | EuAm, AfAm | No | [24,31] |
| KCNC1 | chr11 | 17734781 | 17783057 | rs60349741 | EuAm, AfAm | No | [24] |
| CNIH3 | chr1 | 224616317 | 224740554 | rs1436175, rs10799590, rs12130499, rs298733, rs1436171, and rs1369846 | EuAun | Yes | [26] |
| RGMA | chr15 | 93035271 | 93089211 | rs12442183 | EuAm | Yes | [25] |
| DRD3 | chr3 | 114127580 | 114179052 | rs324029 and rs2654754 | EuAm, AfAm | No | [32,33] |
| DRD4 | chr11 | 637269 | 640706 | rs1800955 | Chinese males | No | [34,35] |
| NRXN3 | chr14 | 78170373 | 79868291 | rs8019381 p | Caucasians | No | [36,37] |
| Chra | Variantb or rsID | BPc | Gene | F_Ad | F_Ue | Conseqn.f | p-value | ORg | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | TGAAA>T | 114142739 | DRD3 | 0.0909 | 0.5455 | ivh | 10.48 | 0.0012 | 0.0833 |
| 18 | rs76838079 | 79873271 | KCNG2 | 0.3182 | 0 | iv | 8.324 | 0.0039 | NA |
| 3 | rs73232565 | 114124222 | - | 0 | 0.2727 | - | 7.527 | 0.0061 | 0 |
| 11 | rs3051820 | 17785864 | - | 0.2727 | 0.6818 | - | 7.379 | 0.0066 | 0.175 |
| 4 | rs1011069 | 41217734 | - | 0.2727 | 0 | - | 6.947 | 0.0084 | NA |
| 14 | rs143010574 | 79227804 | NRXN3 | 0.2727 | 0 | gutvi, iv | 6.947 | 0.0084 | NA |
| 4 | rs7695309 | 41216892 | - | 0.3636 | 0.0455 | - | 6.844 | 0.0089 | 12 |
| 14 | rs7145683 | 79241818 | NRXN3 | 0.3636 | 0.0455 | gutv, iv | 6.844 | 0.0089 | 12 |
| 14 | G>GA | 79242068 | NRXN3 | 0.3636 | 0.0455 | gutv, iv | 6.844 | 0.0089 | 12 |
| 14 | rs12889183 | 79360638 | NRXN3 | 0.5 | 0.1364 | iv | 6.705 | 0.0096 | 6.333 |
| 14 | rs11625994 | 79364803 | NRXN3 | 0.5 | 0.1364 | iv | 6.705 | 0.0096 | 6.333 |
| 14 | rs8008332 | 79365491 | NRXN3 | 0.5 | 0.1364 | iv | 6.705 | 0.0096 | 6.333 |
| 14 | rs2167150 | 79367835 | NRXN3 | 0.5 | 0.1364 | iv | 6.705 | 0.0096 | 6.333 |
| Chra | Variantb or rsID | BPc | Gene | C_Ad | Conseqn.e | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12 | rs773026868 | 50352078 | FAM186A | 11 | fsvf | 13.25 | 0.000272 |
| 11 | rs60494098 | 9091455 | SCUBE2 | 10 | mvg | 12.94 | 0.000321 |
| 1 | rs10907376 | 223394461 | CCDC185 | 9 | mv | 11.31 | 0.000769 |
| 13 | C>A | 29324631 | MTUS2 | 8 | mv | 9.778 | 0.001766 |
| 7 | rs3750050 | 77627396 | PTPN12 | 7 | mv | 8.324 | 0.003912 |
| 7 | rs1046515 | 140694787 | ADCK2 | 7 | mv | 8.324 | 0.003912 |
| 16 | rs308925 | 77735937 | NUDT7 | 7 | mv | 8.324 | 0.003912 |
| 2 | A>G | 207613128 | METTL21A | 7 | mv | 8.324 | 0.003912 |
| 6 | rs1048886 | 70579486 | SDHAF4 | 7 | mv | 8.324 | 0.003912 |
| 16 | rs3869427 | 69954416 | CLEC18A | 7 | mv | 8.324 | 0.003912 |
| 1 | rs147489167 | 248574363 | OR2T34 | 7 | mv | 8.324 | 0.003912 |
| Chra | Gene | #variantsb | list of C_Ac | list of Consequencesd |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | ZMIZ1 | 7 | 5, 5, 5, 4, 4, 4, 4 | fsve, mvf, fsv, fsv, fsv, fsv, fsv |
| 19 | LRFN3 | 6 | 5, 5, 5,5, 5, 5 | idg, pavh, iik, fsv, fsv, fsv |
| 9 | OR1L6 | 4 | 4, 4, 4, 4 | mv, mv, mv, mv |
| 15 | RYR3 | 3 | 5, 5, 4 | fsv, fsv, sgm & fsv |
| 10 | PWWP2B | 3 | 4, 4, 4 | sg, mv, fsv |
| 7 | ZNF92 | 2 | 6, 6 | mv, mv |
| 19 | CYP4F12 | 3 | 4, 4, 4 | mv, mv, sdvn & ntvp |
| 10 | NUTM2D | 2 | 5, 5 | mv, mv |
| ID | Source | Term ID | Term name | (query) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | KEGG | KEGG:04020 | Calcium signaling pathway | |
| 2 | KEGG | KEGG:04713 | Circadian entrainment | |
| 3 | GO:BP | GO:0014808 | release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol by sarcoplasmic reticulum | |
| 4 | KEGG | KEGG:04728 | Dopaminergic synapse | |
| 5 | GO:BP | GO:0051208 | sequestering of calcium ion | |
| 6 | KEGG | KEGG:04340 | Hedgehog signaling pathway | |
| 7 | GO:CC | GO:0033017 | sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane | |
| 8 | WP | WP:WP3929 | Chemokine signaling pathway | |
| 9 | KEGG | KEGG:04921 | Oxytocin signaling pathway | |
| 10 | KEGG | KEGG:04915 | Estrogen signaling pathway | |
| 11 | REAC | REAC:R-HSA-5578775 | Ion homeostasis | |
| 12 | GO:BP | GO:0010646 | regulation of cell communication | |
| 13 | KEGG | KEGG:05032 | Morphine addiction | |
| 14 | KEGG | KEGG:05034 | Alcoholism | |
| 15 | GO:MF | GO:0005219 | ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity | |
| 16 | REAC | REAC:R-HSA-9006934 | Signaling by Receptor Tyrosine Kinases | |
| 17 | GO:MF | GO:0140096 | catalytic activity, acting on a protein | |
| 18 | GO:BP | GO:0006942 | regulation of striated muscle contraction | |
| 19 | GO:BP | GO:0036211 | protein modification process | |
| 20 | GO:BP | GO:1901564 | organonitrogen compound metabolic process | |
| 21 | GO:CC | GO:0098797 | plasma membrane protein complex | |
| 22 | KEGG | KEGG:05031 | Amphetamine addiction | |
| 23 | REAC | REAC:R-HSA-180292 | GAB1 signalosome | |
| 24 | REAC | REAC:R-HSA-111885 | Opioid Signalling | |
| 25 | GO:MF | GO:0005509 | calcium ion binding | |
| 26 | GO:MF | GO:0005102 | signaling receptor binding | |
| 27 | GO:BP | GO:0009725 | response to hormone | |
| 28 | WP | WP:WP3680 | Physico chemical features and toxicity associated pathways |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





