Submitted:
24 September 2024
Posted:
07 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
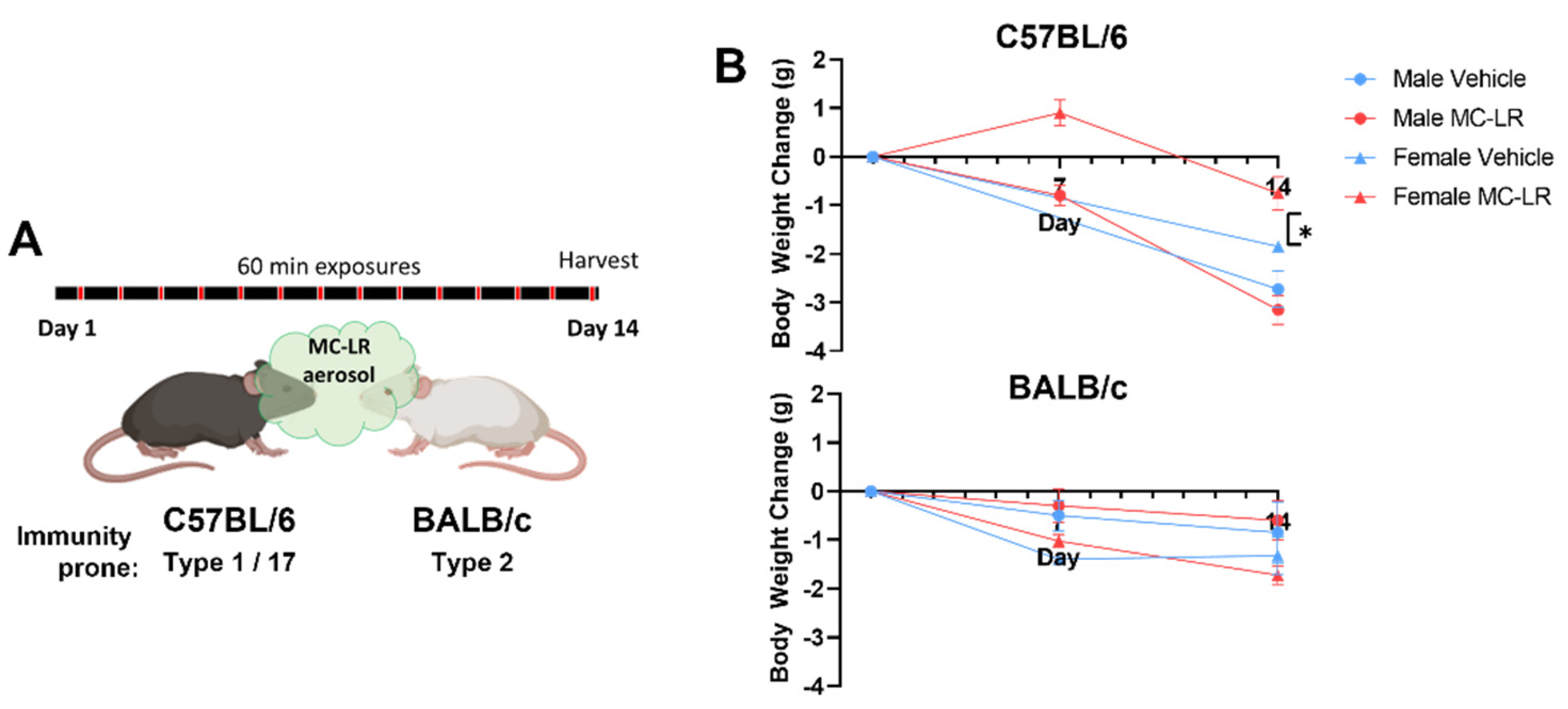
2.1. Murine Strains Exposed to MC-LR via Aerosol Inhalation
2.2. Microcystin-LR Aerosol Inhalation Induces Upregulation of Type 1/Type 17 Inflammation Related Proteins in Murine Lung
2.3. Microcystin-LR Aerosol Exposure Induces Airway Inflammation
2.4. Microcystin-LR Aerosol Inhalation Alters the Lipidomic Profile of the Lungs
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Animals and Aerosol Exposures
5.2. Histology Preparation and Stain
5.3. Histology Scoring
5.4. Bronchoalveolar Lavage
5.5. Protein Measurements
5.6. Lipidomics by Mass Spectroscopy
5.6. Statistics
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xiao, X.; et al. Warming Amplifies the Frequency of Harmful Algal Blooms with Eutrophication in Chinese Coastal Waters. Environmental Science & Technology 2019, 53, 13031–13041. [Google Scholar]
- Nwankwegu, A.S.; et al. Harmful algal blooms under changing climate and constantly increasing anthropogenic actions: the review of management implications. 3 Biotech 2019, 9, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, D.M.; et al. Harmful algal blooms and eutrophication: Examining linkages from selected coastal regions of the United States. Harmful Algae 2008, 8, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazard, S.; et al. Tiny Microbes with a Big Impact: The Role of Cyanobacteria and Their Metabolites in Shaping Our Future. Mar Drugs 2016, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, M.F.; et al. Cyanotoxins and Food Contamination in Developing Countries: Review of Their Types, Toxicity, Analysis, Occurrence and Mitigation Strategies. Toxins (Basel) 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gӓrtner, G.; et al. Algal Toxic Compounds and Their Aeroterrestrial, Airborne and other Extremophilic Producers with Attention to Soil and Plant Contamination: A Review. Toxins (Basel) 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittmann, E.; et al. Cyanobacterial toxins: biosynthetic routes and evolutionary roots. FEMS Microbiol Rev 2013, 37, 23–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernoff, N.; et al. The Comparative Toxicity of 10 Microcystin Congeners Administered Orally to Mice: Clinical Effects and Organ Toxicity. Toxins (Basel) 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolbright, B.L.; et al. Microcystin-LR induced liver injury in mice and in primary human hepatocytes is caused by oncotic necrosis. Toxicon 2017, 125, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernoff, N.; et al. Lack of teratogenicity of microcystin-LR in the mouse and toad. J Appl Toxicol 2002, 22, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arman, T.; et al. Sub-chronic microcystin-LR renal toxicity in rats fed a high fat/high cholesterol diet. Chemosphere 2021, 269, 128773–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lad, A.; et al. Chronic Low Dose Oral Exposure to Microcystin-LR Exacerbates Hepatic Injury in a Murine Model of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Toxins (Basel) 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lad, A.; et al. Antioxidant Therapy Significantly Attenuates Hepatotoxicity following Low Dose Exposure to Microcystin-LR in a Murine Model of Diet-Induced Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Antioxidants (Basel) 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, R.C.; et al. Exposure to the Harmful Algal Bloom (HAB) Toxin Microcystin-LR (MC-LR) Prolongs and Increases Severity of Dextran Sulfate Sodium (DSS)-Induced Colitis. Toxins (Basel) 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, R.C.; et al. CD40 Receptor Knockout Protects against Microcystin-LR (MC-LR) Prolongation and Exacerbation of Dextran Sulfate Sodium (DSS)-Induced Colitis. Biomedicines 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, N.E.; et al. Harmful Algal Bloom Toxins in Aerosol Generated from Inland Lake Water. Environ Sci Technol 2020, 54, 4769–4780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backer, L.C.; et al. Recreational exposure to microcystins during algal blooms in two California lakes. Toxicon 2010, 55, 909–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, I.; et al. Epidemiology of recreational exposure to freshwater cyanobacteria--an international prospective cohort study. BMC Public Health 2006, 6, 93–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannuzzi, L.; et al. An acute case of intoxication with cyanobacteria and cyanotoxins in recreational water in Salto Grande Dam, Argentina. Mar Drugs 2011, 9, 2164–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, J.M.; et al. The toxicity of microcystin LR in mice following 7 days of inhalation exposure. Toxicon 2005, 45, 691–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, A.M.; et al. Exposure to microcystin among coastal residents during a cyanobacteria bloom in Florida. Harmful Algae 2020, 92, 101769–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, V.R.; et al. Repeated intranasal exposure to microcystin-LR affects lungs but not nasal epithelium in mice. Toxicon 2015, 104, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picanco, M.R.; et al. Toxicity of a cyanobacterial extract containing microcystins to mouse lungs. Braz J Med Biol Res 2004, 37, 1225–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, R.M.; et al. Effects of microcystin-LR on mouse lungs. Toxicon 2007, 50, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breidenbach, J.D.; et al. Microcystin-LR aerosol induces inflammatory responses in healthy human primary airway epithelium. Environ Int 2022, 169, 107531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, I.; et al. Why do some asthma patients respond poorly to glucocorticoid therapy? Pharmacol Res 2020, 160, 105189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, A.; et al. Genetic background determines susceptibility to experimental immune-mediated blepharoconjunctivitis: comparison of Balb/c and C57BL/6 mice. Exp Eye Res 2006, 82, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gueders, M.M.; et al. Mouse models of asthma: a comparison between C57BL/6 and BALB/c strains regarding bronchial responsiveness, inflammation, and cytokine production. Inflamm Res 2009, 58, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosmann, T.R. and Coffman, R.L. TH1 and TH2 cells: different patterns of lymphokine secretion lead to different functional properties. Annu Rev Immunol 1989, 7, 145–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, G.M.; et al. Pulmonary and hepatic injury after sub-chronic exposure to sublethal doses of microcystin-LR. Toxicon 2016, 112, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, V.R.; et al. Lung and liver responses to 1- and 7-day treatments with LASSBio-596 in mice subchronically intoxicated by microcystin-LR. Toxicon 2018, 141, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, G.M.; et al. Can LASSBio 596 and dexamethasone treat acute lung and liver inflammation induced by microcystin-LR? Toxicon 2010, 56, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, R.C.; et al. Microcystin-LR (MC-LR) Triggers Inflammatory Responses in Macrophages. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metzemaekers, M.; et al. Neutrophil chemoattractant receptors in health and disease: double-edged swords. Cell Mol Immunol 2020, 17, 433–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishalian, I.; et al. Neutrophils recruit regulatory T-cells into tumors via secretion of CCL17--a new mechanism of impaired antitumor immunity. Int J Cancer 2014, 135, 1178–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, J.R.; et al. Macrophage-derived chemokine (CCL22) is a novel mediator of lung inflammation following hemorrhage and resuscitation. Shock 2014, 42, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.Y.; et al. IL-1alpha modulates neutrophil recruitment in chronic inflammation induced by hydrocarbon oil. J Immunol 2011, 186, 1747–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumpey, T.M.; et al. Role for macrophage inflammatory protein 2 (MIP-2), MIP-1alpha, and interleukin-1alpha in the delayed-type hypersensitivity response to viral antigen. J Virol 2002, 76, 8050–8057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laan, M.; et al. Neutrophil recruitment by human IL-17 via C-X-C chemokine release in the airways. J Immunol 1999, 162, 2347–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrington, L.E.; et al. Interleukin 17-producing CD4+ effector T cells develop via a lineage distinct from the T helper type 1 and 2 lineages. Nat Immunol 2005, 6, 1123–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; et al. A distinct lineage of CD4 T cells regulates tissue inflammation by producing interleukin 17. Nat Immunol 2005, 6, 1133–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trinchieri, G.; et al. Natural killer cell stimulatory factor (NKSF) or interleukin-12 is a key regulator of immune response and inflammation. Prog Growth Factor Res 1992, 4, 355–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shepherd, R.; et al. Sexual Dimorphism in Innate Immunity: The Role of Sex Hormones and Epigenetics. Front Immunol 2020, 11, 604000–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, S.; et al. Clara cell secretory protein and phospholipase A2 activity modulate acute ventilator-induced lung injury in mice. J Appl Physiol (1985) 2005, 98, 1264–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagase, T.; et al. Acute lung injury by sepsis and acid aspiration: a key role for cytosolic phospholipase A2. Nat Immunol 2000, 1, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, S.; et al. Time and pressure dependence of transvascular Clara cell protein, albumin, and IgG transport during ventilator-induced lung injury in mice. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2004, 286, L604–L612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, J.C.; et al. Gadolinium prevents high airway pressure-induced permeability increases in isolated rat lungs. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1998, 84, 1113–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clancy, R.M.; et al. Oxidation of leukotrienes at the omega end: demonstration of a receptor for the 20-hydroxy derivative of leukotriene B4 on human neutrophils and implications for the analysis of leukotriene receptors. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 1984, 81, 5729–5733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, K.A.Z.; et al. Urinary Metabolites of Leukotriene B4 in the Human Subject. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 24449–24460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; et al. Leukotriene B4 Activates Pulmonary Artery Adventitial Fibroblasts in Pulmonary Hypertension. Hypertension 2015, 66, 1227–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Husseini, A.; et al. Increased eicosanoid levels in the Sugen/chronic hypoxia model of severe pulmonary hypertension. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0120157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.H.; et al. Lipoxin A4 and lipoxin B4 inhibit chemotactic responses of human neutrophils stimulated by leukotriene B4 and N-formyl-L-methionyl-L-leucyl-L-phenylalanine. Clin Sci (Lond) 1989, 77, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, B.D.; et al. Multi-pronged inhibition of airway hyper-responsiveness and inflammation by lipoxin A(4). Nat Med 2002, 8, 1018–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Node, K.; et al. Anti-inflammatory properties of cytochrome P450 epoxygenase-derived eicosanoids. Science 1999, 285, 1276–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, S.J.; et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of epoxyeicosatrienoic acids. International journal of vascular medicine 2012, 2012, 605101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellien, J. and Joannides, R. Epoxyeicosatrienoic acid pathway in human health and diseases. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2013, 61, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddipati, K.R. Non-inflammatory Physiology of “Inflammatory” Mediators—Unalamation, a New Paradigm. Front Immunol 2020, 11, 580117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, F.A. Transformations of 5-HETE by activated keratinocyte 15-lipoxygenase and the activation mechanism. Lipids 1990, 25, 618–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Flaherty, J.T. and Thomas, M.J. Effect of 15-lipoxygenase-derived arachidonate metabolites on human neutrophil degranulation. Prostaglandins Leukot Med 1985, 17, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, E.; et al. Identification of a novel and highly potent eosinophil chemotactic lipid in human eosinophils treated with arachidonic acid. J Immunol 1990, 144, 1893–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.W.; et al. Proinflammatory actions of thromboxane receptors to enhance cellular immune responses. J Immunol 2003, 171, 6389–6395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; et al. Role of prostacyclin in the cardiovascular response to thromboxane A2. Science 2002, 296, 539–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belhassen, L.; et al. Improved endothelial function by the thromboxane A2 receptor antagonist S 18886 in patients with coronary artery disease treated with aspirin. J Am Coll Cardiol 2003, 41, 1198–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lumley, P.; et al. GR32191, a highly potent and specific thromboxane A2 receptor blocking drug on platelets and vascular and airways smooth muscle in vitro. Br J Pharmacol 1989, 97, 783–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loomba, R.; et al. Polyunsaturated fatty acid metabolites as novel lipidomic biomarkers for noninvasive diagnosis of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. J Lipid Res 2015, 56, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; et al. Effects of Microcystin-LR on the Microstructure and Inflammation-Related Factors of Jejunum in Mice. Toxins (Basel) 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frolov, A.; et al. Anti-inflammatory properties of prostaglandin E2: deletion of microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1 exacerbates non-immune inflammatory arthritis in mice. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 2013, 89, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birrell, M.A.; et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of PGE2 in the lung: role of the EP4 receptor subtype. Thorax 2015, 70, 740–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.; et al. Macrophage responses to lipopolysaccharide are modulated by a feedback loop involving prostaglandin E2, dual specificity phosphatase 1 and tristetraprolin. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 4350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notter, R.H. (2000) Introduction. In Lung Surfactants: Basic Science and Clinical Applications (Lenfant, C., ed), pp. 2.
- Nakagawa, T.; et al. Optimum immunohistochemical procedures for analysis of macrophages in human and mouse formalin fixed paraffin-embedded tissue samples. J Clin Exp Hematop 2017, 57, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapp, S.; et al. Pulmonary lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-binding protein inhibits the LPS-induced lung inflammation in vivo. J Immunol 2006, 176, 3189–3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; et al. Renal Fibrosis Is Significantly Attenuated Following Targeted Disruption of Cd40 in Experimental Renal Ischemia. J Am Heart Assoc 2020, 9, e014072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, D.J.; et al. Elevated Plasma Marinobufagenin, An Endogenous Cardiotonic Steroid, Is Associated With Right Ventricular Dysfunction and Nitrative Stress in Heart Failure. Circ Heart Fail 2015, 8, 1068–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; et al. mTORC1 is a mechanosensor that regulates surfactant function and lung compliance during ventilator-induced lung injury. JCI Insight 2021, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maddipati, K.R. and Zhou, S.L. Stability and analysis of eicosanoids and docosanoids in tissue culture media. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat 2011, 94, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markworth, J.F.; et al. Human inflammatory and resolving lipid mediator responses to resistance exercise and ibuprofen treatment. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 2013, 305, R1281–R1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddipati, K.R.; et al. Eicosanomic profiling reveals dominance of the epoxygenase pathway in human amniotic fluid at term in spontaneous labor. FASEB J 2014, 28, 4835–4846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




