Submitted:
07 October 2024
Posted:
08 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
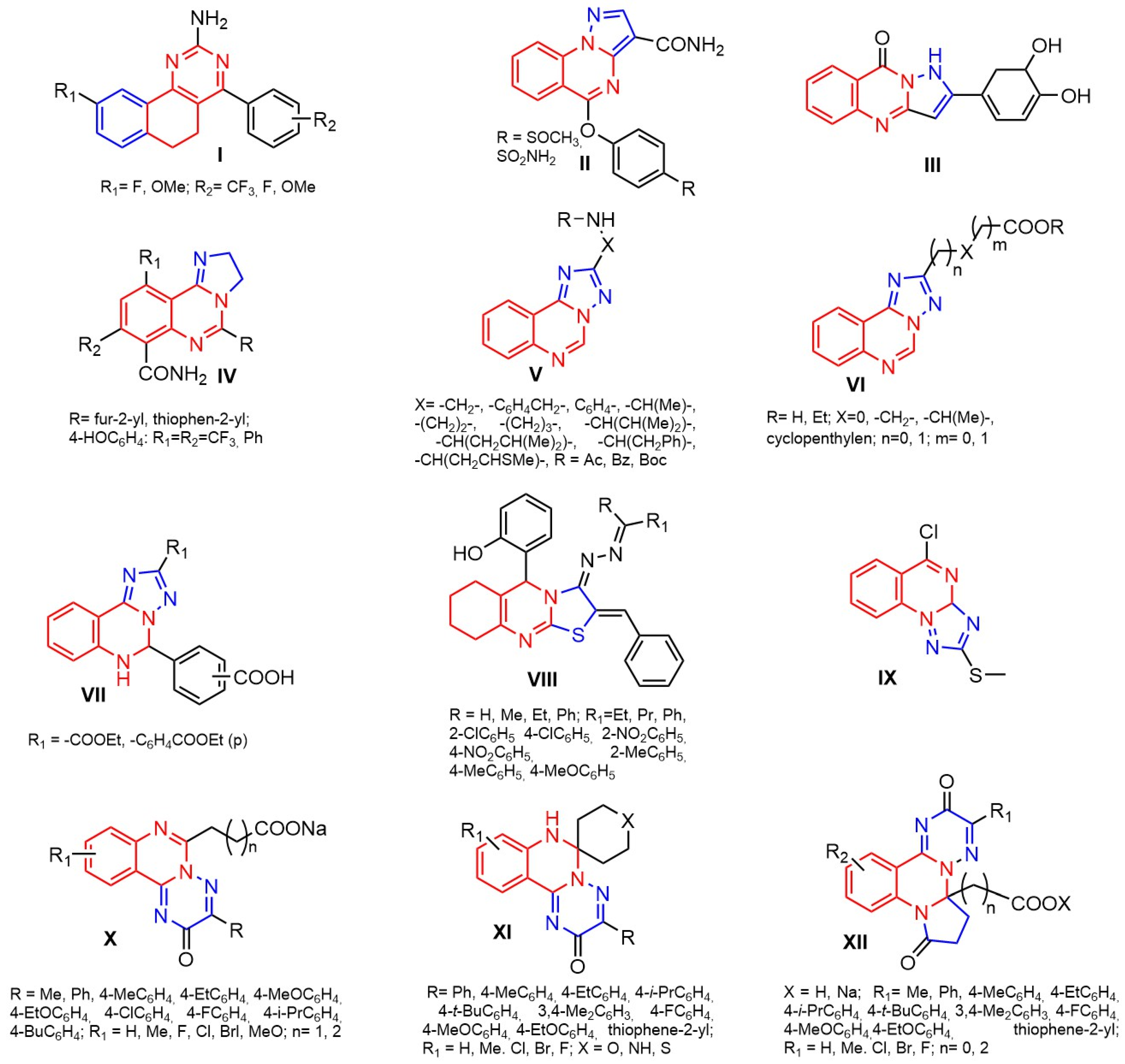
1. Introduction
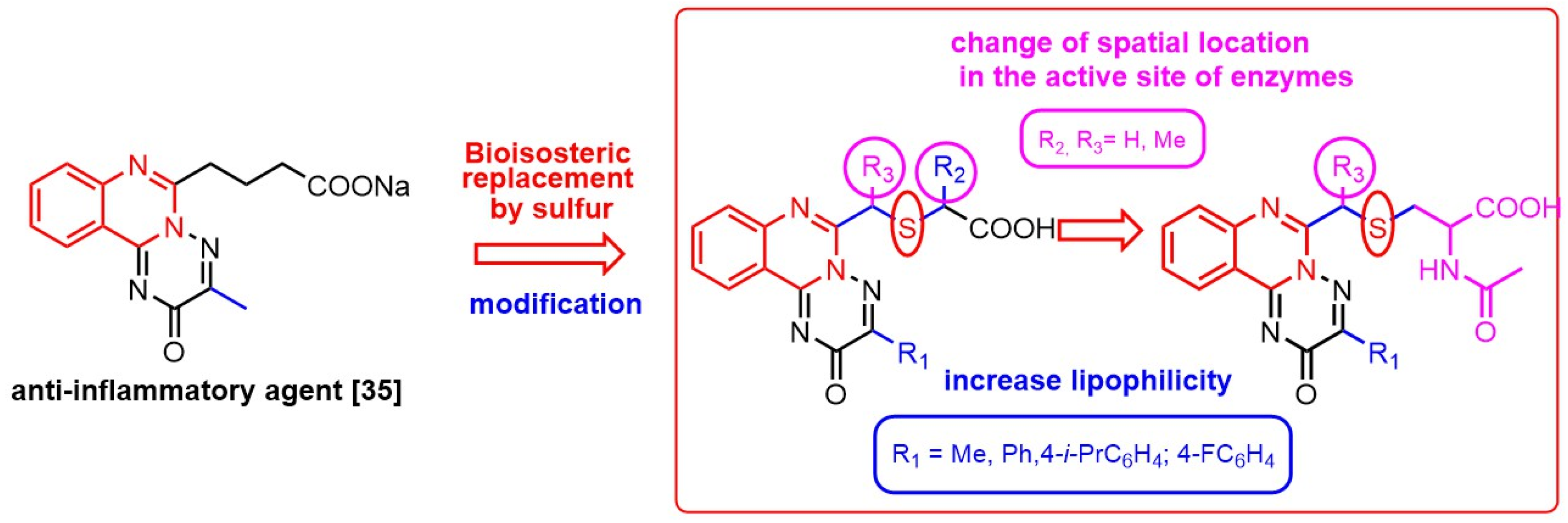
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Molecular Docking
2.2. Chemistry
2.3. Pharmacology
2.4. ADME Prediction
3. Materials and Methods
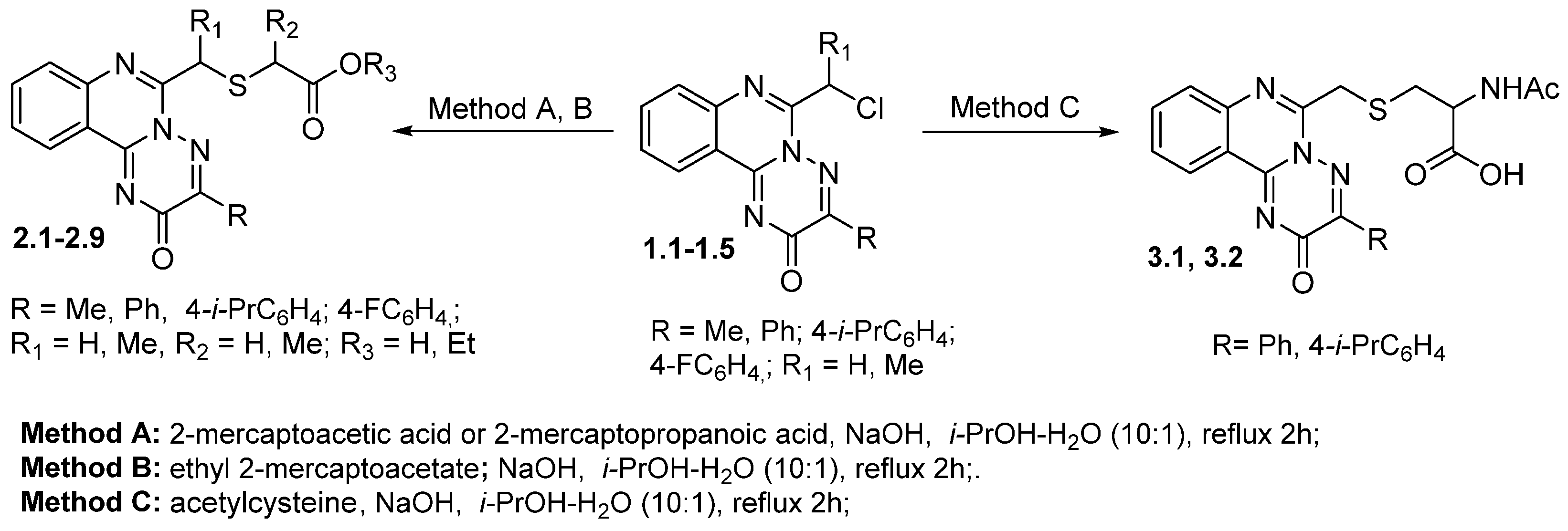
3.1. Chemistry
3.2. Pharmacological/Biological Assays
3.2.1. Anti-Inflammatory Studies
3.2.2. Study of Molecular Markers of Inflammation
4.3. Molecular Docking
4.4. Toxicity Prediction
4.5. SwissADME Prediction
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Drugbank; https://go.drugbank.com/unearth/q?searcher=drugs&query=quinazolines&button=.
- Alagarsamy, V.; Chitra, K.; Saravanan, G.; Solomon, V.R.; Sulthana, M.T.; Narendhar, B. An overview of quinazolines: Pharmacological significance and recent developments. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 151, 628-685. [CrossRef]
- Al-kaf, A. G. Quinazolinone and Quinazoline Derivatives, BoD – Books on Demand, 2020.
- Dash, B. A Review on Quinazolines Heterocycles: A Pharmacophoric Scaffold, Booksclinic Publishing, 2021.
- Karan, R.; Agarwal, P.; Sinha, M.; Mahato, N. Recent Advances on Quinazoline Derivatives: A Potential Bioactive Scaffold in Medicinal Chemistry. ChemEngineering 2021, 5, 73. [CrossRef]
- Gomaa, H. A. M. A comprehensive review of recent advances in the biological activities of quinazolines. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2022, 100, 5, 639-655. doi.:10.1111/cbdd.14129.
- Naman, J.; Tanvi, G.; Snehal, T.; Madhav, J.; Deepali, B. An Explicative Review on the Progress of Quinazoline Scaffold as Bioactive Agents in the Past Decade. Med. Chem. 2023, 19, 3, 211-245. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D. Role of quinazoline in biological activity: a review. Eur. Chem. Bull. 2023, 12, 4, 281-307. [CrossRef]
- Al-Kaf, A. G. Recent Advances on Quinazoline, IntechOpen, 2024.
- Hui, Z.; Xiaoxia, H.; Yue, Z.; Chunlei, T.; Bainian, F. Progress in Synthesis and Bioactivity Evaluation of Pyrazoloquinazolines. Lett. Drug Des. Discov. 2020, 17, 2, 104-113. [CrossRef]
- Saleh, E.A.M.; AL Dawsari, A.M.; Husain, K.; Kutty, I.H.; Rai, K.M.L. Synthesis, Antibacterial, and Antioxidant Evaluation of Novel Series of Condensed Thiazoloquinazoline with Pyrido, Pyrano, and Benzol Moieties as Five- and Six-Membered Heterocycle Derivatives. Molecules 2021, 26, 357. [CrossRef]
- Ettahiri, W.; Salim, R.; Adardour, M.; Ech-chihbi, E.; Yunusa, I.; Alanazi, M.M.; Lahmidi, S.; Barnossi, A.E.; Merzouki, O.; Iraqi Housseini, A. Synthesis, Characterization, Antibacterial, Antifungal and Anticorrosion Activities of 1,2,4-Triazolo [1,5-a]quinazolinone. Molecules 2023, 28, 5340. [CrossRef]
- Kassem, A. F.; Alshehrei, F.; Abbas, E.M.H.; Farghaly, T. A. Synthesis of Azoloquinazolines and Substituted Benzothiazepine as Antimicrobial Agents. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2023, 20, 5, 418-429. [CrossRef]
- Krasovska, N.I.; Koptieva, S. D.; Posudiievska, O. R.; Kyrylakha, S. V.; Vosokoboynik, O. Yu.; Okovytyy, S. I.; Kovalenko, S. I. Methods of synthesis of quinazolines and their condensed analogues – potential anti-inflammatory agents (review). J. Chem. Technol. 2023, 31, 2, 385-410. [CrossRef]
- Nosova, E. V.; Lipunova, G. N.; Permyakova, Y. V.; Charushin, V. N. Quinazolines annelated at the N(3)-C(4) bond: Synthesis and biological activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 271, 116411. [CrossRef]
- Mohammadkhani, L.; Heravi, M.M. Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of Quinazolines and Quinazolinones: An Overview. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 80086. [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.K.; Barde, A.; Rattan, S. A short review on synthetic strategies towards quinazoline based anticancer drug. Arkivoc, 2021, ix, 150-176. [CrossRef]
- Faisal, M.; Saeed, A. Chemical Insights Into the Synthetic Chemistry of Quinazolines: Recent Advances. Front. Chem. 2021, 8, 594717. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Tomar, V.; Joshi, R. K.; Nemiwal, M. Nanocatalyzed synthetic approach for quinazoline and quinazolinone derivatives: A review (2015–present). Synth. Commun. 2022, 52, 6, 795–826. [CrossRef]
- Tamatam, R.; Kim, S-H.; Shin, D. Transition-metal-catalyzed synthesis of quinazolines. Front. Chem. 2023, 11, 1140562. [CrossRef]
- Bansal, R.; Malhotra, A. Therapeutic progression of quinazolines as targeted chemotherapeutic agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 211, 113016. [CrossRef]
- Grover, P.; Bhardwaj, M.; Kapoor, G.; Mehta, L.; Ghai, R.; Nagarajan, K. Advances on Quinazoline Based Congeners for Anticancer Potential. Curr. Org. Chem. 2021, 25, 6, 695-723. [CrossRef]
- Dutta, A.; Sarma, D. Recent advances in the synthesis of Quinazoline analogues as Anti-TB agents. Tuberculosis, 2020, 124, 101986. [CrossRef]
- Cheke, R. S.; Shinde, S. D.; Ambhore, J. P.; Chaudhari, S. R.; Bari, S. B. Quinazoline: An update on current status against convulsions. J. Mol. Struct. 2022, 1248, 131384. [CrossRef]
- Abuelizz, H. A.; Al-Salahi, R. An overview of triazoloquinazolines: Pharmacological significance and recent developments. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 115, 105263. [CrossRef]
- Luan, M-Z.; Zhang, X-F.; Yang, Y.; Meng, Q-G.; Hou, G-G. Anti-inflammatory activity of fluorine-substituted benzo[h]quinazoline-2-amine derivatives as NF-κB inhibitors. Bioorg. Chem. 2023, 132, 106360. [CrossRef]
- Crocetti, L.; Khlebnikov, A.I.; Guerrini, G.; Schepetkin, I.A.; Melani, F.; Giovannoni, M.P.; Quinn, M.T. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Pyrazolo [1,5-a]quinazolines. Molecules 2024, 29, 2421. [CrossRef]
- Hussein, M. A. Synthesis, anti-inflammatory, and structure antioxidant activity relationship of novel 4-quinazoline. Med. Chem. Res. 2013, 22, 10, 4641–4653. [CrossRef]
- Balakumar, C.; Lamba, P.; Pran Kishore, D.; Lakshmi Narayana, B.; Venkat Rao, K.; Rajwinder, K.; Raghuram Rao, A.; Shireesha, B.; Narsaiah, B. Synthesis, anti-inflammatory evaluation and docking studies of some new fluorinated fused quinazolines. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 11, 4904–4913. [CrossRef]
- Martynenko, Yu.; Antypenko, O.; Nosulenko, I.; Berest, G.; Kovalenko, S. Directed Search of Anti-inflammatory Agents Among (3HQuinazoline- 4-ylidene)hydrazides of N-protected Amino acids and their Heterocyclization Products. Anti-Inflammatory & Anti-Allergy Agents in Med. Chem. 2020, 19, 1, 60-71. [CrossRef]
- Krasovska, N.; Stavytskyi, V.; Nosulenko, I.; Karpenko, O.; Voskoboinik, O.; Kovalenko, S. Quinazoline-containing Hydrazydes of Dicarboxylic Acids and Products of Their Structural Modification – A Novel Class of Anti-inflammatory Agents. Acta Chim. Slov. 2021, 68, 2, 395-403. [CrossRef]
- Krasovska, N.; Berest, G.; Belenichev, I.; Severina, H.; Nosulenko, I.; Vosokoboinik, O.; Okovytyy, S.; Kovalenko, S. 5+1-Heterocyclization as preparative approach for carboxy-containing triazolo [1,5-c]quinazolines with anti-inflammatory activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 266, 116137. [CrossRef]
- Selvam, T.P.; Kumar, P.V. Synthesis of Novel 6,7,8,9-Tetrahydro-5H-5-hydroxyphenyl-2-benzylidine- 3-substituted Hydrazino Thiazolo (2,3-b) Quinazoline as Potent Antinociceptive and Anti-inflammatory Agents. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2010, 31, 11, 3265-3271. [CrossRef]
- Zayed, M.F. Medicinal Chemistry of Quinazolines as Analgesic and Anti-Inflammatory Agents. ChemEngineering 2022, 6, 94. [CrossRef]
- Yakubovska, V.V.; Seredinska, N.М.; Voskoboynik, О.Y.; Stepanyuk, G.І.; Kovalenko, S.І. Purposeful search and characteristic of anti-inflammatory activity of sodium (3-R-2-oxo-2Н-[1,2,4]triazino [2,3-c]quinazolin-6-yl)alkylcarboxylates and their halogen containing analogues. Current issues in pharmacy and medicine: science and practice. 2016, 1, 60-66. [CrossRef]
- Kolomoets, O.; Voskoboynik, О.; Antypenko, O.; Berest, G.; Nosulenko, I.; Palchikov, V.; Karpenko, O.; Kovalenko, S. Design, Synthesis and Anti-inflammatory Activity of Derivatives 10-R-3-Aryl-6,7-dihydro-2H-[1,2,4] triazino [2,3-c]quinazolin-2-ones of Spiro-fused Cyclic Frameworks. Acta Chim. Slov. 2017, 64, 4, 902-910. [CrossRef]
- Stavytskyi, V.; Antypenko, O.; Nosulenko, I.; Berest, G.; Voskoboinik, O.; Kovalenko, S. Substituted 3-R-2,8-Dioxo-7,8-dihydro-2H-pyrrolo [1,2-a][1,2,4] triazino [2,3-c]quinazoline-5a(6H)carboxylic Acids and their Salts-a Promising Class of Anti-inflammatory Agents. Anti-Inflammatory & Anti-Allergy Agents in Med. Chem. 2021, 20, 1, 75-88. [CrossRef]
- Hryb, V.V.; Doroshenko, O.M.; Zaichko, N.V.; Stepaniuk, N.H. Comparative characteristics of the influence of the sodium salt of 4-(3-methyl-2-oxo-2H-[1,2,4]triazino [2,3-c]quinazolin-6-yl)butanoic acid and diclofenac on the dynamics of hematological parameters and safety in rats with adjuvant arthritis. Pharmacology and Drug Toxicology. 2015, 6, 46, 53–57.
- Hryb, V.V.; Vernyhorodskyi, S.V.; Stepaniuk, H.I. Comparative analysis of morphological changes in joints when using the sodium salt of 4-(3-methyl-2-oxo-2H-[1,2,4]triazino [2,3-c]quinazolin-6-yl)butanoic acid (compound DSK-38) and diclofenac sodium in the model of adjuvant arthritis. Reports of Morphology. 2015, 2, 340-343.
- Yakubovska, V.V. Effect of sodium salt of 4-(3-methyl-2-oxo-2H-[1,2,4]triazino [2,3-c]quinazolin-6-yl)butanoic acid (DSK-38) on proliferative, alterative phases of inflammation reactions and evaluation of the antipyretic effect in the experiment. Reports of Vinnytsia National Medical University. 2017, 1, 8–11.
- Krasovska, N.I.; Stavytskyi, V.V.; Kholodniak, O.V.; Antypenko, O.M.; Voskoboinik, О.Yu.; Kovalenko, S.I. Pyrrolo[1,2-a]azolo-(azino-)[c]quinazolines and their derivatives as 15-LOX inhibitors: Design, in vitro studies and QSAR-analysis. J. Res. Pharm. 2021, 25, 5, 1-9. [CrossRef]
- Lima, L.M.; Barreiro, E.J. Beyond Bioisosterism: New Concepts in Drug Discovery in Comprehensive Medicinal Chemistry III (Eds: Samuel Chackalamannil, David Rotella, Simon E. Ward), Elsevier, 2017.
- C. D. Gamarra-Sánchez, C. N. Rodriguez-Silva, A. Cordova-Muñoz, L. Asmad-Cruz, C. R. Silva-Correa, V.E. Villarreal-La Torre, In silico design of new ketorolac bioisosteres as anti-inflammatory agents. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2024, 14, 04, 155-162. [CrossRef]
- Chandna, N.; Kumar, S.; Kaushik, P.; Kaushik, D.; Roy Somendu, K.; Girish, G.K.; Jachak Sanjay, M.; Kapoor Jitander, K.; Sharma Pawan, K. Synthesis of novel celecoxib analogues by bioisosteric replacement of sulfonamide as potent anti-inflammatory agents and cyclooxygenase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 15, 4581-4590. [CrossRef]
- Ju, Z.; Li, M.; Xu, J.; Howell, D. C.; Li, Z.; Chen, F-E. Recent development on COX-2 inhibitors as promising anti-inflammatory agents: The past 10 years. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022, 12, 6, 2790-2807. [CrossRef]
- Sidhu, R.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Yuan, C.; Smith, W.L. Comparison of Cyclooxygenase-1 Crystal Structures: Cross-Talk between Monomers Comprising Cyclooxygenase-1 Homodimers. Biochemistry. 2010, 49, 33, 7069-7079. [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.L.; Limburg, D.; Graneto, M.J.; Springer, J.; Hamper, J.R.; Liao, S.; Pawlitz, J.L.; Kurumbail, R.G.; Maziasz, T.; Talley, J.J. ;Kiefer, J.R.; Carter, J. The novel benzopyran class of selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors. Part 2: The second clinical candidate having a shorter and favorable human half-life. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 1, 20, 23, 7159-63. [CrossRef]
- Grytsak, O.A.; Moskalenko, O.S.; Voskoboinik, O.Yu.; Kovalenko, S.I. Synthesis of 6-chloro(dichloro-, trichloro-)-methyl-3-R-6,7dihydro-2H-[1,2,4]triazino [2,3-c]quinazolin-2-ones and their modification in reactions with nucleophilic and non-nucleophilic bases. Vopr. Khimii Khimicheskoi Tekhnologii. 2021, 6, 3-10. [CrossRef]
- Breitmaier E. Structure elucidation by NMR in organic chemistry: a practical guide, third edition, Wiley, 2002.
- Suschek, C.V.; Schnorr, O.; Kolb-Bachofen, V. The role of iNOS in chronic inflammatory processes in vivo: is it damage-promoting, protective, or active at all? Curr Mol Med. 2004, 4, 7, 763-75. [CrossRef]
- Sugita, M.; Sugita, H.; Kim, M.; Mao, J.; Yasuda, Y.; Habiro, M.; Shinozaki, S.; Yasuhara, S.; Shimizu, N.; Martyn, J. A.; Kaneki, M. Inducible nitric oxide synthase deficiency ameliorates skeletal muscle insulin resistance but does not alter unexpected lower blood glucose levels after burn injury in C57BL/6 mice. Metabolism. 2012, 61, 1, 127-36. [CrossRef]
- Nakazawa, H.; Chang, K.; Shinozaki, S.; Yasukawa, T.; Ishimaru, K.; Yasuhara, S.; Yu, Y.; M Martyn, J. A.; Tompkins, R. G.; Shimokado, K.; Kaneki, M. iNOS as a Driver of Inflammation and Apoptosis in Mouse Skeletal Muscle after Burn Injury: Possible Involvement of Sirt1 S-Nitrosylation-Mediated Acetylation of p65 NF-κB and p53. PLoS One. 2017, 18, 12, 1, e0170391. [CrossRef]
- Belenichev, I.; Popazova, O.; Bukhtiyarova, N.; Savchenko, D.; Oksenych, V.; Kamyshnyi, O. Modulating Nitric Oxide: Implications for Cytotoxicity and Cytoprotection. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 504. [CrossRef]
- Kamyshna, I.I.; Pavlovych, L.B.; Maslyanko, V.A.; Kamyshnyi, A.M. Analysis of the transcriptional activity of genes of neuropeptides and their receptors in the blood of patients with thyroid pathology. J. Med. Life 2021, 14, 243–249. [CrossRef]
- Repchuk, Y.; Sydorchuk, L.P.; Sydorchuk, A.R.; Fedonyuk, L.Y.; Kamyshnyi, O.; Korovenkova, O.; Plehutsa, I.M.; Dzhuryak, V.S.; Myshkovskii, Y.M.; Iftoda, O.M.; et al. Linkage of blood pressure, obesity and diabetes mellitus with angiotensinogen gene (AGT 704T>C/rs699) polymorphism in hypertensive patients. Bratisl. Lek. Listy 2021, 122, 715–720.
- European convention for the protection of vertebrate animal used for experimental and other scientific purposes. Council of Europe, Strasbourg, 1986.
- Fehrenbacher, J. C.; Vasko, M. R;. Duarte, D. B. Models of Inflammation: Carrageenan- or Complete Freund’s Adjuvant (CFA)–Induced Edema and Hypersensitivity in the Rat. Curr. Protoc. Pharmacol. 2012, 56, 5.4.1-5.4.7. [CrossRef]
- Lapach, S. N.; Chubenko, A. V.; Babich P.N. Statistical methods in biomedical research using EXCEL. Morion, Kyiv, 2001.
- Banerjee, P.; Eckert, A. O.; Schrey, A. K.; Preissner, R. ProTox-II: a webserver for the prediction of toxicity of chemicals. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 1, 257–263. [CrossRef]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissADME: a free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1. [CrossRef]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. iLOGP: A Simple, Robust, and Efficient Description of n-Octanol/Water Partition Coefficient for Drug Design Using the GB/SA Approach. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2014, 54, 12, 3284–3301. [CrossRef]
- Daina, A.; Zoete, V.A BOILED-Egg To Predict Gastrointestinal Absorption and Brain Penetration of Small Molecules. ChemMedChem. 2016, 11, 11, 1117–1121. [CrossRef]
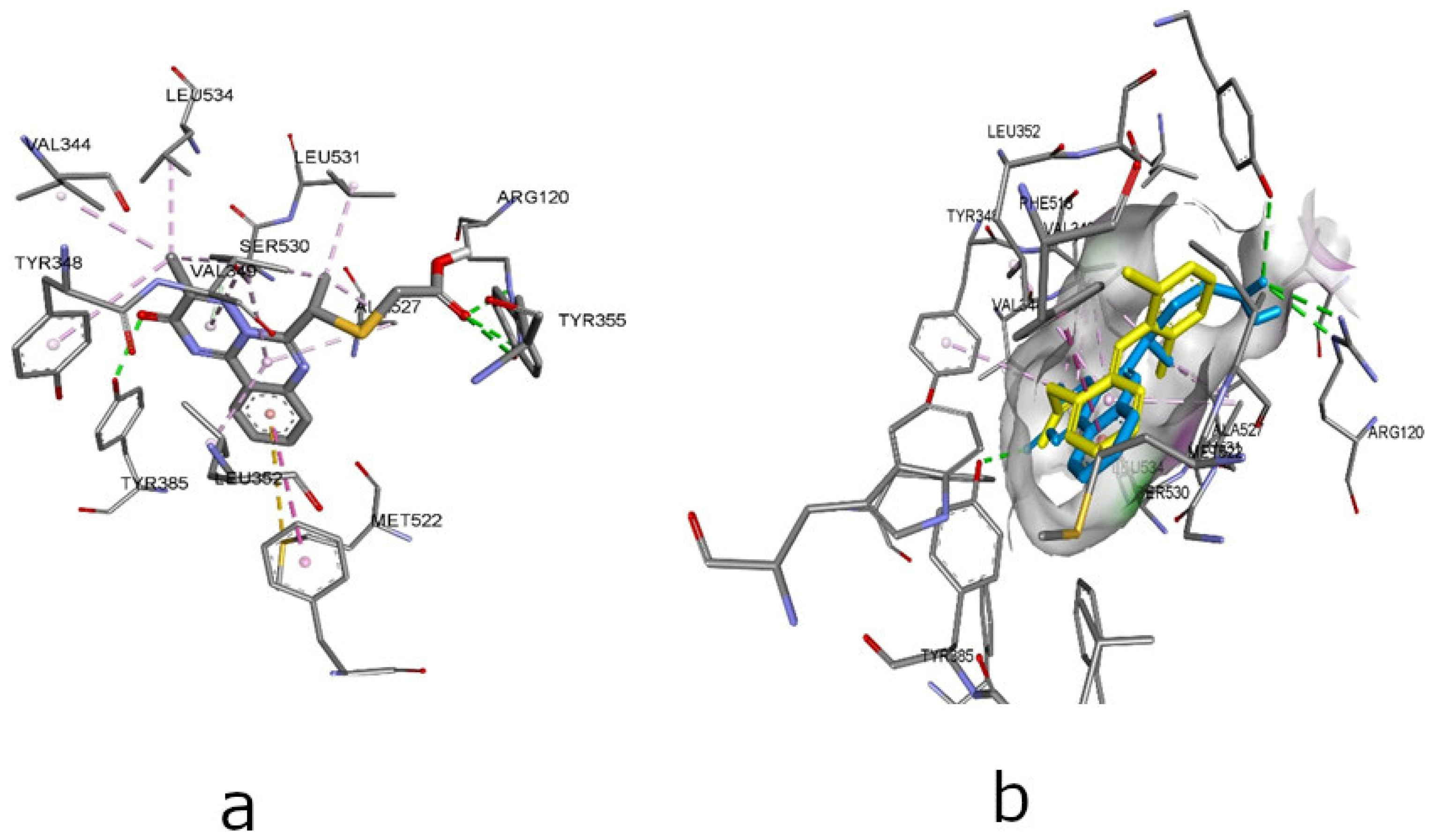
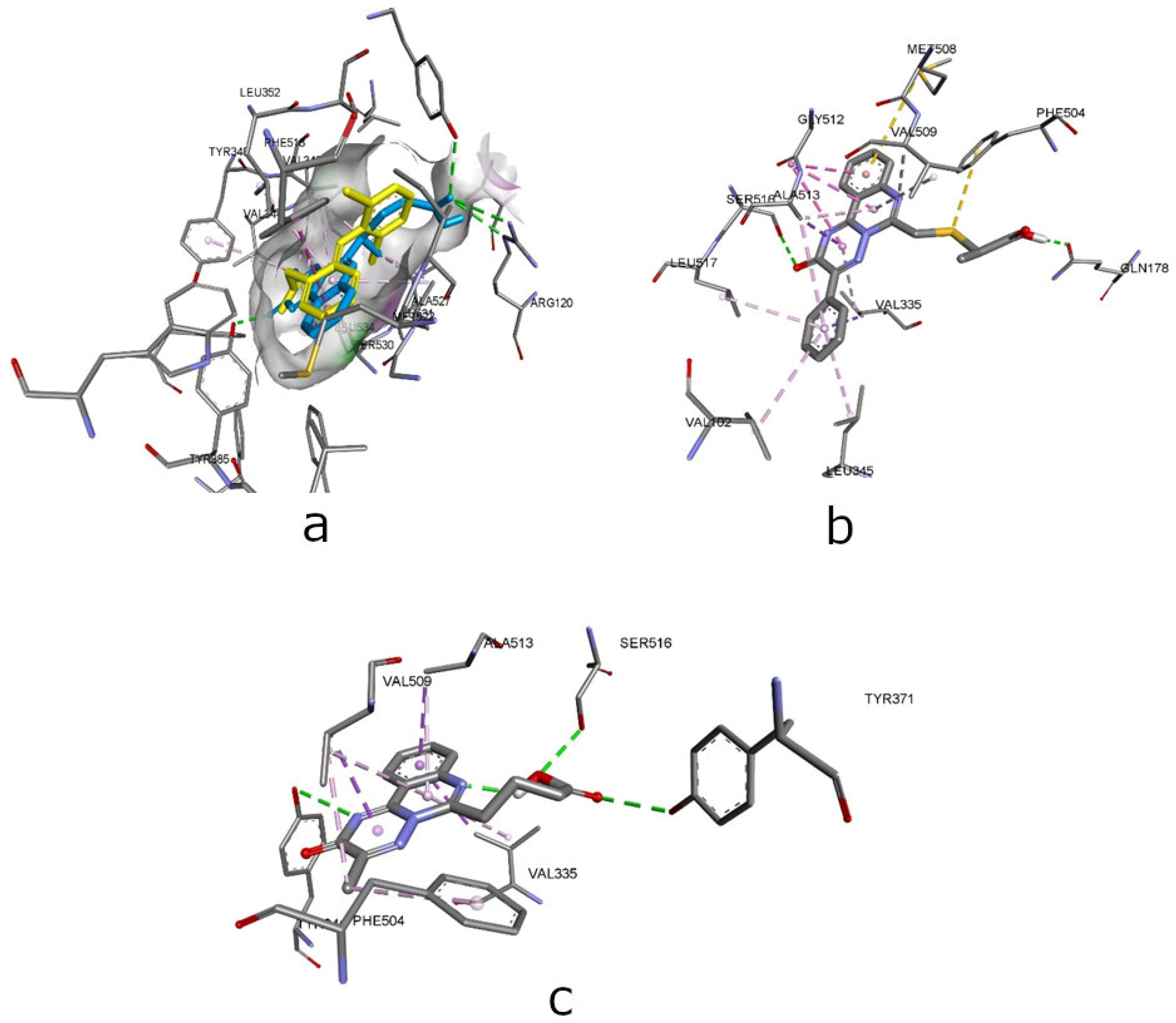
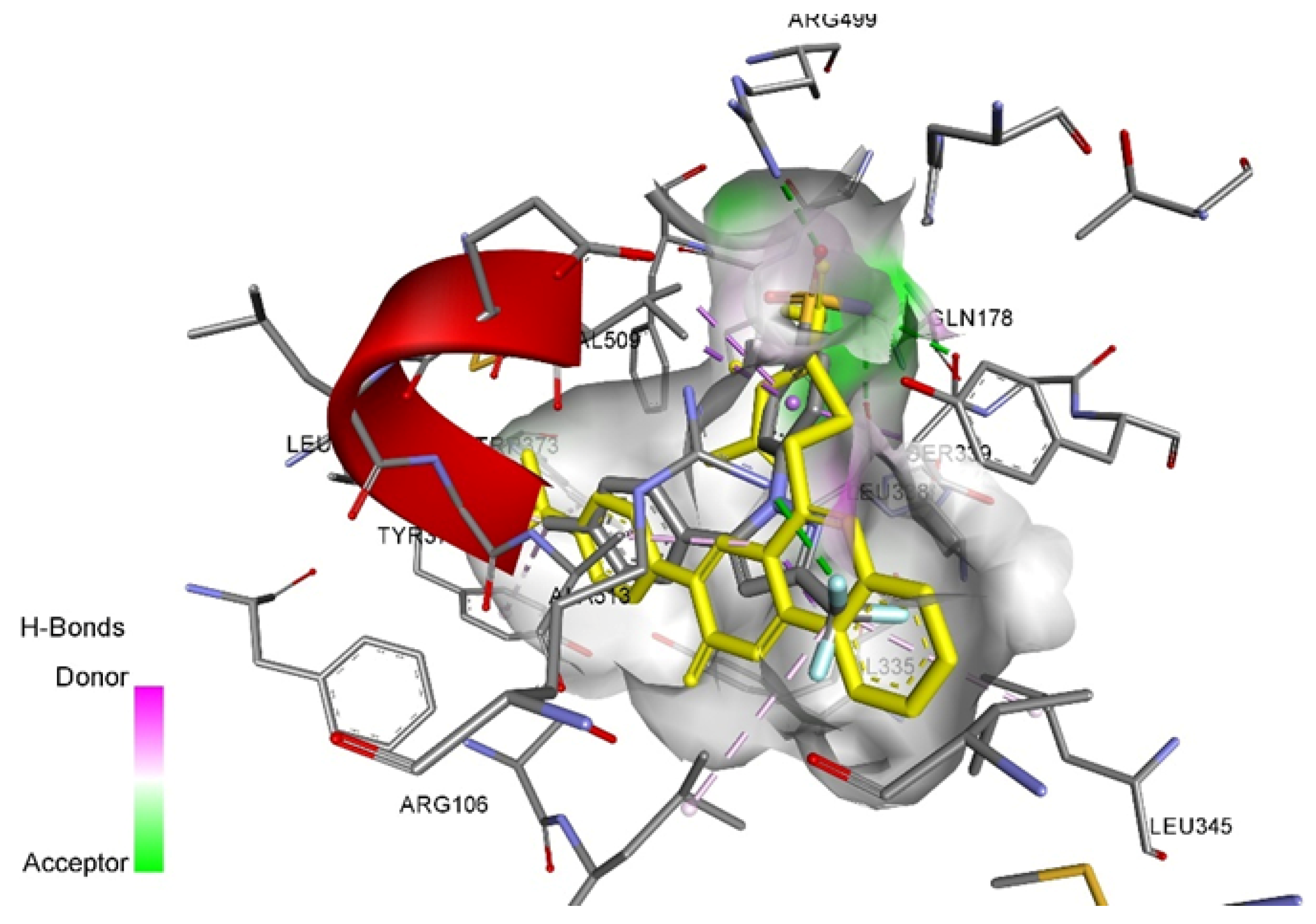
| Compounds | Affinity (kcal/mol) to COX-1 (PDB ID - 3N8Y) | Amino acid moiety and bonding type | Affinity (kcal/mol) to COX-2 (PDB ID – 3LN1) | Amino acid moiety and bonding type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diclofenac | -8.5 | a: Tyr385, Ser530 b: Ala527(3), Leu352(3), Ile523(2), Val349(2), Leu531 |
– | - |
| Celecoxib | – | - | -12.2 | a: Arg106, Arg499, Gln178, Leu338, Ser339 b: Val335, Ser339, Val509(2), Leu370, Val335, Leu345, Leu517, Tyr371, Trp373, Ala513(2) |
| MTB# | -7,7 | a: Ser530, Tyr385, Met522 b: Val349(3), Ala527(3), Leu352(2), Tyr348*, Tyr385, Trp387*, Leu531, Ile523 |
-9,3 | а: Tyr341(2), Ser516, b: Val335, Tyr371, Val509(3), Ala513(2), Phe504, Val335 |
| 2.1 | -6.3 | a: Tyr355*, Tyr385, VAL349; b: Leu352, Ala527(4), Met522*, Tyr348*, Gly526(3)*, Val349, Leu352, Ile523(2); С: met113 |
-10.2 | a: Arg499, Ser516*, Ser339 b: Val509(2), Val335(3), Ala513(5), Leu517, Gly512(2)*, Val102*, Leu345 c: Met508*, Phe504* |
| 2.2 | -5.6 | a: Tyr355*, Val116* b: Val349, Leu352(2), Ala527(6), Met113*, Met522*, Tyr348*, Gly526(3)*, Val349(2), Ile523(2), Leu359*, Leu531 |
-10.2 | a: Ser516*, Gln178, Val509 b: Val335(2), Ala513 (6), Gly512 (3)*, Val509, Val102*, Leu345, Leu517 c: Met508*, Phe504* |
| 2.3 | -4.9 | a: Arg120*, Tyr355* b: Ile89(2*), Leu93*, Val116(3)*, Tyr355*, Ala527 (3), Val349(2), Leu531, Ile523 |
-8.7 | a: Phe504, Gln178 b: Tyr341(4)*, Val335(2), Leu338, Ala513(3), Leu78(2)*, Val102(3)*, Leu345(2), Phe343, Leu338, Val509 |
| 2.4 | -5.3 | a: Tyr355* b: Val116*, Leu352(2), Ala527(5), Gly526(3)*, Val349(3), Ile523(2), Leu359*, Leu531 c: Met113*, Met522*, Tyr348* |
-10.1 | a: Ser516*, Val509 b: Arg106, Ala513, Gly512(3)*, Ala513(5), Val509, Val335(4), Val102*, Leu345, Leu517 c: Met508*, Phe504* |
| 2.5 | -6.6 | a: Arg120(2), Tyr355, Tyr385, Ser530; b: Phe518*, Ala527(2), Val349(4), Leu531, Val344*, Leu534,* Tyr348*, Leu352 c: Met522* |
-9.4 | a: Arg499, Ala513, Ser516* b: Leu338, Val509(3), Trp373, Phe504 (2), Val335(2), Ala513(3), Leu517 c: Phe504, Met508 |
| 2.6 | -6.1 | a: Tyr355*, Tyr385 b: Leu352, Ala527(4), Met522*, Tyr348*, Gly526(3)*, Val349, Leu352, Ile523(2) |
-10.0 | a: Tyr371, Ser516*, Val335, Val509, Ala513; b: His75*, Met508, Val509(3), Phe504*, Val335, Ala513, Leu517, Arg499, Ala 502 c: Trp373 (Pi-Sulfur) |
| 2.7 | -6.2 | a: Tyr355*, Tyr385(2) b: Val116*, Val349(3), Leu352(2), Ala527(4), Met113*, Met522*, Tyr348*, Tyr385, Gly526(2)*, Ile523(2), Leu359*, Leu531 |
-10.1 | a: Arg499, Ser516*, His75* b: Val335, Gly512(3)*, Ala513 (5), Val509, Val335, Val102*, Leu345, Leu517 c: Phe504*, Met508* |
| 2.8 | -2.7 | a: Tyr385(2) b: Ala527(4), Phe518*, Tyr385*, Gly526*, Met113*, Val116(2)*, Leu359(2)*, Tyr355*, Leu352, Val349(2), Ile523, Leu384, Leu531 c: Met522*, Phe205*, Tyr348* |
-10.5 | a: Arg499, His75*; b: Ala513(6), Gly512(3)*, Leu78*, Val102(2), Leu345 (2), Tyr341(2)*, Phe343, Val509, Val335(3), Val102*, Leu517 c: Phe504*, Met508* |
| 2.9 | -4.2 | a: Tyr385(2) b: Ala527(6), Phe518*, Gly526 (3)*, Val349(2), Leu352(2), Ile523, Val116*, Leu359*, Leu531 c: Met522*, Tyr348* |
-10.1 | a: Arg499, Ser516* b: Arg106, Ala513, Gly512(3), Ala513(5), Val509, Val335(2), Val102*, Leu345, Leu517 c: Met508*, Phe504* |
| 3.1 | -5.3 | a: Tyr355*; b: Val349, Leu352(2), Ala527(6), Met113*, Met522*, Tyr348*, Gly526(3)*, Val349(2), Ile523(2) |
-9.3 | a: Ser516*, Val509 b: Arg106, Ala513(6); Gly512(3)*, Val509, Val335(2), Val102*, Leu345, Leu517 c: Met508*, Phe504* |
| 3.2 | -5.8 | a: Arg120* b: Ser530, Val349(3), Leu531(3), Val116(2), Ile345, Leu359(2)*, Ala527(2) c: Met113*, Tyr355* |
-10.8 | a: Ser516*, Gln178 b: Arg106, Ala513, Gly512(3)*, Ala513(5), Val509, Val335(3), Val102*, Val335, Leu345, Leu517 c: Met508*, Phe504* |
| Compounds | Oral toxicity | Prediction: active, probability from (yes/no)** | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Toxicity Index* |
LD50, mg/kg |
Prediction accuracy, % |
HT | CG | IT | MG | CT | |
| 2.1 | IV | 800 | 54.26 | 0.50/no | 0.54/no | 0.99/no | 0.60/no | 0.75/no |
| 2.2 | IV | 800 | 54.26 | 0.50/no | 0.56/no | 0.99/no | 0.59/no | 0.80/no |
| 2.3 | III | 300 | 54.26 | 0.52/no | 0.59/no | 0.96/no | 0.58/no | 0.81/no |
| 2.4 | III | 300 | 54.26 | 0.52/no | 0.55/no | 0.99/no | 0.58/no | 0.80/no |
| 2.5 | IV | 800 | 54.26 | 0.50/no | 0.56/no | 0.99/no | 0.58/no | 0.80/no |
| 2.6 | III | 300 | 54.26 | 0.53/no | 0.57/no | 0.99/no | 0.59/no | 0.79/no |
| 2.7 | IV | 800 | 54.26 | 0.52/no | 0.57/no | 0.99/no | 0.57/no | 0.76/no |
| 2.8 | III | 300 | 54.26 | 0.54/no | 0.61/no | 0.97/no | 0.59/no | 0.77/no |
| 2.9 | IV | 400 | 23,0 | 0.54/no | 0.64/no | 0.95/no | 0.58/no | 0.74/no |
| 3.1 | VI | 10000 | 23,0 | 0.51/no | 0.54/no | 0.99/no | 0.59/no | 0.69/no |
| 3.2 | VI | 10000 | 23,0 | 0.52/no | 0.58/no | 0.99/no | 0.61/no | 0.68/no |
| МТВ# | III | 300 | 54.26 | 0.54/yes | 0.52/no | 0.99/no | 0.57/no | 0.82/no |
| DS#* | III | 53 | 100,0 | 0.81/yes | 0.64/no | 0.99/no | 0.78/no | 0.74/no |
| Compounds | Acute aseptic inflammation («carrageenan» test) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| The healthy paw volume, ml | Edema paw volume on 4h h of exp., ml | АА, % | |
| Control | 1,586±0,058 | 2,416±0,104 | – |
| 2.3 | 1,47±0,08 | 2,27±0,101 | 3,61 |
| 2.5 | 1,49±0,047 | 1,876±0,119 | 53,41 |
| 3.2 | 1,536±0,087 | 1,936±0,088 | 51,81 |
| MТВ | 1.34±0.06 | 2.03±0.05 | 45.77 |
| DS*# | 1,31±0,116 | 1,693±0,049 | 53,82 |
| Biochemical markers | Intact | Control | 2.5 | 3.2 | MTB** |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VEGF, pg/mL | 3,65±0,59 | 3,65±0,59 | 6,34±0,27*# | 12,03±0,47*# | 6,72±0,33*# |
| COX-2, (ng/ml) | 0,97±0,05 | 0,97±0,05 | 3,26±0,20*# | 12,74±0,43*# | 2,36±0,27*# |
| iNOS, (pg/ml) | 1,17±0,14 | 1,17±0,14 | 6,01±0,29*# | 9,87±0,78*# | 7,44±0,28*# |
| nitrotyrosine, (nM/ml) | 2,09±0,20 | 2,09±0,20 | 5,19±0,24*# | 8,31±0,39*# | 8,19±0,24*# |
| IL-1b, pg/ml | 0,33±0,02 | 0,33±0,02 | 0,40±0,01*# | 1,3±0,05*# | 0,51±0,02*# |
| C-reactive protein, (ng/ml) | 1,65±0,14 | 1,65±0,14 | 2,43±0,15*## | 7,04±0,19*# | 2,10±0,23# |
| Physicochemical descriptors & predicted pharmacokinetic properties* | Compound | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 2.5 | 3.2 | MTB | |
| MW (Da) (< 500) | 330.36 | 491.56 | 298.30 |
| n-ROTB (< 10) | 4 | 9 | 4 |
| n-HBA (< 10) | 6 | 7 | 6 |
| n-HBD (≤ 5) | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| TPSA (< 140, Ų) | 122.75 | 151.85 | 97.45 |
| logP (≤ 5) | 1.72 | 3.15 | 1.45 |
| Molar refractivity | 88.27 | 135.94 | 80.68 |
| Gastrointestinal absorption | High | Low | High |
| Blood–brain barrier permeation | no | no | no |
| Lipinski filter | yes | yes | yes |
| Veber filter | yes | no | yes |
| Muegge filter | yes | no | yes |
| Ghose filter | yes | no | yes |
| Egan filter | yes | no | yes |
| Bioavailability Score | 0.56 | 0.11 | 0.56 |
| Lead-likeness | yes | no | yes |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





