1. Introduction
Groundwater is the most used source of drinking water in the Sindh province of Pakistan. This is the single source of drinking water that is readily available to every resident of Sindh province of Pakistan. However, this important source of drinking has emerged as the main cause of diseases in the Sindh province of Pakistan. This source of water is degraded by the overuse of aquifers, excessive application of agricultural fertilizers for crops, dumping of solid waste, discharge of untreated sewage into natural streams, and natural factors related to climate change. The mixing of fecal waste with water is also extremely detrimental to human health and is one of the major causes of water quality deterioration. Although water supply schemes have been introduced in the various parts of Sindh province of Pakistan such as Karachi, Sukkur, Hyderabad, and Jacobabad, almost 80% of the population in the Sindh province extract groundwater for their daily consumption [
1]. Groundwater in the Sindh province of Pakistan is not only used for drinking but also for irrigation and other domestic purposes as well. Groundwater in Sindh province is available in the forms of unconfined aquifers and confined aquifers. People in Sindh province abstract water for their daily use through open-dug wells, with the help of electric pumps, and hand pumps as well. Even in the parts of Sindh province where water supply schemes are working to provide safe water to the consumers, yet population in various rural parts of these districts rely on the groundwater. This is because either water supply schemes are also not sufficient to provide the required quantity of water to the whole population residing in urban and rural parts of Sindh province or using water supply schemes is neither economical for rural populations nor for water supply companies.
Studies have found that access to safe drinking water for the people of the Sindh province of Pakistan is declining day by day. It has also been found that about 7-8% of the population in the rural parts of Sindh province of Pakistan has easy access to safe drinking water, and the remaining population of the province about 92% drink unhealthy and unhygienic water [
2]. Moreover, it also confirmed with the help of research works that about 50% of diseases in Sindh province are associated with poor water quality [
3]. The common diseases that are attributed to the degraded quality of drinking water in the Sindh province of Pakistan include Hepatitis, Cholera, diarrhea, Gastro, Kidney diseases, etc. Aljazeera in 2022 reported that after the flood hit various parts of Sindh, a variety of diseases such as gastro, diarrhea, abdominal issues, and other waterborne diseases erupted in the Sindh province of Pakistan. All diseases were attributed to the consumption of poor- quality drinking water.
Therefore, various scholars have started working on the assessment of the groundwater quality in the Sindh province of Pakistan. In order to facilitate scholars for their research, the government of Sindh also has established water testing laboratories under the umbrella of PCRWR which is the research council in water resources in Pakistan. Hence, this study was proposed to detect the suitability of groundwater in Larkana city of Sindh province of Pakistan for drinking purposes.
Larkana shown in
Figure 1 is located on the right bank of the Indus River. It has a total population of 17.84 million. It is located between earth coordinates 27° 33’ 50.3748’‘ N and 68° 12’ 54.4824’‘ E. Water for irrigation to Larkana city is supplied by Canal that has been provided only for growing the rice crop and that canal flows through the heart of the city. Moreover, this canal offtakes from the Sukkur barrage constructed on the Indus River at Sukkur. The crops that are commonly grown in Larkana include Mustard, Rice, and Wheat.
The source of drinking water in Larkana city is only the groundwater. No water supply schemes have been introduced in Larkana yet. People of Larkana City either are compelled to drink poor groundwater for their survival or borrow water from other sources that are suitable for consumption. Jamali et al. 2022 [
4] revealed while analyzing the quality of groundwater in the UC Ratokot of Larakan that water was extremely contaminated for drinking purposes and people used to borrow water from specified hand pumps where water was found sweaty in taste and did not pose any threat to human health. Lanjwani et al. 2022 [
5] also have found that the groundwater in nearby areas of Larkana is contaminated but people take water from other sources for their daily consumption. Although Non- governmental organizations (NGOs) are facilitating people in taking safe water to their doors, not all the parts of Larkana are covered by the NGOs. On the other hand, solarized water purification units are also provided in a limited number of villages, but no monitoring of such units is done by any executive authorities. For instance, Ahmed et al. 2022 [
6] reported that in a few villages it had been three to five years since people were drinking water from the solarized water treatment units, but residents said that no officials from the government or NGOs looked after these units after installment. That ultimately means people are drinking the same contaminated groundwater not the treated water.
Therefore, this study was an effort to assess the suitability of the groundwater of Larkana City so that the safety of the public can be ensured.
2. Methodology
For the assessment of groundwater samples of Larkana city, a total of forty (15) groundwater samples were collected from Larkana city. Samples were collected in 250 ml plastic water bottles. The samples were given proper labeling and codes so that analysis based on the location of samples should be made properly. Each groundwater sample was analyzed for water quality parameters such as pH, Total dissolved solids (TDS), Electrical conductivity (EC), color, taste, odor, E-Coli, and fecal Coliform. The E-Coli and Faecal Coliforms were also assessed because studies have revealed that in Larkana city the major cause of groundwater contamination is the mixing of fecal waste and animal waste with the groundwater [
7].
Testing of samples was done in the water testing Laboratory of Rohri. The pH and Total dissolved solids were determined by using a TDS meter as well. The concentration of EC was determined by using Equation 1.
EC = TDSEquation (1)
0.646
The equation has been used by many scholars such as Solangi et al. 2019 [
8], etc. Moreover, E-Coli and fecal coliform were measured by using the Membrane Filtration Technique at the Rohri water testing laboratory. However, physical parameters of drinking water quality such as color, odor, and taste were measured on the site by sensory technique. The Color was checked by the naked eye, the smell was determined by the nose, and while taste was checked by the tongue on the site. Once the results were obtained the analysis of results was made by comparing obtained values of each parameter with the WHO guidelines. The WHO recommended values are followed in the whole of Pakistan for the detection of the suitability of drinking water. Moreover, the recommendations of other statuary bodies in Pakistan such as PEPA, NEQS, etc. also follow the recommendation of the WHO.
The detailed methodology and suitable methods for the assessment of various water quality parameters are listed in
Table 1.
3. Result and Discussion
Groundwater samples were properly analyzed for water quality parameter and their observed values were matched with the recommended values of the WHO. The results of each parameter such as pH, Total dissolved solids (TDS), Electrical conductivity (EC), color, taste, odor, E-Coli, and fecal Coliform is individually discussed below.
3.1. pH
The pH indicates the measurement of acidity and alkalinity in water. The value of pH in the drinking water ranges between 0 and 14. Water is considered extremely acidic if its value touches 14 and water is extremely alkaline if it has zero concentration of pH, however, 7 is marked as neutral water. The WHO recommends that the water should neither be extremely acidic nor extremely acidic. Thus, the WHO suggests that the value of the pH in water should be between 6.5 to 8.5. Upon analysis of drinking water samples collected from groundwater resources of Larkana City, it was observed that the value of the concentration of pH in drinking water samples ranged from 6.8 to 8.1. Furthermore, it was also found that none of the samples exhibited pH levels exceeding the permissible limits, indicating that the water is not at risk from pH-related issues.
3.2. Total Dissolved Solid (TDS)
The concentration Total Solids (TDS) is the measurement of the total quantity of organic and inorganic impurities dissolved in water. The WHO says the TDS makes water unsuitable for drinking if its concentration in water goes beyond 1000 ppm. The analysis of groundwater samples disclosed that the value of TDS in Larkana City was between 560 ppm to 2100 ppm. The peak concentration of TDS in driking water was found in the groundwater samples obtained from Mahdi Colony, Sachal Colony, and samples from the QUEST University campus, etc. Overall, 36 samples had a value of TDS beyond permissible limits. Deterioration of groundwater quality based on the TDS may be due to the percolation of salts from dumping sites, and water- logged soil.
3.3. Electrical Conductivity (EC)
Electrical Conductivity is also the measurement of solids and salts in drinking water. The higher concentration of Electrical Conductivity makes water saline in taste. The salinity is also measured from the values of Electrical Conductivity. The WHO has recommended that in suitable drinking water, the concentration of Electrical Conductivity should not be higher than 400 micro-simen per centimeter. When the groundwater samples for Electrical Conductivity were analyzed the results exhibited that the water in Larkana City is also vulnerable to Electrical Conductivity. The concentration of Electrical Conductivity in samples was found between 856 micro-simen per centimeter and 3255 micro-simen per centimeter. The highest value of EC was found in the samples collected from Mahdi Colony, Khohra Complex, Ahsan phase-II colony, etc. Overall, 36 samples had a value of EC beyond permissible limits
3.4. E-Coli and Faecal Coliform
E-Coli is also a group of fecal coliform. Faecal Coliform in water is the presence of human and animal waste in drinking water. This is the most dangerous water quality parameter. The kidney, liver, and abdominal diseases are attributed to the presence of fecal coliform in drinking water. This dangerous parameter is imparted in water by the mixing of sewage with groundwater or surface water. The WHO has recommended that the fecal coliform and E-Coli in drinking water should be zero. When groundwater samples were analyzed for E-Coli and fecal coliform, it was found that samples did not exhibit the presence of E-Coli, however, three samples were found to have a concentration of fecal beyond the permissible limit. The three samples which exhibited the presence of fecal coliform were collected from Yar Muhammad Colony, Mumtaz Colony, and Mahdi Colony.
3.5. Color, Odor and Taste
The Portable water does not have any shape or odor and is sweaty in taste. Each sample for taste, odor, and color was tested by tongue, nose, and eye. The sensory evaluation of groundwater samples, that covered analysis of color, taste, and odor, the results demonstrated that all samples were colorless. However, eight samples presented that taste that was a bitter taste and a sewage-like odor as well. Particularly, the samples gathered from Ahsan-I, Ahsan-II, Mahdi Colony, Sachal Colony, Yaar Muhammad Colony, Mumtaz Colony, Larkana Coach Stand, and Noor Colony displayed a slightly saline and bitter taste, accompanied by an unpleasant odor.
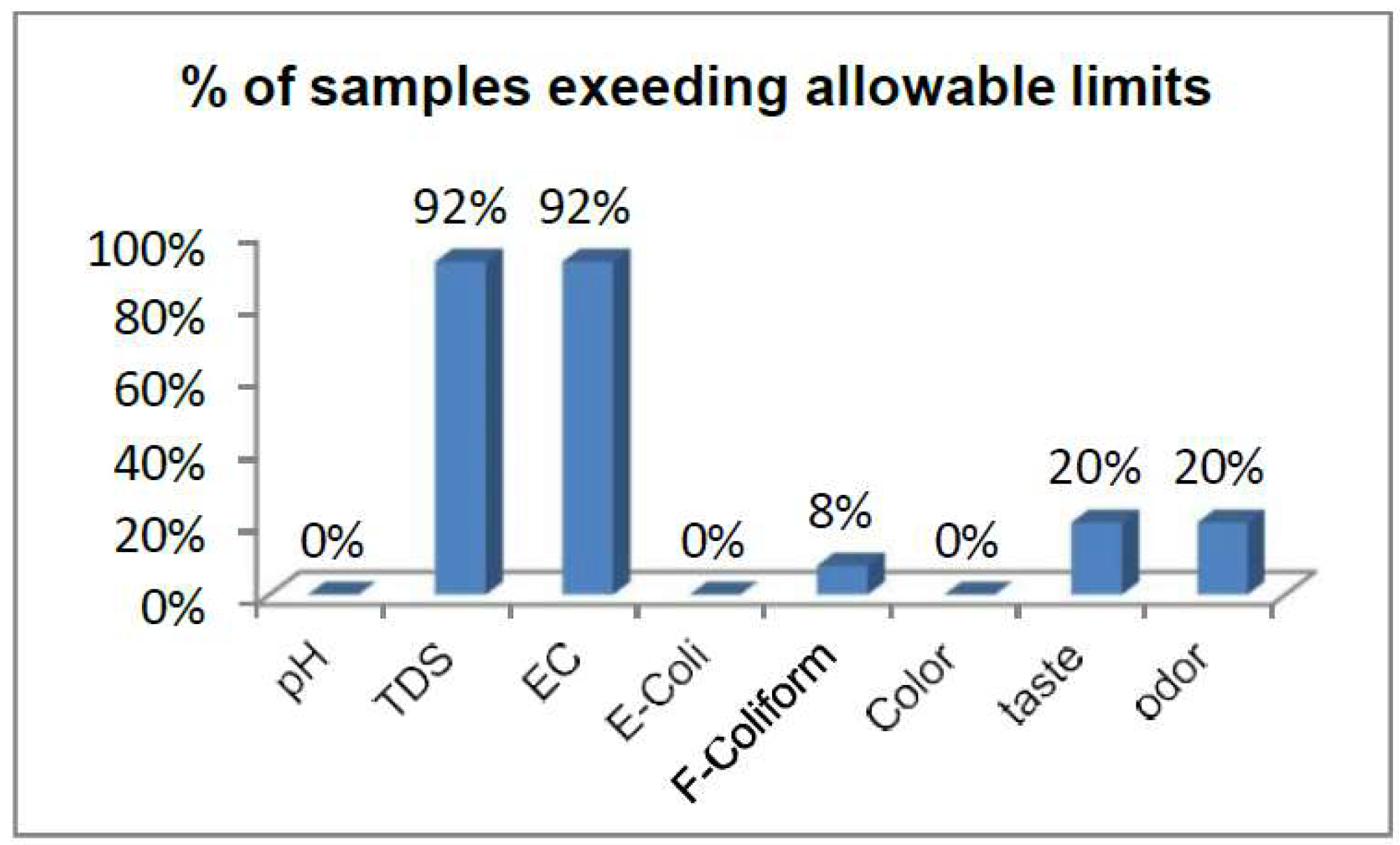
Overall, the results of groundwater samples based on the physical-biological analysis of groundwater samples is shown in
Figure 2.
4. Conclusion
Groundwater quality assessment has become a very important trend of research nowadays. This is because groundwater quality is on the verge of complete deterioration. The reasons behind the degrading quality of groundwater are natural and anthropogenic as well, but anthropogenic reasons are the major cause of poor groundwater quality. Groundwater is the single source of drinking water in Larkana City the residents of Larkana city rely on, that’s why residents of Larkana City are extremely affected by the deteriorating groundwater quality. This study, therefore, was carried out to find the suitability of groundwater focusing on the physical and biological properties of groundwater. The evaluation of groundwater samples divulged that the groundwater is extremely contaminated and its contamination is truly represented by its color, taste, odor, TDS, EC, and fecal coliform. The results of the analysis of forty groundwater samples revealed that although samples were colorless with no turbidity, 20% of the samples exhibited the odor of sewage water. Moreover, 20% of samples exhibited a slightly bitter taste, particularly the samples collected from Ahsan Colony, Mahdi Colony, Sachal Colony, and QUEST campus Larkana. Moreover, 92% of samples had values of Total Solids and EC beyond permissible limits. Further, none of the samples had a concentration of e- Coli above allowable limits, but 8% of samples were found to have fecal Coliform beyond suggested values.
Overall, water was not suitable in many parts of Larkana city. Extensive research on the groundwater of Larkana city is also recommended in which application of mathematical models such as WQI should be made.
References
- Samtio, M. S., Jahangir, T. M., Mastoi, A. S., Lanjwani, M. F., Rajper, R. H., Lashari, R. A., ... & Noonari, M. W. (2023). Impact of rock- water interaction on hydrogeochemical characteristics of groundwater: Using multivariate statistical, water quality index and irrigation indices of chachro sub-district, thar desert, sindh, Pakistan. Groundwater for Sustainable Development, 20, 100878.
- Jamali, M. Z., Solangi, G. S., Keerio, M. A., Keerio, J. A., & Bheel, N. (2023). Assessing and mapping the groundwater quality of Taluka Larkana, Sindh, Pakistan, using water quality indices and geospatial tools. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 20(8), 8849-8862. [CrossRef]
- Qamar, K., Nchasi, G., Mirha, H. T., Siddiqui, J. A., Jahangir, K., Shaeen, S. K., ... & Essar, M. Y. (2022). Water sanitation problem in Pakistan: A review on disease prevalence, strategies for treatment and prevention. Annals of Medicine and Surgery, 104709. [CrossRef]
- Jamali, M. Z., Khoso, S., Soomro, Z., Sohu, S., & Abro, A. F. (2022). EVALUATING THE SUITABILITY OF GROUNDWATER IN PAKISTAN: AN ANALYSIS OF WATER QUALITY USING SYNTHETIC POLLUTION INDEX (SPI) AND WATER QUALITY INDEX (WQI). International Journal of Energy, Environment and Economics, 30(3), 311-328.
- Lanjwani, M. F., Khuhawar, M. Y., & Jahangir Khuhawar, T. M. (2022). Assessment of groundwater quality for drinking and irrigation uses in taluka Ratodero, district Larkana, Sindh, Pakistan. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 102(16), 4134-4157. [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S., Jamali, M. Z., Khoso, S., Azeem, F., & Ansari, A. A. (2022). ASSESSMENT OF GROUNDWATER QUALITY IN RURAL AREAS OF TALUKA DOKRI, SINDH, PAKISTAN, THROUGH PHYSICOCHEMICAL PARAMETERS. International Journal of Energy, Environment and Economics, 30(3), 211-226.
- Jamali, M. Z., Solangi, G. S., & Keerio, M. A. (2020). Assessment of Groundwater Quality of Taluka Larkana, Sindh, Pakistan. International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, 11(5), 795-797.
- Solangi, G. S., Siyal, A. A., Babar, M. M., & Siyal, P. (2019). Evaluation of drinking water quality using the water quality index (WQI), the synthetic pollution index (SPI) and geospatial tools in Thatta district, Pakistan. Desalination and Water Treatment, 160, 202-213. [CrossRef]
- Jamali, M. Z., Solangi, G. S., Keerio, M. A., Keerio, J. A., & Bheel, N. (2023). Assessing and mapping the groundwater quality of Taluka Larkana, Sindh, Pakistan, using water quality indices and geospatial tools. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 20(8), 8849-8862. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).