Submitted:
07 October 2024
Posted:
09 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
This paper presents a comprehensive review of the transformative impact of 3D printing technology on smart cities. As cities face rapid urbanization, resource shortages, and environmental degradation, innovative solutions such as additive manufacturing (AM) offer potential pathways for sustainable urban development. By synthesizing 66 publications from 2015 to 2024, the study examines how 3D printing improves urban infrastructure, enhances sustainability, and fosters community engagement in city planning. Key benefits of 3D printing include reducing construction time and material waste, lowering costs, and enabling the creation of scalable, affordable housing solutions. The paper also addresses emerging areas such as the integration of 3D printing with digital twins (DT), machine learning (ML), and AI to optimize urban infrastructure and predictive maintenance. It highlights the use of smart materials and soft robotics for structural health monitoring (SHM), and repairs. Despite the promising advancements, challenges remain in terms of cost, scalability, and the need for interdisciplinary collaboration among engineers, urban planners, and policymakers. The findings suggest a roadmap for future research and practical applications of 3D printing in smart cities, contributing to the ongoing discourse on sustainable and technologically advanced urban development.
Keywords:
1. Introduction
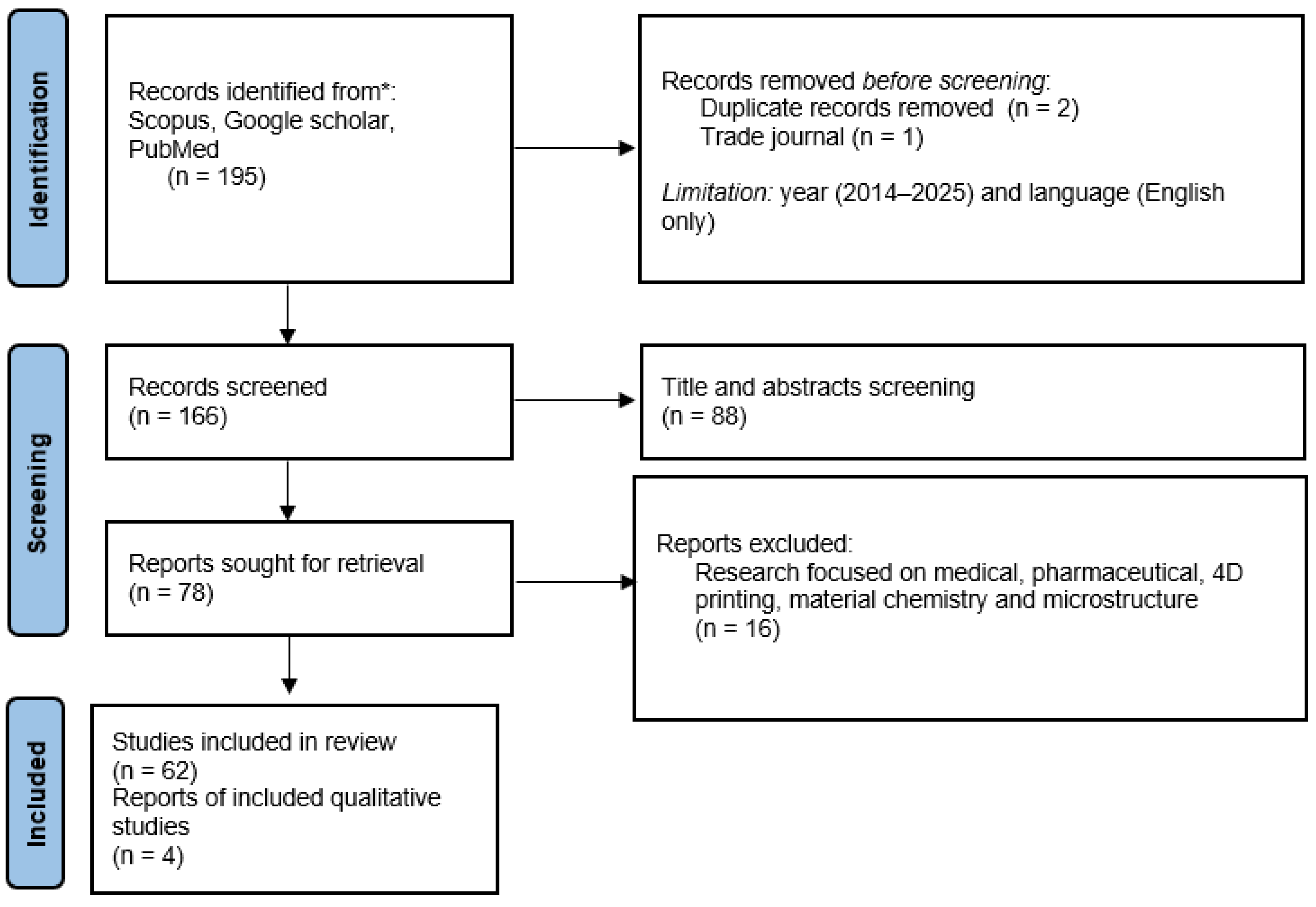
2. Methodology
2.1. In-/Exclusion Criteria
- Regarding the utilization of 3D printing for smart city perspective
- The paper needs to use current 3D printing technologies with a published date later than 2015
- Provide a detailed explanation of the effectiveness of each technology offers
- Must be occurred in the smart city settings
- Only English language used
- Exclude the topics focused on medical, pharmaceutical, automative, 4D printing, material microstructure applications
- General argument
- Trade article
- The paper is based on another study
- The investigation lacks adequate information regarding the AR/VR technology
2.2. Data Extraction
3. Review Analysis and Discussion
3.1. Thematic Analysis on Keywords
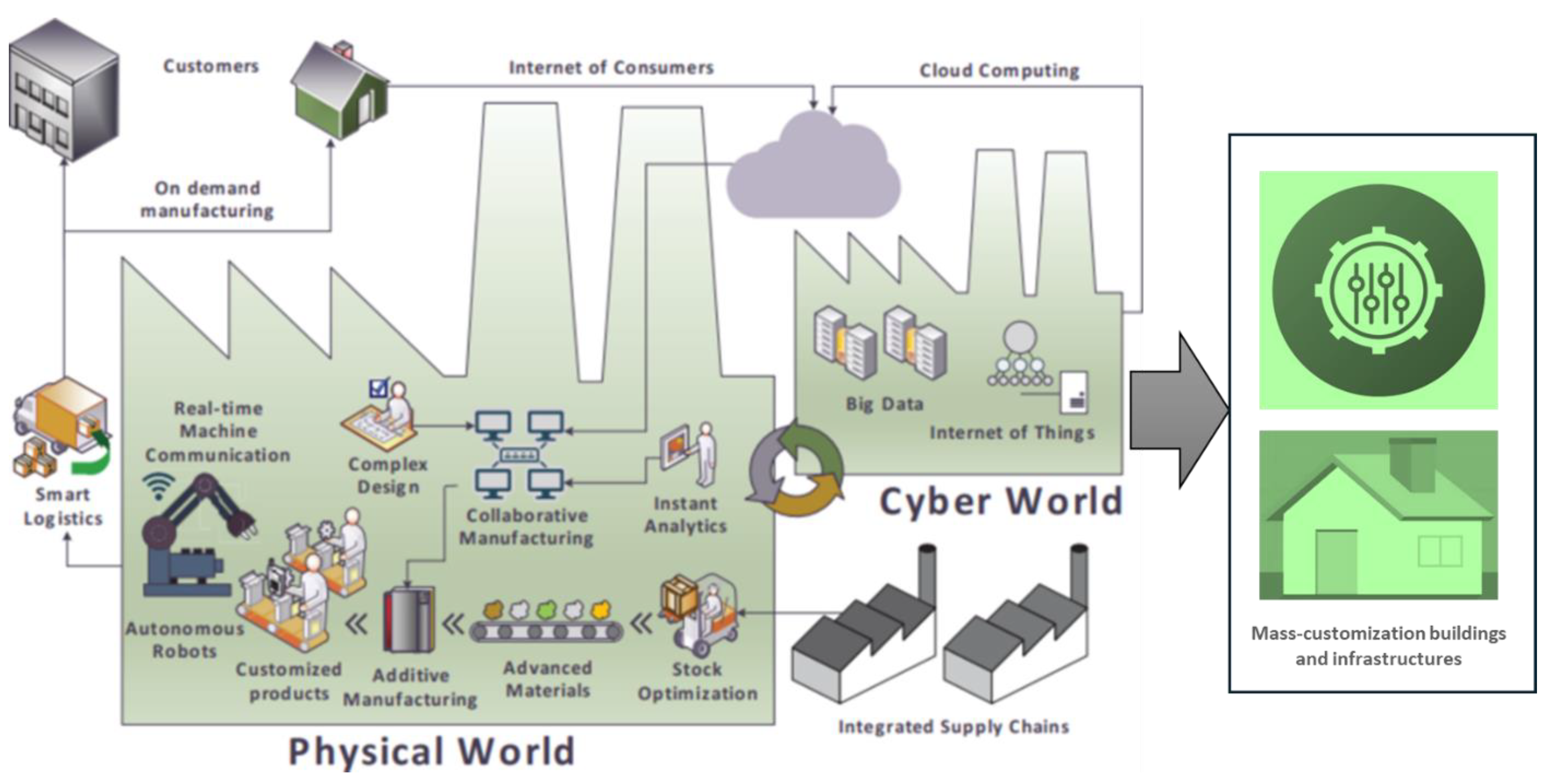
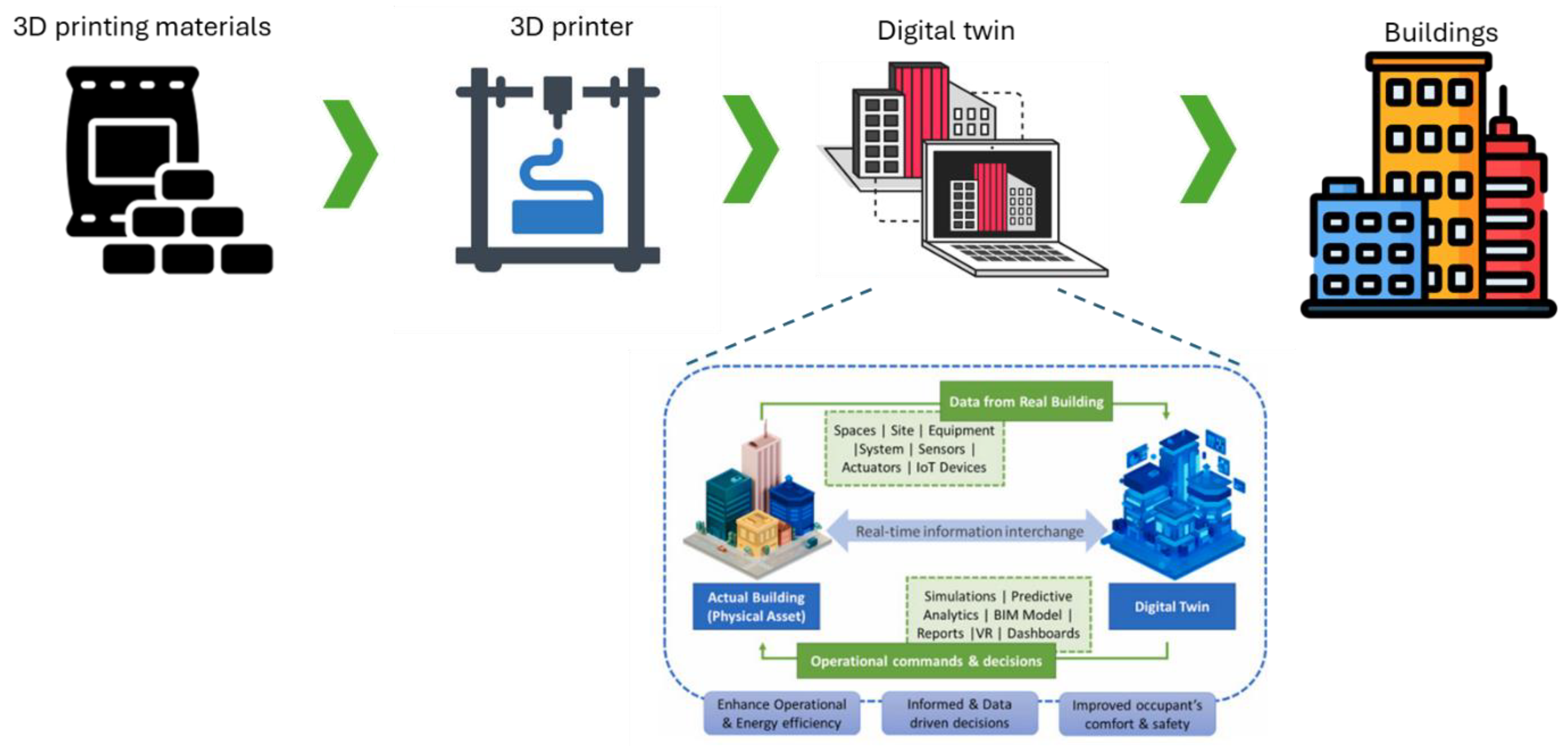
3.2. Digital Twins (DT) in 3D Printing for Smart Cities
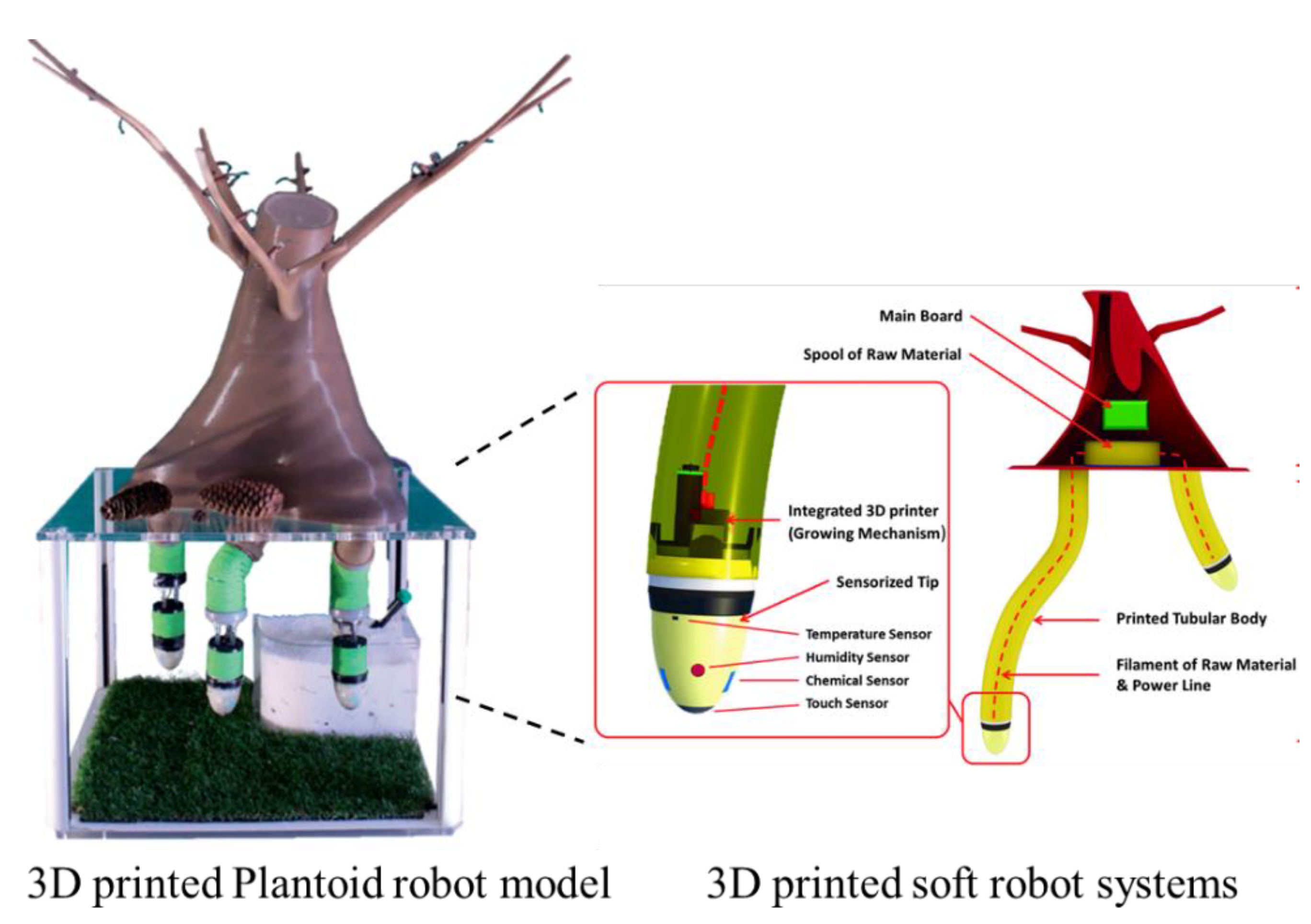
3.4. Smart 3D Printing Materials for Smart Cities
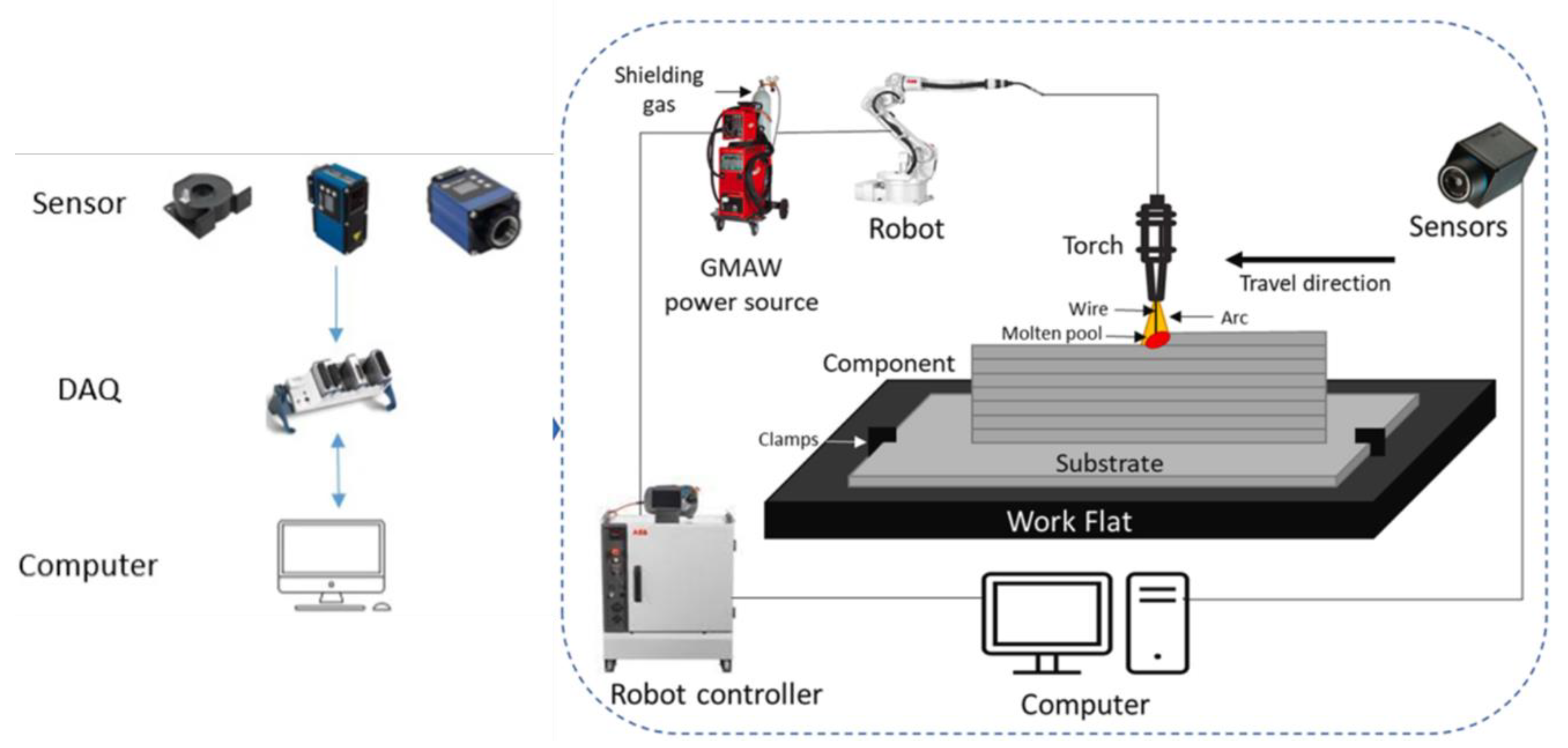
3.6. Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing (WAAM) for Smart Cities
3.7. Machine Learning (ML) in 3D Printing for Smart Cities
3.9. Repair Strategies in 3D Printing for Smart Cities
4. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dixon, T.; Eames, M. Sustainable urban development to 2050: complex transitions in the built environment of cities. In Urban Retrofitting for Sustainability; Routledge, 2014; Volume 19, p. 47. [Google Scholar]
- Asif, M.; Naeem, G.; Khalid, M. Digitalization for sustainable buildings: Technologies, applications, potential, and challenges. Journal of Cleaner Production 2024, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žujović, M.; Obradović, R.; Rakonjac, I.; Milošević, J. 3D printing technologies in architectural design and construction: a systematic literature review. Buildings 2022, 12, 1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwish, L.R.; El-Wakad, M.T.; Farag, M.M. Towards sustainable industry 4.0: A green real-time IIoT multitask scheduling architecture for distributed 3D printing services. Journal of Manufacturing Systems 2021, 61, 196–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Lange, K. W. Planning Principles for Integrating Community Empowerment into Zero-Net Carbon Transformation. Smart Cities 2022, 6, 100–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loy, J.; Novak, J. I. Additive manufacturing for a dematerialized economy. In Sustainable Manufacturing and Design; Elsevier, 2021; pp. 19–45. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.-C.; Yu, S.-N.; Chen, Z.-X.; Weng, Y.-W.; Xue, J.; Liu, X. Promoting additive construction in fast-developing areas: An analysis of policies and stakeholder perspectives. Developments in the Built Environment 2023, 16, 100271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachs, J.D.; Lafortune, G.; Fuller, G.; Drumm, E. Sustainable development report 2023: Implementing the SDG Stimulus; 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Bamigboye, G.O.; Bassey, D.E.; Olukanni, D.O.; Ngene, B.U.; Adegoke, D.; Odetoyan, A.O.; Kareem, M.A.; Enabulele, D.O.; Nworgu, A.T. Waste materials in highway applications: An overview on generation and utilization implications on sustainability. Journal of Cleaner Production 2021, 283, 124581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, G.H. A review of “3D concrete printing”: Materials and process characterization, economic considerations and environmental sustainability. Journal of Building Engineering 2023, 66, 105863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muriungi, K.; Chumo, K. P. Building Future-Proof, Sustainable, and Innovative Startups in Africa Powered by Smart Cities. In Green Computing for Sustainable Smart Cities; CRC Press, 2024; pp. 172–205. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, K.; Zindani, D.; Davim, J. P. Rapid prototyping, rapid tooling and reverse engineering: from biological models to 3D Bioprinters; Walter de Gruyter GmbH & Co KG, 2020; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Jiramarootapong, P.; Prasittisopin, L.; Snguanyat, C.; Tanapornraweekit, G.; Tangtermsirikul, S. In Load carrying capacity and failure mode of 3D printing mortar wall panel under axial compression loading. Second RILEM International Conference on Concrete and Digital Fabrication: Digital Concrete 2020 2, 2020; Springer, 2020; pp. 646–657. [Google Scholar]
- Prasittisopin, L.; Sakdanaraseth, T.; Horayangkura, V. Design and construction method of a 3D concrete printing self-supporting curvilinear pavilion. Journal of Architectural Engineering 2021, 27, 05021006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadakorn, W.; Prasertsuk, S.; Prasittisopin, L. In 3D Cement Printing: DFMA Guideline of Patterned Load-Bearing Walls for Small Residential Units, International Conference on Civil Engineering and Architecture, 2022; Springer, 2022; pp. 19–28. [Google Scholar]
- Bhanye, J.; Lehobo, M. T.; Mocwagae, K.; Shayamunda, R. Strategies for Sustainable Innovative Affordable Housing (SIAH) for low income families in Africa: A rapid review study. Discover Sustainability 2024, 5, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berjozkina, G.; Karami, R. 3D printing in tourism: an answer to sustainability challenges? Worldwide Hospitality and Tourism Themes 2021, 13, 773–788. [Google Scholar]
- Ayad, T. H.; Shehata, A. E. s. The Polential Impact of 3D Printing Technologies on Travel and Hospitality Industry. Journal of Association of Arab Universities for Tourism and Hospitality 2014, 11, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schelly, C.; Anzalone, G.; Wijnen, B.; Pearce, J. M. Open-source 3-D printing technologies for education: Bringing additive manufacturing to the classroom. Journal of Visual Languages & Computing 2015, 28, 226–237. [Google Scholar]
- Maloy, R.; Kommers, S.; Malinowski, A.; LaRoche, I. 3D modeling and printing in history/social studies classrooms: Initial lessons and insights. Contemporary Issues in Technology and Teacher Education 2017, 17, (2), 229–249. [Google Scholar]
- Houser, K. World’s largest 3D-printed affordable housing project launches in Kenya. In Freethink; 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Faleschini, F.; Trento, D.; Masoomi, M.; Pellegrino, C.; Zanini, M. A. Sustainable mixes for 3D printing of earth-based constructions. Construction and Building Materials 2023, 398, 132496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetiranont, S.; Sadakorn, W.; Rugkhapan, N. T.; Prasittisopin, L. Enhancing sustainable railway station design in tropical climates: Insights from Thailand’s architectural theses and case studies. Buildings 2024, 14, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikula, K.; Skrzypczak, D.; Izydorczyk, G.; Warchoł, J.; Moustakas, K.; Chojnacka, K.; Witek-Krowiak, A. 3D printing filament as a second life of waste plastics—A review. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 2021, 28, 12321–12333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhu, N.R.; Erfani, H.; Jadoun, S.; Amir, M.; Thiagarajan, Y.; Chauhan, N.P.S. Fused deposition modelling approach using 3D printing and recycled industrial materials for a sustainable environment: a review. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology 2022, 122, 2125–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartolomei, S.S.; da Silva, F. L, F.; de Moura, E.A.B.; Wiebeck, H. Recycling expanded polystyrene with a biodegradable solvent to manufacture 3D printed prototypes and finishing materials for construction. Journal of Polymers and the Environment 2022, 30, 3701–3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremer, M.; Janoschek, L.; Kaschta, D.; Schneider, N.; Wahl, M. Influence of plastic recycling—a feasibility study for additive manufacturing using glycol modified polyethylene terephthalate (PETG). SN Applied Sciences 2022, 4, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Rubeis, T. 3D-Printed Blocks: Thermal Performance Analysis and Opportunities for Insulating Materials. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Xiao, J.; Li, Z.; Feng, X. Experimental study on the thermal performance of a 3D printed concrete prototype building. Energy and Buildings 2021, 241, 110965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Corcuera, R.; Nuñez-Marcos, A.; Sesma-Solance, J.; Bilbao-Jayo, A.; Mulero, R.; Zulaika, U.; Azkune, G.; Almeida, A. Smart cities survey: Technologies, application domains and challenges for the cities of the future. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks 2019, 15, 1550147719853984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O'Dea, R.E.; Lagisz, M.; Jennions, M.D.; Koricheva, J.; Noble, D.W.; Parker, T.H.; Gurevitch, J.; Page, M.J.; Stewart, G.; Moher, D. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses in ecology and evolutionary biology: a PRISMA extension. Biological Reviews 2021, 96, 1695–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zastrow, M. The new 3D printing. Nature 2020, 578, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Ju, K.; Chen, H.; Mirabolghasemi, A.; Akhtar, S.; Sasmito, A.; Akbarzadeh, A. 3D printed architected shell-based ferroelectric metamaterials with programmable piezoelectric and pyroelectric properties. Nano Energy 2024, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, H.; He, F.; Yuan, L.; Hatamian, H.; Commins, P.; Pan, Z. Online distortion simulation using generative machine learning models: A step toward digital twin of metallic additive manufacturing. Journal of Industrial Information Integration 2024, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salaimanimagudam, M.P.; Jayaprakash, J. Selection of digital fabrication technique in the construction industry—A multi-criteria decision-making approach. Frontiers of Structural and Civil Engineering 2024, 18, 977–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paunikar, S.; Galanopoulos, G.; Rebillat, M.; Wirth, I.; Monteiro, E.; Margerit, P.; Mechbal, N. In Printed PZT Transducers Network for the Structural Health Monitoring of Foreign Object Damage Composite Panel. 11th European Workshop on Structural Health Monitoring, EWSHM 2024; 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Rojek, I.; Marciniak, T.; Mikołajewski, D. Digital Twins in 3D Printing Processes Using Artificial Intelligence. Electronics 2024, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattera, G.; Nele, L.; Paolella, D. Monitoring and control the Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing process using artificial intelligence techniques: a review. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing 2024, 35, 467–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corzo, D.; Alexandre, E.B.; Alshareef, Y.; Bokhari, F.; Xin, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Kosel, J.; Bryant, D.; Lubineau, G.; Baran, D. Cure-on-demand 3D printing of complex geometries for enhanced tactile sensing in soft robotics and extended reality. Materials Today 2024, 78, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shufrin, I.; Pasternak, E.; Dyskin, A. Environmentally Friendly Smart Construction—Review of Recent Developments and Opportunities. Applied Sciences 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botero-Valencia, J.; Martinez-Perez, A.; Hernández-García, R.; Castano-Londono, L. Exploring Spatial Patterns in Sensor Data for Humidity, Temperature, and RSSI Measurements. Data 2023, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, L.; Khouri, D.; Lomakin, K.; Hofmann, A.; Kleinlein, M.; Ullmann, I.; Vossiek, M.; Gold, G. 3D Printed Hemispherically Radiating Antenna for Broadband Millimeter Wave Applications. IEEE Open Journal of Antennas and Propagation 2023, 4, 558–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Zhang, G.; Chiumenti, M.; Cervera, M.; Slimani, M.; Ma, L.; Wei, L.; Lin, X. Smart-substrate: a novel structural design to avert residual stress accretion in directed energy deposition additive manufacturing. Virtual and Physical Prototyping 2023, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymond, L.; Bandala, E.; Coulter, R.; Valentin, N.; Mitchell, K.; Hua, W.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, D.; Jin, Y. Hybrid direct ink writing/embedded three-dimensional printing of smart hinge from shape memory polymer. Manufacturing Letters 2023, 35, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stano, G.; Ovy, S.M., A.I.; Edwards, J.R.; Cianchetti, M.; Percoco, G.; Tadesse, Y. One-shot additive manufacturing of robotic finger with embedded sensing and actuation. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology 2023, 124, 467–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, S.; Stein, M.; Ilic, O. Material Extrusion on an Ultrasonic Air Bed for 3D Printing. Journal of Vibration and Acoustics 2023, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, H.; He, F.; Yuan, L.; Commins, P.; Wang, H.; Pan, Z. Toward a smart wire arc additive manufacturing system: A review on current developments and a framework of digital twin. Journal of Manufacturing Systems 2023, 67, 174–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhall, S.; Rab, S.; Pal, S.K.; Javaid, M.; Khan, A.A.; Haleem, A. Identifying the feasibility of ‘travelator roads’ for modern-era sustainable transportation and its prototyping using additive manufacturing. Sustainable Operations and Computers 2023, 4, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Singh, R.; Ahuja, I. S. Smart Thermoplastics for Maintenance and Repair of Heritage Structures. In Encyclopedia of Materials: Plastics and Polymers; 2022; Volume 1-4, pp. 524–532. [Google Scholar]
- Binder, M.; Stapff, V.; Heinig, A.; Schmitt, M.; Seidel, C.; Reinhart, G. In Additive manufacturing of a passive, sensor-monitored 16MnCr5 steel gear incorporating a wireless signal transmission system. Procedia CIRP 2022, 2022, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjan, R.; Kumar, D.; Kundu, M.; Chandra Moi, S. In A critical review on Classification of materials used in 3D printing process. Materials Today: Proceedings 2022, 2022, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapas, N.; Belikovetsky, S.; Longo, F.; Puliafito, A.; Shabtai, A.; Elovici, Y. In 3D Marketplace: Distributed Attestation of 3D Designs on Blockchain. Proceedings - 2022 IEEE International Conference on Smart Computing, SMARTCOMP 2022; 2022; pp. 311–316. [Google Scholar]
- Alfattni, R. Comprehensive Study on Materials used in Different Types of Additive Manufacturing and their Applications. International Journal of Mathematical, Engineering and Management Sciences 2022, 7, 92–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safaee, S.; Otero, A.; Fei, M.; Liu, T.; Zhang, J.; Chen, R. K. Particle-resin systems for additive manufacturing of rigid and elastic magnetic polymeric composites. Additive Manufacturing 2022, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, B.; Demoly, F.; Zhang, Y.; Qi, H. J.; André, J. C.; Gomes, S. Origami-Based Design for 4D Printing of 3D Support-Free Hollow Structures. Engineering 2022, 12, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Bag, S.; Modgil, S.; Beatriz Lopes de Sousa Jabbour, A.; Kumar, A. Examining the influence of big data analytics and additive manufacturing on supply chain risk control and resilience: An empirical study. Computers and Industrial Engineering 2022, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Chang, J. In Electronics - A First Course for Printed Circuit Board Design, ASEE Annual Conference and Exposition, Conference Proceedings; 2022.
- Kyvelou, P.; Buchanan, C.; Gardner, L. Numerical simulation and evaluation of the world's first metal additively manufactured bridge. Structures 2022, 42, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubin, L.; Nwokedi, I.; Diwan, Y.; Moreno, O.; Kippelen, B. In Luminaire for Connected Lighting System with Spectrum that Mimics Natural Light. 2022 Opportunity Research Scholars Symposium, ORSS 2022; 2022; 2022, pp. 49–52. [Google Scholar]
- Reisch, R.T.; Hauser, T.; Lutz, B.; Tsakpinis, A.; Winter, D.; Kamps, T.; Knoll, A. Context awareness in process monitoring of additive manufacturing using a digital twin. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology 2022, 119, 3483–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubino, M.; Weng, M.; Chen, J.; Saptarshi, S.; Francisco, M.; Francisco, A.; Zhou, C.; Sun, H.; Xu, W. In A Campus Prototype of Interactive Digital Twin in Cyber Manufacturing. In SenSys 2022 - Proceedings of the 20th ACM Conference on Embedded Networked Sensor Systems; 2022; pp. 758–759. [Google Scholar]
- Na, S.; Kim, S.; Moon, S. Additive manufacturing (3D Printing)-applied construction: Smart node system for an irregular building façade. Journal of Building Engineering 2022, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, P.; Santi, G. M.; Leon-Cardenas, C.; Freddi, M.; Donnici, G.; Frizziero, L.; Liverani, A. Molds with advanced materials for carbon fiber manufacturing with 3d printing technology. Polymers 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eleftheriadis, G.K.; Genina, N.; Boetker, J.; Rantanen, J. Modular design principle based on compartmental drug delivery systems. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews 2021, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohn, D.; Zarek, M.; Elyashiv, A.; Sbitan, M. A.; Sharma, V.; Ramanujan, R. V. Remotely triggered morphing behavior of additively manufactured thermoset polymer-magnetic nanoparticle composite structures. Smart Materials and Structures 2021, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwis LS, M.; Bremer, K.; Roth, B. Fiber optic sensors embedded in textile-reinforced concrete for smart structural health monitoring: A review. Sensors 2021, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Yang, F.; Long, Y.; Dong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X. Bulk Ferroelectric Metamaterial with Enhanced Piezoelectric and Biomimetic Mechanical Properties from Additive Manufacturing. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 14903–14914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villacres, J.; Guaman, R.; Menendez, O.; Auat Cheein, F. In 3D Printing Deformation Estimation Using Artificial Vision Strategies for Smart-Construction, IECON Proceedings (Industrial Electronics Conference); 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Mileti, I.; Cortese, L.; Del Prete, Z.; Palermo, E. In Reproducibility and embedding effects on static performace of 3D printed strain gauges. 2021 IEEE International Workshop on Metrology for Industry 4.0 and IoT, MetroInd 4.0 and IoT 2021 - Proceedings, 2021; 2021; pp. 499–504. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Liou, F. Introduction to additive manufacturing. In Additive Manufacturing; 2021; pp. 1–31. [Google Scholar]
- Surie, G. In digital technologies and the world of the future: Implications for the management of technology. In Proceedings of the 30th International Conference of the International Association for Management of Technology, IAMOT 2021 - MOT for the World of the Future, 2021; 2021; pp. 173–189. [Google Scholar]
- Vlachakis, C.; Perry, M.; Biondi, L.; McAlorum, J. 3D printed temperature-sensing repairs for concrete structures. Additive Manufacturing 2020, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Gonzalez, D.; Garcia, J.; Newell, B.; Nawrocki, R. A. In The effects of additive manufacturing and electric poling techniques on PVdF thin films: Towards 3D printed functional materials. ASME 2020 Conference on Smart Materials, Adaptive Structures and Intelligent Systems, SMASIS 2020; 2020; 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Demir, K.; Gu, G. X. Machine Learning for Advanced Additive Manufacturing. Matter 2020, 3, 1541–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hehr, A.; Norfolk, M.; Kominsky, D.; Boulanger, A.; Davis, M.; Boulware, P. Smart build-plate for metal additive manufacturing processes. Sensors 2020, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, D.; Jiang, T.; Xiao, H. In Realtime Control-oriented Modeling and Disturbance Parameterization for Smart and Reliable Powder Bed Fusion Additive Manufacturing, Solid Freeform Fabrication 2018. In Proceedings of the 29th Annual International Solid Freeform Fabrication Symposium - An Additive Manufacturing Conference, SFF 2018; 2020; 2020, pp. 2335–2348. [Google Scholar]
- Castle, H. Disrupting from the Inside: UK Archipreneurs. Architectural Design 2020, 90, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.W.; Tsai, M.J. In Multi-Nozzle Pneumatic Extrusion Based Additive Manufacturing System for Fabricating a Sandwich Structure with Soft and Hard Material. Proceedings - International Conference on Machine Learning and Cybernetics, 2019; 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Dong, S.; Yu, X.; Han, B. A review of the current progress and application of 3D printed concrete. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing 2019, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidi, F.; Aslani, F. Additive manufacturing of cementitious composites: Materials, methods, potentials, and challenges. Construction and Building Materials 2019, 218, 582–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J. SMP Prototype Design and Fabrication for Thermo-responsive Façade Elements. Journal of Facade Design and Engineering 2019, 7, 41–61. [Google Scholar]
- Tay, Y.W., D.; Panda, B.N.; Ting GH, A.; Ahamed, N.M., N.; Tan, M.J.; Chua, C.K. In 3D printing for sustainable construction, Industry 4.0 - Shaping The Future of The Digital World. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Sustainable Smart Manufacturing, S2M 2019, 2019; 2019; pp. 119–123. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.; Mikkilineni, A.K.; Killough, S.M.; Kuruganti, T.; Joshi, P.C.; Hu, A. In Direct-Write Printed Current Sensor for Load Monitoring Applications. 2019 IEEE Power and Energy Society Innovative Smart Grid Technologies Conference, ISGT 2019; 2019; 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Chhetri, S.R.; Faezi, S.; Canedo, A.; Faruque, M.A. A. In QUILT: Quality inference from living digital twins in IoT-enabled manufacturing systems. In IoTDI 2019 - Proceedings of the 2019 Internet of Things Design and Implementation, 2019; 2019; pp. 237–248. [Google Scholar]
- Mallineni, S.S., K.; Dong, Y.; Behlow, H.; Rao, A.M.; Podila, R. A Wireless Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Advanced Energy Materials 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrizubieta, J.I.; Ruiz, J.E.; Martinez, S.; Ukar, E.; Lamikiz, A. In Intelligent nozzle design for the Laser Metal Deposition process in the Industry 4.0, Procedia Manufacturing,; 2017; pp. 1237–1244. [Google Scholar]
- Emon MO, F.; Choi, J.W. In A prelimiary study on 3D printed smart insoles with stretchable piezoresistive sensors for plantar pressure monitoring. ASME International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, Proceedings (IMECE), 2017; 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Mathew, J.; Hauser, C.; Stoll, P.; Kenel, C.; Polyzos, D.; Havermann, D.; Macpherson, W.N.; Hand, D.P.; Leinenbach, C.; Spierings, A.; Koenig-Urban, K.; Maier, R.R.J. Integrating Fiber Fabry-Perot Cavity Sensor into 3-D Printed Metal Components for Extreme High-Temperature Monitoring Applications. IEEE Sensors Journal 2017, 17, 4107–4114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paritala, P.K.; Manchikatla, S.; Yarlagadda, P.K.D.V. In Digital Manufacturing- Applications Past, Current, and Future Trends, Procedia Engineering; 2017; Volume 2017, pp. 982–991. [Google Scholar]
- Gooding, J.; Mahoney, J.F.; Fields, T.D. In 3D printed strain gauge geometry and orientation for embedded sensing. 58th AIAA/ASCE/AHS/ASC Structures, Structural Dynamics, and Materials Conference, 2017; 2017; 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, R.; Curran, S.; Chambon, P.; Post, B.; Love, L.; Wagner, R.; Ozpineci, B.; Chinthavali, M.; Starke, M.; Green, J.; Tryggestad, L.; Lee, B. In Overview of the oak ridge national laboratory advanced manufacturing integrated energy demonstration project: Case study of additive manufacturing as a tool to enable rapid innovation in integrated energy systems. ASME International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, Proceedings (IMECE), 2016; 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Shafaroudi, A.A.; Rankohi, S. In Multifunctional and multiphasics materials as load-bearing structural components. Proceedings, Annual Conference - Canadian Society for Civil Engineering, 2016; 2016; pp. 2108–2116. [Google Scholar]
- Ghazanfari, A.; Li, W.; Leu, M.C.; Zhuang, Y.; Huang, J. Advanced ceramic components with embedded sapphire optical fiber sensors for high temperature applications. Materials and Design 2016, 112, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimionis, J.; Isakov, M.; Koh, B.S.; Georgiadis, A.; Tentzeris, M.M. 3D-Printed Origami Packaging with Inkjet-Printed Antennas for RF Harvesting Sensors. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques 2015, 63, 4521–4532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatani, M.; Lu, Y.; Engeberg, E.D.; Choi, J.W. Combined 3D printing technologies and material for fabrication of tactile sensors. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing 2015, 16, 1375–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuvayanond, W.; Prasittisopin, L. Design for Manufacture and Assembly of Digital Fabrication and Additive Manufacturing in Construction: A Review. Buildings 2023, 13, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristombu Baduge, S.; Navaratnam, S.; Abu-Zidan, Y.; McCormack, T.; Nguyen, K.; Mendis, P.; Zhang, G.; Aye, L. Improving performance of additive manufactured (3D printed) concrete: A review on material mix design, processing, interlayer bonding, and reinforcing methods. Structures 2021, 29, 1597–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadakorn, W.; Prasertsuk, S.; Prasittisopin, L. Improving the structural efficiency of textured three-dimensional concrete printing wall by architectural design. Frontiers of Structural and Civil Engineering 2024, 18, 699–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibri, S.E.; Huang, J.; Jagatheesaperumal, S.K.; Krogstie, J. The synergistic interplay of artificial intelligence and digital twin in environmentally planning sustainable smart cities: A comprehensive systematic review. Environmental Science and Ecotechnology 2024, 20, 100433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagl, G.; Resch, B.; Blaschke, T. Contextual sensing: Integrating contextual information with human and technical geo-sensor information for smart cities. Sensors 2015, 15, 17013–17035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangawongse, S.; Ruangrit, V. Towards a GIS-based Urban Information System to Plan a Smarter Chiang Mai. Nakhara : Journal of Environmental Design and Planning 2015, 11, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Attaran, S.; Attaran, M.; Celik, B.G. Digital Twins and Industrial Internet of Things: Uncovering operational intelligence in industry 4.0. Decision Analytics Journal 2024, 10, 100398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, M. A.; Hagenmaier, M.; Bandte, O.; Parida, V.; Wincent, J. Smart cities, urban mobility and autonomous vehicles: How different cities needs different sustainable investment strategies. Technological Forecasting and Social Change 2022, 184, 121857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Babcock, J.; Pham, T.S.; Bui, T.H.; Kang, M. Smart city as a social transition towards inclusive development through technology: a tale of four smart cities. International Journal of Urban Sciences 2023, 27 (sup1), 75–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasittisopin, L.; Kitkuakul, P.; Chotchakornpant, K.; Rugkhapan, N.T. Implementing the Sister City Policy: Perspectives from Thailand. Nakhara : Journal of Environmental Design and Planning 2024, 23, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Gu, S. Industry 4.0, a revolution that requires technology and national strategies. Complex & Intelligent Systems 2021, 7, 1311–1325. [Google Scholar]
- Belli, L.; Cilfone, A.; Davoli, L.; Ferrari, G.; Adorni, P.; Di Nocera, F.; Dall’Olio, A.; Pellegrini, C.; Mordacci, M.; Bertolotti, E. IoT-enabled smart sustainable cities: Challenges and approaches. Smart Cities 2020, 3, 1039–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimmer, M. Automating Fab Cities: 3D Printing and Urban Renewal. In Automating Cities: Design, Construction, Operation and Future Impact; Wang, B.T., Wang, C.M., Eds.; Springer Singapore: Singapore, 2021; pp. 255–272. [Google Scholar]
- Saad Alotaibi, B.; Ibrahim Shema, A.; Umar Ibrahim, A.; Awad Abuhussain, M.; Abdulmalik, H.; Aminu Dodo, Y.; Atakara, C. Assimilation of 3D printing, Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Internet of Things (IoT) for the construction of eco-friendly intelligent homes: An explorative review. Heliyon 2024, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavi, A.H.; Feng, M.; Jiao, P.; Sharif-Khodaei, Z. The Rise of Smart Cities: Advanced Structural Sensing and Monitoring Systems. Butterworth-Heinemann, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- de Souza, E.A.; Borges, P.H.R.; Stengel, T.; Nematollahi, B.; Bos, F.P. 3D printed sustainable low-cost materials for construction of affordable social housing in Brazil: Potential, challenges, and research needs. Journal of Building Engineering 2024, 87, 108985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.S.Y. In 3D Printing for Smart Urbanism: Towards City Livability, Research and Innovation Forum 2023, Cham, 2024//, 2024; Visvizi, A., Troisi, O., Corvello, V., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2024; pp. 205–217. [Google Scholar]
- Prashar, G.; Vasudev, H.; Bhuddhi, D. Additive manufacturing: expanding 3D printing horizon in industry 4.0. International Journal on Interactive Design and Manufacturing (IJIDeM) 2023, 17, 2221–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrpouya, M.; Dehghanghadikolaei, A.; Fotovvati, B.; Vosooghnia, A.; Emamian, S.S.; Gisario, A. The potential of additive manufacturing in the smart factory industrial 4.0: A review. Applied Sciences 2019, 9, (18), 3865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, K.; Brunoe, T.D.; Jensen, K.N.; Andersen, A.-L. Utilization of Mass Customization in Construction and Building Industry, Managing Complexity, Cham, 2017//, 2017; Bellemare, J., Carrier, S., Nielsen, K., Piller, F.T., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2017; pp. 115–125. [Google Scholar]
- Placino, P.; Rugkhapan, N.T. Making visible concrete’s shadow places: Mixing environmental concerns and social inequalities into building materials. Environment & Urbanization 2024, 36, 195–213. [Google Scholar]
- Syed, A.S.; Sierra-Sosa, D.; Kumar, A.; Elmaghraby, A. IoT in Smart Cities: A Survey of Technologies, Practices and Challenges. Smart Cities 2021, 4, 429–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A. A novel framework for waste management in smart city transformation with industry 4.0 technologies. Research in Globalization 2024, 9, 100234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, L.; Singh, D. A Review on Smart City Using IOT. International Journal of Innovative Research in Computer Science & Technology 2022, 10, 88–91. [Google Scholar]
- Demir, E.; Eyers, D.; Huang, Y. Competing through the last mile: Strategic 3D printing in a city logistics context. Computers & Operations Research 2021, 131, 105248. [Google Scholar]
- Olsson, N.O.E.; Arica, E.; Woods, R.; Madrid, J.A. Industry 4.0 in a project context: Introducing 3D printing in construction projects. Project Leadership and Society 2021, 2, 100033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepasgozar, S.M.E.; Shi, A.; Yang, L.; Shirowzhan, S.; Edwards, D. J. Additive Manufacturing Applications for Industry 4.0: A Systematic Critical Review. Buildings 2020, 10, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, S.; Shukla, V.; Islam, N.; Manghat, S. Construction industry 4.0 and sustainability: an enabling framework. IEEE transactions on engineering management 2021, 71, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsaramirsis, G.; Kantaros, A.; Al-Darraji, I.; Piromalis, D.; Apostolopoulos, C.; Pavlopoulou, A.; Alrammal, M.; Ismail, Z.; Buhari, S. M.; Stojmenovic, M. A modern approach towards an industry 4.0 model: From driving technologies to management. Journal of Sensors 2022, 2022, 5023011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adel, A. The convergence of intelligent tutoring, robotics, and IoT in smart education for the transition from industry 4.0 to 5.0. Smart Cities 2024, 7, 325–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Yang, Y.; Yang, G. Smart supply chain management in Industry 4.0: the review, research agenda and strategies in North America. Annals of Operations Research 2023, 322, 1075–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, H.; Soni, P.; Saeedi, A.; Shahverdi, M.; Dillenburger, B. In 3D Printing and Shape Memory Alloys. 42nd Annual Conference of the Association for Computer Aided Design in Architecture, ACADIA 2022, 2023; ACADIA, 2023; pp. 76–89. [Google Scholar]
- Nicolay, P.; Schlögl, S.; Thaler, S. M.; Humbert, C.; Filipitsch, B. Smart Materials for Green (er) Cities, a Short Review. Applied Sciences 2023, 13, 9289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, R.; Alsamhi, S. H.; Murray, N.; Devine, D. Shape memory alloy-based wearables: a review, and conceptual frameworks on HCI and HRI in Industry 4.0. Sensors 2022, 22, 6802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niazy, D.; Ashraf, M.; Bodaghi, M.; Zolfagharian, A. Resilient city perspective: 4D printing in art, architecture and construction. Materials Today Sustainability 2024, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Xu, J.; Huynh, T.; Abhishek, K.; Kumari, S.; Behera, A. Performance of Smart Alloys in Manufacturing Processes during Subtractive and Additive Manufacturing: A Short Review on SMA and Metal Alloys. Smart 3D Nanoprinting 2022, 267–280. [Google Scholar]
- Pecunia, V.; Occhipinti, L.G.; Hoye, R.L. Emerging indoor photovoltaic technologies for sustainable internet of things. Advanced Energy Materials 2021, 11, 2100698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Don Chua, W.F.; Lim, C.L.; Koh, Y.Y.; Kok, C.L. A Novel IoT Photovoltaic-Powered Water Irrigation Control and Monitoring System for Sustainable City Farming. Electronics 2024, 13, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maraveas, C.; Loukatos, D.; Bartzanas, T.; Arvanitis, K.G.; Uijterwaal, J.F. Smart and solar greenhouse covers: Recent developments and future perspectives. Frontiers in Energy Research 2021, 9, 783587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Guo, X.; Lee, C. Promoting smart cities into the 5G era with multi-field Internet of Things (IoT) applications powered with advanced mechanical energy harvesters. Nano Energy 2021, 88, 106304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, P.; Bhargava, L.; Suhag, A.K.; Choudhary, M.; Singh, S. An era of internet of things leads to smart cities initiatives towards urbanization. Digital Cities Roadmap: IoT-Based Architecture and Sustainable Buildings 2021, 319–350. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Z.; Li, W.; Dong, W.; Sun, Z.; Kodikara, J.; Sheng, D. Multifunctional asphalt concrete pavement toward smart transport infrastructure: Design, performance and perspective. Composites Part B: Engineering 2023, 110937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreu, A.; Lee, H.; Kang, J.; Yoon, Y.J. Self-Healing Materials for 3D Printing. Advanced Functional Materials 2024, 2315046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, K.R.; Down, M.P.; Banks, C. E. Future of additive manufacturing: Overview of 4D and 3D printed smart and advanced materials and their applications. Chemical Engineering Journal 2021, 403, 126162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, J.-T.; Ge, M.; Wu, Y.; Peng, S.; Zheng, L.; Chou, T.Y.; Wu, L. 3D printing of sacrificial thermosetting mold for building near-infrared irradiation induced self-healable 3D smart structures. Chemical Engineering Journal 2022, 427, 131580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczucka-Lasota, B.; Węgrzyn, T.; Silva, A.P.; Jurek, A. AHSS—Construction Material Used in Smart Cities. Smart Cities 2023, 6, 1132–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedi, M.; Al-Jabri, K.; Han, B.; Fangueiro, R.; Lourenço, P.B.; Correia, A.G. Advancing infrastructure resilience: A polymeric composite reinforcement grid with self-sensing and self-heating capabilities. Construction and Building Materials 2024, 435, 136730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Wang, K.; Yang, J.; Huang, J.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, J.; Wang, J.; Yang, H.; Li, S.; Miao, Y. Printable thermochromic hydrogel-based smart window for all-weather building temperature regulation in diverse climates. Advanced Materials 2023, 35, 2211716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Fu, J. Energy efficient thermochromic smart windows based on polymers and metal oxides. Journal of Polymer Science 2024, 62, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Chen, G.; Fu, J. Multifunctional thermochromic smart windows for building energy saving. Journal of Materials Chemistry A 2024. [CrossRef]
- Supian, A.; Asyraf, M.; Syamsir, A.; Najeeb, M.; Alhayek, A.; Al-Dala’ien, R.N.; Manar, G.; Atiqah, A. Thermochromic Polymer Nanocomposites for the Heat Detection System: Recent Progress on Properties, Applications, and Challenges. Polymers 2024, 16, 1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.; He, L.; Xuan, Q.; Liao, Y.; Dai, J.-G.; Lei, D. Phase-change VO2-based thermochromic smart windows. Light: Science & Applications 2024, 13, 255. [Google Scholar]
- Sekhar, M.C.; Veena, E.; Kumar, N.S.; Naidu, K.C.B.; Mallikarjuna, A.; Basha, D.B. A review on piezoelectric materials and their applications. Crystal Research and Technology 2023, 58, 2200130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Mai, Z.; Li, Z.; Yu, Z.; Ci, P.; Dong, S. A 3D-printing approach toward flexible piezoelectronics with function diversity. Materials Today 2023. [CrossRef]
- Pawar, O.; Lim, S. 3D-Printed piezoelectric nanogenerator with aligned graphitic carbon nitrate nanosheets for enhancing piezoelectric performance. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 2024, 654, 868–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Li, H.; Liu, S.; Xiao, Z.; Yuan, X.; Zhai, D.; Zhou, K.; Bowen, C. R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, D. 3D-Printed Flexible PVDF-TrFE Composites with Aligned BCZT Nanowires and Interdigital Electrodes for Piezoelectric Nanogenerator Applications. ACS Applied Polymer Materials 2023, 5, 4879–4888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Lee, P.S. Piezoelectric energy harvesting technology: from materials, structures, to applications. Small Structures 2022, 3, 2100128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Zhu, M.; Feng, X.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, T.; Guo, X.; Chen, T.; Liu, H.; Sun, L.; Lee, C. Intelligent cubic-designed piezoelectric node (iCUPE) with simultaneous sensing and energy harvesting ability toward self-sustained artificial intelligence of things (AIoT). ACS nano 2023, 17, 6435–6451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravikumar, C. In IoT applications powered by piezoelectric vibration energy harvesting device, International Conference on Information and Software Technologies, 2022; Springer, 2022; pp. 171–182. [Google Scholar]
- Tuloup, C.; Harizi, W.; Aboura, Z.; Meyer, Y. Integration of piezoelectric transducers (PZT and PVDF) within polymer-matrix composites for structural health monitoring applications: new success and challenges. International Journal of Smart and Nano Materials 2020, 11, 343–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, W.; Wei, F.; Yao, L.; Xie, S. A review of humidity-driven actuator: toward high response speed and practical applications. Journal of Materials Science 2022, 57, 12202–12235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, A. H.; Ben-Nissan, B. Hydrogel for Biomedical Applications: 3D/4D Printing, Self-healing, Microrobots, and Nanogenerators; Springer Nature, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Kuang, X.; Chen, K.; Dunn, C.K.; Wu, J.; Li, V.C.; Qi, H.J. 3D printing of highly stretchable, shape-memory, and self-healing elastomer toward novel 4D printing. ACS applied materials & interfaces 2018, 10, 7381–7388. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, B.; Li, H.; Wong, T.N.; Qian, S. Development of a Functional Cementitious Mixture with Expanded Graphite for Automated Spray Construction. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering 2023, 35, 04023226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Han, B.; Han, B.; Yu, X.; Zeng, S.; Ou, J. Intelligent concrete with self-x capabilities for smart cities. Journal of Smart Cities 2019, 2, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawongkerd, J.; Vichai, K.; Thamniap, B.; Prasittisopin, L.; Saensuk, O.; Keawsawasvong, S. A Study of Thermoelectric Energy Harvesting on Asphalt Concrete Pavement. Transportation Infrastructure Geotechnology 2024, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhu, H.; Yang, X.; Tan, Q.; Chen, Y. Fabrication and Performance Evaluation of High-Performance SBS-Modified Asphalt through Secondary Modification with Aminated Graphene Oxide. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering 2024, 36, 04024417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Win, T.T.; Prasittisopin, L.; Jongvivatsakul, P.; Likitlersuang, S. Investigating the synergistic effect of graphene nanoplatelets and fly ash on the mechanical properties and microstructure of calcium aluminate cement composites. Journal of Building Engineering 2023, 78, 107710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salah, H.A.; Mutalib, A.A.; Kaish, A.; Syamsir, A.; Algaifi, H.A. Development of ultra-high-performance silica fume-based mortar incorporating graphene nanoplatelets for 3-dimensional concrete printing application. Buildings 2023, 13, 1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulte, J.; Jiang, Z.; Sevim, O.; Ozbulut, O.E. Graphene-reinforced cement composites for smart infrastructure systems. The Rise of Smart Cities 2022, 79–114. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.; Lu, D.; Yin, B.; Leng, Z. Advancing carbon nanomaterials-engineered self-sensing cement composites for structural health monitoring: A state-of-the-art review. Journal of Building Engineering 2024, 109129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Alessandro, A.; Birgin, H.B.; Ubertini, F. In Advanced monitoring of structures and infrastructures through smart composite sensors and systems. Civil Structural Health Monitoring: Proceedings of CSHM-8 Workshop 8, 2021; Springer, 2021; pp. 485–498. [Google Scholar]
- Win, T.T.; Raengthon, N.; Prasittisopin, L. Advanced cement composites: Investigating the role of graphene quantum dots in improving thermal and mechanical performance. Journal of Building Engineering 2024, 96, 110556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Win, T.T.; Prasittisopin, L.; Nganglumpoon, R.; Pinthong, P.; Watmanee, S.; Tolek, W.; Panpranot, J. Chemo-physical mechanisms of high-strength cement composites with suprastructure of graphene quantum dots. Cleaner Materials 2024, 11, 100229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, A.; Yamkasikorn, P.; Wangtawesap, R.; Win, T.T.; Ngamkhanong, C.; Jongvivatsakul, P.; Prasittisopin, L.; Panpranot, J.; Kaewunruen, S. Effect of Graphene Quantum Dots (GQDs) on the mechanical, dynamic, and durability properties of concrete. Construction and Building Materials 2024, 441, 137597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Win, T.T.; Prasittisopin, L.; Nganglumpoon, R.; Pinthong, P.; Watmanee, S.; Tolek, W.; Panpranot, J. Innovative GQDs and supra-GQDs assemblies for developing high strength and conductive cement composites. Construction and Building Materials 2024, 421, 135693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, K.A.; Lino, F.A.; Henríquez, J.R.; Teggar, M.; Laouer, A.; Arici, M.; Benhorma, A.; Rodríguez, D. Enhancement techniques for the reduction of heating and cooling loads in buildings: a review. Journal of Energy and Power Technology 2023, 5, 1–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Block, A.B.; Palou, J.E.; Courtant, M.; Virtuani, A.; Cattaneo, G.; Roten, M.; Li, H.; Despeisse, M.; Hessler-Wyser, A.; Desai, U. Colouring solutions for building integrated photovoltaic modules: A review. Energy and Buildings 2024, 114253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Pero, C.; Leonforte, F.; Aste, N. Building-Integrated Photovoltaics in Existing Buildings: A Novel PV Roofing System. Buildings 2024, 14, 2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciampi, G.; Spanodimitriou, Y.; Scorpio, M.; Rosato, A.; Sibilio, S. Energy performances assessment of extruded and 3d printed polymers integrated into building envelopes for a south Italian case study. Buildings 2021, 11, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, S.; Mustafa, M.A.; Ghadir, G.K.; Al-Tmimi, H.M.; Alani, Z.K.; Rusho, M.A.; Rajeswari, N. Unlocking the potential of polymer 3D printed electronics: Challenges and solutions. Applied Chemical Engineering 2024, 3877–3877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, P.Q.; Courchesne, N.M.D.; Duraj-Thatte, A.; Praveschotinunt, P.; Joshi, N.S. Engineered living materials: prospects and challenges for using biological systems to direct the assembly of smart materials. Advanced Materials 2018, 30, 1704847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Ramanujan, D.; Ramani, K.; Chen, Y.; Williams, C.B.; Wang, C.C.; Shin, Y.C.; Zhang, S.; Zavattieri, P.D. The status, challenges, and future of additive manufacturing in engineering. Computer-aided design 2015, 69, 65–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, J.-h.; Kim, H.; Choi, Y.; Lee, H. 3D printed energy devices: generation, conversion, and storage. Microsystems & Nanoengineering 2024, 10, 93. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Liang, J. Recent development of printed micro-supercapacitors: printable materials, printing technologies, and perspectives. Advanced Materials 2020, 32, 1805864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallin, T.J.; Pikul, J.; Shepherd, R.F. 3D printing of soft robotic systems. Nature Reviews Materials 2018, 3, 84–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, A.; Mondini, A.; Mazzolai, B. Toward self-growing soft robots inspired by plant roots and based on additive manufacturing technologies. Soft robotics 2017, 4, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bier, H.; Hidding, A.; Latour, M.; Oskam, P.; Alavi, H.; Külekci, A. Design-to-Robotic-Production and-Operation for Activating Bio-Cyber-Physical Environments. In Disruptive Technologies: The Convergence of New Paradigms in Architecture; Springer, 2023; pp. 45–57. [Google Scholar]
- Sadeghi, A.; Del Dottore, E.; Mondini, A.; Mazzolai, B. Passive morphological adaptation for obstacle avoidance in a self-growing robot produced by additive manufacturing. Soft robotics 2020, 7, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, S.V.; Sadat, D.; Tasnim, F.; Acosta, D.; Schwendeman, L.; Shahsavari, S.; Dagdeviren, C. Ubiquitous conformable systems for imperceptible computing. foresight 2022, 24, 75–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Block, A.E. HuggieBot: An interactive hugging robot with visual and haptic perception; ETH Zurich, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Hang, K.; Lyu, X.; Song, H.; Stork, J. A.; Dollar, A. M.; Kragic, D.; Zhang, F. Perching and resting—A paradigm for UAV maneuvering with modularized landing gears. Science Robotics 2019, 4, eaau6637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawk, C.; Zhou, H.; Sariyildiz, E.; In Het Panhuis, M.; Spinks, G. M.; Alici, G. Design, modeling, and control of a 3D printed monolithic soft robotic finger with embedded pneumatic sensing chambers. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics 2020, 26, 876–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawk, C.; Sariyildiz, E.; Alici, G. Force control of a 3D printed soft gripper with built-in pneumatic touch sensing chambers. Soft Robotics 2022, 9, 970–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, M.; Roy, A. The rise of interdisciplinarity in engineering education in the era of industry 4.0: implications for management practice. IEEE Engineering Management Review 2021, 49, 56–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, J.; AL-Rawi, M.; Hartley, C. Development of innovative cross-disciplinary engineering showcase. 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Dilibal, S.; Nohut, S.; Kurtoglu, C.; Owusu-Danquah, J. Data-Driven Generative Design Integrated with Hybrid Additive Subtractive Manufacturing (HASM) for Smart Cities. In Data-Driven Mining. In Learning and Analytics for Secured Smart Cities: Trends and Advances; Springer, 2021; pp. 205–228. [Google Scholar]
- Casas-Bocanegra, D.; Gomez-Vargas, D.; Pinto-Bernal, M.J.; Maldonado, J.; Munera, M.; Villa-Moreno, A.; Stoelen, M.F.; Belpaeme, T.; Cifuentes, C. A. In An open-source social robot based on compliant soft robotics for therapy with children with ASD, Actuators, 2020; MDPI, 2020; p. 91. [Google Scholar]
- Xi, W. Enhancing Awareness of Urban Greenbelts through the Integration of Soft Robots and Cultural Storytelling: A More-Than-Human Design Approach. 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, C.; Pan, Z.; Polden, J.; Li, H.; Xu, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Y. A review on wire arc additive manufacturing: Monitoring, control and a framework of automated system. Journal of manufacturing systems 2020, 57, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidan, I.; Huseynov, O.; Ali, M. A.; Alkunte, S.; Rajeshirke, M.; Gupta, A.; Hasanov, S.; Tantawi, K.; Yasa, E.; Yilmaz, O. Recent inventions in additive manufacturing: Holistic review. Inventions 2023, 8, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanzi, C. B.; Waldschmitt, B.; Knaack, U.; Lange, J. Transforming the Construction Industry Through Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing. In Coding Architecture: Designing Toolkits, Workflows, Industry; Springer, 2023; pp. 213–238. [Google Scholar]
- Chadha, K.; Dubor, A.; Cabay, E.; Tayoun, Y.; Naldoni, L.; Moretti, M. Additive Manufacturing for the Circular Built Environment: Towards Circular Construction with Earth-Based Materials. In A Circular Built Environment in the Digital Age; Springer International Publishing Cham, 2024; pp. 111–128. [Google Scholar]
- Dörrie, R.; Laghi, V.; Arrè, L.; Kienbaum, G.; Babovic, N.; Hack, N.; Kloft, H. Combined additive manufacturing techniques for adaptive coastline protection structures. Buildings 2022, 12, 1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Kaewunruen, S. State-of-the-art review on additive manufacturing technology in railway infrastructure systems. Journal of Composites Science 2022, 6, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rane, N.; Choudhary, S.; Rane, J. 4D/5D/6D Printing Technology in the Architecture, Engineering, and Construction (AEC) Industry: Applications, Challenges, and Future Advancements. Engineering, and Construction (AEC) Industry: Applications, Challenges, and Future Advancements (October 20, 2023). 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Khanpara, P.; Tanwar, S. Additive manufacturing: concepts and technologies. A Roadmap to Industry 4.0: Smart Production. Sharp Business and Sustainable Development 2020, 171–185. [Google Scholar]
- Laghi, V.; Palermo, M.; Gasparini, G.; Trombetti, T. Wire and arc additive manufacturing: Wire and arc additive manufacturing technology: A research perspective. Additive Manufacturing for Construction 2023, 141–159. [Google Scholar]
- Nyamuchiwa, K.; Palad, R.; Panlican, J.; Tian, Y.; Aranas Jr, C. Recent Progress in Hybrid Additive Manufacturing of Metallic Materials. Applied Sciences 2023, 13, 8383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, K.; Martinez, O.; Jain, P. Advanced manufacturing and digital twin technology for nuclear energy. Frontiers in Energy Research 2024, 12, 1339836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, M.; Langenberg, S.; Angermann, K.; Meier, H.-R. High-Tech Heritage:(Im) permanence of Innovative Architecture. Birkhäuser, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, P.D.; Nguyen, T.Q.; Tao, Q.; Vogel, F.; Nguyen-Xuan, H. A data-driven machine learning approach for the 3D printing process optimisation. Virtual and Physical Prototyping 2022, 17, 768–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, M.; Vendan, S.A. Data-Driven Models in Machine Learning: An Enabler of Smart Manufacturing. In Big Data Analytics in Smart Manufacturing: Principles and Practices; 2022; pp. 35–68. [Google Scholar]
- Baduge, S.K.; Thilakarathna, S.; Perera, J.S.; Arashpour, M.; Sharafi, P.; Teodosio, B.; Shringi, A.; Mendis, P. Artificial intelligence and smart vision for building and construction 4.0: Machine and deep learning methods and applications. Automation in Construction 2022, 141, 104440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhou, K.; Demoly, F.; Zhao, R.R.; Qi, H.J. Perspective: Machine learning in design for 3D/4D printing. Journal of Applied Mechanics 2024, 91, 030801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chigilipalli, B.K.; Karri, T.; Chetti, S.N.; Bhiogade, G.; Kottala, R.K.; Cheepu, M. A review on recent trends and applications of IoT in additive manufacturing. Applied System Innovation 2023, 6, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talaat, F.M.; Hassan, E. In Artificial intelligence in 3D printing, Enabling Machine Learning Applications in Data Science. Proceedings of Arab Conference for Emerging Technologies 2020, 2021; Springer, 2021; pp. 77–88. [Google Scholar]
- Prasittisopin, L.; Tuvayanond, W. In Machine Learning for Strength Prediction of Ready-Mix Concretes Containing Chemical and Mineral Admixtures and Cured at Different Temperatures. International Conference on Civil Engineering and Architecture, 2023; Springer, 2023; pp. 242–249. [Google Scholar]
- Tuvayanond, W.; Kamchoom, V.; Prasittisopin, L. Efficient machine learning for strength prediction of ready-mix concrete production (prolonged mixing). Construction Innovation 2024. [CrossRef]
- Mehta, P.; Mujawar, M.; LaFrance, S.; Bernadin, S.; Ewing, D.; Bhansali, S. Sensor-Based and Computational Methods for Error Detection and Correction in 3D Printing. ECS Sensors Plus 2024. [CrossRef]
- Pech, M.; Vrchota, J.; Bednář, J. Predictive maintenance and intelligent sensors in smart factory. Sensors 2021, 21, 1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampedro GA, R.; Putra MA, P.; Abisado, M. 3D-AmplifAI: An ensemble machine learning approach to digital twin fault monitoring for additive manufacturing in smart factories. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 64128–64140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suvarna, M.; Büth, L.; Hejny, J.; Mennenga, M.; Li, J.; Ng, Y. T.; Herrmann, C.; Wang, X. Smart manufacturing for smart cities—overview, insights, and future directions. Advanced Intelligent Systems 2020, 2, 2000043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jena, O. P.; Bhushan, B.; Kose, U. Machine learning and deep learning in medical data analytics and healthcare applications; CRC Press, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zain, M.; Keawsawasvong, S.; Thongchom, C.; Sereewatthanawut, I.; Usman, M.; Prasittisopin, L. Establishing efficacy of machine learning techniques for vulnerability information of tubular buildings. Engineered Science 2023, 27, 1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, G.D.; Sing, S.L.; Yeong, W.Y. A review on machine learning in 3D printing: applications, potential, and challenges. Artificial Intelligence Review 2021, 54, 63–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, E.; Brownjohn, J. Three decades of statistical pattern recognition paradigm for SHM of bridges. Structural Health Monitoring 2022, 21, 3018–3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayan, D.S.; Sivasuriyan, A.; Devarajan, P.; Krejsa, M.; Chalecki, M.; Żółtowski, M.; Kozarzewska, A.; Koda, E. Development of Intelligent Technologies in SHM on the Innovative Diagnosis in Civil Engineering—A Comprehensive Review. Buildings 2023, 13, 1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, M.; Lourenço, P.B.; Ramana, G. V. Structural health monitoring of civil engineering structures by using the internet of things: A review. Journal of Building Engineering 2022, 48, 103954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinno, R.; Haghshenas, S.S.; Guido, G.; Rashvand, K.; Vitale, A.; Sarhadi, A. The state of the art of artificial intelligence approaches and new technologies in structural health monitoring of bridges. Applied Sciences 2022, 13, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Liu, X.; Meves, J.; Billings, C.; Liu, Y. 3D Printed and Embedded Strain Sensors in Structural Composites for Loading Monitoring and Damage Diagnostics. Journal of Composites Science 2023, 7, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.; Blanloeuil, P.; Vinoth, T.; Howard, D.; Wang, C. H. In A 3D printed constriction-resistive sensor for the detection of ultrasonic waves. Mater. Res. Proc. 2021, 2021, 272–277. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, T.-H.; Moeinnia, H.; Kim, W. S. 3D printed vorticella-kirigami inspired sensors for structural health monitoring in Internet-of-Things. Materials & Design 2023, 234, 112332. [Google Scholar]
- Fitzpatrick, D.; Billings, C.; Liu, Y. In Lightweight Composites With 3D Printed Sensors for Real-Time Damage Detection. ASME Aerospace Structures, Structural Dynamics, and Materials Conference, 2023; American Society of Mechanical Engineers; 2023; p. V001T01A005. [Google Scholar]
- Hořejší, P.; Novikov, K.; Šimon, M. A smart factory in a Smart City: virtual and augmented reality in a Smart assembly line. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 94330–94340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamato, Y.; Fukumoto, Y.; Kumazaki, H. Proposal of real time predictive maintenance platform with 3D printer for business vehicles. International Journal of Information and Electronics Engineering 2016, 6, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birtchnell, T. 3D printing and the changing logistics of cities. In Handbook of Urban Mobilities; Routledge, 2020; pp. 348–356. [Google Scholar]
- Lipson, H.; Kurman, M. Fabricated: The new world of 3D printing; John Wiley & Sons, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bhanji, S.; Shotz, H.; Tadanki, S.; Miloudi, Y.; Warren, P. In Advanced enterprise asset management systems: Improve predictive maintenance and asset performance by leveraging Industry 4.0 and the Internet of Things (IoT). ASME/IEEE Joint Rail Conference, 2021; American Society of Mechanical Engineers; 2021; p. V001T12A002. [Google Scholar]
- Compare, M.; Baraldi, P.; Zio, E. Challenges to IoT-enabled predictive maintenance for industry 4.0. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2019, 7, 4585–4597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampedro, G.A.; Putra, M.A.P.; Lee, J.-M.; Kim, D.-S. Industrial Internet of Things-Based Fault Mitigation for Smart Additive Manufacturing using Multi-Flow BiLSTM. IEEE Access 2023. [CrossRef]
- Bibri, S.E.; Bibri, S.E. Data-driven smart sustainable cities: A conceptual framework for urban intelligence functions and related processes, systems, and sciences. Advances in the Leading Paradigms of Urbanism and their Amalgamation: Compact Cities, Eco–Cities, and Data–Driven. Smart Cities 2020, 143–173. [Google Scholar]
- Gkontzis, A.F.; Kotsiantis, S.; Feretzakis, G.; Verykios, V.S. Enhancing urban resilience: smart city data analyses, forecasts, and digital twin techniques at the neighborhood level. Future Internet 2024, 16, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, H.; Singh, M.K.; Gupta, M.; Madaan, J. Moving towards smart cities: Solutions that lead to the Smart City Transformation Framework. Technological forecasting and social change 2020, 153, 119281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagia, S.; Bornani, K.; Agrawal, R.; Satlewal, A.; Ďurkovič, J.; Lagaňa, R.; Bhagia, M.; Yoo, C. G.; Zhao, X.; Kunc, V. Critical review of FDM 3D printing of PLA biocomposites filled with biomass resources, characterization, biodegradability, upcycling and opportunities for biorefineries. Applied Materials Today 2021, 24, 101078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luque-del-Castillo, F.-d.-P.; Ladrón-de-Guevara-Muñoz, M.C.; de-Cózar-Macías, Ó.D.; Castillo-Rueda, F. J.; Pérez-García, J.; Martínez-Torres, J.-L. Construction of a Recycled Plastic Filament Winder for 3D Printing, Advances in Design Engineering IV, Cham, 2024//, 2024; Manchado del Val, C., Suffo Pino, M., Miralbes Buil, R., Moreno Sánchez, D., Eds.; Moreno Nieto, D., Eds. Springer Nature Switzerland: Cham, 2024; pp. 502–513. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, H.; Wei, Z.; Bahrami, A.; Kahla, N. B.; Ahmad, A.; Özkılıç, Y. O. Recent advancements and future trends in 3D printing concrete using waste materials. Developments in the Built Environment 2023, 100187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasittisopin, L.; Termkhajornkit, P.; Kim, Y.H. Review of concrete with expanded polystyrene (EPS): Performance and environmental aspects. Journal of Cleaner Production 2022, 366, 132919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krčma, M.; Škaroupka, D.; Vosynek, P.; Zikmund, T.; Kaiser, J.; Palousek, D. Use of polymer concrete for large-scale 3D printing. Rapid Prototyping Journal 2021, 27, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
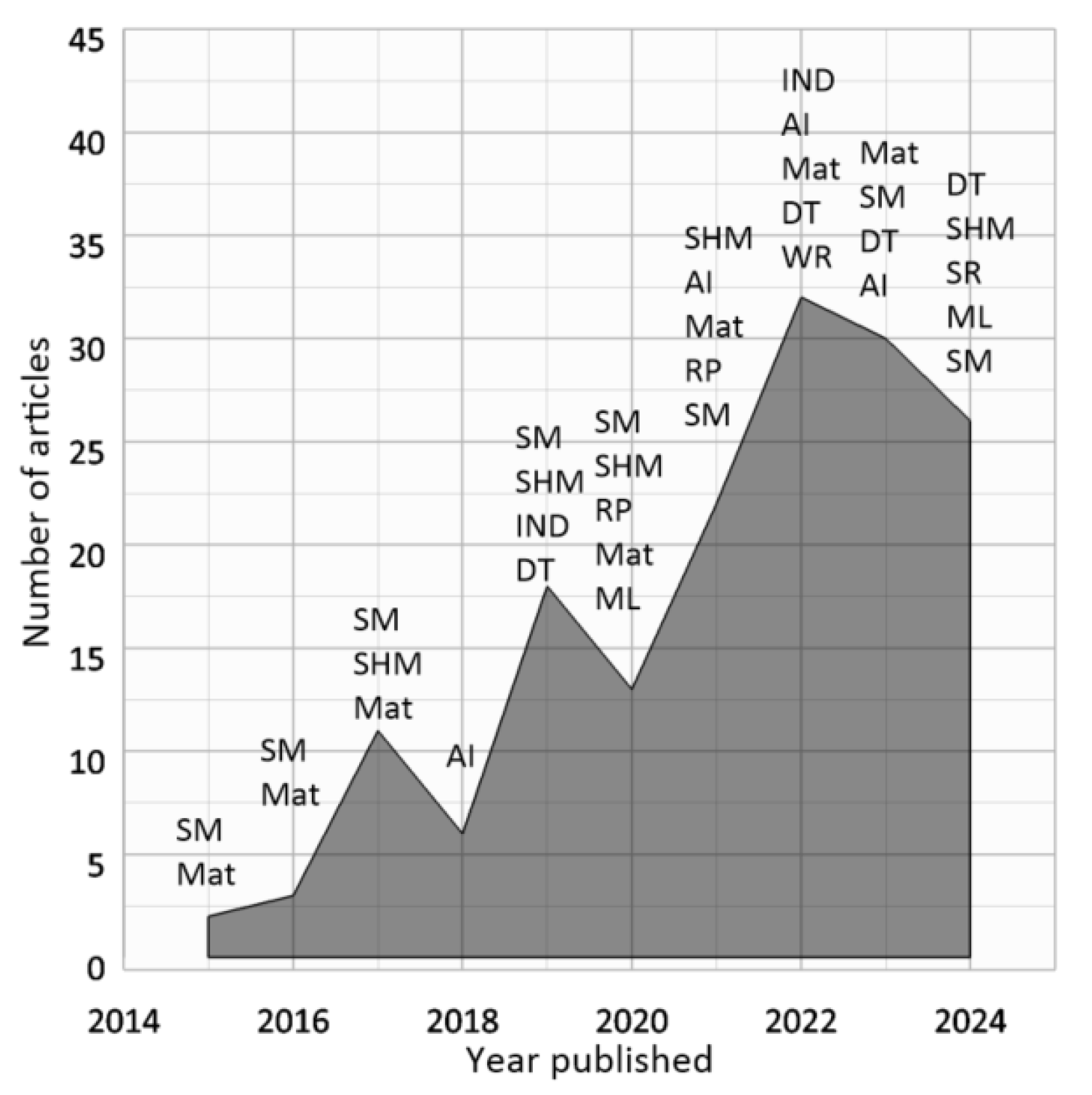
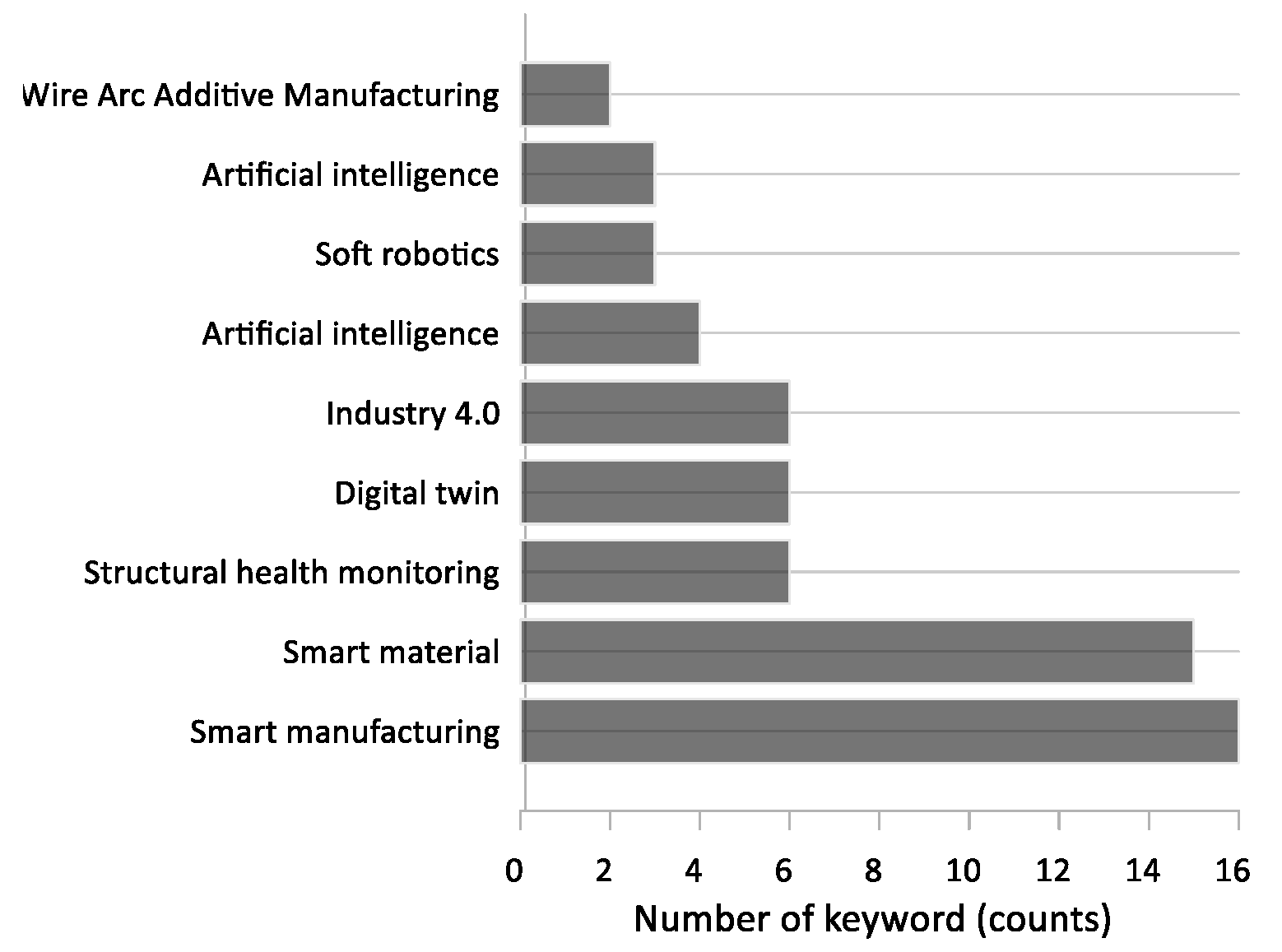
| Title | Year | Journal | Field of study | Source | |
| 3D printed architected shell-based ferroelectric metamaterials with programmable piezoelectric and pyroelectric properties | 2024 | Nano Energy | Smart materials | [33] | |
| Online distortion simulation using generative machine learning models: A step toward digital twin of metallic additive manufacturing | 2024 | Journal of Industrial Information Integration | Digital twin | [34] | |
| Selection of digital fabrication technique in the construction industry—A multi-criteria decision-making approach | 2024 | Frontiers of Structural and Civil Engineering | Smart manufacturing | [35] | |
| Printed PZT Transducers Network for the Structural Health Monitoring of Foreign Object Damage Composite Panel | 2024 | 11th European Workshop on Structural Health Monitoring | Structural health monitoring [36] | ||
| Digital Twins in 3D Printing Processes Using Artificial Intelligence | 2024 | Electronics | Digital twin | Industry 4.0 | [37] |
| Monitoring and control the Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing process using artificial intelligence techniques: a review | 2024 | Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing | Machine learning | Wire arc additive manufacturing | [38] |
| Digitalization for sustainable buildings: Technologies, applications, potential, and challenges | 2024 | Journal of Cleaner Production | Digital twin | [2] | |
| Cure-on-demand 3D printing of complex geometries for enhanced tactile sensing in soft robotics and extended reality | 2024 | Materials Today | Soft robotic | [39] | |
| Environmentally Friendly Smart Construction—Review of Recent Developments and Opportunities | 2023 | Applied Sciences | Digital twin | [40] | |
| Exploring Spatial Patterns in Sensor Data for Humidity, Temperature, and RSSI Measurements | 2023 | Data | Indoor climate | [41] | |
| 3D Printed Hemispherically Radiating Antenna for Broadband Millimeter Wave Applications | 2023 | IEEE Open Journal of Antennas and Propagation | Artificial intelligence | [42] | |
| Smart-substrate: a novel structural design to avert residual stress accretion in directed energy deposition additive manufacturing | 2023 | Virtual and Physical Prototyping | Smart material | [43] | |
| Hybrid direct ink writing/embedded three-dimensional printing of smart hinge from shape memory polymer | 2023 | Manufacturing Letters | Smart material | [44] | |
| One-shot additive manufacturing of robotic finger with embedded sensing and actuation | 2023 | International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology | Smart material | [45] | |
| Material Extrusion on an Ultrasonic Air Bed for 3D Printing | 2023 | Journal of Vibration and Acoustics | Smart material | [46] | |
| Toward a smart wire arc additive manufacturing system: A review on current developments and a framework of digital twin | 2023 | Journal of Manufacturing Systems | Digital twin | [47] | |
| Identifying the feasibility of ‘travelator roads’ for modern-era sustainable transportation and its prototyping using additive manufacturing | 2023 | Sustainable Operations and Computers | Smart manufacturing | [48] | |
| Smart Thermoplastics for Maintenance and Repair of Heritage Structures | 2022 | Encyclopedia of Materials: Plastics and Polymers | Smart material | [49] | |
| Additive manufacturing of a passive, sensor-monitored 16MnCr5 steel gear incorporating a wireless signal transmission system | 2022 | Procedia CIRP | Industry 4.0 | [50] | |
| A critical review on Classification of materials used in 3D printing process | 2022 | Materials Today: Proceedings | Smart material | [51] | |
| 3D Marketplace: Distributed Attestation of 3D Designs on Blockchain | 2022 | Proceedings - 2022 IEEE International Conference on Smart Computing | Industry 4.0 | [52] | |
| Comprehensive Study on Materials used in Different Types of Additive Manufacturing and their Applications | 2022 | International Journal of Mathematical, Engineering and Management Sciences | Smart material | [53] | |
| Particle-resin systems for additive manufacturing of rigid and elastic magnetic polymeric composites | 2022 | Additive Manufacturing | Smart material | [54] | |
| Origami-Based Design for 4D Printing of 3D Support-Free Hollow Structures | 2022 | Engineering | Smart material | [55] | |
| Examining the influence of big data analytics and additive manufacturing on supply chain risk control and resilience: An empirical study | 2022 | Computers and Industrial Engineering | Industry 4.0 | [56] | |
| Electronics - A First Course for Printed Circuit Board Design | 2022 | ASEE Annual Conference and Exposition | Artificial intelligence | [57] | |
| Numerical simulation and evaluation of the world's first metal additively manufactured bridge | 2022 | Structures | Digital twin | [58] | |
| Luminaire for Connected Lighting System with Spectrum that Mimics Natural Light | 2022 | 2022 Opportunity Research Scholars Symposium | Artificial intelligence | [59] | |
| Context awareness in process monitoring of additive manufacturing using a digital twin | 2022 | International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology | Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing | Digital twin | [60] |
| Screen-Printed FSS Plasterboard for Wireless Indoor Applications | 2022 | Mediterranean Microwave Symposium | Artificial intelligence | [60] | |
| A Campus Prototype of Interactive Digital Twin in Cyber Manufacturing | 2022 | Proceedings of the 20th ACM Conference on Embedded Networked Sensor Systems | Industry 4.0 | [61] | |
| Additive manufacturing (3D Printing)-applied construction: Smart node system for an irregular building façade | 2022 | Journal of Building Engineering | Smart manufacturing | [62] | |
| Molds with advanced materials for carbon fiber manufacturing with 3d printing technology | 2021 | Polymers | Smart material | [63] | |
| Modular design principle based on compartmental drug delivery systems | 2021 | Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews | Soft robotic | [64] | |
| Remotely triggered morphing behavior of additively manufactured thermoset polymer-magnetic nanoparticle composite structures | 2021 | Smart Materials and Structures | Soft robotic | [65] | |
| Fiber optic sensors embedded in textile-reinforced concrete for smart structural health monitoring: A review | 2021 | Sensors | Structural health monitoring [66] | ||
| Bulk Ferroelectric Metamaterial with Enhanced Piezoelectric and Biomimetic Mechanical Properties from Additive Manufacturing | 2021 | ACS Nano | Smart material | [67] | |
| 3D Printing Deformation Estimation Using Artificial Vision Strategies for Smart-Construction | 2021 | Industrial Electronics Conference | Artificial intelligence | [68] | |
| Reproducibility and embedding effects on static performance of 3D printed strain gauges | 2021 | IEEE International Workshop on Metrology for Industry 4.0 and IoT | Structural health monitoring [69] | ||
| Introduction to additive manufacturing | 2021 | Additive Manufacturing | Repair | [70] | |
| Digital technology and the world of the future: implications for the management of technology | 2021 | Proceedings of the 30th International Conference of the International Association for Management of Technology | Artificial intelligence | [71] | |
| 3D printed temperature-sensing repairs for concrete structures | 2020 | Additive Manufacturing | Repair | [72] | |
| The effects of additive manufacturing and electric poling techniques on PVdF thin films: Towards 3D printed functional materials | 2020 | ASME 2020 Conference on Smart Materials, Adaptive Structures and Intelligent Systems | Smart material | [73] | |
| Machine learning for advanced additive manufacturing | 2020 | Matter | Machine learning | [74] | |
| Smart build-plate for metal additive manufacturing processes | 2020 | Sensors | Structural health monitoring [75] | ||
| Realtime control-oriented modeling and disturbance parameterization for smart and reliable powder bed fusion additive manufacturing | 2020 | Proceedings of the 29th Annual International Solid Freeform Fabrication Symposium | Smart manufacturing | [76] | |
| Disrupting from the Inside: UK Archipreneurs | 2020 | Architectural Design | Smart manufacturing | [77] | |
| Multi-Nozzle Pneumatic Extrusion Based Additive Manufacturing System for Fabricating a Sandwich Structure with Soft and Hard Material | 2019 | Proceedings - International Conference on Machine Learning and Cybernetics | Smart manufacturing | [78] | |
| A review of the current progress and application of 3D printed concrete | 2019 | Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing | Smart material | [79] | |
| Additive manufacturing of cementitious composites: Materials, methods, potentials, and challenges | 2019 | Construction and Building Materials | Smart manufacturing | [80] | |
| SMP Prototype Design and Fabrication for Thermo-responsive Façade Elements | 2019 | Journal of Facade Design and Engineering | Smart manufacturing | [81] | |
| 3D printing for sustainable construction | 2019 | Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Sustainable Smart Manufacturing | Industry 4.0 | [82] | |
| Direct-Write Printed Current Sensor for Load Monitoring Applications | 2019 | IEEE Power and Energy Society Innovative Smart Grid Technologies Conference | Structural health monitoring [83] | ||
| QUILT: Quality inference from living digital twins in IoT-enabled manufacturing systems | 2019 | Proceedings of the 2019 Internet of Things Design and Implementation | Digital twin | [84] | |
| A Wireless Triboelectric Nanogenerator | 2018 | Advanced Energy Materials | Artificial intelligence | [85] | |
| Intelligent nozzle design for the Laser Metal Deposition process in the Industry 4.0 | 2017 | Procedia Manufacturing | Smart manufacturing | [86] | |
| A prelimiary study on 3D printed smart insoles with stretchable piezoresistive sensors for plantar pressure monitoring | 2017 | ASME International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition Proceedings | Smart manufacturing | [87] | |
| Integrating Fiber Fabry-Perot Cavity Sensor into 3-D Printed Metal Components for Extreme High-Temperature Monitoring Applications | 2017 | IEEE Sensors Journal | Smart material | [88] | |
| Digital Manufacturing- Applications Past, Current, and Future Trends | 2017 | Procedia Engineering | Smart manufacturing | [89] | |
| 3D printed strain gauge geometry and orientation for embedded sensing | 2017 | 58th AIAA/ASCE/AHS/ASC Structures, Structural Dynamics, and Materials Conference | Structural health monitoring [90] | ||
| Overview of the oak ridge national laboratory advanced manufacturing integrated energy demonstration project: Case study of additive manufacturing as a tool to enable rapid innovation in integrated energy systems | 2016 | ASME International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, Proceedings | Smart manufacturing | [91] | |
| Multifunctional and multiphasic materials as load-bearing structural components | 2016 | Proceedings, Annual Conference - Canadian Society for Civil Engineering | Smart material | [92] | |
| Advanced ceramic components with embedded sapphire optical fiber sensors for high temperature applications | 2016 | Materials and Design | Smart material | [93] | |
| 3D-Printed Origami Packaging with Inkjet-Printed Antennas for RF Harvesting Sensors | 2015 | IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques | Smart manufacturing | [94] | |
| Combined 3D printing technologies and material for fabrication of tactile sensors | 2015 | International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing | Smart material | [95] | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).