Submitted:
09 October 2024
Posted:
10 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Preparation of Mucus Extract
2.2. Treatment of Laboratory Animals by Mucus Extract and Scopolamine
2.3. Identification of Proteins on 2D -Gel Electrophoresis, Using Mass Spectrometry and Bioinformatics
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Snail Extract
4.2. Laboratory Animals
4.3. Scopolamine Induced Dementia
4.4. Treatment of the Laboratory Animals
4.5. Extraction of Proteins from the Rat Brain
4.6. 2D-PAGE Analysis
4.7. Trypsin Digestion of Protein Spots
4.8. Mass Spectrometric Analyses (MS and MS/MS)
4.9. Identification of Proteins
5. Conclusion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Knopman, D.S.; Amieva, H.; Petersen, R.C.; Chételat, G.; Holtzman, D.M.; Hyman, B.T.; Nixon, R.A; Jones, D.T. Alzheimer disease. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2021, 7(1), 33. [CrossRef]
- Sanabria-Castro, A.; Alvarado-Echeverría, I.; Monge-Bonilla, C. Molecular Pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s Disease: An Update. Ann Neurosci 2017, 24(1), 46-54. [CrossRef]
- Hajjo, R.; Sabbah, D.A.; Abusara, O.H.; Al Bawab, A.Q. A Review of the Recent Advances in Alzheimer’s Disease Research and the Utilization of Network Biology Approaches for Prioritizing Diagnostics and Therapeutics. Diagnostics 2022; 12(12): 2975, 1-40. [CrossRef]
- Nation, D.A.; Sweeney, M.D.; Montagne, A.; Sagare, A.P.; D’Orazio, L.M.; Pachicano, M.; Sepehrband, F.; Nelson, A.R.; Buennagel, D.P.; Harrington, M.G.; Benzinger, T.L.S.; Fagan, A.M.; Ringman, J.M.; Schneider,L.S.; Morris, J.C.; Chui, H.C.; Law, M.; Toga, A.W.; Zlokovic, B.V. Blood-brain barrier breakdown is an early biomarker of human cognitive dysfunction. Nat. Med 2019, 25, 270–276. [CrossRef]
- Perkovic, M.N.; Paska, A.V.; Konjevod, M.; Kouter, K.; Strac, D.S.; Erjavec, G.N.; Pivac, N. Epigenetics of Alzheimer’s Disease. Biomolecules 2021, 11(2): 195, 1-38. [CrossRef]
- Wenk, G.L. Neuropathologic changes in Alzheimer’s disease. JCP 2003, 64 (9), 7-10. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12934968/.
- Deacon, R.M. Housing, husbandry andbhandling of rodents for behavioral experiments. Nat Protoc 2006, 1(2), 936–946. [CrossRef]
- Benedikz, E.; Kloskowska, E.; Winblad, B. The rat as an animal model of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Cell. Mol. Med 2009, 13(6), 1034-1042. [CrossRef]
- Malekzadeh, S.; Edalatmanesh, M.A.; Mehrabani, D.; Shariati, M. Drugs Induced Alzheimer’s Disease in Animal Model. GMJ 2017, 6(3), 1-12. [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.N.; Yeong, K.Y. Scopolamine, a Toxin-Induced Experimental Model, Used for Research in Alzheimer’s Disease. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 2020, 19(2), 85-93. [CrossRef]
- Yadang, F.S.A.; Nguezeye, Y.; Kom, C.W.; Betote, P.H.D.; Mamat, A.; Tchokouaha, L.R.Y.; Taiwé, G.S.; Agbor, G.A.; Bum, E.N. Scopolamine-Induced Memory Impairment in Mice: Neuroprotective Effects of Carissa edulis (Forssk.) Valh (Apocynaceae) Aqueous Extract. Int J Alzheimers Dis 2020, 6372059, 1-10. [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.H.; Choi, B.J.; Chang, M.S.; Park, S.K. Nelumbo nucifera semen extract improves memory in rats with scopolamine-induced amnesia through the induction of choline acetyltransferase expression. Neurosci Lett 2009, 461(1), 41-44. [CrossRef]
- Perry, E.K.; Tomlinson, B.E.; Blessed, G.; Bergmann, K.; Gibson, P.H.; Perry, R.H. Correlation of cholinergic abnormalities with senile plaques and mental test scores in senile dementia. Br Med J 1978, 2(6150), 1457-1459. [CrossRef]
- Bunadri, P.; Neerati, V.; Merugu, S.; Akondi, B.R. Neuroprotective effect of resveratrol against Scopolamine-induced cognitive impairment and oxidative stress in rats. Arch Biol Sci 2013, 65(4), 1381–1386. [CrossRef]
- Dolashki, A.; Velkova, L.; Daskalova, E.; Zheleva N.; Topalova, Y.; Atanasov, V.; Voelter, W.; Dolashka, P. Antimicrobial Activities of Different Fractions from Mucus of the Garden Snail Cornu aspersum. Biomedicines 2020, 8(9), 315, 1-17. [CrossRef]
- Topalova, Y.; Belouhova, M.; Velkova, L.; Dolashki, A.; Zheleva, N.; Daskalova, E.; Kaynarov, D.; Voelter, W.; Dolashka, P. Effect and Mechanisms of Antibacterial Peptide Fraction from Mucus of C. aspersum against Escherichia coli NBIMCC 8785. Biomedicines 2022, 10(3), 672, 1-19. [CrossRef]
- Velkova, L.; Dolashki, A.; Petrova, V.; Pisareva, E.; Kaynarov, D.; Kermedchiev, M.; Todorova, M.; Dolashka, P. Antibacterial Properties of Peptide and Protein Fractions from Cornu aspersum Mucus. Molecules 2024, 29, 2886. [CrossRef]
- Vassilev, N.G.; Simova, S.D.; Dangalov, M.; Velkova, L.; Atanasov, V.; Dolashki, A.; Dolashka, P. An 1H NMR- and MS-Based Study of Metabolites Profiling of Garden Snail Helix aspersa Mucus. Metabolites 2020, 10(9), 360, 1-15. [CrossRef]
- Sawa, K.; Uematsu, T.; Korenaga, Y.; Hirasawa, R.; Kikuchi, M., Murata K.; Zhang, J.; Gai, X.; Sakamoto, K.; Koyama, T.; Satoh, T. Krebs cycle intermediates protective against oxidative stress by modulating the level of reactive oxygen species in neuronal HT22 cells. Antioxidants 2017, 6(1), 21, 1-9. [CrossRef]
- Tancheva, L.; Lazarova, M.; Velkova, L.; Dolashki, A.; Uzunova, D.; Minchev, B.; Petkova-Kirova, P.; Hassanova, Y.; Gavrilova, P.; Tasheva, K.; Taseva, T.; Hodzhev, Y.; Atanasov, A.G.; Stefanova, M.; Alexandrova, A.; Tzvetanova, E.; Atanasov, V.; Kalfin, R.; Dolashka, P. Beneficial Effects of Snail Helix aspersa Extract in an Experimental Model of Alzheimer’s Type Dementia. JAD 2022, 88(1), 155-175. [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Zeng, X.; Xu, G.; Wang, Z. The Potential Roles of Redox Enzymes in Alzheimer’s Disease: Focus on Thioredoxin. ASN neuro 2021, 13, 1759091421994351, 1-13. [CrossRef]
- Tsvetanova, E.; Alexandrova, A.; Georgieva, A.; Tancheva, L.; Lazarova, M.; Dolashka, P.; Velkova, L.; Dolashki, A.; Atanasov, V.; Kalfin, R. Effect of mucus extract of Helix aspersa on scopolamine-induced cognitive impairment and oxidative stress in rat’s brain. BCC 2020, 52(D), 107-111.
- Kang, D.E.; Woo, J.A. Cofilin, a Master Node Regulating Cytoskeletal Pathogenesis in Alzheimer’s Disease. JAD 2019, 72(1), 131-144. [CrossRef]
- Bishop, P.; Rocca, D.; Henley, J.M. Ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase L1 (UCH-L1): structure, distribution and roles in brain function and dysfunction. Biochem J 2016, 473(16), 2453-2462. [CrossRef]
- Kook, S.Y.; Jeong, H.; Kang, M.J.; Park, R.; Shin, H.J.; Han, S.H.; Son, S.M.; Song, H.; Baik. S.H.; Moon, M.; Yi, E.C.; Hwang, D.; Mook-Jung, I. Crucial role of calbindin-D28k in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease mouse model. Cell Death Differ 2014, 21(10), 1575-1587. [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Gibson, G.E. Up-regulation of the mitochondrial malate dehydrogenase by oxidative stress is mediated by miR-743a. J Neurochem 2011, 118(3), 440-448. [CrossRef]
- Pelucchi, S.; Stringhi, R.; Marcello, E. Dendritic Spines in Alzheimer’s Disease: How the Actin Cytoskeleton Contributes to Synaptic Failure. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21(3), 908, 1-23. [CrossRef]
- Bürklen, T.S.; Schlattner, U.; Homayouni, R.; Gough, K.; Rak, M.; Szeghalmi, A.; Wallimann, T. The creatine kinase/creatine connection to Alzheimer’s disease: CK-inactivation, APP-CK complexes and focal creatine deposits. J Biomed Biotechnol 2006, 2006(3), 35936, 1-12. [CrossRef]
- Kamphuis, W.; Middeldorp, J.; Kooijman, L.; Sluijs, J.A.; Kooi, E.J.; Moeton, M.; Freriks, M.; Mizee, M.R.; Hol, E.M. Glial fibrillary acidic protein isoform expression in plaque related astrogliosis in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 2014, 35(3), 492-510. [CrossRef]
- Sferra, A.; Nicita, F.; Bertini, E. Microtubule Dysfunction: A Common Feature of Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21(19), 7354, 1-37. [CrossRef]
- Campanella, C.; Pace, A.; Bavisotto, C.C.; Marzullo, P.; Gammazza, A.M.; Buscemi, S.; Piccionello, A.P. Heat Shock Proteins in Alzheimer’s Disease: Role and Targeting. Int J Mol Sci 2018, 19(9), 2603, 1-22. [CrossRef]
- Patro, S.; Ratna, S.; Yamamoto, H.A.; Ebenezer, A.T.; Ferguson D.S.; Kaur, A.; McIntyre, B.C.; Snow, R.; Solesio, M.E. ATP Synthase and Mitochondrial Bioenergetics Dysfunction in Alzheimer’s Disease. Int J. Mol Sci 2021, 22(20), 11185, 1-17. [CrossRef]
- Gunning, P.; O’Neill, G.; Hardeman, E. Tropomyosin-based regulation of the actin cytoskeleton in time and space. Physiol Rev 2008, 88(1), 1-35. [CrossRef]
- Gu, Q.; Cuevas, E.; Raymick, J.; Kanungo, J.; Sarkar, S. Downregulation of 14-3-3 Proteins in Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol Neurobiol 2020, 57(1), 32-40. [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, H.Y.; Li, T.; MacDonald, R.; Cho, C.M.; Leclerc, N.; Paudel, H.K. Interaction of 14-3-3ζ with microtubule-associated protein tau within Alzheimer’s disease neurofibrillary tangles. Biochemistry 2013, 52(37), 6445–6455. [CrossRef]
- Selvarasu, K.; Singh, A.K.; Iyaswamy, A.; Sreenivasmurthy, S.G.; Krishnamoorthi, S.; Bera, A.K.; Huang, J.D.; Durairajan, S.S.K. Reduction of kinesin I heavy chain decreases tau hyperphosphorylation, aggregation, and memory impairment in Alzheimer’s disease and tauopathy models. Front Mol Biosci 2022, 9, 1050768, 1-16. [CrossRef]
- Uchida, S.; Shumyatsky, G.P. Deceivingly dynamic: Learning-dependent changes in stathmin and microtubules. Neurobiol Learn Mem 2015, 124, 52-61. [CrossRef]
- Walser, M.; Svensson, J.; Karlsson, L.; Motalleb, R.; Åberg, M.; Kuhn, H.G.; Isgaard, J.; Åberg, N.D. Growth Hormone and Neuronal Hemoglobin in the Brain-Roles in Neuroprotection and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Front. Endocrinol 2021, 11, 606089, 1-15. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhao, B. Oxidative stress and the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2013, 316523, 1-11. [CrossRef]
- Makhaeva, G.F.; Lushchekina, S.V.; Boltneva, N.P.; Sokolov, V.B.; Grigoriev, V.V.; Serebryakova, O.G.; Vikhareva, E.A.; Aksinenko, A.Y.; Barreto, G.E.; Aliev, G.; Bachurin, S.O. Conjugates of γ-carbolines and phenothiazine as new selective inhibitors of butyrylcholinesterase and blockers of NMDA receptors for Alzheimer disease. Sci Rep 2015, 5, 13164, 1-11. [CrossRef]
- Ni, R.; Marutle, A.; Nordberg, A. Modulation of α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor and fibrillary amyloid-β interactions in Alzheimer’s disease brain. JAD 2013, 33(3), 841–851. [CrossRef]
- Sun T.; Yu N.; Zhai L.K.; Li N.; Zhang C.; Zhou L.; Huang Z.; Jiang X.Y.; Shen Y.; Chen Z.Y. (2013) c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK)-interacting protein-3 (JIP3) regulates neuronal axon elongation in a kinesin- and JNK-dependent manner. J Biol Chem 2013, 288(20), 14531-14543. [CrossRef]
- DeSalle, L.M.; Pagano, M. Regulation of the G1 to S transition by the ubiquitin pathway. FEBS Lett 2001, 490(3), 179-189. [CrossRef]
- Chait, B.T.; Kent, S.B. Weighing naked proteins: practical, high-accuracy mass measurement of peptides and proteins. Science 1992, 257(5078), 1885-1894. [CrossRef]
- Chuang, J.Y.; Lee, C.W.; Shih, Y.H.; Yang, T.; Yu, L.; Kuo, Y.M. Interactions between amyloid-beta and hemoglobin: implications for amyloid plaque formation in Alzheimer’s disease. PloS One 2012, 7(3):e33120, 1-10. [CrossRef]
- Dolashka, P.; Atanasov, D. Device for Collecting Extracts from Garden Snail. BG Utility Model Application Number 2656, 08.11.2013. Patent Number 2097, 31 August 2015. Available online: https://portal.bpo.bg/bpo_online/-/bpo/utility-model-detail (accessed on 19 May 2024).
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 1976, 72, 248-254. https://10.1006/abio.1976.9999.
- O’Farrell PH. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975, 250(10), 4007-21.
- Rosenfeld, J.; Capdevielle, J.; Guillemot, J.C.; Ferrara, P. In-gel digestion of proteins for internal sequence analysis after one- or two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Anal. Biochem., 1992, 203, 173-179.
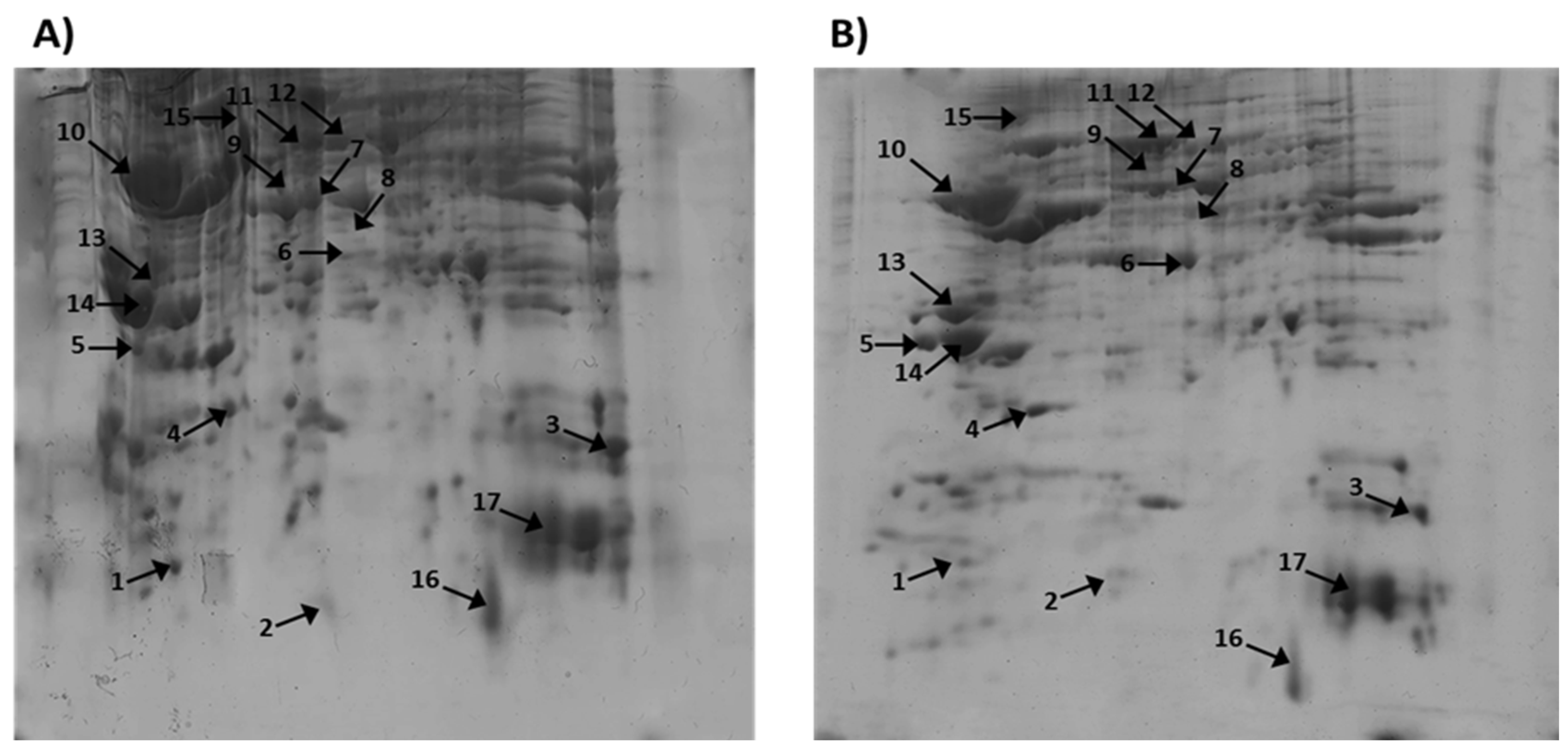
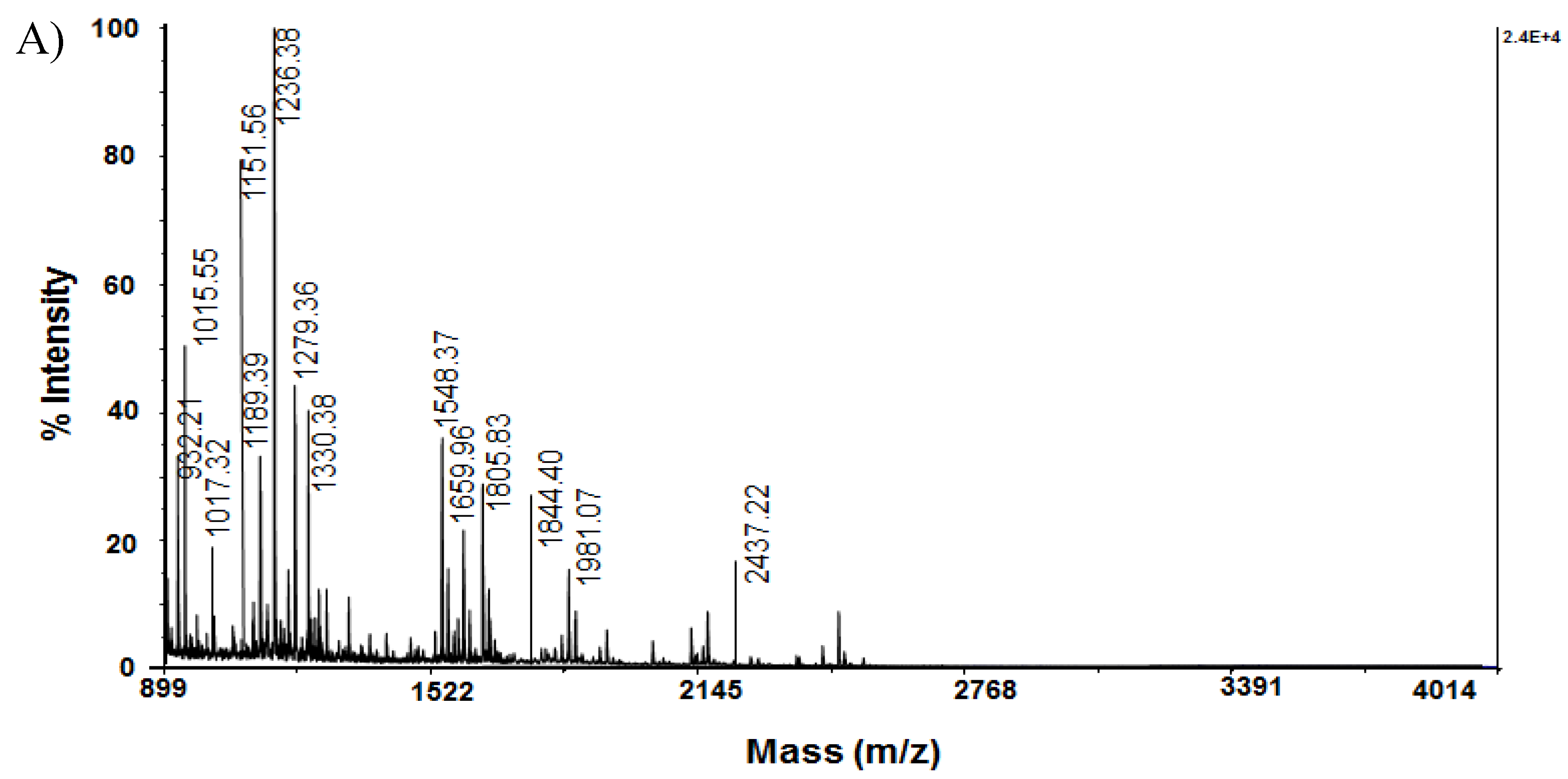
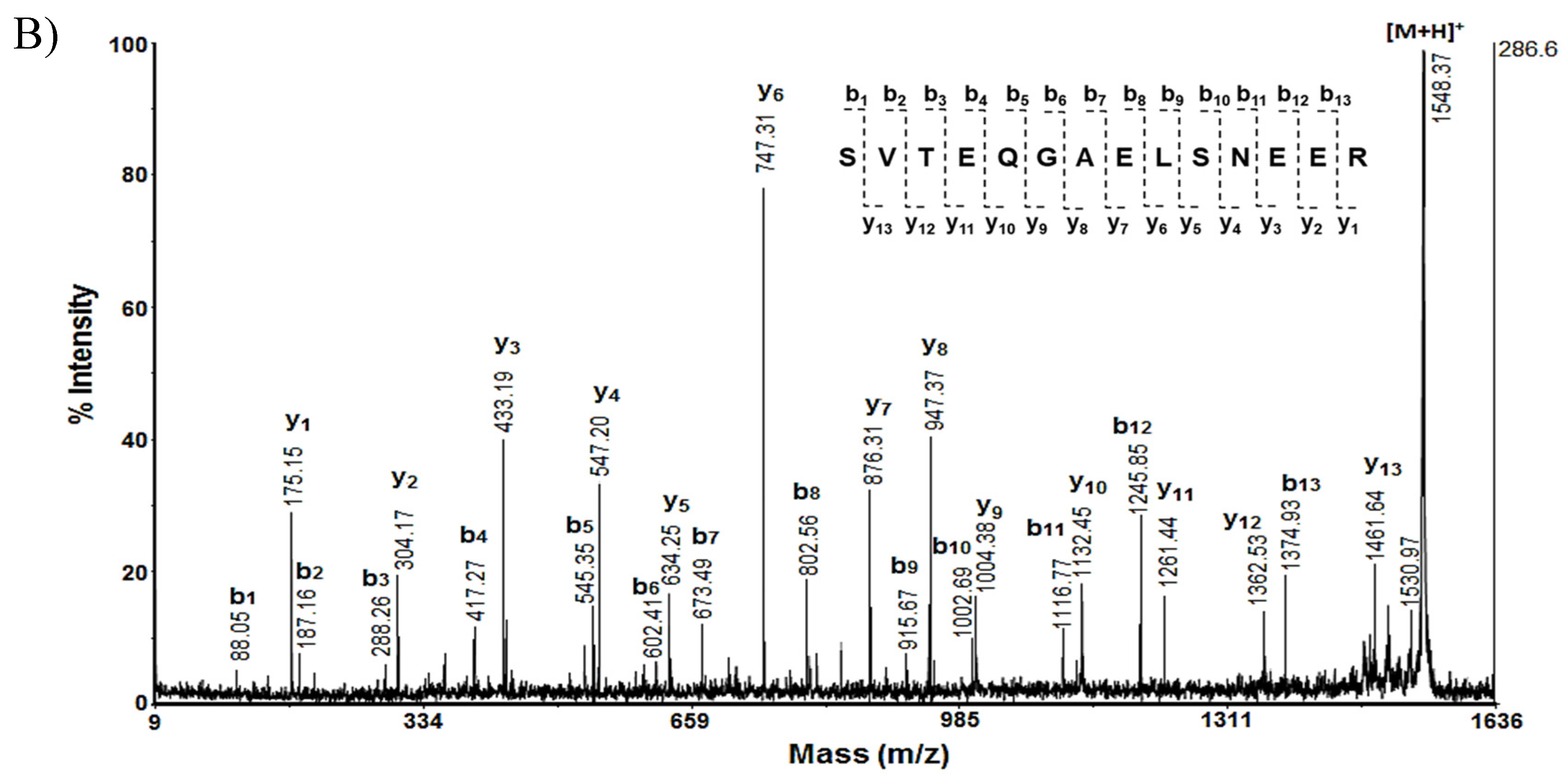
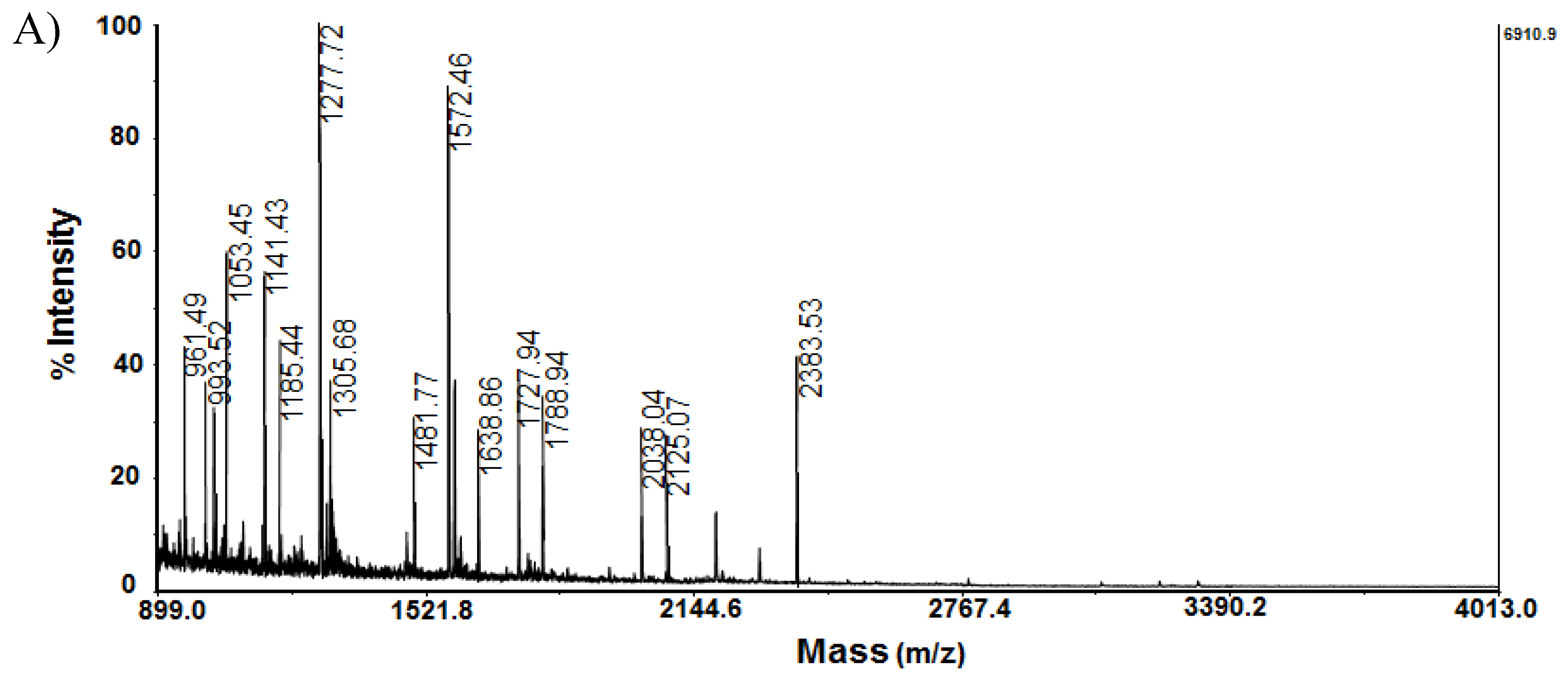
| Spot № | Protein Name | Molecular Function | Biological Process |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Thioredoxin P11232 (THIO_RAT) | Thioredoxin (Trh) nitrosylates the active Cys site of caspase 3 in response to nitric oxide and thereby inhibits caspase-3 activity. | Trh has multiple biological functions, including protective cellular mechanisms against oxidative stress and cytokine-induced damage. Enhancement of endogenous Trx expression and administration of exogenous Trx inducers play neuroprotective roles in BA and activate pro-survival signaling pathways [21]. |
| 2 | Superoxide dismutase [Cu-Zn] P07632, SODC_RAT) | CuZnSOD catalyzes the dismutation of the highly reactive superoxide anion to O2 and to the less reactive species H2O2. | It is suggested that CuZnSOD plays a major role in the antioxidant defense system of nervous tissue. In aging and in AD disease, a decrease in the expression levels of the enzyme is usually observed [22]. |
| 3 | Cofilin-1; P45592, (COF1_RAT) | Cofilin binds to F-actin and exhibits pH-sensitive F-actin depolymeri- zing activity. | Cofilin is required for neural tube morphogenesis and neural crest cell migration. Activated cofilin acts as a bridge between actin and microtubule dynamics by displacing tau from microtubules and leading to tauopathy [23]. |
| 4 | Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase isozyme L1 Q00981 (UCHL1_RAT) | This enzyme is a thiol protease that recognizes and hydrolyzes a peptide bond at the C-terminal glycine of ubiquitin. | There is evidence that UCH L1 binds and co-localizes with monoubiquitin and prolongs the half-life of ubiquitin. and Uch-L1 reduction is part of a cycle that favors Aβ accumulation in vascular injury [24]. |
| 5 | Calbindin P07171 (CALB1_RAT) | Calbindin (CB) buffers cytosolic calcium. It can stimulate membrane Ca2+-ATPase and 3′,5′-cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase. | CB has a critical role in maintaining calcium homeostasis and preventing neuronal death. Experiments have shown that removal of CB from the amyloid precursor protein presenilin in transgenic mice worsens the pathogenesis of AD, suggesting a critical role of CB in the pathogenesis of AD [25]. |
| 6 | Malate dehydrogenase, cytoplasmic O88989 (MDHC_RAT) | Catalyzes the reduction of aromatic alpha-keto acids in the presence of NADH. | It plays an essential role in the malate-aspartate shuttle and the citric acid cycle, important for the mitochondrial supply of NADH for oxidative phosphorylation. The functional significance of MDH elevation in AD is unknown [26]. |
| 7 | Actin, cytoplasmic 1 P60711 (ACTB_RAT) | Actins are highly conserved proteins that are involved in various types of cell motility and are ubiquitously expressed in all eukaryotic cells. | A number of studies have shown that the actin cytoskeleton plays a key role in synaptic function and plasticity. It may be positioned at the crossroads of pathways contributing to AD pathogenesis, i.e., between the amyloid cascade and synaptic dysfunction [27]. |
| 8 | Creatine kinase B-type P07335 (KCRB_RAT) | Creatine kinase (CK ) reversibly catalyzes the transfer of phosphate between ATP and various phosphogens such as creatine phosphate. | CK plays a major role in the cellular energetics of the brain, so any disruption of this enzyme can worsen AD pathology. Cytosolic brain-type creatine kinase (BB-CK) is inactivated by oxidation in patients with AD [28]. |
| 9 | Glial fibrillary acidic protein P47819 (GFAP_RAT) | GFAP is a class III intermediate filament. It is a cell-specific marker that distinguishes astrocytes from other glial cells during development of the central nervous system. | GFAP is a key protein and is a marker of astroglial damage. It is responsible for the structure of the cytoskeleton of glial cells, regulation of the morphology and function of astrocytes, as well as for maintaining the blood-brain barrier. In AD, amyloid plaques are surrounded by reactive astrocytes with increased expression of GFAP filaments [29]. |
| 10 | Tubulin alpha-1B chain Q6P9V9 (TBA1B_RAT) | Tubulin is the main constituent of microtubules, which are composed of α–β-tubulin heterodimers forming linear protofilaments that form a hollow polar cylinder. | Microtubules (MT) are essential components of the cytoskeleton of the cell, which has locomotory functions. A number of studies show that MT-dysfunction can contribute to or be the cause of neurodegenerative processes and AD in particular. Disruption of the neuronal cytoskeleton is a feature of the neurodegenerative brain, and tubulin levels are decreased in the AD brain [30]. |
| 11 | 60 kDa heat shock protein, mitochondrial P63039 (CH60_RAT) | Hsp60 is a chaperone that is localized in the mitochondria and is involved in the correct folding of proteins. | Hsp60 is a protein that, together with Hsp10, is considered essential for mitochondrial protein folding. The role of Hsp60 in AD is still unclear [31,33]. |
| 12 | V-type proton ATPase catalytic subunit A P50516 (VATA_MOUSE) | ATP-synthase is the last enzyme of the mitochondrial electron transport chain, where oxidative phosphorylation takes place in order to synthesize ATP, which is a universal energy carrier in the cell. | In mammalian cells, ATP synthase, in addition to ATP synthesis, can also perform its degradation (ATPase), which indicates the important role of this enzyme in the regulation of cellular bioenergetics and metabolism. The mechanisms of bioenergetic dysfunction incl. dysregulation of ATP synthase in AD remains unclear [32]. |
| 13 | Tropomyosin beta chain P58775 (TPM2_RAT) | Tropomyosin (Tm) binds to actin filaments in muscle and non-muscle cells. In non-muscle cells, it is involved in the stabilization of cytoskeletal actin filaments. | Tm has been shown to be an integral component of the neurofibrillary pathology of Alzheimer’s disease. However, the exact role of Tm in AD pathology is still not well understood [33]. |
| 14 | 14-3-3 protein zeta/delta P63102 (1433Z_RAT) | 14-3-3 is an adapter protein involved in the regulation of a wide range of general and specialized signaling pathways. Binding usually results in modulation of the activity of the protein to which 14-3-3 binds. | 14-3-3 isoforms regulate a wide range of cellular processes such as the cell cycle, transcription, intracellular trafficking, apoptosis, and autophagy [34]. In AD, they are thought to contribute to NFT formation through τ-hyperphosphorylation [35]. |
| 15 | Kinesin-1 heavy chain Q2PQA9 (KINH_RAT) | Kinesin is a microtubule-dependent motor protein required for the normal distribution of mitochondria and lysosomes. Required for anterograde axonal transport of MAPK8IP3/JIP3, which is essential for MAPK8IP3/JIP3 function in axon elongation [43] | Studies have shown that Kinesin-1 heavy chain, which is part of a key molecular motor protein, is involved in tau homeostasis in AD cells and animal models. It has been proposed that reduction of Kinesin-1 heavy chain levels is sufficient to prevent and/or delay abnormal tau behavior in AD and other tauopathies [36]. |
| 16 | Stathmin-4 P63043 (STMN4_RAT) | Stathmin (STM) is a ubiquitous cytosolic phosphoprotein primarily expressed in the nervous system and a member of a family of phosphoproteins that bind to tubulin and destabilize MTs. | STM-4 in the unphosphorylated or hypophosphorylated state binds to tubulin and prevents its polymerization, thereby preventing MTs assembly. After phosphorylation, STM-4 is released from tubulin and allows the formation of MTs. Dysregulation of STM and MTs dynamics has been observed in aged animals and in patients with AD and depression [37]. |
| 17 | Hemoglobin subunit alpha-1/2P01946 (HBA_RAT) | It participates in the transfer of oxygen from the lung to the various peripheral tissues. | Studies have shown that hemoglobin (Hb) binds to Aβ and co-localizes with plaques and vascular amyloid deposits in the brains of AD patients after death. Research by Chuang et al., 2012 suggests that the genesis of some plaques may be a consequence of prolonged amyloid accumulation at sites of vascular injury [38]. |
| № Spot Cortex |
Protein Name (UniProtKB) |
Volume (pixels) Sco |
Volume (pixels) Sco + SE |
MW Exp. |
pI Exp. |
MW Theor |
pI Theor |
Expression |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Thioredoxin; P11232 (THIO_RAT) | 6050118 | 5441182 | 15.081 | 4.48 | 11.673 | 4.80 |  |
| 2 | Superoxide dismutase [Cu-Zn]; P07632 ( SODC_RAT) | 6261736 | 7118268 | 18.158 | 5.51 | 15.912 | 5.88 |  |
| 3) | Cofilin-1; P45592, (COF1_RAT) | 1157164 | 1101119 | 20 | 7.46 | 18.533 | 8.22 |  |
| 4 | Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase isozyme L1; Q00981 (UCHL1_RAT) | 2204242 | 3605218 | 22 | 4.9 | 24.838 | 5.14 |  |
| 5 | Calbindin; P07171 (CALB1_RAT) | 8396846 | 11756730 | 28 | 3.94 | 29.994 | 4.71 |  |
| 6 | Malate dehydrogenase, cytoplasmic; O88989 (MDHC_RAT) | 12166374 | 15772607 | 36 | 5.63 | 36.483. | 6.16 |  |
| 7 | β –Actin; P60711 (ACTB_RAT) | 18729148 | 13744467 | 48 | 5.35 | 41.737 | 5.2 |  |
| 8 | Creatine Kinase B-type; P07335 (KCRB_RAT) |
375048 | 448176 | 40 | 5.52 | 42.725 | 5.4 |  |
| 9 | Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein; P47819 (GFAP_RAT) |
582304 | 583050 | 53 | 5.17 | 49.957 | 5.02 |  |
| 10 | Tubulin α-1 chain; Q6P9V9 (TBA1B_RAT) | 22419986 | 7427465 | 53 | 4.35 | 50.152 | 4.94 |  |
| 11 | 60 kDa heat shock protein, mitochondrial; P63039 (CH60_RAT) | 10059479 | 13101991 | 71 | 5.44 | 60.955 | 5.91 |  |
| 12 | Vacuolar ATP synthase catalytic subunit A; P50516 (VATA_RAT) | 2211577 | 3933414 | 73 | 5.28 | 68.326 | 5.41 |  |
| 13 | Tropomyosin beta chain P58775 (TPM2_RAT) |
2502851 | 451024 | 32.817 | 4.66 | 41.253 | 4.45 |  |
| 14 | 14-3-3 protein zeta/delta P63102 (1433Z_RAT) |
15894376 | 7086121 | 27.754 | 4.73 | 33.326 | 4.46 |  |
| 15 | Kinesin-1 heavy chain Q2PQA9 (KINH_RAT) |
4906008 | 3993752 | 109.463 | 6.06 | 126.318 | 5.51 |  |
| 16 | Stathmin-4; P63043 (STMN4_RAT) | 39377068 | 10224790 | 22.073 | 5.76 | 17.650 | 6.42 |  |
| 17 | Hemoglobin subunit alpha-1/2; P01946 (HBA_RAT) | 27582716 | 2551968 | 15.319 | 7.82 | 21.167 | 7.7 |  |
| Spot No | AAS of peptide |
Mass [M+H]+ | Spot No | AAS of peptide |
Mass [M+H]+ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
6 |
DLDVAVLVGSMPR | 1371.71 |
14 |
MKGDYYR | 932.21 | |
| FVEGLLPNDFSR | 1393.68 | DSTLIMQLLR | 1189.39 | |||
| SQIALKLGVTADDVK | 1558.84 | KEMQPTHPIR | 1236.38 | |||
| VIVVGNPANTNCLTASK | 1700.89 | SVTEQGAELSNEER | 1548.37 | |||
| GEFITTVQQRGAAVIK | 1719.94 | LAEQAERYDDMAACMK | 1844.40 | |||
|
7 |
EITALAPSTMK | 1161.61 |
15 |
KMEENEK | 908.29 | |
| IWHHTFYNELR | 1515.74 | YQQEVDRIK | 1177.35 | |||
| SYELDPGQVITIGNER | 1790.87 | EYELLSDELNQK | 1479.48 | |||
| YPIEHGIVTNWDDMEK | 1946.89 | TQMLDQEELLASTRR | 1791.35 | |||
| VAPEEHPVLLTEAPLNPK | 1954.06 | GLEETVAKELQTLHNLR | 1949.51 | |||
| 10 | YMACCLLYR | 1135.50 | 16 | MTLAAYKEK | 1053.45 | |
| QLFHPEQLITGK | 1410.77 | EAHLAAMLER | 1141.43 | |||
| SIQFVDWCPTGFK | 1527.73 | RKYQEAELLK | 1277.72 | |||
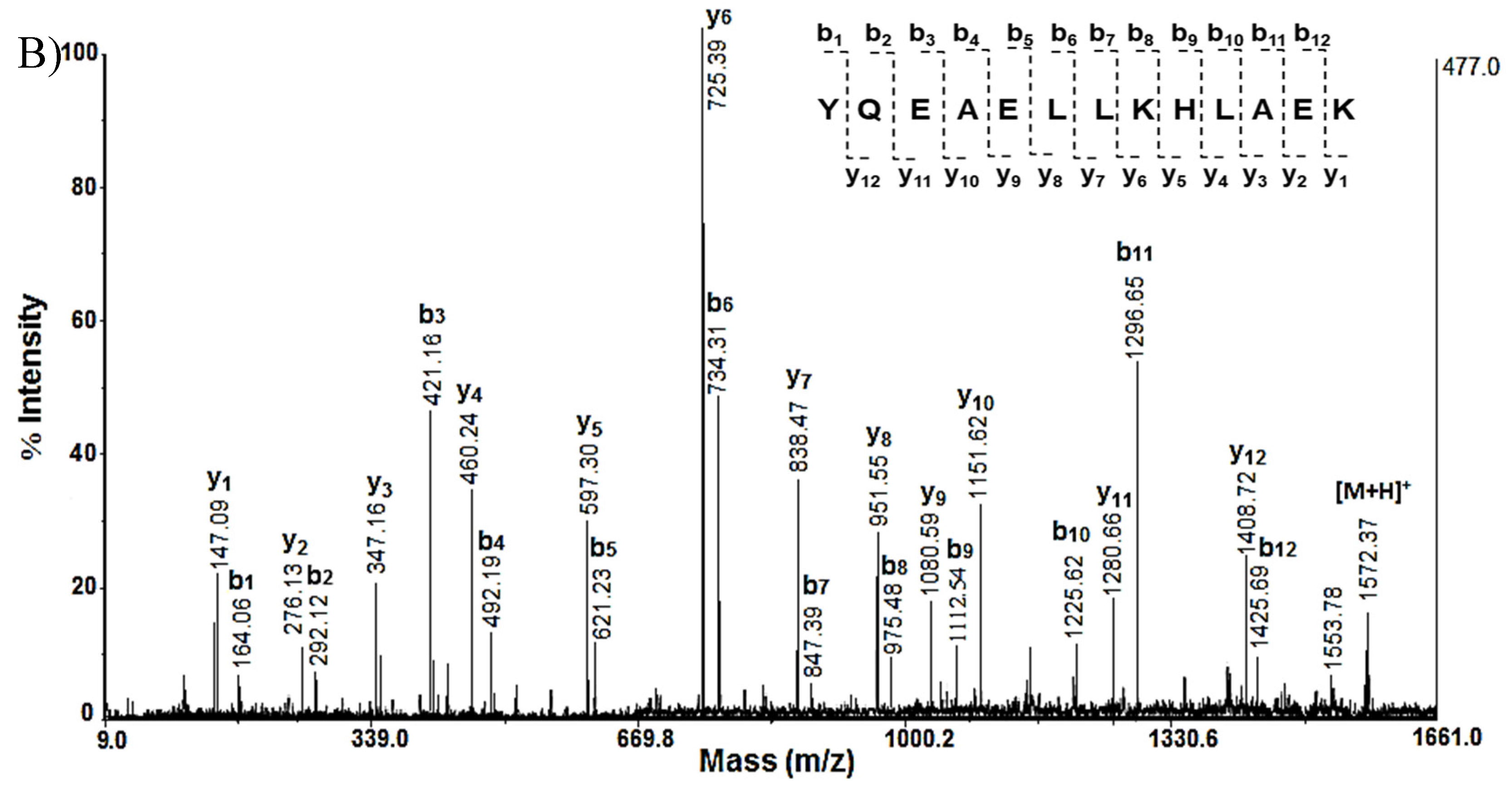
| IHFPLATYAPVISAEK | 1756.67 | YQEAELLKHLAEK | 1572.46 | |||
| EDAANNYARGFYTIGK | 1790.87 | MKELPLVSLFCSCFLSDPLNK | 2383.53 | |||
| KKMQMLK | 907.24 | MFAAFPTTK | 1013.31 | |||
| HIAEDSDR | 941.24 | LRVDPVNFK | 1087.42 | |||
| 13 | AEFAERSVAK | 1107.91 | 17 | IGGHGGEYGEEALQR | 1572.47 | |
| LEEAEKAADESER | 1475.70 | TYFSHIDVSPGSAQVK | 1735.55 | |||
| LEEAEKAADESERGMK | 1791.71 | AADHVEDLPGALSTLSDLHAHK | 2296.75 | |||
| TIDDLEDEVYAQKMKYK | 2088.89 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





