Submitted:
10 October 2024
Posted:
10 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
1. Growth Mechanism
1.1. Synthesis of 2D-In2S3 Nanosheets
1.2. Characterization Techniques
2. Results
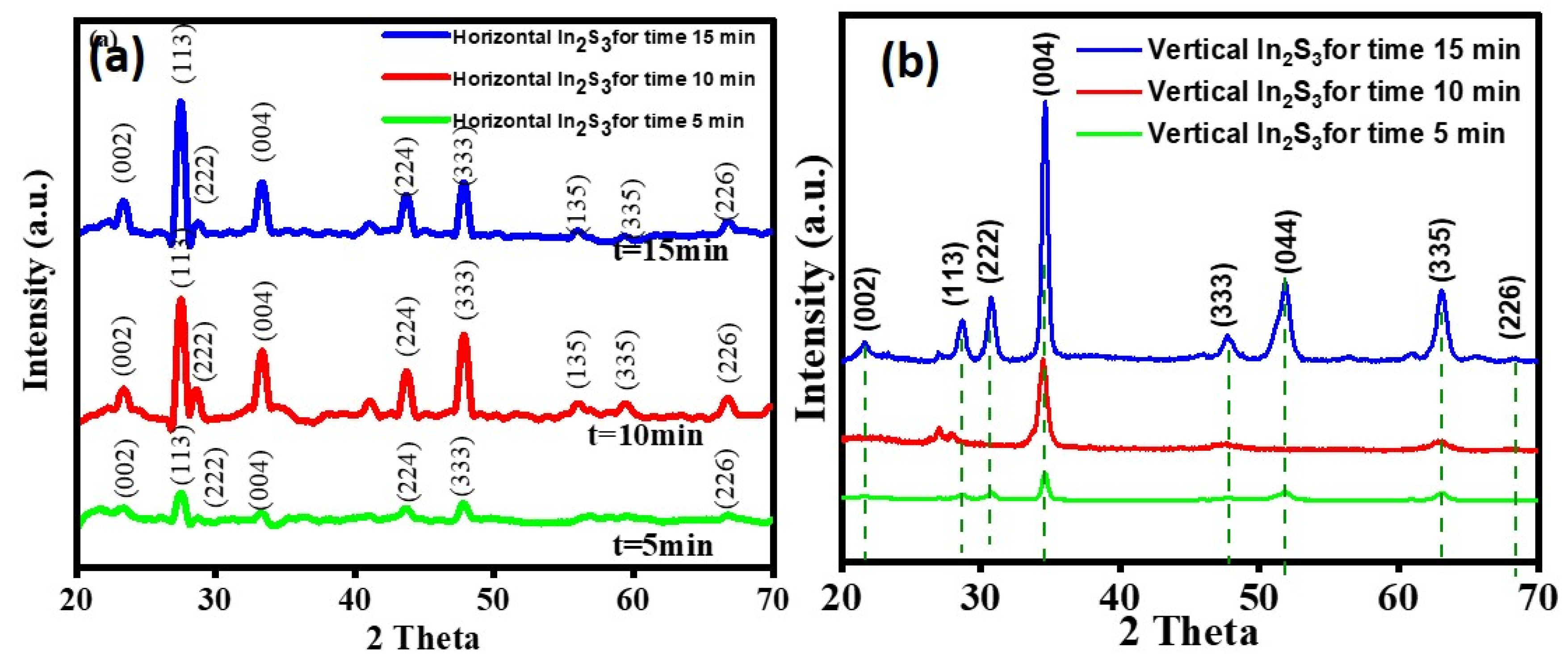
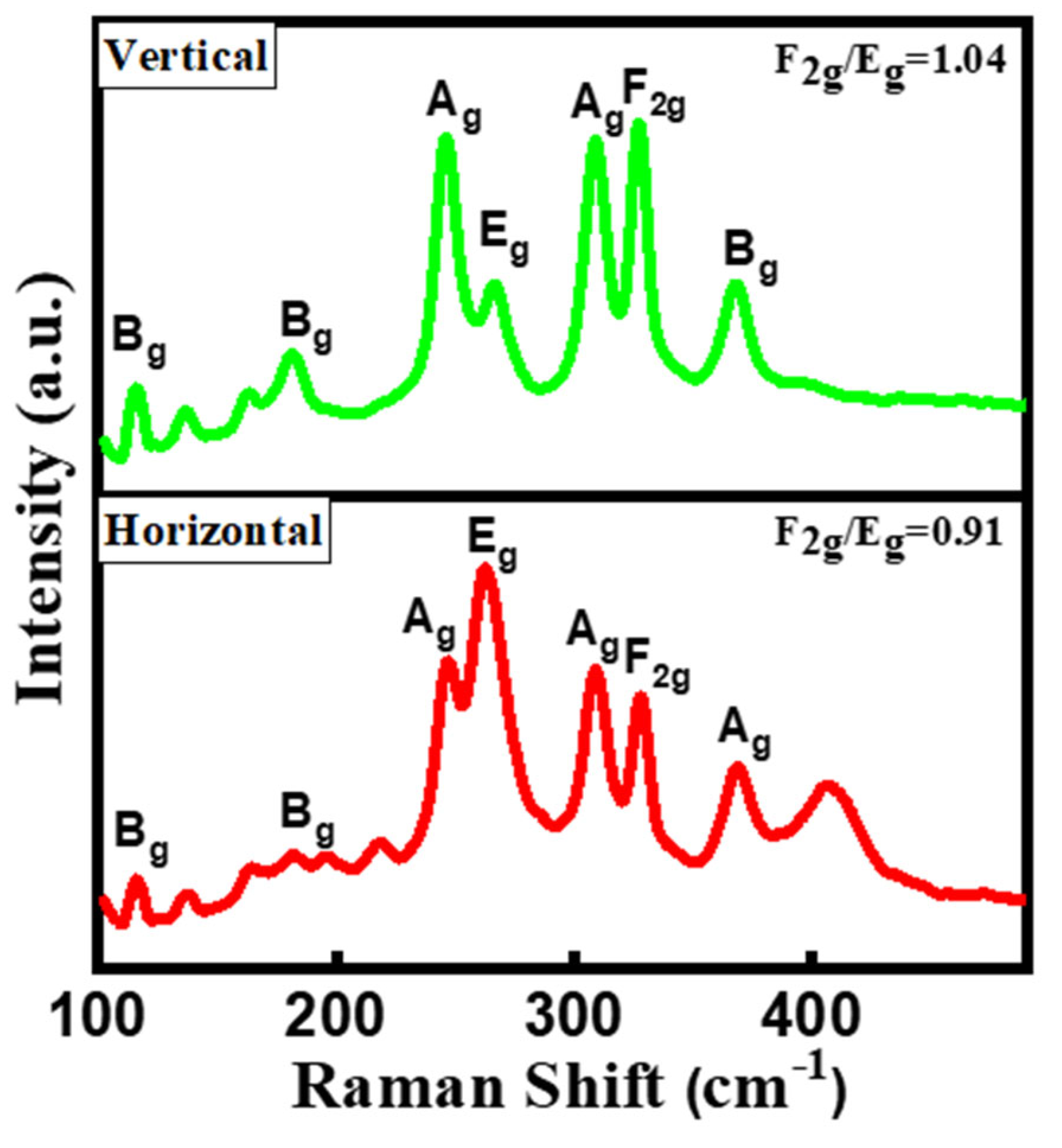
2.1. Structrual and Phase Analysis
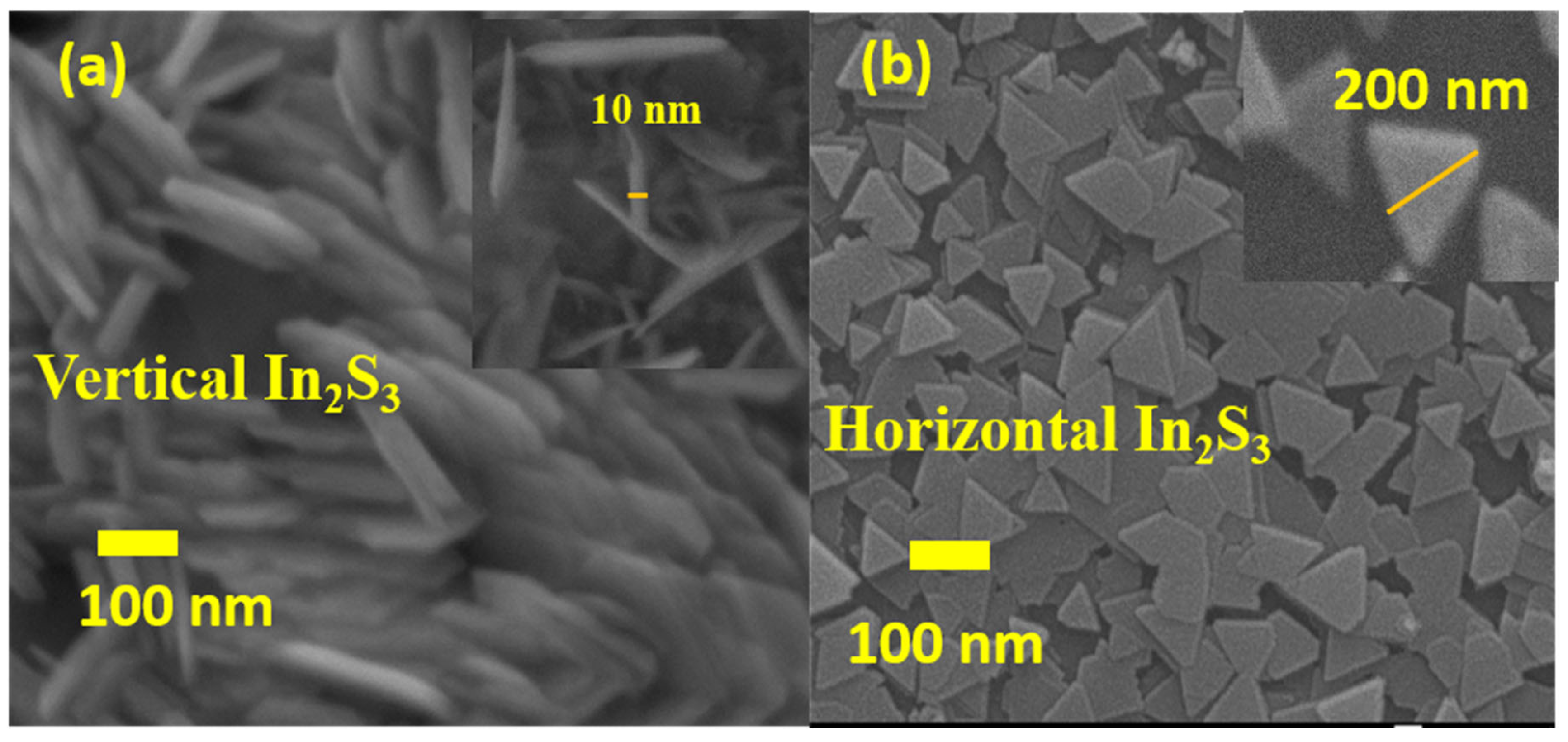
2.2. Morphological Analysis
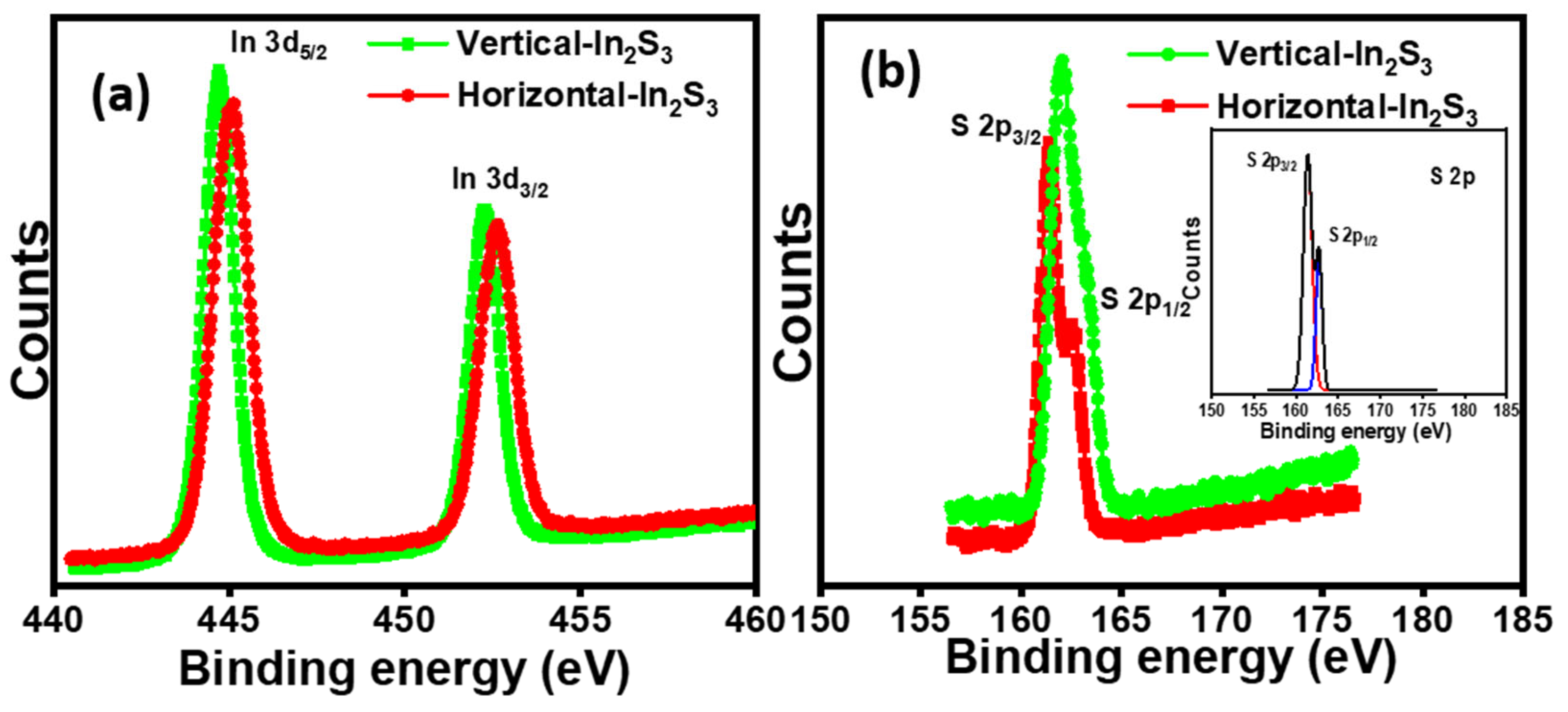
2.3. XPS Analysis
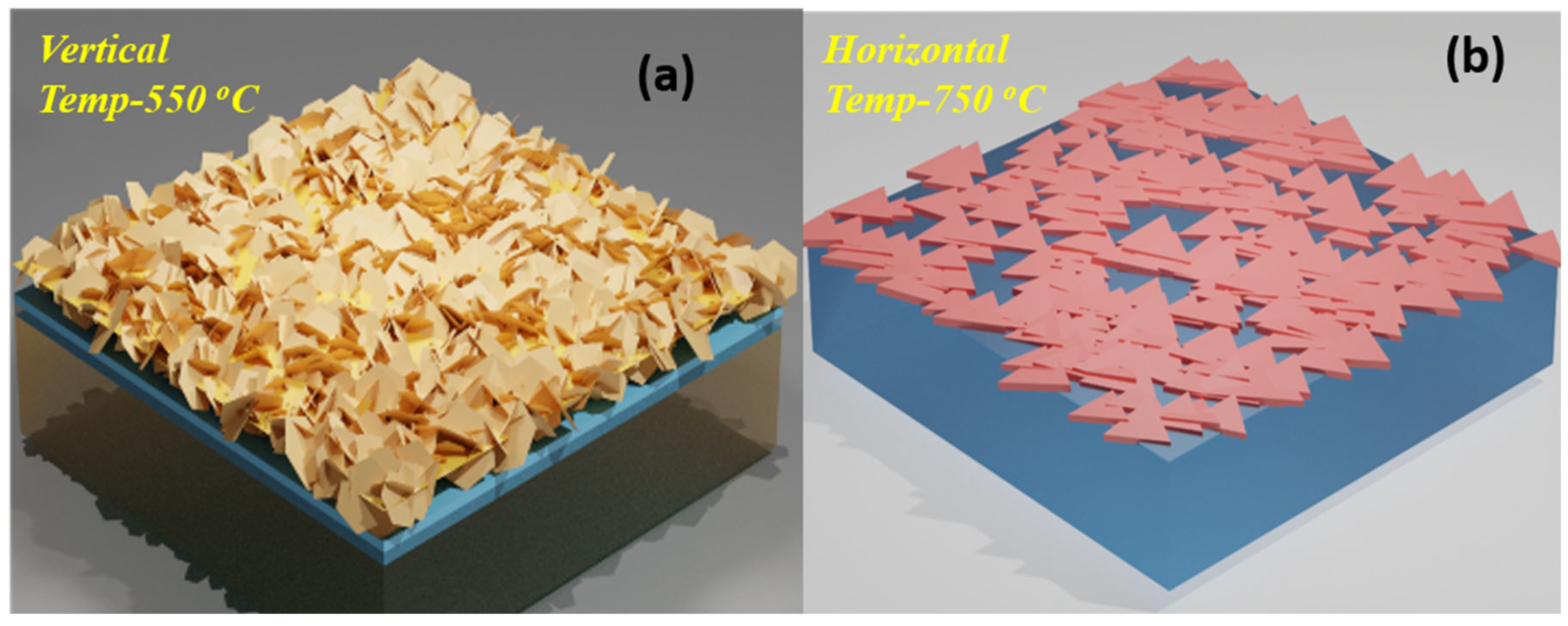
2.4. Growth Mechanism of In2S3 Nanoflakes
3. PEC Measurements
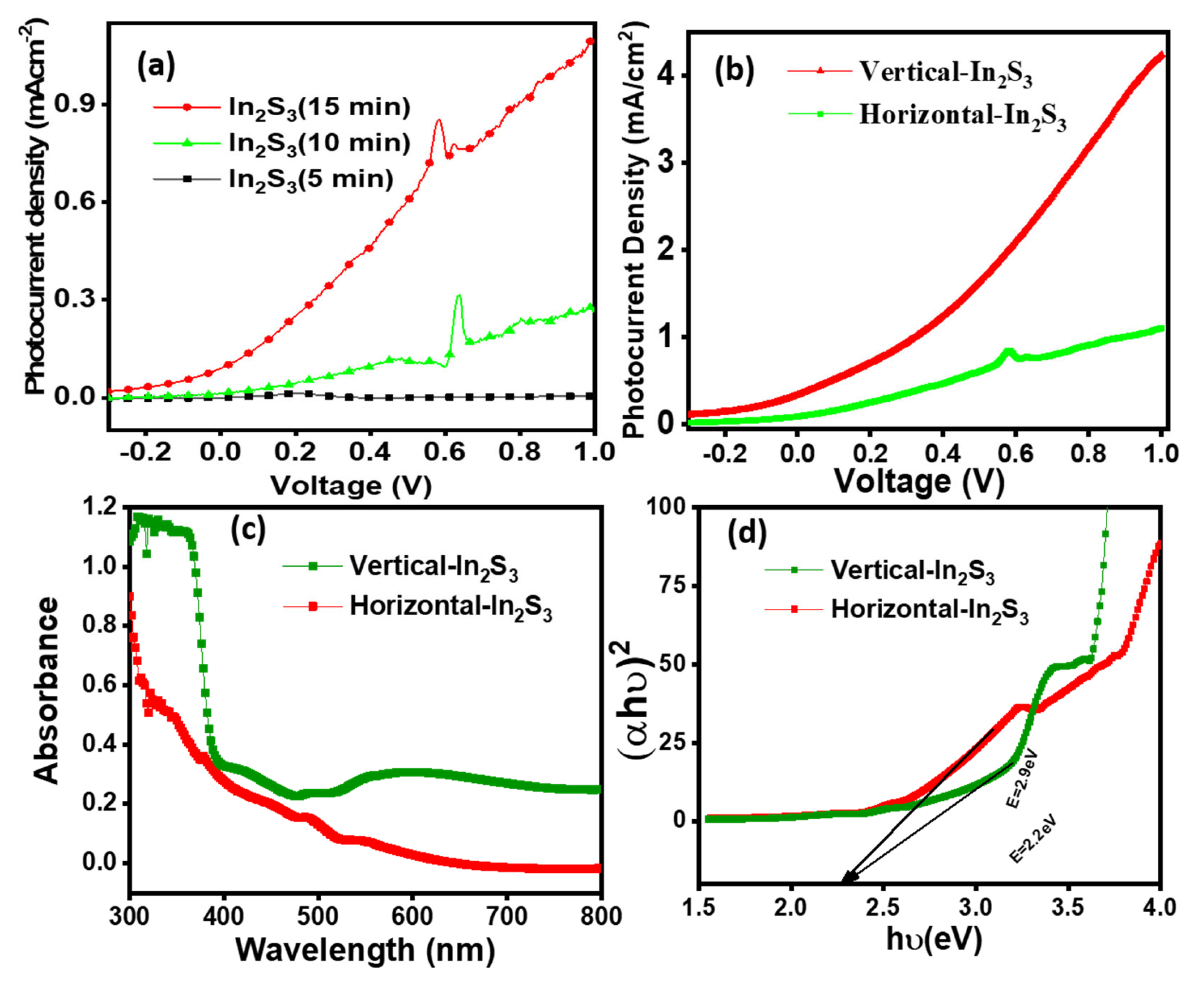
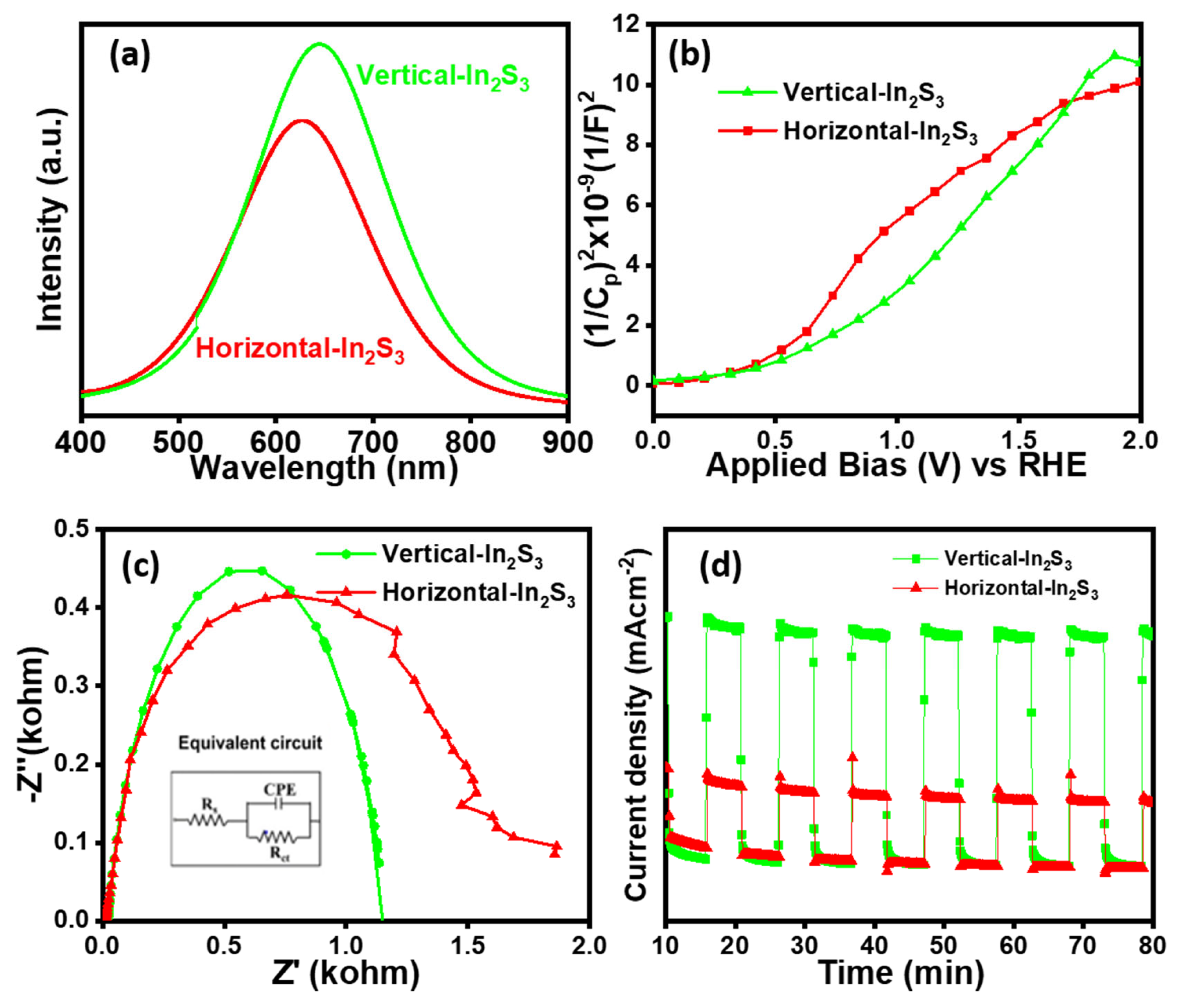
3.1. PEC Performance
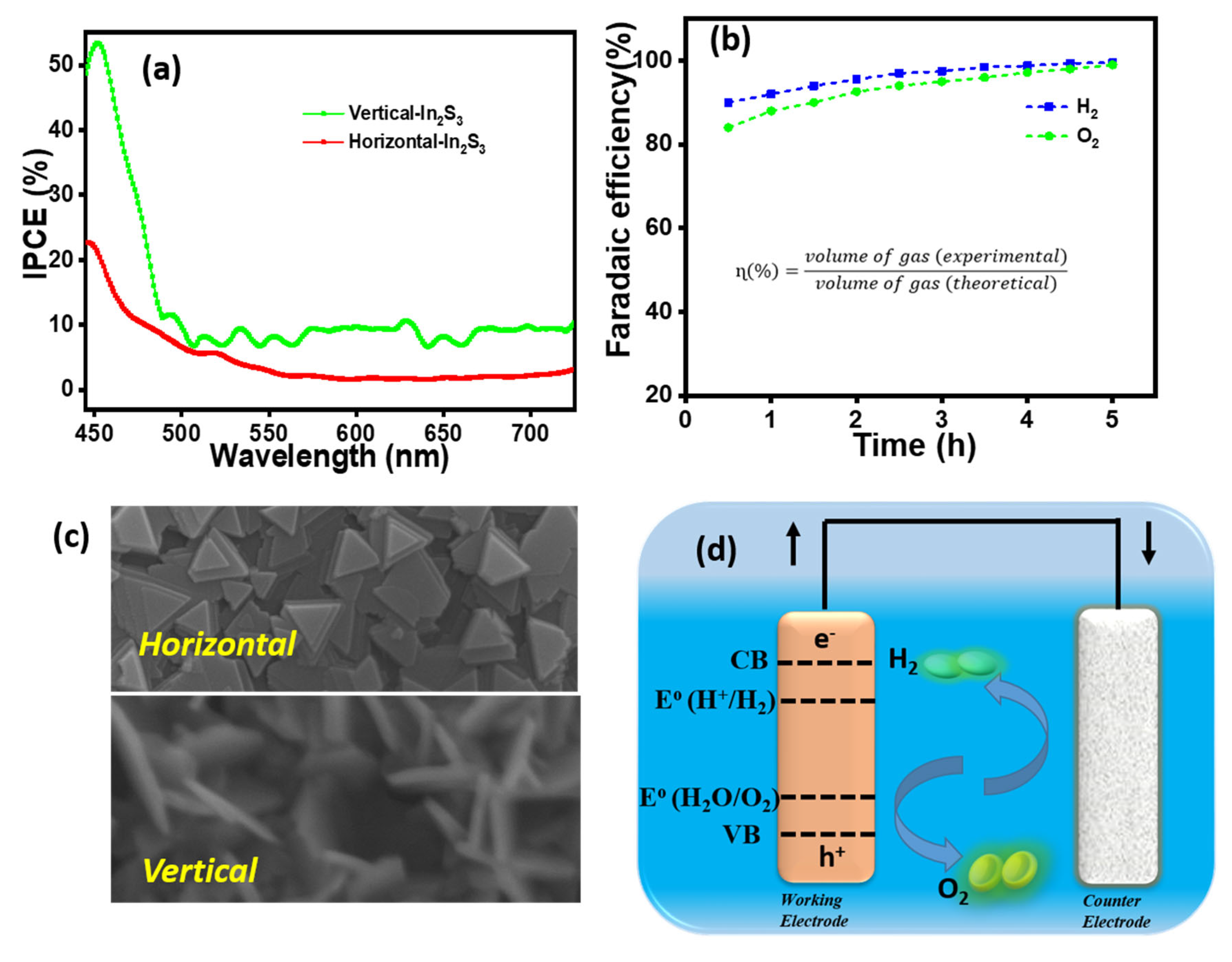
3.2. Quantitative Photoelectrochemical Measurement
Conclusions
Authors Contribution
Declaration of Competing Interest
References
- Y. Li, C. Y. Xu, J. Y. Wang, and L. Zhen, Photodiode-like behavior and excellent photoresponse of vertical Si/monolayer MoS2 heterostructure, Scientific Reports, 2014, 4, 7186. [CrossRef]
- Zhenxing Wang Tofik Ahmed Shifa Yao Wen Fengmei Wang Xueying Zhan, Two-Dimensional Non-Layered Materials: Synthesis, Properties, and Applications, Adv fun materials,2016. [CrossRef]
- H. Xu, J. Wu, Q. Feng, N. Mao, C. Wang, and J. Zhang, High responsivity, and gate tunable graphene-MoS2 hybrid phototransistor, Nano Small 2014, 10, 2300.
- W.Haung, L. gang, H. Li, and T.Zhai, 2D Layered Group-IIIA Metal Chalcogenides: Synthesis, Properties and Applications in Electronics and Optoelectronics, RSC, 2016, 18, 22.
- Xiaobing Li, Jinzhan Su, Liejin Guo, vertically aligned ZnO/In2S3 core/shell heterostructures with enhanced photoelectrochemical properties, JMS,2020, pp. 15773-15784.
- Jih-Sheng Yang and Jih-Jen Wu, Toward Eco-Friendly and Highly Efficient Solar Water Splitting Using In2S3/Anatase/Rutile TiO2 Dual-Staggered-Heterojunction Nanodendrite Array Photoanode, ACS AMI, 2018, pp. 3714-3722.
- F. Liu, Y. Jiang, J.Yang, M.Hang, MoS2 nanodot decorated In2S3 nanoplates: a novel heterojunction with enhanced photoelectrochemical performance, RSC, 2016, 52, 1867.
- Narinder Kaur, Dipika Sharma, B.R. Mehta, Growth of In2S3 nanolayers on F-Mica, SiO2, ZnO, and TiO2 substrates using chemical vapor deposition, MSEB, 2021, pp. 114889-114897.
- Sudiksha Khadka, Thushan E. Wickramasinghe, Miles Lindquist, Ruhi Thorat, Shrouq H. Aleithan, Martin E. Kordesch, and Eric Stinaff, “ As grown tow dimensional MoS2 based photodetectors with naturally formed contacts”, Appl. Phys. Lett. 110, 261109 (2017); https://. [CrossRef]
- J. D. Yao, Z. Q. Zheng, J. M. Shao and G. W. Yang, “Stable, highly responsive and broadband photodetection based on large-area multi-layered WS2 films grown by pulsed-laser deposition, Nanoscale, 2015, 7, 14974-14981.
- Shouli Bai, Qiangqiang Li, Jingyi Han, Xiaojun Yang, Xin Shu, Jianhua Sun, Lixia Sun, Ruixian Luo, Dianqing Li, Aifan Chen, Photoanode of LDH catalyst decorated semiconductor heterojunction of BiVO4/CdS to enhance PEC water splitting efficiency, IJHE,2019, pp. 24642-24652.
- Xinglin Wen, Sijie Chen, Jiaxin Zhao, Wei Du, and Weijie Zhao, “Enhanced Plasmonic Hot-Carrier Transfer in Au/WS2 Heterojunctions under Nonequilibrium Condition”, ACS Photonics.
- J.Yu, Jie. Li, W. Zhang and H. Chang, Synthesis of high-quality two-dimensional materials via chemical vapor deposition, RSC, 2015, 6, 6705-6716.
- Haijin Li, Yuying Gao, Yong Zhou, Fengtao Fan, Qiutong Han, Qinfeng Xu, Xiaoyong Wang, Min Xiao, Can Li, and Zhigang Zou, Construction and Nanoscale Detection of Interfacial Charge Transfer of Elegant Z-Scheme WO3/Au/In2S3 Nanowire Arrays, Nano Letters, 2016, pp. 5547-5552.
- Narinder Kaur, Abhishek Ghosh, Mujeeb Ahmad, Dipika Sharma, Rajendra Singh, B.R. Mehta, “Increased visible light absorption and charge separation in 2 D–3 D In2S3- ZnO heterojunctions for enhanced photoelectrochemical water splitting, Jelcom, 903 (2022) 164007.
- Narinder Kaur, Abhishek Ghosh, Prashant Bisht, Arvind Kumar, Vishakha Kaushik, Nisha Kodan, Rajendra Singh and B.R.mehta, “Enhanced photodetection and a wider spectral range in the In2S3–ZnO 2D–3D heterojunction: combined optical absorption and enhanced carrier separation at the type-II heterojunction”, JMCC. [CrossRef]
- Aldona Jelinska, Krzysztof Bienkowski, Michal Jadwiszczak, Marcin Pisarek, Marcin Strawski, Dominik Kurzydlowski, Renata Solarska, and Jan Augustynski, “Enhanced Photocatalytic Water Splitting on Very Thin WO3 Films Activated by High-Temperature Annealing”, ACS Catalysis 2018 8 (11), 10573-10580.
- Yao, Y.; Sang, D.; Zou, L.; Wang, Q.; Liu, C. A Review on the Properties and Applications of WO3 Nanostructure-Based Optical and Electronic Devices. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2136. https://. [CrossRef]
- Y. Zhao, S. Balasubramanyam, R. Sinha, R. Lavrijsen, M. A. Verheijen, A. A. Bol, and A. Bieberle-Hütter, “Physical and Chemical Defects in WO3 Thin Films and Their Impact on Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting”, ACS AEM, 2018 1 (11), 5887-5895. [CrossRef]
- Yuriy Pihosh, Ivan Turkevych, Kazuma Mawatari, Tomohiro Asai, Takashi Hisatomi, Jin Uemura, Masahiro Tosa, Kiyoshi Shimamura, Jun Kubota, Kazunari Domen, and Takehiko Kitamori, “Nanostructured WO3/BiVO4 Photoanodes for Efficient Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting”, small 2014, 10, No. 18, 3692–3699.
- Narinder Kaur, Dipika Sharma, B.R. Mehta, “Growth of In2S3 nanolayers on F-Mica, SiO2, ZnO, and TiO2 substrates using chemical vapor deposition”, MSEB, Volume 264, 2021, 114889.
- Chang, Y., Wang, J., Wu, F., Tian, W. and Zhai, W., 2020. Structural Design and Pyroelectric Property of SnS/CdS Heterojunctions Contrived for Low-Temperature Visible Photodetectors. Adv Fun Materials, 30(23), p.2001450Hairui Liu, Haifa Zhai, Chunjie Hu, Jien Yang, and Zhiyong Liu, Hydrothermal synthesis of In2O3 nanoparticles hybrid twins hexagonal disk ZnO heterostructures for enhanced photocatalytic activities and stability, Nanoscale research latter, 2017, pp. 2183-2193.
- Michał Mazur, Damian Wojcieszak, Artur Wiatrowski, Danuta Kaczmarek, Aneta Lubańska, Jarosław Domaradzki, Piotr Mazur, Małgorzata Kalisz, “Analysis of amorphous tungsten oxide thin films deposited by magnetron sputtering for application in transparent electronics”, Applied Surface Science, Volume 570, 2021, 151151, ISSN 0169-4332. [CrossRef]
- Narinder Kaur, Dipika Sharma, B.R. Mehta, “Growth of specific geometries such as cubes of In2S3 for PEC water splitting by hydrothermal technique”, Materials Today: Proceedings 50, 7-10.
- Zhiwei Wang, Guang Yang, Chiew Kei Tan, Tam Duy Nguyen, Alfred Iing Yoong Tok, “Amorphous TiO2 coated hierarchical WO3 Nanosheet/CdS Nanorod arrays for improved photoelectrochemical performance”, Applied Surface Science 490 (2019) 411–419.
- Xiaobing Li, Jinzhan Su and Liejin Guo, Vertically aligned ZnO/In2S3 core/shell heterostructures with enhanced photoelectrochemical properties, Journal of Material Science: Materials in electronics, 2020, pp.15773-15784.
- Daniel Commandeur, Joshua McGuckin, Steven Firth, Rong Qian, and Qiao Chen, Goethite and Hematite Hybrid Nanosheet-Decorated YZnO NRs for Efficient Solar Water Splitting, JPCC, 2021, pp. 1673-1683.
- Chih-Hao Lu, Min Hsiung Hon, Chi-Yun Kuan, and Ing-Chi Leu, “Preparation of WO3 nanorods by a hydrothermal method for electrochromic device”, Japanese Journal of Applied Physics 53, 06JG08 (2014).
- Ming Li, X. Tu, Y.Su, J.Lu., Controlled growth of vertically aligned ultrathin In2S3 nanosheet arrays for photoelectrochemical water splitting, Nanoscale,2018,10,1153-1161.
- Song, W., Zhang, R., Bai, X. Exposed crystal facets of WO3 nanosheets by phase control on NO2-sensing performance. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 31, 610–620 (2020).
- Hairui Liu, Haifa Zhai, Chunjie Hu, Jien Yang and Zhiyong Liu, Hydrothermal synthesis of In2O3 nanoparticles hybrid twins’ hexagonal disk ZnO heterostructures for enhanced photocatalytic activities and stability, Nanoscale Research Letters,2017, pp. 466-476.
- Young Bum Lee, Seong Ku Kim, Yi Rang Lim, In Su Jeon, Wooseok Song, Sung Myung, Sun Sook Lee, Jongsun Lim, and Ki-Seok An, “Dimensional-Hybrid Structures of 2D Materials with ZnO Nanostructures via pH-Mediated Hydrothermal Growth for Flexible UV Photodetectors”, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 15031−15037.
- B.Hemanth Kumar, S.Shaji, M.C.Santosh Kumar, Fabrication of visible light photodetector using co-evaporated Indium Sulfide thin films, JMS, 2019,30, 17986-17998.
- Cigdem Tuc Altaf, Nazire Simay Sahsuvar, Nazrin Abdullayeva, Ozlem Coskun, Alihan Kumtepe, Emine Karagoz, Mehmet Sankir, and Nurdan Demirci Sankir, Inverted Configuration of Cu (In, Ga)S2/In2S3 on 3D-ZnO/ZnSnO3 Bilayer System for Highly Efficient Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting, ASC Sustainable chemistry and engineering, 2020, pp. 15209-15222.
- Xiaoyang Feng, Yubin Chen, Zhixiao Qin, Menglong Wang, and Liejin Guo, “Facile Fabrication of Sandwich Structured WO3 Nanoplate Arrays for Efficient Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting” ACS AMI, 2016 8 (28), 18089-1809.
- Wenjuan Huang, Lin Gan, Haotian Yang, Nan Zhou, Renyan Wang, Wanhui Wu, Huiqiao Li, Ying Ma, Haibo Zeng, and Tianyou Zhai, Controlled Synthesis of Ultrathin 2D β-In2S3 with Broadband Photoresponse by Chemical Vapor Deposition, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 1702448.
- Young Bum Lee, Seong Ku Kim, Yi Rang Lim, In Su Jeon, Wooseok Song, Sung Myung, Sun Sook Lee, Jongsun Lim, and Ki-Seok An, “Dimensional-Hybrid Structures of 2D Materials with ZnO Nanostructures via pH-Mediated Hydrothermal Growth for Flexible UV Photodetectors”, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 15031−15037.
- Monika Moun, R singh, 2019, “Study of the photoresponse behavior of a high barrier Pd/MoS2/Pd photodetector”, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 52 325102.
- Ikram, M., Sajid, M.M., Javed, Y. Crystalline growth of tungsten trioxide (WO3) nanorods and their development as an electrochemical sensor for selective detection of vitamin C. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 32, 6344–6357 (2021).
- Haijin Li, Yuying Gao, Yong Zhou, Fengtao Fan, Qiutong Han, Qinfeng Xu, Xiaoyong Wang, Min Xiao, Can Li, and Zhigang Zou, Construction and Nanoscale Detection of Interfacial Charge Transfer of Elegant Z-Scheme WO3/Au/In2S3 Nanowire Arrays, Nano Letters, 2016, pp. 5547-5552.
- Cigdem Tuc Altaf, Nazire Simay Sahsuvar, Nazrin Abdullayeva, Ozlem Coskun, Alihan Kumtepe, Emine Karagoz, Mehmet Sankir, and Nurdan Demirci Sankir, Inverted Configuration of Cu (In, Ga)S2/In2S3 on 3D-ZnO/ZnSnO3 Bilayer System for Highly Efficient Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting, ASC Sustainable chemistry and engineering, 2020, pp. 15209-15222.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




