Submitted:
09 October 2024
Posted:
10 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
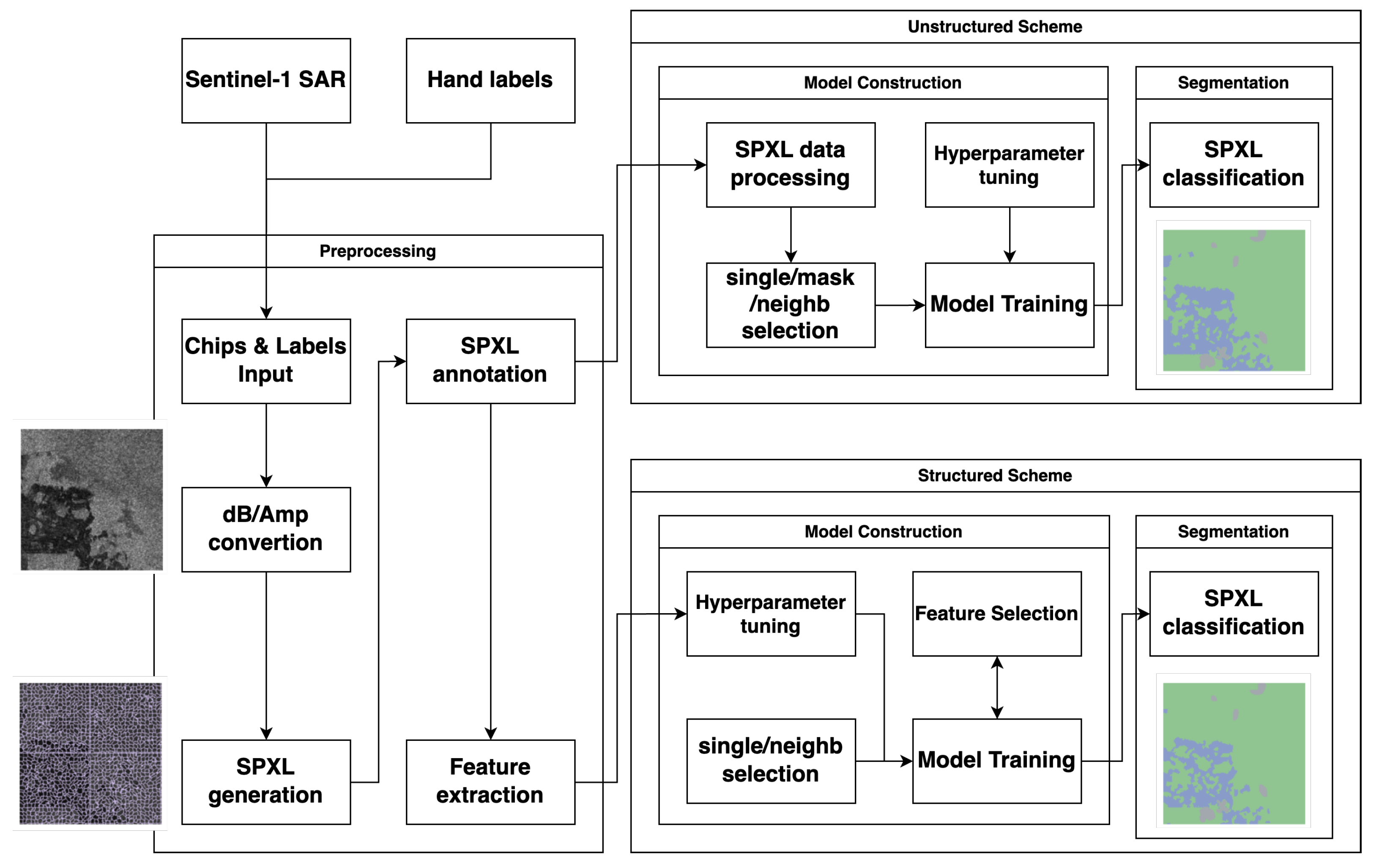
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sen1Floods11 Dataset
2.2. Data Processing
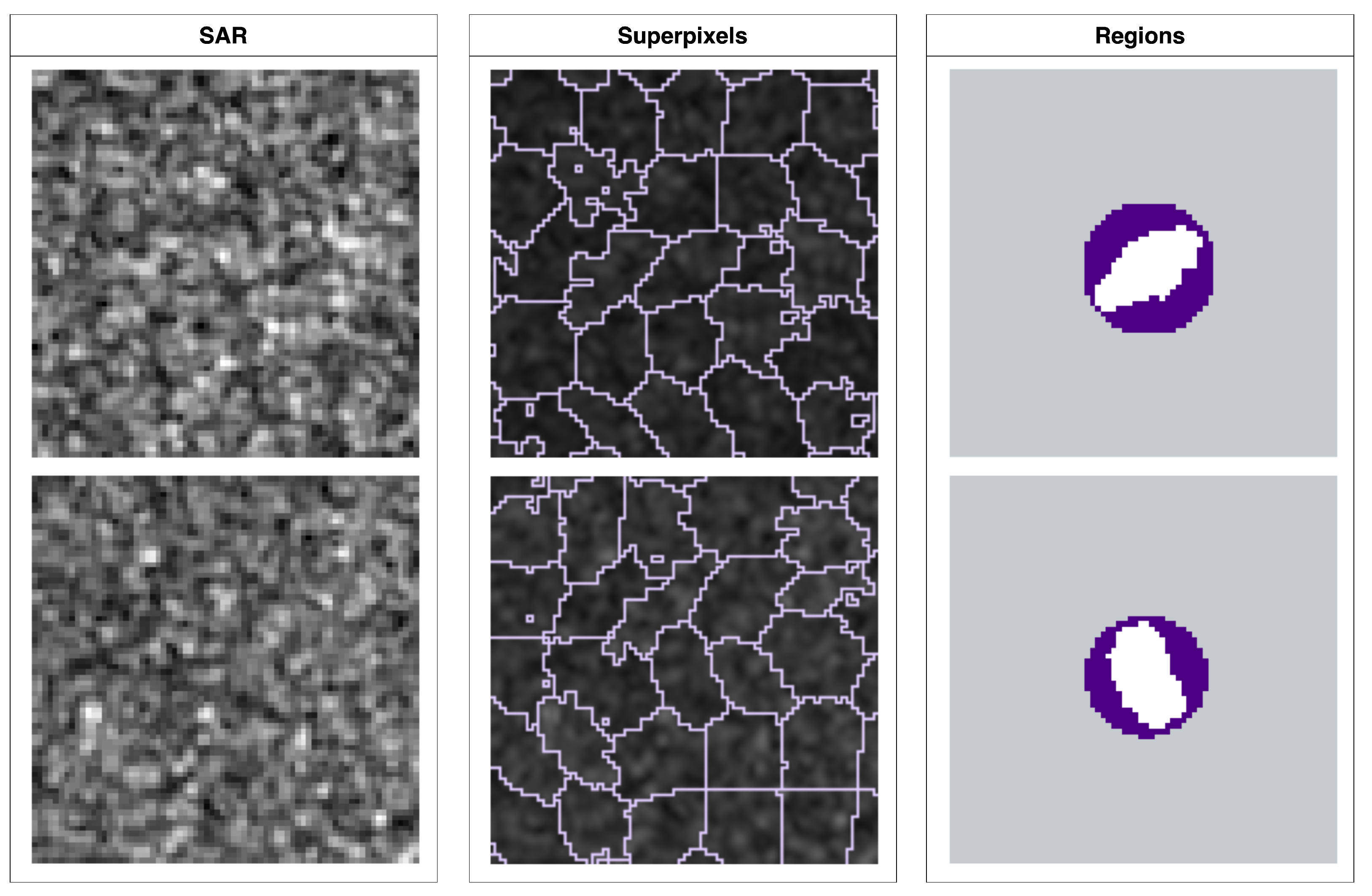
2.3. Superpixel Generation
2.3.1. Block ICM
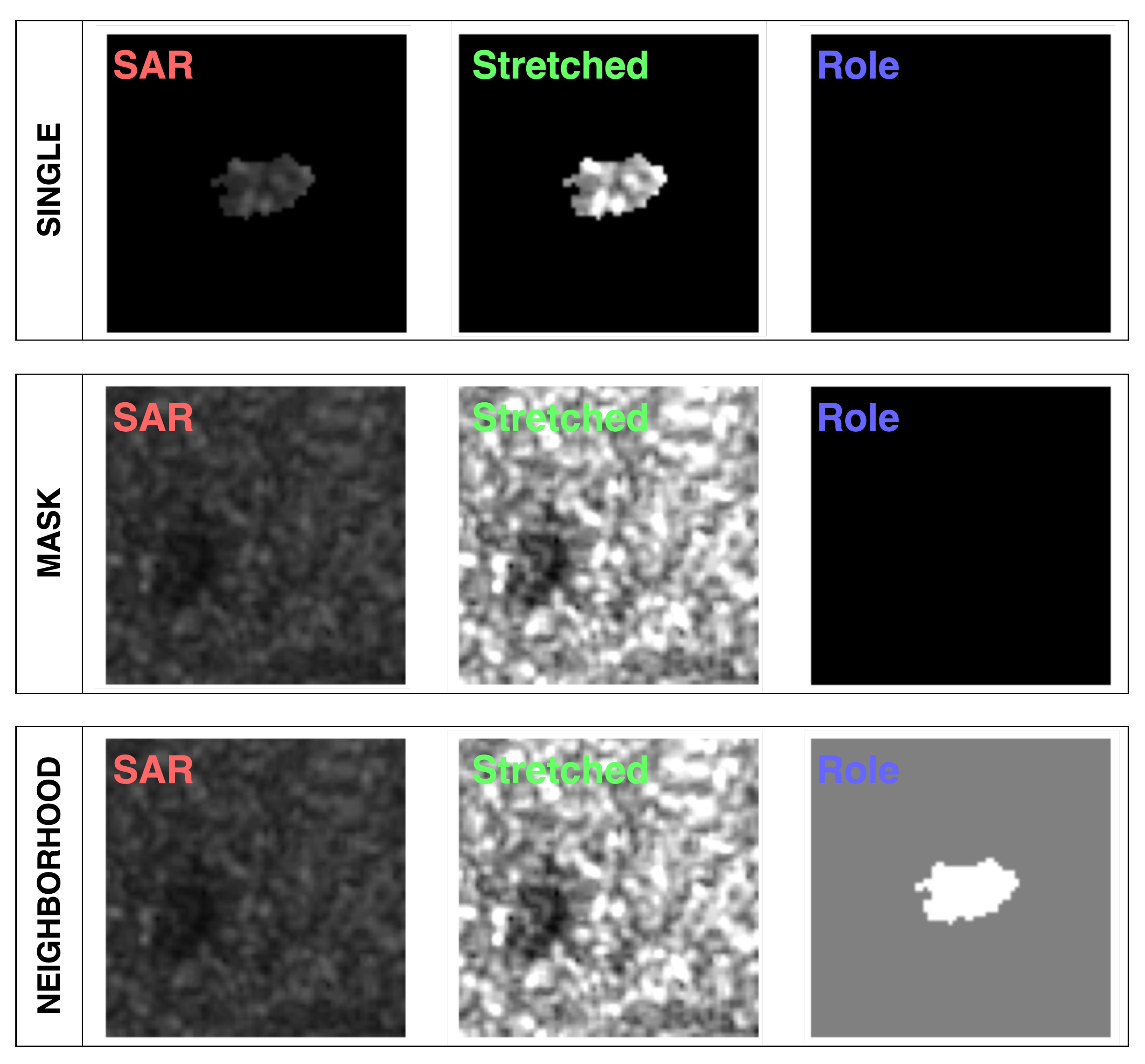
2.3.2. Superpixel Annotation
2.4. Superpixel Classification
2.4.1. Unstructured Data Scheme
2.4.2. Structured Data Scheme
2.5. Performance Metrics
3. Results
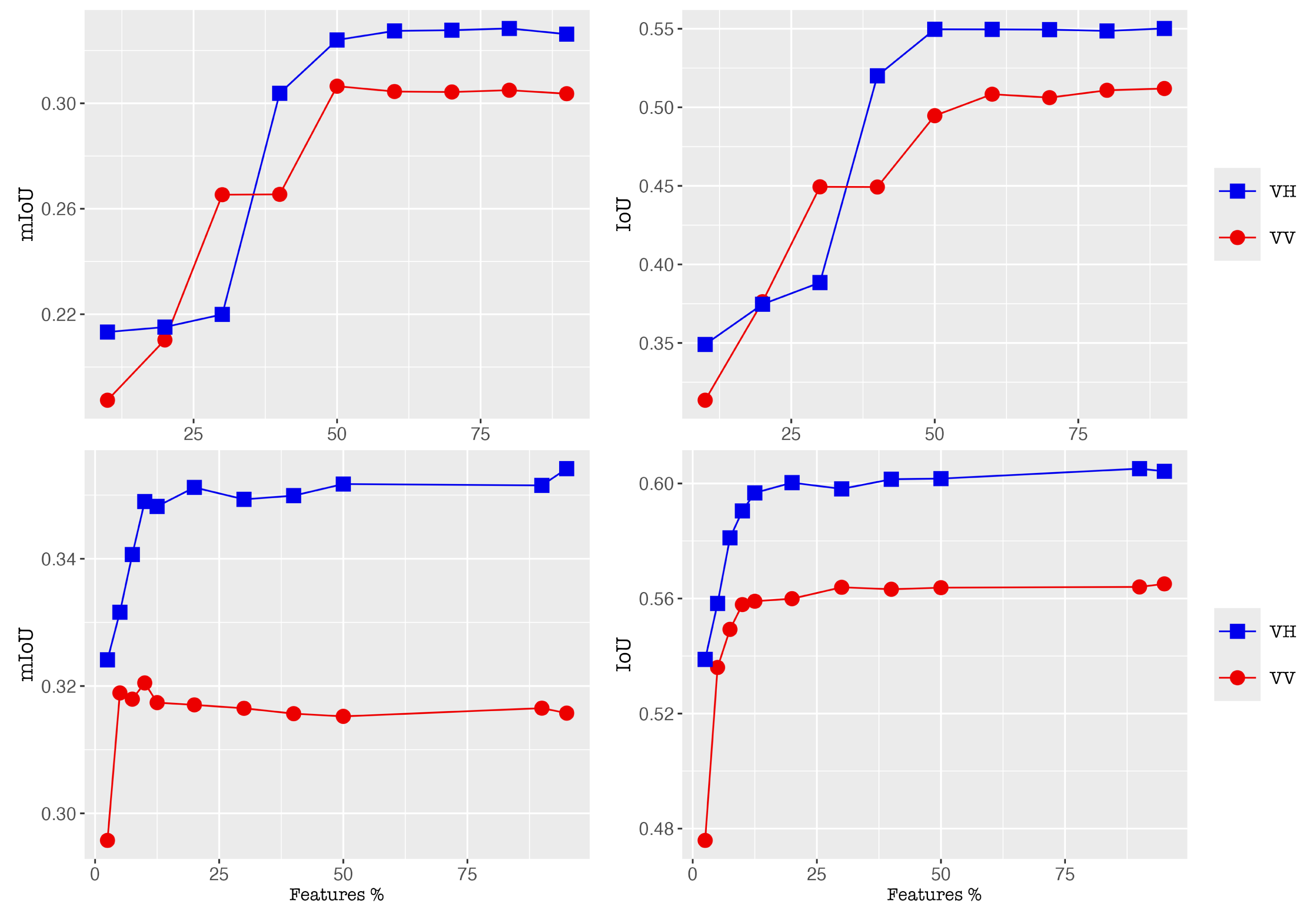
3.1. Parameter Tuning
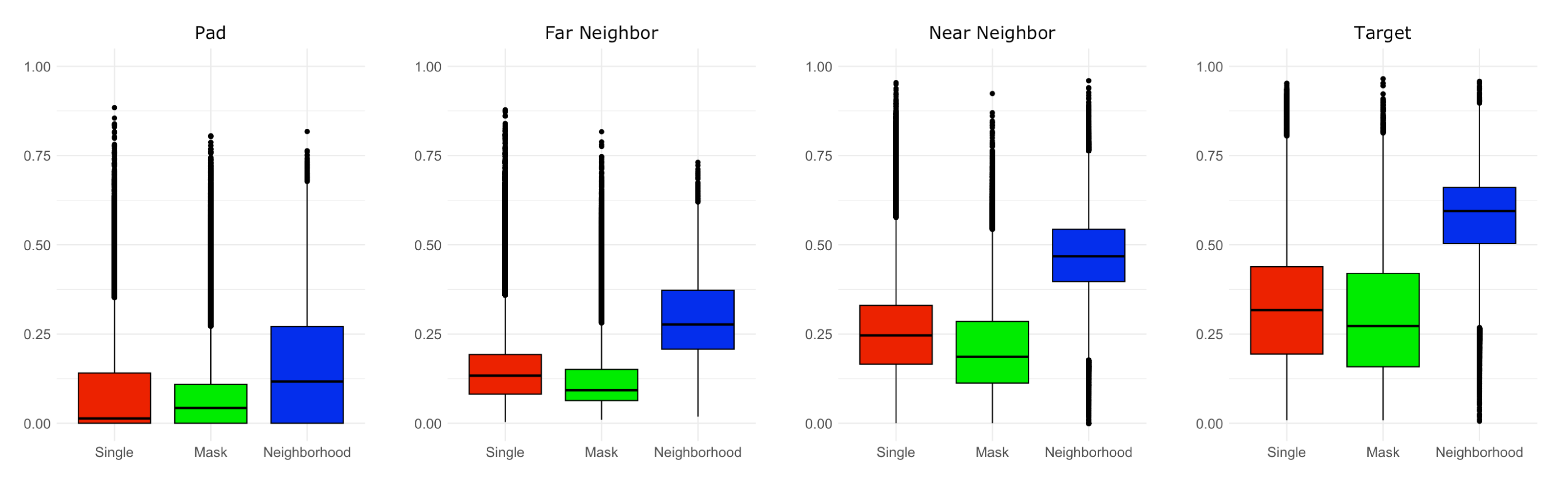
3.2. Feature Selection
3.3. Experimental Study
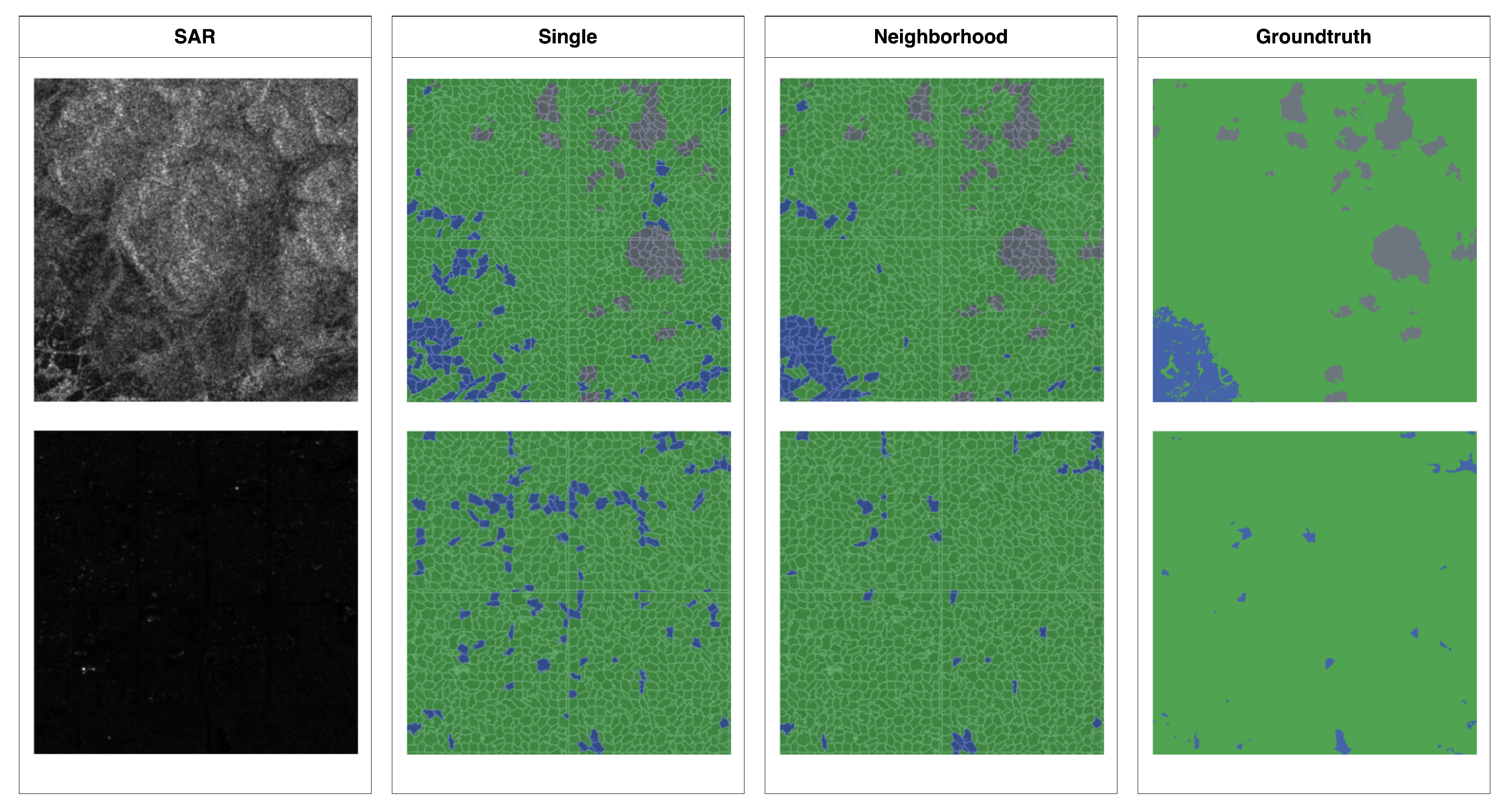
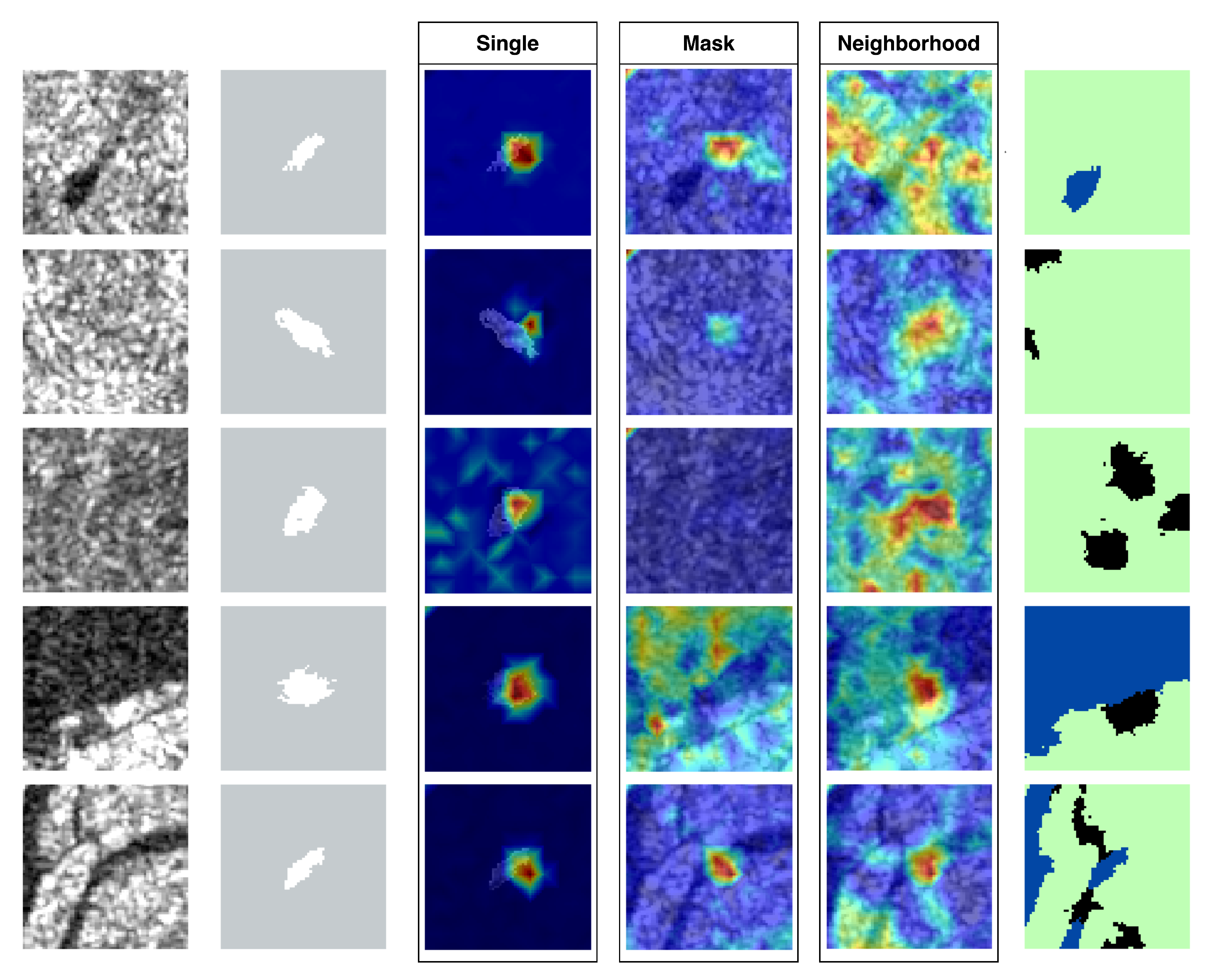
3.4. Qualitative Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MISP | Mixture-based superpixel |
| ICM | Iterated Conditional Modes |
| CD | Change Detection |
| VV | Vertical transmit and Vertical received |
| VH | Vertical transmit and Horizontal received |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| DeiT | Data-efficient image Transformer |
| MSA | Multi-head self-attention |
| MLP | Multi-layer Perceptron |
| SDT | Shallow Deit-Ti |
| XGB | XG boost |
Appendix A. Features for MISP-XGB
| Feature name | Explanation | Model |
|---|---|---|
| mean_cent | The mean value of a superpixel | single/neighb |
| std_cent | The standard deviation of a superpixel | |
| pc25_cent | The 25th percentile | |
| pc50_cent | The 50th percentile | |
| pc75_cent | The 75th percentile | |
| skew_cent | The skewness | |
| deg_cent | The degree of angle | |
| kurtosis_cent | The kurtosis | |
| shannon_entropy_cent | The Shannon entropy | |
| area_cent | The area | |
| num_islands_cent | The number of islands | |
| mean_cs_cent | The mean of a contrast-stretched superpixel | |
| std_cs_cent | The standard deviation of a contrast-stretched superpixel | |
| pc25_cs_cent | The 25th percentile of a contrast-stretched | |
| pc50_cs_cent | The median of a contrast-stretched | |
| pc75_cs_cent | The 75th percentile of a contrast-stretched | |
| skew_cs_cent | The skewness of a contrast-stretched | |
| kurtosis_cs_cent | The kurtosis of s contrast-stretched | |
| shannon_entropy_cs_cent | The Shannon entropy of a contrast-stretched | |
| mean_** | The mean value of the *-th neighborhood of a target superpixel | neighb |
| std_** | The standard deviation of the *-th neighborhood of a target superpixel | |
| pc25_** | The 25th percentile of the *-th neighborhood of a target superpixel | |
| pc50_** | The median of the *-th neighborhood of a target superpixel | |
| pc75_** | The 75th percentile of the *-th neighborhood of a target superpixel | |
| skew_** | *-th neighborhood’s skewness | |
| deg_** | The angle between *-th neighborhood and the base axis | |
| kurtosis_** | *-th neighborhood’s kurtosis | |
| shannon_entropy_** | *-th neighborhood’s Shannon entropy | |
| area_** | *-th neighborhood’s are | |
| num_islands_** | The number of islands of the *-th neighborhood of a target superpixel | |
| mean_cs_** | The mean of the contrast-stretched *-th neighborhood | |
| std_cs_** | The standard deviation of the *-th neighborhood (contrast-stretched) | |
| pc25_cs_** | The 25th percentile of the *-th neighborhood (contrast-stretched) | |
| pc50_cs_** | The median of the *-th neighborhood (contrast-stretched) | |
| pc75_cs_** | The 75th percentile of the *-th neighborhood (contrast-stretched) | |
| skew_cs_** | *-th neighborhood’s skewness (contrast stretched) | |
| kurtosis_cs_** | *-th neighborhood’s kurtosis (contrast stretched) | |
| shannon_entropy_cs_** | *-th neighborhood’s Shannon entropy (contrast stretched) |
Appendix B. Feature importance
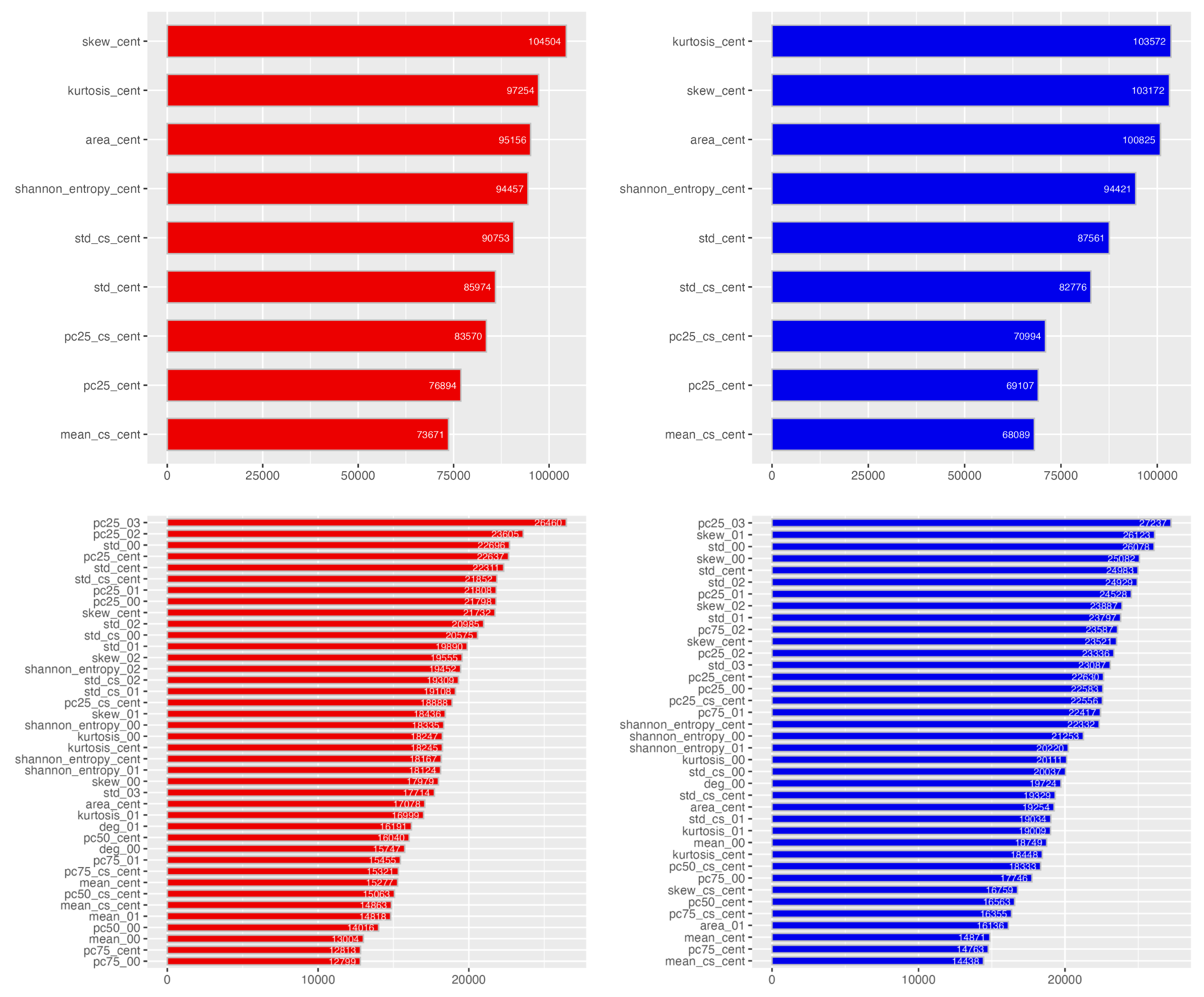
References
- Delmeire, S. Use of ERS-1 data for the extraction of flooded areas. Hydrological processes 1997, 11, 1393–1396. [CrossRef]
- Matgen, P.; Hostache, R.; Schumann, G.; Pfister, L.; Hoffmann, L.; Savenije, H. Towards an automated SAR-based flood monitoring system: Lessons learned from two case studies. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Parts A/B/C 2011, 36, 241–252. [CrossRef]
- Giustarini, L.; Hostache, R.; Matgen, P.; Schumann, G.J.P.; Bates, P.D.; Mason, D.C. A change detection approach to flood mapping in urban areas using TerraSAR-X. IEEE transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 2012, 51, 2417–2430. [CrossRef]
- Santoro, M.; Wegmüller, U. Multi-temporal synthetic aperture radar metrics applied to map open water bodies. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing 2013, 7, 3225–3238. [CrossRef]
- Manjusree, P.; Prasanna Kumar, L.; Bhatt, C.M.; Rao, G.S.; Bhanumurthy, V. Optimization of threshold ranges for rapid flood inundation mapping by evaluating backscatter profiles of high incidence angle SAR images. International Journal of Disaster Risk Science 2012, 3, 113–122. [CrossRef]
- Gulácsi, A.; Kovács, F. Sentinel-1-imagery-based high-resolution water cover detection on wetlands, Aided by Google Earth Engine. Remote Sensing 2020, 12, 1614. [CrossRef]
- Matgen, P.; Schumann, G.; Henry, J.B.; Hoffmann, L.; Pfister, L. Integration of SAR-derived river inundation areas, high-precision topographic data and a river flow model toward near real-time flood management. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation 2007, 9, 247–263. [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Xiong, S.; Zhang, W.; Tang, J.; Li, Z.; An, B.; Li, R. A Near-Real-Time Flood Detection Method Based on Deep Learning and SAR Images. Remote Sensing 2023, 15, 2046. [CrossRef]
- Lang, M.W.; Townsend, P.A.; Kasischke, E.S. Influence of incidence angle on detecting flooded forests using C-HH synthetic aperture radar data. Remote Sensing of Environment 2008, 112, 3898–3907. [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; DeVries, B.; Huang, C.; Lang, M.W.; Jones, J.W.; Creed, I.F.; Carroll, M.L. Automated extraction of surface water extent from Sentinel-1 data. Remote Sensing 2018, 10, 797. [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Wang, L.; Min, L.; Hou, W.; Guo, Z.; Zhao, J.; Li, N. Discrimination of algal-bloom using spaceborne SAR observations of Great Lakes in China. Remote Sensing 2018, 10, 767. [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Niu, S.; Guo, Z.; Wu, L.; Zhao, J.; Min, L.; Ge, D.; Chen, J. Dynamic waterline mapping of inland great lakes using time-series SAR data from GF-3 and S-1A satellites: A case study of DJK reservoir, China. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing 2019, 12, 4297–4314. [CrossRef]
- Lv, W.; Yu, Q.; Yu, W. Water extraction in SAR images using GLCM and support vector machine. In Proceedings of the IEEE 10th international conference on signal processing proceedings, 2010. [CrossRef]
- Martinis, S.; Twele, A. A hierarchical spatio-temporal Markov model for improved flood mapping using multi-temporal X-band SAR data. Remote Sensing 2010, 2, 2240–2258. [CrossRef]
- Nagaraj, R.; Kumar, L.S. Multi scale feature extraction network with machine learning algorithms for water body extraction from remote sensing images. International Journal of Remote Sensing 2022, 43, 6349–6387.
- Sghaier, M.O.; Foucher, S.; Lepage, R. River extraction from high-resolution SAR images combining a structural feature set and mathematical morphology. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing 2016, 10, 1025–1038. [CrossRef]
- D’Addabbo, A.; Refice, A.; Pasquariello, G.; Lovergine, F.P.; Capolongo, D.; Manfreda, S. A Bayesian network for flood detection combining SAR imagery and ancillary data. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 2016, 54, 3612–3625. [CrossRef]
- Asaro, F. A novel statistical-based scale-independent approach to unsupervised water segmentation of SAR images. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2019-2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. IEEE, 2019, pp. 1057–1060. [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, R.C.; Woods, R.E. Digital image processing, fourth ed.; Pearson Education, New York, 2018.
- Zhu, L.; Zhang, J.; Sun, Y. Remote sensing image change detection using superpixel cosegmentation. Information 2021, 12, 94. [CrossRef]
- Jing, W.; Jin, T.; Xiang, D. Fast Superpixel-based clustering algorithm for SAR image segmentation. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters 2021, 19, 1–5. [CrossRef]
- Pappas, O.; Anantrasirichai, N.; Adams, B.; Achim, A. High-resolution Coastline Extraction in SAR Images via MISP-GGD Superpixel Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2021 CIE International Conference on Radar (Radar). IEEE, 2021, pp. 2525–2528. [CrossRef]
- Gharibbafghi, Z.; Tian, J.; Reinartz, P. Modified superpixel segmentation for digital surface model refinement and building extraction from satellite stereo imagery. Remote Sensing 2018, 10, 1824. [CrossRef]
- Xiang, D.; Tang, T.; Zhao, L.; Su, Y. Superpixel generating algorithm based on pixel intensity and location similarity for SAR image classification. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters 2013, 10, 1414–1418. [CrossRef]
- Ke, J.; Guo, Y.; Sowmya, A. A Fast Approximate Spectral Unmixing Algorithm Based on Segmentation. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, 2017, pp. 66–72.
- Levinshtein, A.; Stere, A.; Kutulakos, K.N.; Fleet, D.J.; Dickinson, S.J.; Siddiqi, K. Turbopixels: Fast superpixels using geometric flows. IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence 2009, 31, 2290–2297. [CrossRef]
- Gadhiraju, S.V.; Sahbi, H.; Banerjee, B.; Buddhiraju, K.M. Supervised change detection in satellite imagery using super pixels and relevance feedback. Geomatica 2014, 68, 5–14. [CrossRef]
- Arisoy, S.; Kayabol, K. Mixture-based superpixel segmentation and classification of SAR images. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters 2016, 13, 1721–1725. [CrossRef]
- Nemni, E.; Bullock, J.; Belabbes, S.; Bromley, L. Fully convolutional neural network for rapid flood segmentation in synthetic aperture radar imagery. Remote Sensing 2020, 12, 2532. [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.; Van Merriënboer, B.; Gulcehre, C.; Bahdanau, D.; Bougares, F.; Schwenk, H.; Bengio, Y. Learning phrase representations using RNN encoder-decoder for statistical machine translation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1406.1078 2014. [CrossRef]
- Bahdanau, D.; Cho, K.; Bengio, Y. Neural machine translation by jointly learning to align and translate. arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.0473 2014. [CrossRef]
- Luong, M.T.; Pham, H.; Manning, C.D. Effective approaches to attention-based neural machine translation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1508.04025 2015. [CrossRef]
- Ashish, V. Attention is all you need. Advances in neural information processing systems 2017, 30, I.
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.11929 2020. [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Canny, J. Interpretable learning for self-driving cars by visualizing causal attention. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, 2017, pp. 2942–2950.
- Wollek, A.; Graf, R.; Čečatka, S.; Fink, N.; Willem, T.; Sabel, B.O.; Lasser, T. Attention-based saliency maps improve interpretability of pneumothorax classification. Radiology: Artificial Intelligence 2022, 5, e220187. [CrossRef]
- Won, M.; Chun, S.; Serra, X. Toward interpretable music tagging with self-attention. arXiv preprint arXiv:1906.04972 2019. [CrossRef]
- Bonafilia, D.; Tellman, B.; Anderson, T.; Issenberg, E. Sen1Floods11: A georeferenced dataset to train and test deep learning flood algorithms for sentinel-1. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, 2020, pp. 210–211.
- Pekel, J.F.; Cottam, A.; Gorelick, N.; Belward, A.S. High-resolution mapping of global surface water and its long-term changes. Nature 2016, 540, 418–422. [CrossRef]
- Besag, J. On the statistical analysis of dirty pictures. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society Series B: Statistical Methodology 1986, 48, 259–279. [CrossRef]
- Touvron, H.; Cord, M.; Douze, M.; Massa, F.; Sablayrolles, A.; Jégou, H. Training data-efficient image transformers & distillation through attention. In Proceedings of the International conference on machine learning. PMLR, 2021, pp. 10347–10357.
- Abnar, S.; Zuidema, W. Quantifying attention flow in transformers. arXiv preprint arXiv:2005.00928 2020. [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. Xgboost: A scalable tree boosting system. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 22nd acm sigkdd international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining, 2016, pp. 785–794. [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.H. Stochastic gradient boosting. Computational statistics & data analysis 2002, 38, 367–378. [CrossRef]
- Ben Jabeur, S.; Stef, N.; Carmona, P. Bankruptcy prediction using the XGBoost algorithm and variable importance feature engineering. Computational Economics 2023, 61, 715–741. [CrossRef]
- Manju, N.; Harish, B.; Prajwal, V. Ensemble feature selection and classification of internet traffic using XGBoost classifier. International Journal of Computer Network and Information Security 2019, 11, 37.
- Bai, Y.; Wu, W.; Yang, Z.; Yu, J.; Zhao, B.; Liu, X.; Yang, H.; Mas, E.; Koshimura, S. Enhancement of detecting permanent water and temporary water in flood disasters by fusing sentinel-1 and sentinel-2 imagery using deep learning algorithms: Demonstration of sen1floods11 benchmark datasets. Remote Sensing 2021, 13, 2220. [CrossRef]
- Chaurasia, A.; Culurciello, E. Linknet: Exploiting encoder representations for efficient semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE visual communications and image processing (VCIP). IEEE, 2017, pp. 1–4. [CrossRef]
- Shvets, A.A.; Iglovikov, V.I.; Rakhlin, A.; Kalinin, A.A. Angiodysplasia detection and localization using deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 17th IEEE international conference on machine learning and applications (ICMLA). IEEE, 2018, pp. 612–617. [CrossRef]
- Bereczky, M.; Wieland, M.; Krullikowski, C.; Martinis, S.; Plank, S. Sentinel-1-based water and flood mapping: Benchmarking convolutional neural networks against an operational rule-based processing chain. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing 2022, 15, 2023–2036. [CrossRef]

| Type | Sample size |
|---|---|
| Train (Hand-labeled) | 252 |
| Validation | 89 |
| Test | 90 |
| Bolivia | 15 |
| Scheme | Parameter | Value/Choice |
|---|---|---|
| ]7*Unstructured | Epochs | 80 |
| Learning rate | ||
| Batch size | 512 | |
| Optimizer | AdamW | |
| Loss function | Cross entropy | |
| Weight decay | 0.05 | |
| Dropout | 0.0 | |
| ]9*Structured | Boosting count | 1450 |
| Learning rate | 0.0035 | |
| max depths of tree | 10 | |
| Early stopping round | 250 | |
| Objective function | Binary logistic | |
| L1 regularization | 0.6 | |
| L2 regularization | 1.2 | |
| Tree method | Approx | |
| Column subsample ratio | 0.55 |
| Pol | Scheme | Model | Accuracy | Recall | Precision | F-1 | IoU | mIoU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VV | Unstr | Single | 0.916 | 0.459 | 0.479 | 0.376 | 0.473 | 0.292 |
| Mask | 0.888 | 0.578 | 0.362 | 0.364 | 0.438 | 0.274 | ||
| Neighb | 0.926 | 0.425 | 0.541 | 0.403 | 0.515 | 0.309 | ||
| Str | Single | 0.908 | 0.533 | 0.444 | 0.391 | 0.462 | 0.300 | |
| Neighb | 0.923 | 0.514 | 0.479 | 0.411 | 0.513 | 0.319 | ||
| VH | Unstr | Single | 0.926 | 0.542 | 0.468 | 0.431 | 0.565 | 0.338 |
| Mask | 0.921 | 0.574 | 0.451 | 0.425 | 0.536 | 0.325 | ||
| Neighb | 0.936 | 0.543 | 0.497 | 0.456 | 0.601 | 0.357 | ||
| Str | Single | 0.924 | 0.580 | 0.464 | 0.439 | 0.569 | 0.345 | |
| Neighb | 0.935 | 0.570 | 0.509 | 0.466 | 0.608 | 0.368 |
| Metric | FCNN (HL) | FCNN (S1W) | AlbuNet-34 | MISP-SDT | MISP-XGB | ||
| IoU | n/a | n/a | 0.497 | 0.601 | 0.608 | ||
| mIoU | 0.313 | 0.309 | 0.347 | 0.357 | 0.368 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




