Submitted:
10 October 2024
Posted:
11 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
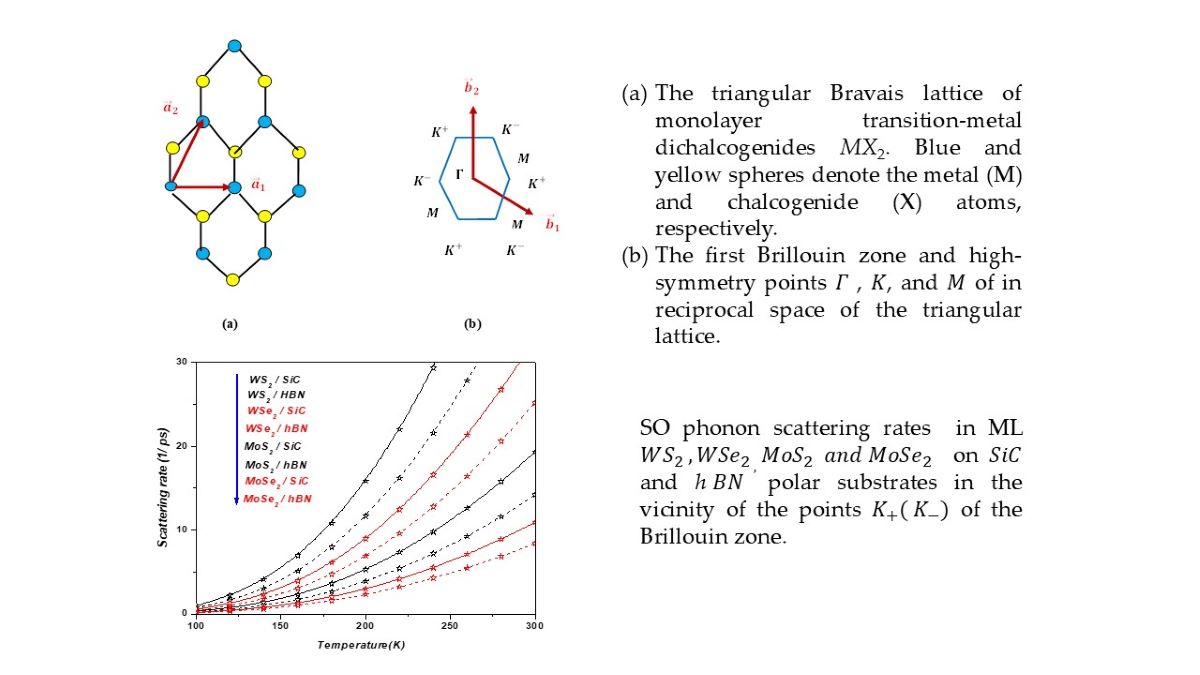
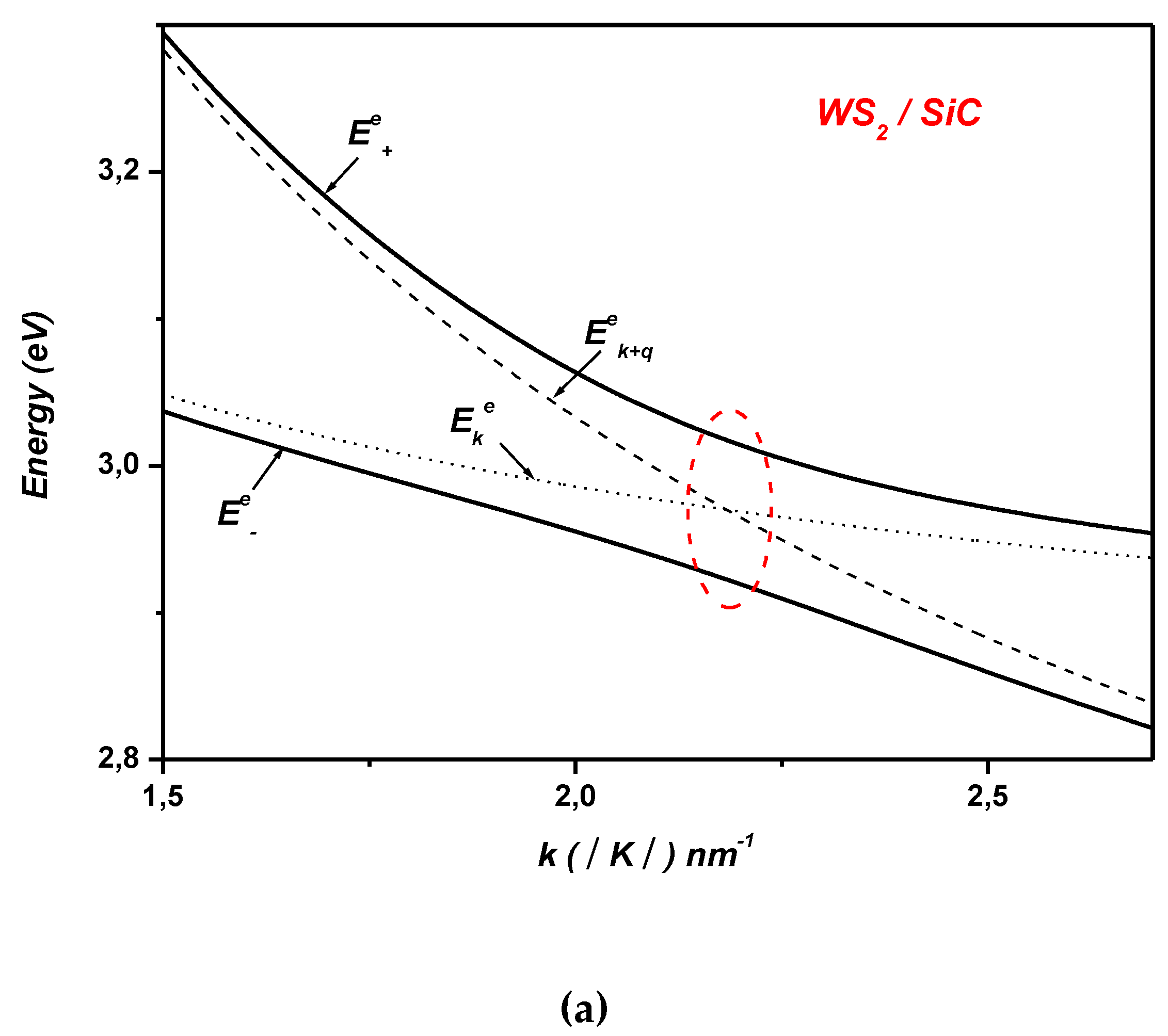
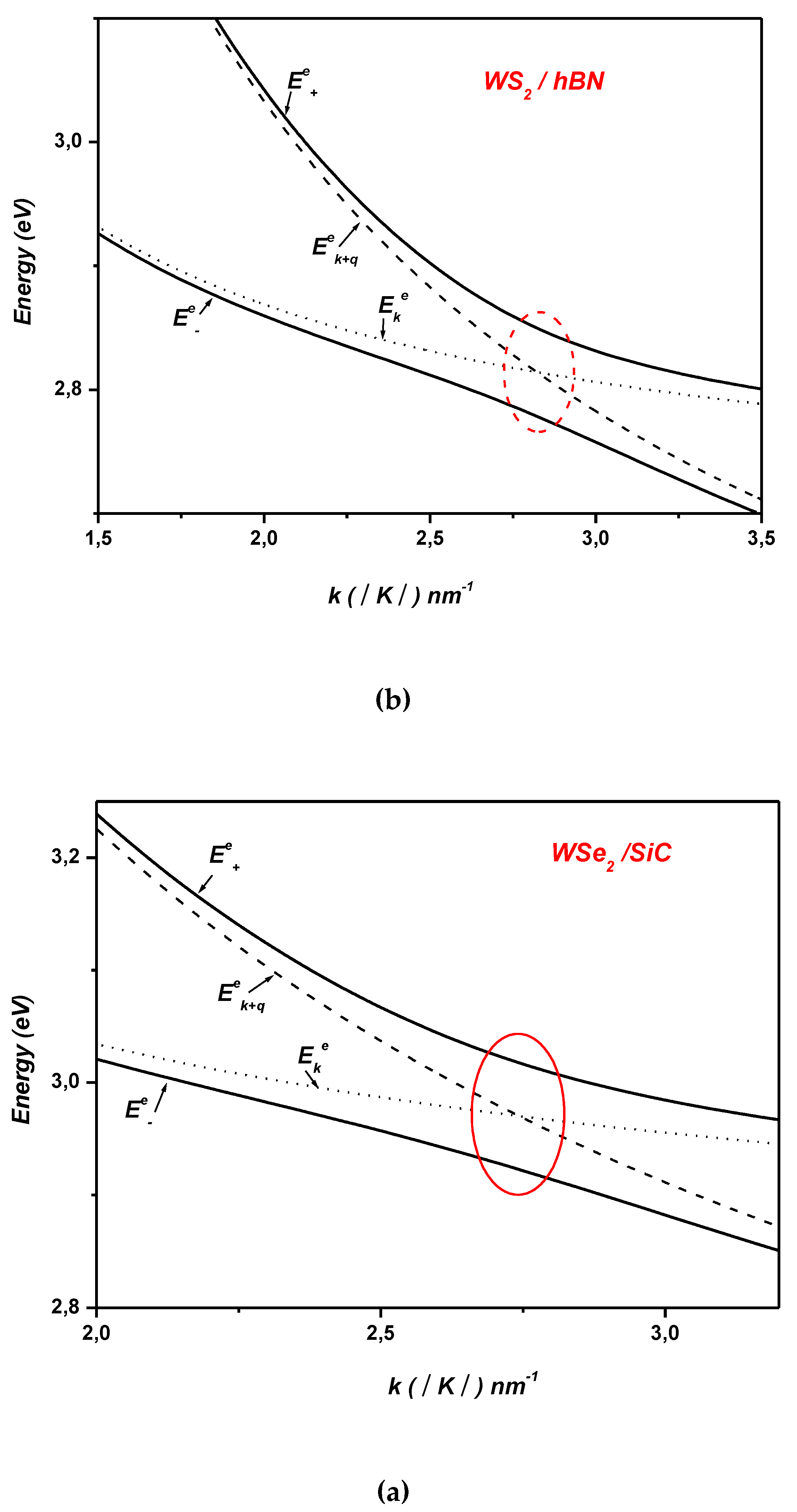
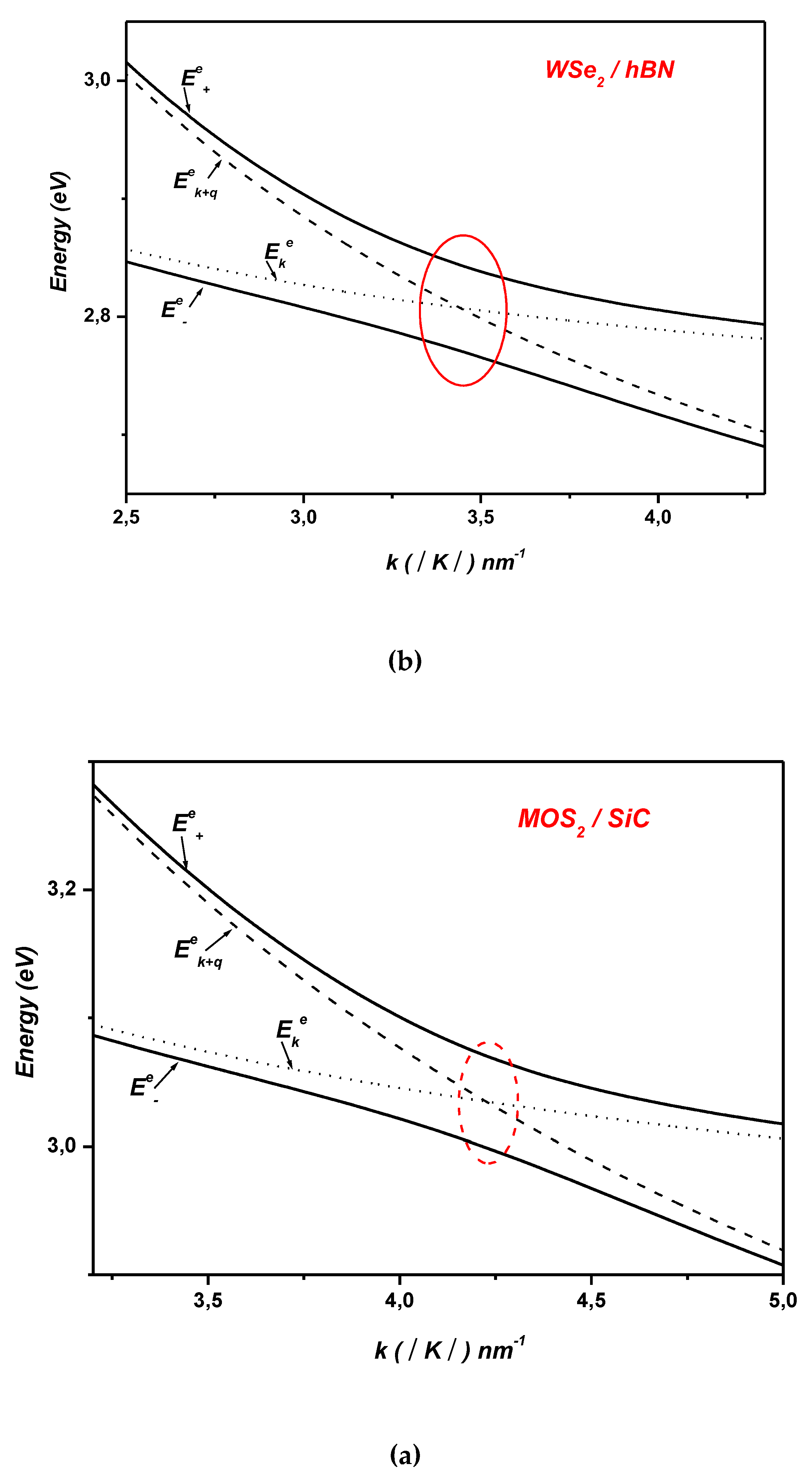
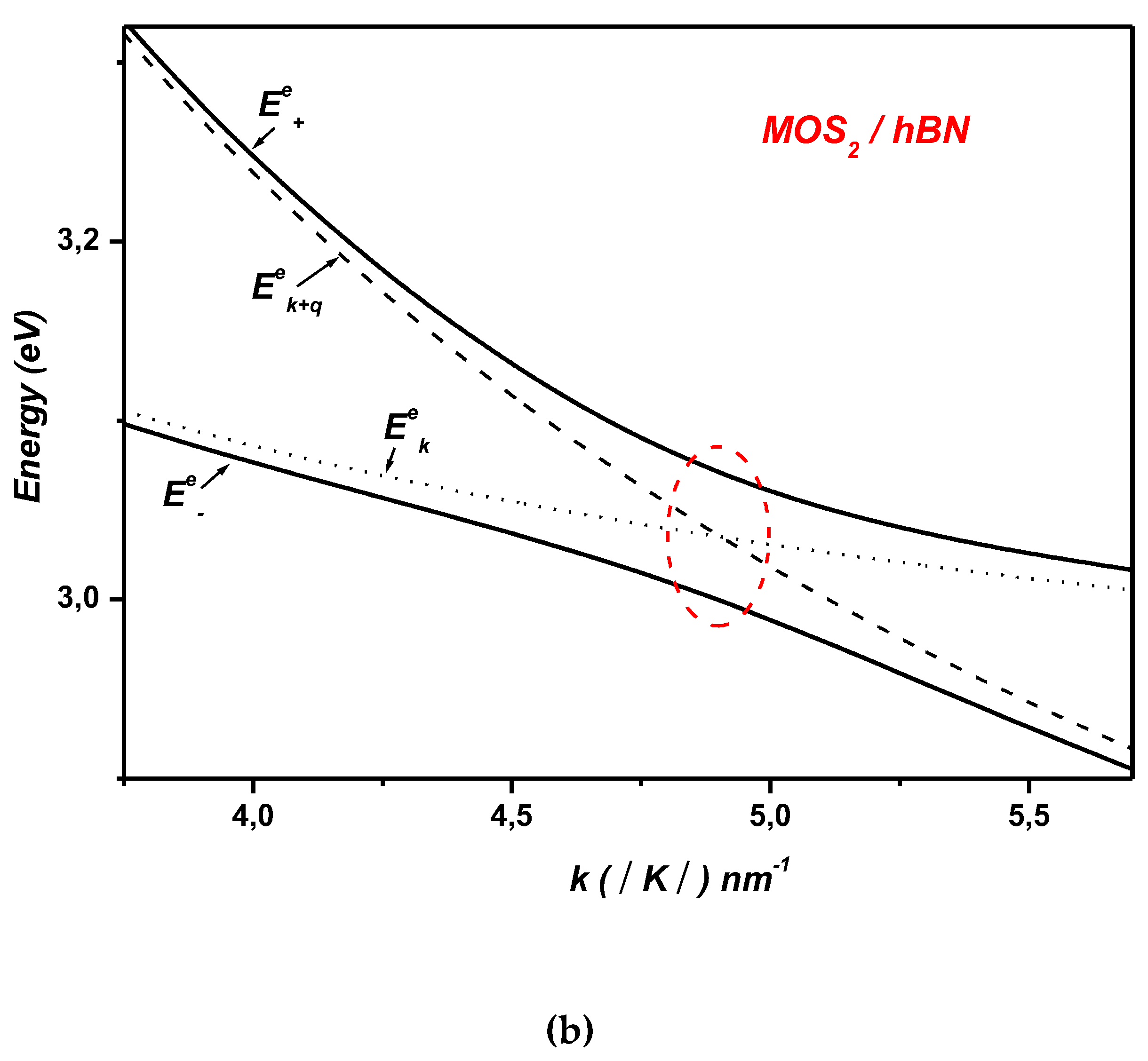
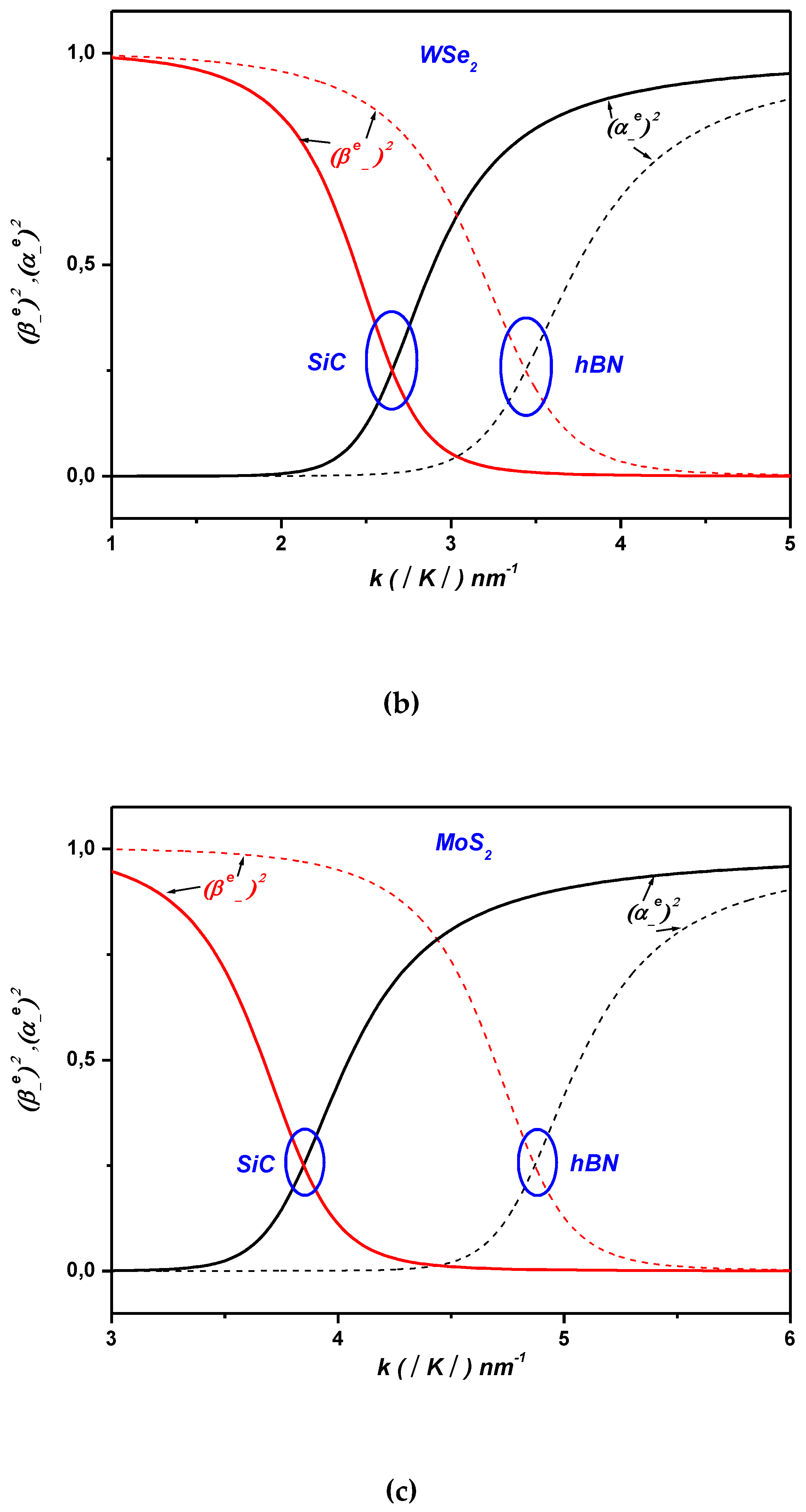
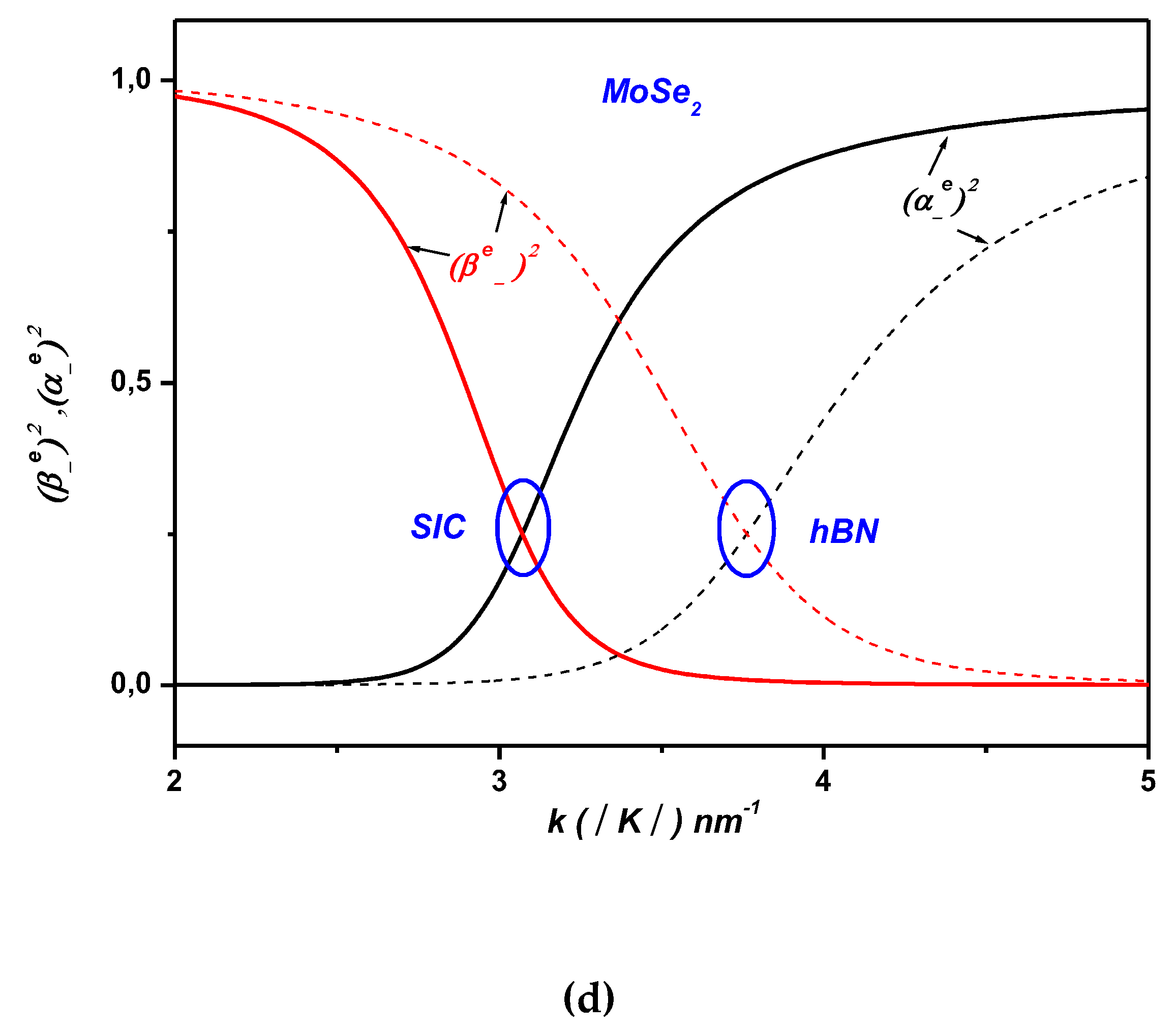
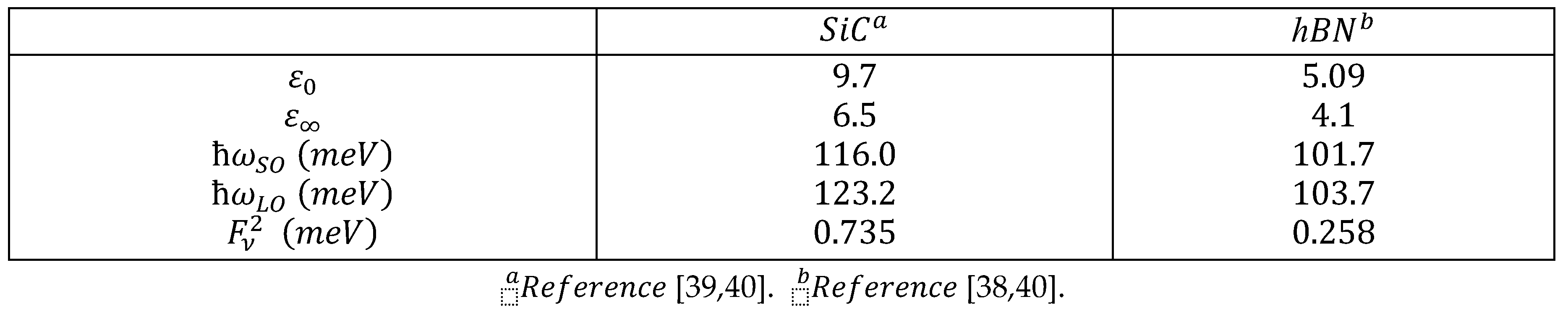
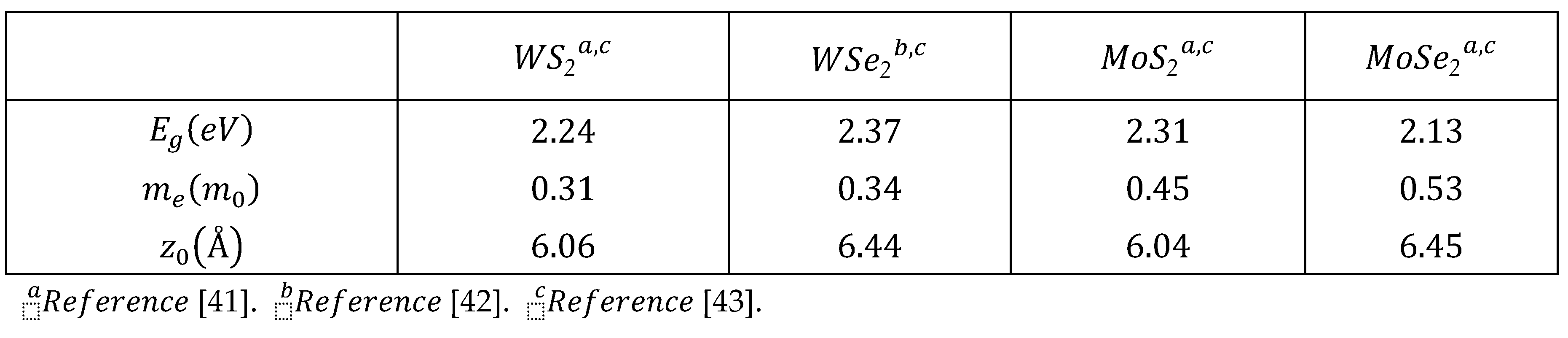
2. Electron-Surface Optical Phonon Interaction in ML TMDCs on and h Dielectric Substrates
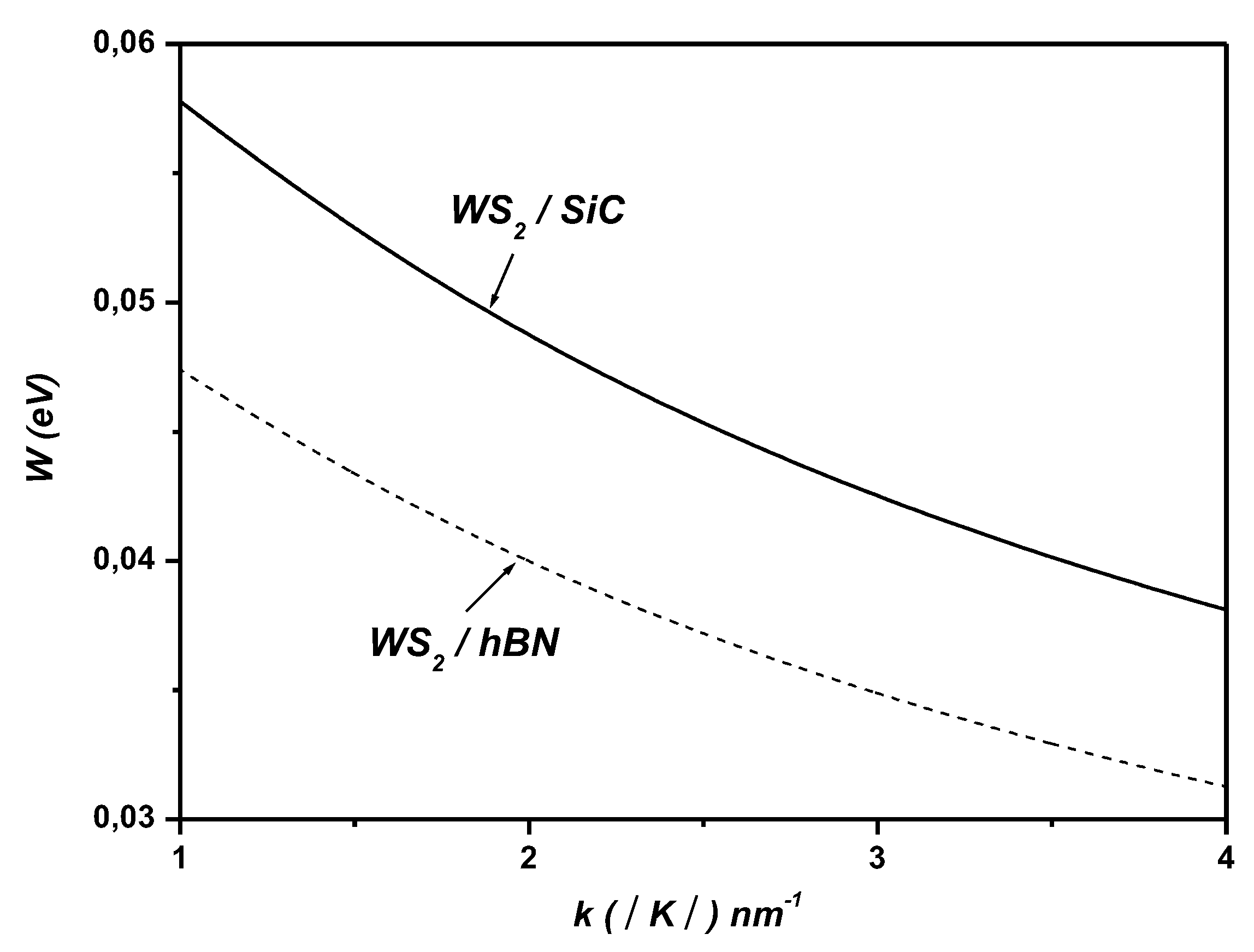
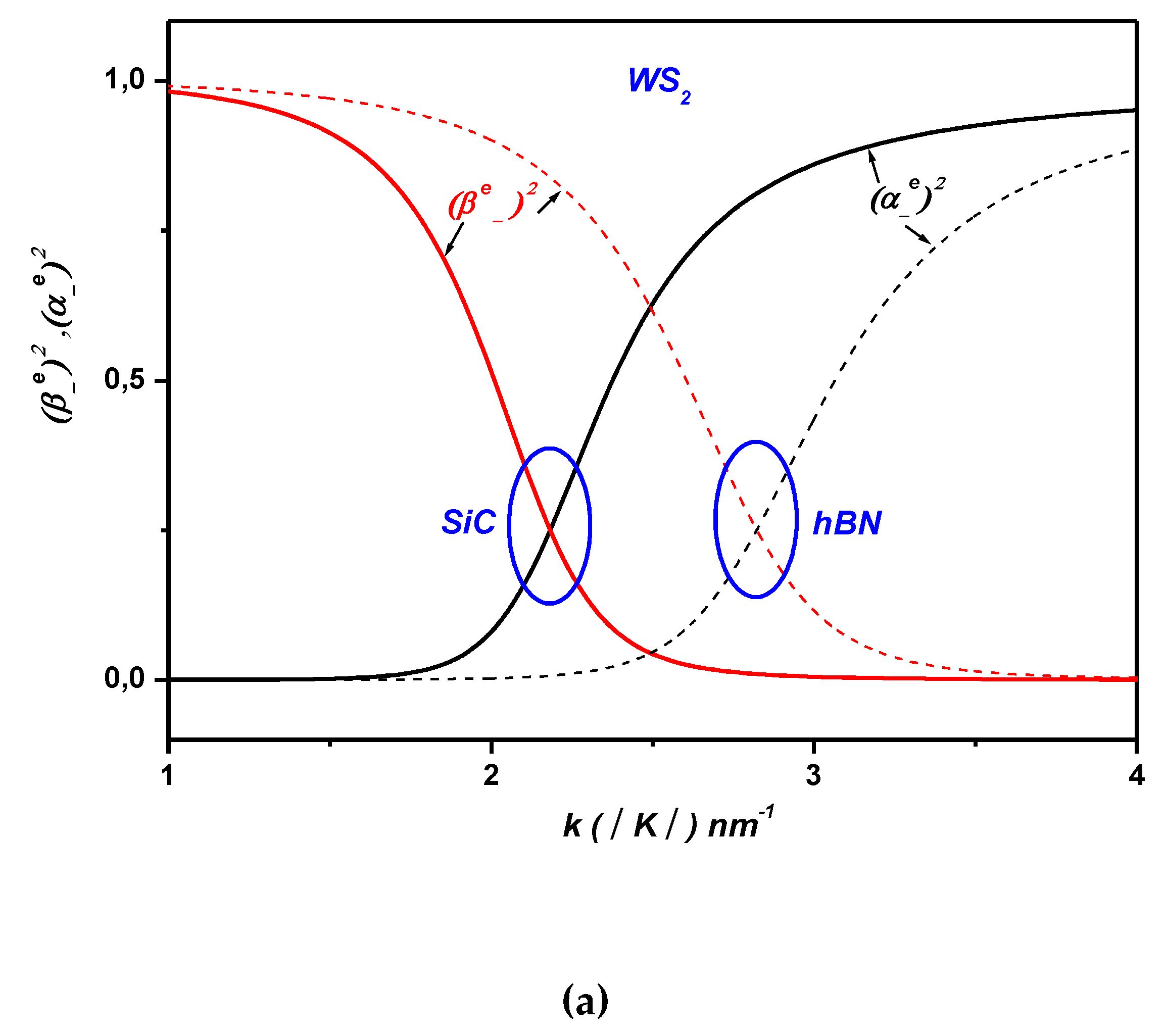
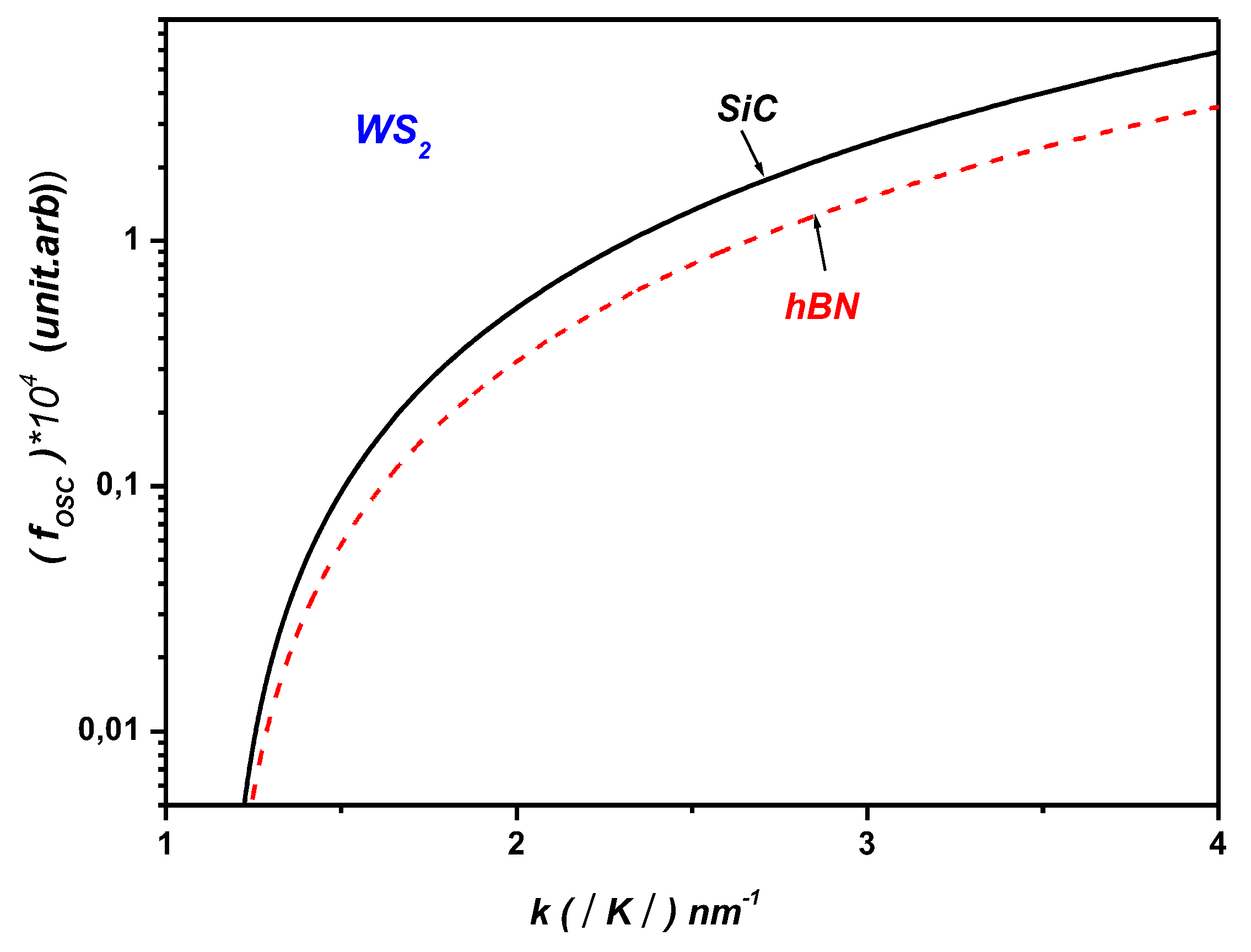
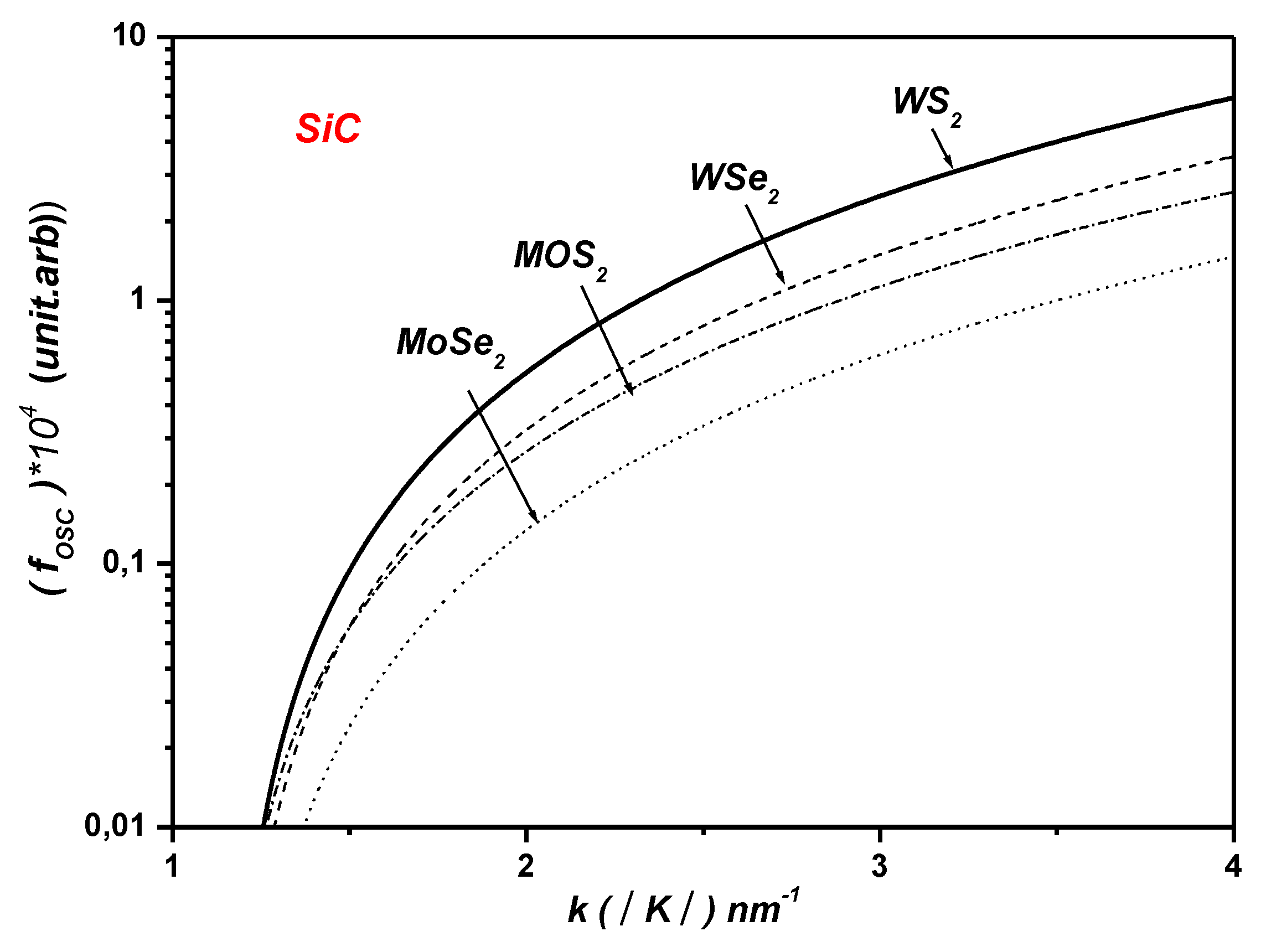
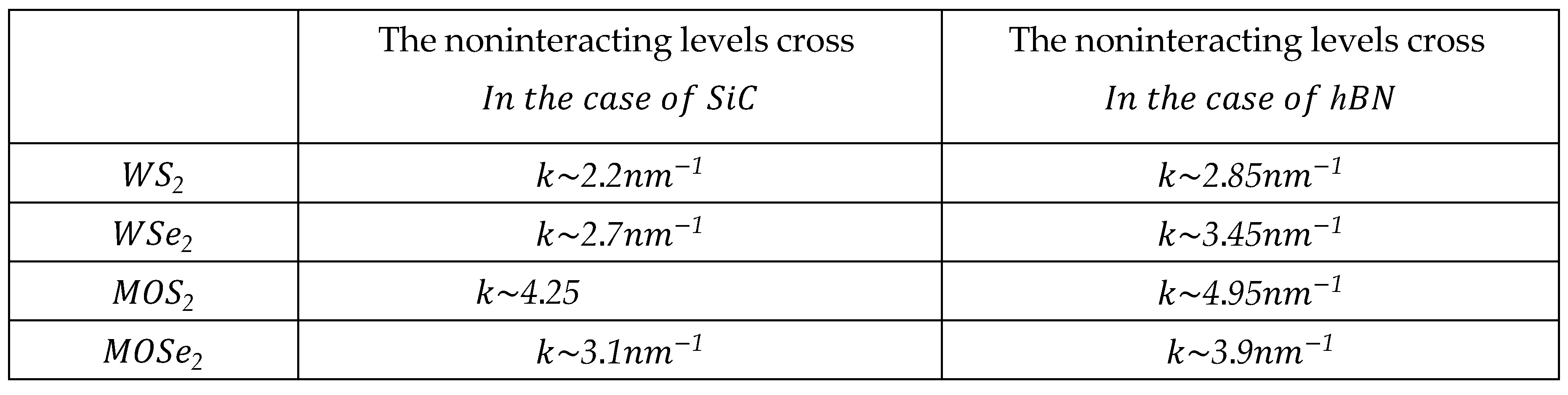
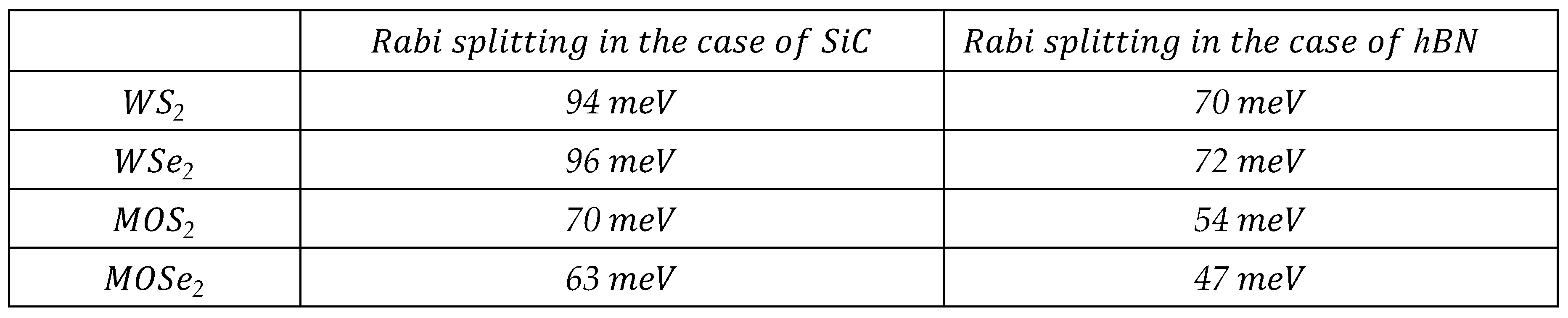
3. Polaronic Oscillator Strength of ML TMDCs on SiC and hBN Polar Substrates
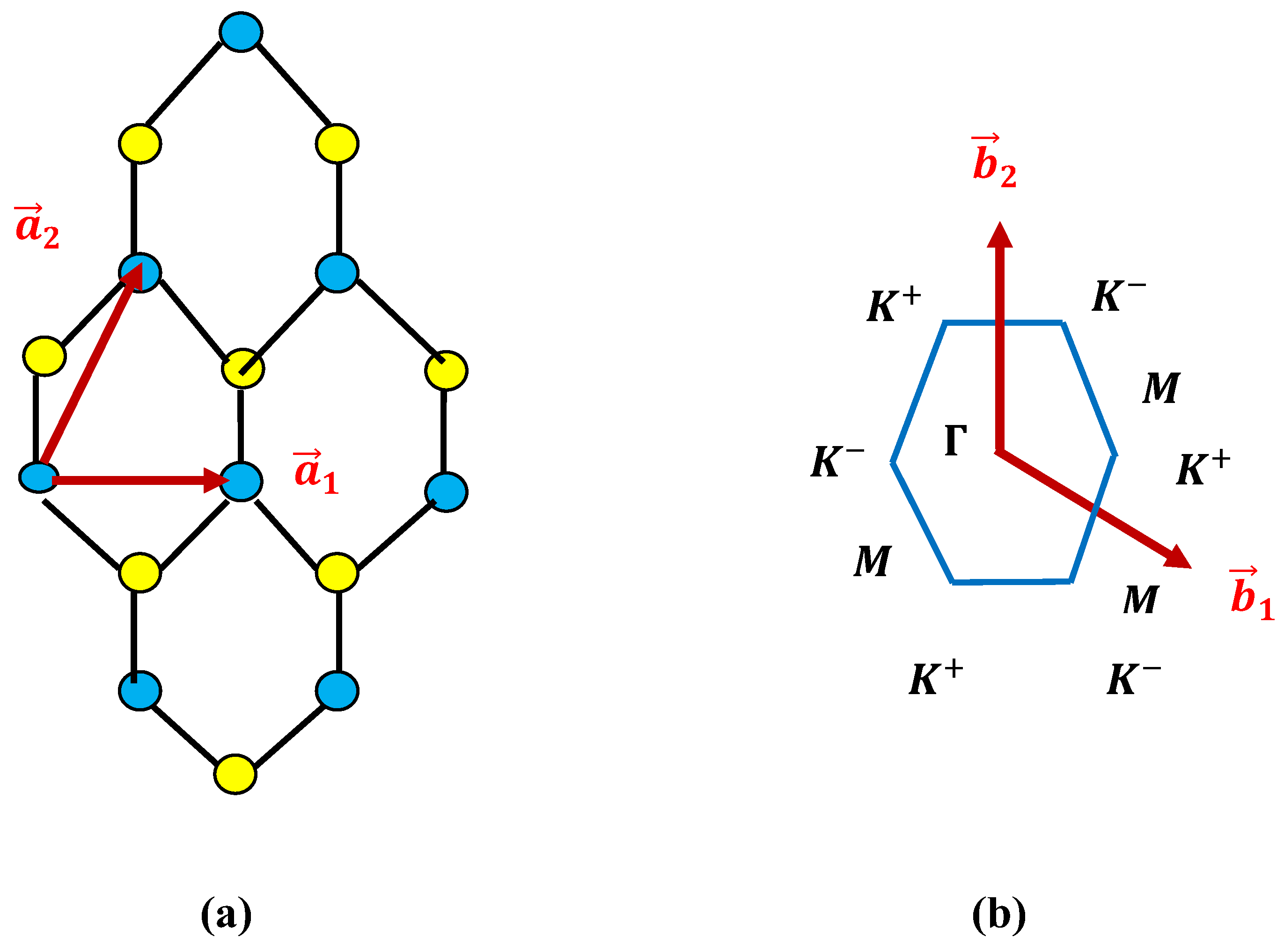
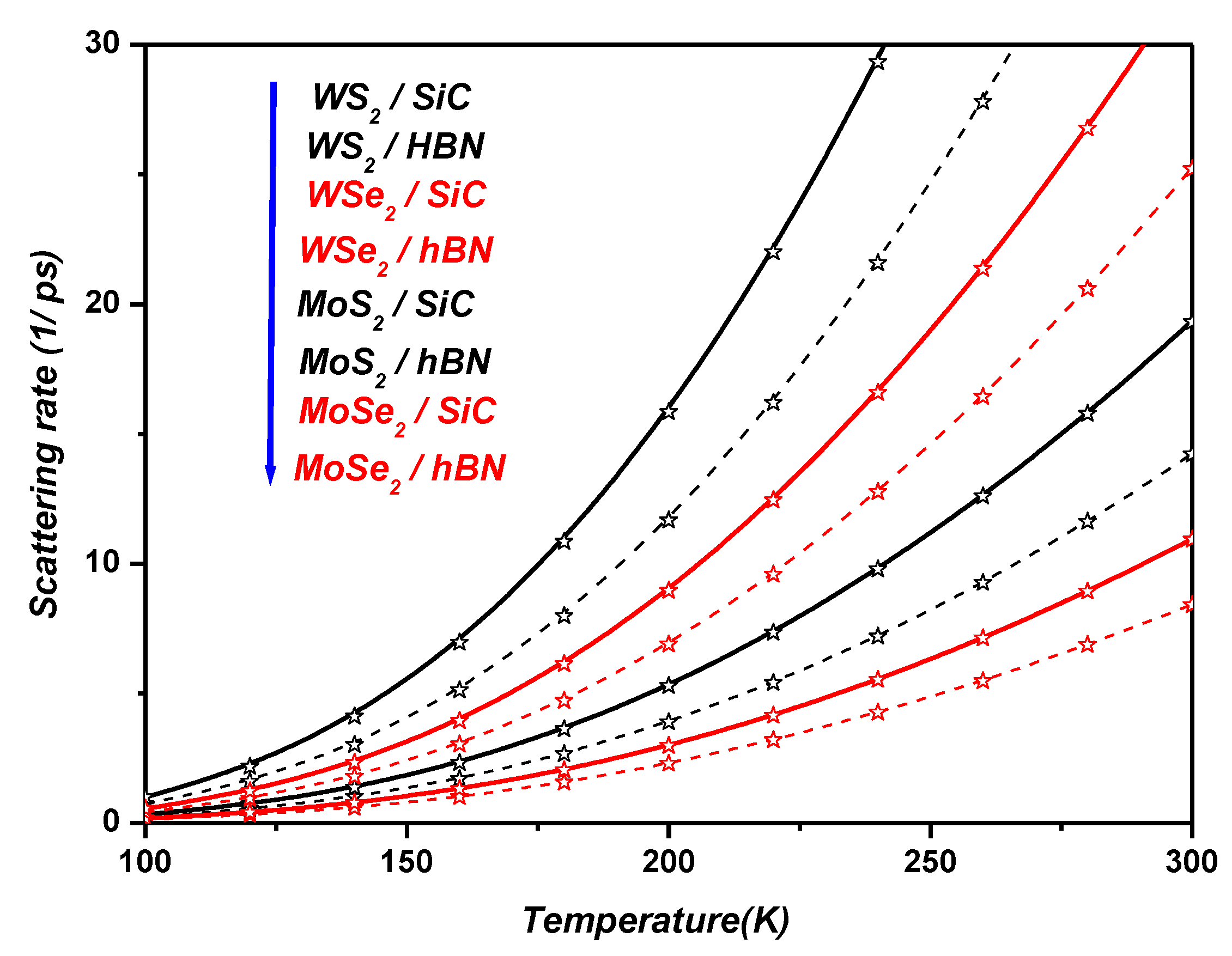
4. Polaronic Scattering Rate of ML TMDCs on SiC and hBN Polar Substrates
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zixuan Wang ; Yecheng Nie ; Haohui Ou ; Dao Chen ; Yingqian Cen ; Jidong Liu ; Di Wu ; Guo Hong ; Benxuan Li ; Guichuan Xing ; and Wenjing Zhang. Electronic and Optoelectronic Monolayer WSe2 Devices via Transfer-Free Fabrication Method. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1368. [CrossRef]
- Tanveer Ahmed ; Jiajia Zha; Kris KH Lin; Hao-Chung Kuo ; Chaoliang Tan, Der-Hsien . Bright and Efficient Light-Emitting Devices Based on 2D Transition Metal Dichalcogenides. Advanced Materials 2023, 35, 2208054. [CrossRef]
- Saju Joseph ; Jainy Mohan ; Seetha Lakshmy ; Simil Thomas ; Brahmananda Chakraborty ; Sabu Thomas ; Nandakumar Kalarikkal. A review of the synthesis, properties, and applications of 2D transition metal dichalcogenides and their heterostructures. Materials Chemistry and Physics 2023, 297, 127332. [CrossRef]
- Chit Siong Lau; Jing Yee Chee; Liemao Cao ; Zi-En Ooi ; Shi Wun Tong ; Michel Bosman ; Fabio Bussolotti ; Tianqi Deng ; Gang Wu, Shuo-Wang Yang, and al.. Gate-Defined Quantum Confinement in CVD 2D WS2. Advanced Materials 2022 , 34, 2103907. [CrossRef]
- Lifu Zhang; Ruihao Ni; You Zhou . Controlling quantum phases of electrons and excitons in moiré superlattices. J. Appl. Phys 2023, 133, 080901. [CrossRef]
- Vincenzo Ardizzone; Luisa De Marco; Milena De Giorgi; Lorenzo Dominici; Dario Ballarini and Daniele Sanvitto. Emerging 2D materials for room-temperature polaritonics. Nanophotonics 2019, 8, 1547–1558. [CrossRef]
- Kaichen Xie ; Xiaosong Li, and Ting Cao. Theory and Ab Initio Calculation of Optically Excited States—Recent Advances in 2D Materials. Advanced Materials 2021, 33, 1904306. [CrossRef]
- Maurizia Palummo ; Marco Bernardi ; Jeffrey C Grossman. Exciton Radiative Lifetimes in Two-Dimensional Transition Metal Dichalcogenides. Nano Letters 2015, 15, 2794–2800. [CrossRef]
- Diana Y. Qiu; Ting Cao; and Steven G. Louie, Nonanalyticity, Valley Quantum Phases, and Lightlike Exciton Dispersion in Monolayer Transition Metal Dichalcogenides: Theory and First-Principles Calculations. Phys. Rev. Lett 2015. 115, 176801. [CrossRef]
- Chung-Che Huang; He Wang; Yameng Cao; Ed Weatherby; Filipe Richheimer; Sebastian Wood; Shan Jiang; Daqing Wei; Yongkang Dong; Xiaosong Lu; and al.. Facilitating Uniform Large-Scale MoS2, WS2 Monolayers, and Their Heterostructures through van der Waals Epitaxy. ACS Appl.Mater.Interfaces 2022, 14, 42365−42373. [CrossRef]
- Naoki Wada; Jiang Pu; Yuhei Takaguchi; Wenjin Zhang; Zheng Liu; Takahiko Endo; Toshifumi Irisawa; Kazunari Matsuda; Yuhei Miyauchi; Taishi Takenobu; Yasumitsu Miyata. Efficient and Chiral Electroluminescence from In-Plane Heterostructure of Transition Metal Dichalcogenide Monolayers. Advanced Functional Materials 2022 ,32, 2203602. [CrossRef]
- C. Robert; B. Han ; P. Kapuscinski ; A. Delhomme ; C. Faugeras ; T. Amand ; M. R. Molas ; M. Bartos ; K. Watanabe ; T. Taniguchi ; B. Urbaszek ; M. Potemski ; and X. Marie. Measurement of the spin-forbidden dark excitons in MoS2 and MoSe2 monolayers. Nature Communications. 2020, 11, 4037. [CrossRef]
- Carrascoso, F. ; Li, H., Frisenda ; R. et al. . Strain engineering in single-, bi- and tri-layer MoS2, MoSe2, WS2 and WSe2. Nano Research 2021 , 14, 1698–1703. [CrossRef]
- M. Mahdouani. Investigation of the electron-surface phonon interaction effects in graphene on a substrate made of polar materials . PHYSE 2017, 87, 192-198. [CrossRef]
- M. Mahdouani; S. Gardelis; R. Bourguiga. The effect of Si impurities on the transport properties and the electron-surface phonon interaction in single layer graphene deposited on polar substrates. Physica B: Condensed Matter. 2018, 550, 171–178. [CrossRef]
- M.Mahdouani; R. Bourguiga. Auger and carrier-surface phonon interaction processes in graphene on a substrate made of polar materials. Superlattices and Microstructures. 2017, 102, 212–220. [CrossRef]
- Vasili Perebeinos; Phaedon Avouris. Inelastic scattering and current saturation in graphene. PHYSICAL REVIEW B 2010, 81, 195442. [CrossRef]
- M. Mahdouani; R. Bourguiga; and S. Jaziri. Polaronic states in Si nanocrystals embedded in SiO2 matrix. Physica E 2008, 41, 228-234. [CrossRef]
- M.Mahdouani; S.Gardelis; and A.G.Nassiopoulou. Role of surface vibration modes in Si nanocrystals within light emitting porous Si at the strong confinement regime. J. Appl. Phys 2011, 110, 023527. [CrossRef]
- S. Gardelis ; A.G. Nassiopoulou; M. Mahdouani; R. Bourguiga; S. Jaziri. Enhancement and red shift of photoluminescence (PL) of fresh porous Si under prolonged laser irradiation or ageing: Role of surface vibration modes. Physica E. 2009, 41, 986–989. [CrossRef]
- Suvodeep Paul ; Saheb Karak ; Saswata Talukdar ; Devesh Negi and Surajit Saha. Influence of Edges and Interlayer Electron–phonon Coupling in WS2/h-BN Heterostructure. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 40077–40085. [CrossRef]
- Colin, M. Chow; Hongyi Yu; Aaron M. Jones; Jiaqiang Yan; David G. Mandrus; Takashi Taniguchi; Kenji Watanabe; Wang Yao; Xiaodong Xu. Unusual Exciton–Phonon Interactions at van der Waals Engineered Interfaces. Nano Lett 2017, 17, 1194–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastian Miller; Jessica Lindlau; Max Bommert; Andre Neumann; Hisato Yamaguchi,Alexander Holleitner; Alexander Högele & Ursula Wurstbauer. Tuning the Fröhlich exciton-phonon scattering in monolayer MoS2. Nature Communications 2019, 10, 807. [CrossRef]
- Sanjay Gopalan; Maarten L. Van de Put; Gautam Gaddemane; and Massimo V. Fischetti. Theoretical Study of Electronic Transport in Two-Dimensional Transition Metal Dichalcogenides: Effects of the Dielectric Environment. Phys. Rev. Applied. 2022, 18, 054062. [CrossRef]
- M. M. Glazov; and E. L. Ivchenko. Valley Orientation of Electrons and Excitons in Atomically Thin Transition Metal Dichalcogenide Monolayers. JETP Letters. 2021, 113, 7–17. [CrossRef]
- M. V. Durnev and M. M. Glazov. Excitons and trions in two-dimensional semiconductors based on transition metal dichalcogenides. Physics–Uspekhi. 2018, 61, 825–845. [CrossRef]
- Kormanyos; G. Burkard; M. Gmitra, J. Fabian; V. Zolyomi; N. D. Drummond; and V. Fal’ko. k·p theory for two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenide semiconductors. 2D Mater. 2015, 2, 022001. [CrossRef]
- Gabriel Antonius and Steven, G. Louie. Theory of exciton-phonon coupling. Phys. Review B 2022, 105, 085111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thibault Sohier; Matteo Calandra; and Francesco Mauri. Two-dimensional Fröhlich interaction in transition-metal dichalcogenide monolayers: Theoretical modeling and first-principles calculations. Phys. Rev. B 2016, 94, 085415. [CrossRef]
- Yixiong Wang ; Chenglin He ; Qin Tan ; Zilan Tang ; Lanyu Huang ; Liang Liu ; Jiaocheng Yin,Ying Jiang ; Xiaoxia Wang and Anlian Pan. Exciton–phonon coupling in two-dimensional layered (BA)2PbI4 perovskite microplates, RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 5893–5899. [CrossRef]
- Jinlong Ma; Dongwei Xu; Run Hu ; Xiaobing Luodoi. Examining two-dimensional Fröhlich model and enhancing the electron mobility of monolayer InSe by dielectric engineering. Journal of Applied Physics 2020, 128, 035107. [CrossRef]
- Nicki Frank Hinsche and Kristian Sommer Thygesen. Electron–phonon interaction and transport properties of metallic bulk and monolayer transition metal dichalcogenide TaS2. 2D Materials 2017, 5, 015009. [CrossRef]
- Xiao; Y., Li, Z.Q.; Wang, Z.W. Polaron effect on the bandgap modulation in monolayer transition metal dichalcogenides. J. Phys. Cond. Matter 2017, 29 , 485001. [CrossRef]
- J. V. Nguepnang ; C. Kenfack-Sadem ; A. Kenfack-Jiotsa ; M. F. C. Fobasso ·Y. Sun. Optical signature of bipolaron in monolayer transition metal dichalcogenides: all coupling approach. Optical and Quantum Electronics. 2021, 53, 728. [CrossRef]
- Devreese, J.T.; Huybrechts, W.; Lemmeks, L. On the optical absorption of free polarons at weak coupling. Physica Status Solidi (b) 1971, 48, 77–86. [CrossRef]
- Daniela, L. Mafra and Paulo T. Araujo. Intra- and Interlayer Electron-Phonon Interactions in 12/12C and 12/13C BiLayer Graphene. Appl. Sci. 2014, 4, 207–239 . [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- S. Q. Wang and G. D. Mahan. Electron Scattering from Surface Excitations .Phys. Rev. B. 1972, 6, 4517. [CrossRef]
- A. V. Rozhkov ; Franco Nori. Exact wave functions for an electron on a graphene triangular quantum dot. PHYSICAL REVIEW B. 2010, 81, 155401. [CrossRef]
- J¨urgen Schiefele, Fernando Sols, and Francisco Guinea, Temperature dependence of the conductivity of graphene on boron nitride. Phys. Rev. B 2012, 85, 195420. [CrossRef]
- R. Geick; C. H. Perry; and G. Rupprecht. Normal Modes in Hexagonal Boron Nitride. Phys. Rev. 1966, 146, 543. [CrossRef]
- B. Han; C. Robert; E. Courtade; M. Manca; S. Shree; T. Amand; P. Renucci; T. Taniguchi; K. Watanabe; X. Marie; L. E. Golub; M. M. Glazov; and B. Urbaszek1. Exciton States in Monolayer MoSe2 and MoTe2 Probed by Up conversion Spectroscopy. PHYSICAL REVIEW X. 2018, 8, 031073. [CrossRef]
- G. Wang; I. C. Gerber; L. Bouet ; D. Lagarde; A. Balocchi; M. Vidal; E. Palleau; T. Amand; X. Marie; and B. Urbaszek. Exciton states in monolayer MoSe2: impact on interband transitions . 2D Materials. 2015, 2, 045005. [CrossRef]
- Akash Laturia; Maarten L. Van de Put. and William G. Vandenberghe. Dielectric properties of hexagonal boron nitride and transition metal dichalcogenides: from monolayer to bulk. 2D Materials and Applications. 2018, 2, 6. [CrossRef]
- L.X.Benedict; S. G. Louie; and M. L. Cohen. Static polarizabilities of single-wall carbon nanotubes. Phys. Rev. B. 1995, 52, 8541. [CrossRef]
- E. H. Hwang and S. Das Sarma . Surface polar optical phonon interaction induced many-body effects and hot-electron relaxation in graphene. Phys.Rev.B. 2013, 87, 115432. [CrossRef]
- Mounira Mahdouani; Meriam Zalfani; Ramzi Bourguiga; Bao-Lian Su. Radiative and non radiative recombinations study in the novel nanocomposites BiVO4/3DOM-TiO2, ZnO/3DOM-TiO2 and BiVO4/3DOM-ZnO: Application to the photocatalysis. Physica E: Low-dimensional Systems and Nanostructures 2019, 108, 269–280. [CrossRef]
- Yu-Chen Chang; Yu-Chiao Chan; Bipul Das; Jiao-Fang Syue; Hsiang-Chi Hu, Yann-Wen Lan; and Ting-Hua L. Distinctive characteristics of exciton-phonon interactions in optically driven MoS2. Phys. Rev. Materials 2024, 8, 074003. [CrossRef]
- J. V. Nguepnang ; C. Kenfack-Sadem ; A. Kenfack-Jiotsa; C. Guimapi; A. J. Fotue &; A. E. Merad. Electron–phonon coupling contribution on the optical absorption and the dynamic of exciton-polaron in monolayer Transition Metal Dichalcogenides. Optical and Quantum Electronics. 2021, 53, 654. [CrossRef]
- Jia-Min Lai, Ya-Ru Xie, Jun Zhang, Detection of electron-phonon coupling in two-dimensional materials by light scattering. Nano Res. 2021, 14, 1711–1733. [CrossRef]
- Ying Jiang ; Shula Chen; Weihao Zheng; Biyuan Zheng and Anlian Pan. Interlayer exciton formation, relaxation, and transport in TMD van der Waals heterostructures. Light: Science & Applications 2021, 10, 72. [CrossRef]
 |
 |
 |
 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





