1. Introduction
Seasonal influenza virus infections pose a significant threat to public health globally, resulting in 3–5 million cases of severe illness and 290,000–650,000 respiratory deaths annually [
1]. Annual vaccination is recommended as the most effective approach for the prevention and control of seasonal influenza [
1,
2]. Annually updated seasonal influenza vaccines confer variable protection due to continual genetic changes in circulating viruses, underscoring the challenges in controlling influenza infections, and the associated morbidity [
3,
4,
5].
The viral hemagglutinin (HA) surface glycoproteins are key determinants of vaccine efficacy against seasonal circulating strains of influenza [
6]. The hemagglutination inhibition (HAI) assay represents the gold standard method for determining influenza vaccine-elicited immune response and quantitative antibody titers for the influenza virus [
7,
8,
9].
New influenza vaccine development is challenging due in part to traditional, labor-intensive, and cumbersome HAI assay methods involving avian red blood cells (RBCs), complex sample preparation, subjectivity, and low assay throughput. In addition, certain clades of A/H3N2 viruses agglutinate avian RBCs poorly and alternative assays such as virus neutralization assays must be used [
10,
11,
12]. A modified novel HAI assay protocol has been developed to generate more reliable and consistent data using human RBCs [
13], avoiding partial hemagglutination or irregular shapes of RBC precipitation with avian-origin RBCs [
14]. A novel automated CypherOne™ Hemagglutination Analyzer (InDevR, Boulder, CO, USA) is also being used to determine and provide a visual permanent record of assay results to eliminate the need for tilting of the HAI plate before image interpretation, thereby simplifying the assay and reducing assay turnaround time [
14]. A recent report employed a combination of guinea pig RBCs (instead of avian RBCs), neuraminidase (NA) inhibitor oseltamivir (to prevent NA-mediated agglutination), and CypherOne™ HAI plate reader-based automation, but focused solely on the HAI assay for H3N2 influenza strains [
15]. Although all these studies reported reproducible and reliable results, there is a need to develop a robust high-throughput HAI assay method for both H1N1 and H3N2 strains as well as B-type viruses by harmonizing the existing protocols.
This study describes an enhanced novel HAI assay method developed using human RBCs (Type O) and egg-derived influenza viruses or Baculovirus/Sf9–produced recombinant virus-like particles (VLPs) for agglutination, oseltamivir treatment of virus/VLP and CypherOne™ Hemagglutination Analyzer to determine titers of HAI antibodies in human serum. Procedurally, the egg-derived virus HAI and the VLP HAI are identical except for the choice of agglutinin. Use of VLP as agglutinins in the HAI assay allows wild-type virus sequences to be utilized avoiding potential serological biasing associated with egg-adapted mutations of egg-derived viruses. In addition, as VLP are non-infectious, they can be used as pandemic strains avoiding the need for higher biosafety level containment. Traditionally, in HAI assays, sample titration is performed in duplicates (variability within 2-fold considered acceptable) [
16,
17], which is time-consuming and escalates the assay cost when handling large quantities of clinical samples. In a clinical study qNIV-E-301 (NCT04120194), only 12 (0.0276%) samples or controls out of the 21,728 samples and controls tested in duplicates for the four homologous (seasonal) strains, had variability exceeding 2-fold between duplicates (data not shown). The extremely low proportion of samples with more than 2-fold variability between the two replicates suggested the possibility of reliably testing samples in singleton with comparable precision and accuracy to testing in duplicates.
The present study describes the validation of the HAI assay using egg-derived influenza viruses or recombinant VLP as agglutinins and human RBCs (hemagglutination indicator particle) for the measurement of anti-influenza HA antibody titers in human serum, with the primary aim of demonstrating its suitability for testing sera from influenza vaccine clinical trials. The study also evaluated the testing of human serum samples in singleton compared to duplicates in the influenza VLP HAI assay. The titers from the validated HAI assay correlated well with those of a qualified microneutralization (MN) assay.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Seasonal Influenza Viruses and VLPs
The validation of HAI assay for egg-derived influenza viruses was performed using four vaccine-homologous 2019-2020 Northern Hemisphere seasonal strains: A/Kansas/14/2017 (A/H3N2), A/Brisbane/02/2018 (A/H1N1), B/Maryland/15/2016 (B/Victoria Lineage), and B/Phuket/3073/2013 (B/Yamagata Lineage). The VLP HAI assay validation included four recombinant Baculovirus/Sf9–produced VLPs [
18] corresponding to the aforementioned homologous seasonal influenza vaccine strains and four VLPs corresponding to four antigenically drifted (heterologous) A(H3N2) viruses: A/California/94/2019, A/Cardiff/0508/2019, A/Netherlands/1268/2019, and A/Tokyo/EH1801/2018.
2.2. Human RBCs
Human RBCs (Type O) with K3EDTA as an anticoagulant (Biological Specialty Corporation/BioIVT, cat. HUMANRBK3-0101896) were used for the HAI assay.
2.3. Test Serum Samples
The serum samples used in the assay validation experiments were from healthy humans (BioIVT, Westbury, NY) self-reporting receipt of influenza vaccine within 1 year before sample collection, human sera that showed positive HAI during the pre-validation serum screening processes, and HA-specific sheep serum samples from virus HA-hyperimmune sheep obtained from the National Institute for Biological Standards and Control and Novavax influenza vaccine non-clinical studies. Negative serum was HA antibody–depleted/stripped human serum (Valley Biomedical, Winchester, VA, USA, cat. HS1200W) diluted 1:2 in PBS. Depletion of HA antibodies from human sera was performed using negative selection by HA–cross-linked agarose beads (by Novavax, Inc., Gaithersburg, MD, USA). All serum samples used in the assay validation are listed in
Table S1.
2.4. HAI Assay Procedure
The HAI assay was conducted per the WHO Manual for the laboratory diagnosis and virology surveillance of influenza [
19], with some modifications (such as human RBCs and the automated assay readout method mentioned below). To remove nonspecific inhibitors of HA, the serum samples were incubated at 37 °C for 18 to 20 h with receptor-destroying enzyme (RDE; Denka Seiken Co., Ltd., cat. 370013) diluted 1:4 in Dulbecco’s Phosphate Buffered Saline with calcium and magnesium (DPBS; Quality Biological, cat. 114-059-101) followed by heat-inactivation at 56 °C for 30 ± 2 min and further diluted to 1:10 with DPBS. In the HAI assay, each RDE-treated sample was diluted 1:2 serially in a 96-well U-bottom microtiter plate (Thermo Fisher Scientific, cat. 2205) for a total of 10 dilutions with DPBS. The viral stock was adjusted to 4 hemagglutination (HAg) units in DPBS with 80 nM of oseltamivir (NA inhibitor; Chem Scene, cat. CS-0553). After incubating with 4 HAg units of the virus, the sample–virus mixture was then incubated with 0.75% human RBCs (BioIVT, cat. HUMANRBK3-0101896) for 80 to 100 min at room temperature (RT). To determine serum antibody titers, HAI assay plates were scored using the automated and validated CypherOne™ Hemagglutination Analyzer (InDevR Inc., Software versions 3.2.0.0 and 4.0.0.19). HAI titers were determined from the reciprocal of the highest serum sample dilution that completely prevented hemagglutination.
2.5. Validation Parameters: Precision, Specificity, Linearity, Sensitivity, Assay Robustness, and Sample Stability
Assay parameters evaluated for each vaccine-homologous strain of egg-derived virus and VLP agglutinins were precision, specificity, linearity, sensitivity (lower limit of quantitation [LLOQ]), robustness, and sample stability. The intra-, inter-, and total-assay precision were tested at both the individual sample and strain levels, representing the overall assay variance of all samples tested for each egg-derived virus/VLP strain. Strain-specific sheep sera were used to test the ability of the HAI assay to measure and differentiate the influenza virus type and subtype-specific antibodies (anti-A/H1N1 [A strain subtype 1 HA], anti-A/H3N2 [A strain subtype 3 HA], and anti-B strain HA antibodies). Negative human serum samples included in the specificity runs were expected to consistently test negative (geometric mean titer [GMT] of 5–7). To determine assay linearity, for each strain, two influenza HAI-positive samples were tested undiluted and further serially diluted in 1:2 dilution series (from 1:2 up to 1:256) in negative serum, with a target of a minimum of six dilutions above the LLOQ. Samples were tested in replicates in a total of six runs by two analysts on 3 days. The expected HAI titers at each dilution were calculated from the overall HAI GMT from all runs of the undiluted sample divided by the dilution factor. The accuracy of the linearity at each dilution was evaluated in terms of % relative bias, where values of 100% or −50% correspond to a titer 2-fold higher or 2-fold lower, respectively, than the expected titer.
The assay sensitivity was determined in terms of the LLOQ, which is the lowest HAI titer with acceptable precision and accuracy. The LLOQ was determined for samples assayed in the linearity tests. Precision (percent geometric coefficient of variation [%GCV] of HAI titers) and accuracy (% relative bias) were estimated across the runs for these samples.
Robustness was tested for all egg-derived virus/VLP strains to evaluate the effect of RBC age (storage time from receipt/collection time), serum–agglutinin incubation time, and serum–agglutinin–RBC incubation time (plate reading time) on the HAI results. For the RBC suspension storage time robustness assay, the panel of serum samples tested using 0.75% RBC stored at 2 to 8 °C for 2 weeks (14 ± 3 days), and 0.75% RBC prepared from 10% RBC suspension stored at 2 to 8 °C for 2 weeks (14 ± 3 days). The HAI GMT of the test storage conditions was compared with the overall HAI GMT from the precision assay runs (utilizing fresh 0.75% RBCs stored at 2 to 8 °C for less than a week [≤7 days]; baseline).
Plate reading time robustness was determined at 75, 90, 120, and 150 min after the addition of 0.75% RBC suspension to serum–virus mixture (incubated for 60 min). The HAI GMTs were compared with the standard 90-min reading time. To evaluate the combined serum–agglutinin incubation time and plate reading time robustness, serum–agglutinin incubation time was varied (50, 60, and 70 min), and for each duration of incubation, the plate reading time was varied (75, 90, 120, and 150 min) after the addition of RBCs. Baseline HAI GMTs were from assay runs in which serum–agglutinin incubation time was 60 min and the plate reading time was 90 min after RBC addition. Additionally, for egg-derived virus/VLP titration and back-titration (virus/VLP titration plate reading time robustness), the plate reading time was determined at 90 ± 10 min following RBC addition.
The stability of RDE-treated samples stored at 2 to 8 °C (1 and 2 months), ≤−20 °C (2 months), and subjected to two freeze/thaw cycles was assessed and compared with the overall HAI GMT from precision runs (baseline; with samples stored at 2 to 8 °C for ≤7 days).The stability of neat (undiluted) serum samples stored at −20 ± 10 °C (1 month) and subjected to seven freeze/thaw cycles (from storage in a −80 ± 10 °C freezer) was assessed using three quality control (QC) samples for each egg-derived virus/VLP strain. The results were compared with the overall GMT from the precision runs (baseline) as described above.
2.6. Singleton (Single Titer) Testing of Serum Samples in the Influenza VLP-HAI Assay
To analyze the influence of singleton testing on individual samples (single titer, i.e., singlicate), the validation data of the VLP HAI assay for the four homologous seasonal vaccine strains were used and reproduced. The GMT and %GCV were determined for the validation dataset of each vaccine-homologous strain. For each serum sample, the GMT and %GCV were determined for 1) singleton titers (N = 24), 2) paired replicate (duplicate) GMT (N = 12), and 3) random titer replicates (duplicate) GMT (N = 12). Random titer pairings were intended to simulate potential titer pairings based on the data collected in validation studies.
The % difference in GMT for randomly chosen replicates (random replicate 1 and random replicate 2) was determined relative to the GMT of paired replicates as shown below.
For assessing the influence of singleton results and paired duplicates on precision (%GCV), 36 serum samples were tested for the four vaccine-homologous strains. The % difference for %GCV of singleton titers and random replicates was calculated relative to the %GCV of paired replicates as shown below.
For evaluating the influence of singleton testing on clinical study results, HAI antibody titer data corresponding to VLPs from the Phase 3 clinical study qNIV-E-301 [
20] were utilized. Besides the aforementioned four vaccine-homologous seasonal influenza strains and the four heterologous viruses, this clinical study included three additional heterologous wild-type strains (A/South Australia/34/2019, A/Idaho/13/2018, and B/Washington/02/2019). Antibody titers using VLP HAI obtained in duplicate (n = 2) from approximately 1286 test subjects and two study protocol arms (2019-2020 Fluzone
® Quadrivalent and Quad-NIV) were used to model the influence of reporting single titer (n = 1) results (randomly selected from one of the paired duplicates) instead of the GMT of paired duplicate (n = 2) values. The per-protocol population included 1279 to 1286 test subjects (two-time points: Day 0 [pre-vaccination] and Day 28 [post-vaccination]; two vaccination groups: 2019-2020 Fluzone Quadrivalent and Quad-NIV). The GMT (by strain and vaccine group) was calculated as the reported GMT (duplicate) values of antibody titers using wild-type sequence VLP-HAI. The results of GMT calculated using paired replicates (duplicates) were compared with the GMT calculated using individual titers that were randomly selected. The randomly selected titer GMT results were determined twice (Random titers 1 and 2). The geometric mean ratio (GMR; post- /pre-vaccination) were determined using the reported GMT from paired duplicate samples [
20] and randomly selected single titers. The random titer pairings included were intended to simulate potential titer pairings based on the data collected in clinical studies.
The percent seroprotection rate (%SPR) was determined using data from study qNIV-E-301. The % of results with titer ≥1:40 was determined using the reported GMT from paired duplicate samples and using randomly selected single titers (Random 1 and Random 2) for subject visits on Day 28. The percent seroconversion rate (%SCR) was also determined using qNIV-E-301 study data. The results (%) for subject visits on Day 0 (unvaccinated) and Day 28 (vaccinated) whereby the titer or GMT on Day 28 was higher by ≥4-fold were determined using the reported GMT from paired duplicate samples and using randomly selected single titers (Random 1 and Random 2).
2.7. Correlation Analysis of the HAI Assay and MN Assay
Serum samples were assessed in the HAI assay (using the same methodology as for validation) and in a qualified influenza MN assay for each indicated wild-type strain (A/Brisbane/02/2018, A/Kansas/14/2017, and B/Maryland/15/2016). The results from final titers of both assays were compared to determine the correlation between them.
2.8. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analyses of validation results were performed using SAS® version 9.4 (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA) in a Windows (Microsoft Corp., Redmond, WA, USA) environment. The intra- and inter-assay precision were assessed by determining the %GCV through the variance component analysis with the sample as a fixed effect and analyst and day as random effects. The correlation between HAI and MN assay results was determined by performing linear regression analysis using GraphPad Prism® software version 9.3.1 (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA, USA).
3. Results
3.1. Assay Validation Parameters
3.1.1. Precision
For the egg-derived HAI assay, all four seasonal influenza homologous virus strains met the acceptance criteria of intra-, inter-, and total-assay precision ≤50% GCV for at least 80% of the samples tested for each strain (A/Kansas/14/2017: 98.2% of the samples, A/Brisbane/02/2018: 95.7%, B/Maryland/15/2016: 97.8%, B/Phuket/3073/2013: 100%) (
Table 1). Similarly, for the VLP HAI assays, intra-, inter-, and total-assay precision were ≤50% GCV for 100% of the samples for A/Kansas/14/2017, A/Brisbane/02/2018, A/Netherlands/1268/2019, and A/Tokyo/EH1801/2018 strains; and >93% of the samples for B/Maryland/15/2016, B/Phuket/3073/2013, A/California/94/2019, and A/Cardiff/0508/2019 strains. Additionally, all egg-derived virus/VLP strains met the acceptance criteria of ≤30% GCV for the overall intra-, inter-, and total-assay precision (
Table 2).
3.1.2. Specificity
In specificity analysis, the overall HAI GMT from strain-homologous immune serum was ≥4-fold higher than that from heterologous serum, thereby meeting the acceptance criterion for both egg-derived and VLP HAI assays. For the egg-derived assay, the overall HAI GMT of subtype/lineage homologous serum was at least 8-fold higher than that of the heterologous serum (A/Kansas/14/2017: 8-fold, A/Brisbane/02/2018: 300-fold, B/Maryland/15/2016: 500-fold, B/Phuket/3073/2013: 20-fold;
Table 3). For the VLP HAI assay, the overall HAI GMT of subtype/lineage homologous serum was ≥4-fold higher than the heterologous serum HAI GMT (A/Kansas/14/2017: 13-fold, A/Brisbane/02/2018: 180-fold, B/Maryland/15/2016: 95-fold, B/Phuket/3073/2013: 33-fold, A/California/94/2019: 22-fold, A/Cardiff/0508/2019: 17-fold, A/Netherlands/1268/2019: 9-fold, A/Tokyo/EH1801/2018: 18-fold;
Table 4). Heterologous sera were either HAI-negative (i.e., HAI GMT of 5) or had low HAI titers compared to the homologous sera. Negative control human serum samples (depleted of anti-HA antibodies) consistently tested negative (GMT of 5; data not shown).
3.1.3. Linearity and LLOQ
All virus strain samples with an expected HAI GMT of ≥8 were included in the linear regression and % relative bias analyses. The linearity of both the egg-derived HAI and VLP HAI assays was successfully demonstrated, with
R2 ranging from 0.9814–0.9999 and 0.9777–0.9999 respectively for all individual samples examined for each egg-derived virus or VLP agglutinin, meeting the acceptance criterion (regression line
R² ≥0.95) (
Figure 1 and
Figure 2;
Tables S2 and S3). Also, the % relative bias for all samples (for both egg-derived virus and VLP agglutinins) was in the acceptance range (−50% to 100% of the expected HAI GMT). In the egg-derived HAI, the %GCV of all samples was <50%. In the VLP HAI, the %GCV was <50% for all sample dilutions except for one sample dilution for B/Phuket/3073/2013 VLP (%GCV of 54.5) (acceptance criteria: %GCV ≤60% (
Tables S4 and S5).
All samples were diluted to an HAI titer of 10, the lowest titer (GMT) that met the acceptance criteria of intra-, inter-, and total-assay %GCV ≤60% and % relative bias between −50 and 100. Hence, LLOQ was set at 10 for the egg-derived virus/VLP HAI assay (data not shown).
3.1.4. Robustness
Robustness analysis of RBC suspension storage time (2 weeks) for egg-derived virus HAI showed that all samples (100%) tested for all four virus strains exhibited HAI GMT % difference ranging from −50% to 100% (2-fold difference) compared to baseline. These findings suggested that RBC suspension can be stored at 2 to 8 °C for up to 2 weeks before use (acceptance criteria: at least 80% of samples with HAI GMT within the 2-fold difference of baseline). In the VLP HAI assay, the majority of the samples (except three) tested for all four VLP strains had HAI GMT % difference within the range of −50% to 100% compared to baseline. However, three of the four strains showed an asymmetric tendency to yield a predominance of −50% to 0% change; suggesting the suitability of RBC suspension storage conditions of 2 to 8 °C for a maximum of 1 week (7 days) before use (
Table S6).
Robustness analysis of plate reading time (75-, 120-, and 150-min) demonstrated an HAI GMT % difference within the range of −50% to 100% compared to the 90 min plate reading reference; suggesting that in both egg-derived virus/VLP HAI assays the plates can be read within a range of 75 min and 150 min after RBC addition (
Table S7). In the combined robustness analysis of serum–virus/VLP incubation time and plate reading time, the HAI GMT % difference of all sample HAI titers read at 75, 90, 120, and 150 min after 50 min to 70 min of egg-derived virus/VLP plus serum incubation were within 2-fold (−50% to 100%) of the baseline reading (
Table S8). However, HAI titers showed more variations when longer incubation times were combined (such as 70 min of egg-derived virus/VLP–serum incubation and 150 min of egg-derived virus/VLP–serum–RBC incubation [plate reading time]); although HAI GMT % difference was still within 2-fold of the baseline. These findings suggest that experimental conditions with egg-derived virus/VLP–serum incubation time between 50 to 60 min, and a plate reading time of 75 to 120 min, can be considered as best practice to maintain result consistency in HAI assays (
Table S8). Furthermore, robustness of plate reading time was also evaluated for 90 ± 10 min after RBC incubation for virus titration and back-titration. Consistent HAI titers were observed at 80- and 100-min post-RBC addition (in line with those at standard 90 min), suggesting that both egg-derived virus and VLP HAI assay titration plates can be read at 90 ± 10 min of RBC incubation (data not shown).
3.1.5. Stability
In the RDE-treated sample stability analysis, HAI GMTs of at least 80% of the samples were within the 2-fold difference of the baseline (−50% to 100%) following storage at 2 to 8 °C for 1 month and 2 months, storage at ≤−20 °C for 2 months, and after undergoing two freeze/thaw cycles in both HAI assays (
Table S9). However, in the egg-derived virus HAI assay, the HAI GMT of samples with 2-month storage showed increasing variability relative to baseline and a trend towards decreasing titers compared to 1-month storage, especially for the A/Kansas/14/2017 and B/Phuket/3073/2013 assays. These findings suggest that to maintain consistency for both egg-derived virus and VLP HAI assays, the storage of RDE-treated samples at 2 to 8 °C should be limited to 1 month prior to testing (
Table S9).
Stability analysis of neat (undiluted) serum samples was included to assess sample stability under potential storage conditions commonly observed in clinical trials. The HAI GMTs of all samples were within the range of −50% to 100% difference of the baseline following seven freeze/thaw cycles and 1-month storage in a −20 °C freezer; suggesting that serum samples remained suitable for both egg-derived virus/VLP HAI assay testing even after undergoing these conditions (data not shown).
3.2. Influence of Singleton (Single Titer) Sample Testing on GMT of Serum Samples
The GMT of singleton titers and paired replicates were identical for all samples with all four homologous seasonal influenza strains. Also, there was no significant difference in the GMT of randomly combined sample pairs compared to that of singleton or paired titers. The randomly chosen replicates showed a %GMT difference of −2.85% to 5.95%, −2.85% to 9.05%, −5.61% to 2.93%, and −5.61% to 5.95% compared to that of paired replicates for A/Kansas/14/2017, A/Brisbane/02/2018, B/Phuket/3073/2013, and B/Maryland/15/2016, respectively (data not shown). These differences in GMT were minimal and not significant (within the acceptable 2-fold assay variability). Thus, the random pairing of titer results does not significantly impact the GMT of either paired or individual titers when assessed at the sample level.
3.3. Influence of Singleton (Single Titer) Results and Paired Duplicates (Mean of Two Titers) on Precision (%GCV) at the Serum Sample Level
Inspection of individual sample level results for all four vaccine-homologous strains (A/Kansas/14/2017, A/Brisbane/02/2018, B/Phuket/3073/2013, and B/Maryland/15/2016) suggests that use of singleton titers, paired replicates, or random replicate data has little influence on precision, as can be seen in
Tables S10–S13. Overall precision for each vaccine-homologous strain was virtually unaffected by the various replicate strategies as assessed by %GCV at the inter-, intra-, and total-assay levels (
Table 5).
3.4. Influence of Singleton (Single Titer) Testing on Clinical Study GMT Results
There was no noticeable difference in GMT determined using paired duplicate results or randomly selected titers for all VLP strains and the vaccine groups (
Table 6; such as for A/Kansas/14/2017: GMT [95% confidence interval {CI}] at Day 28 for 2019-2020 Fluzone Quadrivalent vaccine groups were 90.7 [84.9, 96.9], 91.3 [85.5, 97.6], and 90.8 [85.0, 96.9], respectively for duplicates, random 1 and random 2). Since the GMTs were very close (no statistical difference) with almost overlapping 95% CI between singleton and duplicates, testing samples in singleton had no appreciable influence on clinical GMT results.
3.5. Influence of Singleton (Single Titer) Testing on Clinical Study GMR, SPR and SCR Results
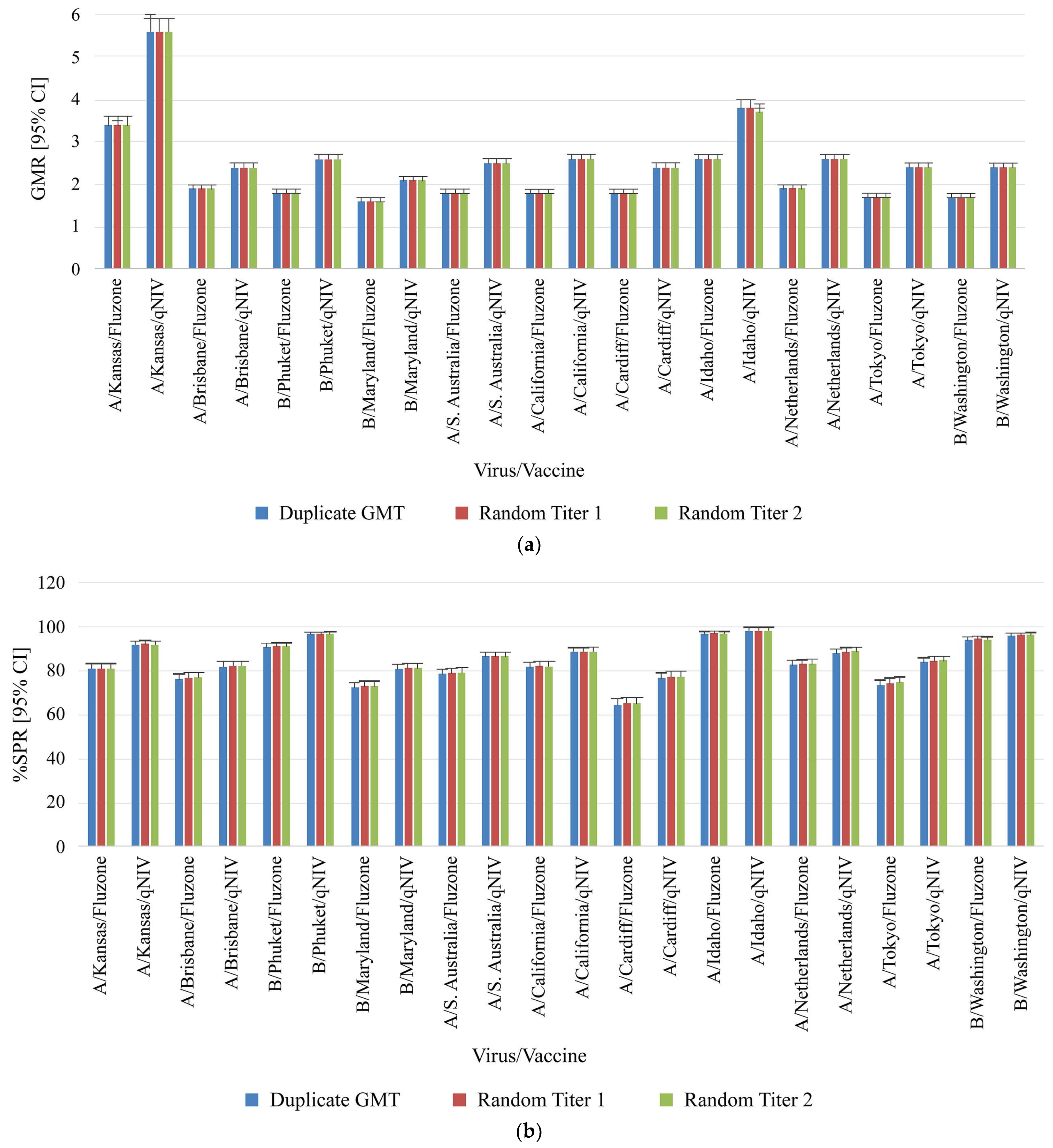
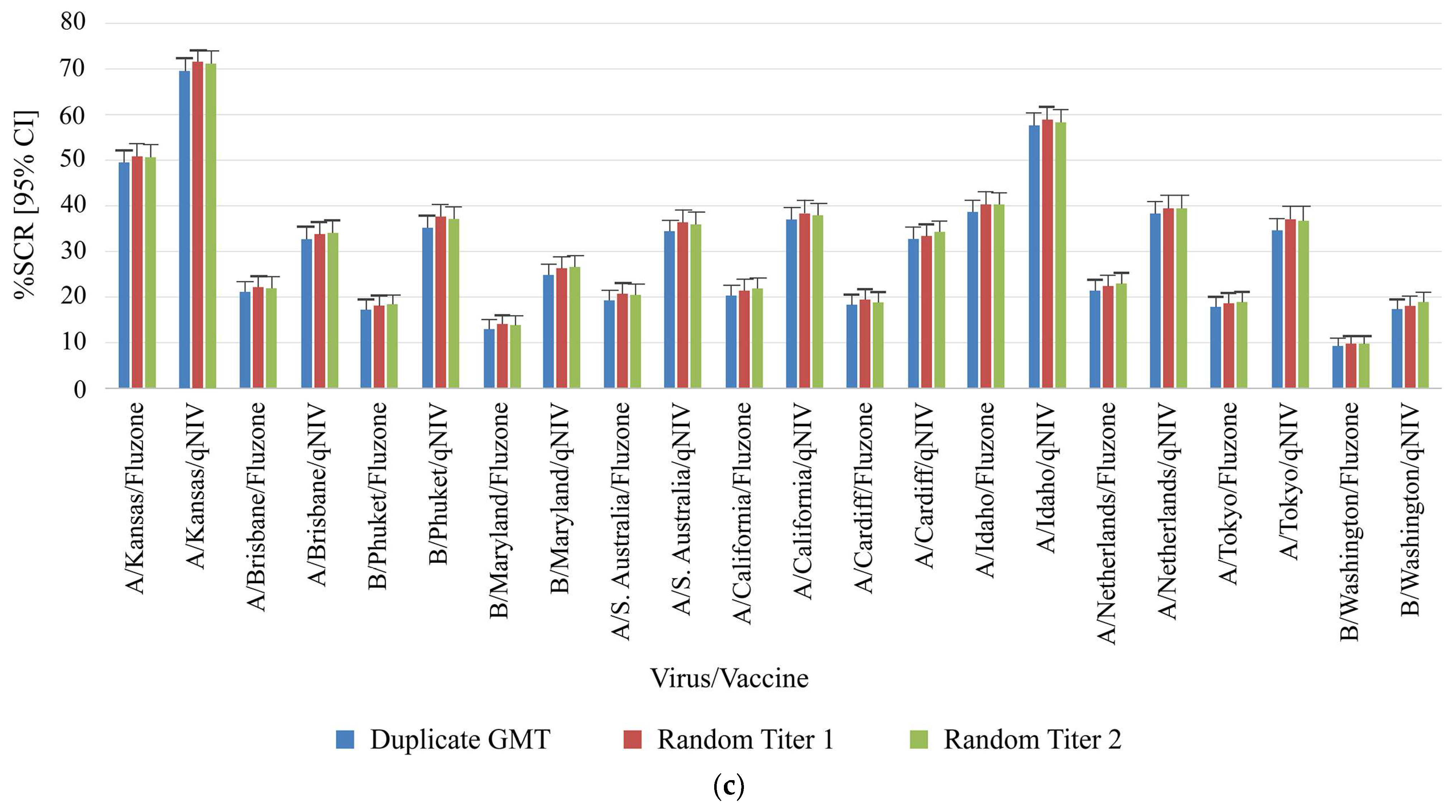
The GMR, %SPR, as well as %SCR, and their corresponding 95% CI from paired duplicates or randomly selected single titers were very similar for each virus strain and protocol arm pair (
Figure 3). Overall, these findings showed that reporting titers in singleton had no impact on the four key clinical metrics of GMT, GMR, SPR, and SCR.
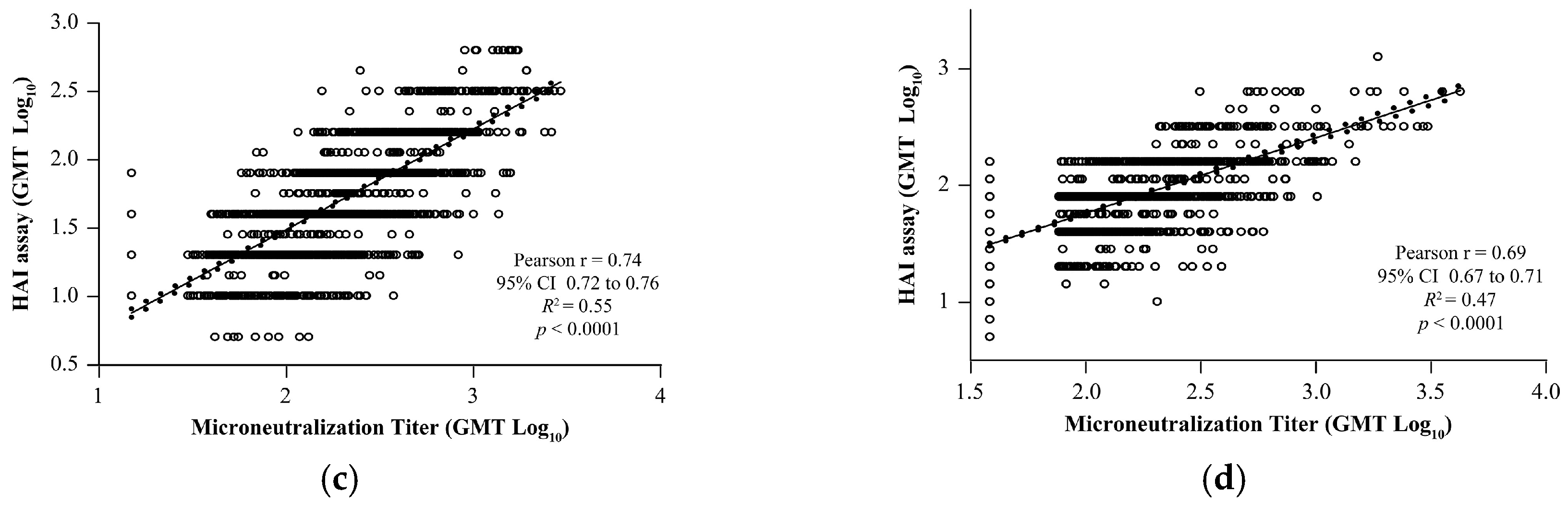
3.6. Correlation Between VLP-Based HAI and Wild-Type Virus MN Assays
To evaluate the concordance of the HAI results with the MN assay, correlation analysis was performed using four different influenza strains. Results of the HAI for both A and B strains demonstrated significant positive correlation with qualified MN assays: A/Brisbane/02/2018 (Pearson’s
r = 0.84,
R2 = 0.70,
p < 0.0001;
Figure 4a), A/Kansas/14/2017 (Pearson’s
r = 0.85,
R2 = 0.73,
p < 0.0001;
Figure 4b), B/Maryland/15/2016 (Pearson’s
r = 0.74,
R2 = 0.55,
p < 0.0001;
Figure 4c), and B/Phuket/3073/2013 (Pearson’s
r = 0.69,
R2 = 0.47,
p < 0.0001;
Figure 4d).
4. Discussion
The data presented in the current work describes the development and validation of a novel robust HAI assay using egg-derived viruses/recombinant VLPs with human RBCs to assess the immunogenicity of seasonal influenza vaccines in clinical trial settings. To our knowledge, this is the first report that uniquely demonstrates the validation of HAI using human RBCs and an automated HAI reader suitable for clinical samples. HAI assay showed acceptable precision, specificity, linearity, sensitivity, and robustness (RBC age [storage time], serum–virus/VLP incubation time, plate reading time) for egg-derived viruses as well as recombinant VLP strains. Furthermore, the singleton analyses using data from VLP HAI validation did not significantly impact GMT or precision (%GCV) at the individual sample level. Similarly, using the HAI titer data for wild-type sequence VLP from Phase 3 clinical study qNIV-E-301 [
20] showed no adverse impact of reporting titers in singleton on all four key clinical metrics (GMT, GMR, SPR, and SCR).
The source and the quality of the RBCs as critical reagents are reported as critical factors in the HAI assay [
24]. In general, RBCs of avian or animal origin are used in HAI assays [
15,
16,
25]. The selection of the appropriate species source of RBCs for the HAI assay remains a challenge given the failure of some recent H3N2 influenza viruses to agglutinate the RBC of common reagent species and non-specific inhibition of hemagglutination (because of non-specific serum interference with hemagglutination of avian RBCs) [
13,
14,
26]. To circumvent these challenges, the present assay protocol used human RBCs (Type O) for the measurement of HAI antibody titers in human serum. Human influenza viruses preferentially bind to α2,6-linked sialic acid (SA) molecules [
11,
27]. Human RBCs (Type O) and guinea pig RBCs, have more α2,6-linked SA molecules on their surfaces, compared with those of avian RBCs [
11,
28]. Makkoch et al. showed that human RBCs (Type O) that lack preexisting antibodies against the pandemic influenza H1N1 virus, yielded HAI titers most comparable to those obtained with turkey RBCs [
29].
Additionally, the assay employed the NA inhibitor oseltamivir to prevent NA-mediated agglutination, which further strengthened the antigenic characterization of HA proteins of seasonal influenza viruses. Although the HAI GMT % difference (−50% to 100%) for both egg-derived and VLP HAI assay results leveraged the use of RBC suspensions stored at 2 to 8 °C for up to 2 weeks, an asymmetric change/trend (−50% to 0%) in HAI GMT was noted for three strains in the VLP HAI assay. These findings recommend a maximum shelf-life of 1 week (7 days) as the most conservative condition for RBC suspension storage (2 to 8 °C) in the HAI assays. Our study results are in line with a previous study that reported a shelf life of up to 1 week for human erythrocytes [
13]. Additionally, it might be useful to prescreen RBCs from donors and virus combinations using QC samples before testing clinical trial sera to avoid any non-specific virus–RBC interaction.
Lack of harmonized and standardized assay readouts can introduce a high degree of variability in HAI antibody titer interpretation. Tilting of HAI plates at 45 ± 60 ° angle to check for a “teardrop pattern” in case of non-specific inhibition with avian RBCs is a commonly followed practice in many research laboratories [
14]. Similar to Wilson et al. [
14], the present study used an automated platform CypherOne
TM Hemagglutination Analyzer for reading HAI plates. The benefits of this platform are numerous: increased objectivity; standardization, consistency of titer interpretation; improved data integrity; reduced assay time, testing costs, possible data transcription errors; and the elimination of subjective biases in the manual scoring of plates as well as a permanent visual image/record to refer back to [
14,
15]. Together, these factors indicate that the CypherOne
TM platform adds significant value to clinical sample testing.
Validation of the HAI method ensures the reliability and reproducibility of results [
13,
15,
16,
30]. Our study validated the egg-derived virus/recombinant VLP HAI assay for precision, specificity, linearity, sensitivity (LLOQ), RBC storage time, serum–virus/VLP incubation time, plate reading time, and serum sample storage and freeze/thaw effects on serum samples. A comprehensive understanding of these validation parameters is crucial for the assessment of clinical samples and assay reliability. In our study, the two HAI methods using human RBCs and either egg-derived influenza viruses or recombinant VLPs met the precision and accuracy criteria in measuring antibody titers in human serum, with overall assay %GCV being <30% for all egg-derived virus/VLP strains, and % relative bias within −50% to 100% (2-fold). Neat (undiluted) sample stability findings showed that serum samples could be used in the HAI assays after up to seven freeze/thaw cycles and after 1 month of storage in a −20 °C freezer. These observations indicate that the validated HAI assays can be used in clinical trials to assess the immunogenicity of egg-derived and recombinant influenza vaccines.
Furthermore, testing samples in singleton in HAI assays can offer advantages in terms of reduced clinical testing time and costs, increased sample throughput, lowers the resource needs and improves time management. Similarly, utilizing the HAI titer data of wild-type sequence VLP HAI from the Phase 3 clinical study, and reporting titers from singleton showed no influence on the four key clinical analysis metrics such as GMT, GMR, SPR, and SCR. This suggests that the seasonal influenza VLP HAI assay samples (pre- and post-vaccination) can be tested routinely in singleton, and the final results can be reported as titers without adversely affecting the data readout and interpretation.
The HAI assay is a more commonly used serological technique for assessing influenza-specific humoral immunity than the MN assay [
31]. The HAI assay identifies antibodies that bind to the globular head of viral HA and prevent virus mediated RBC agglutination, while the MN assay detects functional neutralizing antibodies inhibiting the virus entry/replication in mammalian cells [
32], which may have a broader range of specificities. Given these differences, establishing correlations between the HAI and MN assays would be valuable for comparing vaccine assessments and gaining a comprehensive understanding of immune responses to influenza vaccines [
32]. Our study results revealed a significant correlation between the validated HAI assay and a qualified MN assay (for both A and B strains. These findings indicate that the validated HAI assay results align with other measures of the immune response against seasonal influenza. Strong correlation observed between HAI and MN results in our studies are consistent with previous publications (Veguilla et al. [
33] and Trombetta et al. [
32]), which also showed strong positive correlations between the HAI and MN assays for both A and B influenza strains.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, the validated egg-derived virus and VLP HAI assays with human RBCs performed similarly with comparable precision and accuracy, indicating the suitability for evaluating humoral immune response (HAI) for seasonal influenza in human serum samples from clinical studies. Furthermore, there was no difference in the precision, GMR, SPR, and SCR with singleton determination of titer testing compared with duplicate titer HAI testing. These findings suggest that testing in singleton can offer cost-effectiveness and improve assay throughput, without impacting key study parameters and conclusions from clinical data analysis.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: Preprints.Org, Table S1: Source and details of human and animal serum samples tested in egg-derived and VLP HAI validation assays; Table S2: Results of linearity regression parameters of egg-derived virus HAI assay for four homologous seasonal influenza strains (A/Kansas, A/Brisbane, B/Maryland, and B/Phuket); Table S3: Results of linearity regression parameters of VLP HAI assay for four homologous seasonal influenza strains (A/Kansas, A/Brisbane, B/Maryland, and B/Phuket) and drifted strains (A/California, A/Cardiff, A/Netherlands, and A/Tokyo); Table S4: Accuracy (% Relative bias) and precision (%GCV) of the HAI titers linearity with A/Kansas/14/2017 egg-derived virus/VLP; Table S5: Accuracy (% Relative Bias) and precision (%GCV) of the HAI titers linearity with A/Brisbane/02/2018, B/Maryland/15/2016, B/Phuket/3073/2013, A/California/94/2019, A/Cardiff/0508/2019, A/Netherlands/1268/2019, and A/Tokyo/EH1801/2018 virus strains; Table S6: Assay robustness – effect of human RBC suspension storage time using four homologous seasonal influenza strains (A/Kansas, A/Brisbane, B/Maryland, and B/Phuket); Table S7: Assay robustness – effect of plate reading time (incubation time) using four homologous seasonal influenza strains (A/Kansas, A/Brisbane, B/Maryland, and B/Phuket); Table S8: Assay robustness in terms of HAI GMT % difference from baseline1 – effect of combined serum–egg-derived virus/VLP incubation time and plate reading time using four homologous seasonal influenza strains (A/Kansas, A/Brisbane, B/ Maryland, and B/Phuket); Table S9: Stability of RDE-treated samples in egg-derived and VLP HAI assay using four homologous seasonal influenza strains (A/Kansas, A/Brisbane, B/Maryland, and B/Phuket); Table S10: Total %GCV for singleton titers, paired replicates, and random replicates for A/Kansas/14/2017 VLP HAI assay; Table S11: Total %GCV for singleton titers, paired replicates, and random replicates for A/Brisbane/02/2018 VLP HAI assay; Table S12: Total %GCV for singleton titers, paired replicates, and random replicates for B/Maryland/15/2016 VLP HAI assay; Table S13: Total %GCV for singleton titers, paired replicates, and random replicates for B/Phuket/3073/2013 VLP HAI assay.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.S.V., M.Z., R.K., L.F., V.S., and J.S.P.; methodology, T.S.V. and M.Z.; software, M.Z.; validation, M.Z., A.P., U.P., A.K., S.C.-C., D.S., A.G., K.M., M.W., E.M. and J.S.P.; formal analysis, I.C. and R.C.; investigation, T.S.V. and M.Z.; resources, S.C.-C., Z.L., B.Z. and J.S.P.; data curation, T.S.V., I.C. and R.C.; writing–original draft preparation, T.S.V. and R.K.; writing–review and editing, T.S.V., M.Z., R.K., S.C.-C. and J.S.P.; visualization, T.S.V. and R.K.; supervision, S.C.-C., V.S. and J.S.P.; project administration, S.C.-C. and J.S.P.; funding acquisition, V.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by Novavax, Inc., and the APC was funded by Novavax, Inc.
Institutional Review Board Statement
All the clinical samples used in this study were either from commercial vendors or from vaccine clinical trials conducted by Novavax, Inc. The study protocols for the human clinical trials were conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Institutional Review Board (or Ethics Committee) of Novavax, Inc. (protocols 2019nCoV-ICC-E-101 and qNIV-E-301 dated August 18, 2021, and July 30, 2019, respectively).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects whose samples were used here during the relevant clinical trials in which the samples were collected.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. They are not publicly available due to proprietary subject and sample information.
Acknowledgments
Medical writing and editorial support were provided by Neetu Menghani, Ph.D., and Shalini Vasantha, Ph.D., Indegene Limited, Bengaluru, India. This assistance was funded by Novavax, Inc. The authors acknowledge the Novavax Discovery Department, especially Michael Massare for the reagents and equipment, the Novavax clinical operations, and the Novavax qNIV-E-301 and 2019nCoV-ICC-E-101 study team for the clinical study serum samples. The authors had full control over the manuscript and provided their final approval of all of its content.
Conflicts of Interest
All the authors are employees and stockholders of Novavax, Inc. The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. Besides, the authors declare that this study received funding from Novavax, Inc. The funder had no role in the design of the study, in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Influenza (seasonal). World Health Organization. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/influenza-(seasonal) (accessed on 6 December, 2023).
- Grohskopf, L. A.; Blanton, L. H.; Ferdinands, J. M.; Chung, J. R.; Broder, K. R.; Talbot, H. K. Prevention and Control of Seasonal Influenza with Vaccines: Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices — United States, 2023–24 Influenza Season. MMWR Recomm. Reports 2023, 72 (2). [CrossRef]
- Chiu, C. Seasonal Influenza Vaccines and Hurdles to Mutual Protection. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2016, 22, S113–S119. [CrossRef]
- Becker, T.; Elbahesh, H.; Reperant, L. A.; Rimmelzwaan, G. F.; Osterhaus, A. D. M. E. Influenza Vaccines: Successes and Continuing Challenges. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 224 (Suppl 4), S405–S419. [CrossRef]
- Trombetta, C. M.; Kistner, O.; Montomoli, E.; Viviani, S.; Marchi, S. Influenza Viruses and Vaccines: The Role of Vaccine Effectiveness Studies for Evaluation of the Benefits of Influenza Vaccines. Vaccines 2022, 10 (5), 714.
- Gomez Lorenzo, M. M.; Fenton, M. J. Immunobiology of Influenza Vaccines. Chest 2013, 143 (2), 502–510. [CrossRef]
- Kay, A. W.; Blish, C. A. Immunogenicity and Clinical Efficacy of Influenza Vaccination in Pregnancy. Front Immunol 2015, 6, 289. [CrossRef]
- Ward, B. J.; Pillet, S.; Charland, N.; Trepanier, S.; Landry, N.; Ward, B. J.; Pillet, S.; Charland, N.; Trepanier, S.; Ward, F. B. J.; Pillet, S.; Charland, N.; Couillard, J. The Establishment of Surrogates and Correlates of Protection: Useful Tools for the Licensure of Effective Influenza Vaccines ? Hum Vaccin Immunother 2018, 14 (3), 647–656. [CrossRef]
- Kirchenbaum, G. A.; Sautto, G. A.; Richardson, R. A.; Ecker, J. W.; Ross, T. M. A Competitive Hemagglutination Inhibition Assay for Dissecting Functional Antibody Activity against In Fl Uenza Virus. J Virol 2021, 95 (23), e0237920.
- Medeiros, R.; Escriou, N.; Naffakh, N.; Manuguerra, J.; Werf, S. Van Der. Hemagglutinin Residues of Recent Human A (H3N2) Influenza Viruses That Contribute to the Inability to Agglutinate Chicken Erythrocytes. Virology 2001, 289 (1), 74–85. [CrossRef]
- Gulati, S.; Smith, D. F.; Cummings, R. D.; Couch, R. B.; Griesemer, S. B.; St, K.; Webster, R. G.; Air, G. M. Human H3N2 Influenza Viruses Isolated from 1968 To 2012 Show Varying Preference for Receptor Substructures with No Apparent Consequences for Disease or Spread. PLoS One 2013, 8 (6), e66325. [CrossRef]
- Allen, J. D.; Ross, T. M. H3N2 in Fluenza Viruses in Humans: Viral Mechanisms, Evolution, and Evaluation. Hum Vaccin Immunother 2018, 14 (8), 1840–1847. [CrossRef]
- Morokutti, A.; Redlberger-fritz, M.; Nakowitsch, S.; Krenn, B. M.; Wressnigg, N. Validation of the Modified Hemagglutination Inhibition Assay (MHAI), a Robust and Sensitive Serological Test for Analysis of Influenza Virus-Specific Immune Response. J Clin Virol 2013, 56 (4), 323–30. [CrossRef]
- Wilson, G.; Ye, Z.; Xie, H.; Vahl, S.; Dawson, E.; Rowlen, K. Automated Interpretation of Influenza Hemagglutination Inhibition (HAI) Assay: Is Plate Tilting Necessary? PLoS One 2017, 12 (6), e0179939. [CrossRef]
- Sawant, S.; Gurley, S. A.; Overman, R. G.; Sharak, A.; Mudrak, S. V; Oguiniii, T.; Sempowski, G. D.; Sarzotti-kelsoe, M.; Walter, E. B.; Xie, H.; Pasetti, M. F.; Moody, M. A.; Tomaras, G. D. H3N2 in Fluenza Hemagglutination Inhibition Method Qualification with Data Driven Statistical Methods for Human Clinical Trials. Front Immunol 2023, 14, 1155880. [CrossRef]
- Zacour, M.; Ward, B. J.; Brewer, A.; Tang, P.; Boivin, G.; Li, Y.; Warhuus, M.; Mcneil, S. A. Standardization of Hemagglutination Inhibition Assay for Influenza Serology Allows for High Reproducibility between Laboratories. Clin Vaccine Immunol 2016, 23 (3), 36–42. [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, L.; Syedbasha, M.; Vogt, D.; Hollenstein, Y.; Hartmann, J.; Linnik, J. E.; Egli, A. An Optimized Hemagglutination Inhibition (HI) Assay to Quantify Influenza- Specific Antibody Titers. J Vis Exp 2017, No. 130, 55833. [CrossRef]
- Fries, L.; Smith, G.; Glenn, G. A Recombinant Viruslike Particle Influenza A (H7N9) Vaccine. N Engl J Med 2013, 369 (26), 2564–6. [CrossRef]
- WHO Global Influenza Surveillance Network: Manual for the laboratory diagnosis and virological surveillance of influenza. World Health Organization 2011 Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/manual-for-the-laboratory-diagnosis-and-viro (accessed on 6 December, 2023).
- Shinde, V.; Cho, I.; Plested, J. S.; Agrawal, S.; Fiske, J.; Cai, R.; Zhou, H.; Pham, X.; Zhu, M.; Cloney-clark, S.; Wang, N.; Zhou, B.; Lewis, M.; Price-abbott, P.; Patel, N.; Massare, M. J.; Smith, G.; Keech, C.; Fries, L. Comparison of the Safety and Immunogenicity of a Novel Matrix-M-Adjuvanted Nanoparticle Influenza Vaccine with a Quadrivalent Seasonal Influenza Vaccine in Older Adults: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Lancet Infect Dis 2022, 22 (1), 73–84.
- Shinde, V.; Fries, L.; Wu, Y.; Agrawal, S.; Cho, I.; Thomas, D.; Spindler, M.; Lindner, E.; Hahn, T.; Plested, J.; Flyer, D.; Massare, M.; Zhou, B.; Fix, A.; Smith, G.; Glenn, G. Improved Titers against Influenza Drift Variants with a Nanoparticle Vaccine. N Engl J Med 2018, 378 (24), 2346–2348.
- Stevanovic, G.; Obradovic, A.; Ristic, S.; Petrovic, D.; Mitrovic, D.; Vignjevic, S. F.; Ilic, K.; Stoiljkovic, V.; Lavadinovic, L.; Pelemis, M.; Petrovic, S.; Vidmanic, A.; Popovic, O.; Sparrow, E.; Torelli, G.; Socquet, M.; Holt, R.; Ilieva-borisova, Y.; Tang, Y.; Scorza, F. B.; Flores, J.; Rathi, N. Safety and Immunogenicity of a Seasonal Trivalent Inactivated Split Influenza Vaccine: A Double Blind, Phase III Randomized Clinical Trial in Healthy Serbian Adults. Ther Adv Vaccines Immunother 2020, 8, 2515135520925336. [CrossRef]
- Shinde, V.; Cai, R.; Plested, J.; Cho, I.; Fiske, J.; Pham, X.; Zhu, M.; Cloney-clark, S.; Wang, N.; Zhou, H.; Zhou, B.; Patel, N.; Massare, M. J.; Fix, A.; Spindler, M.; Thomas, D. N.; Smith, G.; Fries, L.; Glenn, G. M. Induction of Cross-Reactive Hemagglutination Inhibiting Antibody and Polyfunctional CD4+ T-Cell Responses by a Recombinant Matrix-M – Adjuvanted Hemagglutinin Nanoparticle Influenza Vaccine. Clin Infect Dis. 2021, 73 (11), e4278–e4287. [CrossRef]
- Ovsyannikova, I. G.; White, S. J.; Albrecht, R. A.; Garcia-Sastre, A.; Poland, G. Turkey versus Guinea Pig Red Blood Cells: Hemagglutination Differences Alter Hemagglutination Inhibition Responses against Influenza A/H1N1. Viral Immunol 2014, 27 (4), 174–8. [CrossRef]
- Waldock, J.; Zheng, L.; Remarque, E. J.; Civet, A.; Hu, B.; Jalloh, L.; Cox, J. Assay Harmonization and Use of Biological Standards To Improve the Reproducibility of the Hemagglutination Inhibition Assay : A FLUCOP Collaborative Study. mSphere 2021, 6 (4), e0056721.
- Manjeet, R.; Mohan, H.; Narang, J.; Pundir, S.; Shekhar, C. A Changing Trend in Diagnostic Methods of Influenza A (H3N2) Virus in Human: A Review. 3 Biotech 2021, 11 (2), 87. [CrossRef]
- Stephenson, I.; Wood, J. M.; Nicholson, K. G.; Zambon, M. C. Sialic Acid Receptor Specificity on Erythrocytes Affects Detection of Antibody to Avian Influenza Haemagglutinin. J Med Virol 2003, 70 (3), 391–8. [CrossRef]
- Ito, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Kida, H. Receptor Specificity of Influenza A Viruses Correlates with the Agglutination of Erythrocytes from Different Animal Species. Virology 1997, 227 (2), 493–9.
- Makkoch, J.; Prachayangprecha, S.; Payungporn, S.; Ph, D.; Chieochansin, T.; Ph, D. Erythrocyte Binding Preference of Human Pandemic Influenza Virus A and Its Effect on Antibody Response Detection. Ann Lab Med 2012, 32 (4), 276–82.
- Noah, D. L.; Hill, H.; Hines, D.; White, E. L.; Wolff, M. C. Qualification of the Hemagglutination Inhibition Assay in Support of Pandemic Influenza Vaccine Licensure ᰔ. Clin Vaccine Immunol 2009, 16 (4), 558–66. [CrossRef]
- Sicca, F.; Martinuzzi, D.; Montomoli, E.; Huckriede, A. Comparison of Influenza-Specific Neutralizing Antibody Titers Determined Using Different Assay Readouts and Hemagglutination Inhibition Titers : Good Correlation but Poor Agreement. Vaccine 2020, 38 (11), 2527–2541. [CrossRef]
- Trombetta, C. M.; Remarque, E.; Mortier, D.; Montomoli, E. Comparison of Hemagglutination Inhibition, Single Radial Hemolysis, Virus Neutralization Assays, and ELISA to Detect Antibody Levels against Seasonal Influenza Viruses. Influ. Other Respir Viruses 2018, 12 (6), 675–686. [CrossRef]
- Veguilla, V.; Hancock, K.; Schiffer, J.; Gargiullo, P.; Lu, X.; Aranio, D.; Branch, A.; Dong, L.; Holiday, C.; Liu, F.; Steward-clark, E.; Sun, H.; Tsang, B.; Wang, D.; Whaley, M.; Bai, Y.; Cronin, L.; Browning, P.; Dababneh, H.; Noland, H.; Thomas, L.; Foster, L.; Quinn, C. P.; Soroka, S. D.; Katz, J. M. Sensitivity and Specificity of Serologic Assays for Detection of Human Infection with 2009 Pandemic H1N1 Virus in U.S. Populations. J Clin Microbiol 2011, 49 (6), 2210–2215. [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
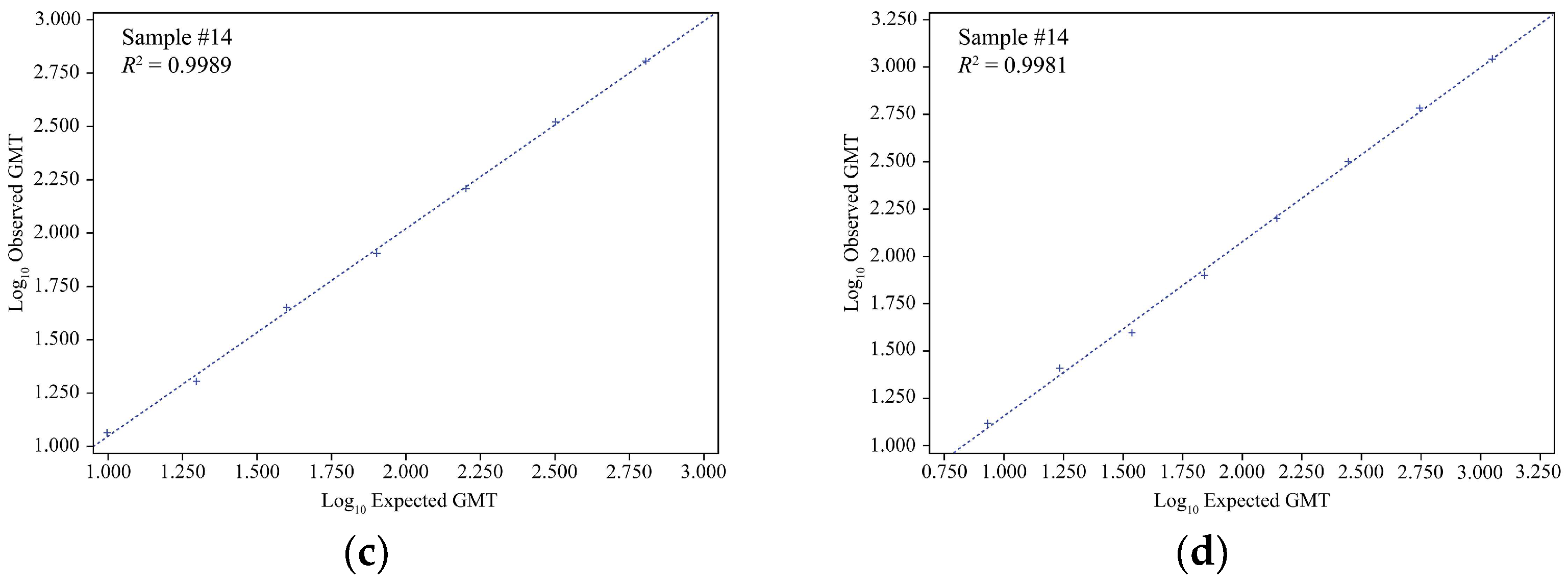
Linearity results of egg-derived virus HAI assay for influenza virus strains. (a) A/Kansas/14/2017, (b) A/Brisbane/02/2018, (c) B/Maryland/15/2016, and (d) B/Phuket/3073/2013. GMT, geometric mean titer; HAI, hemagglutination inhibition; R2, coefficient of determination.
Figure 1.
Linearity results of egg-derived virus HAI assay for influenza virus strains. (a) A/Kansas/14/2017, (b) A/Brisbane/02/2018, (c) B/Maryland/15/2016, and (d) B/Phuket/3073/2013. GMT, geometric mean titer; HAI, hemagglutination inhibition; R2, coefficient of determination.
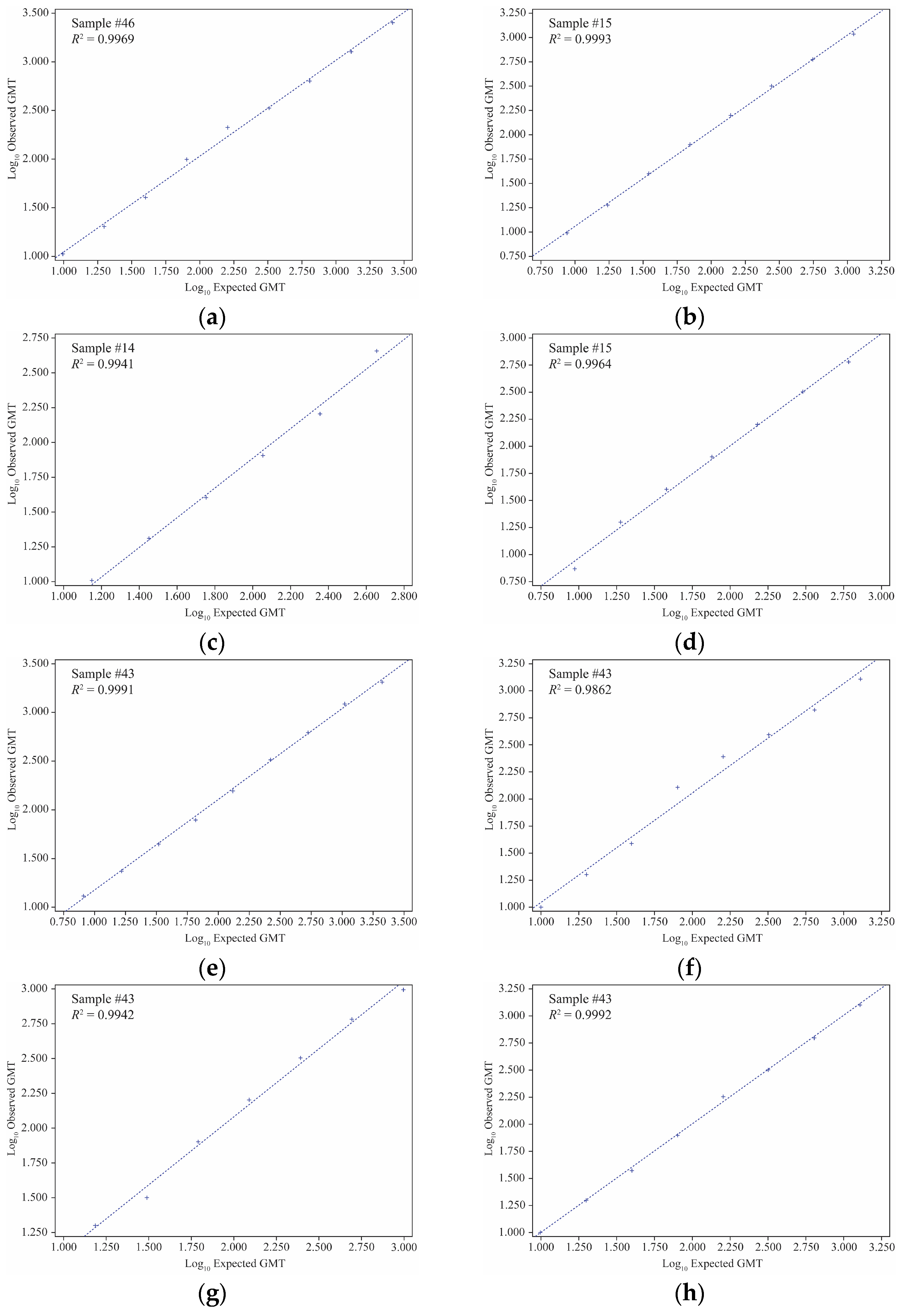
Figure 2.
Linearity results of VLP HAI assay for strains. (a) A/Kansas/14/2017, (b) A/Brisbane/02/2018, (c) B/Maryland/15/2016, (d) B/Phuket/3073/2013, (e) A/California/94/2019, (f) A/Cardiff/0508/2019, (g) A/Netherlands/1268/2019, and (h) A/Tokyo/EH1801/2018. GMT, geometric mean titer; HAI, hemagglutination inhibition; R2, coefficient of determination; VLP, virus-like particle.
Figure 2.
Linearity results of VLP HAI assay for strains. (a) A/Kansas/14/2017, (b) A/Brisbane/02/2018, (c) B/Maryland/15/2016, (d) B/Phuket/3073/2013, (e) A/California/94/2019, (f) A/Cardiff/0508/2019, (g) A/Netherlands/1268/2019, and (h) A/Tokyo/EH1801/2018. GMT, geometric mean titer; HAI, hemagglutination inhibition; R2, coefficient of determination; VLP, virus-like particle.
Figure 3.
Comparison of clinical samples from qNIV-E-301 using duplicate results compared to random titer (singleton) for key study parameters. (
a) Geometric mean ratio, (
b) Seroprotection rate, and (
c) Seroconversion rate for homologous and drifted seasonal influenza strains. Geometric mean ratio (GMR) was defined as the ratio of post-vaccination and pre-vaccination HAI GMTs within the same treatment group [
21]. Seroprotection was defined as a titer of ≥1:40 (a titer that gives a 50% reduction of disease) [
7]. Seroconversion was defined as HAI titer post-vaccination meeting one of the following criteria: either pre-vaccination titer <1:10 and post-vaccination titer ≥1:40, or pre-vaccination titer ≥1:10 and at least a 4-fold increase in post-vaccination titer [
22,
23]. CI, confidence interval; GMR, geometric mean ratio; GMT, geometric mean titer; HAI, hemagglutination inhibition; SCR, seroconversion rate; SPR, seroprotection rate; VLP, virus-like particle.
Figure 3.
Comparison of clinical samples from qNIV-E-301 using duplicate results compared to random titer (singleton) for key study parameters. (
a) Geometric mean ratio, (
b) Seroprotection rate, and (
c) Seroconversion rate for homologous and drifted seasonal influenza strains. Geometric mean ratio (GMR) was defined as the ratio of post-vaccination and pre-vaccination HAI GMTs within the same treatment group [
21]. Seroprotection was defined as a titer of ≥1:40 (a titer that gives a 50% reduction of disease) [
7]. Seroconversion was defined as HAI titer post-vaccination meeting one of the following criteria: either pre-vaccination titer <1:10 and post-vaccination titer ≥1:40, or pre-vaccination titer ≥1:10 and at least a 4-fold increase in post-vaccination titer [
22,
23]. CI, confidence interval; GMR, geometric mean ratio; GMT, geometric mean titer; HAI, hemagglutination inhibition; SCR, seroconversion rate; SPR, seroprotection rate; VLP, virus-like particle.
Figure 4.
Correlation analysis of the validated HAI assay with qualified MN assay for strains. (a) A/Brisbane/02/2018, (b) A/Kansas/14/2017, (c) B/Maryland/15/2016, and (d) B/Phuket/3073/2013. The dotted line shows 95% CI. CI, confidence interval; GMT, geometric mean titer; HAI, hemagglutination inhibition; MN, microneutralization; R2, coefficient of determination.
Figure 4.
Correlation analysis of the validated HAI assay with qualified MN assay for strains. (a) A/Brisbane/02/2018, (b) A/Kansas/14/2017, (c) B/Maryland/15/2016, and (d) B/Phuket/3073/2013. The dotted line shows 95% CI. CI, confidence interval; GMT, geometric mean titer; HAI, hemagglutination inhibition; MN, microneutralization; R2, coefficient of determination.
Table 1.
Summary of results of egg-derived virus and VLP HAI assay sample inter-assay, intra-assay, and total precision for homologous and drifted seasonal influenza strains.
Table 1.
Summary of results of egg-derived virus and VLP HAI assay sample inter-assay, intra-assay, and total precision for homologous and drifted seasonal influenza strains.
| Virus strains |
HAI assay type |
Total sample (N) |
Proportion of samples within acceptance criteria, n (%) |
Intra-assay
%GCV ≤50% |
Inter-assay
%GCV ≤50% |
Total
%GCV ≤50% |
| A/Kansas/14/2017 |
Egg-derived |
56 |
56 (100.0) |
56 (100.0) |
55 (98.2) |
| VLP |
46 |
46 (100.0) |
46 (100.0) |
46 (100.0) |
| A/Brisbane/02/2018 |
Egg-derived |
46 |
46 (100.0) |
44 (95.7) |
44 (95.7) |
| VLP |
46 |
46 (100.0) |
46 (100.0) |
46 (100.0) |
| B/Maryland/15/2016 |
Egg-derived |
46 |
46 (100.0) |
46 (100.0) |
45 (97.8) |
| VLP |
46 |
46 (100.0) |
45 (97.8) |
44 (95.7) |
| B/Phuket/3073/2013 |
Egg-derived |
46 |
46 (100.0) |
46 (100.0) |
46 (100.0) |
| VLP |
46 |
46 (100.0) |
45 (97.8) |
45 (97.8) |
| A/California/94/2019 |
VLP |
48 |
48 (100.0) |
47 (97.9) |
45 (93.8) |
| A/Cardiff/0508/2019 |
48 |
48 (100.0) |
47 (97.9) |
47 (97.9) |
| A/Netherlands/1268/2019 |
48 |
48 (100.0) |
48 (100.0) |
48 (100.0) |
| A/Tokyo/EH1801/2018 |
48 |
48 (100.0) |
48 (100.0) |
48 (100.0) |
Table 2.
Summary of results of egg-derived virus and VLP HAI assay overall precision for homologous and drifted seasonal influenza strains.
Table 2.
Summary of results of egg-derived virus and VLP HAI assay overall precision for homologous and drifted seasonal influenza strains.
| Virus strains |
HAI assay type |
Intra-assay %GCV |
Inter-assay %GCV |
Total %GCV |
| A/Kansas/14/2017 |
Egg-derived |
16.2 |
3.9 |
16.7 |
| VLP |
17.0 |
5.1 |
17.8 |
| A/Brisbane/02/2018 |
Egg-derived |
16.2 |
2.2 |
16.3 |
| VLP |
14.1 |
3.4 |
14.6 |
| B/Maryland/15/2016 |
Egg-derived |
12.4 |
3.0 |
12.8 |
| VLP |
16.4 |
4.8 |
17.1 |
| B/Phuket/3073/2013 |
Egg-derived |
16.0 |
7.1 |
17.6 |
| VLP |
11.2 |
3.3 |
11.7 |
| A/California/94/2019 |
VLP |
18.8 |
10.4 |
21.6 |
| A/Cardiff/0508/2019 |
19.7 |
12.2 |
23.3 |
| A/Netherlands/1268/2019 |
13.2 |
3.9 |
13.8 |
| A/Tokyo/EH1801/2018 |
15.0 |
4.6 |
15.7 |
Table 3.
Summary of the results of HAI assay subtype/lineage-level specificity for seasonal influenza egg-derived viruses using human RBCs for H3N2, H1N1, B/Victoria, and B/Yamagata influenza strains.
Table 3.
Summary of the results of HAI assay subtype/lineage-level specificity for seasonal influenza egg-derived viruses using human RBCs for H3N2, H1N1, B/Victoria, and B/Yamagata influenza strains.
| Sample |
HA of virus type |
Overall HAI GMT |
| A/Kansas/14/2017 (H3N2) |
A/Brisbane/02/2018 (H1N1) |
B/Maryland/15/2016 (B/Victoria) |
B/Phuket/3073/2013 (B/Yamagata) |
| Sample #47 |
H3N2 |
1280 |
5 |
6 |
5 |
| Sample #29 |
H3N2 |
2080 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
| Sample #27 |
H3N2 |
1280 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
| Sample #43 |
H3N2 |
452 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
| Sample #49 |
H1N1 |
160 |
1567 |
7 |
7 |
| Sample #28 |
H1N1 |
5 |
2070 |
5 |
5 |
| Sample #45 |
B/Victoria |
160 |
5 |
2560 |
310 |
| Sample #32 |
B/Victoria |
46 |
5 |
2944 |
368 |
| Sample #41 |
B/Yamagata |
160 |
5 |
5 |
18,784 |
| Sample #31 |
B/Victoria |
80 |
5 |
1280 |
904 |
Table 4.
Summary of results of HAI assay subtype/lineage-level specificity for seasonal influenza VLP using human RBCs for H3N2, H1N1, B/Victoria, and B/Yamagata influenza strains.
Table 4.
Summary of results of HAI assay subtype/lineage-level specificity for seasonal influenza VLP using human RBCs for H3N2, H1N1, B/Victoria, and B/Yamagata influenza strains.
| Sample |
HA of virus type |
Overall HAI GMT |
A/Kansas/14/2017
(H3N2) |
A/Brisbane/02/2018
(H1N1) |
B/Maryland/15/2016 (B/Victoria) |
B/Phuket/3073/2013 (B/Yamagata) |
A/California/94/2019
(H3N2) |
A/Cardiff/0508/2019
(H3N2) |
A/Netherlands/1268/2019 (H3N2) |
A/Tokyo/EH1801/2018 (H3N2) |
| Sample #47 |
H3N2 |
2032 |
5 |
26 |
92 |
359 |
302 |
311 |
185 |
| Sample #29 |
H3N2 |
3116 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
1514 |
1429 |
206 |
5 |
| Sample #27 |
H3N2 |
1318 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
1318 |
508 |
854 |
381 |
| Sample #43 |
H3N2 |
1437 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
8366 |
1280 |
3948 |
2560 |
| Sample #49 |
H1N1 |
147 |
2560 |
15 |
80 |
127 |
76 |
78 |
39 |
| Sample #28 |
H1N1 |
5 |
2850 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
| Sample #45 |
B/Victoria |
101 |
14 |
2487 |
190 |
120 |
78 |
80 |
40 |
| Sample #32 |
B/Victoria |
5 |
5 |
4663 |
309 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
| Sample #41 |
B/Yamagata |
78 |
5 |
5 |
10,240 |
170 |
71 |
127 |
78 |
| Sample #31 |
B/Victoria |
5 |
5 |
960 |
55 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
| Sample #51 |
H3N2 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
2487 |
640 |
– |
1437 |
| Sample #50 |
H3N2 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
3836 |
– |
– |
622 |
| Sample #52 |
H3N2 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
359 |
1208 |
– |
| Sample #53 |
H3N2 |
– |
– |
– |
– |
– |
1356 |
640 |
– |
Table 5.
Overall results for precision (%GCV) for singleton VLP HAI titers and replicate (duplicate) GMT for four homologous influenza strains.
Table 5.
Overall results for precision (%GCV) for singleton VLP HAI titers and replicate (duplicate) GMT for four homologous influenza strains.
| Strain |
Parameter |
%GCV |
| Intra-assay |
Inter-assay |
Total-assay |
| A/Kansas/14/2017 |
Singleton titers |
16.0 |
5.5 |
16.9 |
| Paired replicates |
16.0 |
5.5 |
16.9 |
| Random replicates 1 |
16.6 |
5.5 |
17.5 |
| Random replicates 2 |
16.5 |
5.2 |
17.3 |
| A/Brisbane/02/2018 |
Singleton titers |
15.8 |
3.0 |
16.1 |
| Paired replicates |
15.8 |
3.0 |
16.1 |
| Random replicates 1 |
16.2 |
4.2 |
16.8 |
| Random replicates 2 |
16.2 |
2.8 |
16.4 |
| B/Maryland/15/2016 |
Singleton titers |
17.1 |
6.8 |
18.4 |
| Paired replicates |
17.1 |
6.8 |
18.4 |
| Random replicates 1 |
16.9 |
6.5 |
18.2 |
| Random replicates 2 |
17.0 |
6.7 |
18.3 |
| B/Phuket/3073/2013 |
Singleton titers |
10.1 |
2.9 |
10.6 |
| Paired replicates |
10.1 |
2.9 |
10.6 |
| Random replicates 1 |
10.5 |
2.9 |
10.9 |
| Random replicates 2 |
10.5 |
2.9 |
10.9 |
Table 6.
Comparison of qNIV-E-301 GMT of HAI antibody titers for duplicate and randomly selected titers (singleton) from VLP HAI clinical testing for selected homologous and drifted seasonal influenza strains.
Table 6.
Comparison of qNIV-E-301 GMT of HAI antibody titers for duplicate and randomly selected titers (singleton) from VLP HAI clinical testing for selected homologous and drifted seasonal influenza strains.
| Strain |
Protocol arm (N) |
Visit |
GMT (95% CI) |
| Duplicate |
Random titer 1 |
Random titer 2 |
| A/Kansas/14/2017 |
Fluzone
Quadrivalent (1286) |
Day 0 |
26.5 (25.4, 27.7) |
26.5 (25.3, 27.7) |
26.5 (25.4, 27.7) |
| Day 28 |
90.7 (84.9, 96.9) |
91.3 (85.5, 97.6) |
90.8 (85.0, 96.9) |
| Quad-NIV (1280) |
Day 0 |
27.3 (26.1, 28.6) |
27.4 (26.1, 28.7) |
27.4 (26.1, 28.7) |
| Day 28 |
153.6 (143.9, 163.9) |
153.2 (143.6, 163.5) |
153.5 (143.8, 163.8) |
| A/Brisbane/02/2018 |
Fluzone
Quadrivalent (1286) |
Day 0 |
32.4 (30.7, 34.2) |
32.4 (30.7, 34.2) |
32.3 (30.6, 34.1) |
| Day 28 |
62.7 (59.2, 66.4) |
62.8 (59.3, 66.5) |
62.5 (59.0, 66.2) |
| Quad-NIV (1280) |
Day 0 |
31.7 (30.0, 33.5) |
31.7 (30.0, 33.4) |
31.7 (30.1, 33.5) |
| Day 28 |
76.6 (72.4, 81.1) |
76.4 (72.2, 80.9) |
76.5 (72.3, 81.0) |
| B/Maryland/15/2016 |
Fluzone
Quadrivalent (1286) |
Day 0 |
29.5 (28.3, 30.8) |
29.6 (28.3, 30.9) |
29.5 (28.3, 30.8) |
| Day 28 |
47.2 (45.2, 49.4) |
47.4 (45.3, 49.6) |
47.5 (45.4, 49.6) |
| Quad-NIV (1280) |
Day 0 |
29.8 (28.5, 31.1) |
29.8 (28.5, 31.2) |
29.7 (28.4, 31.1) |
| Day 28 |
62.8 (59.8, 66.0) |
62.6 (59.7, 65.8) |
63.0 (60.0, 66.1) |
| B/Phuket/3073/2013 |
Fluzone
Quadrivalent (1286) |
Day 0 |
44.3 (42.7, 46.1) |
44.3 (42.6, 46.0) |
44.2 (42.5, 46.0) |
| Day 28 |
78.4 (75.1, 81.9) |
78.3 (75.0, 81.8) |
78.8 (75.4, 82.3) |
| Quad-NIV (1280) |
Day 0 |
45.8 (44.0, 47.7) |
45.8 (44.0, 47.7) |
46.0 (44.1, 47.9) |
| Day 28 |
118.3 (113.0, 123.8) |
118.0 (112.8, 123.5) |
118.3 (113.1, 123.8) |
| A/South Australia/34/2019 |
Fluzone
Quadrivalent (1286) |
Day 0 |
38.3 (36.6, 40.1) |
38.3 (36.6, 40.1) |
38.3 (36.6, 40.1) |
Fluzone
Quadrivalent (1284) |
Day 28 |
70.4 (66.3, 74.7) |
70.4 (66.3, 74.7) |
70.4 (66.4, 74.7) |
| Quad-NIV (1280) |
Day 0 |
39.3 (37.5, 41.2) |
39.2 (37.4, 41.1) |
39.1 (37.3, 41.0) |
| Day 28 |
98.1 (92.1, 104.4) |
98.3 (92.3, 104.6) |
97.7 (91.8, 104.1) |
| A/California/94/2019 |
Fluzone
Quadrivalent (1286) |
Day 0 |
44.0 (42.0, 46.0) |
43.9 (41.9, 46.0) |
43.9 (41.9, 46.0) |
| Day 28 |
80.6 (75.9, 85.6) |
80.4 (75.7, 85.5) |
80.4 (75.7, 85.4) |
| Quad-NIV (1280) |
Day 0 |
44.5 (42.4, 46.7) |
44.5 (42.4, 46.7) |
44.6 (42.5, 46.8) |
| Day 28 |
115.0 (108.0, 122.4) |
114.7 (107.7, 122.1) |
114.9 (107.9, 122.3) |
| A/Cardiff/0508/2019 |
Fluzone
Quadrivalent (1286) |
Day 0 |
25.7 (24.7, 26.6) |
25.6 (24.7, 26.6) |
25.7 (24.7, 26.7) |
| Day 28 |
45.4 (43.1, 47.8) |
45.5 (43.2, 47.9) |
45.4 (43.1, 47.8) |
| Quad-NIV (1280) |
Day 0 |
27.0 (26.0, 28.1) |
26.9 (25.9, 28.0) |
27.0 (25.9, 28.1) |
| Day 28 |
63.9 (60.5, 67.6) |
63.8 (60.4, 67.5) |
63.9 (60.5, 67.6) |
| A/Idaho/13/2018 |
Fluzone
Quadrivalent (1286) |
Day 0 |
52.9 (50.9, 55.0) |
52.9 (50.9, 54.9) |
52.9 (50.9, 55.0) |
Fluzone
Quadrivalent (1283) |
Day 28 |
136.8 (129.5, 144.6) |
136.8 (129.4, 144.6) |
136.7 (129.3, 144.6) |
| Quad-NIV (1279) |
Day 0 |
53.6 (51.6, 55.8) |
53.8 (51.7, 55.9) |
53.9 (51.8, 56.0) |
| Day 28 |
202.5 (191.2, 214.4) |
202.4 (191.2, 214.3) |
202.2 (190.9, 214.2) |
| A/Netherlands 1268/2019 |
Fluzone
Quadrivalent (1286) |
Day 0 |
39.6 (38.0, 41.3) |
39.7 (38.0, 41.4) |
39.5 (37.8, 41.2) |
Fluzone
Quadrivalent (1284) |
Day 28 |
74.7 (70.6, 79.0) |
74.7 (70.6, 79.1) |
74.9 (70.8, 79.3) |
| Quad-NIV (1280) |
Day 0 |
39.4 (37.7, 41.2) |
39.6 (37.8, 41.4) |
39.4 (37.7, 41.2) |
| Day 28 |
102.3 (96.5, 108.5) |
102.1 (96.3, 108.4) |
102.2 (96.4, 108.4) |
| A/Tokyo/EH1801/2018 |
Fluzone
Quadrivalent (1286) |
Day 0 |
31.2 (30.1, 32.3) |
31.1 (30.1, 32.3) |
31.3 (30.2, 32.4) |
Fluzone
Quadrivalent (1284) |
Day 28 |
54.5 (51.7, 57.4) |
54.4 (51.6, 57.3) |
54.6 (51.9, 57.5) |
| Quad-NIV (1280) |
Day 0 |
32.2 (31.0, 33.4) |
32.3 (31.1, 33.5) |
32.2 (31.0, 33.4) |
| Day 28 |
78.0 (73.8, 82.5) |
78.0 (73.8, 82.5) |
78.1 (73.8, 82.6) |
| B/Washington/02/2019 |
Fluzone
Quadrivalent (1286) |
Day 0 |
48.4 (46.8, 50.1) |
48.3 (46.7, 50.0) |
48.3 (46.7, 50.0) |
Fluzone
Quadrivalent (1283) |
Day 28 |
71.4 (69.0, 74.0) |
71.4 (68.9, 73.9) |
71.4 (68.9, 74.0) |
| Quad-NIV (1279) |
Day 0 |
48.7 (47.0, 50.5) |
49.0 (47.2, 50.8) |
48.5 (46.8, 50.3) |
| Day 28 |
88.2 (84.7, 91.8) |
87.9 (84.3, 91.5) |
88.3 (84.8, 91.9) |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).