1. Introduction
Public worry is still raised by the long-lasting physical and mental health problems that have resulted from severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection. The COVID-19 pandemic’s worldwide effects include aspects related to sociopsychology, health, and the economy [
1,
2,
3]. Many of the patients who have recovered from corona virus disease 2019 (COVID-19) have been described as having symptoms that continue for several months after they first became ill. Long COVID, post-COVID-19 syndrome, chronic COVID syndrome, post-acute sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC), or post-COVID-19 fatigue are some names for this illness [
4,
5,
6]. However, this manuscript will adopt the term “post-COVID-19 fatigue”.
Alarmingly, post-COVID-19 fatigue is not limited to elderly patients with severe illness; younger generations with mild to moderate symptoms are also affected. More-over, more than half of young adults have reported symptoms that last longer than six months, suggesting that long-term physical and mental repercussions might occur even in cases of mild-to-moderate illness [
7,
8,
9]. Many theories concerning the duration of symptoms after SARS-CoV-2 infection are being offered by new research. Addition-ally, post-COVID-19 fatigue is thought to be caused by the immune system imbalance and residual virus particles in the body. Results showing that SARS-CoV-2 ribonucleic acid (RNA) was still present in COVID-19-infected people’s excretions several months after infection lend support to this. Moreover, studies have shown evidence of a viral presence in several tissues, including the brain [
10,
11]. Moreover, patients with chronic autoimmune diseases also experience persistent symptoms associated with post-COVID-19 fatigue [
12]. The probability or intensity of long-term symptoms does not seem to be correlated with the severity of the initial illness [
13].
In addition to the pathological consequences, lockdowns and the increasing use of remote work have had a profound impact on socio-economic dynamics and face-to-face contact. These changes have introduced temporal distortions, likely contributing to prolonged psychological and physiological disruptions [
14,
15]. Nutritional modifications and a reduction in daily physical activity may potentially have a substantial impact on the results of post-COVID-19 fatigue [
16]. It is becoming more and more clear that post-COVID-19 fatigue may trigger a secondary public health emergency, especially when it comes to cerebrovascular illnesses including depression, stroke, and cognitive decline [
17,
18].
Moreover, multiple reports have shown that the COVID-19 pandemic’s isolation and lockdown protocols have harmed children’s emotional and physical health. While many young people and children infected with SARS-CoV-2 have moderate disease or show no symptoms at all, however, new research suggests that in the months after infection, 5–10% of all children may show new symptoms, including neurological and neurocognitive sequelae [
19,
20]. Owing to the wide range of symptoms linked to COVID-19, there is no specific treatment option available at this time. Although this topic needs further research through additional studies, it is fortunate that most children with post-COVID-19 fatigue tend to recover faster than most adults. There is currently a great deal of clinical and basic research being carried out to try and under-stand the processes behind post-COVID-19 fatigue produced by SARS-CoV-2, even though the possible mechanisms of vascular and neurological involvement during SARS and MERS infections have been largely understood. Further research is needed to improve our capacity to predict and mitigate the impact of post-infectious sequelae, specifically on cerebrovascular outcomes. The fact that post-COVID-19 fatigue is a complex illness involving multiple organs, cell types, and chemicals highlights the significance of thorough research in this field.
Thus, highlighting the neurovascular, cellular, and molecular mechanisms linked to post-COVID-19 fatigue, this narrative review focuses on the molecular consequences of dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPPIV). DPPIV’s putative role as a co-receptor for SARS-CoV-2 has attracted a lot of attention. Specifically, DPPIV is an important regulator of diabetes, obesity, hypertension, inflammation, and glucose metabolism—all of which are linked to the chronic cerebrovascular dysfunctions that follow COVID-19.
2. SARS-CoV-2, Post-COVID-19 Fatigue, and Multi-Organ Injury
The coronavirus is described as a glycoprotein-based surface spiked positive-stranded RNA virus enclosed in an envelope. It is a member of a large family of viruses that have long been present in both humans and animals around the globe. These viruses can cause everything from minor respiratory ailments to serious respiratory diseases. Of these, seven distinct coronavirus types have been found in humans: Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV), severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV), and human coronaviruses (HCoV) including HCoV-OC43, HCoV-229E, HKU1, and HCoV-NL63 [
21]. These variants stand out due to their high pathogenicity and transmissibility. Moreover, SARS-CoV-2 is the sixth coronavirus reported to infect people. It is genetically identical to SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV, which are also present in bats. The neurological symptoms of the three major SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV, and SARS-CoV-2 outbreaks that resulted in worldwide pandemics show both variances and commonalities [
21,
22,
23]. Moreover, SARS-CoV, which was discovered in 2002, and MERS-CoV, which was discovered in 2011, share sequence similarities, according to recent research using the next-generation sequencing of the SARS-CoV-2 genome [
24,
25].
Even though most people infected with COVID-19 eventually recover, a consider-able percentage of people in different age groups experience several symptoms, including post-exertional malaise, for a lengthy time [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5,
6,
7,
8,
9]. Recent findings indicate that an unbalanced autoimmune reaction and persistent virus particles in the body could cause these post-COVID-19 fatigue symptoms. Studies have shown that the virus is present in several tissues, including the brain [
10,
11]. Moreover, post-COVID-19 fatigue symptoms are similarly persistent in those with chronic autoimmune diseases [
10,
26].
Thus, the goal of the ongoing study is to understand the origins and consequences of SARS-CoV-2 infection, with a focus on the long-term effects on various organs and tissues. COVID-19 was first identified as a respiratory disease, but it has now been linked to multiple organ failures and neurological disorders [
27,
28,
29]. In this case, the viral infection in the lungs triggers responses that can eventually develop into a systemic event impacting several organs, such as the heart, and brain, and different hematologic abnormalities, regardless of the disease’s original severity. A slow and progressive failure of the gastrointestinal, endocrine, hepatic, renal, and circulatory systems may result from this trend [
27,
28,
29,
30]. The multi-organ injury and sequelae symptoms in post-COVID-19 fatigue are summarized in
Table 1.
Heart and Brain Crosstalk: Roles of Thrombo-Inflammation and Post-COVID-19 Fatigue
As COVID-19 symptoms persist, manifestations affecting the cardio-cerebrovascular systems are increasingly apparent. COVID-19 affects both large and small blood vasculature, raising the risk of thrombosis, and has a major effect on the coagulation cascade, hence leading to thrombo-inflammation. Over time, these problems may result in increased rates of morbidity and mortality from cardio-cerebrovascular diseases [
30,
42]. According to a recent study by the National Institute of Health and other studies, it was reported that the coronavirus can travel through systemic microcirculation to the brain and heart within a few days of infection and can stay there for a long time. Furthermore, research has shown that micro-clots can form in smaller blood vessels, which can obstruct cerebral blood flow. About 20% to 30% of COVID-19 patients who are sick have these clots [
43,
44].
There is evidence that SARS-CoV-2 is present in the brain’s hypothalamus and cerebrospinal fluid of COVID-19 patients. It is thought that the remaining virus population causes vascular inflammation, which results in symptoms related to cerebrovascular accidents. Reports of ischemic strokes, intracranial bleeding, and cerebral venous thrombosis have all been connected to the COVID-19-related clotting condition [
31,
45]. Uncontrolled immunological and inflammatory responses, which mediate hypercoagulability, endothelial dysfunction, and thrombosis, most likely start the clotting process. These processes may result in a rise in heart attacks, strokes, and deaths [
32,
46]. It is interesting to note that neuro-invasion and cerebrovascular symptoms are present in about two-thirds of post-COVID-19 fatigue patients. Headache, taste and smell abnormalities, encephalopathy, ischemic stroke, Guillain–Barré syndrome, cognitive impairment, dizziness, fast heartbeat, post-traumatic stress disorder, mini-strokes, anxiety, depression, and other mental health conditions are some of these symptoms [
31,
32,
33,
34,
35,
36,
37]. Therefore, it is conceivable that the harm caused by COVID-19 to the central nervous system (CNS) and various organs may be progressive, necessitating extended periods for the recovery and restoration of normal activities [
40,
41].
3. Current Updates on Molecular and Cellular Mechanism of Post-COVID-19 Fatigue
Although the involvement of multiple microstructural (i.e., cellular) and molecular components in SARS-CoV-2 infection is well-known, the exact processes underlying post-COVID-19 fatigue are still vague. Extensive studies have been conducted to identify the complex pathways associated with post-COVID-19 fatigue. It is well-reported that the coronavirus attaches itself to the cell surface during the first stage of infection, acting as a portal for further infection. The vulnerability of a cell to viral infection is determined by the presence of receptors and cofactors on the cell surface. On the other hand, COVID-19 primarily targets cells in the kidneys, heart, lungs, immune system, and brain’s neuronal and glial cells. However, digestive epithelium offers a different entrance point for SARS-CoV-2, which results in gastrointestinal symptoms. This may lead to the disruption of the intestinal barrier and systemic inflammation, which could impact the function of the CNS and the enteric nervous system [
47,
48]. Hence, post-COVID-19 fatigue may be linked to a variety of microstructural alterations or determinants, molecular effects, meso-structural reactions, and symptoms.
3.1. Microstructural Changes—Endothelial Cells (ECs)
Endothelial cells (ECs) are essential for maintaining barrier integrity, restricting the entry of circulating inflammatory cells and chemicals and regulating vascular tone under normal physiological conditions. The lining of blood vessels, such as arteries, veins, capillaries, and lymphatic vessels, is made up of ECs, which come into direct touch with virus particles and blood in circulation. ECs also produce several factors and enzymes that control blood coagulation, platelet adhesion, immunological response, and vascular relaxation and contraction [
49]. ECs in blood arteries play a critical role in SARS-CoV-2 infection, causing damage, advancing COVID-19 illness, and perhaps spreading the infection to other organs. Increased thrombotic and inflammatory processes are intimately associated with microvascular EC dysfunction and have been connected to the symptoms of post-COVID-19 fatigue [
50].
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptors are expressed on the surface of ECs, which allows SARS-CoV-2 to enter through its high-affinity spike protein. Endothelial injury, malfunction, and blood vessel damage result from this interaction. As a result, cytokines, chemokines, P-selectin, E-selectin, and intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) are created, and these adhesion molecules draw different cells, including platelets, to the artery walls. Aggregation, coagulopathy, and a higher frequency of thrombotic events are all encouraged by this. Moreover, vasculitis is triggered by SARS-CoV-2 infection in the heart, which also causes dysfunction and chronic inflammation. Following EC dysfunction, SARS-CoV-2 virus particles in the brain may lead to blood–brain barrier (BBB) damage, triggering an innate immune reaction and escalating inflammation within brain microvascular ECs [
50,
51].
3.2. Microstructural Changes—Neuro–Glia–Vascular Unit (NGVU)
Recently, it has been well-documented that CNS cells are involved in COVID-19 infection. It has been discovered that SARS-CoV-2 directly infects human peripheral sensory neurons through interaction with the ACE2 receptor, leading to deficits in chemosensory perception [
47]. Furthermore, COVID-19 has been linked, particularly in the hippocampus region of the brain, to neuronal degeneration and a reduction in neurogenesis. These results raise the possibility of memory impairment and long-term neurological problems, possibly through oxidative stress and neuro-inflammation processes [
52]. Additionally, there is a recognized regulatory role that this connection between ECs and the NGVU plays in cerebrovascular disorders. Research has indicated that SARS-CoV-2 causes hypoxic brain alterations that impact the cerebellum and cerebrum, among other brain regions. As a result, this causes the death of neurons in important regions such as the hippocampus, cerebral cortex, and the cerebellum’s Purkinje cell layer [
53].
The systemic inflammatory reactions that begin in the peripheral areas may be the cause of the CNS issues seen in post-COVID-19 fatigue patients. Furthermore, viral infection activates glial cells, including microglia and astrocytes, which may increase the vulnerability to neurodegenerative illnesses [
54]. According to recent studies, the SARS-CoV-2 infection causes an inflammatory response that activates both astrocytic and microglial processes [
55]. These processes are linked to aberrant phenotypes in the interactions between astrocytes and the vasculature, which are essential for preserving the BBB integrity. Peripheral cell infiltration into the brain is facilitated in COVID-19 patients by an impaired BBB. Moreover, even in the absence of overt clinical neurological symptoms, increased levels of secreted neural and glial proteins, such as serum neurofilament (sNfL) and serum glial fibrillary acidic protein (sGFAP), suggest neuro–glial degeneration in people with COVID-19 [
56,
57].
3.3. Meso-Structural Responses—Pro-Inflammatory Cells
It has been shown that the SARS-CoV-2-infection-induced dysregulated host-inflammatory response exacerbates hypercoagulability, EC dysfunction, and thrombosis. These variables exacerbate cerebrovascular disease, which raises the risk of stroke and its associated mortality [
58]. Previous studies have extensively described the complex and distinct cellular immune response during acute, resolving, or progressive COVID-19. Activated immune cells have been found in the blood of COVID-19 patients for a significant amount of time, from one to eight months after infection [
59]. Research has demonstrated the involvement of monocytes and different subtypes of macrophages in the lung, which is correlated with outcomes in COVID-19-affected people [
60]. Furthermore, lymphocytes, which are made up of B cells, T cells, and natural killer cells, are other vital immune components. Studies have also shown that those with post-COVID-19 fatigue had different T-cell characteristics, such as worn-out T cells and fewer CD4+ and CD8+ effector memory cells [
61,
62].
3.4. Molecular Mechanism of Post-COVID-19 Fatigue
Understanding the molecular processes and feedback loops that underlie COVID-19 is essential for developing treatment strategies that will lessen the disease’s long-term effects. Through its interactions with the genome, the virus modifies the intricate structures of proteins and DNA, changing gene expression and causing immunological dysregulation. Since these molecular changes may have long-term effects, it is critical to comprehend and target them in therapeutic interventions [
63].
An important biological mechanism linked to increased illness severity and persistence is the overproduction of pro-inflammatory cytokines (or cytokine storms) caused by the virus. These include interferon (IFN) -γ, IFN-γ-inducible protein 10, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (GCSF), macrophage inflammatory protein-1 alpha (MIP-1α), and tumour necrotic factor alpha (TNF-α), in addition to interleukins such IL-1β, IL-2, IL-6, IL-7, IL-8, IL-10, and IL-17 [
64,
65]. When the transcription factor such as nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) is activated, cytokines and chemokines are produced, which attract and activate immune cells from the circulation. An uncontrolled cytokine storm worsens organ failure, vascular permeability, adhesion characteristics, pro-coagulation of blood, and COVID-19-mediated inflammation and oxidative stress, along with long-lasting tissue damage. Higher blood biomarkers of the vascular system in post-COVID-19 fatigue patients suggest that angiogenesis-regulating molecules are important components of this pathophysiological mechanism [
66,
67].
Additional molecular biomarkers linked to COVID-19 comprise pro-calcitonin, phospholipids, D-dimer, serum ferritin, and C-reactive protein. These biomarkers function as indications of severe organ failure and are implicated in the production of micro-clots. Furthermore, the increased expression of surface proteins that indicate endothelial dysfunction includes E-selectin, vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM-1), and ICAM-1. These molecular factors have the potential to worsen issues in the neurological, cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, liver, and kidney systems [
68,
69]. Thus, the identification of the post-COVID-19 fatigue prevalence and the molecular factors that underlie it has great potential for identifying therapeutic targets that will either stop the illness from starting or lessen its symptoms. Through a comprehensive comprehension of the distinct biochemical pathways implicated in post-COVID-19 fatigue, scholars might identify possible therapies aimed at attenuating its impact, thereby providing alleviation to individuals enduring symptoms.
On the other hand, the first phase of the infectious viral life cycle is represented by the recognition of and interactions with cellular receptors. It is a well-known fact that the SARS-CoV-2 virus binds to the ACE2 receptor, which is located on the surface of cells in the digestive and respiratory systems, to begin the infection process [
70]. However, DPPIV, neuropilin-1 (NRP1), and transmembrane serine protease type 2 (TMPRSS2) are other molecules that have been discovered as possible targets for the virus [
71]. The expression of several molecular receptors on the cell surface could therefore be connected to different routes of viral entry for SARS-CoV-2 [
71]. Moreover, DPPIV offers unique insights that distinguish it from the ACE2 pathway, particularly in its broader involvement in metabolic and inflammatory pathways. Unlike ACE2, which is mainly linked to direct viral entry, DPPIV is deeply involved in regulating glucose metabolism, immune responses, and chronic inflammation, all of which are key in the progression of post-COVID-19 fatigue and cerebrovascular complications [
72]. The most common comorbidities seen in COVID-19 patients were immune system, cardiovascular, neurological, and diabetic diseases, as well as hypertension, atherosclerosis, and other conditions. Surprisingly, type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is linked to DPPIV in these illnesses. Further investigation into how DPPIV affects COVID-19 intensity, and the length of persistent symptoms is, therefore, necessary [
73,
74,
75].
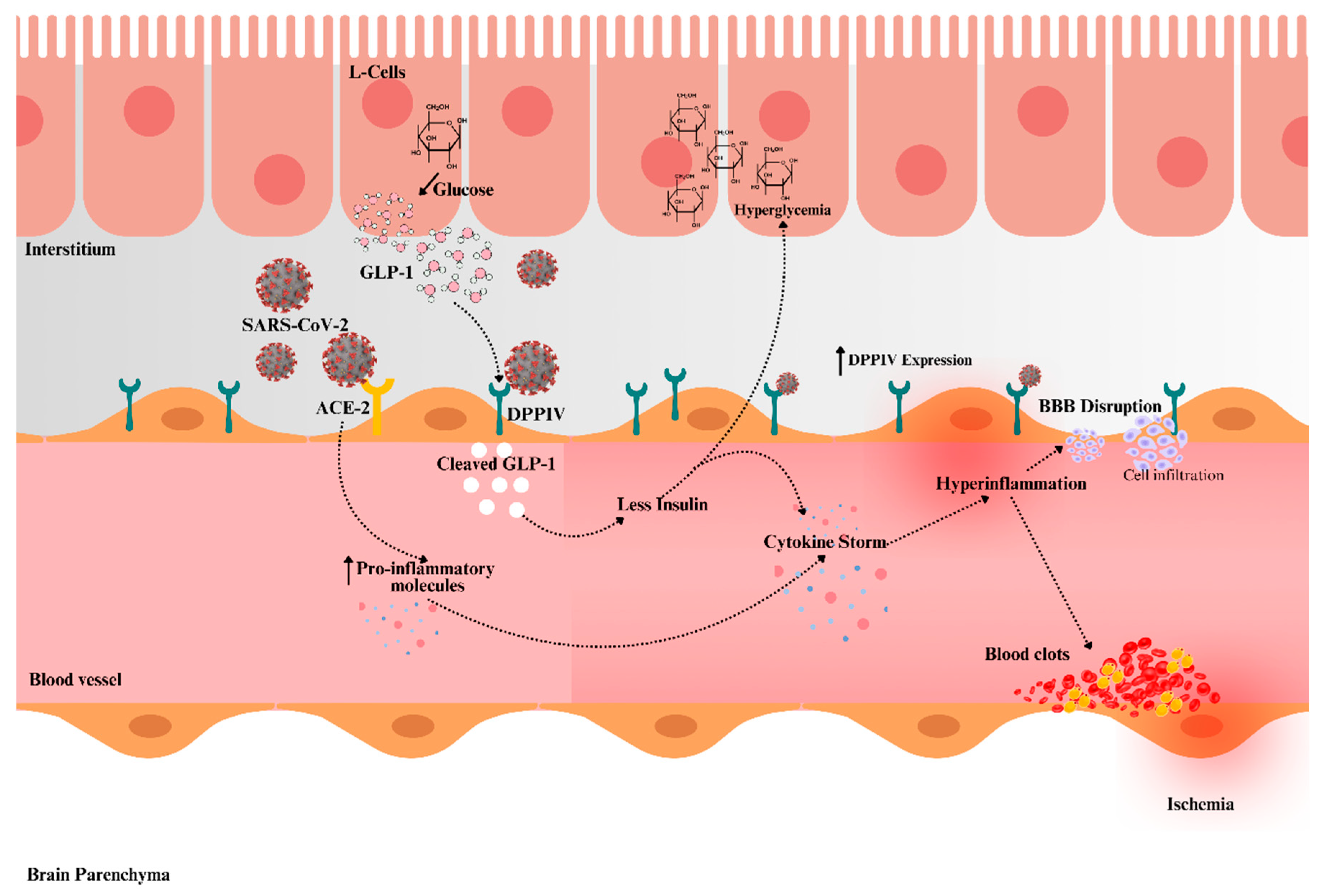
Furthermore, DPPIV’s enzymatic role in degrading glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) links it to hyperglycemia, a significant risk factor for severe COVID-19 outcomes [
74]. This hyperglycemic state, often exacerbated in patients with metabolic disorders such as diabetes, fuels systemic inflammation and endothelial dysfunction, which increases the risk of microvascular damage in the brain [
76]. Unlike ACE2, DPPIV not only facilitates viral entry, but also amplifies the metabolic and inflammatory disruptions that contribute to the long-term neurovascular damage seen in post-COVID-19 patients.
Thus, while ACE2 primarily acts as the gateway for SARS-CoV-2 infection, DPPIV may putatively serve as both a co-receptor and a key mediator of the metabolic and inflammatory cascades that aggravate the course of infection [
77,
78]. This dual role makes DPPIV a potential therapeutic target not just for limiting viral entry, but for managing the chronic complications, such as stroke and cognitive decline, that are linked to metabolic and cerebrovascular dysregulation in COVID-19 survivors.
4. Novel Insights into DPPIV’s Role in Metabolic Syndrome and COVID-19
The course and results of COVID-19 are considerably impacted by metabolic diseases such as T2DM [
74]. Chemokines and their receptors have been identified as a shared pathway between T2DM and COVID-19 by an investigation of pathway connections. By controlling the functions of chemokines, glucose homeostasis, and metabolism, DPPIV is essential in T2DM [
74]. Notably, there is a substantial correlation between hyperglycemia and diabetes and elevated DPPIV activity. It is well-known that DPPIV causes disruptions in glucose metabolism by degrading active GLP-1, which raises blood glucose levels [
76]. As illustrated in
Figure 1, DPPIV’s enzymatic activity reduces GLP-1 levels, exacerbating hyperglycemia, which, alongside the SARS-CoV-2-induced cytokine storm, leads to endothelial dysfunction, increased microthrombi, and heightened cerebrovascular risks.
It is conceivable that metabolic syndrome associated with comorbidities including obesity, diabetes, and cerebrovascular disorders is related to hyperglycemia, which may promote viral shedding and reproduction. This could, therefore, worsen COVID-19-related inflammation and cause endothelial dysfunction. Moreover, a hyperglycemic state is brought on by the multi-systemic inflammation associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection; on the other hand, this hyperglycemic state may facilitate viral replication [
79]. The uncontrolled glycosylation of SARS-CoV-2 modifies viral epitopes, facilitating the evasion of immune system detection. This evasion leads to a more severe and prolonged COVID-19 infection in hyperglycemic diabetic individuals [
80].
Moreover, many physiological systems, such as metabolism, obesity, autoimmunity, the immune system, endocrine functions, inflammation, cellular activities, and thrombotic cerebrovascular disorders like stroke, are known to be regulated by the adaptable transmembrane and circulating protein DPPIV [
81]. Numerous cell types, including T cells, B cells, NK cells, certain macrophage subsets, hematopoietic stem cells, and hematopoietic progenitor cells, have a broad expression of this protein. It can also be found on the surface of acinar, endothelial, and bone marrow cells in a variety of organs, including the kidney, liver, intestines, lung, spleen, and pancreas [
81,
82]. Moreover, when DPPIV is enzymatically active, it behaves as a homodimer, whereby numerous cytokines, including interferons, hepatocyte NF-1α, and hypoxia-inducible factor-1α, can strongly stimulate its expression. Pro-inflammatory diseases like obesity, diabetes, and atherosclerosis, and cerebral and cardiovascular disorders like stroke are associated with markedly elevated DPPIV levels [
81,
82,
83]. Through its effects on inflammatory signaling pathways, stimulation of vascular smooth cell proliferation, and induction of oxidative stress in various cell types, imbalanced levels of DPPIV may make these pathological states worse. Alarmingly, DPPIV’s immunomodulatory effects can cause inflammation on both a local and systemic level. It has been shown that DPPIV may promote T-cell activation, proliferation, and signal transduction, among other aspects of lymphocyte function. Moreover, after an acute infection, DPPIV is likely involved in a new regulatory mechanism that suppresses the immune response against the SARS-CoV-2 virus [
84].
4.1. Potential Role of DPPIV as Receptor for SARS-CoV-2 Infection
In addition to controlling inflammation and hyperglycemia, DPPIV has recently attracted attention concerning SARS-CoV-2 infection because it may act as a co-receptor for the virus. Remarkably, DPPIV has been found to function as a co-receptor for the entry of some viruses, such as the coronavirus MERS-CoV and the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) [
85]. Studies reveal that DPPIV’s critical binding sites required for this interaction coincide with those that MERS-CoV-S binds to. Additionally, it has been established that DPPIV serves as a useful receptor for cellular invasion when it comes to Human Coronavirus-Erasmus Medical Center (hCoV-EMC). Antibodies directed against DPP4 did, in fact, successfully prevent hCoV-EMC infection in Huh-7 and human bronchial epithelial cells [
85,
86,
87].
Moreover, protein–protein docking experiments using crystal structures have demonstrated a strong affinity between DPPIV and the spike-receptor-binding domain of SARS-CoV-2, which is particularly noteworthy [
88]. Furthermore, silico computational studies have indicated DPPIV as a likely SARS-CoV-2 receptor. Building on these discoveries and hypotheses, a growing body of research suggests that DPPIV might serve as a functional co-receptor for human coronaviruses, hence aiding in the transmission of SARS-CoV-2 [
88,
89,
90,
91].
4.2. Emerging Research on DPPIV and COVID-19
In this context, DPPIV has been analyzed in COVID-19 studies ranging from pre-clinical, including animal models and in-vitro studies, to clinical and observational ones. These collectively provide important insights into how DPPIV influences disease progression, with particular emphasis on inflammation, glucose metabolism, and cerebrovascular outcomes.
Pre-clinical animal studies, including its involvement in COVID-19, have investigated the involvement of DPPIV during viral infections. Evidence from recent animal models indicated that DPPIV inhibition led to lower inflammation and neurovascular damage attributed to COVID-19-like symptoms [
92]. These findings point out the enzyme’s contribution to the inflammation process, particularly in exacerbating the cytokine storm leading to endothelial dysfunction and cerebrovascular complications.
For instance, recent findings have identified that the inhibition of DPPIV in animal models could mitigate SARS-CoV-2-induced endothelial injury in the brain, reducing the incidence of microthrombi [
93,
94]. Such a model has, until now, helped establish the role of the enzyme in increasing COVID-19-related cerebrovascular risks, especially in aged and diabetic animal models. DPPIV inhibitors such as gliptins (i.e., saxagliptin, alogliptin sitagliptin, and linagliptin) have also been a focus of various clinical studies concerning COVID-19 patients, specifically those with T2DM. They are said to decrease the severity of COVID-19 through the limited viral entry and modulation of the immune response [
95,
96]. Additionally, diabetic patients receiving DPPIV inhibitors had lower viral loads, reduced levels of inflammatory markers, and a lower incidence of cerebrovascular complications compared to controls [
97].
Observational studies further stress the high activity of DPPIV with the poor outcomes in COVID-19 disease. For example, elderly COVID-19 patients reported that higher levels of DPPIV were related to increased cerebrovascular complications such as stroke and cognitive decline [
98,
99]. Such observations have shown that DPPIV acts as a potential biomarker for the anticipation of cerebrovascular risks among post-COVID-19 patients, particularly among patients with comorbid conditions like diabetes and hypertension.
All in all, the studies presented highlight DPPIV’s central role in modulating COVID-19 severity, particularly through its effects on inflammation, immune response, and glucose metabolism. In animal models, DPPIV inhibition has shown promise in reducing the impact of COVID-19 on the brain and cardiovascular system. Meanwhile, clinical trials suggest that DPPIV inhibitors may offer therapeutic potential, especially for diabetic patients who are more prone to severe outcomes. Observational studies further support the enzyme’s involvement in post-COVID-19 cerebrovascular complications.
5. DDPIV and Post-COVID-19 Fatigue: Impact on Cerebrovascular Disease
Vascular disorders, including embolisms and thrombotic cerebrovascular diseases, as well as cardiovascular diseases, hypertension, diabetes, and obesity, are the main comorbidities linked to post-COVID-19 fatigue. Severe COVID-19 cases can cause vascular integrity to be disrupted, coagulation and inflammatory responses to be triggered, and atherosclerosis to be encouraged, all of which increase the risk of cerebrovascular disorders. The virus can also harm the structure and function of the brain, which can lead to long-term cognitive impairment.
Alarmingly, those with COVID-19 who have abnormalities in their glucose metabolism are more likely to die from vascular–neurological issues and to experience other COVID-19-related complications down the road. This could put them at risk for COVID-19’s long-term repercussions. Thus, DPPIV, i.e., a vascular system component that affects glucose metabolism, is essential in controlling these disorders. A recent study has shown that DPPIV is dysregulated in the brain after a stroke. Through an in vitro functional study, recent reports have discovered that DPPIV inhibits the migration of neural progenitor cells and decreases the angiogenic capacity of brain ECs mediated by stromal cell-derived factor 1 (SDF1). The processes of tissue remodeling and repair in the brain following a stroke may be hampered by the overexpression of DPPIV in response to ischemia/reperfusion injury [
100].
Table 2 summarizes the role of DPPIV in post-COVID-19 cerebrovascular complications.
DPPIV plays a multifaceted role in the pathophysiology of COVID-19, particularly concerning cerebrovascular complications. Its ability to exacerbate endothelial dysfunction, promote inflammation, and disrupt glucose metabolism highlights the enzyme’s critical role in increasing the risk of post-COVID-19 cerebrovascular events. As such, DPPIV may represent both a key biomarker for predicting cerebrovascular complications and a potential therapeutic target for mitigating these risks in high-risk COVID-19 patients, especially those with metabolic comorbidities. While the exact mechanisms of DPPIV’s involvement in SARS-CoV-2 infection are still being explored, the existing evidence suggests that targeting DPPIV may reduce the risk of long-term cerebrovascular complications, including stroke and cognitive decline, in post-COVID-19 patients. Future research should continue to explore the therapeutic potential of DPPIV inhibitors in reducing both acute and chronic COVID-19 outcomes.
Studies have shown that DPPIV inhibitors may protect against stroke and vascular illnesses. Research on DPPIV, both scientific and clinical, has drawn interest not just in diabetes but also in cerebrovascular disorders. Thus, it is possible that increased DPPIV levels, which support hyperglycemia and increased inflammation brought on by cytokine storms, are connected to the long-term neurological problems and vascular cognitive impairment linked to COVID-19. DPPIV has been identified as a potential factor aggravating inflammation and the long-term effects of viral infections, according to the research evaluated in this context. Consequently, using DPPIV inhibitors in COVID-19 patients may offer a simple method of reducing viral entrance and replication, even if the patient has diabetes. This strategy may provide efficient therapeutic approaches to counteract inflammation and metabolic disruptions brought on by COVID-19. However, a more thorough investigation is required to clarify DPPIV’s role in post-COVID-19 fatigue.
5.1. Confounding Factors Influencing DPPIV-Mediated Post-COVID-19 Fatigue and Cerebrovascular Complications
Age, genetic predisposition, and the presence of comorbidities, including diabetes, hypertension, and obesity, may further modulate the severity of fatigue and cerebrovascular complications post-COVID-19 through the interaction with DPPIV activity [
101]. Indeed, it has been documented that these comorbid conditions modulate the levels and activities of DPPIV, leading to exacerbated inflammation and metabolic pathways that drive severe outcomes in COVID-19 patients.
Aging is associated with a natural increase in DPPIV activity [
102], which, in the cases of elderly patients affected by COVID-19, may worsen the outcome. According to the obtained data, elderly patients exhibit increased circulating levels of DPPIV, which are associated with an increased inflammatory response and a higher risk of developing cerebrovascular complications [
74]. For example, one multicenter cohort study reported that, among elderly COVID-19 patients, high levels of DPPIV were associated with a higher incidence of stroke and cognitive decline, probably as a result of increased endothelial dysfunction and microthrombus formation [
103]. This age-dependent increase in the enzymatic activity of DPPIV may further potentiate the cytokine storm observed in severe COVID-19 and thus contribute to post-COVID-19 fatigue and neurovascular damage. Thus, the increased inflammation burden in elderly subjects, along with high levels of DPPIV, places them at greater risk for neurological complications long after SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Moreover, metabolic disorders such as T2DM, obesity, and hypertension are directly associated with increased DPPIV activity, which, in turn, is associated with the severity of COVID-19 and its complications [
74]. DPPIV has an important role in glucose metabolism; patients with T2DM have increased levels of DPPIV due to GLP-1 degradation [
74]. This leads to hyperglycemia, considered a risk factor for poor outcomes in COVID-19. Moreover, in diabetic or obese patients, the hyperglycemic environment mediates viral replication and systemic inflammation, ameliorating the risks of cerebrovascular complications such as stroke and cognitive impairment [
104,
105]. Very recent studies also reported that COVID-19 diabetic patients with high DPPIV levels had more severe cerebrovascular events compared to non-diabetic COVID-19 patients, further underlining the pivotal role this enzyme plays in bridging metabolic dysfunction to COVID-19 severity [
106].
This was also true for hypertension, another frequent comorbidity in COVID-19 patients, which presented higher levels of DPPIV [
74]. Perhaps through the exacerbation of endothelial dysfunction and inflammation, known comorbid conditions that may be particularly exacerbated by the presence of DPPIV, individuals with hypertension would indeed suffer worse cerebrovascular outcomes. Moreover, genetic predispositions related to single nucleotide polymorphisms in the gene encoding DPPIV or related pathways could be relevant in determining the poor outcomes of some individuals affected by COVID-19 [107]. Although direct studies relating genetic predisposition to DPPIV-mediated COVID-19 complications are still emerging, there is evidence to date that polymorphisms in the gene encoding DPPIV influence its expression and activity [108]. These genetic variations may modulate the predisposition of an individual to the neurovascular and metabolic complications associated with COVID-19.
Moreover, genetic factors related to immune response and inflammation may interact with DPPIV activity. For example, individuals with a predisposition to heightened inflammatory responses may experience a more severe cytokine storm when combined with elevated DPPIV activity, leading to prolonged post-COVID-19 fatigue and cerebrovascular dysfunction.
Table 3 summarizes the confounding factors influencing DPPIV-mediated COVID-19 outcomes.
These confounding factors highlight the multifaceted nature of DPPIV’s influence on COVID-19 severity, particularly in post-COVID-19 fatigue and cerebrovascular complications. Age-related increases in DPPIV activity, combined with comorbidities such as diabetes and hypertension, significantly exacerbate the inflammatory and metabolic disruptions caused by COVID-19. Future research should focus on understanding the genetic predispositions that may further modulate DPPIV activity and how these factors collectively contribute to long-term COVID-19 sequelae.
5.2. Future Recommendations
Post-COVID-19 fatigue presents a multifaceted challenge, characterized by a diverse array of symptoms that can manifest regardless of the initial severity of the disease. The primary focus in addressing post-COVID-19 fatigue lies in comprehending its progression and identifying effective treatment strategies, i.e., in this case, focusing on DPPIV. Researchers are beginning to delineate the specific clinical, cellular, and molecular mechanisms underlying post-COVID-19 fatigue symptoms and DPPIV. Neurovascular disorders may play a role in driving the progression of post-COVID-19 fatigue, with SARS-CoV-2 infection and the role of DPPIV as a co-receptor potentially causing tissue and cellular damage, as well as exacerbating inflammatory or autoimmune responses due to disruptions in the proteolytic enzyme activities, catalysis, and molecular signaling pathways.
While existing research has contributed to our understanding of the mechanisms underlying post-COVID-19 fatigue, numerous unanswered questions persist and warrant urgent attention to mitigate its effects. Identifying additional molecular determinants and target proteins, i.e., DPPIV, is crucial for alleviating the substantial burden of post-COVID-19 fatigue. Metabolomics, proteomics, whole-genome sequencing, and gut microbiome studies offer promising avenues to unravel the pathophysiological processes underlying post-COVID-19 fatigue. The integration of data from basic science and clinical research is essential for gaining insight into the viral invasion into various tissues, particularly the brain, where it leads to neurological dysfunctions. Developing improved therapies to mitigate long-term cerebrovascular disease incidence and progression resulting from SARS-CoV-2 infection hinges on these investigations. Finally, further extensive research is undoubtedly necessary in order to evaluate and devise targeted treatment strategies for combating the persistent effects of post-COVID-19 fatigue.
6. Conclusions
In conclusion, from this review, the immense potential of DPPIV has become clear not only as a co-receptor of SARS-CoV-2 but also as a main mediator in metabolic–inflammatory cascades leading to the aggravation of post-COVID-19 fatigue and cerebrovascular complications. Its participation in glucose metabolism, immune regulation, and endothelial dysfunction, therefore, places it at the heart of the chronic cerebrovascular outcomes that accompany COVID-19 survivors, such as neurovascular damage, stroke, and cognitive decline. Targeting DPPIV with therapeutic inhibitors holds immense promise toward the mitigation of long-term cardiovascular and cerebrovascular risks, particularly in post-COVID-19 fatigue patients with comorbidities that include diabetes and hypertension. Further studies are necessary to demonstrate the exact molecular mechanisms and establish the therapeutic value of DPPIV inhibitors in the management of post-COVID fatigue as an effective way to reduce the public health burden of this debilitating condition.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.M.N.C.M.N. and M.D.C.R.; resources, C.M.N.C.M.N. and M.D.C.R.; data curation, C.M.N.C.M.N.; writing—original draft preparation, C.M.N.C.M.N.; writing—review and editing, C.M.N.C.M.N., M.D.C.R., U.J., M.Z.M., H.A.H., M.M.G., and E.N.K.C; funding acquisition, M.D.C.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study received the MSU Publication Grant (MPG-004-022024-FHLS).
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our sincere gratitude to all the author members for their invaluable guidance, support, and encouragement throughout the preparation of this manuscript. We are also deeply appreciative of Management and Science University (MSU) for providing the MSU Publication Grant (MPG-004-022024-FHLS). Special thanks go to colleagues, friends, and family members for their understanding and continuous support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. COVID Data Tracker. 2022. Available online: https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#datatracker-home (accessed on 8 November 2023).
- Hu, B.; Guo, H.; Zhou, P. , and Shi Z.L.. Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, M.; Ferrando, S.J.; Dornbush, R.; Lynch, S.; Shahar, S.; Klepacz, L.; Smiley, A. Impact of COVID-19 on employment: Sociodemographic, medical, psychiatric and neuropsychological correlates. Front. Rehabil. Sci. 2023, 4, 1150734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, H.E.; McCorkell, L.; Vogel, J.M.; et al. Long COVID: Major findings, mechanisms and recommendations. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuznik, B.I.; Shapovalov, K.G.; Chalisova, N.I. Changes in the State of Vital Systems with Long COVID-19. Biology Bulletin Reviews 2023, 13, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becerra-García, J.A.; Sánchez-Gutiérrez, T. Long-COVID psychological symptoms in child and adolescent population: A standardized proposal for its exploration. Enferm. Infecc. Microbiol. Clin. 2023, 41, 384–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.; Gupta, N.; Esang, M. Long COVID in Children and Adolescents. Prim. Care Companion CNS Disord. 2022, 24, 21r03218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guido, C. A. , Lucidi, F., Midulla, F., Zicari, A. M., Bove, E., Avenoso, F., Amedeo, I., Mancino, E., Nenna, R., De Castro, et al. Neurological and psychological effects of long COVID in a young population: A cross-sectional study. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 925144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batra, A. , Clark, J. R., Kang, A. K., Ali, S., Patel, T. R., Shlobin, N. A., Hoffman, S. C., Lim, P. H., Orban, Z. S., Visvabharathy, L., et al. Persistent viral RNA shedding of SARS-CoV-2 is associated with delirium incidence and six-month mortality in hospitalized COVID-19 patients. Geroscience 2022, 44, 1241–1254. [Google Scholar]
- Natarajan, A. , Zlitni, S., Brooks, E. F., Vance, S. E., Dahlen, A., Hedlin, H., Park, R. M., Han, A., Schmidtke, D. T., Verma, R.,et al. Gastrointestinal symptoms and fecal shedding of SARSCoV-2 RNA suggest prolonged gastrointestinal infection. Med 2022, 3, 371–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, J.D.; Atyeo, C.; Zur, Y.; Cook, C.E.; Patel, N.J.; Vanni, K.M.; Kowalski, E.N.; Qian, G.; Srivatsan, S.; Shadick, N.A.; et al. Humoral immunity to an endemic coronavirus is associated with postacute sequelae of COVID-19 in individuals with rheumatic diseases. Sci. Transl. Med. 2023, 6, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Kessel, S. A. M. , Olde Hartman, T. C., Lucassen, P. L. B. J., & van Jaarsveld, C. H. M. Post-acute and long-COVID-19 symptoms in patients with mild diseases: A systematic review. Fam. Pract. 2022, 39, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rioux, P.; Chaumon, M.; Demers, A. , Fitzback-Fortin, H., Kübel, S. L., Lebrun, C., Mendoza-Duran, E., Micillo, L., Racine, C., Thibault, N., van Wassenhove, V., & Grondin, S.. Psychological Time during the COVID-19 Lockdown: Canadian Data. Timing Time Percept. 2022, 10, 326–343. [Google Scholar]
- Medline, A. , Hayes, L., Valdez, K., Hayashi, A., Vahedi, F., Capell, W., Sonnenberg, J., Glick, Z., & Klausner, J. D. Evaluating the impact of stay-at-home orders on the time to reach the peak burden of Covid-19 cases and deaths: Does timing matter? BMC Public. Health 2020, 20, 1750. [Google Scholar]
- Elisabeth, A.L.; Karlen, S.B.; Magkos, F. The Effect of COVID-19-related Lockdowns on Diet and Physical Activity in Older Adults: A Systematic Review. Aging Dis. 2021, 12, 1935–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holdsworth, D. A. , Chamley, R., Barker-Davies, R., O'Sullivan, O., Ladlow, P., Mitchell, J. L., Dewson, D., Mills, D., May, S. L. J., Cranley, M.; et al. Comprehensive clinical assessment identifies specific neurocognitive deficits in working-age patients with long-COVID. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0267392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, A. , Shah, M., Ahmad, S. A., Premraj, L., Wildi, K., Li Bassi, G., Pardo, C. A., Choi, A., & Cho, S. M. Pathogenesis Underlying Neurological Manifestations of Long COVID Syndrome and Potential Therapeutics. Cells 2023, 12, 816. [Google Scholar]
- Avittan, H.; Kustovs, D. Cognition and Mental Health in Pediatric Patients Following COVID-19. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 5061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govil-Dalela, T.; Sivaswamy, L. Neurological Effects of COVID-19 in Children. Pediatr. Clin. N. Am. 2021, 68, 1081–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, B.T.; Bryan, A. Emerging respiratory infections: The infectious disease pathology of SARS, MERS, pandemic influenza, and Legionella. Semin. Diagn. Pathol. 2019, 36, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees, A.R. Immunological challenges of the “new” infections: Corona viruses. A New Hist. Vaccines Infect. Dis. 2022, 395–450. [Google Scholar]
- Desforges, M. , Le Coupanec, A., Dubeau, P., Bourgouin, A., Lajoie, L., Dubé, M., & Talbot, P. J. Human coronaviruses and other respiratory viruses: Underestimated opportunistic pathogens of the central nervous system? Viruses 2019, 12, 14. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chiara, M. , D'Erchia, A. M., Gissi, C., Manzari, C., Parisi, A., Resta, N., Zambelli, F., Picardi, E., Pavesi, G., Horner, D. S., & Pesole, G. Next generation sequencing of SARS-CoV-2 genomes: Challenges, applications and opportunities. Brief. Bioinform. 2021, 22, 616–630. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- John, G. , Sahajpal, N. S., Mondal, A. K., Ananth, S., Williams, C., Chaubey, A., Rojiani, A. M., & Kolhe, R. Next-generation sequencing (NGS) in COVID-19: A tool for SARS-CoV-2 diagnosis, monitoring new strains and phylodynamic modeling in molecular epidemiology. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2021, 43, 845–867. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Galeotti, C.; Bayry, J. Autoimmune and inflammatory diseases following COVID-19. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2020, 16, 413–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, S. R. , Ramelli, S. C., Grazioli, A., Chung, J. Y., Singh, M., Yinda, C. K., Winkler, C. W., Sun, J., Dickey, J. M., Ylaya, K.,; et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection and persistence throughout the human body and brain. Nature, 2022, 612(7941), 758–763. Dennis, A., Cuthbertson, D. J., Wootton, D., Crooks, M., Gabbay, M., Eichert, N., Mouchti, S., Pansini, M., Roca-Fernandez, A., Thomaides-Brears, H.; et al. Multi-organ impairment and Long COVID: A 1-year prospective, longitudinal cohort study. J. R. Soc. Med. 2022, 116, 97–112. [Google Scholar]
- Dennis, A. , Wamil, M., Alberts, J., Oben, J., Cuthbertson, D. J., Wootton, D., Crooks, M., Gabbay, M., Brady, M., Hishmeh, L., et al. Multiorgan impairment in low-risk individuals with post- COVID-19 syndrome: A prospective, community-based study. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e048391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, E. M. , Mackman, N., Warren, R. Q., Wolberg, A. S., Mosnier, L. O., Campbell, R. A., Gralinski, L. E., Rondina, M. T., van de Veerdonk, F. L., Hoffmeister, K. M.,et al. Understanding COVID-19-associated coagulopathy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2022, 22, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kansagra, A. P. , Goyal, M. S., Hamilton, S., & Albers, G. W. Collateral effect of COVID-19 on stroke evaluation in the United States. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 400–401. [Google Scholar]
- Newell, K.L.; Waickman, A.T. Inflammation, immunity, and antigen persistence in post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection Immunity and inflammation in post-acute sequelae of SARSCoV-2 infection. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2022, 77, 102228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toscano, G. , Palmerini, F., Ravaglia, S., Ruiz, L., Invernizzi, P., Cuzzoni, M. G., Franciotta, D., Baldanti, F., Daturi, R., Postorino, P.,et al. Guillain-Barré syndrome associated with SARS-CoV-2. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 2574–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lao, W.P.; Imam, S.A.; Nguyen, S.A. Anosmia, hyposmia, and dysgeusia as indicators for positive SARS-CoV-2 infection. World J. Otorhinolaryngol.-Head Neck Surg. 2020, 6, S22–S25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spudich, S.; Nath, A. Nervous system consequences of COVID-19. Science 2022, 375, 267–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akimoto, T. , Hara, M., Tasaki, K., Kurosawa, Y., Nakamoto, T., Hirose, S., Mizoguchi, T., Yokota, Y., Ninomiya, S., & Nakajima, H.. Delayed encephalopathy after COVID-19: A case series of six patients. Medicine 2022, 101, e31029. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Taube, M. Depression and brain fog as long-COVID mental health consequences: Difficult, complex and partially successful treatment of a 72-year-old patient-A case report. Front. Psychiatry 2023, 14, 1153512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savardashtaki, A.; Johnston, T.P.; Sahebkar, A. COVID-19 and cardiac injury: Clinical manifestations, biomarkers, mechanisms, diagnosis, treatment, and follow up. Expert. Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2021, 19, 345–357. [Google Scholar]
- Bowe, B. , Xie, Y., Xu, E., & Al-Aly, Z.. Kidney outcomes in Long COVID. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 32, 2851–2862. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S. , Farland, L. V., Gaskins, A. J., Mortazavi, J., Wang, Y. X., Tamimi, R. M., Rich-Edwards, J. W., Zhang, D., Terry, K. L., Chavarro, J. E., et al. Association of laparoscopically confirmed endometriosis with long COVID-19: A prospective cohort study. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2023, 228, 714.e1–714.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D. , Weng, S., Xia, C., Ren, Y., Liu, Z., Xu, Y., Yang, X., Wu, R., Peng, L., Sun, L., et al. Gastrointestinal symptoms of long COVID-19 related to the ectopic colonization of specific bacteria that move between the upper and lower alimentary tract and alterations in serum metabolites. BMC Med. 2023, 21, 264. [Google Scholar]
- Levi, M. , Thachil, J., Iba, T., & Levy, J. H. Coagulation abnormalities and thrombosis in patients with COVID-19. Lancet Haematol. 2020, 7, e438–e440. [Google Scholar]
- Lukiw, W.J.; Pogue, A.; Hill, J.M. SARS-CoV-2 Infectivity and Neurological Targets in the Brain. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2022, 42, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douaud, G. , Lee, S., Alfaro-Almagro, F., Arthofer, C., Wang, C., McCarthy, P., Lange, F., Andersson, J. L. R., Griffanti, L., Duff, E.,et al. SARS-CoV-2 is associated with changes in brain structure in UK biobank. Nature 2022, 604, 697–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntaios, G. , Michel, P., Georgiopoulos, G., Guo, Y., Li, W., Xiong, J., Calleja, P., Ostos, F., González-Ortega, G., Fuentes, B., et al. Characteristics and outcomes in patients with COVID-19 and acute ischemic stroke: The global COVID-19 stroke registry. Stroke 2020, 51, e254–e258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karnik, M. , Beeraka, N. M., Uthaiah, C. A., Nataraj, S. M., Bettadapura, A. D. S., Aliev, G., & Madhunapantula, S. V. A Review on SARS-CoV-2-Induced Neuroinflammation, Neurodevelopmental Complications, and Recent Updates on the Vaccine Development. Mol. Neurobiol. 2021, 58, 4535–4563. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lyoo, K. S. , Kim, H. M., Lee, B., Che, Y. H., Kim, S. J., Song, D., Hwang, W., Lee, S., Park, J. H., Na, W., et al. Direct neuronal infection of SARS-CoV-2 reveals cellular and molecular pathology of chemosensory impairment of COVID-19 patients. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2022, 11, 406–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahlberg, M. D. , Blair, R. V., Doyle-Meyers, L. A., Midkiff, C. C., Zenere, G., Russell-Lodrigue, K. E., Monjure, C. J., Haupt, E. H., Penney, T. P., Lehmicke, G.,et al. Cellular events of acute, resolving or progressive COVID-19 in SARS-CoV-2 infected non-human primates. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 6078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michiels, C. Endothelial cell functions. J. Cell Physiol. 2003, 196, 430–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavriilaki, E.; Eftychidis, I.; Papassotiriou, I. Update on endothelial dysfunction in COVID-19: Severe disease, long COVID-19 and pediatric characteristics. J. Lab. Med. 2021, 45, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarnawski, A.S.; Ahluwalia, A. Endothelial cells and blood vessels are major targets for COVID-19-induced tissue injury and spreading to various organs. World J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 28, 275–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayat, A. H. , Azimi, H., Hassani Moghaddam, M., Ebrahimi, V., Fathi, M., Vakili, K., Mahmoudiasl, G. R., Forouzesh, M., Boroujeni, M. E., Nariman, Z., et al. COVID-19 causes neuronal degeneration and reduces neurogenesis in human hippocampus. Apoptosis 2022, 27, 852–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plantone, D. , Locci, S., Bergantini, L., Manco, C., Cortese, R., Meocci, M., Cavallaro, D., d'Alessandro, M., Bargagli, E., & De Stefano, N.. Brain neuronal and glial damage during acute COVID-19 infection in absence of clinical neurological manifestations. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2022, 93, 1343–1348. [Google Scholar]
- Klein, R.S.; Garber, C.; Howard, N. Infectious immunity in the central nervous system and brain function. Nat. Immunol. 2017, 18, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongchitrat, P.; Chanmee, T.; Govitrapong, P. Molecular Mechanisms Associated with Neurodegeneration of Neurotropic Viral Infection. Mol. Neurobiol. 2023, 61, 2881–2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beckman, D. , Bonillas, A., Diniz, G. B., Ott, S., Roh, J. W., Elizaldi, S. R., Schmidt, B. A., Sammak, R. L., Van Rompay, K. K. A., Iyer, S. S., & Morrison, J. H.. SARS-CoV-2 infects neurons and induces neuroinflammation in a non-human primate model of COVID-19. Cell Rep. 2022, 41, 111573. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zorzo, C.; Solares, L.; Mendez, M.; Mendez-Lopez, M. Hippocampal alterations after SARS-CoV-2 infection: A systematic review. Behav. Brain Res. 2023, 455, 114662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, J. , Wood, J., Jaycox, J. R., Dhodapkar, R. M., Lu, P., Gehlhausen, J. R., Tabachnikova, A., Greene, K., Tabacof, L., Malik, A. A., et al. Distinguishing features of Long COVID identified through immune profiling. Nature 2023, 623, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glynne, P. , Tahmasebi, N., Gant, V., & Gupta, R.Long COVID following mild SARS-CoV-2 infection: Characteristic T cell alterations and response to antihistamines. J. Investig. Med. 2022, 70, 61–67. [Google Scholar]
- Arun, S.; Storan, A.; Myers, B. Mast cell activation syndrome and the link with long COVID. Br. J. Hosp. Med. 2022, 83, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peluso, M. J. , Lu, S., Tang, A. F., Durstenfeld, M. S., Ho, H. E., Goldberg, S. A., Forman, C. A., Munter, S. E., Hoh, R., Tai, V., et al. Markers of immune activation and inflammation in individuals with postacute sequelae of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 224, 1839–1848. [Google Scholar]
- Barnes, B. J. , Adrover, J. M., Baxter-Stoltzfus, A., Borczuk, A., Cools-Lartigue, J., Crawford, J. M., Daßler-Plenker, J., Guerci, P., Huynh, C., Knight, J. S., et al. Targeting Potential Drivers of COVID-19: Neutrophil Extracellular Traps. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217, e20200652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R. , Lee, J. H., Kim, J., Xiong, F., Hasani, L. A., Shi, Y., Simpson, E. N., Zhu, X., Chen, Y. T., Shivshankar, P., et al. SARS-CoV-2 restructures host chromatin architecture. Nat. Microbiol. 2023, 8, 679–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M. S. , Johansson, A., Jonsson, J., & Schiöth, H. B. Review Dissecting the Molecular Mechanisms Surrounding Post-COVID-19 Syndrome and Neurological Features. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4275. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ragab, D. , Salah Eldin, H., Taeimah, M., Khattab, R., & Salem, R.. The COVID-19 cytokine storm; what we know so far. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1446. [Google Scholar]
- Scurati, R. , Papini, N., Giussani, P., Alberti, G., & Tringali, C.. The Challenge of Long COVID-19 Management: From Disease Molecular Hallmarks to the Proposal of Exercise as Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12311. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, M. A. , Knauer, M. J., Nicholson, M., Daley, M., Van Nynatten, L. R., Martin, C., Patterson, E. K., Cepinskas, G., Seney, S. L., Dobretzberger, V., et al. Elevated vascular transformation blood biomarkers in Long-COVID indicate angiogenesis as a key pathophysiological mechanism. Mol. Med. 2022, 28, 122. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gomes, S. M. R. , Brito, A. C. S., Manfro, W. F. P., Ribeiro-Alves, M., Ribeiro, R. S. A., da Cal, M. S., Lisboa, V. D. C., Abreu, D. P. B., Castilho, L. D. R., Porto, L. C. M. S., et al. High levels of pro-inflammatory SARS-CoV-2-specific biomarkers revealed by in vitro whole blood cytokine release assay (CRA) in recovered and long-COVID-19 patients. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0283983. [Google Scholar]
- Petrella, C. , Nenna, R., Petrarca, L., Tarani, F., Paparella, R., Mancino, E., Di Mattia, G., Conti, M. G., Matera, L., Bonci, E., et al. Serum NGF and BDNF in Long-COVID-19 Adolescents: A Pilot Study. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, M. , Kleine-Weber, H., Schroeder, S., Krüger, N., Herrler, T., Erichsen, S., Schiergens, T. S., Herrler, G., Wu, N. H., Nitsche, A., et al. SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor. Cell 2020, 181, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adimulam, T.; Arumugam, T.; Gokul, A.; Ramsuran, V. Genetic Variants within SARS-CoV-2 Human Receptor Genes May Contribute to Variable Disease Outcomes in Different Ethnicities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y. , Zhang, Z., Yang, L., Lian, X., Xie, Y., Li, S., Xin, S., Cao, P., & Lu, J.. The MERS-CoV receptor DPP4 as a candidate binding target of the SARS-CoV-2 spike. iScience 2020, 23, 101160. [Google Scholar]
- Nag, S. , Mandal, S., Mukherjee, O., Mukherjee, S., & Kundu, R. DPP-4 Inhibitors as a savior for COVID-19 patients with diabetes. Future Virol. 2023, 18, 321–333. [Google Scholar]
- Bassendine, M. F. , Bridge, S. H., McCaughan, G. W., & Gorrell, M. D. COVID-19 and comorbidities: A role for dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP4) in disease severity? J. Diabetes 2020, 12, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, K. C. H. , He, Q., Bennett, A. N., Li, J., & Chan, K. H. K. Shared genetic mechanism between type 2 diabetes and COVID-19 using pathway-based association analysis. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 1063519. [Google Scholar]
- Deacon, C.F. Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibition with sitagliptin: A new therapy for type 2 diabetes. Expert. Opin. Investig. Drugs 2007, 16, 533–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, A.N.; Gupta, A.M.; Banerjee, D.; Chakrabarti, J.; Raghavendra, P.B. B. Unraveling DPP4 Receptor Interactions with SARS-CoV-2 Variants and MERS-CoV: Insights into Pulmonary Disorders via Immunoinformatics and Molecular Dynamics. Viruses 2023, 15, 2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sebastián-Martín, A.; Sánchez, B.G.; Mora-Rodríguez, J.M.; Bort, A.; Díaz-Laviada, I. Role of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 (DPP4) on COVID-19 Physiopathology. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Icard, P. , Lincet, H., Wu, Z., Coquerel, A., Forgez, P., Alifano, M., & Fournel, L. The key role of Warburg effect in SARS-CoV-2 replication and associated inflammatory response. Biochimie 2021, 180, 169–177. [Google Scholar]
- Mehdipour, A.R.; Hummer, G. Dual nature of human ACE2 glycosylation in binding to SARSCoV-2 spike. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2100425118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambeir, A. M. , Durinx, C., Scharpé, S., & De Meester, I. Dipeptidyl-peptidase IV from bench to bedside: An update on structural properties functions clinical aspects of the enzyme, DPP IV. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2003, 40, 209–294. [Google Scholar]
- Arscott, W. T. , LaBauve, A. E., May, V., & Wesley, U. V. Suppression of neuroblastoma growth by dipeptidyl peptidase IV: Relevance of chemokine regulation and caspase activation. Oncogene 2009, 28, 479–491. [Google Scholar]
- Gorrell, M.D. Dipeptidyl peptidase IV and related enzymes in cell biology and liver disorders. Clin. Sci. 2005, 108, 277–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemann, C. , Wagner, L., Stephan, M., & von Hörsten, S.. Cut to the chase: A review of CD26/dipeptidyl peptidase-4’s (DPP4) entanglement in the immune system. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2016, 185, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lu, G. , Hu, Y., Wang, Q., Qi, J., Gao, F., Li, Y., Zhang, Y., Zhang, W., Yuan, Y., Bao, J.,; et al. Molecular Basis of Binding between Novel Human Coronavirus MERS-CoV and Its Receptor CD26. Nature 2013, 500, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callebaut, C. , Krust, B., Jacotot, E., & Hovanessian, A. G. T cell activation antigen, CD26, as a cofactor for entry of HIV in CD4+ cells. Science 1993, 262, 2045–2050. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Raj, V.S.; Mou, H.; Smits, S.L.; et al. Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 is a functional receptor for the emerging human coronavirus-EMC. Nature 2013, 495, 251–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooke, G.N.; Prischi, F. Structural and functional modelling of SARS-CoV-2 entry in animal models. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vankadari, N.; Wilce, J.A. Emerging WuHan (COVID-19) coronavirus: Glycan shield and structure prediction of spike glycoprotein and its interaction with human CD26. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 601–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radzikowska, U. , Ding, M., Tan, G., Zhakparov, D., Peng, Y., Wawrzyniak, P., Wang, M., Li, S., Morita, H., Altunbulakli, C. et al. Distribution of ACE2, CD147, CD26, and other SARSCoV-2 associated molecules in tissues and immune cells in health and in asthma, COPD, obesity, hypertension, and COVID-19 risk factors. Allergy 2020, 75, 2829–2845. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Q. , Zhang, W., Li, T., Yang, G., Zhu, W., Chen, N., & Jin, H.. Interrelationship between 2019-nCov receptor DPP4 and diabetes mellitus targets based on protein interaction network. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 188. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A. , Singh, R. S., Sarma, P., Batra, G., Joshi, R., Kaur, H., Sharma, A. R., Prakash, A., & Medhi, B. A Comprehensive Review of Animal Models for Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2, SARS-CoV, and MERS-CoV. Virol. Sin. 2020, 35, 290–304. [Google Scholar]
- Pitocco, D.; Tartaglione, L.; Viti, L.; Di Leo, M.; Pontecorvi, A.; Caputo, S. SARS-CoV-2 and DPP4 inhibition: Is it time to pray for Janus Bifrons? Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2020, 163, 108162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groppa, S.A.; Ciolac, D.; Duarte, C.; Garcia, C.; Gasnaș, D.; Leahu, P.; Efremova, D.; Gasnaș, A.; Bălănuță, T.; Mîrzac, D.; et al. Molecular Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2/COVID-19 Pathogenicity on the Central Nervous System: Bridging Experimental Probes to Clinical Evidence and Therapeutic Interventions. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2022, 1376, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mahgoub, S.; Fatahala, S.S.; Sayed, A.I.; Atya, H.B.; El-Shehry, M.F.; Afifi, H.; Awad, S.M.; El-Hameed, R.H.A.; Taha, H. Novel hit of DPP-4Is as promising antihyperglycemic agents with dual antioxidant/anti-inflammatory effects for type 2 diabetes with/without COVID-19. Bioorg. Chem. 2022, 128, 106092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Su, X.; Cao, W.; Tan, M.; Zhu, G.; Gao, J.; Zhou, L. The Discovery and Characterization of a Potent DPP-IV Inhibitory Peptide from Oysters for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Based on Computational and Experimental Studies. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.M.; Park, J.H. Pleiotropic Benefits of DPP-4 Inhibitors Beyond Glycemic Control. Clin. Med. Insights Endocrinol. Diabetes. 2021, 14, 11795514211051698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajpal, A.; Sayyed Kassem, L.; Aron, D.C. Management of diabetes in elderly patients during the COVID-19 pandemic: Current and future perspectives. Expert. Rev. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 16, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nádasdi, Á.; Sinkovits, G.; Bobek, I.; Lakatos, B.; Förhécz, Z.; Prohászka, Z.Z.; Réti, M.; Arató, M.; Cseh, G.; Masszi, T.; et al. Decreased circulating dipeptidyl peptidase-4 enzyme activity is prognostic for severe outcomes in COVID-19 inpatients. Biomark. Med. 2022, 16, 317–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesley, U. V. , Hatcher, J. F., Ayvaci, E. R., Klemp, A., & Dempsey, R. J. Regulation of Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV in the Post-stroke Rat Brain and In Vitro Ischemia: Implications for Chemokine-Mediated Neural Progenitor Cell Migration and Angiogenesis. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 4973–4985. [Google Scholar]
- Rudroff, T.; Workman, C.D.; Bryant, A.D. Potential Factors That Contribute to Post-COVID-19 Fatigue in Women. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Jung, C.H.; Han, S.; Park, C.Y. Increasing Age Associated with Higher Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibition Rate Is a Predictive Factor for Efficacy of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors. Diabetes Metab. J. 2022, 46, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinosoglou, K. , Schinas, G., Bletsa, E., Bristianou, M., Lanaras, L., Michailides, C., Katsikas, T., Barkas, F., Liberopoulos, E., Kotsis, V., et al. COVID-19 Outcomes and Diabetes Mellitus: A Comprehensive Multicenter Prospective Cohort Study. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.J.; Hwang, J.; Ahn, J.; Park, S.J.; Song, E.; Jang, A.; Choi, K.M.; Baik, S.H.; Yoo, H.J. Ischaemic stroke in patients with diabetes requiring urgent procedures during the COVID-19 pandemic in South Korea: A retrospective, nationwide, population-based cohort study using data from the National Emergency Department Information System. BMJ Open 2023, 13, e074381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malempati, M.; Patel, M.; Patel, J. Ischemic stroke and COVID-19 infection—A review of clinical case reports. Egypt J. Intern. Med. 2024, 36, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, N.; Naik, D.; Sahoo, J.; Kamalanathan, S. Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors in COVID-19: Beyond glycemic control. World J. Virol. 2022, 11, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posadas-Sánchez, R.; Sánchez-Muñoz, F.; Guzmán-Martín, C.A.; Hernández-Díaz Couder, A.; Rojas-Velasco, G.; Fragoso, J.M.; Vargas-Alarcón, G. Dipeptidylpeptidase-4 levels and DPP4 gene polymorphisms in patients with COVID-19. Association with disease and with severity. Life Sci. 2021, 276, 119410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhargave, A.; Devi, K.; Ahmad, I.; Yadav, A.; Gupta, R. Genetic variation in DPP-IV gene linked to predisposition of T2DM: A case control study. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2022, 21, 1709–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).