Submitted:
09 October 2024
Posted:
15 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Methods
Case Review
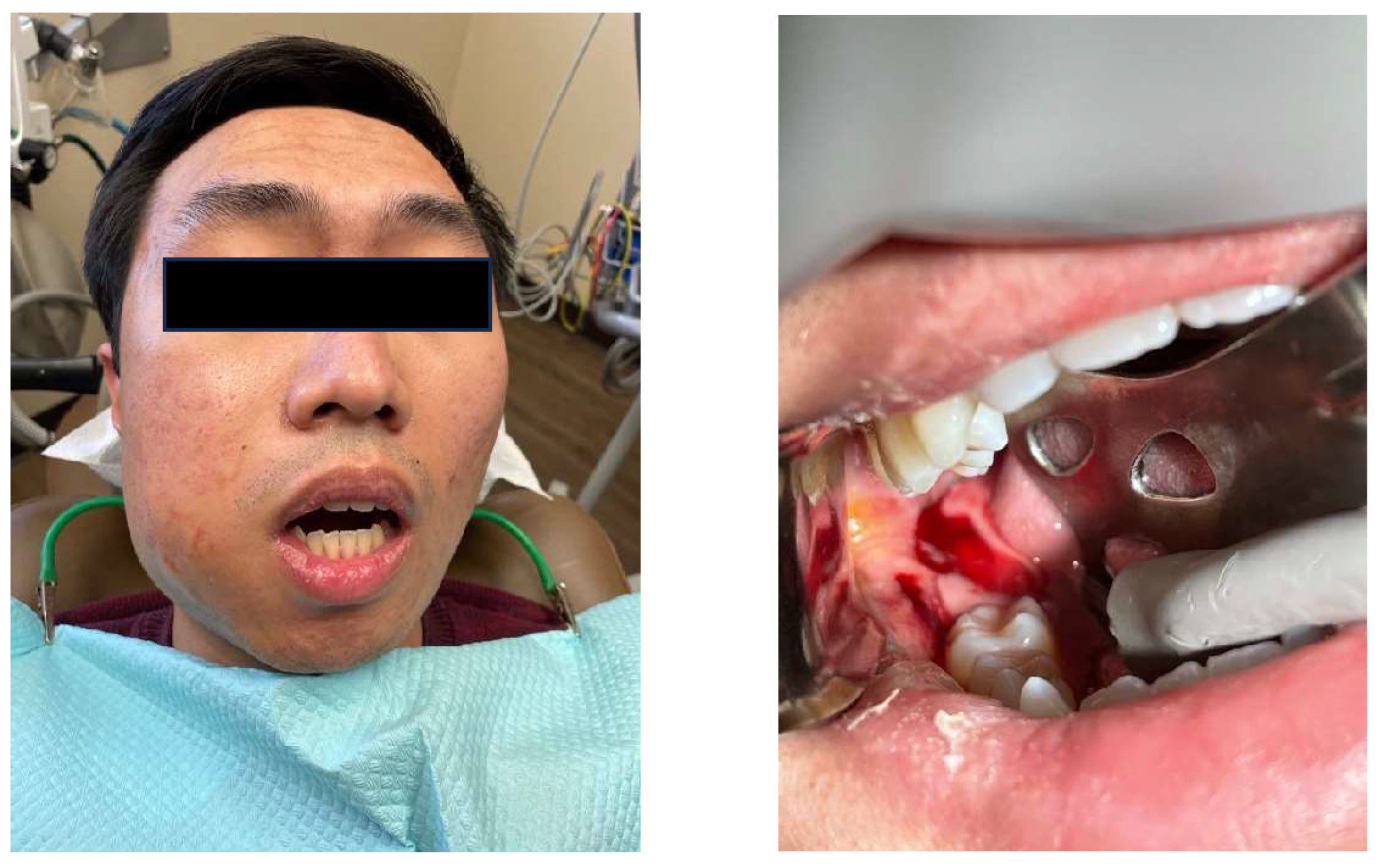
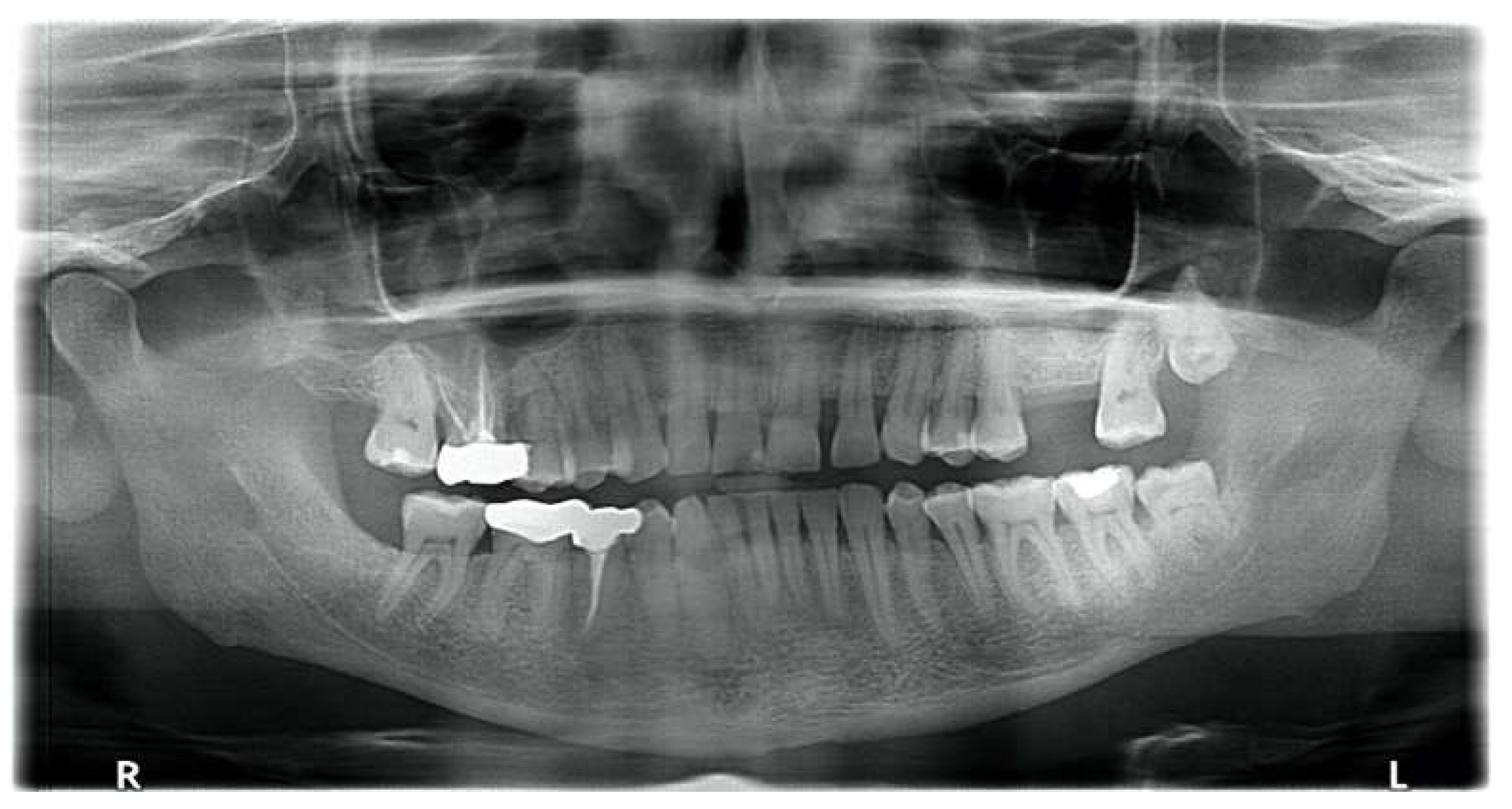
CASE 1: Perialveolar Infection
CASE 2: Multi-space Odontogenic Infection
CASE 3: Severe Pericoronitis
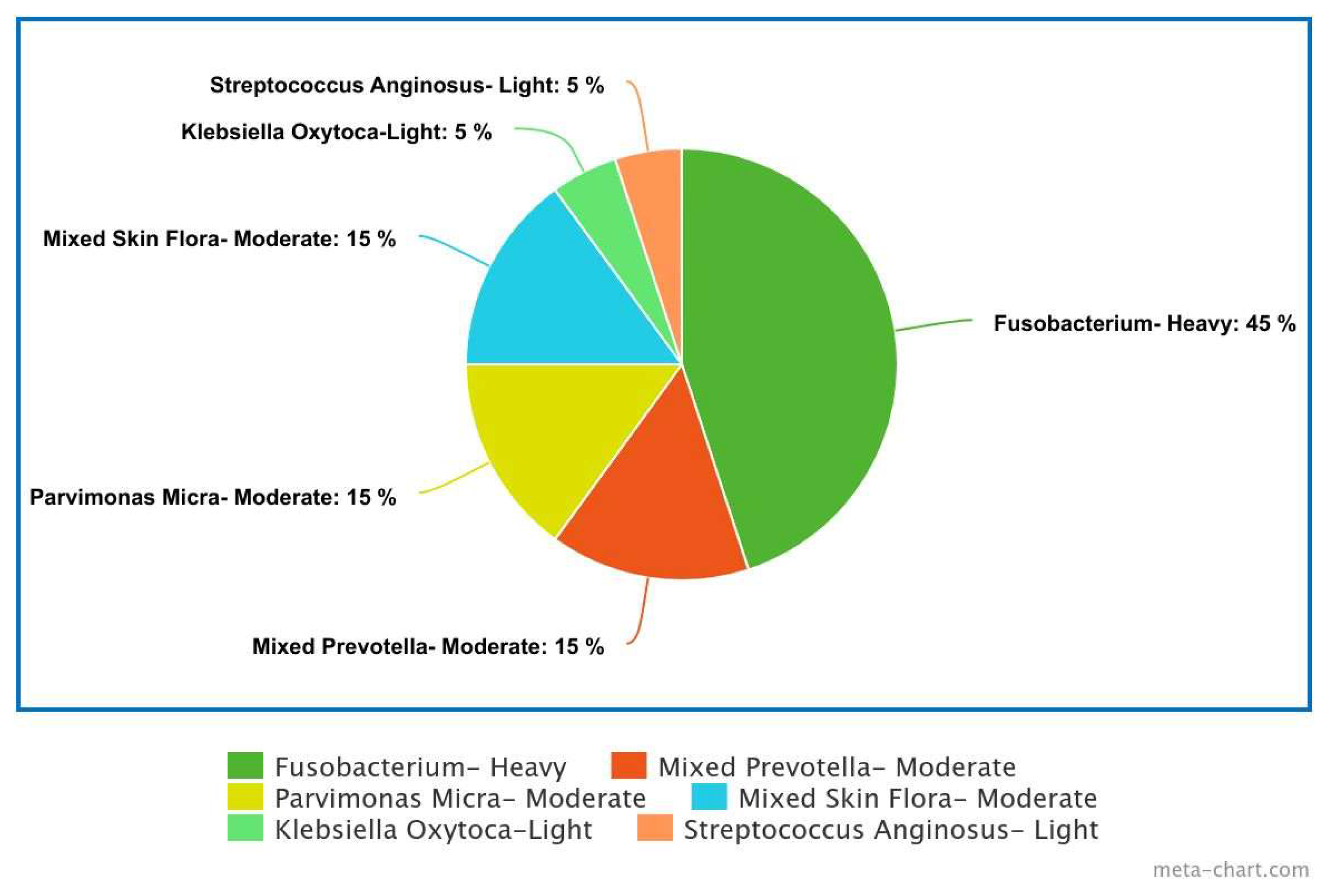
Oral Microflora and Odontogenic Infections
Prevotella Pathogenesis
Prevotella and Odontogenic Infections
Metronidazole
Metronidazole and The Disulfiram-Like Reaction
Odontogenic Infections and Antibiotic Susceptibility
Conclusions
References
- Kau, S., et al., The facultative human oral pathogen Prevotella histicola in equine cheek tooth apical/ periapical infection: a case report. BMC Vet Res, 2021. 17(1): p. 343. [CrossRef]
- Fe Marques, A., et al., Septic arthritis of the knee due to Prevotella loescheii following tooth extraction. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal, 2008. 13(8): p. E505-7.
- Al-Nawas, B. and M. Maeurer, Severe versus local odontogenic bacterial infections: comparison of microbial isolates. Eur Surg Res, 2008. 40(2): p. 220-4. [CrossRef]
- Hupp, J.R., E. Ellis, and M.R. Tucker, Contemporary oral and maxillofacial surgery. Seventh edition. ed. 2019, Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier. xii, 708 pages. [CrossRef]
- Cuevas-Gonzalez, M.V., et al., Antimicrobial resistance in odontogenic infections: A protocol for systematic review. Medicine (Baltimore), 2022. 101(50): p. e31345. [CrossRef]
- Ardila, C.M. and J.A. Bedoya-Garcia, Antimicrobial resistance in patients with odontogenic infections: A systematic scoping review of prospective and experimental studies. J Clin Exp Dent, 2022. 14(10): p. e834-e845.
- Huang, X., et al., Microbial Profile During Pericoronitis and Microbiota Shift After Treatment. Front Microbiol, 2020. 11: p. 1888.
- Ribeiro, M.H.B., et al., Microbial profile of symptomatic pericoronitis lesions: a cross-sectional study. J Appl Oral Sci, 2020. 28: p. e20190266.
- Kaneko, A., et al., Antimicrobial susceptibility surveillance of bacterial isolates recovered in Japan from odontogenic infections in 2013. J Infect Chemother, 2020. 26(9): p. 882-889.
- Sakamoto, H., et al., Necrotizing Fasciitis of the Neck due to an Odontogenic Infection: A Case Report. J Infect Chemother, 1996. 2(4): p. 290-293. [CrossRef]
- Heim, N., et al., Microbiology and antibiotic sensitivity of head and neck space infections of odontogenic origin. Differences in inpatient and outpatient management. J Craniomaxillofac Surg, 2017. 45(10): p. 1731-1735. [CrossRef]
- Bahl, R., et al., Odontogenic infections: Microbiology and management. Contemp Clin Dent, 2014. 5(3): p. 307-11. [CrossRef]
- Singh, M., D.H. Kambalimath, and K.C. Gupta, Management of odontogenic space infection with microbiology study. J Maxillofac Oral Surg, 2014. 13(2): p. 133-9.
- Plum, A.W., A.J. Mortelliti, and R.E. Walsh, Microbial flora and antibiotic resistance in odontogenic abscesses in Upstate New York. Ear Nose Throat J, 2018. 97(1-2): p. E27-E31.
- Shakya, N., et al., Epidemiology, Microbiology and Antibiotic Sensitivity of Odontogenic Space Infections in Central India. J Maxillofac Oral Surg, 2018. 17(3): p. 324-331.
- Kwon, G.B. and C.H. Kim, Microbial isolates and antibiotic sensitivity in patients hospitalized with odontogenic infections at a tertiary center over 10 years. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2023. 49(4): p. 198-207.
- Düzgüneş, N., Medical microbiology and immunology for dentistry. 2016, Chicago: Quintessence Publishing Co, Inc. xi, 290 pages.
- Socransky, S.S., et al., Microbial complexes in subgingival plaque. J Clin Periodontol, 1998. 25(2): p. 134-44.
- Shah, H.N. and D.M. Collins, Prevotella, a new genus to include Bacteroides melaninogenicus and related species formerly classified in the genus Bacteroides. Int J Syst Bacteriol, 1990. 40(2): p. 205-8. [CrossRef]
- Shenker, B.J., L. Vitale, and J. Slots, Immunosuppressive effects of Prevotella intermedia on in vitro human lymphocyte activation. Infect Immun, 1991. 59(12): p. 4583-9. [CrossRef]
- Shah, H.N. and S.E. Gharbia, Biochemical and chemical studies on strains designated Prevotella intermedia and proposal of a new pigmented species, Prevotella nigrescens sp. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol, 1992. 42(4): p. 542-6. [CrossRef]
- Labbe, S. and D. Grenier, Characterization of the human immunoglobulin G Fc-binding activity in Prevotella intermedia. Infect Immun, 1995. 63(7): p. 2785-9.
- Jansen, H.J., D. Grenier, and J.S. Van der Hoeven, Characterization of immunoglobulin G-degrading proteases of Prevotella intermedia and Prevotella nigrescens. Oral Microbiol Immunol, 1995. 10(3): p. 138-45.
- Beem, J.E., W.E. Nesbitt, and K.P. Leung, Identification of hemolytic activity in Prevotella intermedia. Oral Microbiol Immunol, 1998. 13(2): p. 97-105.
- Leung, W.K., et al., Microbiology of the pericoronal pouch in mandibular third molar pericoronitis. Oral Microbiol Immunol, 1993. 8(5): p. 306-12.
- Potempa, M., et al., Interpain A, a cysteine proteinase from Prevotella intermedia, inhibits complement by degrading complement factor C3. PLoS Pathog, 2009. 5(2): p. e1000316.
- Matsui, H., et al., Phenotypic characterization of polysaccharidases produced by four Prevotella type strains. Curr Microbiol, 2000. 41(1): p. 45-9. [CrossRef]
- Doke, M., et al., Nucleases from Prevotella intermedia can degrade neutrophil extracellular traps. Mol Oral Microbiol, 2017. 32(4): p. 288-300. [CrossRef]
- Nagaoka, S., et al., Interleukin-8 gene expression by human dental pulp fibroblast in cultures stimulated with Prevotella intermedia lipopolysaccharide. J Endod, 1996. 22(1): p. 9-12. [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J., et al., Prevotella intermedia lipopolysaccharide stimulates release of tumor necrosis factor-alpha through mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways in monocyte-derived macrophages. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol, 2007. 51(2): p. 407-13.
- Alugupalli, K.R. and S. Kalfas, Inhibitory effect of lactoferrin on the adhesion of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans and Prevotella intermedia to fibroblasts and epithelial cells. APMIS, 1995. 103(2): p. 154-60.
- Berglundh, T., et al., The use of metronidazole and amoxicillin in the treatment of advanced periodontal disease. A prospective, controlled clinical trial. J Clin Periodontol, 1998. 25(5): p. 354-62.
- Poulet, P.P., D. Duffaut, and J.P. Lodter, Evaluation of the Etest for determining the in-vitro susceptibilities of Prevotella intermedia isolates to metronidazole. J Antimicrob Chemother, 1999. 43(4): p. 610-1.
- Augthun, M. and G. Conrads, Microbial findings of deep peri-implant bone defects. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants, 1997. 12(1): p. 106-12.
- van Winkelhoff, A.J., et al., beta-Lactamase producing bacteria in adult periodontitis. J Clin Periodontol, 1997. 24(8): p. 538-43.
- Sharma, G., et al., Fumarate and nitrite reduction by Prevotella nigrescens and Prevotella buccae isolated from Chronic Periodontitis patients. Microb Pathog, 2023. 176: p. 106022. [CrossRef]
- Le Goff, A., et al., Evaluation of root canal bacteria and their antimicrobial susceptibility in teeth with necrotic pulp. Oral Microbiol Immunol, 1997. 12(5): p. 318-22. [CrossRef]
- Tek, M., et al., The predominant bacteria isolated from radicular cysts. Head Face Med, 2013. 9: p. 25. [CrossRef]
- Vata, A., et al., Polymicrobial Bacterial Meningitis in a Patient with Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media: Case Report and Literature Review. Medicina (Kaunas), 2023. 59(8).
- Sobottka, I., et al., In vitro activity of moxifloxacin against bacteria isolated from odontogenic abscesses. Antimicrob Agents Chemother, 2002. 46(12): p. 4019-21.
- Sanchez, R., et al., Severe odontogenic infections: epidemiological, microbiological and therapeutic factors. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal, 2011. 16(5): p. e670-6.
- Rush, D.E., et al., Clindamycin versus Unasyn in the treatment of facial cellulitis of odontogenic origin in children. Clin Pediatr (Phila), 2007. 46(2): p. 154-9.
- Kuriyama, T., et al., Antimicrobial susceptibility of major pathogens of orofacial odontogenic infections to 11 beta-lactam antibiotics. Oral Microbiol Immunol, 2002. 17(5): p. 285-9.
- Warnke, P.H., et al., Penicillin compared with other advanced broad spectrum antibiotics regarding antibacterial activity against oral pathogens isolated from odontogenic abscesses. J Craniomaxillofac Surg, 2008. 36(8): p. 462-7. [CrossRef]
- Sobottka, I., et al., Microbiological analysis of a prospective, randomized, double-blind trial comparing moxifloxacin and clindamycin in the treatment of odontogenic infiltrates and abscesses. Antimicrob Agents Chemother, 2012. 56(5): p. 2565-9. [CrossRef]
- Cachovan, G., et al., Radiography-based score indicative for the pathogenicity of bacteria in odontogenic infections. Acta Odontol Scand, 2014. 72(7): p. 530-6. [CrossRef]
- Baty, J.J., S.N. Stoner, and J.A. Scoffield, Oral Commensal Streptococci: Gatekeepers of the Oral Cavity. J Bacteriol, 2022. 204(11): p. e0025722.
- Khalil, D., et al., Oral microflora and selection of resistance after a single dose of amoxicillin. Clin Microbiol Infect, 2016. 22(11): p. 949.e1-949.e4.
- Dingsdag, S.A. and N. Hunter, Metronidazole: an update on metabolism, structure-cytotoxicity and resistance mechanisms. J Antimicrob Chemother, 2018. 73(2): p. 265-279.
- Lofmark, S., C. Edlund, and C.E. Nord, Metronidazole is still the drug of choice for treatment of anaerobic infections. Clin Infect Dis, 2010. 50 Suppl 1: p. S16-23. [CrossRef]
- Lamp, K.C., et al., Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the nitroimidazole antimicrobials. Clin Pharmacokinet, 1999. 36(5): p. 353-73. [CrossRef]
- Karamanakos, P.N., et al., Pharmaceutical agents known to produce disulfiram-like reaction: effects on hepatic ethanol metabolism and brain monoamines. Int J Toxicol, 2007. 26(5): p. 423-32. [CrossRef]
- Alonzo, M.M., T.V. Lewis, and J.L. Miller, Disulfiram-like Reaction With Metronidazole: An Unsuspected Culprit. J Pediatr Pharmacol Ther, 2019. 24(5): p. 445-449.
- Poeschl, P.W., et al., Antibiotic susceptibility and resistance of the odontogenic microbiological spectrum and its clinical impact on severe deep space head and neck infections. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod, 2010. 110(2): p. 151-6.
- Kuriyama, T., et al., Bacteriologic features and antimicrobial susceptibility in isolates from orofacial odontogenic infections. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod, 2000. 90(5): p. 600-8.
- Kuriyama, T., et al., Past administration of beta-lactam antibiotics and increase in the emergence of beta-lactamase-producing bacteria in patients with orofacial odontogenic infections. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod, 2000. 89(2): p. 186-92.
- Egwari, L.O., et al., Bacteriological and clinical evaluation of twelve cases of post-surgical sepsis of odontogenic tumours at a referral centre. East Afr Med J, 2008. 85(6): p. 269-74.
- Boyanova, L., et al., Anaerobic bacteria in 118 patients with deep-space head and neck infections from the University Hospital of Maxillofacial Surgery, Sofia, Bulgaria. J Med Microbiol, 2006. 55(Pt 9): p. 1285-1289.
- Eick, S., W. Pfister, and E. Straube, Antimicrobial susceptibility of anaerobic and capnophilic bacteria isolated from odontogenic abscesses and rapidly progressive periodontitis. Int J Antimicrob Agents, 1999. 12(1): p. 41-6.
- Patel, M., The prevalence of beta lactamase-producing anaerobic oral bacteria in South African patients with chronic periodontitis. SADJ, 2011. 66(9): p. 416-8.
- Alou, L., et al., In vitro killing activity of crevicular concentrations of tinidazole plus common oral antibiotics against high-density mixed inocula of periodontal pathogens in strict anaerobic conditions. J Periodontol, 2010. 81(1): p. 131-8.
- Roche, Y. and R.N. Yoshimori, In-vitro activity of spiramycin and metronidazole alone or in combination against clinical isolates from odontogenic abscesses. J Antimicrob Chemother, 1997. 40(3): p. 353-7.
- Chan, Y. and C.H. Chan, Antibiotic resistance of pathogenic bacteria from odontogenic infections in Taiwan. J Microbiol Immunol Infect, 2003. 36(2): p. 105-10.
- Kuriyama, T., et al., Incidence of beta-lactamase production and antimicrobial susceptibility of anaerobic gram-negative rods isolated from pus specimens of orofacial odontogenic infections. Oral Microbiol Immunol, 2001. 16(1): p. 10-5.
- Maestre, J.R., et al., Odontogenic bacteria in periodontal disease and resistance patterns to common antibiotics used as treatment and prophylaxis in odontology in Spain. Rev Esp Quimioter, 2007. 20(1): p. 61-7.
- Chunduri, N.S., et al., Evaluation of bacterial spectrum of orofacial infections and their antibiotic susceptibility. Ann Maxillofac Surg, 2012. 2(1): p. 46-50.
- Bigus, S., et al., Antibiotic resistance of the bacterial spectrum of deep space head and neck infections in oral and maxillofacial surgery - a retrospective study. Clin Oral Investig, 2023. 27(8): p. 4687-4693. [CrossRef]
- Humphries: R., et al., Overview of Changes to the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, M100, 31st Edition. J Clin Microbiol, 2021. 59(12): p. e0021321. [CrossRef]


| Anaerobic Gram-negative rods MBC (μg/mL) |
||
| Ampicillin + Sulbactam | 1 | Susceptible |
| Clindamycin | 256 | Resistant |
| Meropenem | 0.25 | Susceptible |
| Metronidazole | 0.5 | Susceptible |
| Susceptibility | ||
| Prevotella intermedia | ||
| Antibiotic | Interpretation | Value Comment (μg/mL) |
| Ampicillin + Sulbactam | Susceptible | <=0.03 |
| Clindamycin | Susceptible | <=0.03 |
| Meropenem | Susceptible | 0.06 |
| Metronidazole | Susceptible | 0.12 |
| Fusobacterium Species | ||
| Ampicillin + Sulbactam | Susceptible | <=0.03 |
| Clindamycin | Susceptible | 0.06 |
| Meropenem | Susceptible | 0.03 |
| Metronidazole | Susceptible | <=0.03 |
| Ampicillin-Sulbactam | Pipercillin-tazobactam | Imipenem | Meropenem | |||||||||
| Anaerobic Organisms | # of strains | %S | %R | # of strains | %S | %R | # of strains | %S | %R | # of strains | %S | %R |
| Prevotella spp. | 29 | 97 | 3 | 63 | 100 | 0 | 29 | 100 | 0 | 92 | 98 | 0 |
| Fusobacterium spp | 20 | 100 | 0 | 55 | 96 | 2 | 75 | 95 | 4 | 20 | 100 | 0 |
| Anaerobic gram positive cocci | - | - | - | 1853 | 99 | 1 | 134 | 99 | 0 | 1647 | 100 | 0 |
| Clostridium perfringens | 15 | 100 | 0 | 410 | 100 | 0 | 23 | 100 | 0 | 417 | 100 | 0 |
| Clostridioides | 76 | 99 | 0 | 542 | 93 | 0 | 480 | 69 | 4 | 609 | 99 | 0 |
| Clostridium spp. | - | 439 | 94 | 1 | 71 | 99 | 0 | 390 | 100 | 0 | ||
| Penicillin | Clindamycin | Moxifloxacin | Metronidazole | |||||||||
| Anaerobic Organisms | # of strains | %S | %R | # of strains | %S | %R | # of strains | %S | %R | # of strains | %S | %R |
| Prevotella spp. | 63 | 100 | 0 | 29 | 69 | 28 | 92 | 66 | 25 | 92 | 99 | 0 |
| Fusobacterium spp | - | - | - | 75 | 77 | 21 | 75 | 68 | 23 | 75 | 95 | 5 |
| Anaerobic gram positive cocci | 1647 | 100 | 0 | 1826 | 97 | 3 | 300 | 72 | 21 | 0 | 100 | 0 |
| Clostridium perfringens | 402 | 90 | 4 | 425 | 83 | 12 | 23 | 83 | 9 | 425 | 100 | 0 |
| Clostridioides | 533 | 6 | 37 | 1013 | 32 | 38 | 480 | 74 | 25 | 1343 | 100 | 0 |
| Clostridium spp. | 390 | 69 | 13 | 461 | 67 | 25 | 71 | 62 | 35 | 461 | 100 | 119 |
| Resistant strains (n [%]) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amoxicillin | Meropenem | Clindamycin | Metronidazole | |
| Species | ||||
| Breakpoint (mg/L) | R>2 | R>8 | R>4 | R>4 |
| P. baroniae (n=2) | 1 (50.0) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| P. bergensis (n=3) | 2 (66.7) | 0 | 2 (66.7) | 0 |
| P. bivia (n=17) | 9 (52.9) | 0 | 2 (11.8) | 1 (5.9) |
| P. buccae (n=13) | 5 (38.5) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| P. buccalis (n=3) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| P. copri (n=2) | 1 (50.0) | 0 | 1 (50.0) | 0 |
| P. denticola (n=7) | 4 (57.1) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| P. disiens (n=4) | 1 (25.0) | 0 | 2 (50.0) | 0 |
| P. histicola (n=2) | 1 (50.0) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| P. intermedia (n=4) | 1 (25.0) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| P. jejuni (n=2) | 2 (100) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| P. melaninogenica (n=21) | 14 (66.7) | 0 | 1 (4.8) | 1 (4.8) |
| P. nigrescens (n=4) | 3 (75.0) | 0 | 1 (25.0) | 0 |
| P. oris (n=2) | 2 (100) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| P. timonensis (n=6) | 1 (16.7) | 0 | 1 (16.7) | 0 |
| Prevotella spp. (n=7) | 1 (14.3) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Total, n (%) | 48 (48.5) | 0 | 10 (10.1) | 2 (2.0) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





