Submitted:
12 October 2024
Posted:
14 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
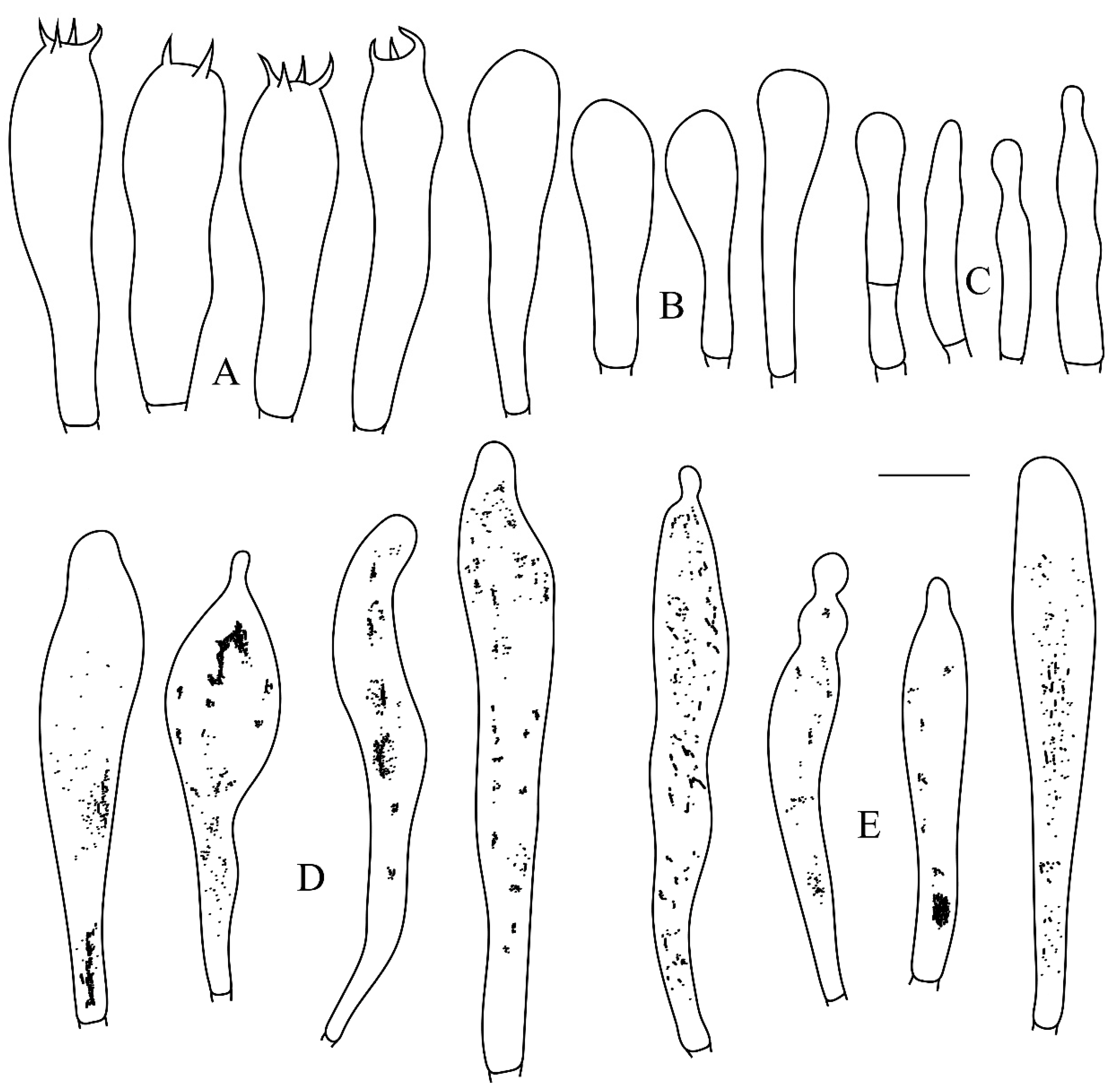
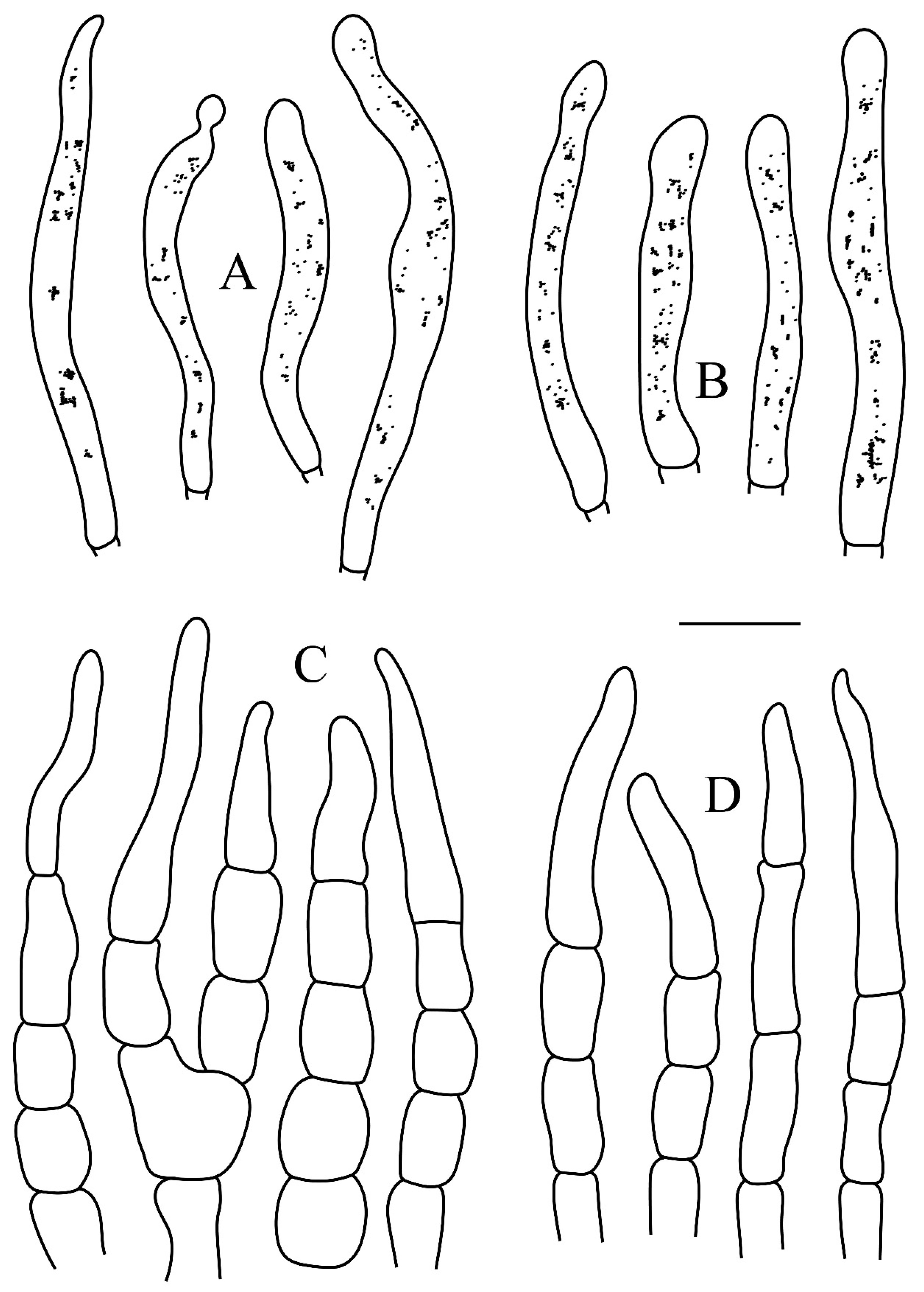
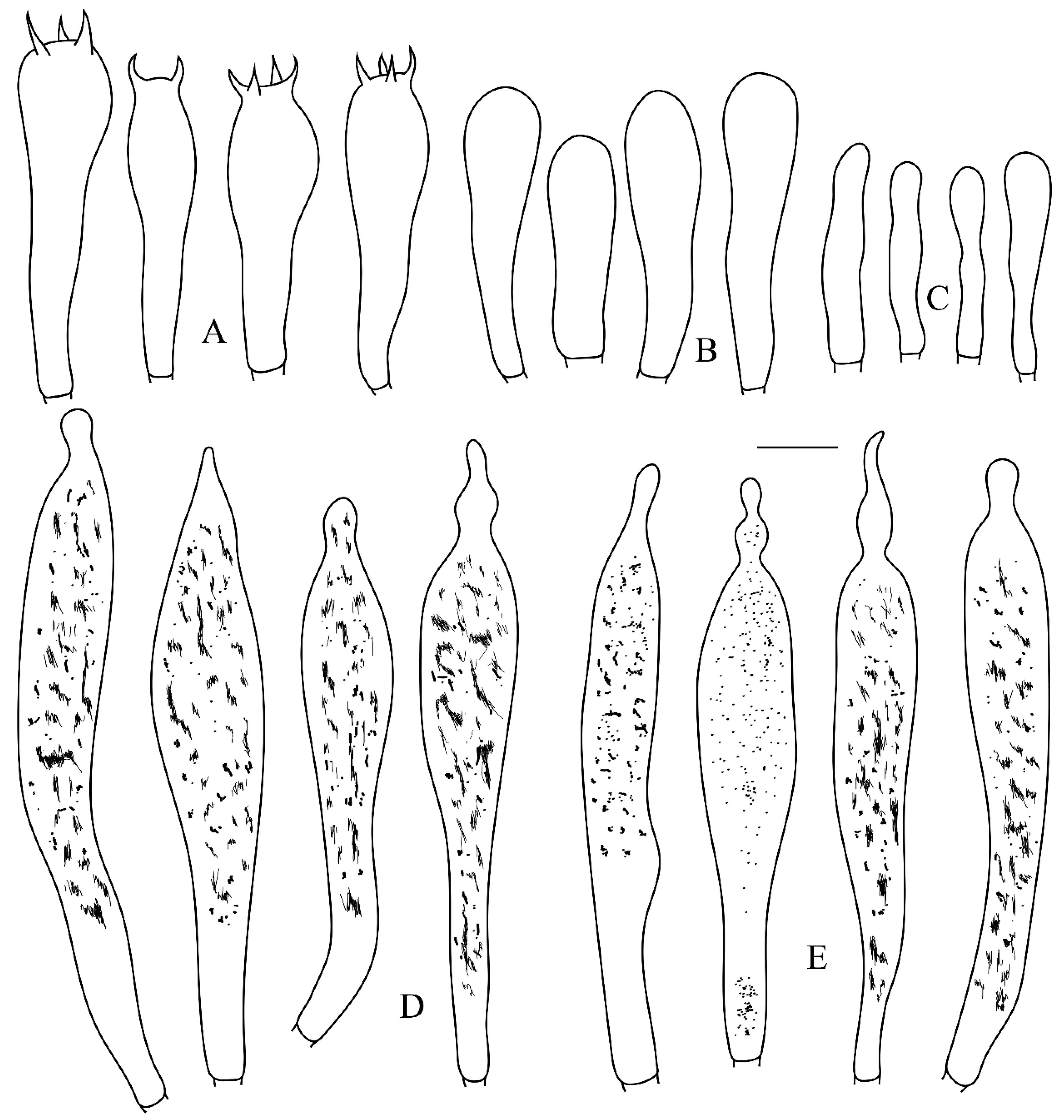
2.1. Morphological Studies
2.2. Molecular Study
2.3. Phylogenetic Analyses
3. Results
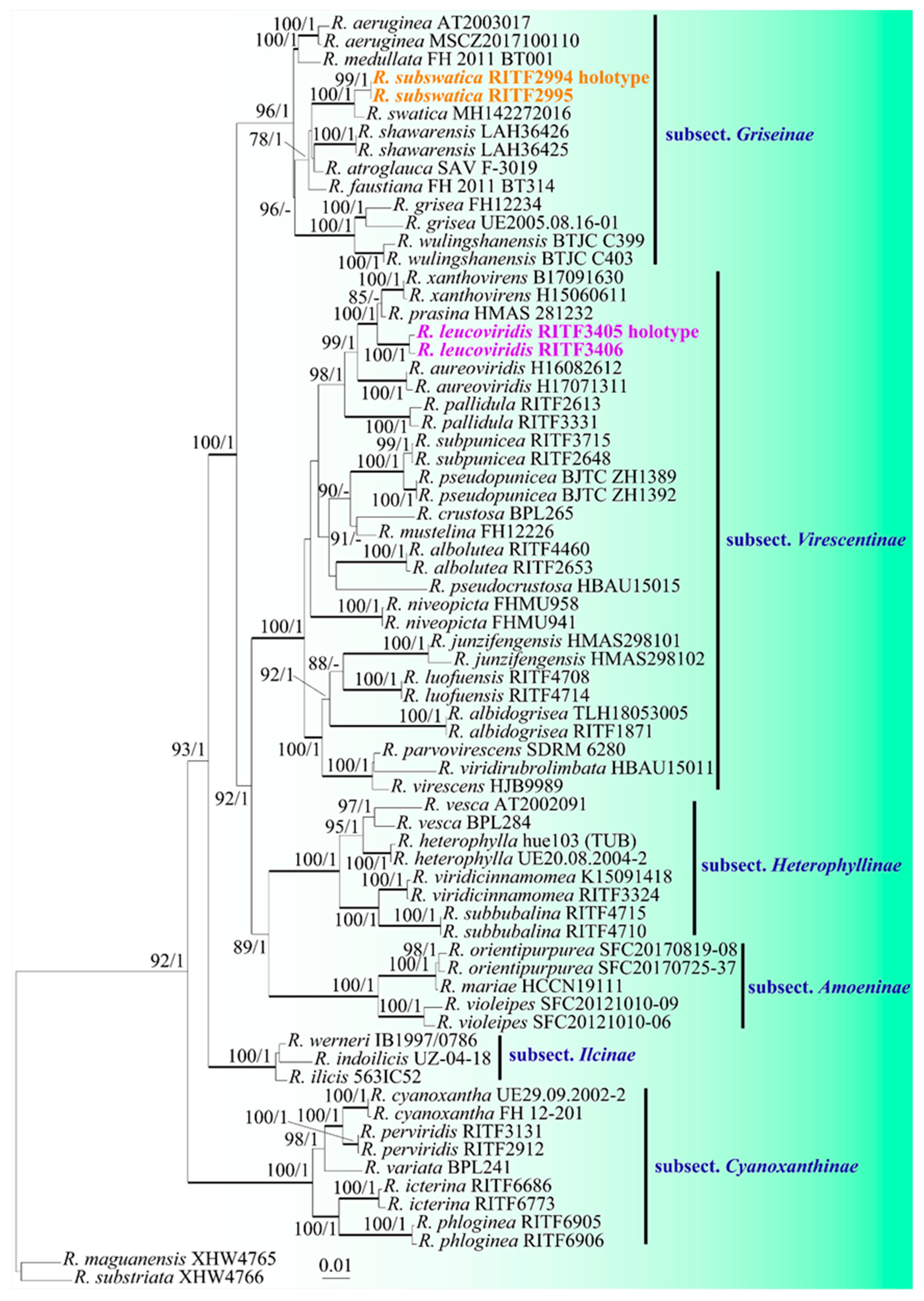
3.1. Phylogeny
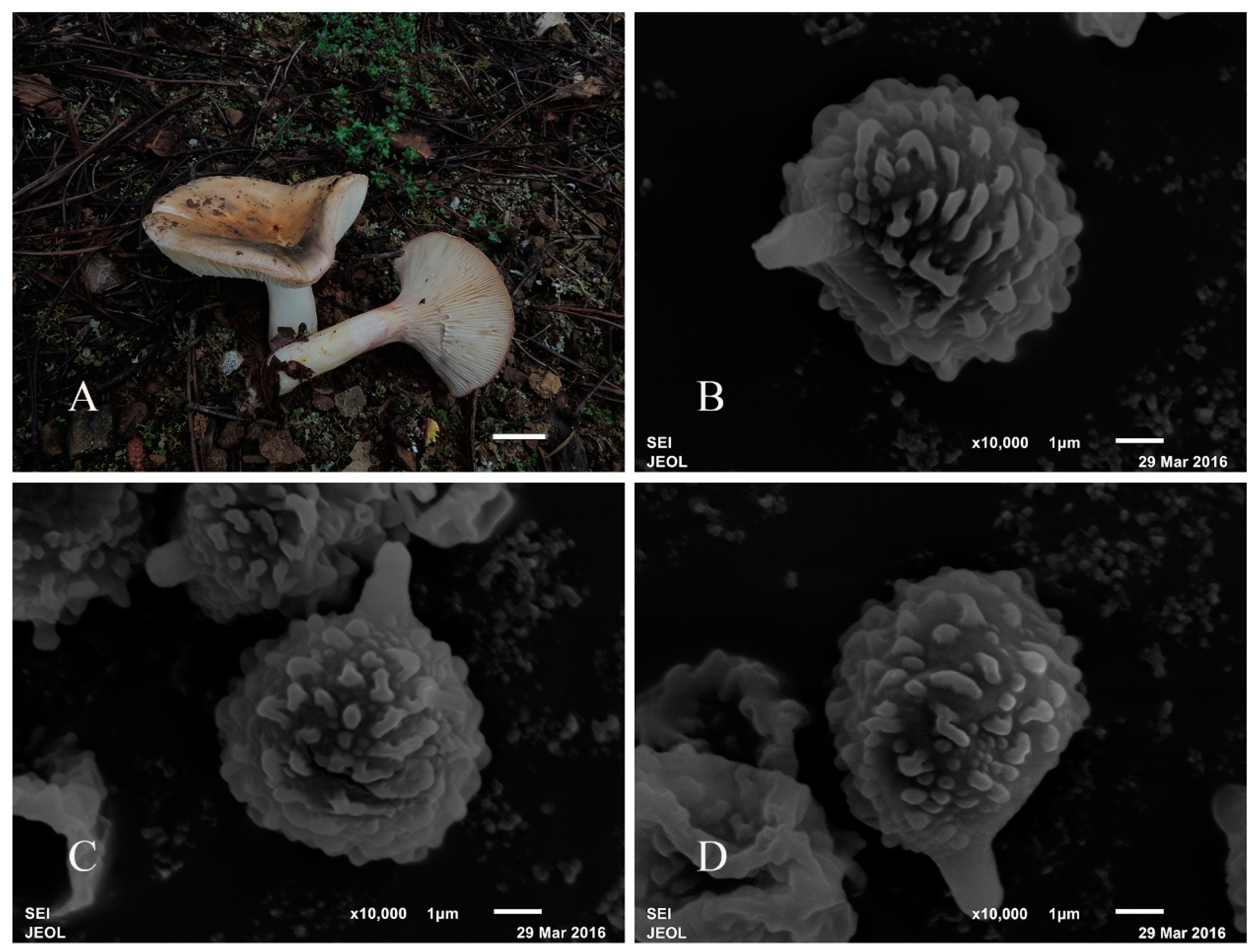
3.2. Taxonomy
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Buyck, B.; Zoller, S.; Hofstetter, V. Walking the thin line… ten years later: the dilemma of above- versus below-ground features to support phylogenies in the Russulaceae (Basidiomycota). Fungal Divers. 2018, 89, 267–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, MQ.; Cao, B.; Liu, F.; Boekhout, T.; Denchev, T.T.; Schoutteten, N.; Denchev, C.M.; Kemler, M.; Gorjón, S.P.; et al. Phylogenomics, divergence times and notes of orders in Basidiomycota. Fungal Divers. 2024, 89, 127–406. [Google Scholar]
- Adamčík, S.; Looney, B.; Caboň, M.; Jančovičová, S.; Adamčíková, K.; Avis, P.G.; Barajas, M.; Bhatt, R.P.; Corrales, A.; Das, K.; Hampe, F.; Ghosh, A.; et al. The quest for a globally comprehensible Russula language. Fungal Divers. 2019, 99, 369–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijayawardene, N.N.; Hyde, K.D.; Dai, D.Q.; Sánchez-García, M.; Goto, B.T.; Saxena, R.K.; Erdoğdu, M.; Selçuk, F.; et al. Outline of Fungi and fungus-like taxa–2021. Mycosphere 2022, 13, 53–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackel, J.; Henkel, T.W.; Moreau, P.A.; De Crop, E.; Verbeken, A.; Sà, M.; Buyck, B.; Neves, M.A.; Vasco-Palacios, A.; Wartchow, F.; Schimann, H.; Carriconde, F.; et al. Biogeographic history of a large clade of ectomycorrhizal fungi, the Russulaceae, in the Neotropics and adjacent regions. New Phytol. 2022, 236, 698–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Looney, B.; Miyauchi, S.; Morin, E.; Drula, E.; Courty, P.E.; Kohler, A.; Kuo, A.; Labutti, K.; Pangilinan, J.; Lipzen, A.; et al. Evolutionary transition to the ectomycorrhizal habit in the genomes of a hyperdiverse lineage of mushroom-forming fungi. New Phytol. 2022, 233, 2294–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noffsinger, C.R.; Adamčikova, K.; Eberhardt, U.; Caboň, M.; Bazzicalupo, A.; Buyck, B.; Kaufmann, H.; Weholt, Ø.; Looney, B.P.; Matheny, P.B.; Berbee, M.L.; Tausan, D.; Adamčik, S. Three new species in Russula subsection Xerampelinae supported by genealogical and phenotypic coherence. Mycologia 2024, 116, 322–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudsen, H.; Borgen, T. Russulaceae in Greenland. In Arctic and Alpine Mycology 1; University of Washington Press: Seattle, WA, USA, 1982; pp. 1–559. [Google Scholar]
- Looney, B.P.; Meidl, P.; Piatek, M.J.; Miettinen, O.; Martin, F.M.; Matheny, P.B.; Labbé, J.L. Russulaceae: a new genomic dataset to study ecosystem function and evolutionary diversification of ectomycorrhizal fungi with their tree associates. New Phytol. 2018, 218, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.H. Taxonomic comments on edible species of Russulaceae. Mycosystema 2020, 39, 1617–1639. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.H.; Wang, J.; Li, S.H.; Qin, W.Q.; Li, H.J.; Wang, X.H. Clarifying the identity of marketed edible Huotanjun (Burnt Charcoal Mushroom) in southern China. Mycol. Prog. 2023, 22, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Zhou, L.W.; Yang, Z.L.; Bau, T.; Li, T.H.; Dai, Y.C. Resource diversity of Chinese macrofungi: edible, medicinal and poisonous species. Fungal Diversi. 2019, 98, 1–76. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, C.Y.; Shi, L.Y.; Wang, J.; Xiang, Z.; Li, S.M.; Li, G.J.; Yang, H. Species diversity of Russula virescens complex “qingtoujun” in southern China. Mycosystema 2020, 39, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Buyck, B.; Zoller, S.; Hofstetter, V. Walking the thin line... ten years later: The dilemma of above- versus below-ground features to support phylogenies in the Russulaceae (Basidiomycota). Fungal Divers. 2018, 89, 267–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buyck, B.; Wang, X.H.; Adamčíková, K.; Caboň, M.; Jančovičová, S.; Hofstetter, V.; Adamčík, S. One step closer to unravelling the origin of Russula: subgenus Glutinosae subg. nov. Mycosphere 2020, 11, 285–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buyck, B.; Horak, E.; Cooper, J.A.; Wang, X.H. Russula subgen. Cremeoochraceae sub gen. nov.: A very small and ancient lineage sharing with Multifurca (Russulaceae) an identical, largely circum-Pacific distribution pattern. Fungal Syst. Evol. 2024, 14, 109–126. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.J.; Li, S.M.; Buyck, B.; Zhao, S.Y.; Xie, X.J.; Shi, L.Y.; Deng, C.Y.; Meng, Q.F.; Sun, Q.B.; Yan, J.Q.; Wang, J.; Li, M. Three new Russula species in sect. Ingratae (Russulales, Basidiomycota) from southern China. MycoKeys 2021, 84, 103–139. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.; Song, J.; Chen, Y.L.; Zhang, J.H.; Liang, J.F. Morphological and phylogenetic evidence for two new species of Russula subg. Heterophyllidia from Guangdong Province of China. MycoKeys 2021, 82, 139–157. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Song, Y. Species of Russula subgenus Heterophyllidiae (Russulaceae, Basidiomycota) from Dinghushan biosphere reserve. Eur. J. Taxon. 2022, 826, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.X.; Liang, Z.Q.; Zeng, N.K. Notes on four species of Russula subgenus Heterophyllidiae (Russulaceae, Russulales) from southern China. Front. Microbiol 2023, 14, 1140127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.L.; Chen, B.; Liang, R.X.; Wang, S.K.; An, M.Y.; Zhang, J.H.; Liang, J.Y.; Wang, Y.X.; Gao, X.L.; Liang, J.F. Four new species of Russula subsect. Cyanoxanthinae from China (Russulales, Russulaceae). MycoKeys 2024, 107, 21–50. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.L.; Liang, J.F.; Wang, S.K.; Chen, B.; Zhang, J.H.; An, M.Y.; Li, X.; Gao, X.L.; Chen, X.; Liao, J.P. Notes on two new species of Russula subsect. cyanoxanthinae (Russulaceae, Russulales) from southern china. Mycol. Prog 2024, 23, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornerup, A.; Wanscher, J.H. Taschenlexikon der Farben, 3rd ed.; Muster-Schmidt Verlag: Göttingen, Germany, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Adamčík, S.; Marhold, K. Taxonomy of the Russula xerampelina group. I. Morphometric study of the Russula xerampelina group in Slovakia. Mycotaxon 2000, 76, 463–480. [Google Scholar]
- Buyck, B. The study of microscopic features in Russula 2. Sterile cells of the hymenium. Russulales News 1991, 1, 62–85. [Google Scholar]
- Caboň, M.; Eberhardt, U.; Looney, B.; Hampe, F.; Kolařík, M.; Jančovičová, S.; Verbeken, A.; Adamčík, S. New insights in Russula subsect. Rubrinae: Phylogeny and the quest for synapomorphic characters. Mycol. Prog. 2017, 16, 877–892. [Google Scholar]
- Buyck, B. Valeur taxonomique du bleu de crésyl pour le genre Russula. Bull. De La Société Mycol. De Fr. 1989, 105, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.L.; Liang, J.F. An improved protocol for extraction of DNA from macrofungi. Guangdong Fore. Sci. Tech. 2011, 27, 13–16. [Google Scholar]
- White, T.J.; Bruns, T.; Lee, S.; Taylor, J. Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. PCR Protocols: A Guide to Methods and Applications; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1990; Volume 18, pp. 315–322. [Google Scholar]
- Vilgalys, R.; Hester, M. Rapid genetic identification and mapping enzymatically amplified ribosomal DNA from several Cryptococcus species. J. Bacteriol. 1990, 172, 4238–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.J.; Hall, B.D. Body plan evolution of ascomycetes, as inferred from an RNA polymerase II, phylogeny. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 13, 4507–4512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matheny, P.B. Improving phylogenetic inference of mushrooms with RPB1 and RPB2 nucleotide sequences (Inocybe; Agaricales). Mol. Phyl. Evol. 2005, 35, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, T.A. BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Hyde, K.D.; Tennakoon, D.S.; Jeewon, R.; Bhat, D.J.; Maharachchikumbura, S.S.N.; Rossi, W.; Leonardi, M.; Lee, H.B.; Mun, H.Y.; et al. Fungal diversity notes 1036-1150: taxonomic and phylogenetic contributions on genera and species of fungal taxa. Fungal Divers 2019, 96, 1–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Li, J.W.; Buyck, B.; Zheng, J.F.; Qiu, L.H. Russula verrucospora sp. nov. and R. xanthovirens sp. nov., two novel species of Russula (Russulaceae) from southern China. Cryptogamie Mycol 2018, 39, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarnari, M. Monografia illustrate de genere Russula in Europa; Secondo, T., Ed.; AMB, Centro Studi Micologici: Trento, Italy, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Buyck, B.; Mitchell, D.; Parrent, J. Russula parvovirescens sp. nov., a common but ignored species in the eastern United States. Mycologia 2006, 98, 612–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, J.Z. A study on Russula viridi-rubrolimata sp. nov. and its related species of subsection Virescentinas. Acta Mycol Sin 1983, 2, 34–37. [Google Scholar]
- Adamčík, S.; Jančovičová, S.; Buyck, B. The Russulas described by Charles Horton Peck. Cryptogamie Mycol 2018, 39, 3–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwar, S.; Aziz, T.; Hanif, M.; Ilyas, S.; Shaheen, S. Russula swatica: A new species of Russula based on molecular, light microscopy, and scanning electron microscopy analyses from Swat Valley of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province of Pakistan. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2019, 82, 1700–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mleczko, P. ; M. Kozak, and S. Zubek. Russula medullata (russulales, basidiomycota): A new species in the mycobiota or Poland. Pol. Bot. J. 2010; 55, 483–488. [Google Scholar]
- Crous, P.W.; Cowan, D.A.; Maggs-Kölling, G.; Yilmaz, N.; Larsson, E.; Angelini, C.; Brandrud, T.E.; Dearnaley, J.D.W.; et al. Fungal Planet description sheets: 1112-1181. Persoonia 2020, 45, 251–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Taxon | Voucher | Location | ITS | LSU | RPB2 | mtSSU |
| R. aeruginea | AT2003017 | Sweden | DQ421999 | DQ421999 | DQ421946 | – |
| R. aeruginea | MSCZ2017100110 | China | MH422576 | MK881944 | – | MK882072 |
| R. albidogrisea | TLH18053005 | China | MN275581 | MN839562 | MT085637 | MN839610 |
| R. albidogrisea | RITF1871 | China | MW397095 | MW397128 | – | MW403841 |
| R. albolutea | RITF2653 | China | MT672478 | MW397120 | MW411340 | MW403833 |
| R. albolutea | RITF4460 | China | MT672475 | MW397121 | MW411341 | MW403834 |
| R. atroglauca | SAV F-3019 | Slovakia | MT738270 | MT738248 | MT732156 | – |
| R. aureoviridis | H17071311 | China | MN275564 | MN839561 | MT085636 | MN839609 |
| R. aureoviridis | H16082612 | China | KY767809 | MK881920 | – | MK882048 |
| R. crustosa | BPL265 | USA | KT933966 | KT933826 | KT933898 | – |
| R. cyanoxantha | FH 12-201 | Germany | KR364093 | KR364225 | KR364341 | – |
| R. cyanoxantha | UE29.09.2002-2 | France | DQ422033 | DQ422033 | DQ421970 | – |
| R. faustiana | FH 2011 BT314 | Germany | MT738277 | MT738253 | MT732162 | – |
| R. grisea | FH12234 | Germany | KT934006 | KT933867 | KT933938 | – |
| R. grisea | UE2005.08.16-01 | Germany | DQ422030 | DQ422030 | DQ421968 | – |
| R. heterophylla | hue103 (TUB) | Europe | AF418609 | AF325309 | – | – |
| R. heterophylla | UE20.08.2004-2 | Sweden | DQ422006 | DQ422006 | DQ421951 | – |
| R. icterina | RITF6686 | China | PP700452 | PP700462 | PP707790 | PP700443 |
| R. icterina | RITF6773 | China | PP700453 | PP700463 | PP707792 | PP700445 |
| R. ilicis | 563IC52 | Europe | AY061682 | – | – | – |
| R. indoilicis | UZ-04-18 | India | MW547505 | – | – | – |
| R. junzifengensis | HMAS298101 | China | OR826832 | OR826833 | OR915864 | OR941507 |
| R. junzifengensis | HMAS298102 | China | OR880061 | OR880054 | OR915865 | OR941508 |
| R. leucoviridis | RITF3405 | China | PQ373872 | PQ373868 | PQ381291 | PQ373876 |
| R. leucoviridis | RITF3406 | China | PQ373873 | PQ373869 | PQ381292 | PQ373877 |
| R. luofuensis | RITF4708 | China | MW646975 | MW646987 | – | MW646998 |
| R. luofuensis | RITF4714 | China | MW646977 | MW646989 | – | MW647000 |
| R. maguanensis | XHW4765 | China | MH724918 | MH714537 | MH939989 | OQ586179 |
| R. mariae | HCCN19111 | South Korea | KF361762 | KF361812 | KF361712 | – |
| R. medullata | FH 2011 BT001 | Germany | MT738280 | MT738256 | MT732166 | – |
| R. mustelina | FH12226 | Germany | KT934005 | KT933866 | KT933937 | – |
| R. niveopicta | FHMU958 | China | OP837461 | OP837453 | – | – |
| R. niveopicta | FHMU941 | China | OP837462 | OP837454 | – | – |
| R. orientipurpurea | SFC20170819-08 | South Korea | MT017550 | – | MT199638 | MT196926 |
| R. orientipurpurea | SFC20170725-37 | South Korea | MT017548 | – | MT199639 | MT196927 |
| R. pallidula | RITF2613 | China | MH027958 | MH027960 | MH091698 | MW403845 |
| R. pallidula | RITF3331 | China | MH027959 | MH027961 | MH091699 | MW403846 |
| R. parvovirescens | SDRM 6280 | USA | MK532789 | – | – | – |
| R. perviridis | RITF3131 | China | OR907098 | OR907072 | OR914548 | OR934523 |
| R. perviridis | RITF2912 | China | OR907100 | OR907070 | OR914547 | OR934522 |
| R. phloginea | RITF6905 | China | OR907116 | OR907051 | OR914555 | OR934516 |
| R. phloginea | RITF6906 | China | OR907117 | OR907055 | OR914558 | OR934520 |
| R. prasina | HMAS 281232 | China | MH454351 | – | – | – |
| R. pseudocrustosa | HBAU15015 | China | MT337520 | – | – | – |
| R. pseudopunicea | BJTC ZH1392 | China | OP133164 | OP133204 | OP156853 | OP143937 |
| R. pseudopunicea | BJTC ZH1389 | China | OP133163 | OP133203 | OP156852 | OP143936 |
| R. shawarensis | LAH36425 | Pakistan | MT738293 | MT738267 | MT732176 | – |
| R. shawarensis | LAH36426 | Pakistan | MT738292 | MT738268 | MT732177 | – |
| R. subbubalina | RITF4710 | China | MW646978 | MW646990 | – | MW647001 |
| R. subbubalina | RITF4715 | China | MW646979 | MW646991 | – | MW647002 |
| R. subpunicea | RITF3715 | China | MN833635 | MW397124 | MW411344 | MW403837 |
| R. subpunicea | RITF2648 | China | MN833638 | MW397125 | MW411345 | MW403838 |
| R. substriata | XHW4766 | China | MH724921 | MH714540 | MH939992 | OQ371394 |
| R. subswatica | RITF2994 | China | PQ373870 | PQ373866 | – | PQ373874 |
| R. subswatica | RITF2995 | China | PQ373871 | PQ373867 | – | PQ373875 |
| R. swatica | MH142272016 | Pakistan | MK389374 | – | – | – |
| R. variata | BPL241 | USA | KT933959 | KT933818 | KT933889 | – |
| R. vesca | AT2002091 | Sweden | DQ422018 | DQ422018 | DQ421959 | – |
| R. vesca | BPL284 | USA | KT933978 | KT933839 | KT933910 | – |
| R. violeipes | SFC20121010-06 | South Korea | KF361808 | KF361858 | KF361758 | – |
| R. violeipes | SFC20121010-09 | South Korea | KF361807 | KF361857 | KF361757 | – |
| R. virescens | HJB9989 | Belgium | DQ422014 | DQ422014 | DQ421955 | – |
| R. viridicinnamomea | RITF3324 | China | MW397098 | MW397130 | MW411348 | MW403847 |
| R. viridicinnamomea | K15091418 | China | MK049972 | MK881938 | – | MK882066 |
| R. viridirubrolimbata | HBAU15011 | China | MT337526 | – | – | – |
| R. werneri | IB1997/0786 | Sweden | DQ422021 | – | – | – |
| R. wulingshanensis | BTJC C403 | China | OP133166 | OP133206 | OP156855 | OP143939 |
| R. wulingshanensis | BTJC C399 | China | OP133165 | OP133205 | OP156854 | OP143938 |
| R. xanthovirens | H15060611 | China | MG786056 | MN839560 | T085635 | MN839608 |
| R. xanthovirens | B17091630 | China | MG786055 | MK881928 | – | MK882056 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




