1. Introduction
By 2050, more than two million people worldwide will be over 60 years of age [
1]. These demographic changes will cause an increase in chronic non-communicable diseases (CNCDs) such as cardiovascular and respiratory diseases, diabetes, cancer, and mental disorders, which are already major causes of illness, death, and disability in the Americas [
1,
2]. Moreover, mental disorders, substance use, injuries caused by traffic accidents, and interpersonal violence can lead to disabilities [
2].
Disability limits the equal participation of people in society [
3] and increases the demand and need for health services and long-term care [
4], owing to the dependence that disabilities generate. In most cases, this care is provided by a family member who does not receive remuneration [
5,
6]. Chronicity, which is characterized by the progression of disease over time and its inherent complications, gives rise to a situation of dependence, which in turn necessitates the presence of a caregiver.
The care provided by caregivers involves helping with transportation, preparing food, cleaning the house, washing and mending clothes, providing personal care, administering treatment, performing medical procedures, scheduling, managing care actions, and taking care of financial activities [
6]. The care of people in a situation of dependency is mostly related to poverty and is considered a private problem that must be solved by the family; it is a task that is mainly delegated to the women of the family [
7,
8].
Historically, women have been considered responsible for caregiving tasks because of their nature and gender-cultural influences [
8,
9]. These influences guide women to take care of their children or parents out of moral responsibility or debt; in addition, they face strong social pressure to take on the role of caregiver [
1]. Thus, the feminization of care persists. The care of sick people is delegated to women because of their status as mothers, wives, or daughters, which makes them responsible for these tasks and their costs. This responsibility limits their social, economic, and affective development in the public sphere, which then perpetuates the gender inequalities that endure today [
10].
Changes are occurring in the caregiver landscape for older adults; the number of men taking on the role of caregiver has increased in recent years [
11,
12,
13]. Despite this change, a greater proportion of women continue to exercise the role of caregiver, compared to men [
11,
13]. These differences in representation between men and women in caregiving are due to gender stereotypes that consider caregiving as a ‘feminine issue’ and a ‘feminine-type’ activity [
14].
However, male informal caregivers also face significant pressures. For example, male informal caregivers experience greater social distancing than women [
15], which negatively impacts their emotional and psychological well-being. In addition, men who take on the role of informal caregivers often face pressure to challenge gender stereotypes with the need to find a balance between caregiving and maintaining their masculine identity [
16,
17], which can lead to stress and feelings of isolation.
The understanding of how men approach caregiving, their coping mechanisms, and how this influences their identity and self-concept is still not as well understood as for women informal caregivers. The entry of men into what has traditionally been considered a predominantly female field should guide the understanding of how masculinities are constructed and carried out by men in caregiving tasks [
13]. Although men represent a minority among informal caregivers [
18], promoting greater male participation in informal care is necessary.
Breaking the roles traditionally assigned to women in care may be the change necessary for eliminating gender inequalities, which could in turn improve the quality of life of dependents, informal caregivers, and their families [
19]. Male informal caregivers are increasingly recognizing the importance of their roles in providing emotional and practical support to their loved ones, which is challenging the entrenched gender norms in society [
15].
Caring for people with chronic diseases negatively affects women’s health and well-being, as women represent the majority of informal caregivers. They experience greater stress and face worsening economic situations, resulting in poorer physical and psychological health compared to male informal caregivers [
8]. However, male informal caregivers also experience particular challenges, related to the increased effort to maintain their identity by adhering to masculine norms with a protective approach to caregiving, and reluctance to seek help or talk about their emotions leading to social distancing, which negatively affects their lives [
16]. It is essential to consider gender differences in caregiving experiences to promote inclusion and equity of informal caregivers.
This study collates and evaluates the voices of men and women who have taken on the responsibility of caregiving. We examine the tapestry of experiences that combine love and commitment. We explore the experiences of mothers, sons, daughters, wives, and husbands who have transformed their lives to care for loved ones who are in a situation of chronicity and exhibit a high degree of dependence; these are people who have taken on the caregiver role with strength and determination. Therefore, we propose a phenomenological-hermeneutic qualitative study aiming to understand the lived experiences of caregivers of people with CNCDs, and the meanings of care developed from the perspective of men and women, during their interactions with people afflicted by chronicity.
3. Results
Twenty informal caregivers—twelve women and eight men—were interviewed. The men were caregivers only to adults (
Table 1).
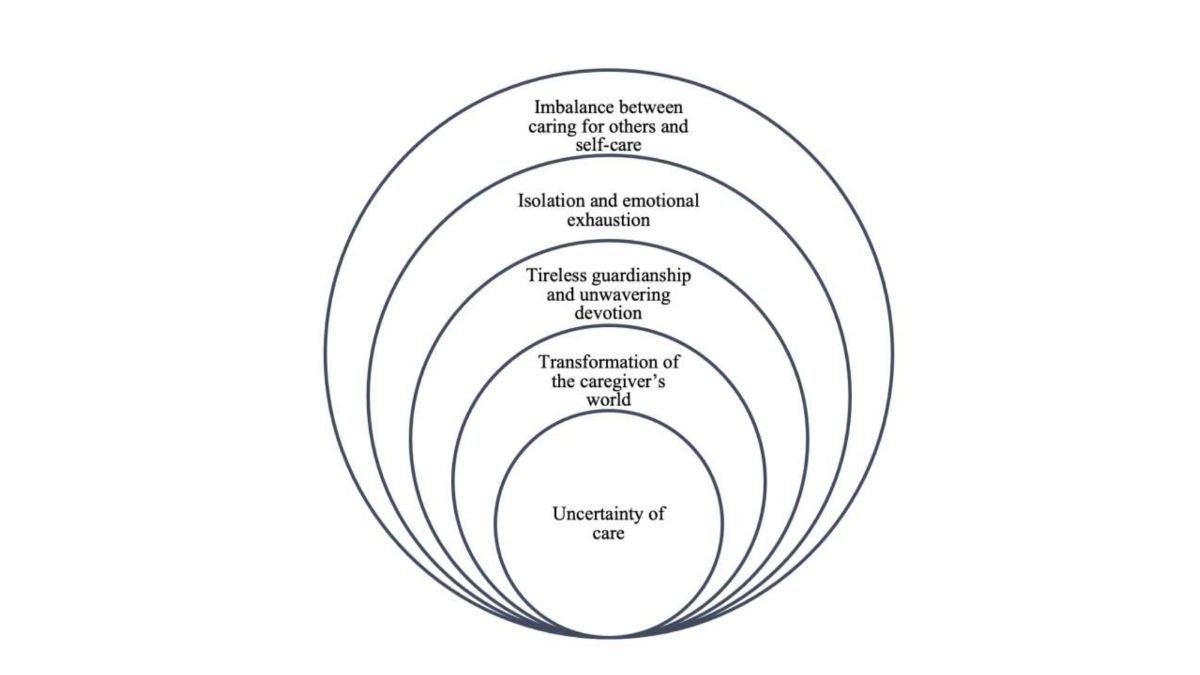
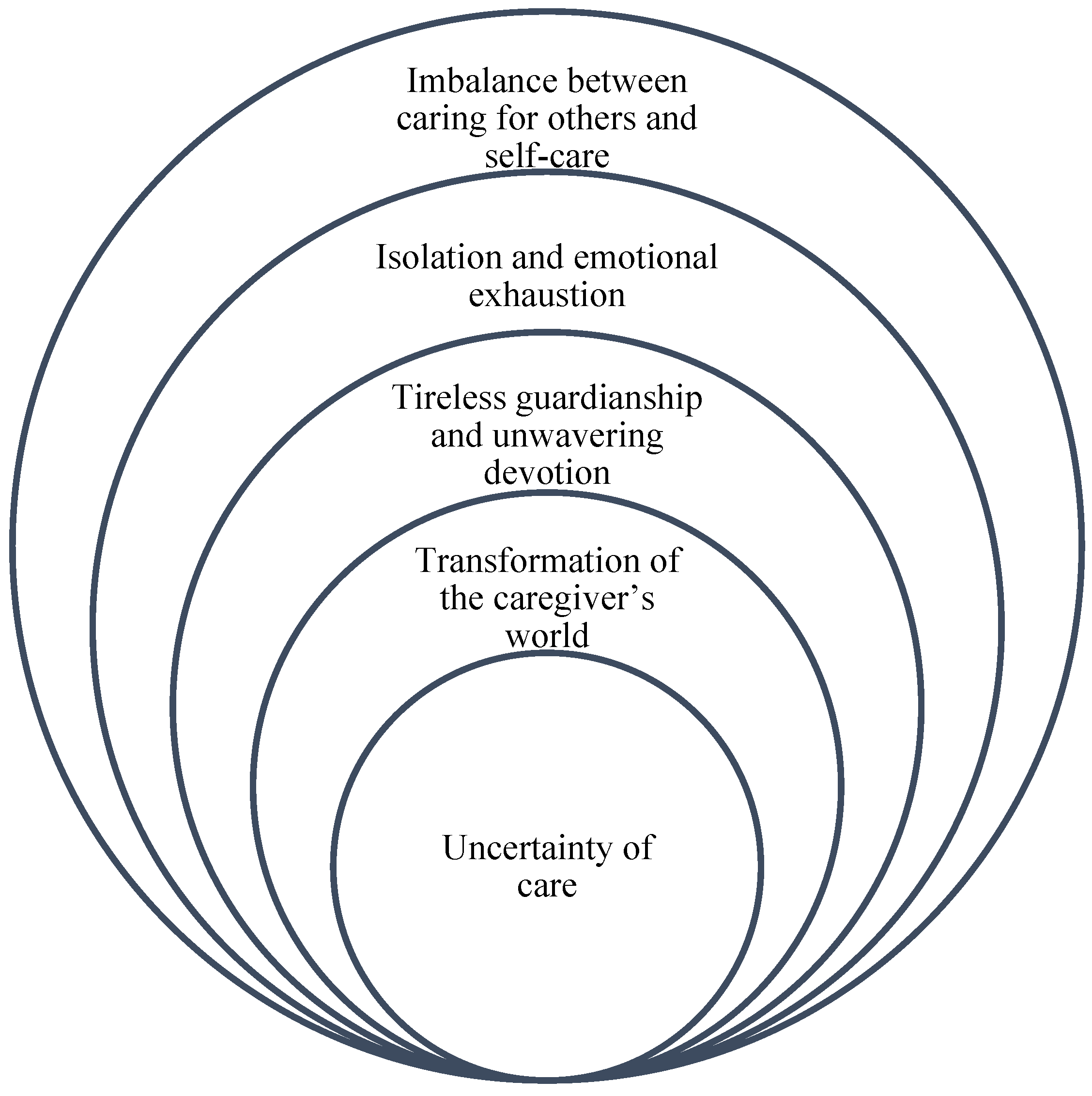
Analysis of the data yielded the following themes: uncertainty of care; transformation of the caregiver’s world; tireless guardianship and unwavering devotion; isolation and emotional exhaustion; and imbalance between caring for others and self-care. (
Figure 1).
Figure 1 symbolizes how each of the themes that emerged are interconnected and how one inevitably leads to the other. The uncertainty of caregiving is the basis that triggers a series of transformations and commitments that culminate in burnout and imbalance between caring for others and caring for oneself. This structure reflects the complex and multifaceted nature of informal caregivers' experience, where each issue is not only an independent phenomenon, but also part of an interrelated process that defines the totality of their experience.
Uncertainty of Care
Caregivers face harsh scenarios in light of their loved ones’ situations. It is not easy to assimilate reality; coping with the illness of loved ones without knowing how to take care of them is a complex and difficult challenge. The caregivers expressed that it was initially difficult to accept and understand the situation, and that over time, they learned to understand the patient better and communicate more effectively. They also expressed constant concern and a sense of insecurity about their loved one's futures, and their roles as caregivers. The constant challenges and difficulties produced anxiety, fear of ignorance and change, and feelings of emotional burden owing to the uncertainty associated with caregiving.
Women experienced a sense of uncertainty and constant anxiety. They used terms like ‘anxiety’, ‘loneliness’, and ‘emotional exhaustion’ to describe their experiences. They highlighted uncertainty about the future, the feeling of being in limbo, and not knowing what would happen next.
“The hardest thing about taking care of a person is living with the anxiety that one day they may leave... We may go to bed one night and find they do not wake up the next day.” (Olga)
“Ever since the beginning, I have felt uncertainty, loneliness, and permanent emotional exhaustion.” (Camila)
“For me, at the beginning, I felt fear, restlessness and anxiety, not knowing what was going to happen.” (Rocío)
“I was not used to dealing with a sick person like that... I cry; I sometimes sit down to cry about what has happened to me, that is, to have been left alone like this, to be with him like this.” (Melba)
In contrast, the men adopted a more pragmatic and process-oriented stance, focusing on the need to gradually adapt and acquire knowledge about the disease as the caregiving process progressed. This attitude may reflect an objective problem-solving approach adopted by the men.
“At first you are trying to adjust to the situation, it is like a process. As you are not fully prepared to understand it, the adjustment is always a difficult step.” (José)
“They (healthcare staff) only say ‘Give the drug to your mom like this or that’...and that's it. No one explains anything further to us.” (Pablo)
“Hemodialysis is too hard, sometimes you see difficulties in some things and if you go back...you don't know what to do.” (Raúl)
“I am worried about what will happen to my wife when I am no longer with her.” (Jairo)
Transformation of the Caregiver’s World
The participants' new roles imply adaptation and profound transformations of their lives, highlighting the necessity to develop emotional skills, such as patience, to meet the needs of their loved ones, which often go beyond the provision of just physical assistance. Some caregivers described the internal conflict they often faced between the desire to give up owing to emotional exhaustion, and the responsibility and commitment required to take care of their loved ones. It was the latter emotion that drove them to keep going.
Women highlighted the emotional and physical impacts of caregiving on their lives. They expressed the constant burden of responsibility, the internal struggle between tiredness and dedication, and reorientation of priorities toward the well-being of the person being cared for. Their approach was emotional and subjective, highlighting personal challenges and the transformation of their worlds, based on the demands of caregiving.
“I do not rest from taking care of her, I have no rest... I have to keep an eye on her, do my job and keep an eye on the child, one forgets to take care of oneself.” (Olga)
“One has to do more work; more dedication and effort is required on an emotional, economic, physical level, everything, everything... Sometimes you get up, and you do not want to start, you do not want to go on, but just seeing him... realizing how much he needs our care, that he needs us one hundred percent, you go back and start again.” (Rocío)
“Everything has been a process that has been carried out gradually. You must have a lot of patience; if you do not have patience, it is difficult, and sometimes there are inconveniences.” (Beatrice)
“Well, it changes everything because you do not think about anything else, you do not focus... you only think about the well-being of that person.” (Mery)
Men adapted to the role of caregivers by developing patience and managing their emotional burdens. Although they experienced stress, they showed the willingness to learn and adjust to the demands of caregiving. They highlighted the need to remain calm and attentive to the needs of their loved ones.
“I think the most important thing is patience. That is what I was telling them: I had to change to become patient. I know that the patients have an attitude, you have to get used to it and adapt to that change, right? You must be patient to understand their situation.” (Joseph)
“Well, it was difficult for me, but then you need to stand up and take on the burden.” (Jaime)
“Patient with a sick person, that is what you should be, I think. Give them their medicines on time and pay attention to everything that happens.” (Mario)
“For example, when I need to leave, the nurse stays. However, I cannot walk calmly, I get stressed. I am always stressed; sometimes I forget... but no, soon I stop doing other jobs... I have to go back to the stress of the illness.” (Pedro)
“Well, I would go and pick her up, bring her back and she would go to bed, because she didn't come in the mood for anything..., to handle the stress that they handle, plus the bad temper that was added... I would make lunch, help to pick up the mess or something.” (Raúl)
“I have to take care of everything she needs because I am responsible for her and that's the way it should be, sometimes I get stressed because there are many things, and all of them are important, so I tell myself I need to be patient.” (Jairo)
Tireless Guardianship and Unwavering Devotion
The caregivers expressed the need to be constantly attentive to their loved ones. This meant being available 24 hours a day and adapting their routines to meet patients’ needs. The care involved vigilance and attention to the changes in the patient’s condition. They had to be alert even at night, which prevented them from getting a good night's rest and led to stress, anxiety, and emotional exhaustion.
For women, care focused on the fragility and specific needs of the person in their charge. Caring was a responsibility that they took on with devotion; however, they did not necessarily see it as a moral obligation derived from the past, but as an expression of love and care toward a loved one who needed constant attention.
“I take constant care of her... I do not allow a third party to come and take care of my daughter, because she is fragile... first my daughter, then the rest, and even I can wait.” (Olga)
“I get up, give him breakfast, his medications, I have to be very attentive; I have to give my son food. So now I am living in terrible chaos, I have no one to help me. I have dedicated myself only to taking care of J.” (Ana)
Men perceived caregiving as a moral obligation. They felt that they could not abandon their parent/patient because of their gratitude for the love they received during their upbringing. Their commitment to caregiving was a way to give back what they received and express their gratitude toward the person they cared for.
“She is my mom, and I have always been looking out for her, and at this moment, she needs me the most; how am I going to abandon her? Especially as she never abandoned us.” (Pablo)
“Perhaps when I was little, when I was born, she went through similar situations with me... at the time, she did everything, now it is my turn to do it for her.” (José)
“I became aware that I have to stay with him until God gives me life and health, and to have the hope that he will be transplanted.” (Nicolás)
Isolation and Emotional Exhaustion
Caregivers expressed feelings of emotional and physical exhaustion, social isolation, the loss of other activities, and a constant psychological burden in their day-to-day lives, which negatively affected their quality of life and triggered depression and anxiety. Their social lives were affected by the demands of caregiving. They could not participate in social or leisure activities, and often sacrificed their social lives to ensure proper care.
The women highlighted the emotional exhaustion and sense of isolation they experienced as caregivers. They expressed an intense emotional burden and a sense of loneliness in their caregiving experience, as well as a lack of external support to cope with it.
“She is the priority, well, the truth is that I do not have a lot of time for myself; my priority is my daughter, as long as she is well, I am well...” (Berta)
“The only thing I go out for is medical appointments. I cannot say, ‘Oh, I am going to a shopping mall this afternoon, to hang out, to window shop’... I cannot... you cannot go out.” (Rocío)
“The caregiver works in solitude, a solitude that we are dragged into by the journey that people with Alzheimer’s make; we carry anguish, sadness, depression, a heavy suitcase that no one helps us carry.” (Beatrice)
Men mentioned the stress and physical fatigue associated with caregiving, and their concerns about leaving the person in their care alone. Their lives were centered around the practical responsibility of caregiving, which limited their ability to enjoy activities outside the home.
“You focus on the sick person...stress, and that makes you tired even if you are sitting there looking at him lying there.” (Mario)
“If I go out, she stays alone; because at these moments, I am thinking about it; because I leave her in a chair and she stays there, and because she does not sit up, you cannot go out.” (Felipe)
“I am tired and sick but I have to keep an eye on her, she was an excellent wife, now it is up to me to take care of her.” (Jairo)
Imbalance between Caring for Others and Self-Care
These excerpts show how informal caregivers face an imbalance between dedicating themselves to the care of their loved ones and attending to their own needs and desires. Responsibility toward others often takes precedence over self-care.
Women neglected their needs and desires, prioritizing the needs of their loved ones. Their identities and independence were often subordinated to their roles as caregivers, which led to an imbalance between caring for others and themselves.
“First comes my daughter. Sometimes, I ask myself the same thing: one forgets about being a woman and a person, when one is mother to a child with a disability or a person with a disability; sometimes I need to go out but do not, because she comes first.” (Olga)
“I take a back seat, my tiredness and pain are not important, it is not that it does not hurt. However, I care more about taking care of my mother; she always needs me, and I can wait, I can handle this.” (Luisa)
Men mentioned the challenge of balancing their own needs and desires with the demands of caregiving. Although they expressed the importance of caring for the person in their charge, they also mentioned the necessity of meeting their own needs for rest and well-being.
“You have to stop doing personal things for the good of the person, because what matters is the person. However, the situation in which we both live is complicated.” (Philip)
“I come home tired from work, wanting to sleep, but then I find her unwell; I have to... try to distract her, but I also want to go to sleep; so it’s these things that make me feel guilty. I see it, but I can't do anything about this situation.” (Jaime)
4. Discussion
The literature shows that the burden of care falls predominantly on women [
1,
7,
19,
27,
28], resulting in gender inequalities in healthcare that continue to grow [
29]. These inequalities occur in addition to other societal gender disparities. It is crucial to recognize and address these gender inequalities in the context of informal care, which is becoming increasingly necessary in the present day [
7], and to promote equity in health and society in general [
19]. The social constructs of masculinity influence men’s caregiving roles in society. Male identities are shaped by the social and cultural expectations of caregiving and parenting. These constructions impact gender equality and highlight the importance of challenging entrenched gender stereotypes to promote meaningful change toward a more equitable society [
30].
In the present study, men and women experienced uncertainty differently. Women experienced anguish, suffering, and uncertainty about the future, whereas men acquired knowledge to manage the disease and adapted gradually. Rabiei et al. [
31] established that caregivers experienced frustration and felt like they were being held captive by disease-related complications. They faced difficulties in coping with them. Tolerance of the permanent suffering of the patient increased the caregivers' difficulties and frustration. In addition to feelings of inferiority, worry and uncertainty about the future are common to caregivers from all cultures, especially in the context of medical care, which makes relatives and caregivers feel captive to the disease; many surrender to it.
Caregivers perceived that their worlds had been transformed: women because of the burden of care, fatigue, and emotional and physical impacts, and men because of stress. However, men learned to manage their stresses and respond to care needs. In chronicity, the lives of caregivers and sick people change because of the pragmatic adjustments they must make in their lives; they implement strategies that allow them to face the disease and manage the burden of caregiving [
32].
Women feel physically and emotionally exhausted by their caregiving roles, which highlights and reinforces traditional female stereotypes about caregivers and limits the possibilities of pursuing their interests, personal needs, professional ambitions, sexual identity, and social status. In turn, male caregivers may block some emotional aspects of caregiving, suppress emotions, and restructure their caregiving roles. When this is achieved, they experience a sense of honor in that success and a sense of self-management [
33].
Women provide care with unwavering will, focusing on the patient's condition of fragility with devotion, and as an expression of love. Men take care of their loved ones as a moral obligation and out of feelings of gratitude. Caregiving roles make women feel morally obligated to ‘do their duty’, but they can also provoke feelings of guilt when those expectations are not met [
1]. For men, caregiving entails practical and emotional support; this is often manifested as ‘caring for’, which relates to caregiving through the performance of tasks, and ‘being concerned about’, which refers to the emotional aspects of caregiving. These may include the generalized relational and affective elements of ‘being supportive’ [
13].
Caregivers’ isolation and exhaustion are related to their 24-hour dedication to care. Women feel that their lives are complicated in such a way that they cannot perform other activities of daily living or leisure [
7,
34] because they must always dedicate themselves to their loved ones. They recognize that playing the role of caregiver causes a greater emotional and physical burden [
7] because they sacrifice their time and their own needs for the well-being and joy of the person they care for; their dedication is unconditional. Men experience stress and fatigue, their lives are centered around care, and their outings are restricted. The role of caregivers makes them relinquish their old jobs and being providers of their homes, having conversations with friends, and solving problems; they simultaneously suffer economic losses and experience a lack of future projects to look forward to [
35].
For both men and women, the transition to the role of a caregiver causes anguish and fear. Without knowledge of how to exercise their new roles, they fear not being able to meet the demands of care. They learn to provide care over time [
36], and their levels of stress and anxiety about their experiences increase [
37]. This fear of making mistakes affects the caregivers’ mental and emotional health.
Caregivers also experience intense distress when forced to leave those they care for alone [
36]. The fear that mishaps or emergencies will occur during their absence generates constant concern for the well-being of loved ones. Sometimes, they feel guilty for being absent, which can generate internal conflicts between care responsibilities and personal needs.
The literature points to caregivers’ difficult task of balancing their responsibilities while providing care. Female caregivers are unaware of their own needs and desires, and they often sacrifice their time, energy, and personal aspirations to ensure the well-being of the person they care for. In contrast, men try to maintain a balance between their needs and the demands of care. Both men and women who are informal caregivers experience a loss of direction in their lives, leisure time, and life projects [
35]. Being a caregiver produces negative effects that are aggravated by the differences between the two sexes. In general, women are more bound to their homes, have less leisure time, and sleep less than men [
19].