Submitted:
14 October 2024
Posted:
15 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Electric Fleet Growth and Grid Impacts
1.2. EV Charging Power Management Strategies And Distributed Generation Coupling
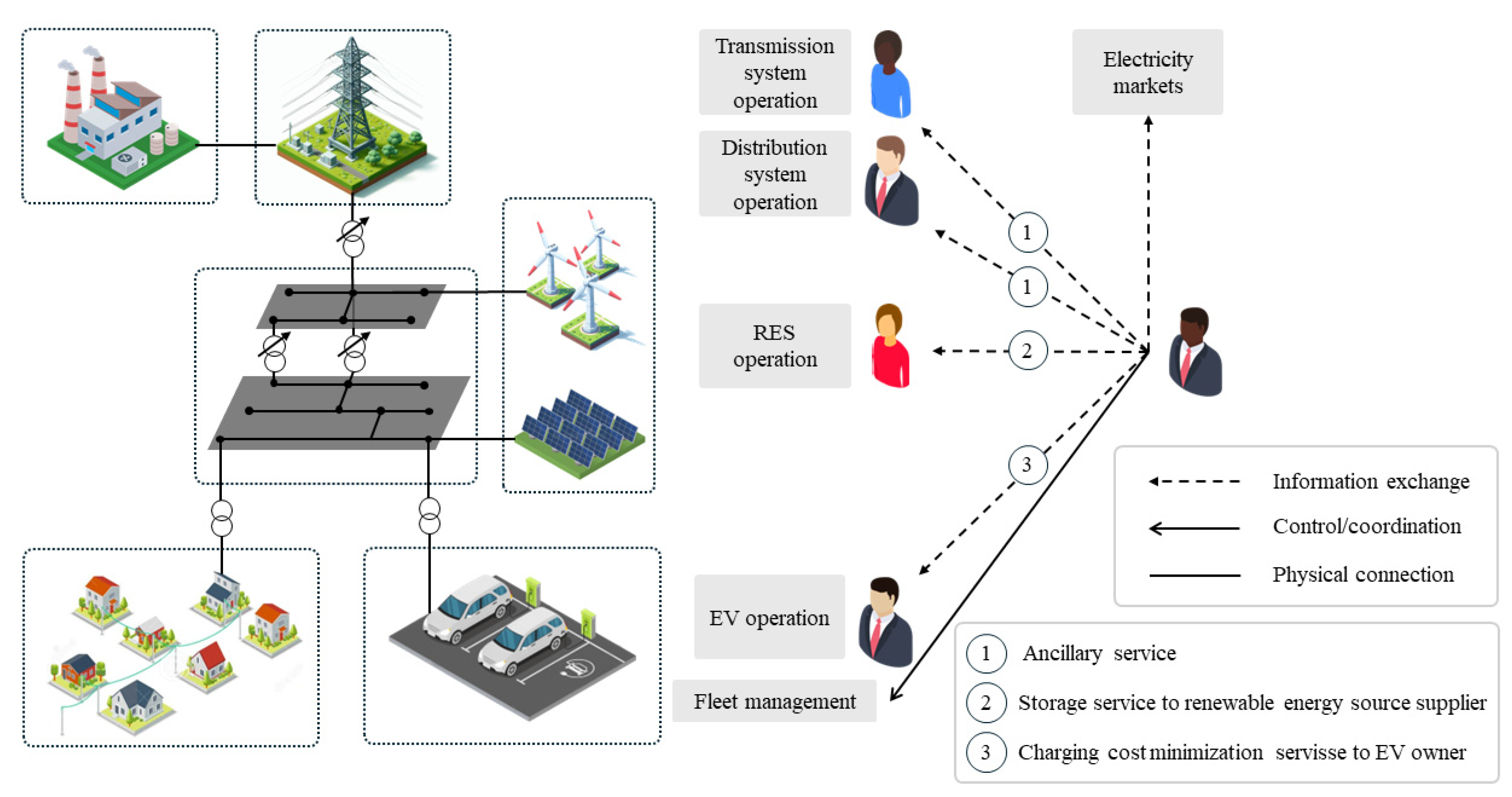
2. Power Grid Infrastructure Management
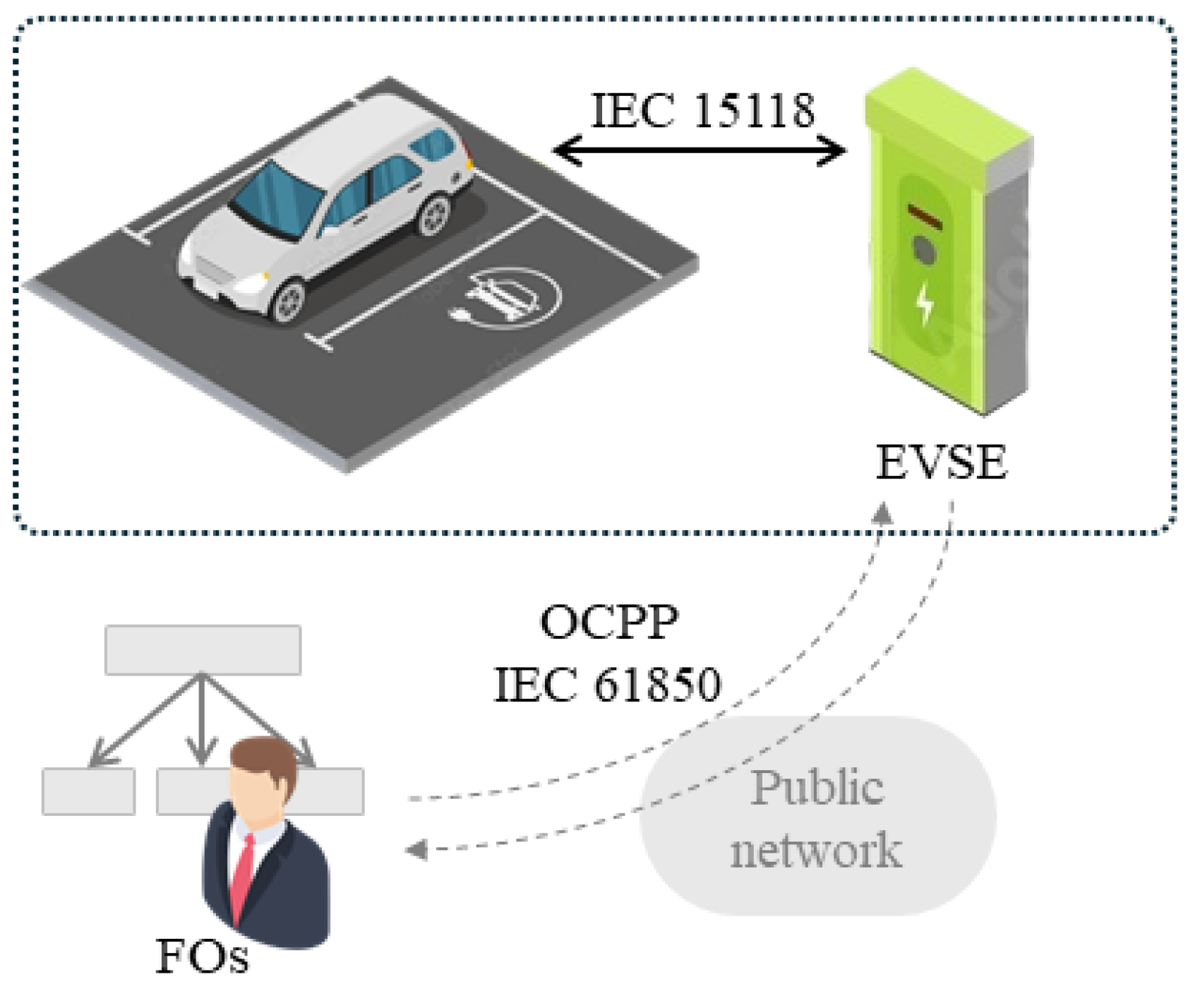
3. Control and Supervision of Electric Vehicle Supply Units
4. Proposed Control Architecture
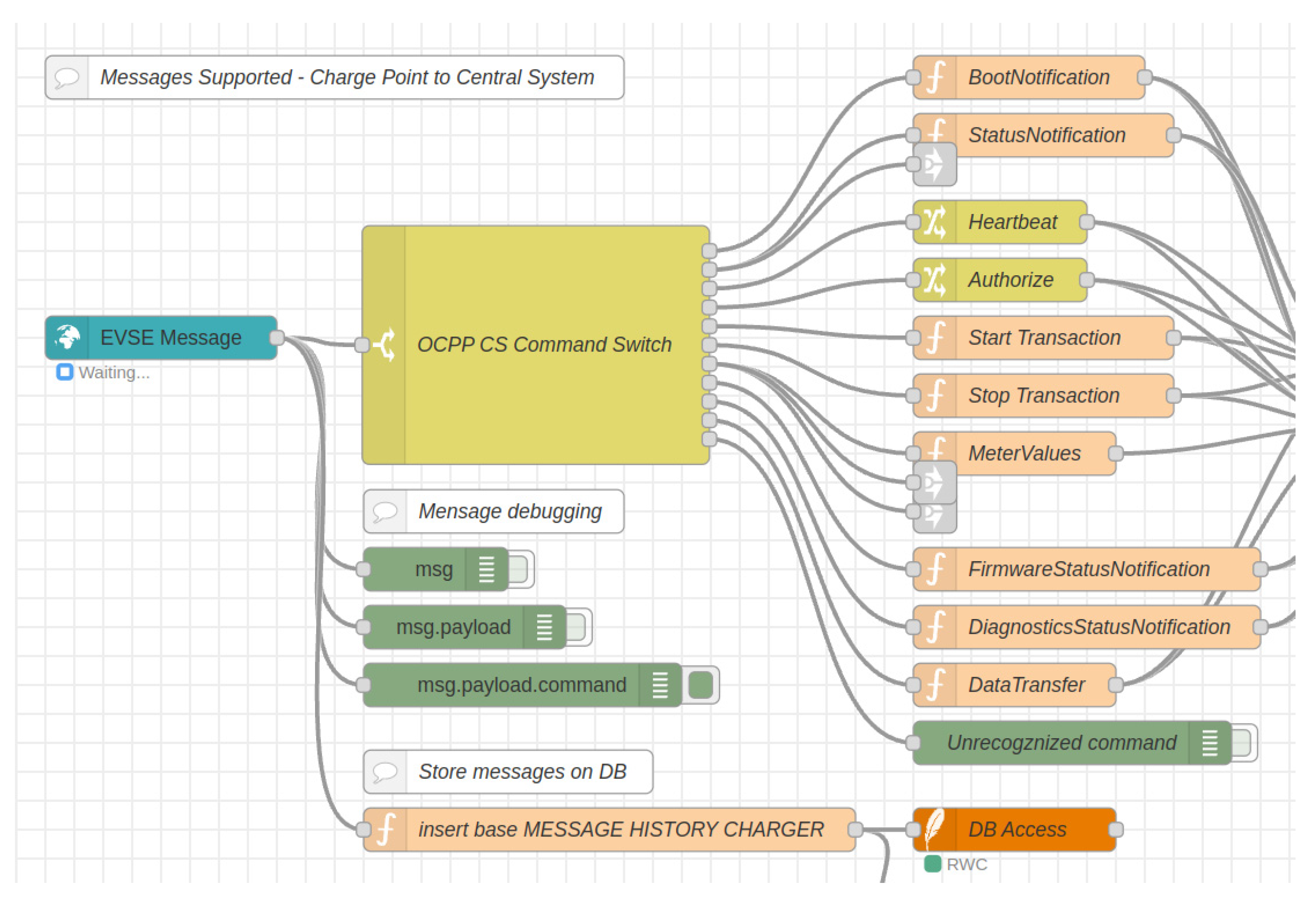
4.1. OCPP request - Sending and Receiving Algorithm
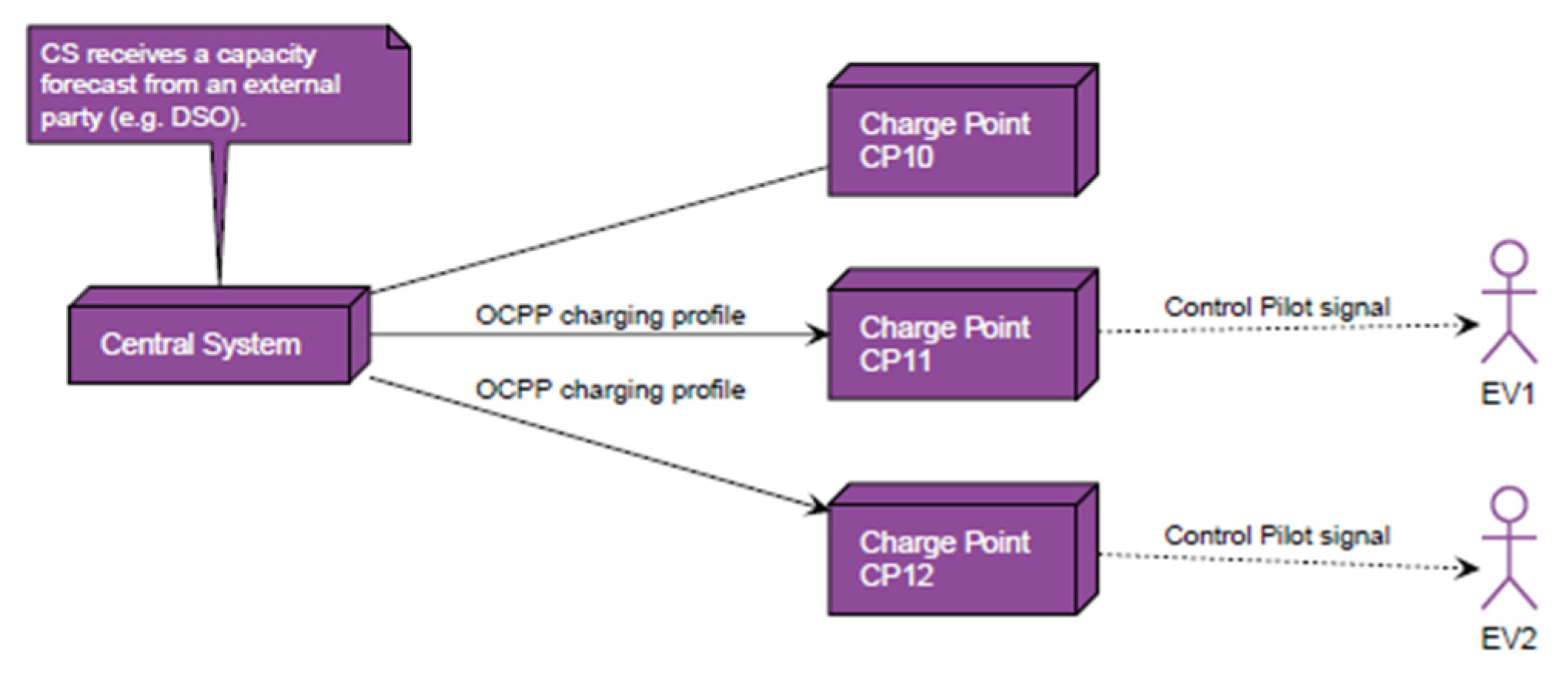
4.2. Central Smart Charging
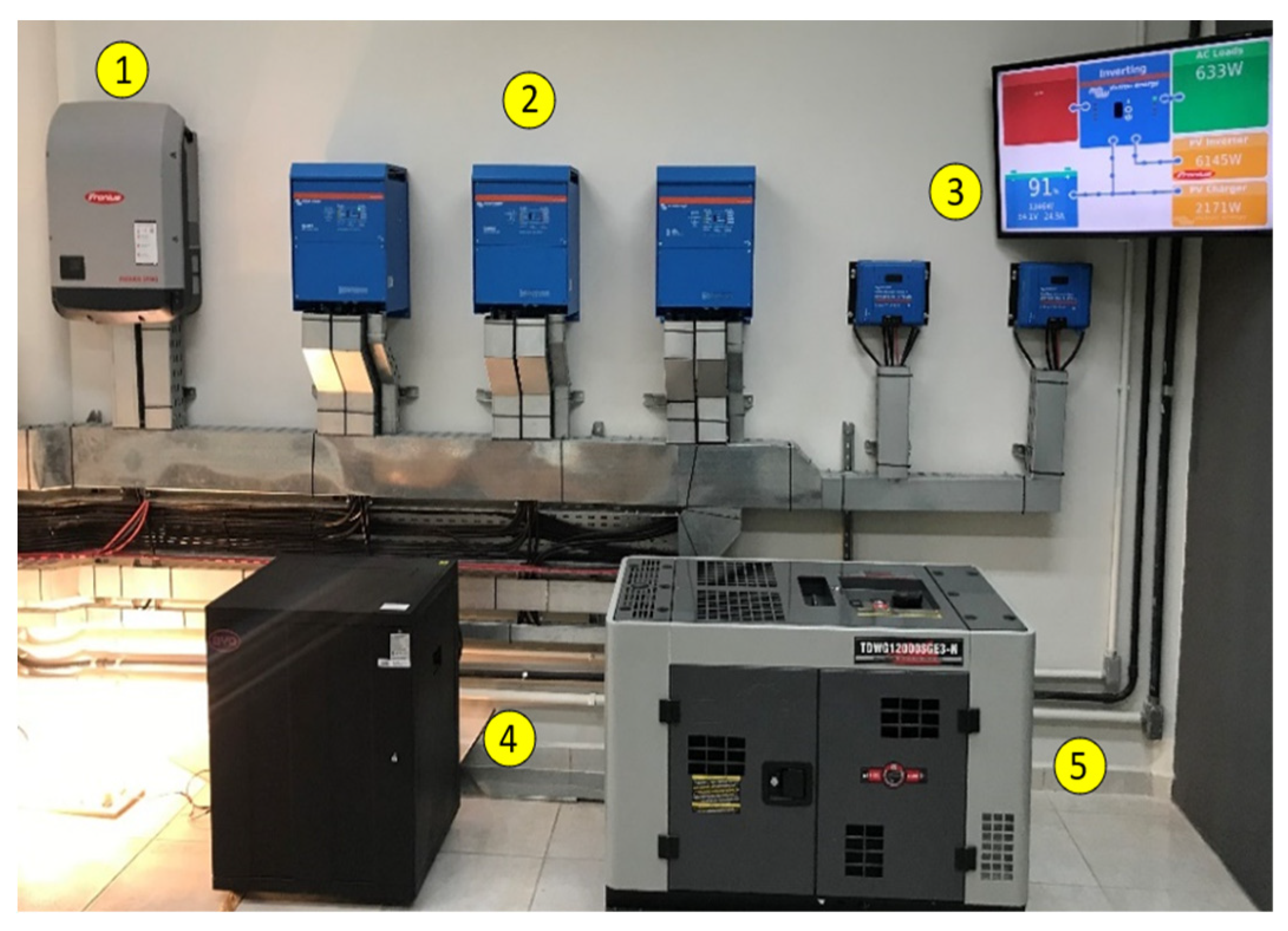
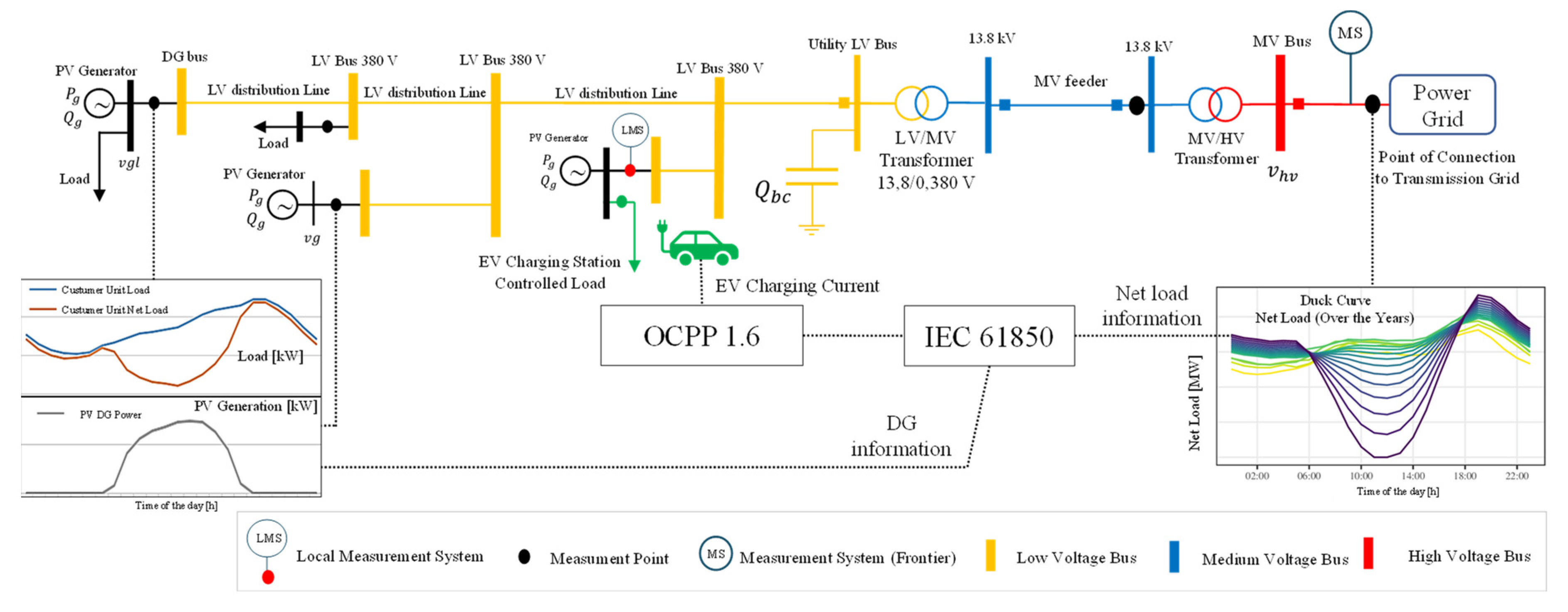
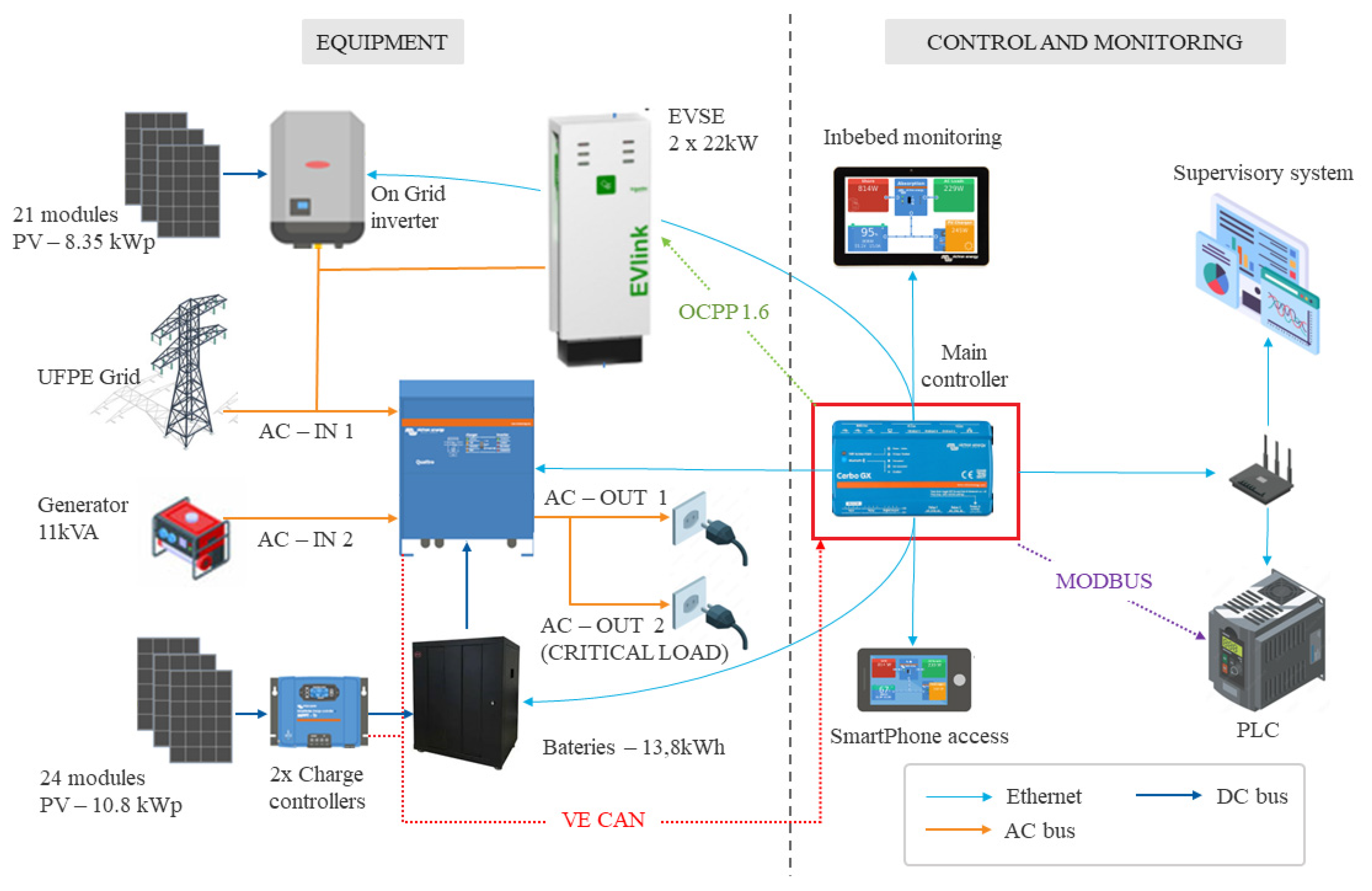
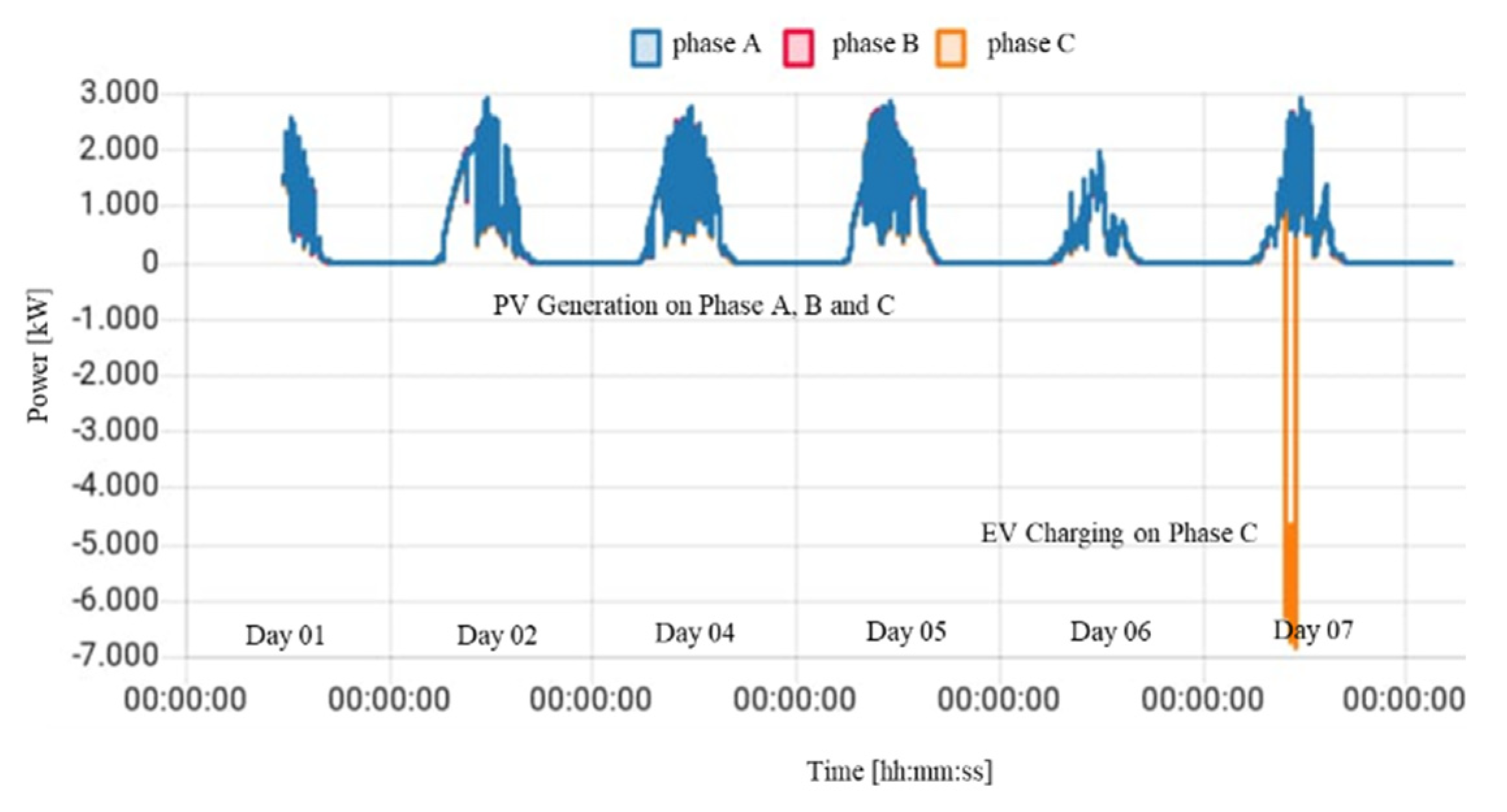
4.3. Storage and Mobility Laboratory – LAM Microgrid
5. Measurement Results and Implementation of Smart Charging Strategy - Control by Charging Profile
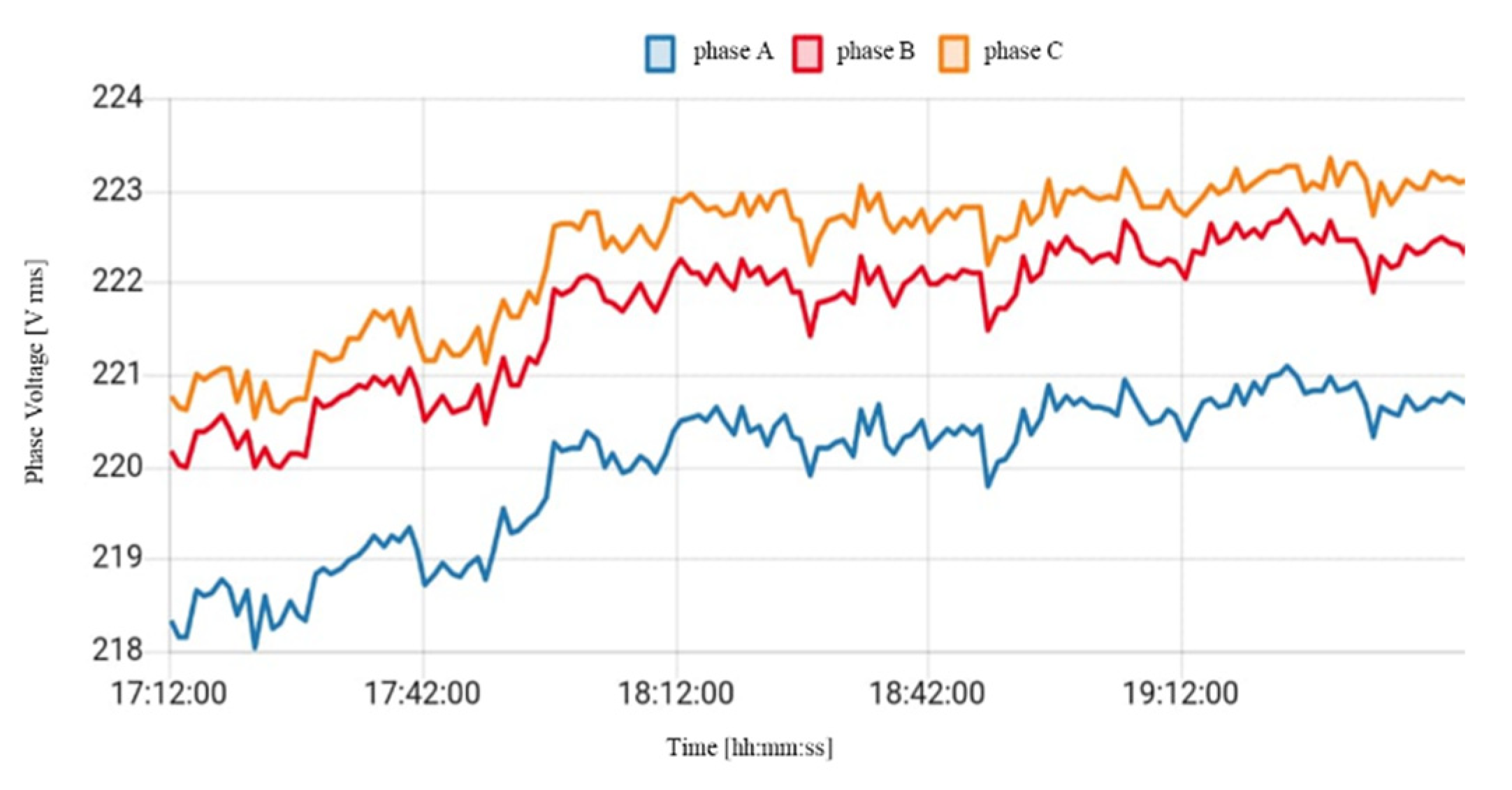
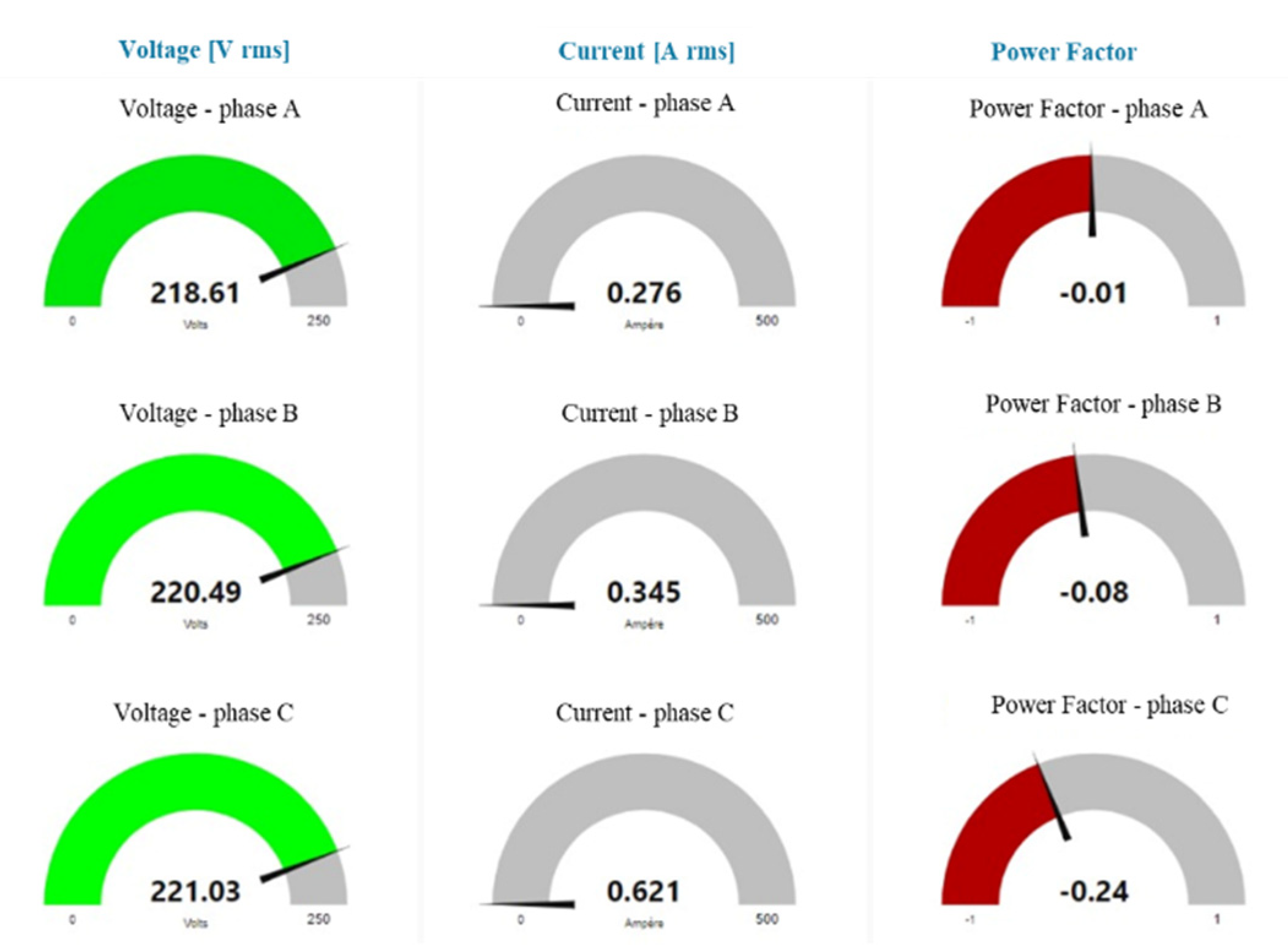
5.1. Standard (without Control) Charging Scenario
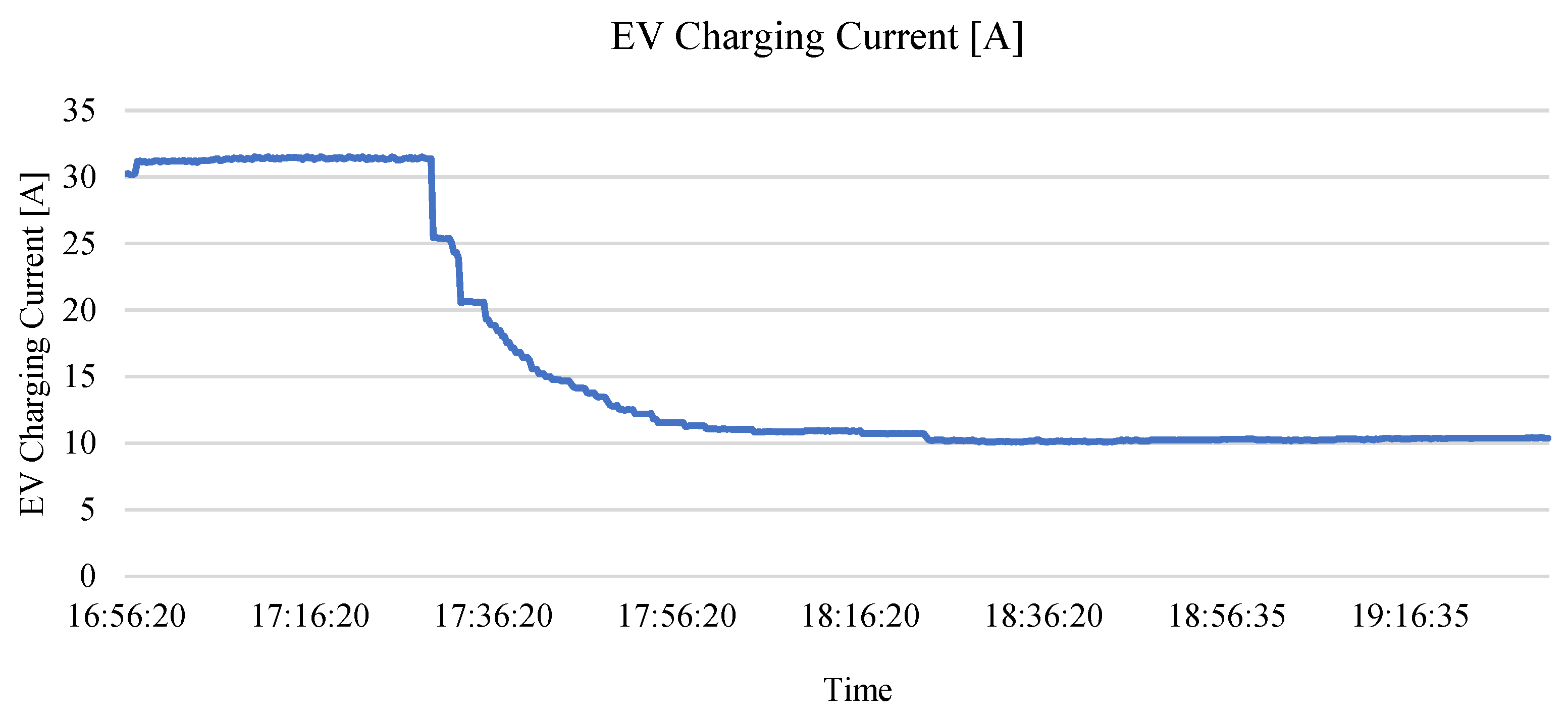
5.2. Smart Charging Strategy – Dynamic Limited Current Test Using OCPP Network
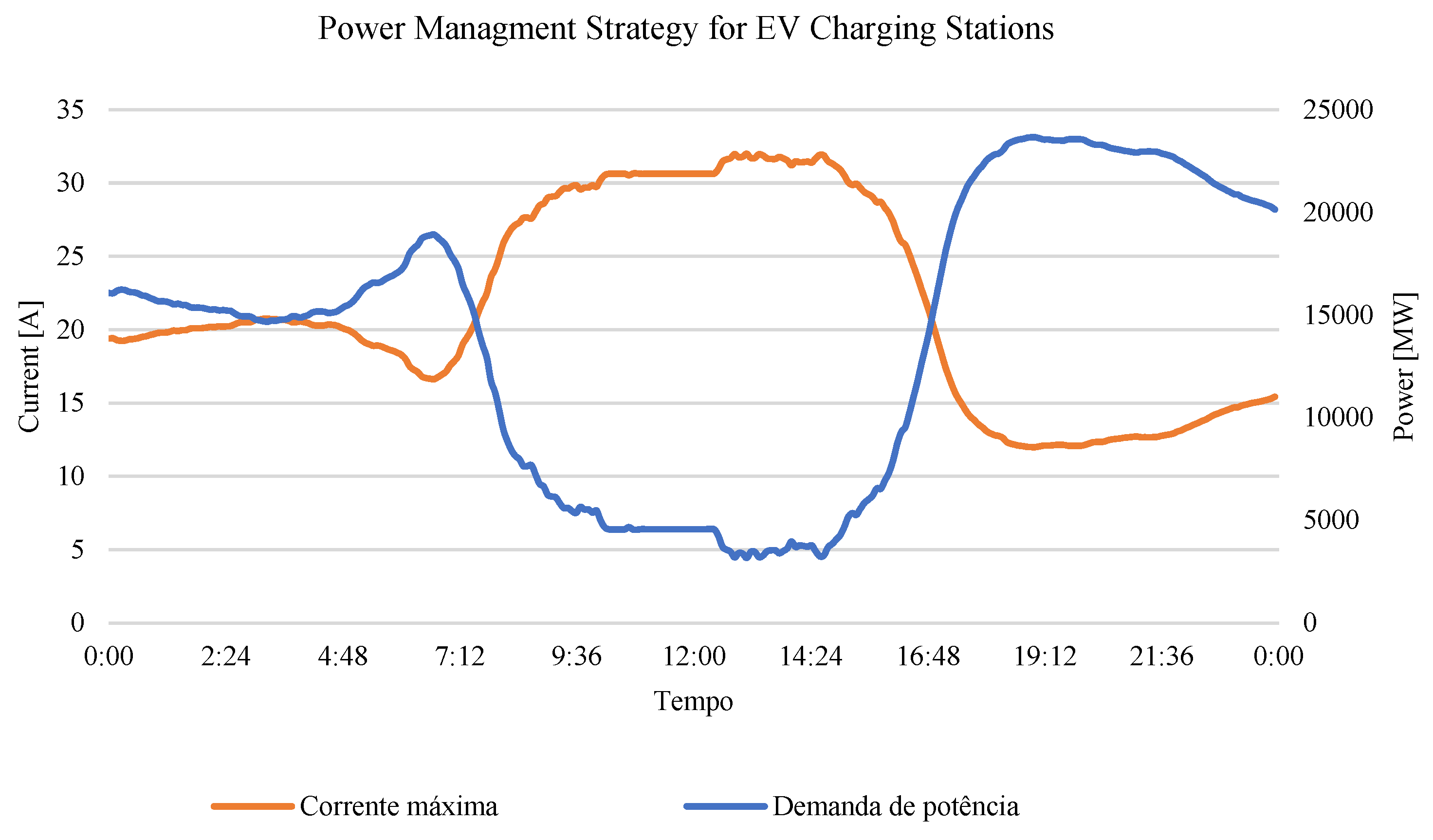
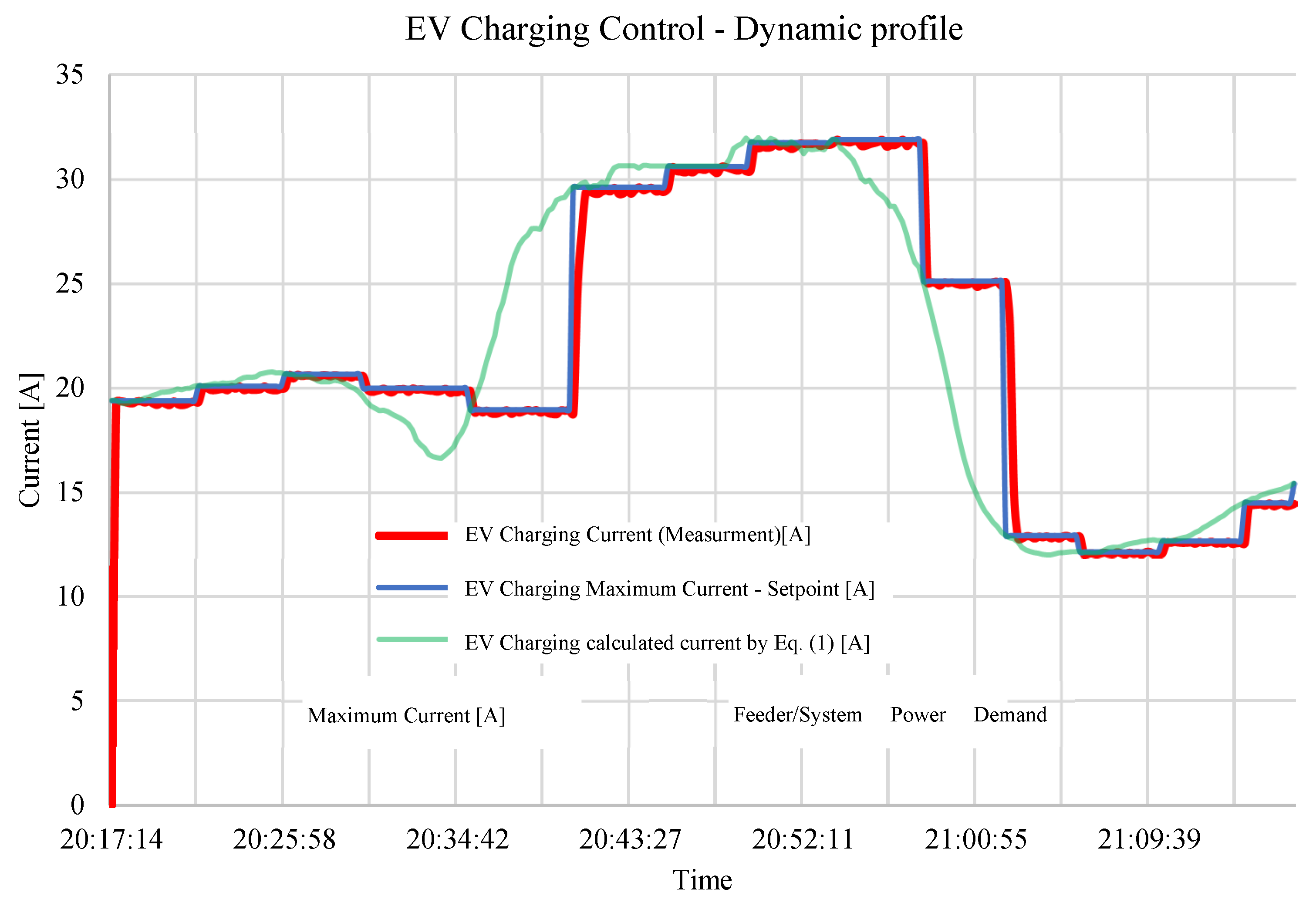
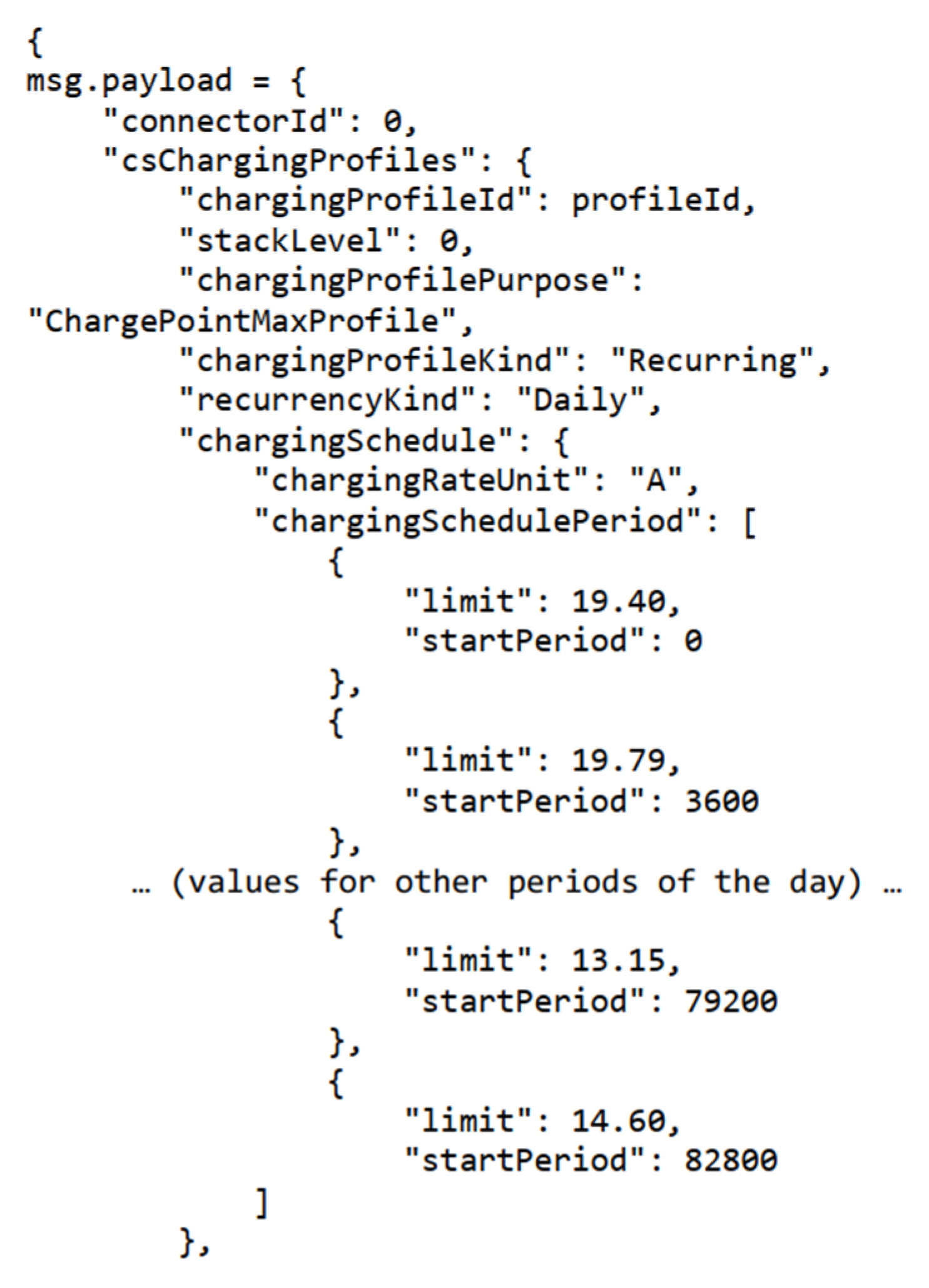
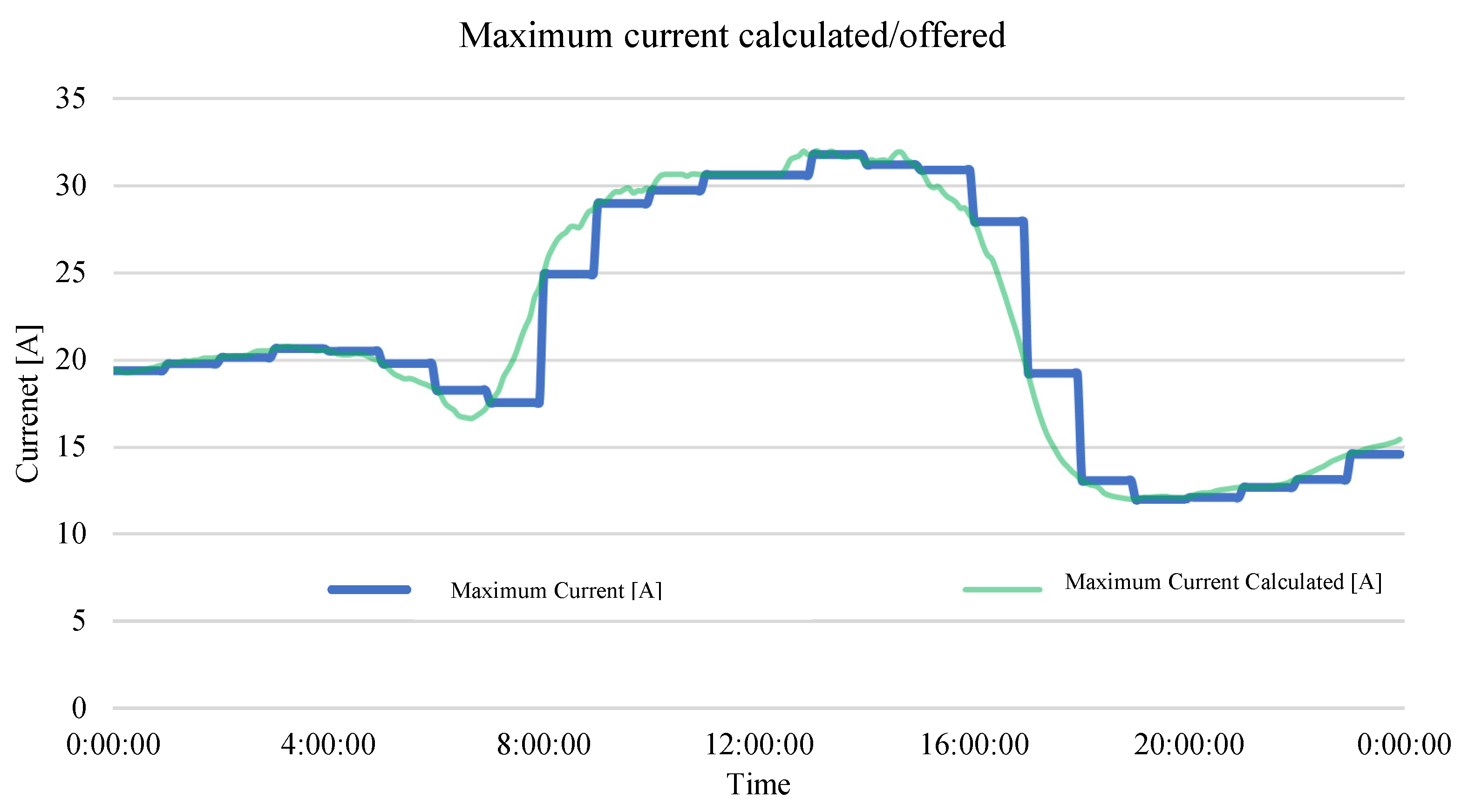
5.3. Smart Charging: Control by Charging Profile
6. Smart Charging Strategy - Dynamic Current Limited Using IEC 61850 Network
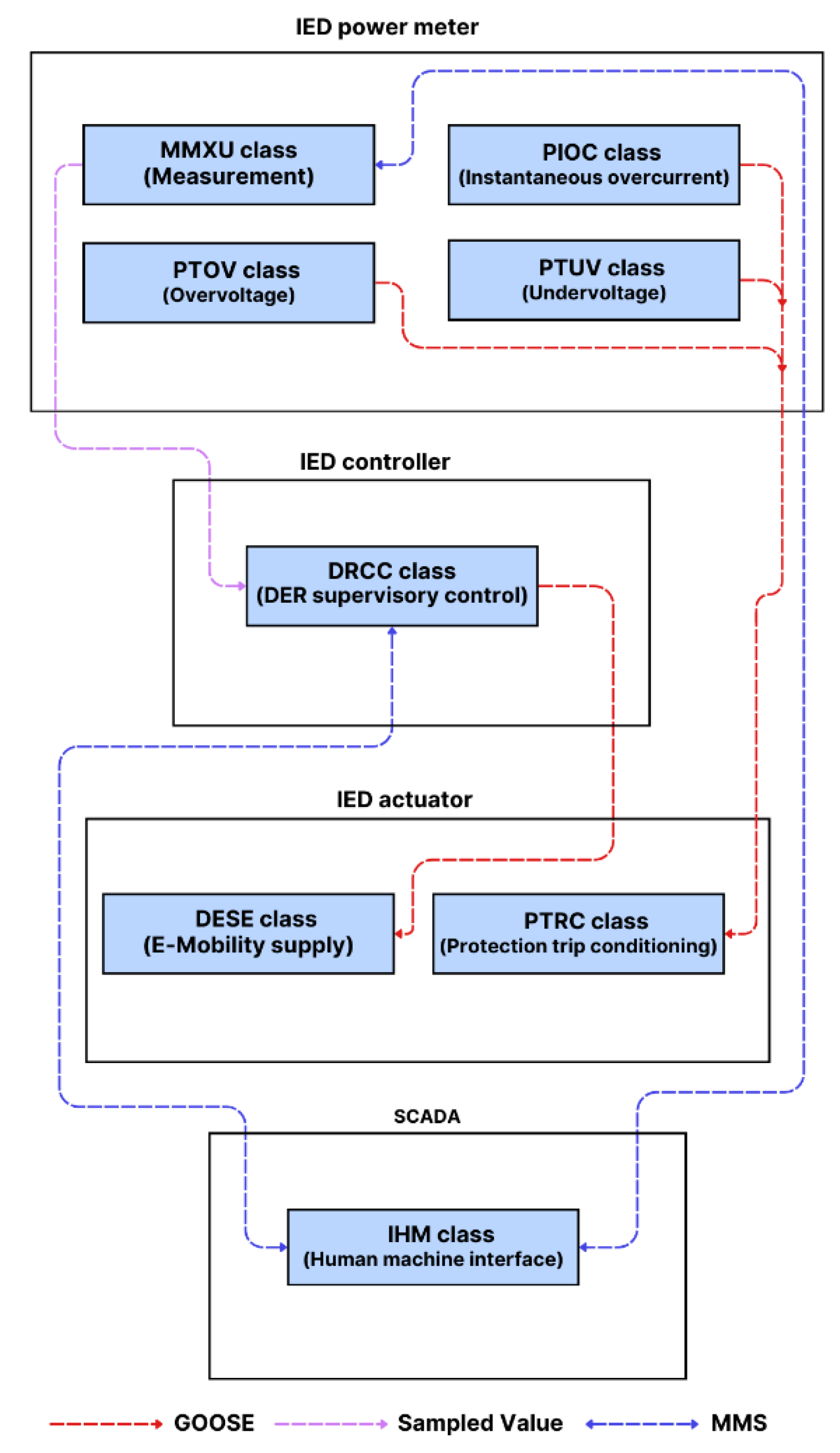
6.1. IEC 61850 Information Modeling Highlighting the Distribution of Intelligent Electronic Device (IED)
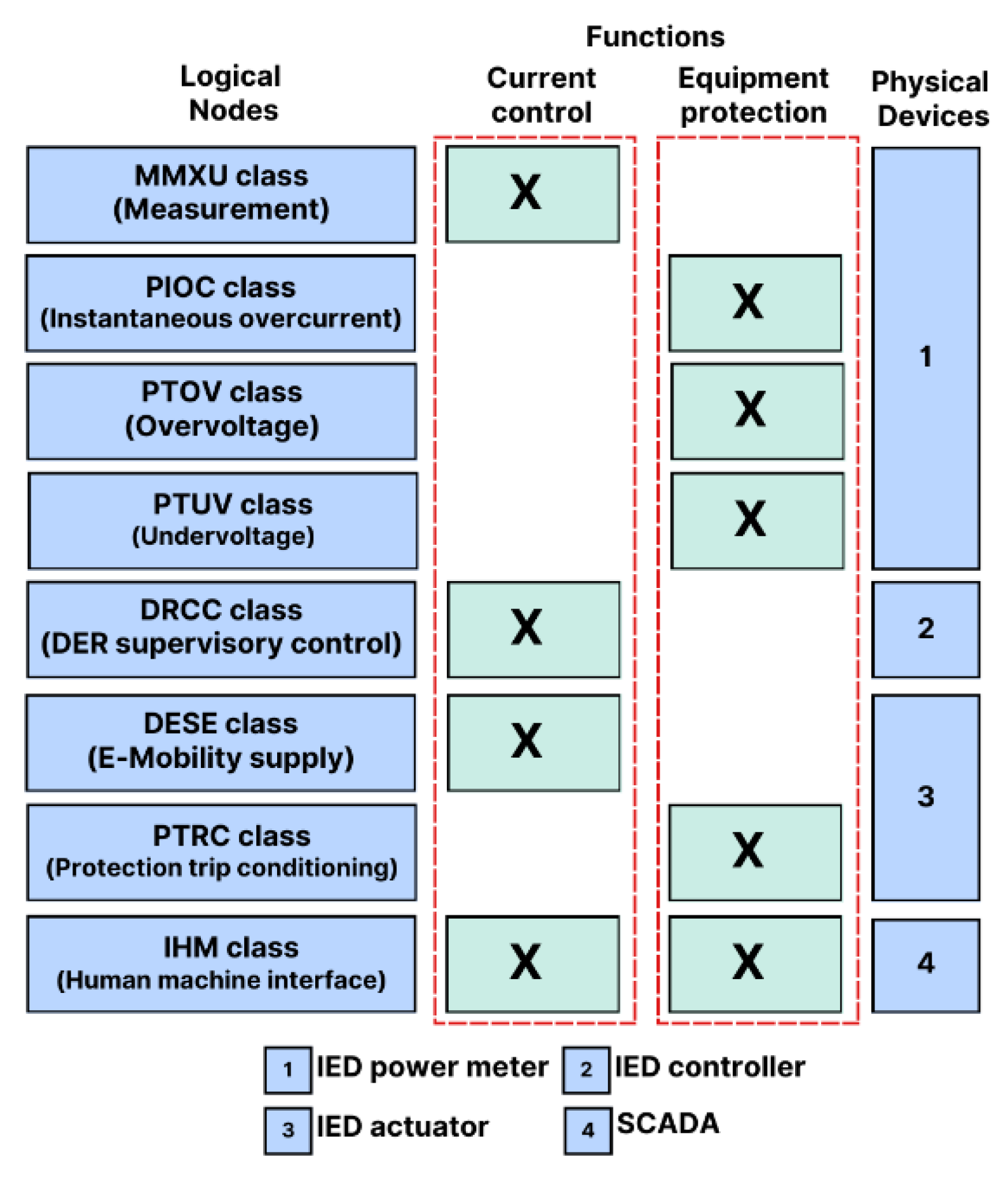
6.2. Relationship between Functions, Logical Nodes, and Physical Devices
6.3. Implementation of Lib IEC 61850 in Smart Meter and Actuator IEDS
6.3.1. Power Meter IED Implemented on ESP32
6.3.2. Controller IED Implemented on Raspberry Pi
6.3.3. Actuator IED Implemented on ESP32
7. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- C. V. C. Kouridis, “Towards decarbonizing road transport: Environmental and social benefit of vehicle fleet electrification in urban areas of Greece,” Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, January 2022.
- M. Schmidt, P. Staudt and C. Weinhardt, “Decision support and strategies for the electrification of commercial fleets,” Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, August 2021.
- D. A. G. Nikita O. Kapustin, “Long-term electric vehicles outlook and their potential impact on electric grid,” Energy Policy, February 2020.
- T. Chen, X.-P. Zhang, J. Wang, J. Li, C. Wu, M. Hu and H. Bian, “A Review on Electric Vehicle Charging Infraestructure Development in the UK,” International Journal of Science and Research Archive, 10 2023.
- Y. L. X. L. H. W. Yijing Zhu, “Carbon mitigation and health effects of fleet electrification in China’s Yangtze River Delta,” Environment International, October 2023.
- J. S. A. K. e. P. K. K. Zamasz, “The Impact of Fleet Electrification on Carbon Emissions: A Case Study from Poland”.
- S. Glyniadakis and J. A. P. Balestieri, “Brazilian light vehicle fleet decarbonization scenarios for 2050,” Energy Policy, October 2023.
- United States Environmental Protection Agency, “Greenhouse Gas Emissions,” EPA, 5 June 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.epa.gov/ghgemissions/sources-greenhouse-gas-emissions. [Accessed 22 June 2024].
- C. J. Meinrenken and K. S. Lackner, “Fleet view of electrified transportation reveals smaller potential to reduce GHG emissions,” Applied Energy, vol. 138, pp. 393-403, 15 January 2015.
- J. Druitt and W.-G. Früh, “Simulation of demand management and grid balancing with electric vehicles,” Journal of Power Sources, vol. 216, pp. 104-116, October 2012.
- Open Charge Alliance, “OCPP & IEC 61850: a winning team,” 8 September 2023. [Online]. Available: https://openchargealliance.org/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/Whitepaper-OCPP-IEC-61850-a-winning-team-Report-No.-23-3107-08-09-2023-Version.-1.0.pdf.
- A. Gerodimos, L. Maglaras, M. A. Ferrag, N. Ayres and I. Kantzavelou, “IoT: Communication protocols and security threats,” Internet of Things and Cyber-Physical Systems, vol. 3, pp. 1-13, 2023.
- Y. Xiong, B. Wang, Z. Cao, C.-C. Chu, H. Pota and R. Gadh, “Extension of IEC61850 with smart EV charging,” 2016 IEEE Innovative Smart Grid Technologies - Asia (ISGT-Asia), pp. 294-299, November 2016.
- C. A. A. C. W. Jens Schmutzler, “Evaluation of OCPP and IEC 61850 for smart charging electric vehicles,” 2013 World Electric Vehicle Symposium and Exhibition (EVS27), 11 2013.
- L. R. d. Miranda, “NORMA GLOBAL DE COMUNICAÇÃO EM SUBESTAÇÕES - IEC61850,” SNPTEE - Seminário Nacional de Produção e Transmissão de Energia Elétrica, 10 2005.
- Open Charge Alliance, “Open Charge Point Protocol 1.6,” Open Charge Alliance, March 2019. [Online]. Available: https://openchargealliance.org/my-oca/ocpp/. [Accessed February 2024].
- B. M. Al-Alawi and T. H. Bradley, “Review of hybrid, plug-in hybrid, and electric vehicle market modeling Studies,” Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, vol. 21, pp. 190-203, May 2013.
- P. Kotler, K. L. Keller and S. Yamamoto, Administração de Marketing, Pearson Universidades, 2018.
- Statista, “Electric Vehicles - United States,” [Online]. Available: https://www.statista.com/outlook/mmo/electric-vehicles/united-states. [Accessed February 2024].
- Statista, “Annual passenger car sales in the United States from 1951 to 2022,” [Online]. Available: https://www.statista.com/statistics/199974/us-car-sales-since-1951/#:~:text=U.S.%3A%20Annual%20car%20sales%201951%2D2022&text=The%20U.S.%20auto%20industry%20sold. [Accessed February 2024].
- S. Shepherd, P. Bonsall and G. Harrison, “Factors affecting future demand for electric vehicles: A model based study,” Transport Policy, vol. 20, pp. 62-74, March 2012.
- M. S. d. Oliveira, C. C. L. D. Santos, J. F. C. Castro, L. Tavares, D. Marques, P. A. C. Rosas, L. H. A. D. Medeiros and F. Bradaschia, “EV demand forecasting based on logistic growth method applied to infrastructure planning for fast charging allocation integrated with storage and solar photovoltaic energy system,” CIRED Porto Workshop 2022: E-mobility and power distribution systems, 6 2022.
- J. Castro, D. Marques, L. Tavares, N.K.L.Dantas, A. Fernandes, J. Tuo, L. d. Medeiros and P. Rosas, “Energy and Demand Forecasting Based on Logistic Growth Method for Electric Vehicle Fast Charging Station Planning with PV Solar System,” Energies, vol. 15, p. 6106, 2022.
- S. Vasconcelos, J. Castro, L. Limongi, G. A. 1, P. R. 1, L. D. Medeiros, D. Marques, A. Fernandes, J. Qi, L. Tavares, A. Filho and N. Dantas, “Operation of EV charging station with a photovoltaic system to reduce the impact on the distribution grid,” in 27th International Conference on Electricity Distribution (CIRED 2023), Rome, Italy, 12-15 June 2023, p. 3963 – 3967.
- J. F. C. Castro, R. A. Roncolatto, A. R. Donadon, V. E. M. S. Andrade, P. Rosas, R. G. Bento, J. G. Matos, F. A. Assis, F. C. R. Coelho, R. Quadros, J. I. Y. Ota, L. C. P. Silva and R. K. Carneiro, “Microgrid Applications and Technical Challenges—The Brazilian Status of Connection Standards and Operational Procedures,” Energies, vol. 6(6), p. 2893, 2023.
- M. N. Martins, J. Castro, D. Marques, P. Rosas, G. Rissi, A. Fernandes, X. Luo, L. A. D. Medeiros, A. Lima, M. Brito, G. Maia and A.S.M. Vasconcelos, “Assessment of battery energy storage system operating modes in a microgrid for electric vehicles charging,” in 27th International Conference on Electricity Distribution (CIRED 2023), Rome, Italy, 12-15 June 2023.
- F. A. Assis, F. C. R. Coelho, J. F. C. Castro, A. R. DonadoN, P. A. C. R. Ronaldo A. Roncolatto 1, V. E. M. S. Andrade, R. G. Bento, L. C. P. Silva, J. G. I. Cypriano and O. R. Saavedra, “Assessment of Regulatory and Market Challenges in the Economic Feasibility of a Nanogrid: A Brazilian Case,” Energies, vol. 17(2), p. 341, 9 January 2024.
- R. C. G. II, L. Wang and M. Alam, “The impact of plug-in hybrid electric vehicles on distribution networks: A review and outlook,” Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, vol. 15, pp. 544-553, 2011.
- B. Hudson, G. Razeghi and S. Samuelsen, “Mitigating impacts associated with a high-penetration of plug-in electric vehicles on local residential smart grid infraestructure,” Journal of Power Sources, vol. 593, February 2024.
- R. Ufa, Y. Malkova, V. Rudnik, M. Andreev and V. Borisov, “A review on distributed generation impacts on electric power system,” International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, vol. 47, pp. 20347-20361, 1 June 2022.
- Y. G. Landera, O. C. Zevallos, R. C. Neto, J. F. C. Castro and F. A. S. Neves, “A Review of Grid Connection Requirements for Photovoltaic Power Plants,” Energies, vol. 16, p. 2093, 21 February 2023.
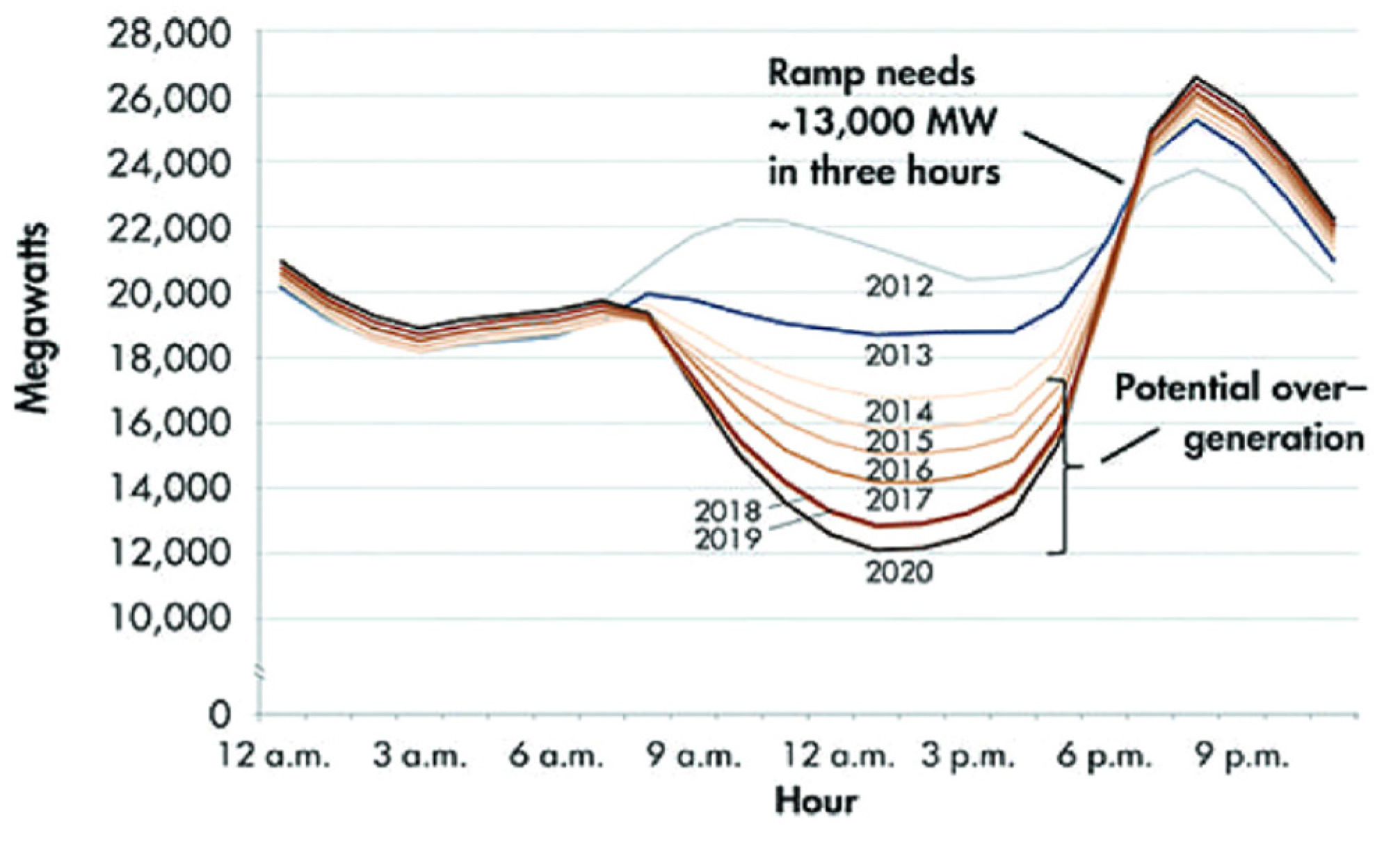
- H. O. R. Howlader, M. M. Sediqi, A. M. Ibrahimi and T. Senjyu, “Optimal Thermal Unit Commitment for Solving Duck Curve Problem by Introducing CSP, PSH and Demand Response,” IEEE Access, pp. 4834-4844, 2018.
- P. Denholm, M. O’Connell, G. Brinkman and J. Jorgenson, “Overgeneration from Solar Energy in California: A Field Guide to the Duck Chart,” 2015.
- California Independent System Operator, “What the duck curve tells us about managing a green grid,” FAST FACTS, 2016.
- V. M. L. Filho, A. S. M. Vasconcelos, W. A. S. Junior, N. K. L. Dantas, A. M. C. Arcanjo, A. C. M. Souza, A. L. Fernandes, K. Zhang, K. Wu, J. F. C. Castro, L. H. A. d. Medeiros and A. M. A. Maciel, “Impact Analysis and Energy Quality of Photovoltaic, Electric Vehicle and BESS Lead-Carbon Recharge Station in Brazil,” Energies, vol. 16(5), p. 2397, 2023.
- A. Ulbig and G. Andersson, “Analyzing Operational Flexibility of Power Systems,” International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, vol. 72, December 2013.
- “Energy storage to reduce renewable energy curtailment,” IEEE Power and Energy Society General Meeting, 2012.
- P. Denholm and M. Hand, “Grid flexibility and storage required to achieve very high penetration of variable renewable electricity,” Energy Policy, vol. 39, pp. 1817-1830, March 2011.
- N. Navid and G. Rosenwald, “Market Solutions for Managing Ramp Flexibility With High Penetration of Renewable Resource,” IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Energy, vol. 3, pp. 784-790, October 2012.
- R. Bhat, M. Begovic, I. Kim and J. Crittenden, “Effects of PV on Conventional Generation,” 47th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, pp. 2380-2387, 2014.
- A. Akrami, M. Doostizadeh and F. Aminifar, “Power system flexibility: an overview of emergence to evolution,” Journal of Modern Power Systems and Clean Energy, vol. 7, September 2019.
- T. Cioara, I. Anghel, M. Antal, S. Crisan and I. Salomie, “Data center optimization methodology to maximize the usage of locally produced renewable energy,” in 2015 Sustainable Internet and ICT for Sustainability, Madrid, Spain, 2015.
- S. Mohajeryami, P. Schwarz and P. T. Baboli, “Including the behavioral aspects of customers in demand response model: Real time pricing versus peak time rebate,” in 2015 North American Power Symposium (NAPS), Charlotte, NC, USA, 2015.
- J. Delgado, R. Faria, P. Moura and A. T. d. Almeida, “Impacts of plug-in electric vehicles in the portuguese electrical grid,” Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, vol. 62, pp. 372-385, July 2018.
- J. Hu, H. Morais, T. Sousa and M. Lind, “Electric vehicle fleet management in smart grids: A review of services, optimization and control aspects,” Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, vol. 56, pp. 1207-1226, 4 2015.
- D. Dallinger and M. Wietschel, “Grid integration of intermittent renewable energy sources using price-responsive plug-in electric vehicles,” Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, vol. 16, pp. 3370-3382, June 2012.
- Open Charge Alliance, “CONNECTING THE EV CHARGING INDUSTRY,” [Online]. Available: https://openchargealliance.org/. [Accessed 2 2024].
- S. Gao, K. T. Chau, C. Liu, D. Wu and C. C. Chan, “Integrated Energy Management of Plug-in Electric Vehicles in Power Grid With Renewables,” IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2014.
- L. Lu, X. Han, J. Li, J. Hua and M. Ouyang, “A review on the key issues for lithium-ion battery management in electric vehicles,” Journal of Power Sources, 3 2013.
- E. D. Kostopoulos, G. C. Spyropoulos and J. K. Kaldellis, “Real-world study for the optimal charging of electric vehicles,” Energy Reports, 11 2019.
- Schneider, “EVlink: OCPP guide,” 2018. [Online].
- California ISO, “Today’s Outlook,” [Online]. Available: https://www.caiso.com/TodaysOutlook/Pages/index.html. [Accessed 2 2024].
- S. Hamdare, D. J. Brown, Y. Cao and M. Aljaidi, “EV Charging Management and Security for Multi-Charging Stations Environment,” IEEE Open Journal of Vehicular Technology, vol. 5, 2024.
- A. Martínez-Gutiérrez, J. Díez-González, P. Verde and R. F.-G. a. H. Perez, “Hyperconnectivity Proposal for Smart Manufacturing,” IEEE Access, vol. 11, pp. 70947-70959, 2023.
- N. Das, A. Haque, H. Zaman and S. M. a. S. Islam, “Exploring the Potential Application of IEC 61850 to Enable Energy Interconnectivity in Smart Grid Systems,” IEEE Access, vol. 12, pp. 56910-56923, 2024.
- A. Apostolov and B. Muschlitz, “Object modeling of measuring functions in IEC 61850 based IEDs,” IEEE PES Transmission and Distribution Conference and Exposition, vol. 2, pp. 471-476, 2003.
- IEC, “Communication networks and systems for power utility automation – part 7-1: Basic communication structure – principles and models,” International Electrotechnical Commission, 2007.
- IEEE, “Communication networks and systems for power utility automation – part 7-4: Basic communication structure – compatible logical node classes and data object classes,” International Electrotechnical Commission, 2010.
- IEEE, “Communication networks and systems for power utility automation – part 7-3: Basic communication structure – common data classes,” International Electrotechnical Commission, 2010.
- IEEE, “Communication networks and systems for power utility automation – part 7-2: Basic information and communication structure – Abstract communication service interface (ACSI),” International Electrotechnical Commission, 2010.
- IEEE, “Specific communication service mapping (SCSM) – Mappings to MMS (ISO 9506-1 and ISO 9506-2) and to ISO/IEC 8802-3,” International Electrotechnical Commission, 2010.

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




