1. Introduction
Recently, the variable domain of the heavy chain of heavy chain (VHH) antibodies, which differs from conventional IgG, has attracted attention. VHH antibodies were initially discovered in the blood of camelids by Hamers and his colleagues in 1993 [
1], revealing that 20%–40% of camelid antibodies are VHH antibodies with only a single heavy chain [
2,
3,
4,
5,
6]. VHH antibodies are characterized by their small molecular weight because of their single domain, thermal stability and capacity to refold. Moreover, these antibodies are a major attraction because of the ease of molecular design through protein engineering. As of 2021, there were 12 pipelines globally developing VHH pharmaceuticals, of which four have VHH molecules in phase 2 clinical trials [
7]. Although the usefulness of VHH antibodies is undisputed, until 10 years ago, it was necessary to immunize camelids, which are more challenging to raise than mice, making the process expensive and time-consuming. Therefore, we constructed a simple artificial VHH library to obtain VHH antibodies in a test tube without immunizing camelids and conducted selection experiments by evolutionary molecular engineering that showed antibody activity against survivin [
8]. Several artificial VHH libraries have recently been designed, and in vitro selection for VHH antibodies without immunizing animals is becoming standard practice [
9]. We recently constructed an artificial VHH antibody library (PharmaLogical library) that allows us to obtain VHH antibodies with high affinity and specificity against various antigens, including membrane proteins [
10]. For example, we successfully obtained neutralizing VHH antibodies against COVID-19 by in vitro selection using cDNA display with a naive VHH library [
11].
The COVID-19 pandemic increased concern about the inhalation delivery technique to the lungs. In particular, DPI (dry powder inhaler) is a promising dosage form because it can be more economical, environmentally friendly and easy for patients to use themselves compared with other delivery techniques. However, DPI generally requires a precise particle size of an inhalable powder for efficient delivery to the lungs, i.e., 1–5 mm diameter [
12]. In general, inhalation drugs often have a wide distribution of particle sizes, resulting in variations in the amount of drug reaching the lungs, and this issue affects their therapeutic effect. Furthermore, unintended larger particle sizes can cause inertial impaction and deposition in the oral cavity, pharynx or larynx, increasing the frequency of side effects [
13]. Therefore, uniformly controlled powder formulation is desired to resolve this issue.
The FDD (fine droplet drying) process, a unique powderization technique using inkjet technology, was developed for designing functional micron-sized particles [
14]. Several studies of the FDD process applied to pharmaceutical formulation have been reported [
15,
16,
17]. A feature of this process is the size uniformity of discharged droplets from the inkjet head. The diameter of the discharged droplets is quite fine, approximately 10 mm, and considerably uniform. Such a feature should facilitate milder air drying than general spray drying methods. In a previous study, the FDD process was applied to develop a salmon calcitonin-loaded inhalable powder [
16]. The salmon-calcitonin included in the powder was found to have no significant conformational changes and did not aggregate. Thus, the FDD process can potentially be used to develop powder formulations with biopharmaceuticals.
In this context, combining VHH antibodies with the FDD process can potentially deliver VHH antibody particles deep into the lungs, making delivery effective against respiratory diseases. For example, VHH antibodies that neutralize viruses such as severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2, respiratory syncytial virus and influenza, bacteria that cause nontuberculous mycobacteria lung disease and fungi causing pulmonary mycosis can be utilized as therapeutic agents to treat respiratory infections.
In this report, the applicability of the FDD process for preparing inhalable dry powder formulations of a VHH antibody was investigated. The FDD process successfully produced VHH antibody-loaded powders (VHHp) under mild drying conditions, achieving powderization without adverse effects such as aggregation and reduced binding activity. Several VHHp were evaluated based on their aggregation, binding, particle and in vitro inhalable properties.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
D-mannitol for molecular biology was purchased from Molecular Depot LLC (San Diego, CA, USA). The VHH antibody for anti-human serum albumin (HSA-VHH antibody) was synthesized by Ajinomoto Co., Inc. (Tokyo, Japan). Distilled water, human serum albumin (HSA), phosphate-buffered saline (PBS, pH 7.4) and Tween-20 were obtained from Fujifilm Wako Pure Chemical Corporation (Osaka, Japan).
2.2. Preparation of the VHH Antibody-Loaded Powders
VHHp was prepared using the previously reported FDD procedure [
15]. Briefly, the VHH antibody (1,300 mg) and mannitol (6.5 mg) were dissolved in 0.1× PBS, with a total solid content of 2% (w/w). The solution was magnetically stirred for 1 h on a ceramic hot stirrer (AS ONE Corp., Osaka, Japan) and filtered through a polytetrafluoroethylene filter with a 1 µm pore size (Millipore Corporation, Burlington, MA, USA). Droplets of sample solution were generated using a customized inkjet head based on MH2420 (RICOH, Tokyo, Japan) and dried with hot air under the following conditions: driving frequency and voltage of piezo element at 310 kHz and 10 V, respectively, and an airflow rate of 50 m
3/h. Three air temperature conditions (i.e., 35, 50 and 65 °C) were chosen to test aggregation of the VHH antibody during powderization by the FDD process. The three VHHp samples were prepared using the same method and conditions, except for the airflow temperature.
2.3. Physicochemical Evaluation
2.3.1. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Analysis
The aggregation rate of the HSA-VHH antibody in VHHp was analyzed by size exclusion chromatography (SEC) with an ACQUITY UPLC H-Class PLUS Bio System (Waters). The analysis was performed using an ACQUITY Premier Protein SEC column (250 Å, 1.7 μm, 4.6 × 150 mm, Waters) according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
2.3.2. Bio-Layer Interferometry
The binding affinity of the HSA-VHH antibody or the HSA-VHH antibody in VHHp to HSA was measured using an Octet RED 384 instrument (Sartorius) and analyzed using Octet software, v1.2.1.5 (Molecular Devices). The HSA-VHH antibody in PBS-T (PBS plus 0.05% Tween-20, pH 7.4) was immobilized on an Anti-Penta-HIS (HIS1K) biosensor chip according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Various concentrations (200, 100, 50, 25, 12.5, 6.25, 3.13 nmol/L) of analyte solutions containing HSA were loaded.
2.3.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
The surface morphology of VHHp was evaluated using a VE-8800 instrument (KEYENCE Corp., Osaka, Japan). Platinum/palladium coating was carried out using an E-1030 magnetron sputtering device (Hitachi Ltd., Tokyo, Japan). The thickness of the platinum/palladium coating was 10 nm, and the accelerating voltage was 5 kV in the SEM experiment.
2.3.4. Laser Diffraction
A Microtrac MT3000II (MicrotracBel, Osaka, Japan) particle size measuring system with laser diffraction under dry conditions was used to measure the particle sizes of VHHp at a pressure of 0.2 MPa. The span factor was calculated as SPAN = (d90 − d10)/d50, where d10, d50 and d90 represent the diameter of the particle size at 10%, 50% and 90%, respectively, which is the calculated volume.
2.3.5. Andersen Cascade Impactor
Cascade impactor analysis was carried out to estimate the inhalation properties of VHHp using an AN-200 system (Tokyo Dylec Corp., Tokyo, Japan), as shown in
Figure S1. Thirty milligrams of sample filled a JP No. 2 hard capsule of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose, and the capsule was installed in a JetHaler
® (Tokico System Solutions, Ltd., Kanagawa, Japan). The formulation in each capsule was dispersed through the device at 28.3 L/min for 10 s × 3 times, and the amount of sample in each stage (stages 0–7) and that in the capsule were measured using an electronic balance (Shimadzu Corporation, Tokyo, Japan). The FPF (fine particle fraction) value was defined as the ratio of total drug deposited in stage 2 and lower.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Appearance and Particle Size Distribution of VHHp
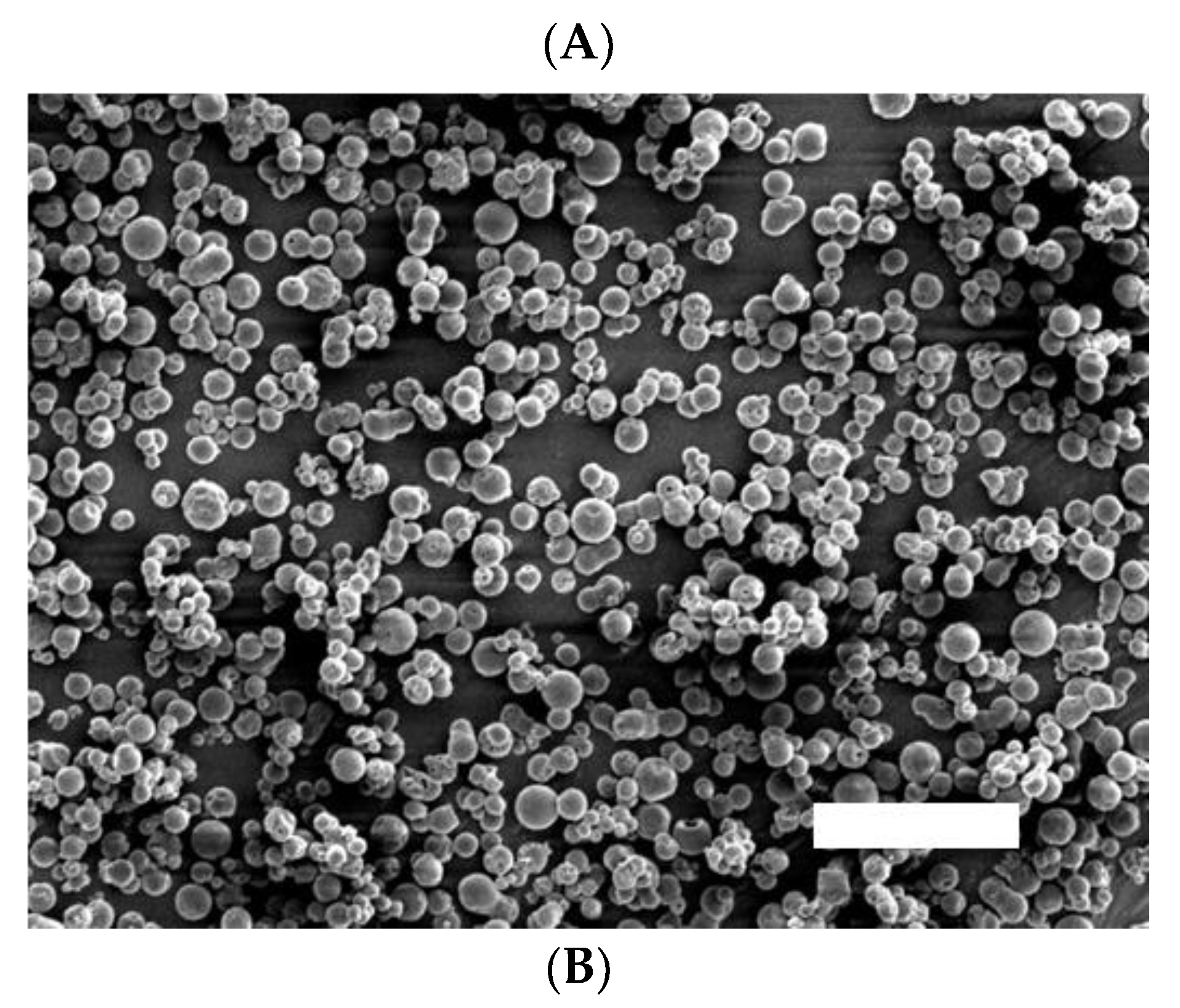
Expected drawbacks (e.g., aggregation and degradation) of VHH antibodies through the powderization process were the main concerns in this study [
18]. Thus, mild air-drying conditions were preferred to avoid such drawbacks. The schematic diagram of the FDD process adapted for the powderization of the VHH antibody is shown in
Figure 1. VHHp, including the HSA-VHH antibody, were produced through the FDD process with air temperatures of 35, 50 and 65 °C, which are relatively low compared with general temperatures used in the spray drying process [
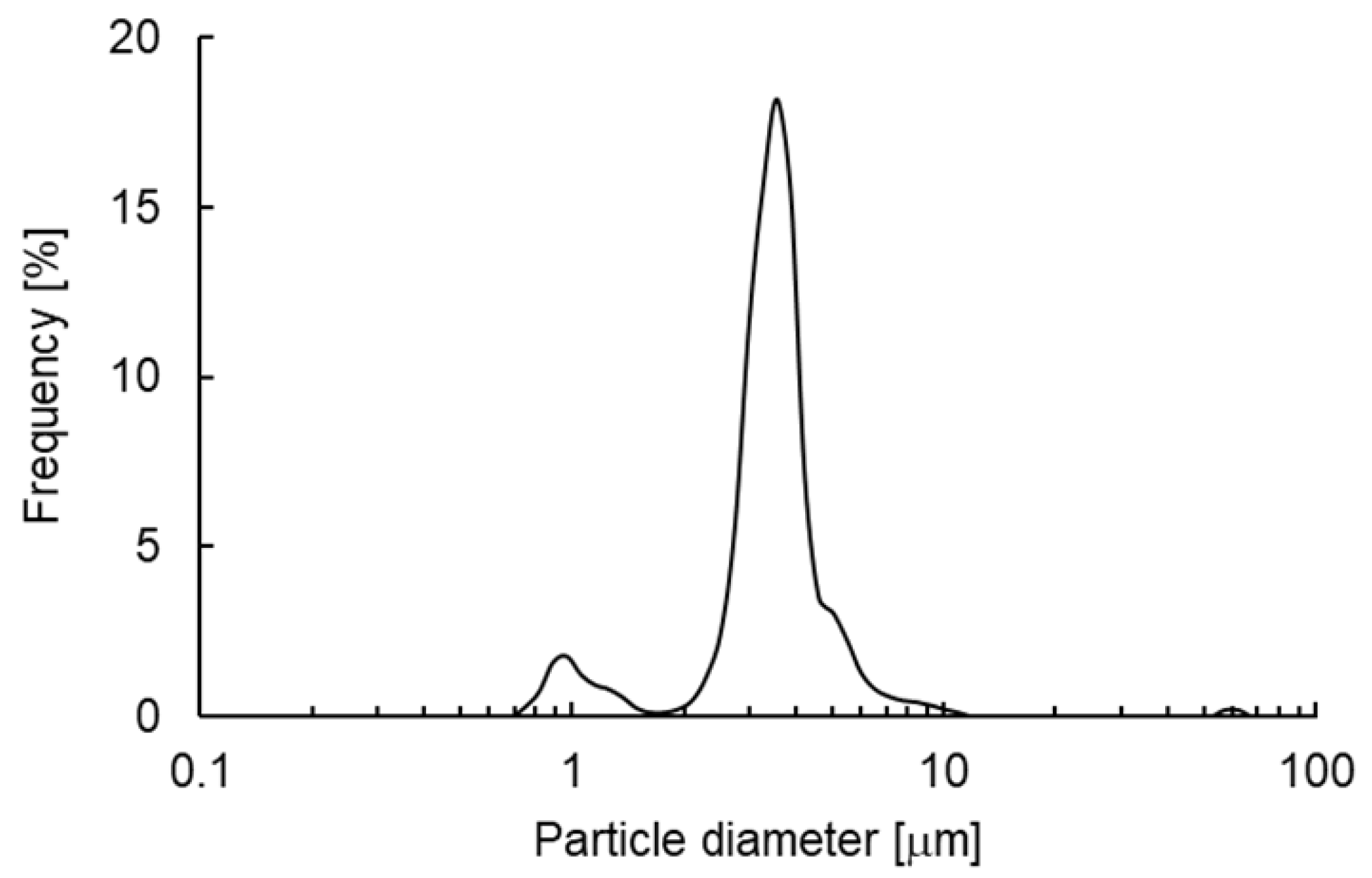
19]. SEM analysis revealed that each VHHp was a spherical particle with a uniform size (
Figure 2A). From the results of laser diffraction analysis, the particle diameter of the VHHp prepared with air drying conditions of 35, 50 and 65 °C were 3.6, 3.5 and 3.6 mm, and the SPAN factor values of VHHp were calculated to be 0.7, 0.7 and 0.6, respectively (
Figure 2B). In a previous study, a relationship between mannitol-particle morphology and airflow temperature was investigated [
20], revealing that the particle morphology was influenced by the airflow temperature with a high temperature of 120 °C generating a rough surface. In contrast, VHHp prepared with an airflow of 35 °C adopted a spherical shape and smooth surface. This difference in drying conditions may be responsible for the observed size uniformity of discharged droplets. Higher drying temperatures generally generate greater polydispersity, with larger droplets formed compared with the average droplet size. In contrast, monodispersed droplets, like those prepared with the FDD process, may not require extra heat during drying. Previous studies have produced and evaluated several kinds of pharmaceutical powders using the FDD process [15-17], with mild air drying conditions as a standard approach. In this context, the FDD process may effectively control the surface morphology of VHHp, possibly leading to the fine flowability of the powder because of its small contact area [
21]. Moreover, powderization of VHH antibodies may improve their storage stability and yield uniform solubility derived from particle size uniformity [22, 23]. Thus, the FDD process represents a potential option for preparing drug-loaded fine powder formulations, especially heat-sensitive drugs such as biomolecules.
3.2. VHH Antibody Properties in VHHp
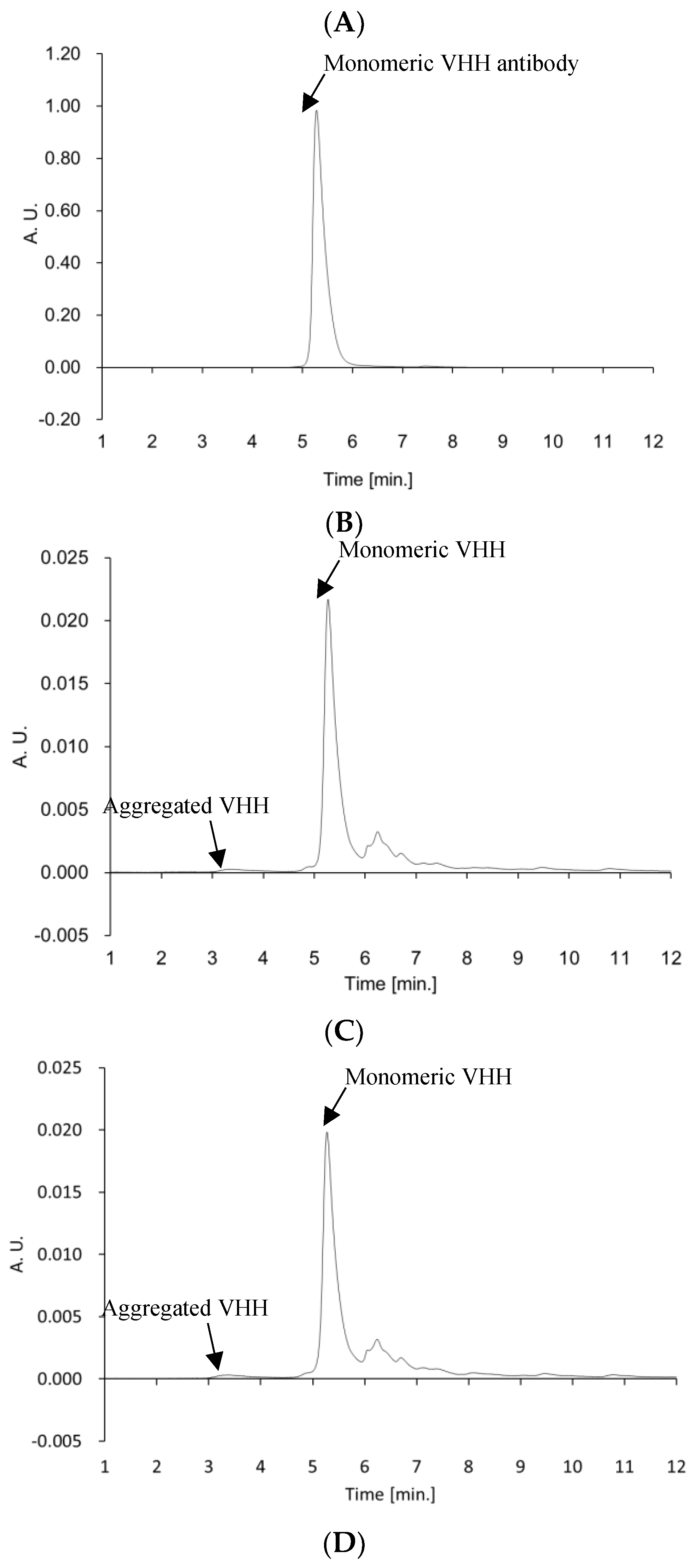
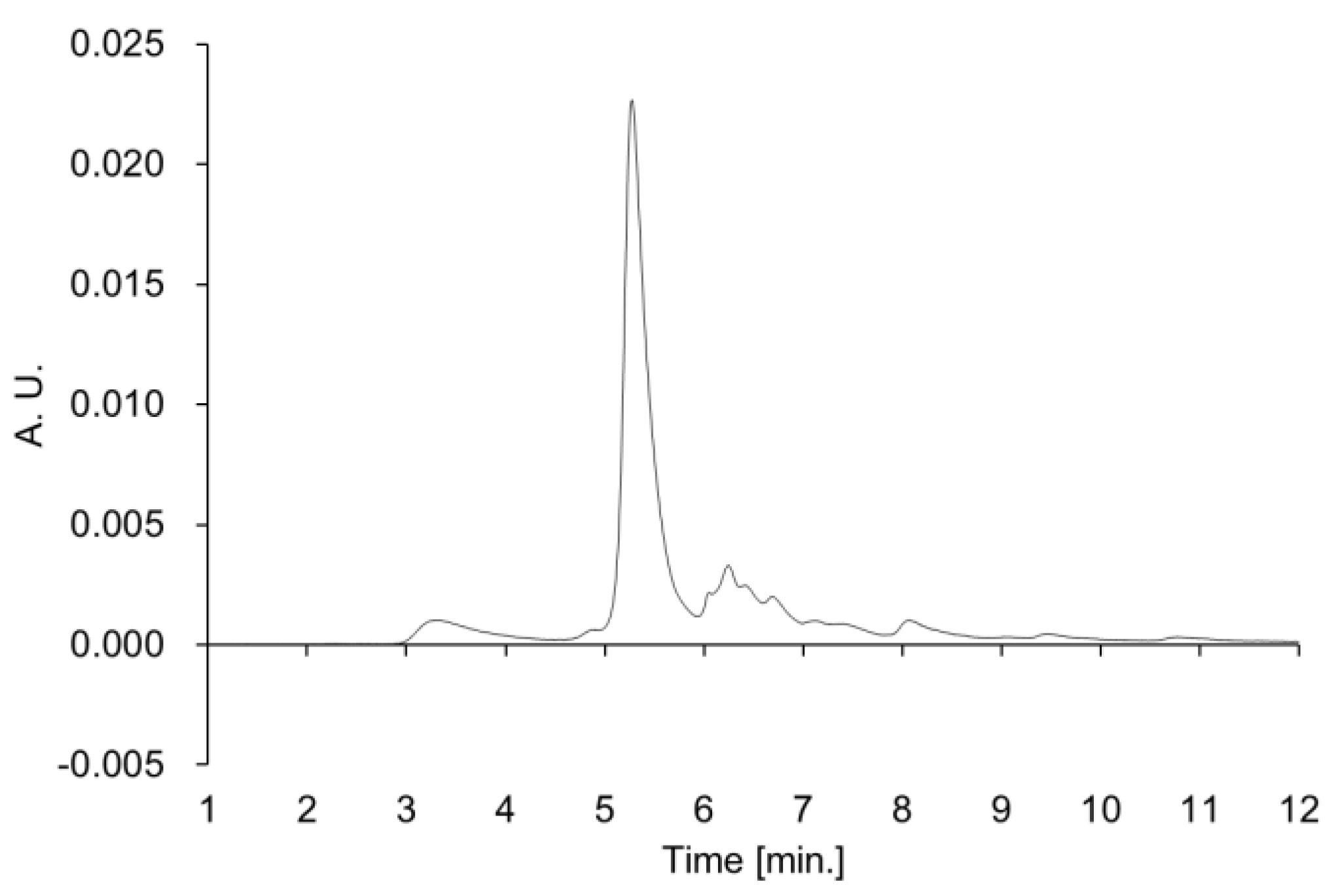
The VHH antibody in VHHp may be affected by environmental conditions during the FDD process. Therefore, HPLC analysis and bio-layer interferometry were conducted to clarify whether the physical characteristics of the VHH antibody were altered after the FDD process. HPLC analysis confirmed that the VHH antibody aggregated in VHHp (
Figure 3and
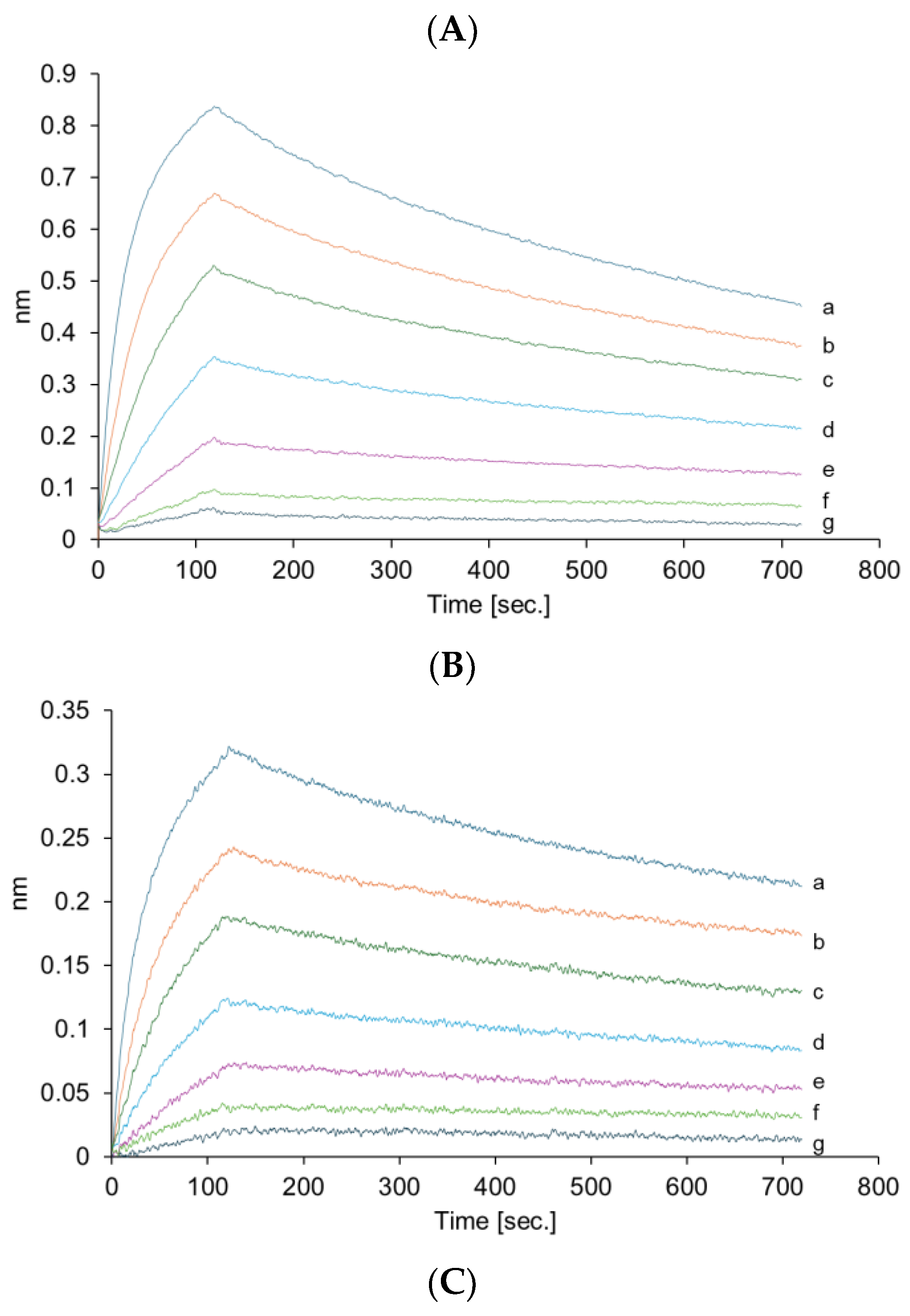
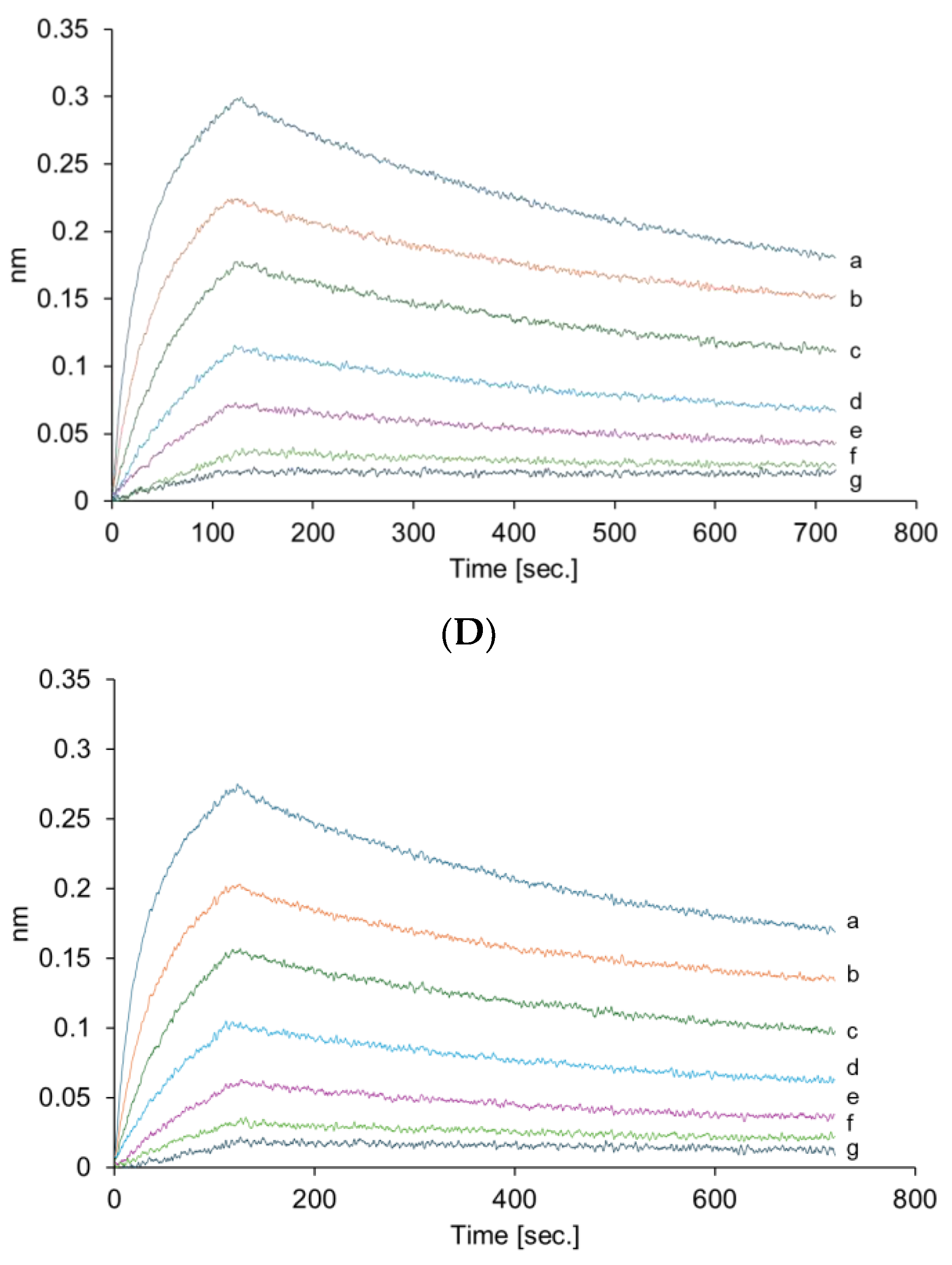
Figure S2). Regardless of the amount of aggregates, the binding activity of the VHH antibodies in each VHHp sample did not change when compared with VHH antibodies before powderization (
Figure 4). A previous study reported that the temperature in the manufacturing process is a critical factor responsible for aggregation [
18]. The aggregation ratio of the VHH antibody in VHHp samples was dependent on the airflow temperature, with the highest aggregation ratio of 9% observed under the airflow condition of 65 °C. A correlation between aggregation ratio and airflow temperature can be partly explained by the aggregation temperature (
Tagg) of the VHH antibody. The
Tagg of the VHH antibody was determined to be 48.8 ± 8.4 °C, which is similar to the temperature of the air drying during the FDD process. This observation may explain why the observed aggregation ratio under the airflow condition of 65 °C was clearly high compared with other VHHp samples. In this context, the structure of the VHH antibody may be influenced by the environment in the powderization process, and mild conditions may be required for VHHp powderization. Nonetheless, the aggregation ratios of the VHH antibodies for every VHHp sample were below 10%. This observation may explain the similar binding affinities of each VHHp in the bio-layer interferometry analysis. Thus, we postulate that the condition settings used for the powderization process are important in maintaining the native VHH antibody properties in VHHp. These insights may facilitate various applications of VHH antibodies for pharmaceutical use, especially for preparing dry powder inhalers. By designing the function of VHH antibodies through evolutionary engineering [
24] or designing multivalent VHH antibodies through protein engineering [
10], inhalable VHH antibody drugs may potentially be utilized for treating lung cancer, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, idiopathic interstitial pneumonias and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Additionally, formulating VHH antibodies with larger particle sizes for neurogenic diseases potentially offers intranasal medications, with peptide drugs reported as promising candidates for treating central nervous system diseases [
25]. Inhalation via pulmonary administration may effectively treat systemic diseases with reduced side effects [
26], indicating that powdered VHH antibodies produced using FDD technology can be applied to various unmet medical needs.
Table 1.
HPLC and bio-layer interferometry analysis of prepared VHHp.
Table 1.
HPLC and bio-layer interferometry analysis of prepared VHHp.
| |
Native VHH |
VHHp (35 °C) |
VHHp (50 °C) |
VHHp (65 °C) |
| Aggregation (%) |
0.00 |
1.77 |
3.09 |
9.06 |
|
KD (M) |
4.56 × 10-9
|
3.95 × 10-9
|
4.51 × 10-9
|
4.18 × 10-9
|
|
kon (M/s) |
2.08 × 105
|
1.57 × 105
|
1.74 × 105
|
1.86 × 105
|
|
koff (s–1) |
9.48 × 10-4
|
6.18 × 10-4
|
7.87 × 10-4
|
7.75 × 10-4
|
3.3. Inhalation Properties of VHHp
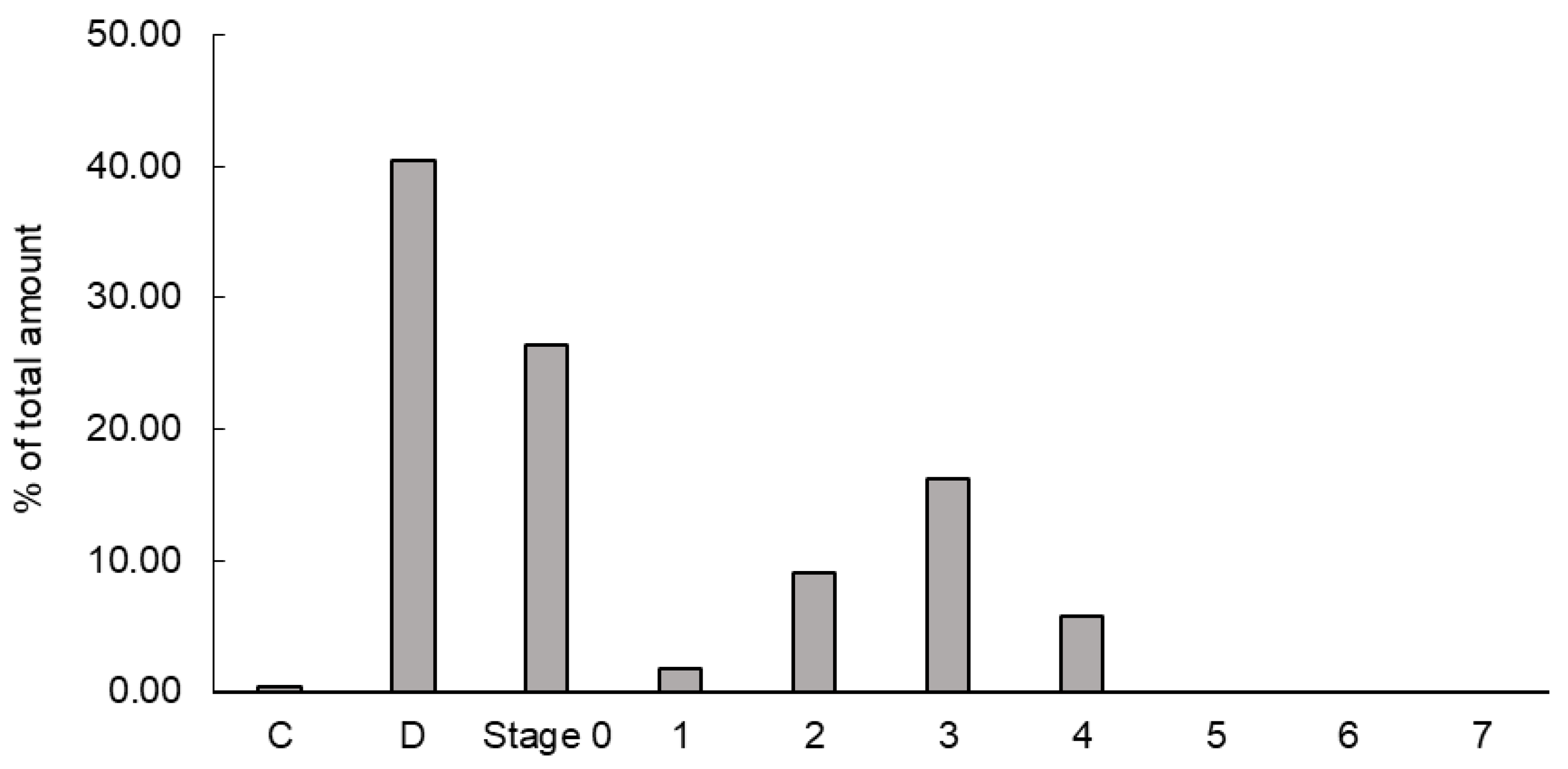
VHHp generated by airflow drying at 35 °C was used to evaluate the inhalation properties. The SEM image of VHHp showed that it had a smooth surface and spherical shape, possibly leading to the good flow ability of VHHp because of its low surface area-to-volume. To estimate the in vivo deposition of VHHp after inhalation, the in vitro inhalation properties were evaluated by Andersen cascade impactor analysis. The deposition pattern of VHHp after inhalation with JetHelar
®, a simple inhalation device, is shown in
Figure 5. The calculated FPF value of VHHp was 31.1%, representing a fine inhalation property. The FPF value of mannitol particles with a diameter of 4 mm was previously evaluated, and FPF was reported to be 28.3% at an airflow of 60 L/min [
27]. The airflow of the past study was approximately two-fold higher than that used for VHHp. In this context, VHHp may have finer inhalation properties than particles produced by the general spray drying method. However, the FPF value generally tends to vary depending on the measurement conditions and device. The findings indicate the applicability of VHHp as an inhalable powder for intratracheal administration.
4. Conclusions
The micro-sized-VHHp prepared using the FDD process had a spherical shape and smooth surface with a narrow size distribution. The amount of aggregated VHH antibody in VHHp depended on the airflow temperature used in the FDD process, and low temperatures provided lower aggregation amounts of the VHH antibody. The binding capabilities of VHH antibodies in VHHp were very similar in each sample, although the amounts of aggregated VHH antibodies in each sample differed. VHHp displayed fine inhalation properties in the cascade impactor test, indicating suitability for pharmaceutical applications, especially as an inhalable formulation. The findings show that the FDD process may be suitable for preparing various VHH antibody powder formulations, including pharmaceutical formulations.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org.
References
- Hamers-Casterman, C.; Atarhouch, T.; Muyldermans, S.; Robinson, G.; Hammers, C.; Songa, E. B.; Bendahman, N.; Hammers, R. Naturally Occurring Antibodies Devoid of Light Chains. Nature 1993. [CrossRef]
- Van Der Linden, R.; De Geus, B.; Stok, W.; Bos, W.; Van Wassenaar, D.; Verrips, T.; Frenken, L. Induction of Immune Responses and Molecular Cloning of the Heavy Chain Antibody Repertoire of Lama Glama. J. Immunol. Methods 2000. [CrossRef]
- Rothbauer, U.; Zolghadr, K.; Tillib, S.; Nowak, D.; Schermelleh, L.; Gahl, A.; Backmann, N.; Conrath, K.; Muyldermans, S.; Cardoso, M. C.; Leonhardt, H. Targeting and Tracing Antigens in Live Cells with Fluorescent Nanobodies. Nat. Methods 2006. [CrossRef]
- Maass, D. R.; Sepulveda, J.; Pernthaner, A.; Shoemaker, C. B. Alpaca (Lama Pacos) as a Convenient Source of Recombinant Camelid Heavy Chain Antibodies (VHHs). J. Immunol. Methods 2007. [CrossRef]
- De Simone, E. A.; Saccodossi, N.; Ferrari, A.; Leoni, J. Development of ELISAs for the Measurement of IgM and IgG Subclasses in Sera from Llamas (Lama Glama) and Assessment of the Humoral Immune Response against Different Antigens. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2008. [CrossRef]
- Blanc, M. R.; Anouassi, A.; Abed, M. A.; Tsikis, G.; Canepa, S.; Labas, V.; Belghazi, M.; Bruneau, G. A One-step Exclusion-binding Procedure for the Purification of Functional Heavy-chain and Mammalian-type Γ-globulins from Camelid Sera. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2009. [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Gao, Y.; Han, J. Application Progress of the Single Domain Antibody in Medicine. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Mochizuki, Y.; Kimura, S.; Akazawa-Ogawa, Y.; Hagihara, Y.; Nemoto, N. Anti-Survivin Single-Domain Antibodies Derived from an Artificial Library Including Three Synthetic Random Regions by in Vitro Selection Using CDNA Display. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018. [CrossRef]
- Moutel, S.; Bery, N.; Bernard, V.; Keller, L.; Lemesre, E.; De Marco, A.; Ligat, L.; Rain, J. C.; Favre, G.; Olichon, A.; Perez, F. NaLi-H1: A Universal Synthetic Library of Humanized Nanobodies Providing Highly Functional Antibodies and Intrabodies. Elife 2016. [CrossRef]
- Murakami, T.; Kumachi, S.; Matsunaga, Y.; Sato, M.; Wakabayashi-Nakao, K.; Masaki, H.; Yonehara, R.; Motohashi, M.; Nemoto, N.; Tsuchiya, M. Construction of a Humanized Artificial VHH Library Reproducing Structural Features of Camelid VHHs for Therapeutics. Antibodies 2022. [CrossRef]
- Haga, K.; Takai-Todaka, R.; Matsumura, Y.; Song, C.; Takano, T.; Tojo, T.; Nagami, A.; Ishida, Y.; Masaki, H.; Tsuchiya, M.; Ebisudani, T.; Sugimoto, S.; Sato, T.; Yasuda, H.; Fukunaga, K.; Sawada, A.; Nemoto, N.; Murata, K.; Morimoto, T.; Katayama, K. Nasal Delivery of Single-Domain Antibody Improves Symptoms of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in an Animal Model. PLoS Pathog. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Jabbal, S.; Poli, G.; Lipworth, B. Does Size Really Matter?: Relationship of Particle Size to Lung Deposition and Exhaled Fraction. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017. [CrossRef]
- Heyder, J. Particle Transport onto Human Airway Surfaces. Eur. J. Respir. Dis. 1982.
- Norikane, Y.; Nakamura, H.; Oogaki, M.; Sekiguchi, Y. A Droplet Discharge Method, a Droplet Discharge Device and Ink-Jet Record Device, 2011.
- Suzuki, H.; Moritani, T.; Morinaga, T.; Seto, Y.; Sato, H.; Onoue, S. Amorphous Solid Dispersion of Cyclosporine A Prepared with Fine Droplet Drying Process: Physicochemical and Pharmacokinetic Characterization. Int. J. Pharm. 2017. [CrossRef]
- Sato, H.; Tabata, A.; Moritani, T.; Morinaga, T.; Mizumoto, T.; Seto, Y.; Onoue, S. Design and Characterizations of Inhalable Poly(Lactic-Co-Glycolic Acid) Microspheres Prepared by the Fine Droplet Drying Process for a Sustained Effect of Salmon Calcitonin. Molecules 2020. [CrossRef]
- Moritani, T.; Usui, H.; Morinaga, T.; Sato, H.; Onoue, S. Cyclosporine A-Loaded Ternary Solid Dispersion Prepared with Fine Droplet Drying Process for Improvement of Storage Stability and Oral Bioavailability. Pharmaceutics 2023. [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Rey, M.; Lang, D. A. Aggregates in Monoclonal Antibody Manufacturing Processes. Biotechnology and Bioengineering. 2011. [CrossRef]
- Chiou, D.; Langrish, T. A. G.; Braham, R. The Effect of Temperature on the Crystallinity of Lactose Powders Produced by Spray Drying. J. Food Eng. 2008. [CrossRef]
- Maas, S. G.; Schaldach, G.; Littringer, E. M.; Mescher, A.; Griesser, U. J.; Braun, D. E.; Walzel, P. E.; Urbanetz, N. A. The Impact of Spray Drying Outlet Temperature on the Particle Morphology of Mannitol. Powder Technol. 2011. [CrossRef]
- Kaerger, J. S.; Edge, S.; Price, R. Influence of Particle Size and Shape on Flowability and Compactibility of Binary Mixtures of Paracetamol and Microcrystalline Cellulose. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2004. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Solomos, M.; Axnanda, S.; Chen, C.; Figus, M.; Schenck, L.; Sun, C. C. Varied Bulk Powder Properties of Micro-Sized API within Size Specifications as a Result of Particle Engineering Methods. Pharmaceutics 2022. [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Villen, F.; Gallego, I.; Sainz-Ramos, M.; Ordoyo-Pascual, J.; Ruiz-Alonso, S.; Saenz-del-Burgo, L.; O’Mahony, C.; Pedraz, J. L. Stability of Monoclonal Antibodies as Solid Formulation for Auto-Injectors: A Pilot Study. Pharmaceutics 2023. [CrossRef]
- Yonehara, R.; Kumachi, S.; Kashiwagi, K.; Wakabayashi-Nakao, K.; Motohashi, M.; Murakami, T.; Yanagisawa, T.; Arai, H.; Murakami, A.; Ueno, Y.; Nemoto, N.; Tsuchiya, M. A Novel Agonist with Homobivalent Single-Domain Antibodies That Bind the FGF Receptor 1 Domain III Functions as an FGF2 Ligand. J. Biol. Chem. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Akita, T.; Kimura, R.; Akaguma, S.; Nagai, M.; Nakao, Y.; Tsugane, M.; Suzuki, H.; Oka, J. ichiro; Yamashita, C. Usefulness of Cell-Penetrating Peptides and Penetration Accelerating Sequence for Nose-to-Brain Delivery of Glucagon-like Peptide-2. J. Control. Release 2021. [CrossRef]
- Guérin, M.; Lepeltier, E. Nanomedicines via the Pulmonary Route: A Promising Strategy to Reach the Target? Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2024, 14 (8), 2276–2297. [CrossRef]
- Glover, W.; Chan, H. K.; Eberl, S.; Daviskas, E.; Verschuer, J. Effect of Particle Size of Dry Powder Mannitol on the Lung Deposition in Healthy Volunteers. Int. J. Pharm. 2008. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).