Submitted:
15 October 2024
Posted:
16 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
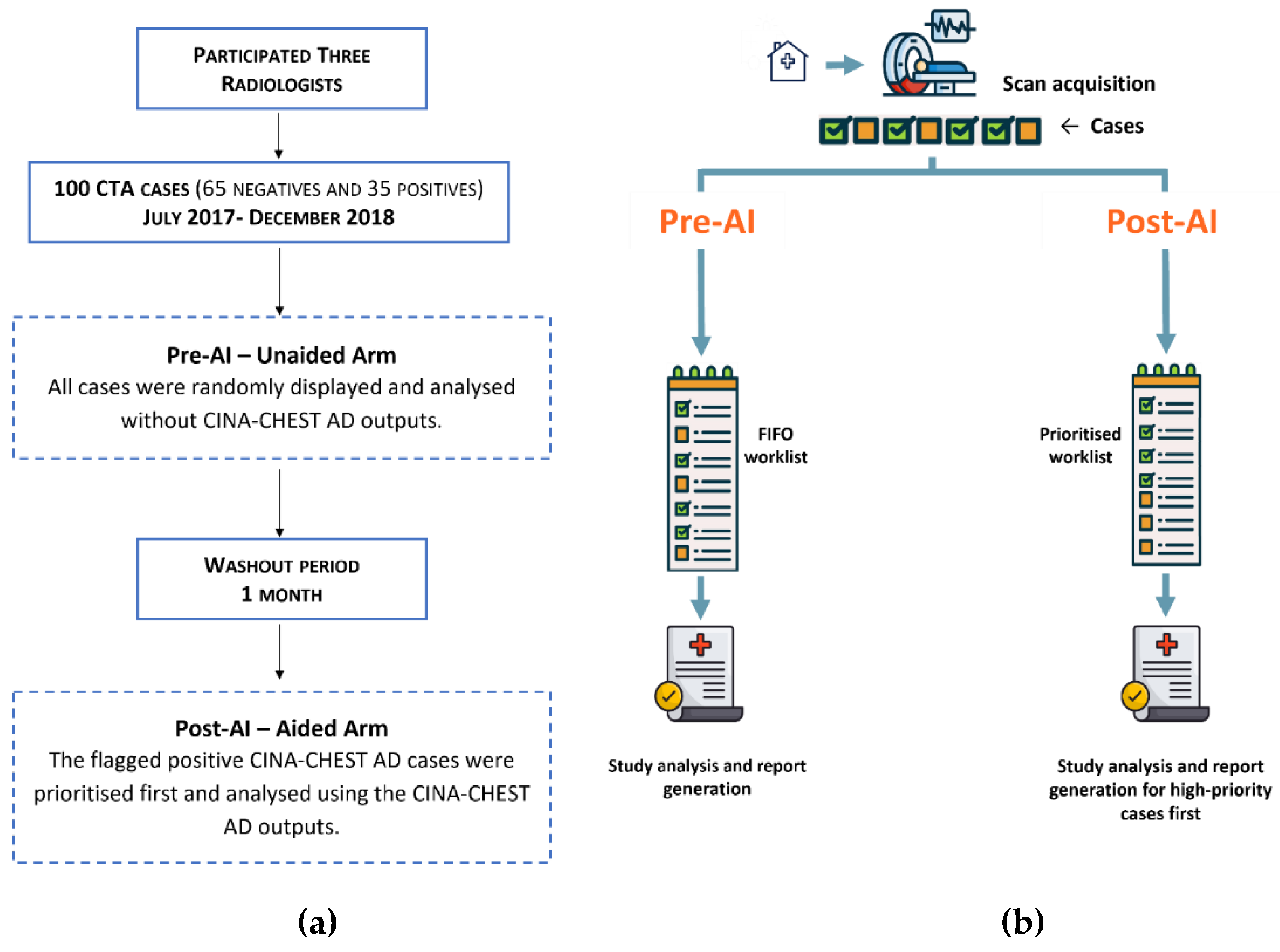
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. The Ground Truth
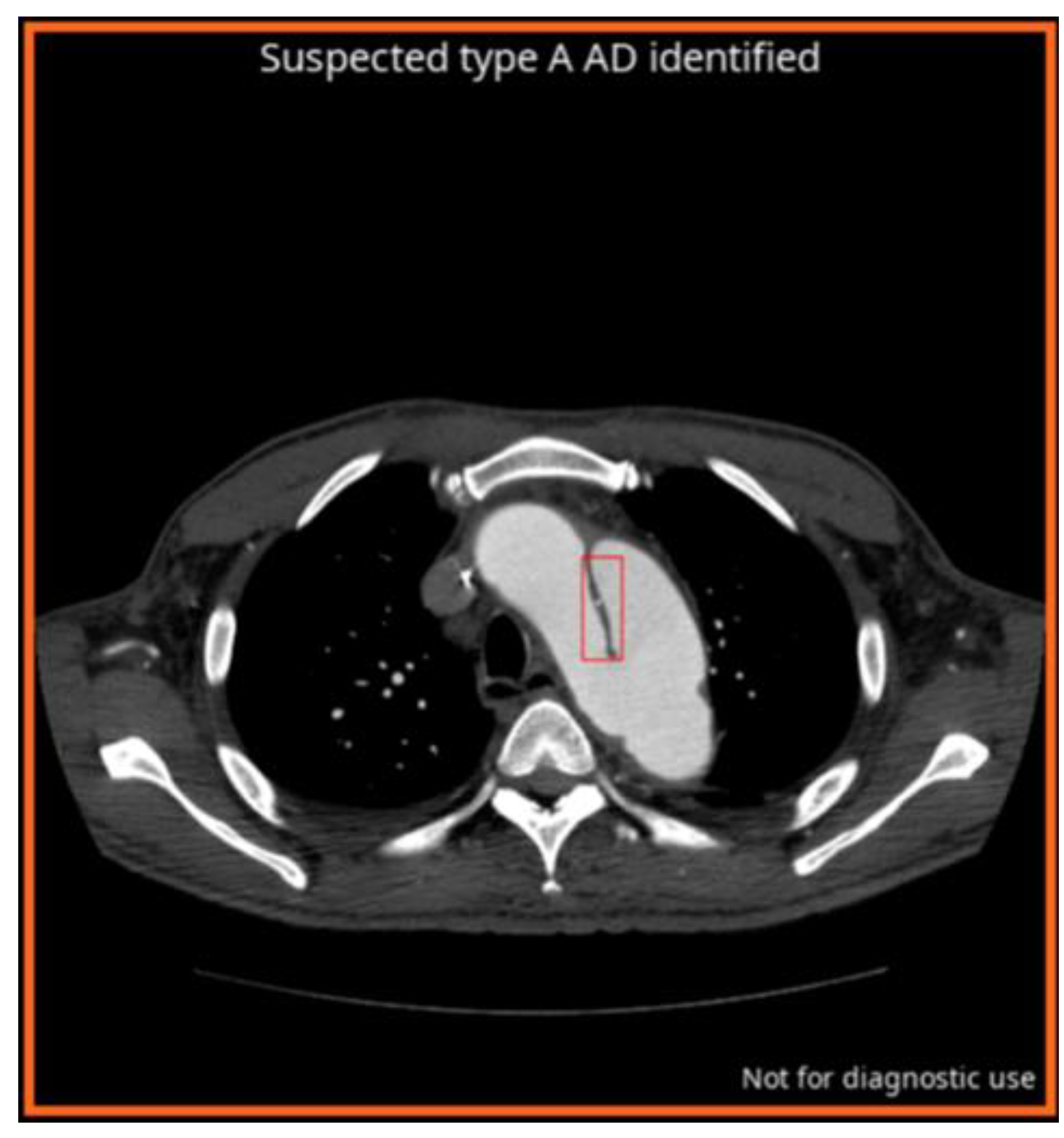
2.2.1. AI Algorithm for AD
2.3. Multi-Reader Multi-Case (MRMC) Study
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. AI and Readers Performance
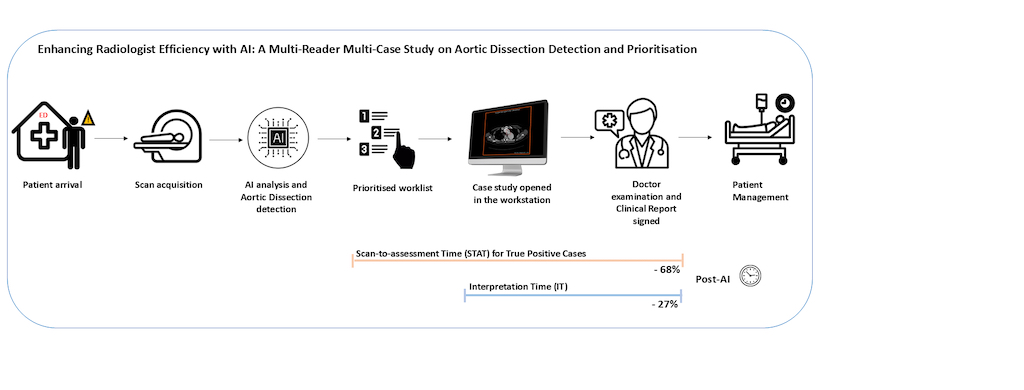
3.2. Comparison of Scan-to-Assessment Time
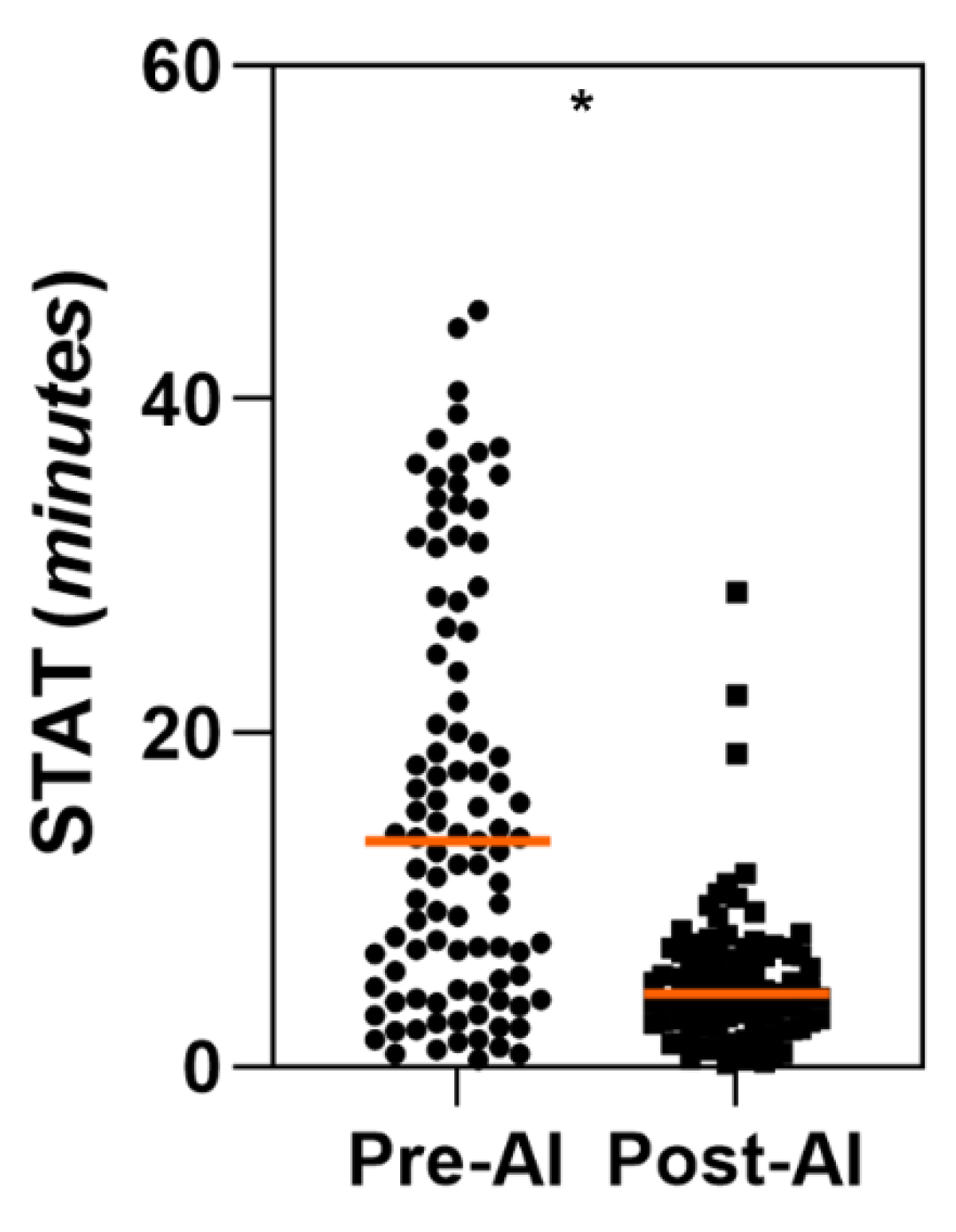
3.2.1. STAT for AD True Positives Cases
3.2.2. STAT for All Cases
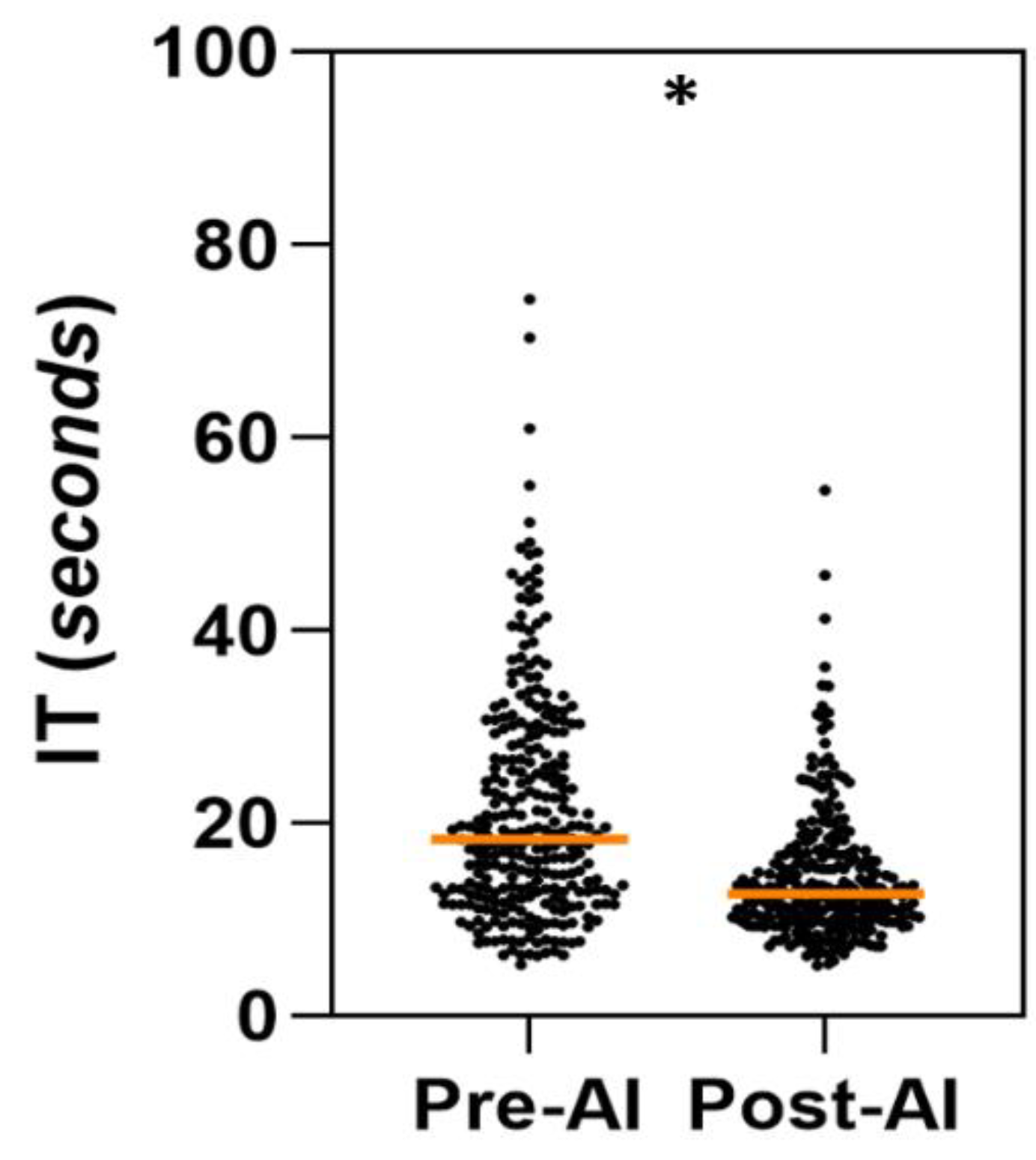
3.3. Comparison of Per-Case Interpretation Time (IT)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Konstantinides SV, Meyer G, Becattini C, et al. 2019 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism developed in collaboration with the European Respiratory Society (ERS). European Heart Journal 2020;41(4):543–603. [CrossRef]
- Gawinecka J, Schönrath F, Eckardstein A von. Acute aortic dissection: pathogenesis, risk factors and diagnosis. Swiss Medical Weekly 2017;147(3334):w14489–w14489. [CrossRef]
- Acharya M. Diagnosis and acute management of type A aortic dissection. Br J Cardiol 2023. [CrossRef]
- Kesävuori R, Kaseva T, Salli E, Raivio P, Savolainen S, Kangasniemi M. Deep learning-aided extraction of outer aortic surface from CT angiography scans of patients with Stanford type B aortic dissection. European Radiology Experimental 2023;7(1):35. [CrossRef]
- Isselbacher EM, Preventza O, Hamilton Black J, et al. 2022 ACC/AHA Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Aortic Disease: A Report of the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation 2022;146(24):e334–482. [CrossRef]
- Sebastià C, Pallisa E, Quiroga S, Alvarez-Castells A, Dominguez R, Evangelista A. Aortic dissection: diagnosis and follow-up with helical CT. Radiographics 1999;19(1):45–60; quiz 149–50. [CrossRef]
- De León Ayala IA, Chen Y-F. Acute aortic dissection: an update. Kaohsiung J Med Sci 2012;28(6):299–305. [CrossRef]
- Coady MA, Rizzo JA, Goldstein LJ, Elefteriades JA. NATURAL HISTORY, PATHOGENESIS, AND ETIOLOGY OF THORACIC AORTIC ANEURYSMS AND DISSECTIONS. Cardiology Clinics 1999;17(4):615–35. [CrossRef]
- Taylor-Phillips S, Stinton C. Fatigue in radiology: a fertile area for future research. Br J Radiol 2019;92(1099):20190043. [CrossRef]
- The Royal College of Radiologists. Turnaround times – what are we seeing? | The Royal College of Radiologists n.d. https://www.rcr.ac.uk/news-policy/policy-reports-initiatives/turnaround-times-what-are-we-seeing/ (accessed July 24, 2024).
- Zaschke L, Habazettl H, Thurau J, et al. Acute type A aortic dissection: Aortic Dissection Detection Risk Score in emergency care – surgical delay because of initial misdiagnosis. European Heart Journal Acute Cardiovascular Care 2020;9(3_suppl):S40–7. [CrossRef]
- Froehlich W, Tolenaar JL, Harris KM, et al. Delay from Diagnosis to Surgery in Transferred Type A Aortic Dissection. Am J Med 2018;131(3):300–6. [CrossRef]
- Dey D, Slomka PJ, Leeson P, et al. Artificial Intelligence in Cardiovascular Imaging. J Am Coll Cardiol 2019;73(11):1317–35. [CrossRef]
- Ojeda P, Zawaideh M, Mossa-Basha M, Haynor D. The utility of deep learning: evaluation of a convolutional neural network for detection of intracranial bleeds on non-contrast head computed tomography studies. In: Angelini ED, Landman BA, eds. Medical Imaging 2019: Image Processing. San Diego, United States: SPIE; 2019;128. [CrossRef]
- Hunter B, Chen M, Ratnakumar P, et al. A radiomics-based decision support tool improves lung cancer diagnosis in combination with the Herder score in large lung nodules. eBioMedicine 2022;86. [CrossRef]
- Schmuelling L, Franzeck FC, Nickel CH, et al. Deep learning-based automated detection of pulmonary embolism on CT pulmonary angiograms: No significant effects on report communication times and patient turnaround in the emergency department nine months after technical implementation. European Journal of Radiology 2021;141:109816. [CrossRef]
- Petry M, Lansky C, Chodakiewitz Y, Maya M, Pressman B. Decreased Hospital Length of Stay for ICH and PE after Adoption of an Artificial Intelligence-Augmented Radiological Worklist Triage System. Radiology Research and Practice 2022;2022:1–7. [CrossRef]
- Xu X, He Z, Niu K, Zhang Y, Tang H, Tan L. An Automatic Detection Scheme of Acute Stanford Type A Aortic Dissection Based on DCNNs in CTA Images. Proceedings of the 2019 4th International Conference on Multimedia Systems and Signal Processing. Guangzhou China: ACM; 2019;16–20. [CrossRef]
- Laletin V, Ayobi A, Chang PD, et al. Diagnostic Performance of a Deep Learning-Powered Application for Aortic Dissection Triage Prioritization and Classification. Diagnostics 2024;14(17):1877. [CrossRef]
- U.S FOOD & DRUGS ADMINISTRATION. BriefCase for AD - K222329. 510(k) Premarket Notification. 2022.
- Harris RJ, Kim S, Lohr J, et al. Classification of Aortic Dissection and Rupture on Post-contrast CT Images Using a Convolutional Neural Network. J Digit Imaging 2019;32(6):939–46. [CrossRef]
- Baltruschat I, Steinmeister L, Nickisch H, et al. Smart chest X-ray worklist prioritization using artificial intelligence: a clinical workflow simulation. Eur Radiol 2021;31(6):3837–45. [CrossRef]
- FRALICK D, ZHENG JZ, Wang B, TU XM, FENG C. The Differences and Similarities Between Two-Sample T-Test and Paired T-Test. Shanghai Arch Psychiatry n.d.;29(3):184–8.
- Gaskin CM, Patrie JT, Hanshew MD, Boatman DM, McWey RP. Impact of a Reading Priority Scoring System on the Prioritization of Examination Interpretations. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2016;206(5):1031–9. [CrossRef]
- Fleischmann D, Afifi RO, Casanegra AI, et al. Imaging and Surveillance of Chronic Aortic Dissection: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging 2022;15(3):e000075. [CrossRef]
- Lovatt S, Wong CW, Schwarz K, et al. Misdiagnosis of aortic dissection: A systematic review of the literature. Am J Emerg Med 2022;53:16–22. [CrossRef]
- Lloyd-Jones DM. Cardiovascular Health and Protection Against CVD. Circulation 2014;130(19):1671–3. [CrossRef]
- Freundt M, Kolat P, Friedrich C, et al. Preoperative Predictors of Adverse Clinical Outcome in Emergent Repair of Acute Type A Aortic Dissection in 15 Year Follow Up. J Clin Med 2021;10(22):5370. [CrossRef]
- Mastrodicasa D, Codari M, Bäumler K, et al. Artificial Intelligence Applications in Aortic Dissection Imaging. Seminars in Roentgenology 2022;57(4):357–63. [CrossRef]
- Huang L-T, Tsai Y-S, Liou C-F, et al. Automated Stanford classification of aortic dissection using a 2-step hierarchical neural network at computed tomography angiography. Eur Radiol 2022;32(4):2277–85. [CrossRef]
- Hata A, Yanagawa M, Yamagata K, et al. Deep learning algorithm for detection of aortic dissection on non-contrast-enhanced CT. Eur Radiol 2021;31(2):1151–9. [CrossRef]
- Soffer S, Klang E, Shimon O, et al. Deep learning for pulmonary embolism detection on computed tomography pulmonary angiogram: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep 2021;11(1):15814. [CrossRef]
- Topff L, Ranschaert ER, Bartels-Rutten A, et al. Artificial Intelligence Tool for Detection and Worklist Prioritization Reduces Time to Diagnosis of Incidental Pulmonary Embolism at CT. Radiology: Cardiothoracic Imaging 2023;5(2):e220163. [CrossRef]
- Shapiro J. Shorter Time to Assessment and Anticoagulation with Decreased Mortality in Patients with Pulmonary Embolism Following Implementation of Artificial Intelligence Software 2024.
- Davis MA, Rao B, Cedeno PA, Saha A, Zohrabian VM. Machine Learning and Improved Quality Metrics in Acute Intracranial Hemorrhage by Noncontrast Computed Tomography. Current Problems in Diagnostic Radiology 2022;51(4):556–61. [CrossRef]
- Müller FC, Raaschou H, Akhtar N, Brejnebøl M, Collatz L, Andersen MB. Impact of Concurrent Use of Artificial Intelligence Tools on Radiologists Reading Time: A Prospective Feasibility Study. Academic Radiology 2022;29(7):1085–90. [CrossRef]
- Brown M, Browning P, Wahi-Anwar MW, et al. Integration of Chest CT CAD into the Clinical Workflow and Impact on Radiologist Efficiency. Academic Radiology 2019;26(5):626–31. [CrossRef]
- Yacoub B, Varga-Szemes A, Schoepf UJ, et al. Impact of Artificial Intelligence Assistance on Chest CT Interpretation Times: A Prospective Randomized Study. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2022;219(5):743–51. [CrossRef]

| Scanner makers | Occurrence (%) | Slice Thickness | Occurrence (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GE MEDICAL SYSTEMS | 59 (62.11%) | ST < 1 mm | 4 (4%) | |
| SIEMENS | 21 (22.1%) | 1 ≤ ST ≤ 2.5mm | 83 (87%) | |
| CANON (Formerly TOSHIBA) | 10 (10.53%) | ST ≤ 3mm | 8 (9%) | |
| PHILIPS | 5 (5.26%) | |||
| TOTAL 95 | ||||
| Parameter % [95% CI] | Reader 1 | Reader 2 | Reader 3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-AI | Post-AI | Pre-AI | Post-AI | Pre-AI | Post-AI | |
| Accuracy |
98.95%
[94.33-99.97%] |
97.89%
[92.60-99.74%] |
97.895%
[92.60-99.74%] |
97.895%
[92.60-99.74%] |
97.895%
[92.60-99.74%] |
98.94%
[94.27-99.97%] |
| Sensitivity |
100%
[89.99-100.0%] |
100%
[89.99-100.0%] |
100%
[89.99-100.0%] |
94.27%
[80.84-99.3%] |
97.143%
[85.08-99.92%] |
97.143%
[85.08-99.92%] |
| Specificity |
98.33%
[91.20-99.96%] |
96.66%
[88.47-99.59%] |
96.66%
[88.47-99.59%] |
100%
[94.03-100.0%] |
98.33%
[91.20-99.96%] |
100%
[94.03-100.0%] |
| AUROC |
0.992
[0.947-1.0] |
0.983
[0.933-0.999] |
0.983
[0.933-0.999] |
0.971
[0.915-0.995] |
0.977
[0.924-0.997] |
0.986
[0.937-0.999] |
| STAT for True Positive AD cases | Unaided Arm Time (min) Mean ± SD [95% CI] |
Aided Arm Time (min) Mean ± SD [95% CI] |
Aided - Unaided Difference (min) Mean ± SD [95% CI] |
|---|---|---|---|
|
All readers (N = 99) |
15.84 ± 12.22 [13.37, 18.31] |
5.07 ± 4.24 [4.23, 5.91] |
-10.77* ± 12.96 [-13.36, -8.18] |
|
Reader 1 (N = 33) |
9.45 ± 6.41 [7.17, 11.72] |
4.36 ± 3.36 [3.17, 5.56] |
-5.08* ± 7.05 [-7.64, -2.53] |
|
Reader 2 (N = 33) |
19.72 ± 14.09 [14.06, 25.38] |
4.53 ± 3.83 [3.17, 5.88] |
-15.19* ± 14.69 [-20.39, -9.98] |
|
Reader 3 (N = 33) |
18.36 ± 12.29 [13.79, 22.94] |
6.32 ± 5.06 [4.53, 8.10] |
-12.04* ± 13.85 [-18.62, -5.46] |
| Readers’ experience | Unaided Arm Time (min) Mean ± SD [95% CI] |
Aided Arm Time (min) Mean ± SD [95% CI] |
Aided - Unaided Difference (min) Mean ± SD [95% CI] |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Junior (N = 33) |
9.45 ± 6.41 [7.17, 11.72] |
4.36 ± 3.36 [3.17, 5.56] |
-5.08* ± 7.05 [-7.64, -2.53] |
|
Senior (N = 66) |
19.04 ± 13.41 [15.74, 22.67] |
5.43 ± 4.54 [4.31, 6.54] |
-13.63* ± 14.25 [-17.12, -10.13] |
| STAT for all cases | Unaided Arm Time (min) Mean ± SD [95% CI] |
Aided Arm Time (min) Mean ± SD [95% CI] |
Aided - Unaided Difference (min) Mean ± SD [95% CI] |
|---|---|---|---|
|
All readers (N = 285) |
17.17 ± 12.16 [15.75, 18.60] |
12.54 ± 7.15 [11.71, 13.86] |
-4.62* ± 13.06 [-6.14, -3.10] |
|
Reader 1 (N = 95) |
10.18 ± 6.10 [8.94, 11.43] |
10.64 ± 5.55 [9.51, 11.76] |
0.45 ± 7.78 [1.13, 2.04] |
|
Reader 2 (N = 95) |
21.46 ± 13.50 [18.71, 24.21] |
11.62 ± 6.61 [10.28, 13.04] |
-9.84* ± 14.33 [-12.76, -6.92] |
|
Reader 3 (N = 95) |
19.85 ± 12.32 [17.34, 22.36] |
15.37 ± 8.22 [13.70, 17.94] |
-4.48* ± 13.33 [-7.33, -1.63] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





