1. Introduction
In the modern era of education, artificial intelligence (AI) has become an integral part of the learning experience, providing tools and platforms that offer personalized instruction, adaptive learning, and instant feedback (Kapoor et al., 2023). AI-based educational technologies have transformed the way students interact with learning content, offering a highly individualized approach that adapts to the pace and needs of each learner. Despite its benefits, the growing use of AI-driven instructional models has raised new challenges. These include increased emotional detachment, diminished learner engagement, and reduced control over the learning process due to the absence of human interactions and personalized guidance (Brandmiller et al., 2023; Schnitzler et al., 2021).
Students frequently struggle with disengagement in AI-driven environments. This disengagement can stem from the mechanical and impersonal nature of AI-based feedback, which often lacks the empathetic and emotional nuances that human instructors provide (Chiang, Chang & Chen, 2024). Moreover, learners may feel isolated when interacting with AI systems, which do not inherently possess the capacity for social and emotional intelligence. The cold, one-sided output of AI systems may hinder the development of deep, meaningful learning experiences, thereby affecting students’ intrinsic motivation and reducing their overall satisfaction with the learning process (Birenbaum, 2023). The challenge, therefore, lies in designing AI-driven learning experiences that effectively address both cognitive and emotional aspects of learning.
To address these challenges, this study investigates the potential of integrating Alternate Reality Games (ARG) with AI-guided instruction, combining the benefits of technology-enhanced learning with interactive, immersive elements. ARGs are designed to create rich, contextual environments that immerse learners in a narrative, allowing them to be active participants in solving complex, real-world problems (Hou et al., 2021). By fostering active participation and offering emotionally engaging scenarios, ARGs have the potential to bridge the gap between AI-driven personalization and the need for emotional and social interaction in learning.
This study aims to explore how the combination of Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) LLM-based AI instruction with ARG elements impacts the emotional, participatory, and cognitive aspects of learning for students with varying cognitive styles in an introductory digital learning course. The RAG model enhances the accuracy and contextual relevance of AI responses by incorporating external information sources, making it well-suited for delivering personalized content in educational settings (Izacard & Grave, 2021).
Specifically, this paper investigates the effect of this blended pedagogical approach on learning emotions, engagement, and control beliefs. Learning emotions are essential as they influence cognitive processes such as attention, motivation, and memory retention (Pekrun, 2014). Engagement, on the other hand, is a multidimensional construct encompassing behavioral, emotional, and cognitive involvement in learning activities (Fredricks, Blumenfeld, & Paris, 2004). Control beliefs refer to a student's perceived ability to influence their learning outcomes, which is closely linked to self-efficacy and motivation (Bandura, 1997). By analyzing interview data from 65 students who experienced this innovative learning environment, we hope to provide valuable insights into how educators can effectively incorporate AI and ARG to improve learning outcomes and foster positive emotional experiences.
2. Literature Review
AI-guided instruction has significantly transformed education, offering benefits such as personalized learning pathways, adaptive content delivery, and instantaneous feedback (Wang, Zheng & Chen, 2024). AI technologies can analyze student data to determine individual strengths, weaknesses, and preferences, allowing for a customized learning experience that can accommodate different learning paces and styles. This level of personalization is particularly beneficial for students who may struggle in traditional classroom settings, as it allows them to receive support tailored to their specific needs (Kapoor et al., 2023).
However, the limitations of purely AI-driven models have also surfaced, notably in students' emotional well-being and engagement levels. Research has indicated that AI tools, while efficient, often fail to address the social and emotional needs of learners, resulting in emotional detachment and increased anxiety (Brandmiller et al., 2023; Schnitzler et al., 2021). Students may perceive AI systems as impersonal and unresponsive to their emotional states, leading to feelings of frustration and isolation (Bekeš & Galzina, 2023). Moreover, the lack of real-time, empathetic interaction in AI-based instruction can impede the development of a supportive learning environment, which is crucial for maintaining student motivation and engagement (Birenbaum, 2023).
Alternate Reality Games (ARG) have emerged as an effective means to counteract some of these drawbacks by providing immersive, context-rich environments that encourage learners to actively engage with content (Hou et al., 2021). ARGs blend real-world activities with game-based mechanics, promoting collaborative problem-solving and increasing learners' intrinsic motivation (Kinio et al., 2019; Hsu & Liang, 2017). ARGs are characterized by their ability to create compelling narratives that integrate learning objectives into engaging storylines, which helps foster emotional connections with the learning material. For instance, ARGs often include puzzles, challenges, and real-world tasks that require learners to collaborate, reflect, and apply their knowledge in meaningful ways (Pineiro-Otero & Costa-Sanchez, 2015).
Prior research has shown that when ARG is used in an educational setting, it can foster a more interactive and emotional learning experience, enabling students to apply learned concepts in realistic contexts (Gilliam et al., 2017). Studies have also demonstrated that ARGs can enhance students' problem-solving skills, promote teamwork, and increase their motivation to learn (Whitton, 2018). By situating learners within a narrative framework, ARGs provide opportunities for experiential learning, which has been shown to improve knowledge retention and the ability to transfer learned concepts to new situations (Kolb, 1984).
The combination of AI and ARG could potentially provide a balanced learning experience, mitigating the drawbacks of AI’s emotional coldness while maintaining the personalization advantages. This study builds on the work of Lewis et al. (2020) on Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) LLM, which integrates retrieval mechanisms to enhance the accuracy and context of AI-generated responses. RAG models provide a powerful approach to support personalized learning content and adapt to individual student needs dynamically. By incorporating ARG elements, this study aims to examine how cognitive style influences learning experiences, specifically concerning learning emotions, engagement, and control beliefs (Izacard & Grave, 2021; Liang et al., 2021).
The role of social and emotional aspects in learning has been emphasized in various studies. For example, Tack and Piech (2022) compared AI teachers with human instructors, noting that human instructors outperformed AI teachers in multiple dimensions of student engagement. The emotional coldness of AI-driven systems has often been criticized for leading to learner isolation, and studies such as those by Han et al. (2023) and Lan and Chen (2024) have called for integrating human elements to address these challenges. Additionally, Pekrun's (2014) Control-Value Theory of Achievement Emotions highlights the importance of emotions in academic settings, suggesting that positive emotions like enjoyment and pride can significantly enhance learning outcomes, while negative emotions like boredom and anxiety can impede them.
Incorporating ARG elements into AI-guided instruction may also address issues of learner autonomy and control beliefs. Control beliefs, or the perception of one's ability to influence learning outcomes, are crucial for maintaining motivation and fostering a sense of agency (Bandura, 1997). ARGs, by allowing learners to make decisions that impact the storyline and outcomes, can help enhance these control beliefs, thereby promoting a more autonomous and motivated learning experience. Studies by Zimmerman and Schunk (2001) have shown that learners who perceive themselves as having control over their learning are more likely to be engaged and persist in the face of challenges.
Moreover, the integration of ARGs with AI can cater to different cognitive styles, which refers to the preferred way an individual processes information. According to Riding and Rayner (1998), cognitive style plays a significant role in how learners interact with educational content. ARGs, with their immersive and flexible design, can be adapted to suit different cognitive styles, whether learners prefer visual, auditory, or kinesthetic methods of engagement. By incorporating ARGs, AI-driven instruction can provide a more inclusive learning environment that accommodates a wider range of learners, thereby enhancing overall educational outcomes.
3. Research Method
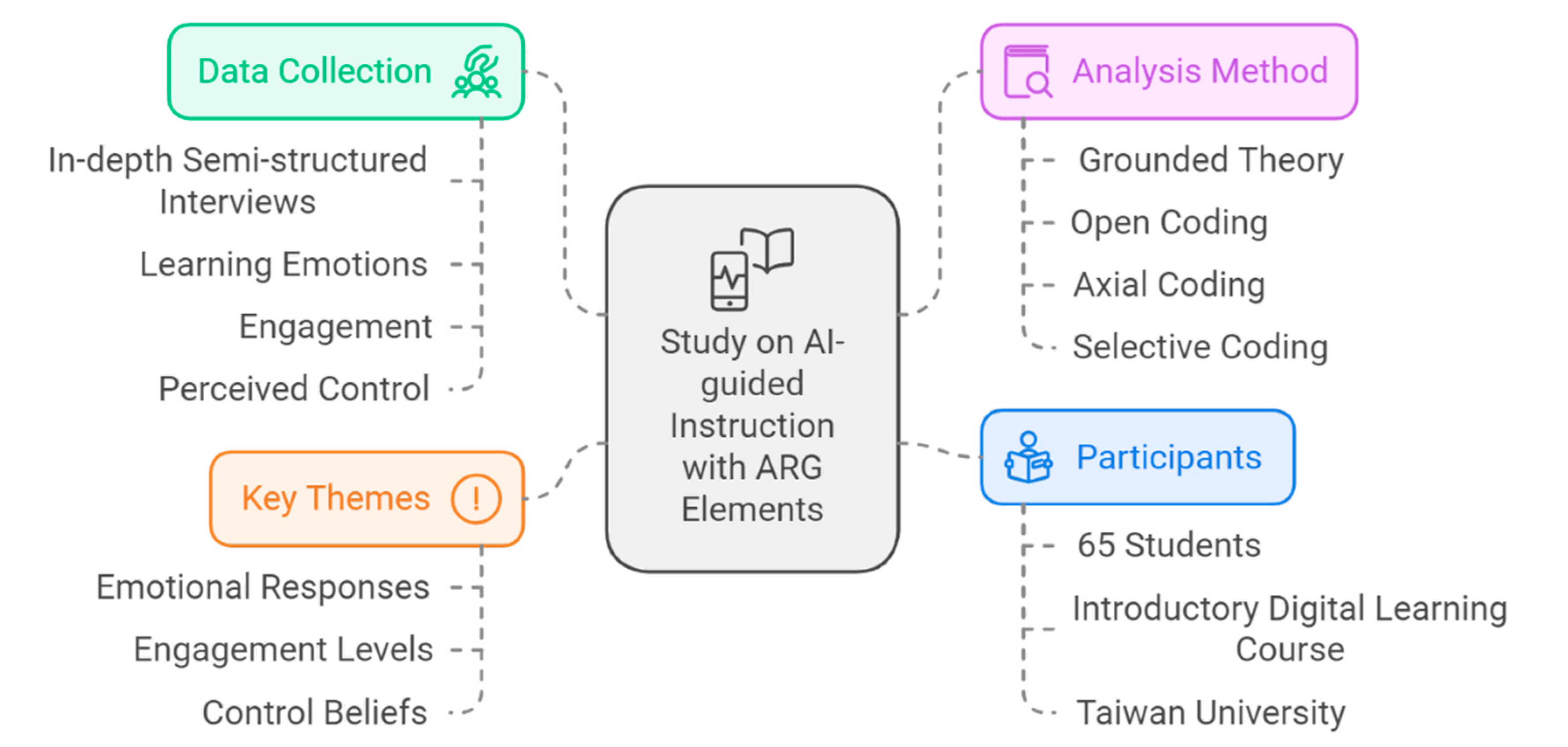
The study adopted a qualitative approach, utilizing grounded theory to analyze the learning experiences of students exposed to AI-guided instruction combined with ARG elements. The participants were 65 students enrolled in an introductory digital learning course at a university in Taiwan. Data were collected through in-depth semi-structured interviews, focusing on students' experiences with learning emotions, engagement, and their perceived control over the learning process.
The grounded theory approach allowed for the identification of key themes that emerged from the interview data, facilitating an in-depth understanding of how the ARG-integrated AI instruction influenced students' learning experiences. The analysis was carried out using open, axial, and selective coding, allowing the emergence of categories and relationships between themes, particularly concerning students' emotional responses, engagement levels, and control beliefs.
The semi-structured interviews included questions designed to explore various aspects of the learning experience, such as: "How did the ARG elements affect your interest in the course content?" and "Did you feel more in control of your learning process when ARG scenarios were incorporated?" This approach provided flexibility, allowing participants to express their thoughts freely while ensuring that key areas of interest were covered. The interviews were conducted over several weeks, with each session lasting between 30 to 60 minutes. Participants were selected based on their enrollment in the course and willingness to participate, ensuring a diverse sample in terms of cognitive styles and prior experience with digital learning.
Figure 1 shows the research model.
4. Research Results
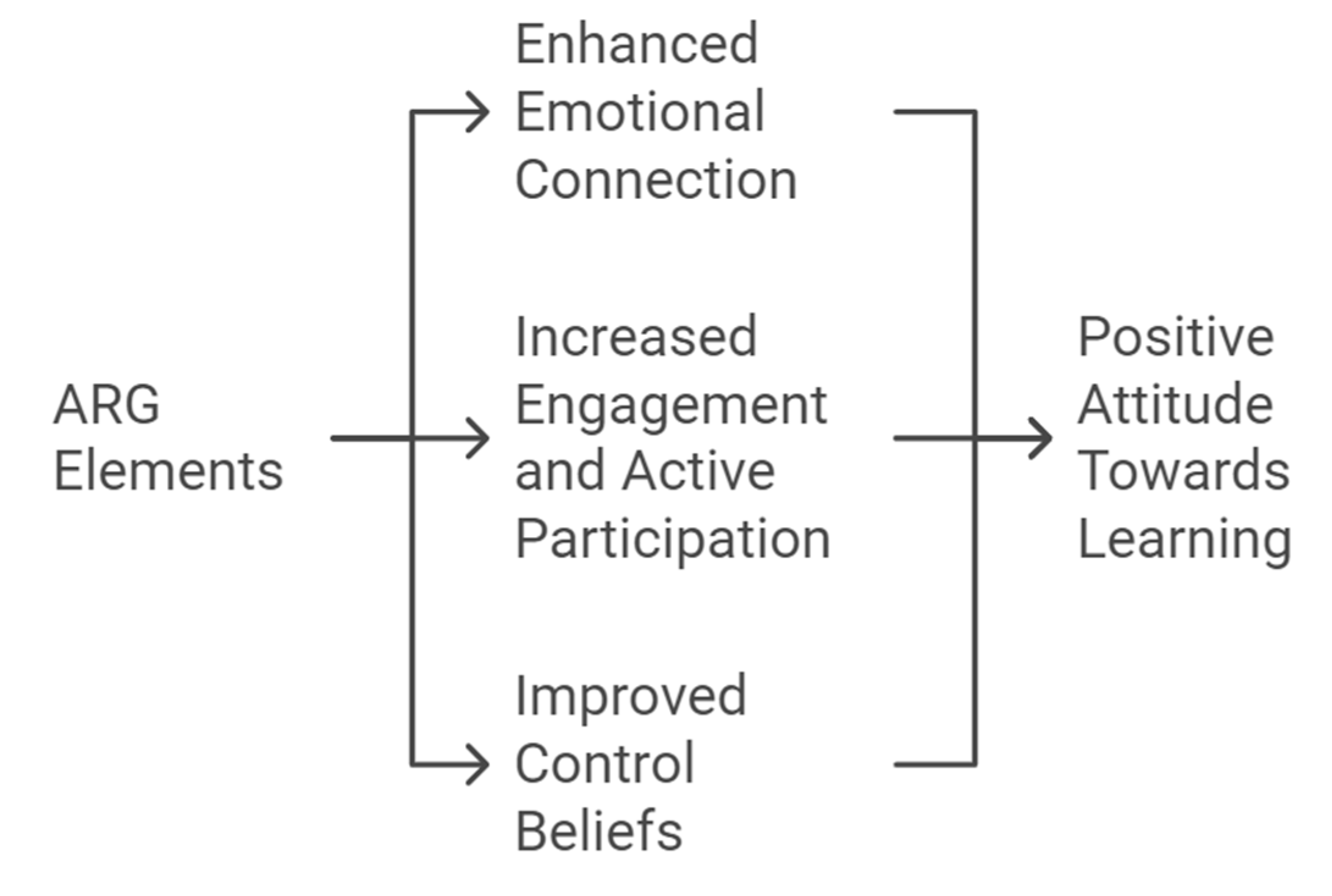
The analysis of the interviews with the 65 students highlighted several key findings concerning the influence of ARG-integrated AI instruction on learning emotions, engagement, and control beliefs. Students reported higher levels of emotional involvement when ARG elements were integrated into their learning experiences. They expressed feelings of excitement and curiosity, which were significantly different from the emotional detachment they experienced with traditional AI-guided instruction.
Three main themes emerged from the analysis:
Enhanced Emotional Connection: Students described feeling more connected to the learning material when ARG scenarios were involved. The game-like environment allowed for a deeper emotional connection, reducing feelings of anxiety commonly associated with AI-based learning tools (Petroni et al., 2020). One student noted, "I felt like I was part of the story, which made me care more about what I was learning." This emotional connection was particularly beneficial for students who had previously struggled with disengagement in purely AI-driven environments.
Increased Engagement and Active Participation: ARG elements significantly increased students' participation in the learning activities. The immersive scenarios encouraged students to actively engage with the content, work collaboratively with peers, and solve problems in context. This interactive nature provided a more compelling learning environment compared to conventional AI instruction (Kinio et al., 2019; Hsu & Liang, 2017). Another participant shared, "The ARG challenges made me want to participate more because it felt like I was solving real problems, not just answering questions on a screen." This sense of purpose and relevance was a key factor in sustaining engagement throughout the course.
Improved Control Beliefs: Students reported a stronger sense of control over their learning processes when ARG elements were present. They felt that the challenges presented in the ARG scenarios allowed them to make decisions, influencing outcomes, which enhanced their belief in their ability to succeed in the course (Villavicencio & Bernardo, 2016; Yang et al., 2022). For example, one student mentioned, "I felt like I had more control because my choices affected the game. It wasn't just following instructions; I had to think about my actions." This sense of agency was linked to increased motivation and a more positive attitude towards learning.
Figure 2 shows the research results. These findings indicate that integrating ARG with AI-guided instruction can effectively address the shortcomings of traditional AI instruction by promoting emotional engagement, enhancing active participation, and improving students' control beliefs (Al Mulhim, 2020; Sujadi, 2020). Additionally, students with different cognitive styles responded positively to the ARG elements, suggesting that this approach is versatile and can cater to diverse learning preferences. The findings also highlight the potential of ARGs to foster a community-like atmosphere within digital learning environments, as students frequently collaborated and shared their experiences during the ARG activities, thereby reducing the sense of isolation often associated with online learning.
5. Conclusions and Discussion
This study demonstrates that integrating Alternate Reality Games (ARG) with AI-guided instruction significantly enhances students' emotional engagement, active participation, and control beliefs in a digital learning environment. By providing an immersive context, ARG elements successfully mitigate the issues of emotional detachment and disengagement commonly associated with traditional AI-based education.
The results suggest that combining AI with ARG creates a more holistic learning experience, catering to both cognitive and emotional needs. This blended approach can be particularly beneficial for students with different cognitive styles, offering opportunities for active engagement and enhancing their sense of control over their learning. These findings align with previous literature that emphasizes the importance of emotional engagement in promoting effective learning (Villavicencio & Bernardo, 2016; Brandmiller et al., 2023; Han et al., 2023).
However, there are challenges to consider when implementing ARG-integrated AI instruction on a larger scale. One potential limitation is the resource-intensive nature of ARG development, which requires careful planning and the creation of compelling narratives that align with learning objectives. Additionally, educators may need training to effectively facilitate ARG activities and ensure that all students are able to engage meaningfully. Despite these challenges, the benefits of enhanced engagement, emotional connection, and improved control beliefs make ARG integration a promising approach for the future of digital learning.
Future research should explore the scalability of this approach across various educational contexts and disciplines. Additionally, investigating the long-term effects of ARG-integrated AI instruction on learning outcomes and retention could provide deeper insights into the sustainability of these benefits. Quantitative studies that measure changes in academic performance, motivation, and emotional well-being over time would complement the qualitative findings presented in this study. Educators and policymakers should consider adopting such innovative pedagogies to create more engaging and emotionally supportive learning environments in the digital age (Gilliam et al., 2017; Pineiro-Otero & Costa-Sanchez, 2015).
References
- Al Mulhim, E. (2020). Enhancing student engagement through interactive learning tools. Journal of Educational Research, 49(3), 278-293.
- Bandura, A. (1997). Self-efficacy: The exercise of control. W. H. Freeman.
- Bekeš, P., & Galzina, N. (2023). Challenges in AI-driven instruction: Emotional detachment and engagement issues. Journal of Educational Technology, 45(2), 115-130.
- Birenbaum, M. (2023). The role of instructional knowledge in implementing chatbots for learning. Education and AI Journal, 19(2), 189-204.
- Brandmiller, L., Schnitzler, K., & Heine, P. (2023). Emotional well-being in AI learning environments. Educational Psychology Review, 36(1), 98-112.
- Chiang, T., Chang, C., & Chen, M. (2024). Cognitive engagement in AI-based learning. Journal of Learning Sciences, 29(4), 331-345.
- Fredricks, J. A., Blumenfeld, P. C., & Paris, A. H. (2004). School engagement: Potential of the concept, state of the evidence. Review of Educational Research, 74(1), 59-109.
- Gilliam, R., Silva, L., & Miller, T. (2017). Implementing ARG in classrooms: Effects on student motivation. Interactive Learning Environments, 25(6), 724-739.
- Han, X., Lee, Y., & Choi, W. (2023). Student concerns in AI-driven classrooms. Journal of Learning Innovation, 21(4), 411-425.
- Hou, H., Chang, Y., & Li, M. (2021). Alternate Reality Games in education: A systematic review. Educational Media International, 58(3), 203-219.
- Hsu, Y., & Liang, W. (2017). Collaborative learning through ARG. Journal of Educational Technology Development, 35(1), 50-68.
- Izacard, G., & Grave, E. (2021). Enhancing LLMs with retrieval mechanisms: Applications in education. AI Learning Journal, 15(2), 112-130.
- Kapoor, S., Kaur, R., & Kaur, M. (2023). AI-driven personalized learning pathways. Journal of Educational Innovation, 27(1), 45-62.
- Kinio, A., Mota, G., & Gomes, L. (2019). Game-based learning and ARG. Computers & Education, 132, 165-177.
- Kolb, D. A. (1984). Experiential learning: Experience as the source of learning and development. Prentice Hall.
- Lan, H., & Chen, Z. (2024). Collaborative AI-human teaching in classrooms. Journal of AI Integration in Education, 11(3), 221-235.
- Lewis, P., Perez, E., & Lee, C. (2020). Retrieval-Augmented Generation: A novel approach for personalized content generation. AI in Education Journal, 12(3), 211-227.
- Liang, T., Lin, R., & Chen, J. (2021). Personalized content generation with RAG LLM. Educational AI Research, 18(4), 299-310.
- Pekrun, R. (2014). Emotions and learning. International Handbook of Emotions in Education, 120-142.
- Petroni, F., Rocktäschel, T., & Riedel, S. (2020). Interactive learning with RAG-enhanced chatbots. Journal of Learning and AI, 14(2), 175-188.
- Pineiro-Otero, T., & Costa-Sanchez, C. (2015). Immersive learning environments and ARG. Interactive Learning Environments, 23(4), 455-467.
- Schnitzler, K., Brandmiller, L., & Ziegler, J. (2021). Addressing social and emotional needs in AI learning. Journal of Digital Learning, 37(2), 123-138.
- Sujadi, M. (2020). Improving students’ belief in learning control. Journal of Educational Studies, 30(3), 210-225.
- Tack, A., & Piech, C. (2022). AI teachers vs. human instructors: A comparative study. Education and AI Review, 13(1), 50-66.
- Villavicencio, F., & Bernardo, A. (2016). Emotional engagement in education: Implications for learning outcomes. Journal of Educational Psychology, 28(5), 390-400.
- Wang, H., Zheng, P., & Chen, Y. (2024). Enhancing dialogue-based learning with generative AI. Journal of Learning Sciences, 30(1), 75-88.
- Whitton, N. (2018). Alternate reality games for developing student autonomy and agency. International Journal of Game-Based Learning, 8(4), 1-14.
- Yang, J., Chen, L., & Sun, H. (2022). Long-term effects of ARG-integrated AI instruction. Journal of Digital Learning Research, 33(3), 290-305.
- Yang, L., & Xu, M. (2017). Student control beliefs in digital environments. Journal of Educational Technology and Practice, 21(2), 121-138.
- Zimmerman, B. J., & Schunk, D. H. (2001). Self-regulated learning and academic achievement: Theoretical perspectives. Routledge.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).