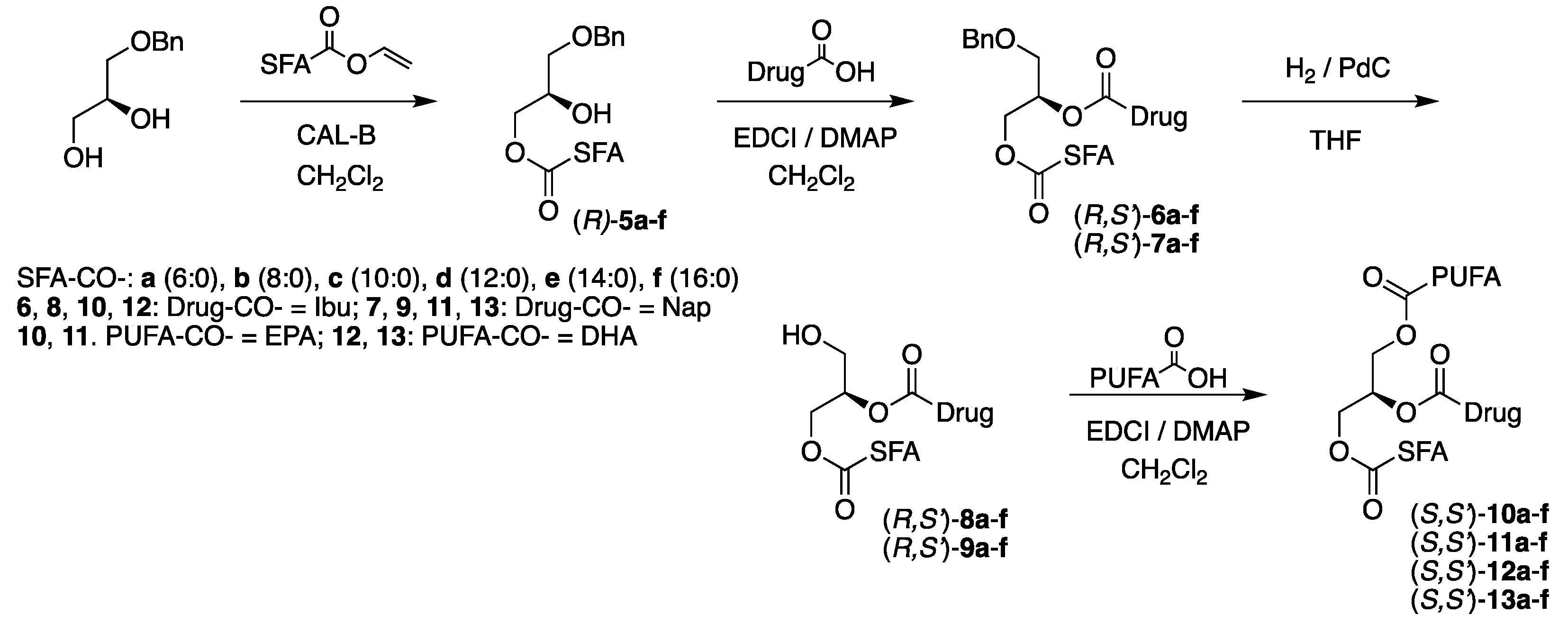
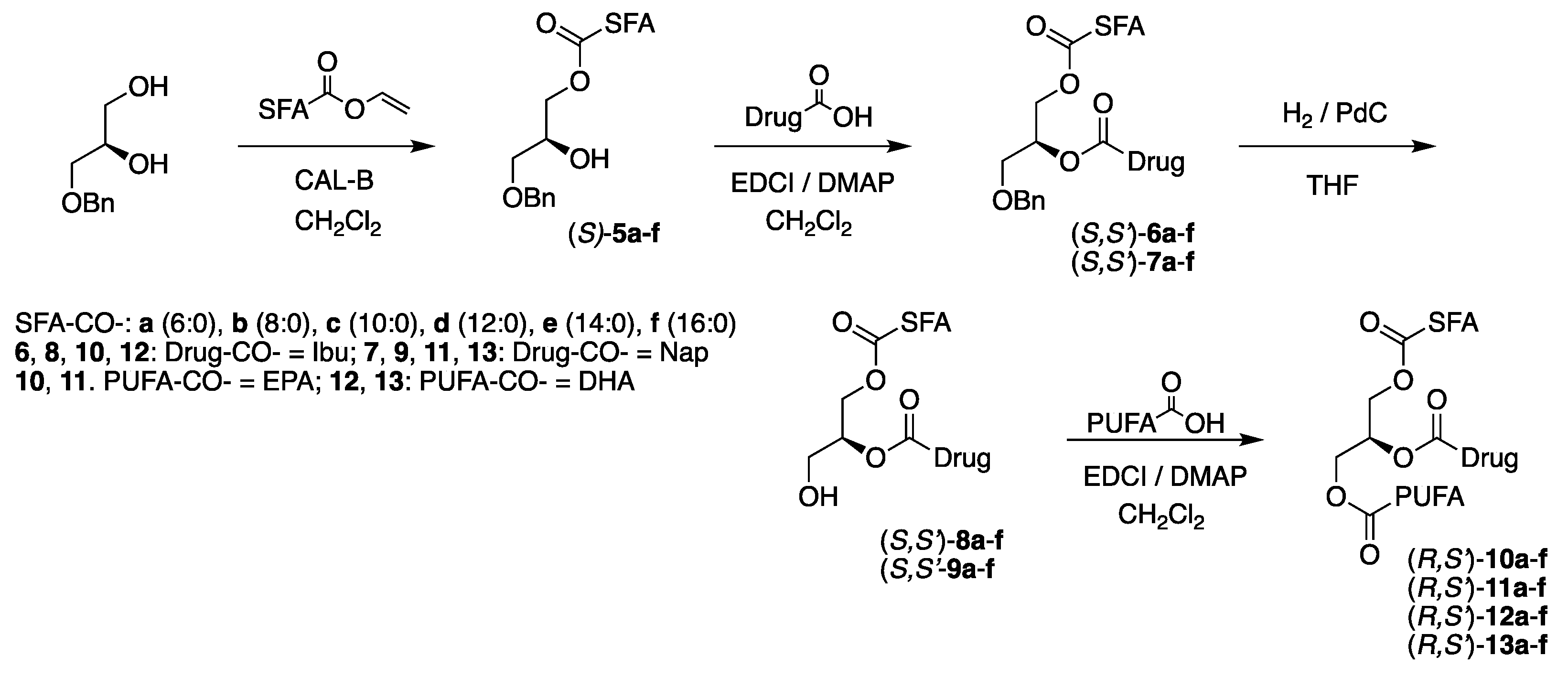
3.3. The Coupling of the Active Drugs: Synthesis of (R,S’)-6a-f, (S,S’)-6a-f, (R,S’)-7a-f and (S,S’)-7a-f
3.3.1. Synthesis of 1-O-benzyl-3-hexanoyl-2-[(S)-2-(4-isobutylphenyl)propanoyl]-sn-glycerol, (R,S’)-6a
To a solution of 1-O-benzyl-3-hexanoyl-sn-glycerol (R)-5a (93 mg, 0.332 mmol) and (S)-ibuprofen (83 mg, 0.401 mmol) in CH2Cl2 (3 mL) were added DMAP (36 mg, 0.292 mmol) and EDCI (68 mg, 0.352 mmol). The solution was stirred on a magnetic stirrer at room temperature for 12 h. The reaction was disconnected by passing the reaction mixture through a short column packed with silica gel by use of Et2O/CH2Cl2 (1:9). The solvent was removed in vacuo on a rotary evaporator. The concentrate was applied to a silica gel chromatography using petroleum ether/ethyl acetate (7:3) as eluent, which afforded the product (R,S’)-6a as a pale-yellow oil, in 80% yield (152 mg, 0.267 mmol). [α]20D = -0.77 (c. 9.7, CH2Cl2). IR (NaCl, νmax / cm-1): 3028 (s), 2956 (vs), 2932 (vs), 2869 (vs), 1740 (vs), 1162 (br s). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δH: 7.34-7.25 (m, 3H, Ph-H), 7.21 (m, 2H, Ibu-2,6 and 2H, Ph-H), 7.07 (d, J=8.1 Hz, 2H, Ibu-3,5), 5.27-5.21 (m, 1H, CH sn-2), 4.42-4.34 (m, 1H, CH2 sn-3 and 2H, PhCH2), 4.20 (dd, J=11.9, 6.6 Hz, 1H, CH2 sn-3), 3.72 (q, J=7.2 Hz, 1H, CHCH3), 3.55-3.46 (m, 2H, CH2 sn-1), 2.43 (d, J=7.2 Hz, 2H, CH2CH(CH3)2), 2.26 (t, J=7.5 Hz, 2H, CH2COO), 1.83 (nonet, J=6.7 Hz, 1H, CH(CH3)2), 1.64-1.54 (m, 2H, CH2CH2COO), 1.50 (d, J=7.2 Hz, 3H, CHCH3), 1.36-1.25 (m, 4H, CH2), 0.90 (t, J=6.8 Hz, 3H, CH2CH3), 0.89 (d, J=6.6 Hz, 6H, CH(CH3)2) ppm. 13C{H} NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δC: 174.0 (Ibu), 173.4 (SFA), 140.5, 137.7, 137.5, 129.3 (2), 128.3 (2), 127.6 (2), 127.5 (2), 127.2, 73.3, 70.6, 68.2, 62.6, 45.1, 45.0, 34.0, 31.2, 30.1, 24.5, 22.4 (2), 22.3, 18.5, 13.9 ppm. HRMS (ESI) m/z: [M + Na]+ calcd for C29H40O5Na 491.2768; found, 491.2764.
3.3.2–6. Synthesis of (R,S’)-6b – (R,S’)-6f
3.3.7. Synthesis of 3-O-benzyl-1-hexanoyl-2-[(S)-2-(4-isobutylphenyl)propanoyl]-sn-glycerol, (S,S’)-6a
The same procedure was followed as described for (R,S’)-6a using 3-O-benzyl-1-hexanoyl-sn-glycerol (S)-5a (36 mg, 0.128 mmol), (S)-ibuprofen (30 mg, 0.145 mmol), CH2Cl2 (2 mL), DMAP (14 mg, 0.115 mmol) and EDCI (26 mg, 0.136 mmol). Purification on a silica gel chromatography using pet. ether/ethyl acetate (4:1) as eluent afforded the product (S,S’)-6a as a pale-yellow oil, in 93% yield (56 mg, 0.119 mmol). [α]20D = +22.2 (c. 5.6, CH2Cl2). IR (NaCl, νmax / cm-1): 3024 (s), 2957 (vs), 2934 (vs), 2865 (vs), 1743 (vs), 1162 (br s). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δH: 7.37-7.26 (m, 5H, Ph-H), 7.19 (d, J=8.1 Hz, 2H, Ibu-2,6), 7.06 (d, J=8.1 Hz, 2H, Ibu-3,5), 5.26-5.20 (m, 1H, CH sn-2), 4.51 (AB q, J=12.1 Hz, 2H, PhCH2), 4.24 (dd, J=11.6, 3.9 Hz, 1H, CH2 sn-1), 4.12 (dd, J=11.9, 6.8 Hz, 1H, CH2 sn-1), 3.72 (q, J=7.2 Hz, 1H, CHCH3), 3.63-3.55 (m, 2H, CH2 sn-3), 2.43 (d, J=7.2 Hz, 2H, CH2CH(CH3)2), 2.11 (t, J=7.6 Hz, 2H, CH2COO), 1.83 (nonet, J=6.7 Hz, 1H, CH(CH3)2), 1.48 (m, 2H, CH2CH2COO and 3H, CHCH3), 1.33-1.20 (m, 4H, CH2), 0.90 (t, J=6.9 Hz, 3H, CH2CH3), 0.88 (d, J=6.6 Hz, 6H, CH(CH3)2) ppm. 13C{H} NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δC: 174.2 (Ibu), 173.4 (SFA), 140.6, 137.9, 137.6, 129.4 (2), 128.6 (2), 127.9 (2), 127.7 (2), 127.3, 73.5, 70.6, 68.5, 62.7, 45.3, 45.2, 34.0, 31.4, 30.1, 24.6, 22.5 (2), 22.4, 18.4, 14.1 ppm. HRMS (ESI) m/z: [M + Na]+ calcd for C29H40O5Na 491.2768; found, 491.2764.
3.3.8–12. Synthesis of (S,S’)-6b – (S,S’)-6f
3.3.13. Synthesis of 1-O-benzyl-3-hexanoyl-2-[(S)-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoyl]-sn-glycerol, (R,S’)-7a
To a solution of 1-O-benzyl-3-hexanoyl-sn-glycerol (R)-5a (93 mg, 0.332 mmol) and (S)-naproxen (92 mg, 0.401 mmol) in CH2Cl2 (3 mL) were added DMAP (36 mg, 0.292 mmol) and EDCI (68 mg, 0.352 mmol). The solution was stirred on a magnetic stirrer at room temperature for 12 h. The reaction was disconnected by passing the reaction mixture through a short column packed with silica gel by use of Et2O/CH2Cl2 (1:9). The solvent was removed in vacuo on a rotary evaporator. The concentrate was applied to a silica gel chromatography using petroleum ether/ethyl acetate (7:3) as eluent, which afforded the product (R,S’)-7a as a clear oil, in 90% yield (147 mg, 0.299 mmol). [α]20D = -3.9 (c. 10.0, CH2Cl2). IR (NaCl, νmax / cm-1): 3062 (s), 3031 (s), 2957 (vs), 2935 (vs), 2871 (vs), 1739 (vs), 1634 (vs), 1174 (br s). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δH: 7.70-7.65 (m, 3H, H-1,4,8 Nap), 7.41 (dd, J=8.5, 1.8 Hz, 1H, H-3 Nap), 7.24-7.21 (m, 3H, Ph-H), 7.14 (dd, J=8.9, 2.6 Hz, 1H, H-7 Nap), 7.12-7.09 (m, 2H, Ph-H and 1H, Nap-5), 5.27 (dtd, J=6.6, 5.0, 3.7 Hz, 1H, CH sn-2), 4.39-4.27 (m, 1H, CH2 sn-3 and 2H, PhCH2), 4.21 (dd, J=11.9, 6.6 Hz, 1H, CH2 sn-3), 3.91 (s, 3H, OCH3), 3.89 (q, J=7.2, 1H, CHCH3), 3.54-3.44 (m, 2H, CH2 sn-1), 2.22 (t, J=7.5 Hz, 2H, CH2COO), 1.64-1.54 (m, 2H, CH2CH2COO and 3H, CHCH3), 1.33-1.21 (m, 4H, CH2), 0.89 (t, J=6.9 Hz, 3H, CH2CH3) ppm. 13C{H} NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δC: 173.9 (Nap), 173.4 (SFA), 157.6, 137.7, 135.4, 133.68, 129.2, 128.9, 128.2 (2), 127.6, 127.4 (2), 127.1, 126.2, 126.0, 118.9, 105.6, 73.2, 70.7, 68.2, 62.6, 55.3, 45.4, 34.0, 31.2, 24.58, 22.3, 18.5, 13.9 ppm. HRMS (ESI) m/z: [M + Na]+ calcd for C30H36O6Na 515.2404; found, 515.2396.
3.3.14–18. Synthesis of (R,S’)-7b – (R,S’)-7f
3.3.19. Synthesis of 3-O-benzyl-1-hexanoyl-2-[(S)-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoyl]-sn-glycerol, (S,S’)-7a
To a solution of 3-O-benzyl-1-hexanoyl-sn-glycerol (S)-5a (36 mg, 0.128 mmol) and (S)-naproxen (34 mg, 0.147 mmol) in CH2Cl2 (2.3 mL) were added DMAP (15 mg, 0.121 mmol) and EDCI (28 mg, 0.145 mmol). The solution was stirred on a magnetic stirrer at room temperature for 16 h. The reaction was disconnected by passing the reaction mixture through a short column packed with silica gel by use of Et2O/CH2Cl2 (1:9). The solvent was removed in vacuo on a rotary evaporator. The concentrate was applied to a silica gel chromatography using petroleum ether/ethyl acetate (8.5:1.5) as eluent, which afforded the product (S,S’)-7a as a clear oil, in 97% yield (58 mg, 0.124 mmol). [α]20D = +20.8 (c. 3.4, CH2Cl2). IR (NaCl, νmax / cm-1): 3058 (s), 3028 (s), 2956 (vs), 2932 (vs), 2855 (vs), 1742 (vs), 1635 (vs), 1170 (br s). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δH: 7.73-7.63 (m, 3H, H-1,4,8 Nap), 7.41 (dd, J=8.6, 1.8 Hz, 1H, H-3 Nap), 7.36-7.26 (m, 5H, Ph-H), 7.14 (dd, J=8.9, 2.5 Hz, 1H, H-7 Nap), 7.10 (d, J=2.5 Hz, 1H, Nap-5) 5.26-5.20 (m, 1H, CH sn-2), 4.51 (AB q, J=12.1 Hz, 2H, PhCH2), 4.23 (dd, J=11.9, 3.7 Hz, 1H, CH2 sn-1), 4.13 (dd, J=11.9, 6.9 Hz, 1H, CH2 sn-1), 3.91 (s, 3H, OCH3), 3.72 (q, J=7.1, 1H, CHCH3), 3.61-3.59 (m, 2H, CH2 sn-3), 1.94-1.87 (m, 2H, CH2COO), 1.58 (d, J=7.2 Hz, 3H, CHCH3), 1.40-1.31 (m, 2H, CH2CH2COO), 1.23-1.15 (m, 2H, CH2CH2CH3), 1.13-1.03 (m, 2H, CH2CH3), 0.85 (t, J=7.2 Hz, 3H, CH2CH3) ppm. 13C{H} NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δC: 174.1 (Nap), 173.4 (SFA), 157.8, 137.8, 135.6, 133.8, 129.4, 129.1, 128.5 (2), 127.9, 127.7 (2), 127.2, 126.4, 126.1, 119.1, 105.7, 73.4, 70.7, 68.5, 62.6, 55.4, 45.6, 33.8, 31.3, 24.4, 22.4, 18.5, 14.0 ppm. HRMS (ESI) m/z: [M + Na]+ calcd for C30H36O6Na 515.2404; found, 515.2405.
3.3.20–24. Synthesis of (S,S’)-7b – (S,S’)-7f
3.4. The Removal of the Benzyl Protective Group: Synthesis of (R,S’)-8a-f, (S,S’)-8a-f, (R,S’)-9a-f and (S,S’)-9a-f
3.4.1. Synthesis of 3-hexanoyl-2-[(S)-2-(4-isobutylphenyl)propanoyl]-sn-glycerol, (R,S’)-8a
Pd/C catalyst (26 mg) was placed into a 25 mL flame-dried two-necked round-bottom flask equipped with a magnetic stirrer under nitrogen atmosphere at room temperature and the flask sealed with a septum. A solution of 1-O-benzyl-3-hexanoyl-2-[(S)-2-(4-isobutylphenyl)propanoyl]-sn-glycerol, (R,S’)-6a (116 mg, 0.236 mmol) dissolved in dry THF (7 mL) was added with a syringe, followed by n-hexane (11.2 mL). A balloon filled with hydrogen gas was then mounted on a syringe and stuck through the septum. The mixture was stirred while the hydrogen gas was blown through the flask to replace the nitrogen atmosphere with hydrogen. Then a tiny drop of perchloric acid was added and the solution stirred vigorously at room temperature while being monitored with TLC. When the reaction came to completion according to the TLC (approximately 15 minutes) the flask was promptly opened and the acid neutralized by adding NaHCO3 (s). Then the solution was filtered, and the solvent removed in vacuo on a rotary evaporator. The crude product was applied to a 4% boric acid impregnated flash silica gel chromatography using petroleum ether/ethyl acetate (7:3) as eluent, wich afforded the product (R,S’)-8a as a pale-yellow oil, in 84% yield (75 mg, 0.198 mmol). [α]20D = +23.9 (c. 4.0, CH2Cl2). IR (NaCl, νmax / cm-1): 3500 (br), 2956 (vs), 2932 (vs), 2870 (vs), 1739 (vs), 1165 (br s). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δH: 7.19 (d, J=8.2 Hz, 2H, Ibu-2,6), 7.10 (d, J=8.1 Hz, 2H, Ibu-3,5), 5.07-5.02 (m, 1H, CH sn-2), 4.30 (dd, J=11.9, 4.4 Hz, 1H, CH2 sn-3), 4.21 (dd, J=11.9, 5.9 Hz, 1H, CH2 sn-3), 3.73 (q, J=7.1 Hz, 1H, CHCH3), 3.61-3.56 (m, 2H, CH2 sn-1), 2.44 (d, J=7.1 Hz, 2H, CH2CH(CH3)2), 2.29 (t, J=7.6 Hz, 2H, CH2COO), 1.84 (nonet, J=6.7 Hz, 1H, CH(CH3)2), 1.67-1.57 (m, 2H, CH2CH2COO), 1.50 (d, J=7.2 Hz, 3H, CHCH3), 1.34-1.27 (m, 4H, CH2), 0.90 (t, J=6.1 Hz, 3H, CH2CH3), 0.88 (d, J=6.6 Hz, 6H, CH(CH3)2) ppm. 13C{H} NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δC: 174.3 (Ibu), 173.8 (SFA), 140.9, 137.8, 129.6 (2), 127.1 (2), 72.7, 62.1, 61.5, 45.3, 45.1, 34.2, 31.4, 30.3, 24.7, 22.5 (2), 22.4, 18.4, 14.1 ppm. HRMS (ESI) m/z: [M + Na]+ calcd for C22H34O5Na 401.2298; found, 401.2297.
3.4.2–6. Synthesis of (R,S’)-8b – (R,S’)-8f
3.4.7. Synthesis of 1-hexanoyl-2-[(S)-2-(4-isobutylphenyl)propanoyl]-sn-glycerol, (S,S’)-8a
The same procedure was followed as described for (R,S’)-8a using Pd/C catalyst (13 mg), 3-O-benzyl-1-hexanoyl-2-[(S)-2-(4-isobutylphenyl)propanoyl]-sn-glycerol (S,S’)-6a (30 mg, 0.064 mmol), THF (4 mL) and n-hexane (5.6 mL). Purification on 4% boric acid impregnated flash silica gel chromatography using pet. ether/ethyl acetate (3:2) as eluent, afforded the product (S,S’)-8a as a pale-yellow oil, in 95% yield (23 mg, 0.061 mmol). [α]20D = +5.65 (c. 2.3, CH2Cl2). IR (NaCl, νmax / cm-1): 3474 (br), 2956 (vs), 2870 (vs), 1740 (vs), 1513 (vs), 1165 (br s). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δH: 7.19 (d, J=8.2 Hz, 2H, Ibu-2,6), 7.10 (d, J=8.1 Hz, 2H, Ibu-3,5), 5.07-5.02 (m, 1H, CH sn-2), 4.30 (dd, J=11.9, 4.4 Hz, 1H, CH2 sn-1), 4.14 (dd, J=11.9, 6.0 Hz, 1H, CH2 sn-1), 3.72-3.63 (m, 2H, CH2 sn-3 and 1H, CHCH3), 2.44 (d, J=7.1 Hz, 2H, CH2CH(CH3)2), 2.18 (t, J=7.6 Hz, 2H, CH2COO), 1.91 (t, J=6.5 Hz, 1H, OH), 1.84 (nonet, J=6.8 Hz, 1H, CH(CH3)2), 1.55 (m, 2H, CH2CH2COO), 1.50 (d, J=7.2 Hz, 3H, CHCH3), 1.34-1.27 (m, 4H, CH2), 0.90 (t, J=6.1 Hz, 3H, CH2CH3), 0.88 (d, J=6.6 Hz, 6H, CH(CH3)2) ppm. 13C{H} NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δC: 174.5 (Ibu), 173.8 (SFA), 140.8, 137.4, 129.5 (2), 127.2 (2), 72.7, 62.0, 61.7, 45.2, 45.2, 34.1, 31.4, 30.3, 24.6, 22.5 (2), 22.4, 18.4, 14.0 ppm. HRMS (ESI) m/z: [M + Na]+ calcd for C22H34O5Na 401.2298; found, 401.2295.
3.4.8–12. Synthesis of (S,S’)-8b – (S,S’)-8f
3.4.13. Synthesis of 3-hexanoyl-2-[(S)-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoyl]-sn-glycerol, (R,S’)-9a
Pd/C catalyst (24 mg) was placed into a 25 mL flame-dried two-necked round-bottom flask equipped with a magnetic stirrer under nitrogen atmosphere at room temperature and the flask sealed with a septum. A solution of 1-O-benzyl-3-hexanoyl-2-[(S)-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoyl]-sn-glycerol, (R,S’)-7a (107 mg, 0.217 mmol) dissolved in dry THF (6.4 mL) was added with a syringe, followed by n-hexane (10.3 mL). A balloon filled with hydrogen gas was then mounted on a syringe and stuck through the septum. The mixture was stirred while the hydrogen gas was blown through the flask to replace the nitrogen atmosphere with hydrogen. Then a tiny drop of perchloric acid was added and the solution stirred vigorously at room temperature while being monitored with TLC. When the reaction came to completion according to the TLC (approximately 15 minutes) the flask was promptly opened and the acid neutralized by adding NaHCO3 (s). Then the solution was filtered, and the solvent removed in vacuo on a rotary evaporator. The crude product was applied to a 4% boric acid impregnated flash silica gel chromatography using petroleum ether/ethyl acetate (1:1) as eluent, wich afforded the product (R,S’)-9a as a pale-yellow oil, in 98% yield (86 mg, 0.213 mmol). [α]20D = +5.63 (c. 1.6, CH2Cl2). IR (NaCl, νmax / cm-1): 3358 (br), 2926 (vs), 2856 (vs), 1739 (vs), 1632 (vs). 1606 (vs). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δH: 7.71-7.66 (m, 3H, Nap-1,4,8), 7.38 (dd, J=8.5, 1.9 Hz, 1H, Nap-3), 7.14 (dd, J=8.9, 2.5 Hz, 1H, Nap-7), 7.10 (d, J=2.5 Hz, 1H, Nap-5), 5.14-5.01 (m, 1H, CH sn-2), 4.31 (dd, J=11.9, 4.3 Hz, 1H, CH2 sn-3), 4.27-4.19 (m, 1H, CH2 sn-3), 3.91 (s, 3H, OCH3), 3.91-3.82 (m, 1H, CHCH3), 3.61-3.57 (m, 2H, CH2 sn-1), 2.27-2.24 (m, 2H, CH2COO), 2.23-2.20 (bs, 1H, OH), 1.58 (d, J=7.2 Hz, 3H, CHCH3), 1.56 (quint, J=7.2 Hz, 2H, CH2CH2COO), 1.38-1.22 (m, 4H, CH2), 0.89 (t, J=7.0 Hz, 3H, CH2CH3) ppm. 13C{H} NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δC: 174.3 (Nap), 173.8 (SFA), 157.9, 135.6, 133.9, 129.4, 129.0, 127.4, 126.1, 126.0, 119.3, 105.8, 72.8, 62.1, 61.5, 55.5, 45.6, 34.2, 31.1, 24.7, 22.4, 18.5, 14.0 ppm. HRMS (ESI) m/z: [M + Na]+ calcd for C23H30O6Na 425.1935; found, 425.1934.
3.4.14–18. Synthesis of (R,S’)-9b – (R,S’)-9f
3.4.19. Synthesis of 1-hexanoyl-2-[(S)-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoyl]-sn-glycerol, (S,S’)-9a
The same procedure was followed as described for (R,S’)-9a using Pd/C catalyst (3 mg), 3-O-benzyl-1-hexanoyl-2-[(S)-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoyl]-sn-glycerol, (S,S’)-7a (14 mg, 0.028 mmol), THF (1 mL) and n-hexane (1.5 mL). Purification on 4% boric acid impregnated flash silica gel chromatography using pet. ether/ethyl acetate (3:2) as eluent, afforded the product (S,S’)-9a as a pale-yellow oil, in 97% yield (11 mg, 0.027 mmol). [α]20D = +8.60 (c. 1.0, CH2Cl2). IR (NaCl, νmax / cm-1): 3421 (br), 3060 (s), 2925 (vs), 2856 (vs), 1739 (vs), 1634 (s), 1607 (vs), 1162 (br s). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δH: 7.73-7.65 (m, 3H, Nap-1,4,8), 7.39 (dd, J=8.5, 1.9 Hz, 1H, Nap-3), 7.14 (dd, J=8.9, 2.6 Hz, 1H, Nap-7), 7.10 (d, J=2.6 Hz, 1H, Nap-5), 5.08 (m, 1H, CH sn-2), 4.19 (dd, J=11.9, 4.4 Hz, 1H, CH2 sn-1), 4.27-4.13 (dd, J=11.9, 6.1, Hz, 1H, CH2 sn-1), 3.91 (s, 3H, OCH3), 3.96-3.84 (m, 1H, CHCH3), 3.74-3.69 (m, 2H, CH2 sn-3), 2.23-2.20 (bs, 1H, OH), 2.05-1.89 (m, 2H, CH2COO), 1.59 (d, J=7.1 Hz, 3H, CHCH3), 1.44-1.33 (m, 2H, CH2CH2COO), 1.38-1.06 (m, 4H, CH2), 0.85 (t, J=7.2 Hz, 3H, CH2CH3) ppm. 13C{H} NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δC: 174.5 (Nap), 173.7 (SFA), 157.9, 135.4, 133.9, 129.4, 129.1, 127.3, 126.2, 126.1, 119.2, 105.7, 72.8, 61.9, 61.7, 55.5, 45.6, 33.9, 31.3, 29.9, 24.5, 18.5, 14.0 ppm. HRMS (ESI) m/z: [M + Na]+ calcd for C23H30O6Na 425.1935; found, 425.1932.
3.4.20–24. Synthesis of (S,S’)-9b – (S,S’)-9f
3.5. Coupling of EPA: Synthesis of (S,S’)-10a-f, (R,S’)-10a-f, (S,S’)-11a-f and (R,S’)-11a-f
3.5.1. Synthesis of 1-[5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)-eicosa-5,8,11,14,17-pentaenoyl]-3-hexanoyl-2-[(S)-2-(4-isobutylphenyl)propanoyl]-sn-glycerol, (S,S’)-10a
To a solution of 3-hexanoyl-2-[(S)-2-(4-isobutylphenyl)propanoyl]-sn-glycerol (R,S’)-8a (45 mg, 0.118 mmol) and EPA as a free acid (33 mg, 0.108 mmol) in CH2Cl2 (4 mL) were added DMAP (13 mg, 0.106 mmol) and EDCI (28 mg, 0.143 mmol). The solution was stirred on a magnetic stirrer at room temperature for 12 h. The reaction was disconnected by passing the reaction mixture through a short column packed with silica gel by use of Et2O/CH2Cl2 (1:9). The solvent was removed in vacuo on a rotary evaporator. The residue was applied to a silica gel chromatography using petroleum ether/ethyl acetate (8.5:1.5) as eluent, which afforded the product (S,S’)-10a as a yellow oil, in 90% yield (70 mg, 0.106 mmol). [α]20D = +11.7 (c. 6.0, CH2Cl2). IR (NaCl, νmax / cm-1): 3013 (s), 2959 (vs), 2933 (vs), 2871 (vs), 1743 (vs), 1656 (s). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δH: 7.18 (d, J=8.1 Hz, 2H, Ibu-2,6), 7.07 (d, J=8.1 Hz, 2H, Ibu-3,5), 5.44-5.28 (m, 10H, =CH), 5.35-5.32 (m, 1H, CH sn-2), 4.30 (dd, J=11.9, 4.2 Hz, 1H, CH2 sn-1/3), 4.19 (dd, J=11.9, 4.5 Hz, 1H, CH2 sn-1/3), 4.13 (dd, J=11.9, 6.0 Hz, 1H, CH2 sn-1/3), 4.07 (dd, J=11.9, 6.4 Hz, 1H, CH2 sn-1/3), 3.70 (q, J=7.1 Hz, 1H, CHCH3), 2.86-2.78 (m, 8H, =CHCH2CH=), 2.43 (d, J=7.2 Hz, 2H, CH2CH(CH3)2), 2.28 (t, J=7.2 Hz, 2H, CH2COO EPA), 2.18 (t, J=7.5 Hz, 2H, CH2COO), 2.10-2.05 (m, 4H, CH2CH2CH= and =CHCH2CH3), 1.84 (nonet, J=6.8 Hz, 1H, CH(CH3)2), 1.63-1.48 (m, 4H, CH2CH2COO SFA and CH2CH2COO EPA), 1.49 (d, J=7.2 Hz, 3H, CHCH3), 1.32-1.29 (m, 4H, CH2), 0.97 (t, J=7.5 Hz, 3H, CH3 EPA), 0.90 (t, J=7.2 Hz, 3H, CH3 SFA), 0.89 (d, J=6.6 Hz, 6H, CH(CH3)2) ppm. 13C{H} NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δC: 173.9 (Ibu), 173.4 (SFA), 173.0 (EPA), 140.7, 137.4, 132.2, 129.4 (2), 129.0, 128.71, 128.4, 128.3, 128.3, 128.2, 128.0, 128.3, 127.3 (2), 127.2, 69.3, 62.2, 62.1, 45.2, 45.2, 34.1, 33.4, 31.4, 30.3, 26.6, 25.8 (2), 25.7 (2), 24.7, 24.7, 22.5 (2), 22.4, 20.7, 18.5, 14.4, 14.0 ppm. HRMS (ESI) m/z: [M + Na]+ calcd for C42H62O6Na 685.4439; found, 685.4439.
3.5.2–6. Synthesis of (S,S’)-10b – (S,S’)-10f
3.5.7. Synthesis of 3-[5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)-eicosa-5,8,11,14,17-pentaenoyl]-1-hexanoyl-2-[(S)-2-(4-isobutylphenyl)propanoyl]-sn-glycerol, (R,S’)-10a
The same procedure was followed as described for (S,S’)-10a using 1-hexanoyl-[(S)-2-(4-isobutylphenyl)propanoyl]-sn-glycerol (S,S’)-8a (19 mg, 0.050 mmol), EPA (16 mg, 0.053 mmol), CH2Cl2 (3 mL), DMAP (7 mg, 0.054 mmol) and EDCI (14 mg, 0.073 mmol). Purification on a silica gel chromatography using pet. ether/ethyl acetate (8.5:1.5) as eluent afforded the product (R,S’)-10a as a pale-yellow oil, in 74% yield (25 mg, 0.037 mmol). [α]20D = +6.50 (c. 2.0, CH2Cl2). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δH: 7.18 (dd, J=8.1, 1.7 Hz, 2H, Ibu-2,6), 7.07 (dd, J=8.1, 3.8 Hz, 2H, Ibu-3,5), 5.45-5.29 (m, 10H, =CH), 5.28-5.22 (m, 1H, CH sn-2), 4.30 (dd, J=11.9, 4.3 Hz, 1H, CH2 sn-1/3), 4.21 (dd, J=11.9, 4.3 Hz, 1H, CH2 sn-1/3), 4.15 (dd, J=11.9, 6.4 Hz, 1H, CH2 sn-1/3), 4.06 (dd, J=11.9, 6.3 Hz, 1H, CH2 sn-1/3), 3.70 (q, J=7.1 Hz, 1H, CHCH3), 2.87-2.77 (m, 8H, =CHCH2CH=), 2.44 (d, J=7.2 Hz, 2H, CH2CH(CH3)2), 2.33-2.22 (m, 2H, CH2COO EPA), 2.18-2.04 (m, 6H, CH2COO SFA, CH2CH2CH= and =CHCH2CH3), 1.84 (nonet, J=6.8 Hz, 1H, CH(CH3)2), 1.74-1.58 (m, 2H, CH2CH2COO EPA), 1.57-1.50 (m, 2H, CH2CH2COO SFA), 1.49 (d, J=7.2 Hz, 3H, CHCH3), 1.33-1.20 (m, 4H, CH2), 0.97 (t, J=7.5 Hz, 3H, CH3 EPA), 0.89 (d, J=6.6 Hz, 6H, CH(CH3)2), 0.88 (t, J=6.5 Hz, 3H, CH3 SFA) ppm. 13C{H} NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δC: 173.9 (Ibu), 173.3 (SFA), 173.1 (EPA), 140.7, 137.4, 132.2, 129.4 (2), 129.1, 129.0, 128.7, 128.4, 128.4, 128.3, 128.2, 128.0, 127.3 (2), 127.2, 69.4, 62.3, 62.1, 45.2, 45.2, 34.0, 33.5, 31.4, 30.3, 26.7, 25.8 (2), 25.7 (2), 24.8, 24.6, 22.5 (2), 22.4, 20.7, 18.5, 14.4, 14.0 ppm. HRMS (ESI) m/z: [M + Na]+ calcd for C42H62O6Na 685.4439; found, 685.4430.
3.5.8–12. Synthesis of (R,S’)-10b – (R,S’)-10f
3.5.13. Synthesis of 1-[5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)-eicosa-5,8,11,14,17-pentaenoyl]-3-hexanoyl-2[(S)-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoyl]-sn-glycerol, (S,S’)-11a
To a solution of 3-hexanoyl-2-[(S)-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoyl]-sn-glycerol (R,S’)-9a (35 mg, 0.087 mmol) and EPA as a free acid (28 mg, 0.093 mmol) in CH2Cl2 (4 mL) were added DMAP (11 mg, 0.094 mmol) and EDCI (24 mg, 0.127 mmol). The solution was stirred on a magnetic stirrer at room temperature for 12 h. The reaction was disconnected by passing the reaction mixture through a short column packed with silica gel by use of Et2O/CH2Cl2 (1:9). The solvent was removed in vacuo on a rotary evaporator. The residue was applied to a silica gel chromatography using petroleum ether/ethyl acetate (7:3) as eluent, which afforded the product (S,S’)-11a as a yellow oil, in 91% yield (54 mg, 0.079 mmol). [α]20D = +8.12 (c. 5.0, CH2Cl2). IR (NaCl, νmax / cm-1): 3012 (s), 2960 (vs), 2933 (vs), 2872 (vs), 1735 (vs), 1634 (vs), 1607 (vs). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δH: 7.72-7.65 (m, 3H, Nap-1,4,8), 7.38 (dd, J=8.5, 1.9 Hz, 1H, Nap-3), 7.14 (dd, J=8.9, 2.5 Hz, 1H, Nap-7), 7.10 (d, J=2.5 Hz, 1H, Nap-5), 5.46-5.31 (m, 10H, =CH), 5.33-5.19 (m, 1H, CH sn-2), 4.30 (dd, J=11.9, 4.2 Hz, 1H, CH2 sn-1/3), 4.20-4.10 (m, 2H, CH2 sn-1/3), 4.07 (dd, J=11.9, 6.4 Hz, 1H, CH2 sn-1/3), 3.90 (s, 3H, OCH3), 3.85 (q, J=7.5 Hz, 1H, CHCH3), 2.87-2.71 (m, 8H, =CHCH2CH=), 2.30-2.19 (m, 2H, CH2COO EPA), 2.12-2.04 (m, 2H, CH2COO SFA), 2.00 (td, J=7.6, 5.6 Hz, 2H, CH2CH2CH=), 1.96-1.90 (m, 2H, =CHCH2CH3), 1.62-1.52 (m, 5H, CH2CH2COO SFA and CHCH3), 1.46 (quint, J=7.3 Hz, 2H, CH2CH2COO EPA), 1.35-1.19 (m, 4H, CH2), 0.97 (t, J=7.5 Hz, 3H, CH3 EPA), 0.89 (t, J=7.0 Hz, 3H, CH3 SFA) ppm. 13C{H} NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δC: 173.8 (Nap), 173.3 (SFA), 172.9 (EPA), 157.8, 135.3, 133.8, 132.1, 129.4, 129.0, 128.93, 128.89, 128.7, 128.4, 128.3, 128.3, 128.2, 128.0, 127.2, 127.1, 126.2, 126.1, 119.1, 105.6, 69.5, 62.1, 62.1, 55.4, 45.5, 34.1, 33.2, 31.3, 26.5, 25.7, 25.7 (2), 25.7, 24.6, 24.5, 22.4, 20.7, 18.4, 14.4, 14.0 ppm. HRMS (ESI) m/z: [M + Na]+ calcd for C43H58O7Na 709.4075; found, 709.4062.
3.5.14-18. Synthesis of (S,S’)-11b – (S,S’)-11f
3.5.19. Synthesis of 3-[5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)-eicosa-5,8,11,14,17-pentaenoyl]-1-hexanoyl-2[(S)-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoyl]-sn-glycerol, (R,S’)-11a
To a solution of 1-hexanoyl-2-[(S)-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoyl]-sn-glycerol (S,S’)-9a (12 mg, 0.030 mmol) and EPA as a free acid (10 mg, 0.033 mmol) in CH2Cl2 (1.3 mL) were added DMAP (4 mg, 0.033 mmol) and EDCI (8 mg, 0.044 mmol). The solution was stirred on a magnetic stirrer at room temperature for 12 h. The reaction was disconnected by passing the reaction mixture through a short column packed with silica gel by use of Et2O/CH2Cl2 (1:9). The solvent was removed in vacuo on a rotary evaporator. The residue was applied to a silica gel chromatography using petroleum ether/ethyl acetate (7:3) as eluent, which afforded the product (R,S’)-11a as a yellow oil, in 80% yield (16 mg, 0.024 mmol). [α]20D = +4.20 (c. 1.0, CH2Cl2). IR (NaCl, νmax / cm-1): 3059 (br), 3012 (s), 2958 (vs), 2872 (vs), 1740 (vs, 1634 (s), 1607 (s). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δH: 7.72-7.63 (m, 3H, Nap-1,4,8), 7.38 (dd, J=8.5, 1.8 Hz, 1H, Nap-3), 7.14 (dd, J=8.9, 2.4 Hz, 1H, Nap-7), 7.10 (d, J=2.4 Hz, 1H, Nap-5), 5.45-5.31 (m, 10H, =CH), 5.33-5.19 (m, 1H, CH sn-2), 4.30 (dd, J=11.9, 4.2 Hz, 1H, CH2 sn-1/3), 4.17 ((dd, J=8.2, 3.7 Hz, 2H, CH2 sn-1/3), 4.14 (dd, J=8.2, 3.6 Hz, 1H, CH2 sn-1/3), 4.06 (dd, J=11.9, 6.4 Hz, 1H, CH2 sn-1/3), 3.91 (s, 3H, OCH3), 3.86 (q, J=7.1 Hz, 1H, CHCH3), 2.80-2.76 (m, 8H, =CHCH2CH=), 2.29-2.23 (m, 2H, CH2COO EPA), 2.12-2.03 (m, 4H, CH2COO SFA and CH2CH2CH=), 1.97-1.91 (m, 2H, =CHCH2CH3), 1.65 (quint, J=7.4 Hz, 2H, CH2CH2COO SFA), 1.57 (d, J=7.1 Hz, CHCH3), 1.44-1.33 (m, 2H, CH2CH2COO EPA), 1.32-1.07 (m, 4H, CH2), 0.97 (t, J=7.6 Hz, 3H, CH3 EPA), 0.89 (t, J=7.2 Hz, 3H, CH3 SFA) ppm. 13C{H} NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δC: 173.9 (Nap), 173.3 (SFA), 173.1 (EPA), 157.9, 135.4, 133.9, 132.2, 131.0, 129.4, 129.08, 129.05, 129.0, 128.9, 128.7, 128.4, 128.4, 128.2, 128.0, 127.24, 127.17, 126.3, 126.1, 119.2, 105.7, 69.5, 62.3, 62.0, 55.4, 45.5, 34.1, 33.2, 31.3, 26.5, 25.8, 25.70 (2), 25.66, 24.8, 24.6, 22.4, 20.7, 18.5, 14.4, 14.0 ppm. HRMS (ESI) m/z: [M + Na]+ calcd for C43H58O7Na 709.4075; found, 709.4075.
3.5.20-24. Synthesis of (R,S’)-11b – (R,S’)-11f
3.6. Coupling of DHA: Synthesis of (S,S’)-12a-f, (R,S’)-12a-f, (S,S’)-13a-f and (R,S’)-13a-f
3.6.1. Synthesis of 1-[4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)-docosa-4,7,10,13,16,19-hexaenoyl]-3-hexanoyl-2-[(S)-2-(4-isobutylphenyl)propanoyl]-sn-glycerol, (S,S’)-12a
To a solution of 3-hexanoyl-2-[(S)-2-(4-isobutylphenyl)propanoyl]-sn-glycerol (R,S’)-8a (23 mg, 0.061 mmol) and DHA as a free acid (36 mg, 0.108 mmol) in CH2Cl2 (4 mL) were added DMAP (13 mg, 0.106 mmol) and EDCI (28 mg, 0.143 mmol). The solution was stirred on a magnetic stirrer at room temperature for 12 h. The reaction was disconnected by passing the reaction mixture through a short column packed with silica gel by use of Et2O/CH2Cl2 (1:9). The solvent was removed in vacuo on a rotary evaporator. The residue was applied to a silica gel chromatography using petroleum ether/ethyl acetate (8.5:1.5) as eluent, which afforded the product (S,S’)-12a as a yellow oil, in 81% yield (35 mg, 0.049 mmol). [α]20D = +9.95 (c. 2.0, CH2Cl2). IR (NaCl, νmax / cm-1): 3013 (vs), 2957 (vs), 2928 (vs), 2870 (vs), 1743 (vs). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δH: 7.18 (d, J=8.1 Hz, 2H, Ibu-2,6), 7.07 (d, J=8.1 Hz, 2H, Ibu-3,5), 5.44-5.28 (m, 12H, =CH), 5.35-5.32 (m, 1H, CH sn-2), 4.30 (dd, J=11.9, 4.2 Hz, 1H, CH2 sn-1/3), 4.19 (dd, J=11.9, 4.5 Hz, 1H, CH2 sn-1/3), 4.13 (dd, J=11.9, 6.0 Hz, 1H, CH2 sn-1/3), 4.08 (dd, J=11.9, 6.4 Hz, 1H, CH2 sn-1/3), 3.70 (q, J=7.2 Hz, 1H, CHCH3), 2.90-2.78 (m, 10H, =CHCH2CH=), 2.43 (d, J=7.2 Hz, 2H, CH2CH(CH3)2), 2.34-2.19 (m 6H, CH2CH2COO DHA and CH2COO SFA), 2.10-2.06 (m, 2H, =CHCH2CH3), 1.83 (nonet, J=6.8 Hz, 1H, CH(CH3)2), 1.65-1.55 (m, 2H, CH2CH2COO SFA), 1.49 (d, J=7.2 Hz, 3H, CHCH3), 1.37-1.24 (m, 4H, CH2), 0.97 (t, J=7.5 Hz, 3H, CH3 DHA), 0.90 (t, J=7.2 Hz, 3H, CH3 SFA), 0.89 (d, J=6.6 Hz, 6H, CH(CH3)2) ppm. 13C{H} NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δC: 173.8 (Ibu), 173.3 (SFA), 172.5 ( DHA), 140.6, 137.3, 132.1, 129.4 (2), 129.3, 128.6, 128.4, 128.32, 128.29, 128.14, 128.12, 128.05, 127.9, 127.7 (2), 127.2, 127.1, 69.2, 62.1, 62.1, 45.09, 45.07, 34.0, 33.8, 31.3, 30.2, 25.7 (2), 25.63, 25.59 (2), 24.6, 22.6, 22.4 (2), 22.3, 20.6, 18.4, 14.3, 13.9 ppm. HRMS (ESI) m/z: [M + Na]+ calcd for C44H64O6Na 711.4595; found, 711.4584.
3.6.2–6. Synthesis of (S,S’)-12b – (S,S’)-12f
3.6.7. Synthesis of 3-[4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)-docosa-4,7,10,13,16,19-hexaenoyl]-1-hexanoyl-2-[(S)-2-(4-isobutylphenyl)propanoyl]-sn-glycerol, (R,S’)-12a
To a solution of 1-hexanoyl-2-[(S)-2-(4-isobutylphenyl)propanoyl]-sn-glycerol (S,S’)-8a (12 mg, 0.032 mmol) and DHA as a free acid (12 mg, 0.035 mmol) in CH2Cl2 (1.5 mL) were added DMAP (4 mg, 0.029 mmol) and EDCI (7 mg, 0.035 mmol). The solution was stirred on a magnetic stirrer at room temperature for 12 h. The reaction was disconnected by passing the reaction mixture through a short column packed with silica gel by use of Et2O/CH2Cl2 (1:9). The solvent was removed in vacuo on a rotary evaporator. The residue was applied to a silica gel chromatography using petroleum ether/ethyl acetate (9:1) as eluent, which afforded the product (R,S’)-12a as a yellow oil, in 81% yield (18 mg, 0.026 mmol). [α]20D = +6.73 (c. 1.8, CH2Cl2). IR (NaCl, νmax / cm-1): 2973 (vs), 2926 (vs), 1742 (vs). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δH: 7.18 (d, J=7.7 Hz, 2H, Ibu-2,6), 7.07 (d, J=7.7 Hz, 2H, Ibu-3,5), 5.54-5.27 (m, 12H, =CH), 5.27-5.23 (m, 1H, CH sn-2), 4.30 (dd, J=11.9, 4.3 Hz, 1H, CH2 sn-1/3), 4.19-4.13 (m, 2H, CH2 sn-1/3), 4.06 (dd, J=11.9, 6.3 Hz, 1H, CH2 sn-1/3), 3.70 (q, J=7.2 Hz, 1H, CHCH3), 2.90-2.78 (m, 10H, =CHCH2CH=), 2.43 (d, J=7.1 Hz, 2H, CH2CH(CH3)2), 2.40-2.27 (m 4H, CH2CH2COO DHA), 2.15 (m, 2H, =CHCH2CH3), 2.08 (t, J=7.4 Hz, 2H, CH2COO SFA), 1.83 (nonet, J=6.8 Hz, 1H, CH(CH3)2), 1.65-1.55 (m, 2H, CH2CH2COO SFA), 1.49 (d, J=7.2 Hz, 3H, CHCH3), 1.37-1.24 (m, 4H, CH2), 0.97 (t, J=7.5 Hz, 3H, CH3 DHA), 0.90 (d, J=6.6 Hz, 6H, CH(CH3)2), 0.89 (t, J=7.2 Hz, 3H, CH3 SFA) ppm. 13C{H} NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δC: 174.0 (Ibu), 173.3 (SFA), 172.7 (DHA), 140.6, 137.3, 132.2, 129.6 (2), 129.4, 128.7, 128.4, 128.3, 128.23 (2), 128.16, 128.0, 127.9, 127.8, 127.7 (2), 127.3, 69.3, 62.4, 62.1, 45.2, 45.1, 34.0, 33.8, 32.1, 30.3, 29.8 (2), 25.8, 25.7 (2), 24.9, 22.9, 22.8 (2), 22.5, 20.7, 18.5, 14.31, 14.27 ppm. HRMS (ESI) m/z: [M + Na]+ calcd for C44H64O6Na 711.4595; found, 711.4590.
3.6.8–12. Synthesis of (R,S’)-12b – (R,S’)-12f
3.6.13. Synthesis of 1-[4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)-docosa-4,7,10,13,16,19-hexaenoyl]-3-hexanoyl-2-[(S)-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoyl]-sn-glycerol, (S,S’)-13a
To a solution of 3-hexanoyl-2-[(S)-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoyl]-sn-glycerol (R,S’)-9a (35 mg, 0.087 mmol) and DHA as a free acid (31 mg, 0.093 mmol) in CH2Cl2 (4 mL) were added DMAP (11 mg, 0.094 mmol) and EDCI (24 mg, 0.127 mmol). The solution was stirred on a magnetic stirrer at room temperature for 12 h. The reaction was disconnected by passing the reaction mixture through a short column packed with silica gel by use of Et2O/CH2Cl2 (1:9). The solvent was removed in vacuo on a rotary evaporator. The residue was applied to a silica gel chromatography using petroleum ether/ethyl acetate (7:3) as eluent, which afforded the product (S,S’)-13a as a yellow oil, in 84% yield (52 mg, 0.073 mmol). [α]20D = +6.81 (c. 5.2, CH2Cl2). IR (NaCl, νmax / cm-1): 3013 (vs), 2961 (vs), 2934 (vs), 2873 (vs), 1743 (vs), 1607 (vs). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δH: 7.72-7.62 (m, 3H, Nap-1,4,8), 7.38 (dd, J=8.5, 1.9 Hz, 1H, Nap-3), 7.13 (dd, J=8.9, 2.5 Hz, 1H, Nap-7), 7.09 (d, J=2.5 Hz, 1H, Nap-5), 5.43-5.23 (m, 12H, =CH), 5.21-5.14 (m, 1H, CH sn-2), 4.30 (dd, J=11.9, 4.2 Hz, 1H, CH2 sn-1/3), 4.18 (dd, J=11.9, 4.3 Hz, 1H, CH2 sn-1/3), 4.14 (dd, J=11.9, 6.1 Hz, 1H, CH2 sn-1/3), 4.07 (dd, J=11.9, 6.5 Hz, 1H, CH2 sn-1/3), 3.90 (s, 3H, OCH3), 3.86 (q, J=7.5 Hz, 1H, CHCH3), 2.88-2.74 (m, 10H, =CHCH2CH=), 2.27-2.21 (m, 2H, CH2COO DHA), 2.20-2.13 (m, 2H, CH2COO DHA), 2.12-1.99 (m, 4H, CH2COO SFA and =CHCH2CH3), 1.61-1.52 (m, 5H, CH2CH2COO SFA and CHCH3), 1.35-1.20 (m, 4H, CH2), 0.97 (t, J=7.5 Hz, 3H, CH3 DHA), 0.89 (t, J=7.0 Hz, 3H, CH3 SFA) ppm. 13C{H} NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δC: 173.9 (Nap), 173.4 (SFA), 172.5 (DHA), 157.8, 135.3, 133.9, 132.2, 129.4 (2), 129.0, 128.7, 128.6, 128.41, 128.38, 128.3, 128.21, 128.16, 128.0, 127.8, 127.23, 127.15, 126.2, 126.1, 119.2, 105.7, 69.5, 62.18, 62.15, 55.4, 45.5, 34.1, 33.7, 31.4, 25.8 (2), 25.7, 25.6 (2), 24.6, 22.5, 22.4, 20.7, 18.4, 14.1, 14.0 ppm. HRMS (ESI) m/z: [M + Na]+ calcd for C45H60O7Na 735.4231; found, 735.4227.
3.6.14–18. Synthesis of (S,S’)-13b – (S,S’)-13f
3.6.19. Synthesis of 3-[4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)-docosa-4,7,10,13,16,19-hexaenoyl]-1-hexanoyl-2-[(S)-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoyl]-sn-glycerol, (R,S’)-13a
To a solution of 1-hexanoyl-2-[(S)-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)propanoyl]-sn-glycerol (S,S’)-9a (12 mg, 0.030 mmol) and DHA as a free acid (11 mg, 0.033 mmol) in CH2Cl2 (1.3 mL) were added DMAP (4 mg, 0.033 mmol) and EDCI (8 mg, 0.044 mmol). The solution was stirred on a magnetic stirrer at room temperature for 12 h. The reaction was disconnected by passing the reaction mixture through a short column packed with silica gel by use of Et2O/CH2Cl2 (1:9). The solvent was removed in vacuo on a rotary evaporator. The residue was applied to a silica gel chromatography using petroleum ether/ethyl acetate (8.5:1.5) as eluent, which afforded the product (R,S’)-13a as a yellow oil, in 74% yield (22 mg, 0.022 mmol). [α]20D = +8.80 (c. 0.6, CH2Cl2). IR (NaCl, νmax / cm-1): 3013 (vs), 2960 (vs), 2932 (vs), 1732 (vs), 1634 (s), 1607 (s). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δH: 7.72-7.62 (m, 3H, Nap-1,4,8), 7.38 (dd, J=8.5, 1.9 Hz, 1H, Nap-3), 7.13 (dd, J=8.9, 2.5 Hz, 1H, Nap-7), 7.10 (d, J=2.5 Hz, 1H, Nap-5), 5.46-5.26 (m, 12H, =CH), 5.31-5.21 (m, 1H, CH sn-2), 4.30 (dd, J=11.9, 4.2 Hz, 1H, CH2 sn-1/3), 4.21-4.10 (m, 2H, CH2 sn-1/3), 4.06 (dd, J=11.9, 6.4 Hz, 1H, CH2 sn-1/3), 3.91 (s, 3H, OCH3), 3.70 (q, J=7.2 Hz, 1H, CHCH3), 2.89-2.77 (m, 10H, =CHCH2CH=), 2.46-2.28 (m, 4H, CH2COO DHA), 2.14-2.01 (m, 2H, CH2COO SFA), 2.01-1.88 (m, 2H, =CHCH2CH3), 1.58 (d, J=7.2 Hz, 3H, CHCH3), 1.37 (quint, J=7.5 Hz, 2H, CH2CH2COO SFA), 1.30-1.20 (m, 4H, CH2), 0.97 (t, J=7.5 Hz, 3H, CH3 DHA), 0.84 (t, J=7.0 Hz, 3H, CH3 SFA) ppm. 13C{H} NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δC: 173.9 (Nap), 173.3 (SFA), 172.7 (DHA), 157.9, 135.4, 133.9, 132.2, 129.6, 129.4, 129.1, 128.7, 128.5, 128.44, 128.41, 128.3, 128.23, 128.16, 128.0, 127.8, 127.24, 127.17, 126.3, 126.1, 119.2, 105.7, 69.5, 62.4, 62.0, 55.4, 45.5, 34.0, 33.8, 31.3, 25.8 (2), 25.7, 25.7 (2), 24.4, 22.7, 22.4, 20.7, 18.5, 14.4, 14.0 ppm. HRMS (ESI) m/z: [M + Na]+ calcd for C45H60O7Na 735.4231; found, 735.4231.
3.6.20–24. Synthesis of (R,S’)-13b – (R,S’)-13f