Submitted:
16 October 2024
Posted:
17 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
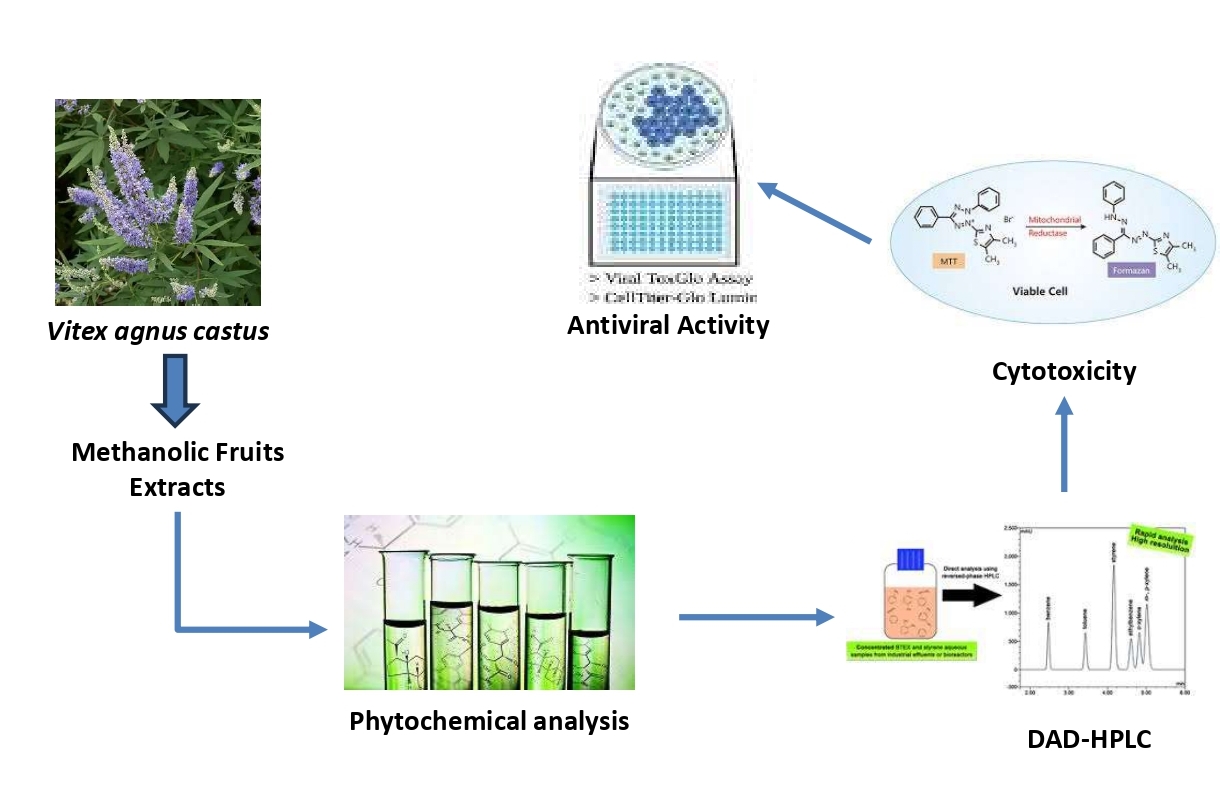
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
2.1.1. Collection and Identification of the Plant
2.1.2. Preparation of the Crude Plant Extract
2.1.3. Phytochemical Analyses and Polyphenol Content
2.1.4. Determination of Tannin Contents
2.1.5. Determination of Minerals
2.1.6. Determination of Nitrogen
2.1.7. Cytotoxicity of Vitex Fruits Methanolic Extracts against HEp-2 Cells
2.1.8. Antiviral Activity Test of Methanolic Extracts
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Phytochemical Screening
3.2. Determination of Minerals
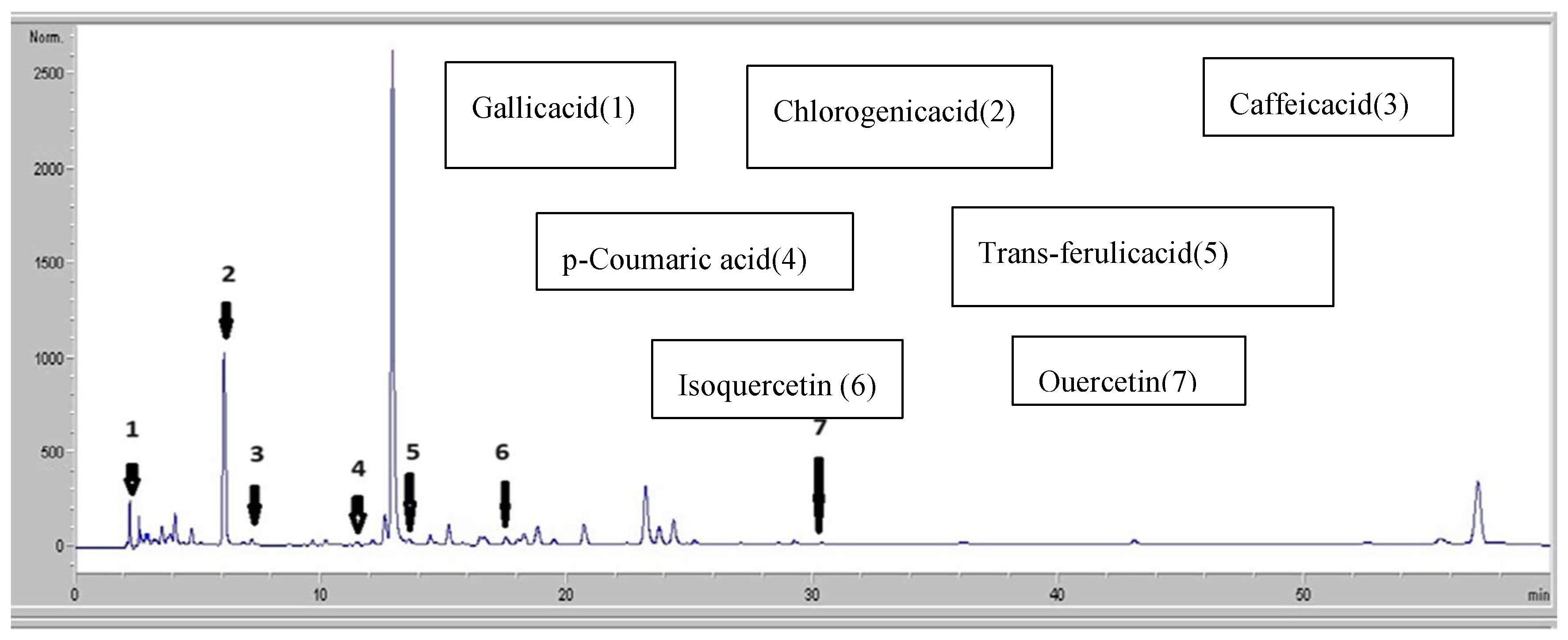
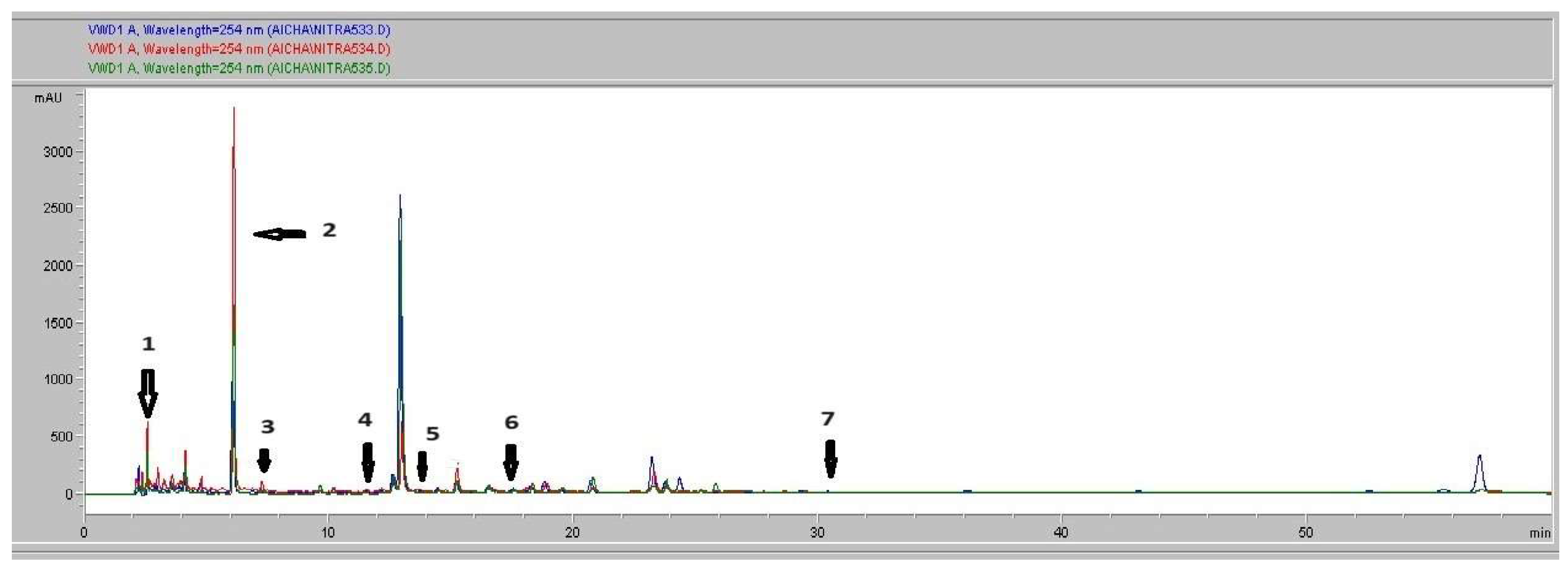
3.3. HPLC-DAD Analysis
| Peak | Compound Identification |
Similarity Area |
RT (min) Retention Time |
Content (µg/ ml) Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Gallicacid | 607 ,33 | 2.63 | 23 |
| 2 | Chlorogenicacid | 8819,53 | 6.11 | 709.89 |
| 3 | Caffeicacid | 247,66 | 7.39 | 19.093 |
| 4 | p-Coumaricacid | 633,6 | 11.46 | 99.33 |
| 5 | Trans-ferulicacid | 1435,63 | 13.52 | 85.842 |
| 6 | Isoquercetin | 1208,73 | 17.6 | 49.46 |
| 7 | Quercetin | 577,78 | 31.03 | 21.14 |
3.4. Antioxidant Activity
3.5. Antiviral Activity
4. Conclusion
References
- Francis, A.; Bruno, D.G. Endobiogeny and Medicinal Plants: From Meaning in Physiology to Practice in Phytotherapy. Elsevier Masson, 2020, 400.
- Yi, F.; Xu, L.J.; Meng, H.; Dong, Y.M.; Liu, H.B.; Xiao, P.G. In Silico Approach to Reveal the Pharmacological Material Basis of Traditional Medicinal Plants. Menton. Med. 2018, 13, 33. [Google Scholar]
- Rani, A.; Sharma, A. The Genus Vitex: A Review. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2013, 7(14), 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertone-Johnson, E.R.; Hankinson, S.E.; Johnson, S.R.; Manson, J.E. Timing of Alcohol Use and the Incidence of Premenstrual Syndrome and Probable Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder. J. WomensHealth (Larchmt) 2009, 18(12), 1945–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masure, C. Chaste Tree (Vitex agnus-castus L.): Interest and Use in Premenstrual Syndrome. Doctoral Thesis, Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2018, 127.
- Bruneton J. Toxic Plants: Dangerous Vegetation for Humans and Animals. 3rd revised and expanded edition. Éditions Tec & Doc Lavoisier &EMinter, Paris. 2005.
- Ulusoy, Ş.; İnal, E.; Küpeli Akkol, E.; Çiçek, M.; Kartal, M.; Sobarzo-Sánchez, E. Evaluation of the anti-obesity effect of Sambucus nigra L. (elderberry) and Vitex agnus-castus L. (chasteberry) extracts in high-fat diet-induced obese rats. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1410854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.N.; Friesen, J.B.; Webster, D.; Nikolic, D.; Van Breemen, R.B.; Wang, Z.J.; Fong, H.H.; Farnsworth, N.R.; Pauli, G.F. Phytoconstituents from Vitex agnus-castus Fruits. Fitoterapia 2011, 82(4), 528–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azofeifa, G.; Quesada, S.; Boudard, F.; Morena, M.; Cristol, J.P.; Perez, A.M.; Vaillant, F.; Michel, A. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory in vitro activities of phenolic compounds from tropical highland blackberry (Rubus adenotrichos). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 5798–5804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacampagne, S. Localization and Characterization of Tannins in Grape Skins: Impact of the Physicochemical Organization of Cell Walls on Tannic Composition, Fruit Quality, and Typicity of Bordeaux Grapes. Ph.D. Thesis, Sciences, Bordeaux 2, 2010, p. 294.
- Thaçi, S.; Krasniqi, B.; Dërmaku-Sopjani, M.; Rifati-Nixha, A.; Abazi, S.; Sopjani, M. Vasorelaxant Effects of the Vitex agnus-castus Extract. Evid. BasedComplement. Altern. Med. 2022,(1), 7708781. [CrossRef]
- Stöckigt, J.; Sheludk, Y.; Unger, M.; Gerasimenko, I.; Warzecha, H.; Stöckigt, D. High-Performance Liquid Chromatographic, Capillary Electrophoretic and Capillary Electrophoretic-Electrospray Ionisation Mass Spectrometric Analysis of Selected Alkaloid Groups. J. Chromatogr. A 2002, 967(1), 85–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arokiyaraj, S.; Perinbam, K.; Vivek, P.; Udaya Prakash, N.K. Free Radical Scavenging and In Vitro Cytotoxic Activity of Agnuside from Vitex agnus-castus (Verbenaceae). J. Pharm. Res. 2012, 5(5), 2548–2552. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.J.; Wang, C.J.; Kuo, H.C.; Chou, F.P.; Jean, L.F.; Tseng, T.H. Induction of Apoptosis by Luteolin in Human Hepatoma HepG2 Cells Involving Mitochondria Translocation of Bax/Bak and Activation of JNK. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2005, 203(2), 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Tang, M.; Wu, J. The determination of flavonoid contents in mulberry and their scavenging effects on superoxide radicals. Foods 1999, 64, 555–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkol, E.K.; Karpuz, B.; Türkcanoğlu, G.; Coşgunçelebi, F.G.; Taştan, H.; Aschner, M.; Khatkar, A.; Sobarzo-Sánchez, E. The Phytochemical Profile and Biological Activity of Malva neglecta Wallr. in Surgically Induced Endometriosis Model in Rats. Molecules 2022, 27, 7869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awah, F.M.; Uzoegwu, P.N.; Ifeonu, P.; Oyugi, J.O.; Rutherford, J.; Yao, X.; Fehrmann, F.; Fowke, K.R.; Eze, M.O. Free radical scavenging activity, phenolic contents, and cytotoxicity of selected Nigerian medicinal plants. Foods 2012, 131, 1279–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, H.R.; Ferreira, T.A.; Genovese, M.I. Antioxidant capacity and mineral content of pulp and peel from commercial cultivars of citrus from Brazil. Foods 2012, 134, 1892–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Z.; Tang, M.; Wu, J. The determination of flavonoid contents in mulberry and their scavenging effects on superoxide radicals. Foods 1999, 64, 555–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miliauskas, G.; Venskutonis, P.R.; Van Beek, T.A. Screening of radical scavenging activity of some medicinal and aromatic plant extracts. Foods 2004, 85, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schofield P,Mbugua DM, Pell A N. . Analyses of condensed tannins: a review Animal Food and Technology.2001, 91, 21-40. [CrossRef]
- Broadhurst, R.B.; Jones, W.T. Analysis of condensed tannins using acidified vanillin. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1978, 29, 788–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimler, D.; Vignolini, P.; Dini, M.G.; Romani, A. Antiradical activity and polyphenol composition of local Brassicaceae edible varieties. Foods 2006, 99, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savy, M.; Martin-Prével, Y.; Traissac, P.; Delpeuch, F. Measuring dietary diversity in rural Burkina Faso: comparison of a 1-day and a 3-day dietary recall. Public Health Nutr. 2007, 10, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stämpfli, R.; Brühwiler, P.; Mourad, S.; Verdejo, R.; Shaffer, M. Development and Characterisation of Carbon Nanotube-Reinforced Polyurethane Foams. EMPA Activities 2007, 26, 51.Landoulsi, A.; Roumy, V.; Riviere, C.; Sahpaz, S.; Benhamida, J.; Hennebelle, T. Chemical composition and pharmacological activities of Tunisian species of the genus Eryngium L. (Apiaceae). Open Sci. 2018, 1-23.
- Zhang W, Torabinejad M, Li Y. Evaluation of cytotoxicity of MTAD using the MTT-tetrazolium method. J Endod. 2003,29(10), 654-7. tfc. [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Chipman, P.R.; Howitt, J.; et al. Interaction of Coxsackievirus B3 with the Full Length Coxsackievirus-Adenovirus Receptor. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2001, 8(10), 874-878.Kimmis BD, Downing C, Tyring S. Hand-foot-and-mouth disease caused by coxsackievirus A6 on the rise. Cutis. 2018, 102(5), 353-356.
- Berrani A, Marmouzi I, Kharbach M, et al. Anabasis aretioidesCoss. &Moq. phenolic compounds exhibit in vitro hypoglycemic, antioxidant and antipathogenic properties. J Basic Clin PhysiolPharmacol. 2018. 30(2), 251-257. [CrossRef]
- Kikalishvili, B.; Zurabashvili, D.; Sulakvelidze, T.; Malania, M.; Turabelidze, D. Georgian Med. News 2016, (256-257), 77-81.
- Ozkaya, F., Unak, P., Medine, E.I. et al. 18FDG conjugated magnetic nanoparticle probes: synthesis and in vitro investigations on MCF-7 breast cancer cells. J RadioanalNucl Chem 295, 1789–1796 (2013). [CrossRef]
- Lee HJ, Wang CJ, Kuo HC, Chou FP, Jean LF, Tseng TH. Induction apoptosis of luteolin in human hepatoma HepG2 cells involving mitochondria translocation of Bax/Bak and activation of JNK. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2005, 203(2), 124-131. [CrossRef]
- Ohyama K, Akaike T, Imai M, Toyoda H, Hirobe C, Bessho T. Human gastric signet ring carcinoma (KATO-III) cell apoptosis induced by Vitex agnus-castus fruit extract through intracellular oxidative stress. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2005;37(7):1496-1510. [CrossRef]
- Boujbiha, M.A.; Chahdoura, H.; Adouni, K.; Ziani, B.E.C.; Snoussi, M.; Chakroun, Y.; Ciudad-Mulero, M.; Fernández-Ruiz, V.; Achour, L.; Selmi, B.; Morales, P.; Flamini, G.; Mosbah, H. Wild Vitex agnus-castus L.: Phytochemical Characterization, Acute Toxicity, and Bioactive Properties. Molecules2023, 28(13), 5096. [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, D.; Chaudhary, M.A.; Raza, A.; et al. Comparative study of antibacterial activity and mineral contents of various parts of Verbena officinalis Linn. Asian Journal of Chemistry 2012, 24(1), 68–72. [Google Scholar]
- Mesaik, M.A.; Azizuddin; Murad, S.; Khan, K.M.; Tareen, R.B.; Ahmed, A.; Atta-ur-Rahman; Choudhary, M.I. Isolation and immunomodulatory properties of a flavonoid, casticinfromVitex agnus-castus.Phytother Res.2009, 23(11), 1516–20. [CrossRef]
- Skrzypczak-Pietraszek, E.; Piska, K.; Pietraszek, J. Enhanced production of the pharmaceutically important polyphenolic compounds in Vitex agnus-castusL. shoot cultures by precursor feeding strategy. Eng. Life Sci. 2018, 18(5), 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamov, G.V.; Rendyuk, T.D.; Saybel, O.L.; Dargaeva, T.D.; Tsitsilin, A.N.; Bokov, D.O. Vitex agnus-castus: Botanical features and area, chemical composition of fruit, pharmacological properties, and medicinal uses. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 12(03), 034–044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrani, A.; Marmouzi, I.; Bouyahya, A.; Kharbach, M.; El Hamdani, M.; El Jemli, M.; Lrhorfi, A.; Zouarhi, M.; Faouzi, M.E.A.; Bengueddour, R. Phenolic Compound Analysis and Pharmacological Screening of Vitex agnus-castus Functional Parts. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 6695311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asdadi, A.; Hamdouch, A.; Oukacha, A.; Moutaj, R.; Gharby, S.; Harhar, H.; El Hadek, M.; Chebli, B.; Idrissi Hassani, L.M. Study on chemical analysis, antioxidant and in vitro antifungal activities of essential oil from wild Vitex agnus-castus L. seeds growing in the area of Argan Tree of Morocco against clinical strains of Candida responsible for nosocomial infections. J. Mycol. Med. 2015, 25(4), e118–e127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, M.; Yuan, B.; Kikuchi, H.; Saito, M.; Ohyama, K.; Hirobe, C.; Oshima, T.; Hosoya, T.; Morita, H.; Toyoda, H. Growth inhibition of a human colon carcinoma cell, COLO 201, by a natural product, Vitex agnus-castus fruits extract, in vivo and in vitro. Adv. Biol. Chem. 2012, 2, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, R.A.; Dickinson, A.J. A century of studying plant secondary metabolism-From "what?" to "where, how, and why?". Plant Physiol. 2024, 195(1), 48–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allahtavakoli, M.; Honari, N.; Pourabolli, I.; Arababadi, M.K.; Ghafarian, H.; Roohbakhsh, A.; Shamsizadeh, A. Vitex agnus-castus extract improves learning and memory and increases the transcription of estrogen receptor α in the hippocampus of ovariectomized rats. Base Clin. Neurosci. 2015, 6(3), 185. [Google Scholar]
- Powers, C.N.; Setzer, W.N. A molecular docking study of phytochemical estrogens mimicking plant-based dietary supplements. In Silico Pharmacol. 2015, 3(1), 1–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basavalingappa, R.H.; Arumugam, R.; Lasrado, N.; Yalaka, B.; Massilamany, C.; Gangaplara, A.; Riethoven, J.J.; Xiang, S.H.; Steffen, D.; Reddy, J. Viral myocarditis involves the generation of autoreactive T cells with multiple antigen specificities that localize in lymphoid and non-lymphoid organs in the mouse model of CVB3 infection. Mol. Immunol. 2020, 124, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejan, S.; Marina, S.; Jasmina, G.L.; Ana, D.; Ana, C.I.; Mihailo, R.; Dragoljub, G. Chemical composition and antimicrobial activity of Vitex agnus-castus L. fruits and leaves essential oils. Food Chem. 2011, 128(4), 1017–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouikha, A.; Rezig, D.; Driss, N.; et al. Circulation and Molecular Epidemiology of Enteroviruses in Paralyzed, Immunodeficient, and Healthy Individuals in Tunisia, a Country with a Polio-Free Status for Decades. Viruses 2021, 13(3), 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mone, K.; Lasrado, N.; Sur, M.; Reddy, J. Vaccines against Group B Coxsackieviruses and Their Importance. Vaccines 2023, 11(2), 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Increased detections and severe neonatal disease associated with coxsackievirus B1 infection—United States, 2007. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2008, 57(20), 553-556.
- Khan, M.A.; Rahman, A.A.; Islam, S.; et al. A Comparative Study on the Antioxidant Activity of Methanolic Extracts from Different Parts of Morus alba L. (Moraceae). BMC Res. Notes 2013, 6, 24. [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, J.L.; Leitão, S.G.; Monache, F.D.; Miranda, M.M.; Santos, M.G.; Romanos, M.T.; Wigg, M.D. In vitro antiviral effect of flavonoid-richextracts of Vitex polygama (Verbenaceae) against acyclovir-resistantherpes simplex virus type 1. Phytomedicine 2001, 8(6), 477–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves JL, Leitão SG, Monache FD, Miranda MM, Santos MG, Romanos MT, Wigg MD. In vitro antiviral effect of flavonoid-rich extracts of Vitex polygama (Verbenaceae) against acyclovir-resistant herpes simplex virus type 1. Phytomedicine. 2001 Nov;8(6):477-80. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sogame, M.; Naraki, Y.; Sasaki, T.; Seki, M.; Yokota, K.; Masada, S.; Hakamatsuka, T. Quality Assessment of Medicinal Products and Dietary Supplements Containing Vitex agnus-castus by HPLC Fingerprint and Quantitative Analyses. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2019, 67(6), 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Phytochemical Compounds | Values (mg/g VACME) |
| Total phenolic content (mg G AE/g Ext) | 16.89±0.04 |
| Total flavonoid content (mg ECat/g Ext) | 10.28 ±0.22 |
| Total flavonol content (mg ER/g Ext) | 04.37±0.01 |
| Total tannin content (mg EAT/g Ext) | 19.13±0.86 |
|
Content (mg/100 g dw) |
N | 1640 |
| P | 270 | |
| K | 1620 | |
| Ca | 1000 | |
| Na | 120 | |
| Mg | 500 | |
| Fe | 203.55 | |
| Cu | 4.60 | |
| B | 61.00 | |
| Zn | 27.53 |
| IC50 (mg/ml) | Ascorbic Acid | Methalonic extract |
|---|---|---|
| DPPH scavenging assay | 0.018 ±1.27b | 0.501±1.19b |
| ABTS scavenging assay | 0.067±0.08b | 0.585±0.59b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





