1. Introduction
Urbanization and Land Use in Kathmandu
Figure 1 illustrates the capital city, Kathamndu Metropolitan City - the focal point of the study.
Various land use and land cover (LULC) studies in Kathmandu Metropolitan City (KMC) (see
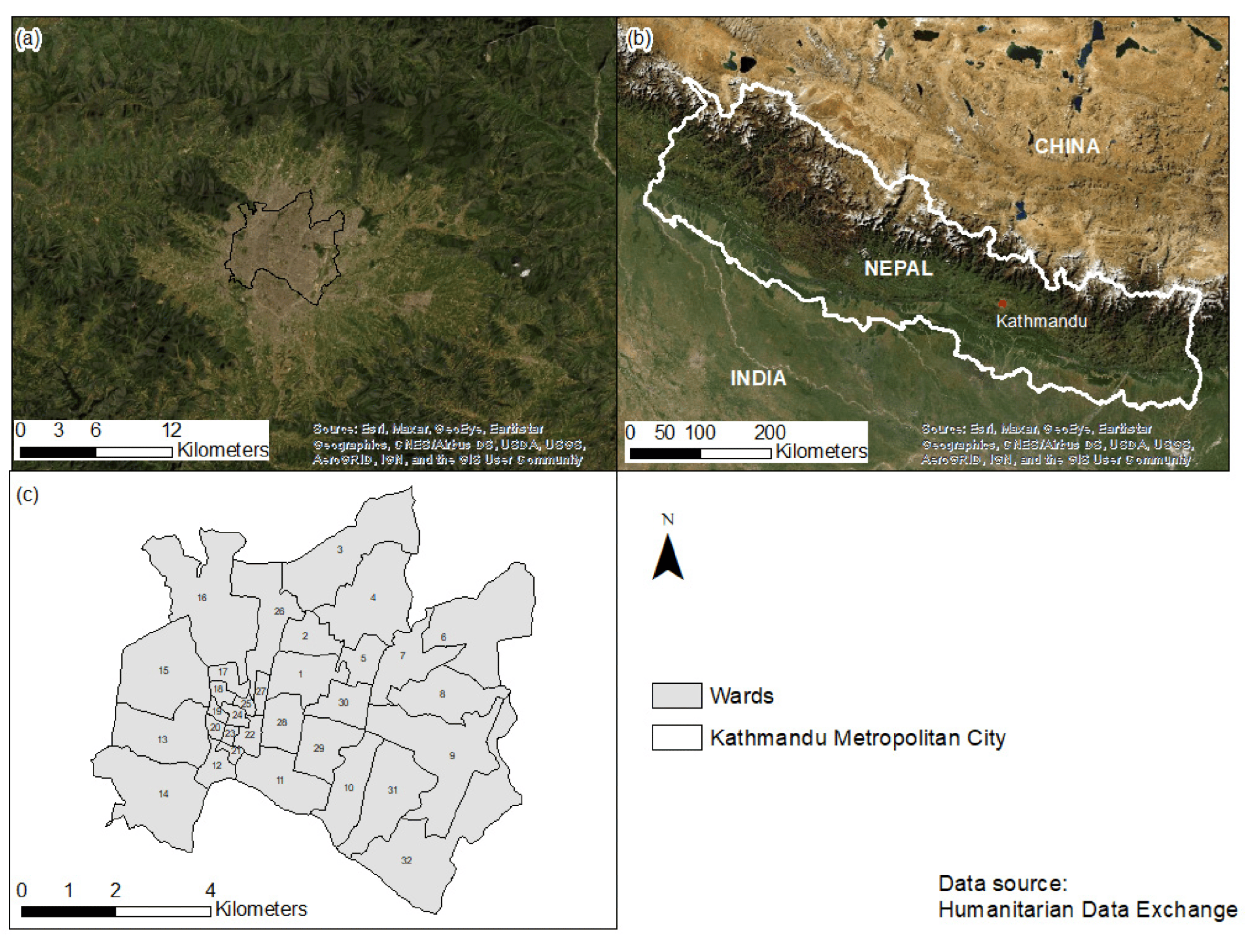
Figure 2) have highlighted the negative impacts of rapid urbanization and population growth. These studies point to environmental challenges such as the Urban Heat Island (UHI) effect [
1,
2], where urban areas exhibit significantly higher temperatures than surrounding rural areas [
3].
Impact of Land Use Change on UHI
Changes in land cover properties alter the thermal properties, surface radiation (energy emitted from the Earth’s surface), and humidity of urban areas, which contributes to the UHI effect [
4]. Evaluating UHI in rapidly urbanizing cities like Kathmandu is crucial to understand changes in surface albedo (reflectivity), emissivity (radiation efficiency), and evapotranspiration (water transfer from land to the atmosphere) [
5]. The rise in UHI affects natural and human systems by altering rainfall patterns, worsening air quality, and increasing risks of floods and water contamination [
6,
7].
Global Evidence and Land Surface Temperature (LST) Studies
Globally, extensive evidence shows the link between urbanization and rising land surface temperatures (LST) [
8,
9,
10]. LST is a critical factor in quantifying UHI effects [
11]. Monitoring LST through remote sensing (RS) technologies provides insights into how land use changes impact surface temperatures.
Remote Sensing in UHI Studies
There is a growing body of literature demonstrating the benefits of satellite remote sensing for monitoring urban LULC patterns and LST [
12,
13,
15]. Studies such as those by Estoque et al. [
13] examined LST patterns in Southeast Asian megacities, while Athukorala and Murayama [
15] analyzed spatial variations in land use and surface heat islands in Accra, Ghana. Jiang et al. [
16] explored how urbanization in the U.S. Midwest influenced LST and surface moisture, while Yan et al. [
4] assessed the warming effects of urbanization in Chinese urban areas. These studies provide essential insights into UHI mitigation strategies and contribute to urban planning aimed at reducing the UHI effect [
4,
10,
16].
Figure 1.
Nepal, Kathmandu Metropolitan City.
Figure 1.
Nepal, Kathmandu Metropolitan City.
Figure 2.
Kathmandu Metropolitan City, Nepal; (a) Geographic location of KMC; (b) Land cover comparison between KMC and its surroundings; (c) Administrative wards in KMC.
Figure 2.
Kathmandu Metropolitan City, Nepal; (a) Geographic location of KMC; (b) Land cover comparison between KMC and its surroundings; (c) Administrative wards in KMC.
Urbanization and Thermal Comfort in KMC
Kathmandu, as one of the most developed cities in Nepal in terms of population and economic growth, has seen rapid increases in built-up areas. Thermal comfort (the perception of temperature as comfortable or uncomfortable) has become a significant issue in Kathmandu [
1], with recent studies by Maharjan et al. [
17] addressing this problem. This paper aims to forecast LST in Kathmandu, contributing to strategies that could enhance thermal comfort and mitigate UHI effects.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dataset Information
The dataset used for this study was sourced from the Open Data Nepal platform, titled “Climate Data”. It is available in CSV format and contains daily time-series data related to climate variables such as temperature, relative humidity, precipitation levels, surface pressure, specific humidity, and wind speed. The dataset covers the period from 1981 to 2019 and includes records for 62 districts in Nepal. However, the model was primarily trained and evaluated on data from the Kathmandu Metropolitan City (KMC). No additional datasets or external data sources were used in this project.
2.2. Study Area
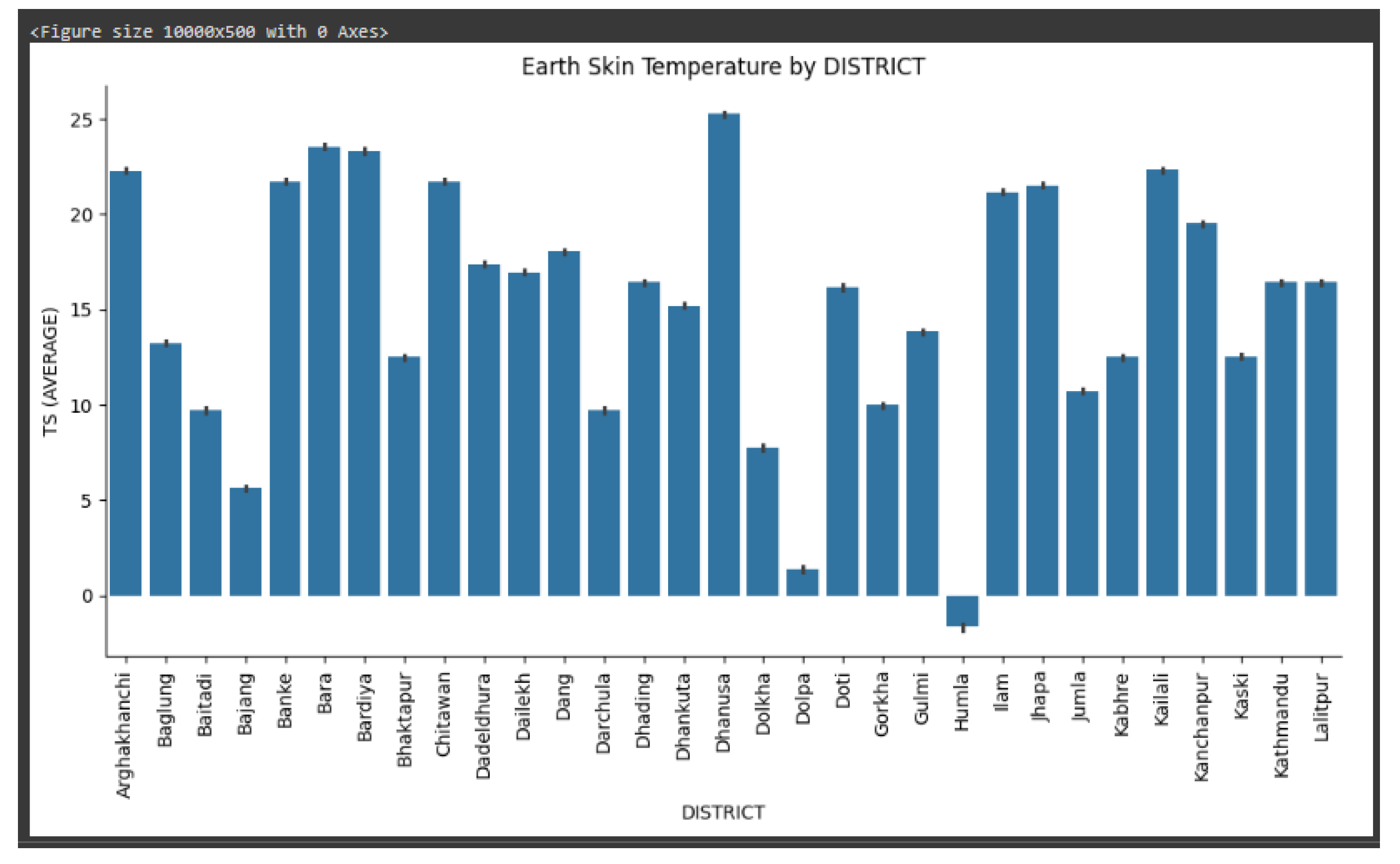
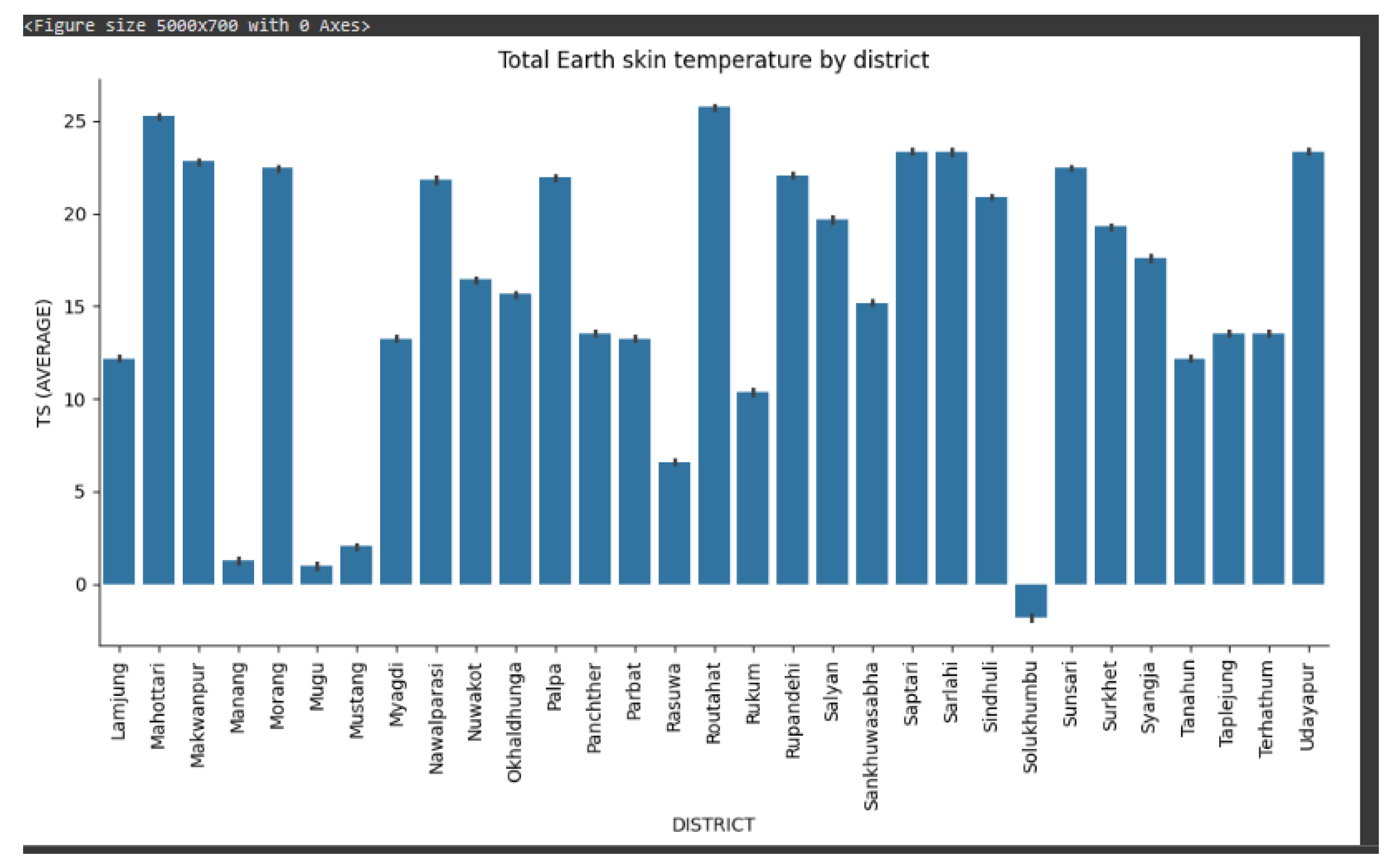
While we have recorded data of skin temperature for 62 districts provided by Open Data Nepal as shown in the figure, we focused on the capital city, KMC for the reasons of immediate study and assumption of quick implementation of action based on the research.
Figures showcasing recorded LST against Districts:
Figure 3.
District VS TS 1.
Figure 3.
District VS TS 1.
The study area is limited to the Kathmandu Metropolitan City (KMC), located in the central region of Nepal. Although the dataset includes data for 62 districts, this research focuses solely on forecasting for Kathmandu. The data provides insights into the urban climate patterns within KMC, which is rapidly urbanizing.
Figure 4.
District VS TS 2.
Figure 4.
District VS TS 2.
2.3. Tools and Software
The following tools and libraries were used for data processing and analysis:
Pandas for data manipulation and analysis.
NumPy for numerical computations.
Matplotlib and Seaborn for data visualization.
Prophet for time series forecasting, which is an open-source software designed for time series analysis.
The entire development and model training was carried out using Google Colab, a cloud-based environment suitable for machine learning projects.
2.4. Model Information
The machine learning models used in this study include:
Exponential Smoothing (ES): This method was used for univariate time series forecasting. It is well-suited for short-term forecasting with a single variable.
Prophet: This model was used for multivariate forecasting, incorporating multiple climate variables such as temperature, humidity, and precipitation. The default hyperparameters of the Prophet model were utilized for this study.
2.5. Data Preprocessing
To prepare the dataset for analysis:
Handling Missing Data: Missing values in the dataset were handled using interpolation methods to ensure continuity of the time series data.
Data Normalization: The dataset was normalized using the Min-Max Scaler to transform all variables into a common range (typically between 0 and 1). This ensured that features with larger ranges did not dominate the model’s predictions.
2.6. Evaluation Metrics
The following metrics were used to evaluate the performance of the models:
Mean Absolute Error (MAE): Measures the average magnitude of errors in the predictions.
R2 Score: Measures the proportion of variance in the dependent variable that is predictable from the independent variables.
2.7. Experimental Setup
The entire process of training and testing the models was conducted in Google Colab, an online platform offering a cloud-based Python environment. Although Google Colab supports GPU acceleration, no specific hardware configurations or GPU setups were used for this study.
2.8. Methodology
Exponential Smoothing (ES) was employed for univariate analysis, forecasting the temperature time series data for Kathmandu.
Prophet Model was applied for multivariate time series forecasting, using multiple climatic variables such as temperature, humidity, and precipitation.
The dataset was divided into training and testing subsets to evaluate the model’s performance. Cross-validation was not explicitly performed, but the split ensured robust model validation.
2.9. Deployment
After model training, the resulting forecasting model was deployed using
Django, a Python web framework. This deployment enabled users to interact with the model and obtain forecasts for Land Surface Temperature (LST). However, the deployed model is not publicly available, and specific configurations for deployment have been made available in the github repository [
14].
3. Results
3.1. Models
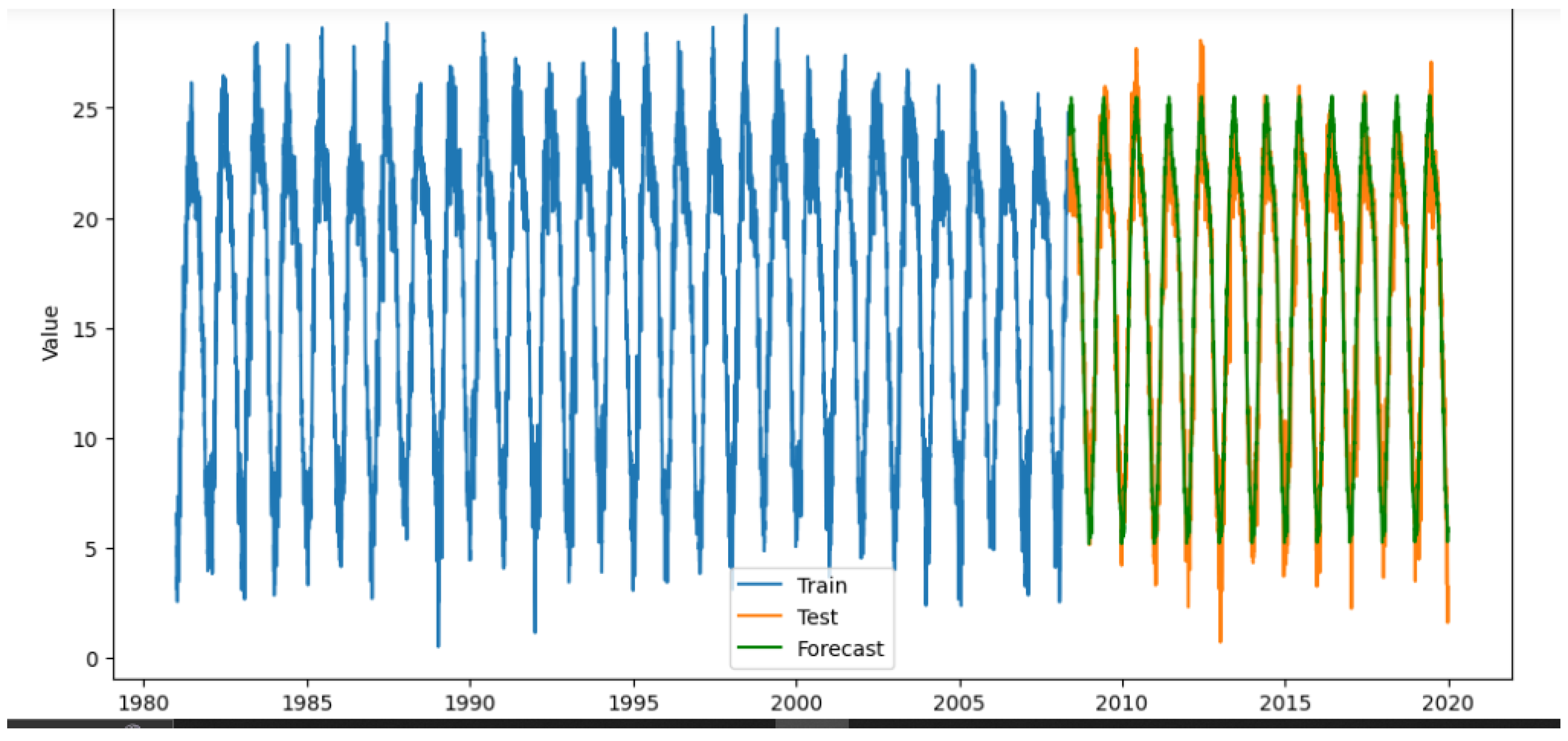
Exponential Smooth Forecast
Figure 5.
Exponential Smoothing Model Forecast.
Figure 5.
Exponential Smoothing Model Forecast.
Mean Absolute Error (MAE): 1.2082659975428822
R-squared (R²) Score: 0.9425295902006932
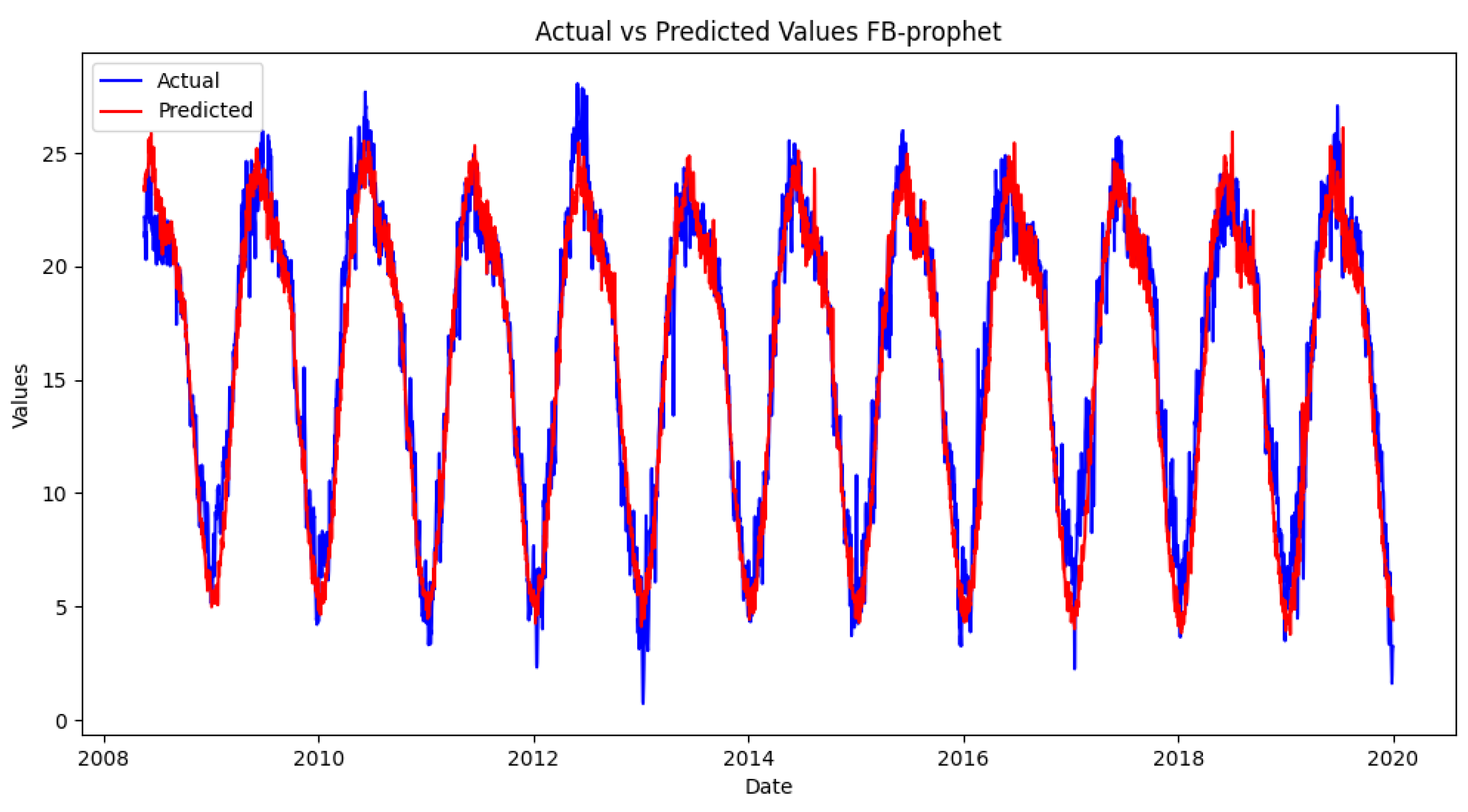
FB Prophet
Figure 6.
FB Prophet Model Forecast.
Figure 6.
FB Prophet Model Forecast.
Mean Absolute Error (MAE): 1.1958573696229469
R-squared (R²) Score: 0.9404890481566638
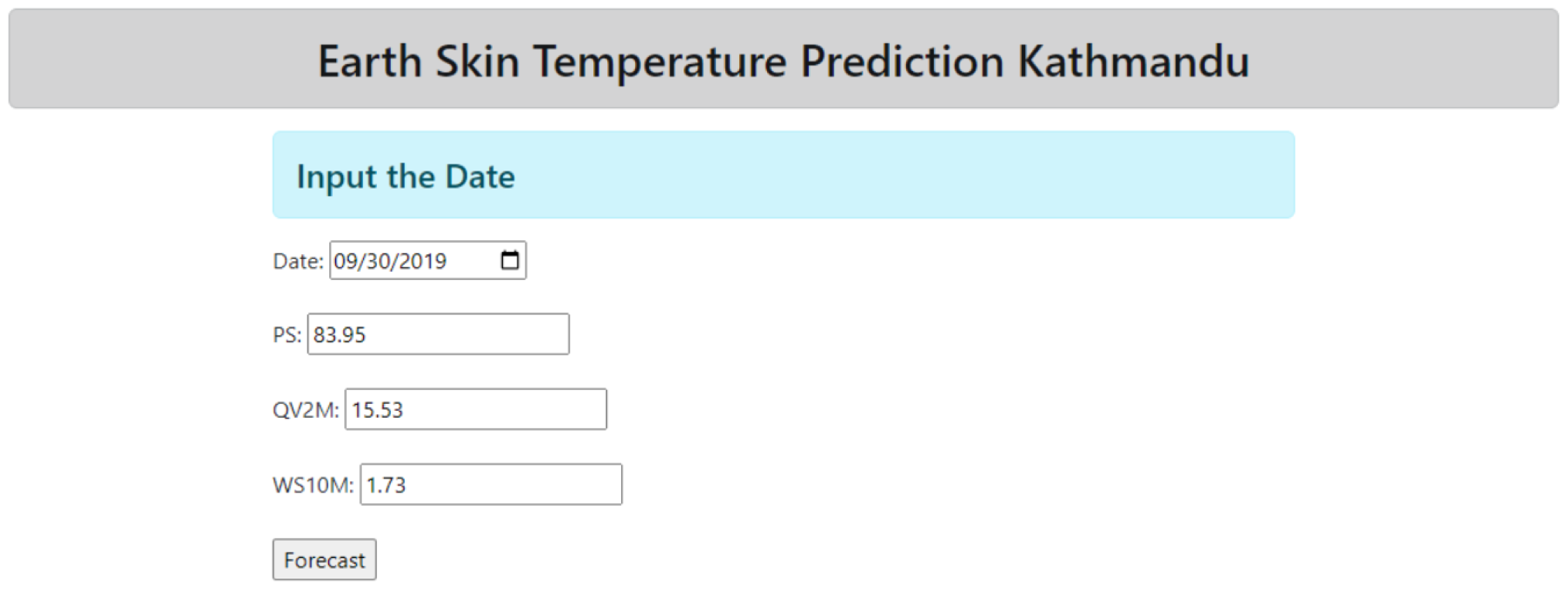
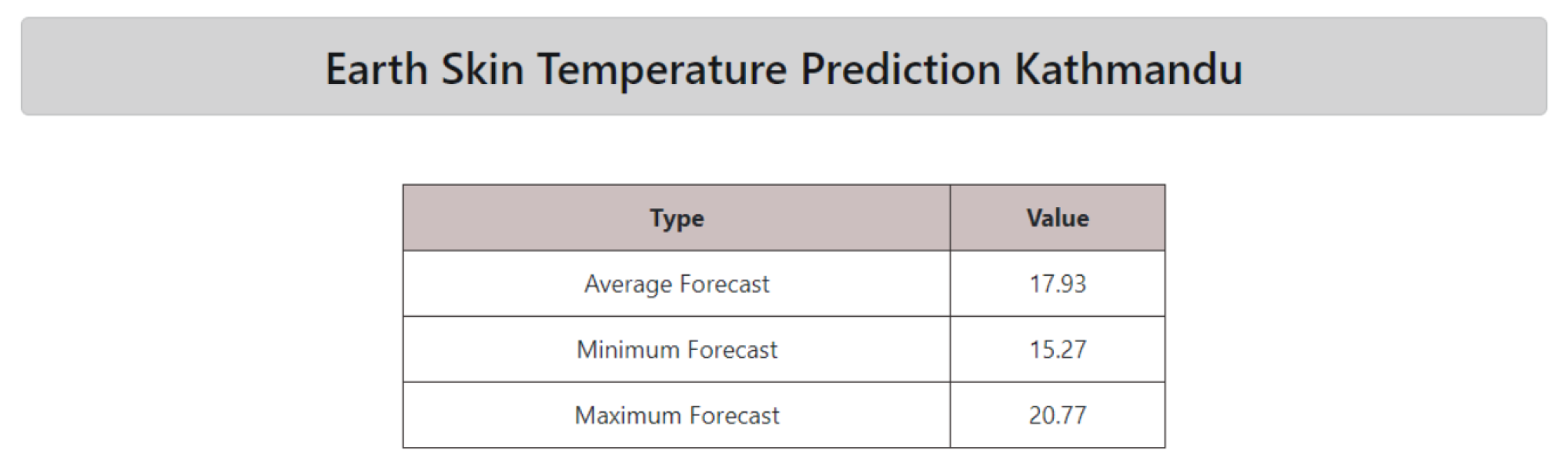
3.2. User Interface
The user interface to use the model has been made minimalist. The requirements for the prediction to be made are: (i) Date, (ii)PS, (iii)QV2M and (iv)WS10M. The model works in the backend with these features to showcase the output in the range of minimum to maximum as well as the average forecast.
Overall, these results indicate that the Prophet model provides more accurate forecasts of temperature, humidity, and precipitation levels in KMC, contributing valuable insights for climate studies and urban planning. Future research could explore the integration of additional variables or alternative modeling techniques to enhance forecasting accuracy further.
4. Discussion
As a researcher working on the Climate Analysis Nepal project, the goal is to identify the most accurate model for climate forecasting, which can inform policy-making and urban planning in KMC. Satellite imageries provide an appropriate data of different data scale to evaluate LST, UHI and such observations.
4.1. Impact of ML Model in LST Forecasting
Machine Learning(ML) has revolutionized in various field of study specially in research through integration of vast, multi-dimensional datasets. Hence two of such models - Exponential Smoothing (ES) and Prophet have been used for Earth Skin Temperature accounting seasonal patterns, trends, and other climatic factors.
The impact of ML models leads to improved accuracy in predicting temperature variations and UHI effects. This accuracy is critical for policy-making, urban planning, and disaster management, particularly in rapidly urbanizing cities like Kathmandu, where the consequences of climate change and urban heat can be profound.
In this model, both univariate (Exponential Series) and multivariate model (Prophet model) have been applied for foreceasting LST trends.
4.2. Implications and Future Research Directions
These findings have significant implications for climate studies, urban planning, and policy-making in KMC. The Prophet model’s ability to provide more accurate forecasts can inform disaster management, water resource planning, and climate-resilient infrastructure development. Future research could explore the integration of additional variables, such as urban heat island effects or land use changes, as well as alternative modeling techniques to enhance forecasting accuracy. Additionally, assessing the long-term impacts of climate variability on urban infrastructure and public health in KMC could yield valuable insights for creating more resilient urban environments.
5. Conclusion
Through our prediction model, we have demonstrated Prophet model outperforms the Exponential models because of prophet model’s ability to capture both maximum and mean values of the dataset. This characteristics enhances the accuracy of predictions.
These results underscore the Prophet model’s effectiveness in capturing climate variability, providing valuable insights for urban planning, disaster management, and resource allocation in KMC. Future research should explore additional variables and methodologies to enhance predictive accuracy and address climate challenges in urban settings.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.P. and S.P.; methodology, S.P.; software, G.M.A, P.P.; formal analysis, investigation H.B.; resources, S.P.; data curation, and writing—original draft preparation, G.M.A.; writing—review and editing, S.P., G.M.A; visualization, S.P., P.P.; validation and supervision, S.P., P.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
No Funding available.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not Applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not Applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dipson Pokhrel and Biswash Kafle for the critical suggestions, software recommendations and technical support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| KMC |
Kathmandu Metropolitan City |
| UHI |
Urban Heat Island |
| LST |
Land Surface Temperature |
| RS |
Remote Sensing |
| LULC |
Land Use and Land Cover |
| MEERA-2 |
Modern-Era Retrospective analysis for Research and Applications, Version 2 |
| MAE |
Mean Absolute Error |
| ML |
Machine Learning |
| R² |
Coefficient of Determination |
| RMSE |
Root Mean Squared Error |
| MDPI |
Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute |
| DOAJ |
Directory of open access journals |
| TLA |
Three letter acronym |
| LD |
Linear dichroism |
References
- Bhandari, S.; Zhang, C. Urban Green Space Prioritization to Mitigate Air Pollution and the Urban Heat Island Effect in Kathmandu Metropolitan City, Nepal. Land 2022, 11, 2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurung, A.; Son, J.-Y.; Bell, M.L. Particulate matter and risk of hospital admission in the Kathmandu Valley, Nepal: A case-crossover study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 186, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrestha, S.; Baral, B.; Dhital, N.B.; Yang, H.H. Assessing air pollution tolerance of plant species in vegetation traffic barriers in Kathmandu Valley, Nepal. Sustain. Environ. Res. 2021, 31, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Du, S.; Fan, J.; Peng, C. Urbanization and warming in highly developed urban agglomerations: Evidence from the Chinese Yangtze River Delta. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4047. [Google Scholar]
- Donlon, C.; Berruti, B.; Buongiorno, A.; et al. The global monitoring for environment and security (GMES) sentinel-3 mission. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 37–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Kong, W.; Sun, B. The changing trend of heat island intensity and main influencing factors during 1993–2012 in Xi’an city. J. Nat. Resour. 2015, 30, 974–985. [Google Scholar]
- Kumari, B.; Tayyab, M.; Mallick, J.; Khan, M.F.; Rahman, A. Satellite-driven land surface temperature using Landsat data and its association with built-up and green cover over urban Delhi, India. Remote Sens. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 1, 63–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Piao, S.; Ciais, P.; Friedlingstein, P.; et al. Surface urban heat island across 419 global big cities. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 696–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseka, H.; Zhang, H.; Sun, Y.; Su, H.; Lin, H.; Lin, Y. Urbanization and its impacts on land surface temperature in Colombo Metropolitan Area, Sri Lanka, from 1988 to 2016. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, G.; Avdan, U.; Avdan, Z.Y. Urban heat island analysis using Landsat 8 satellite data: A case study in Skopje, Macedonia. MDPI Proc. 2018, 2, 358. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Ishikawa, H.; Oku, Y.; Hu, Z. An algorithm for land surface temperature retrieval using three thermal infrared bands of himawari-8. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. Ser. II 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Zhang, L.; Sun, Z.; Meng, F.; Wang, L.; Sun, Y. Characterizing spatial and temporal trends of surface urban heat island effect in an urban main built-up area: A 12-year case study in Beijing, China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 204, 826–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estoque, R.C.; Murayama, Y.; Myint, S.W. Effects of landscape composition and pattern on land surface temperature: An urban heat island study in the megacities of Southeast Asia. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 195, 117–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adhikari, G. *Climate Analysis Nepal* [Online]. Available online: https://github.com/GajanandaAdhikari/Climate-Analysis-Nepal/tree/master (accessed on 24 September 2024).
- Athukorala, P.; Murayama, Y. Quantitative assessment of surface urban heat islands based on multiple endmember spectral mixture analysis: A case study of Accra, Ghana. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1018. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Hou, X.; Yuan, H.; et al. Effects of urbanization on land surface temperature and surface moisture in the midwestern United States. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 4880–4898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharjan, M.; Shakya, B.M.; Aryal, A.; Thapa, B.R. Thermal comfort in Kathmandu Valley: Trends and recommendations for improvement. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4072. [Google Scholar]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).