Submitted:
21 October 2024
Posted:
22 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Reduced Graphene Oxide Doped with MnO2
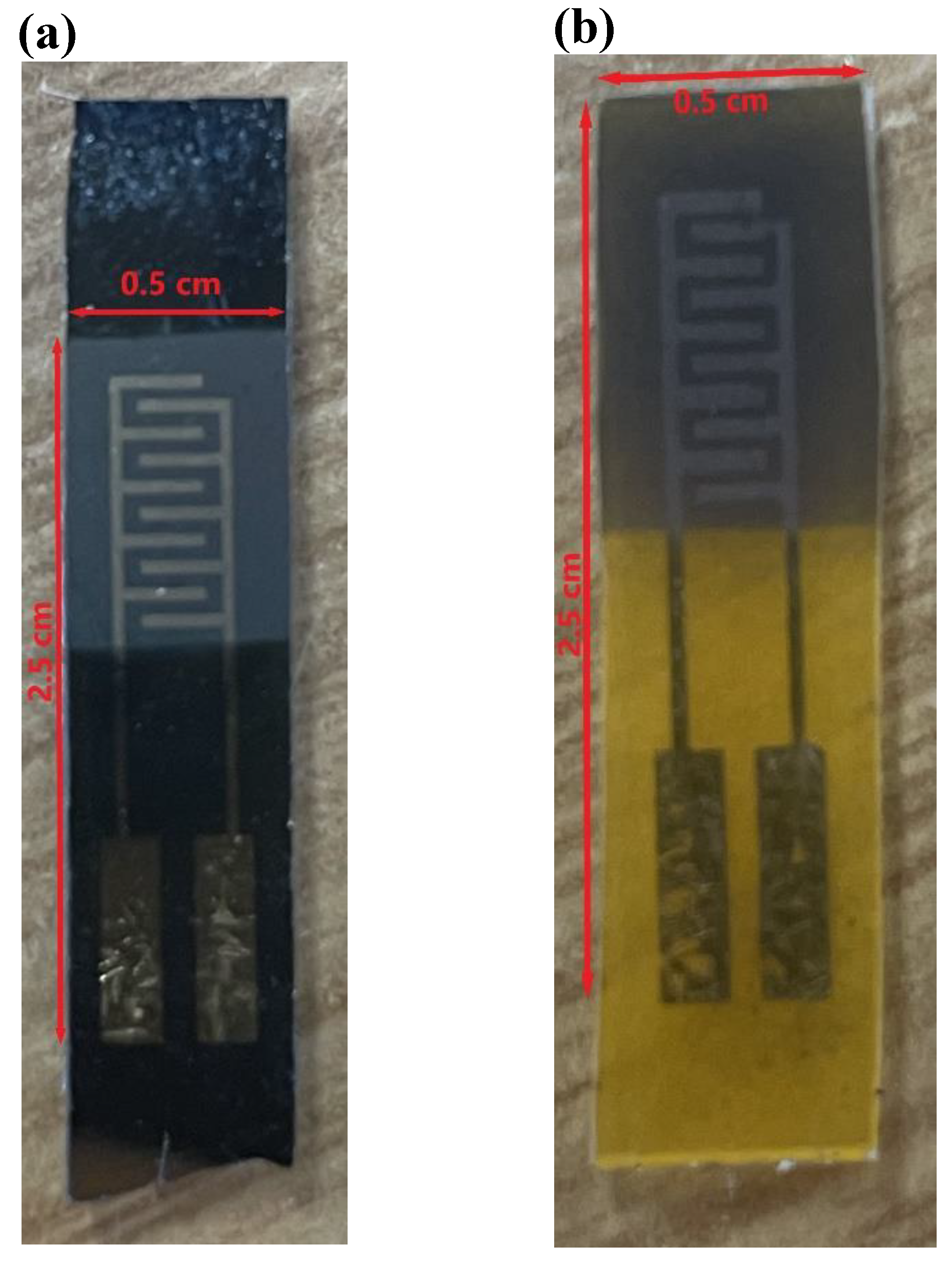
2.2. Substrates Preparation and Material Deposition
2.3. Material Characterization and Gas Sensing Measurements
3. Results
3.1. Sensitive Layer Characterization
3.1.1. Raman
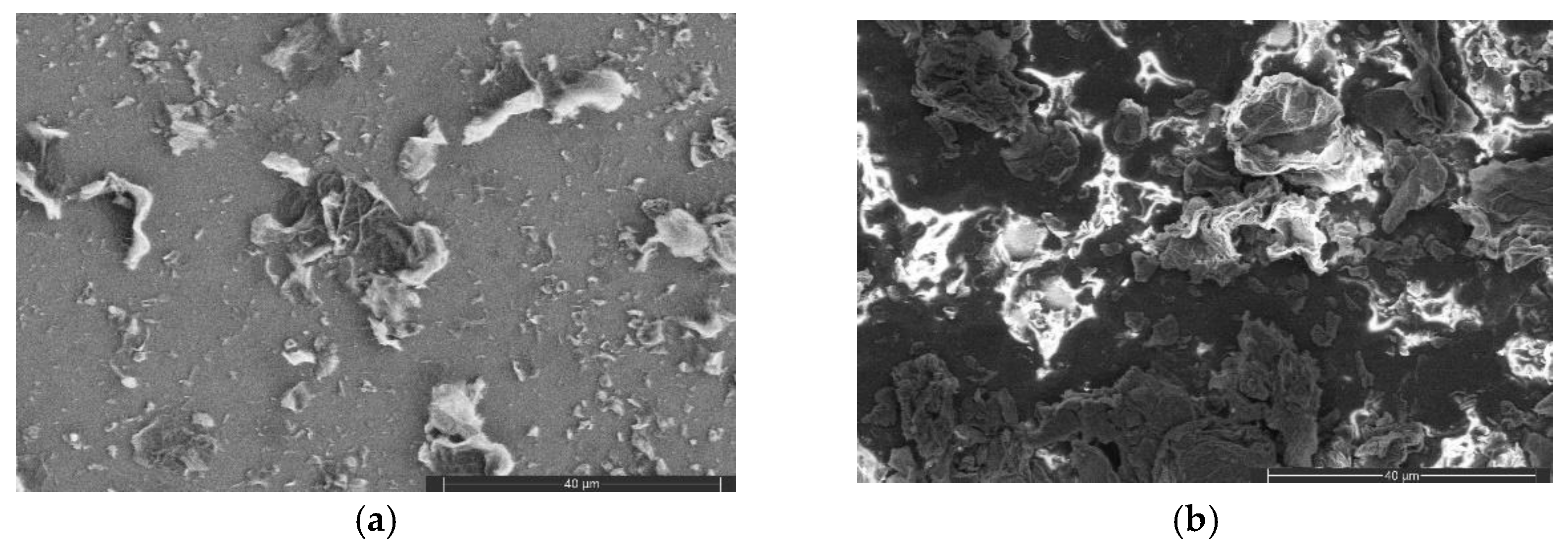
3.1.2. FESEM
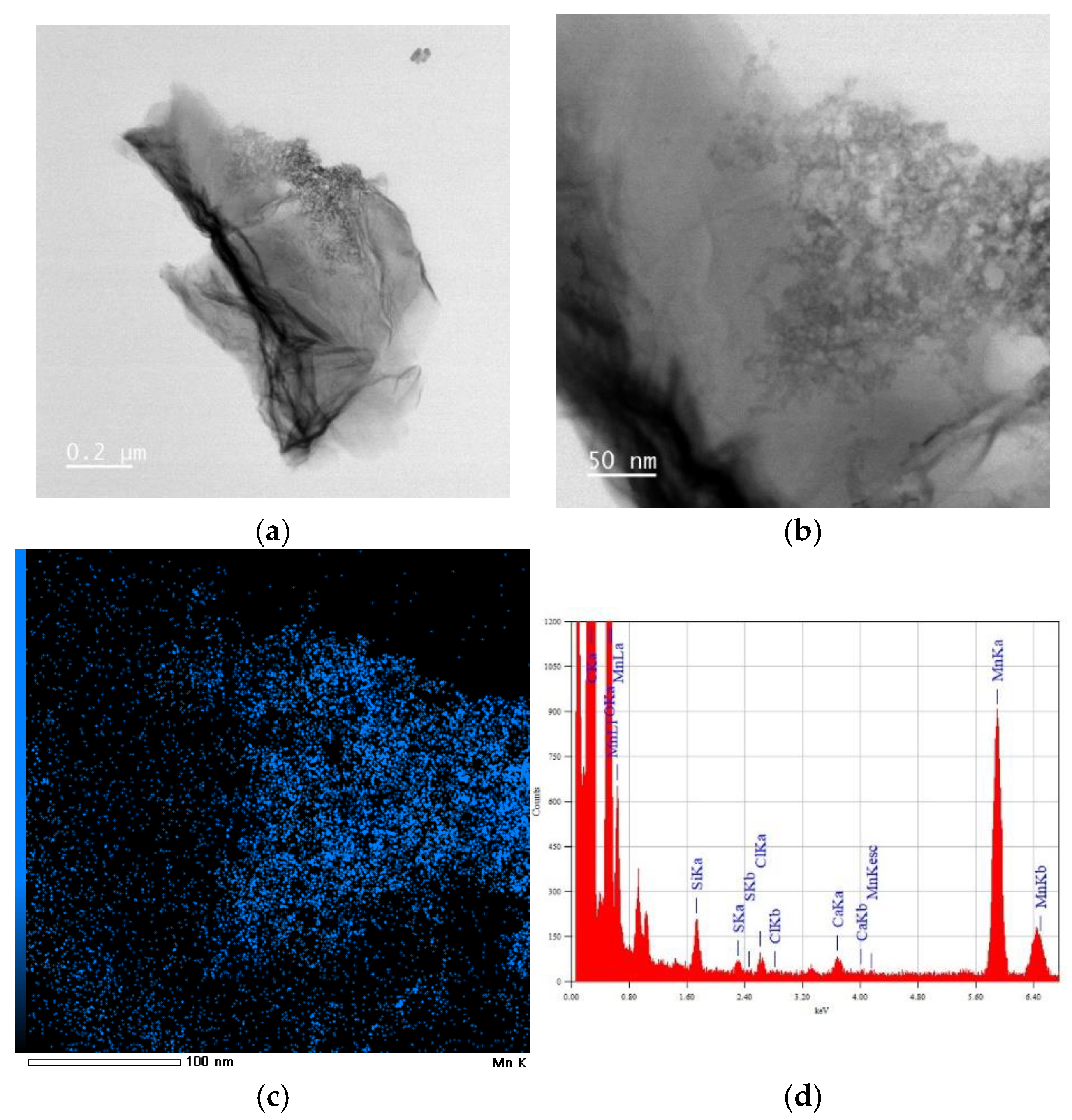
3.1.3. HRTEM
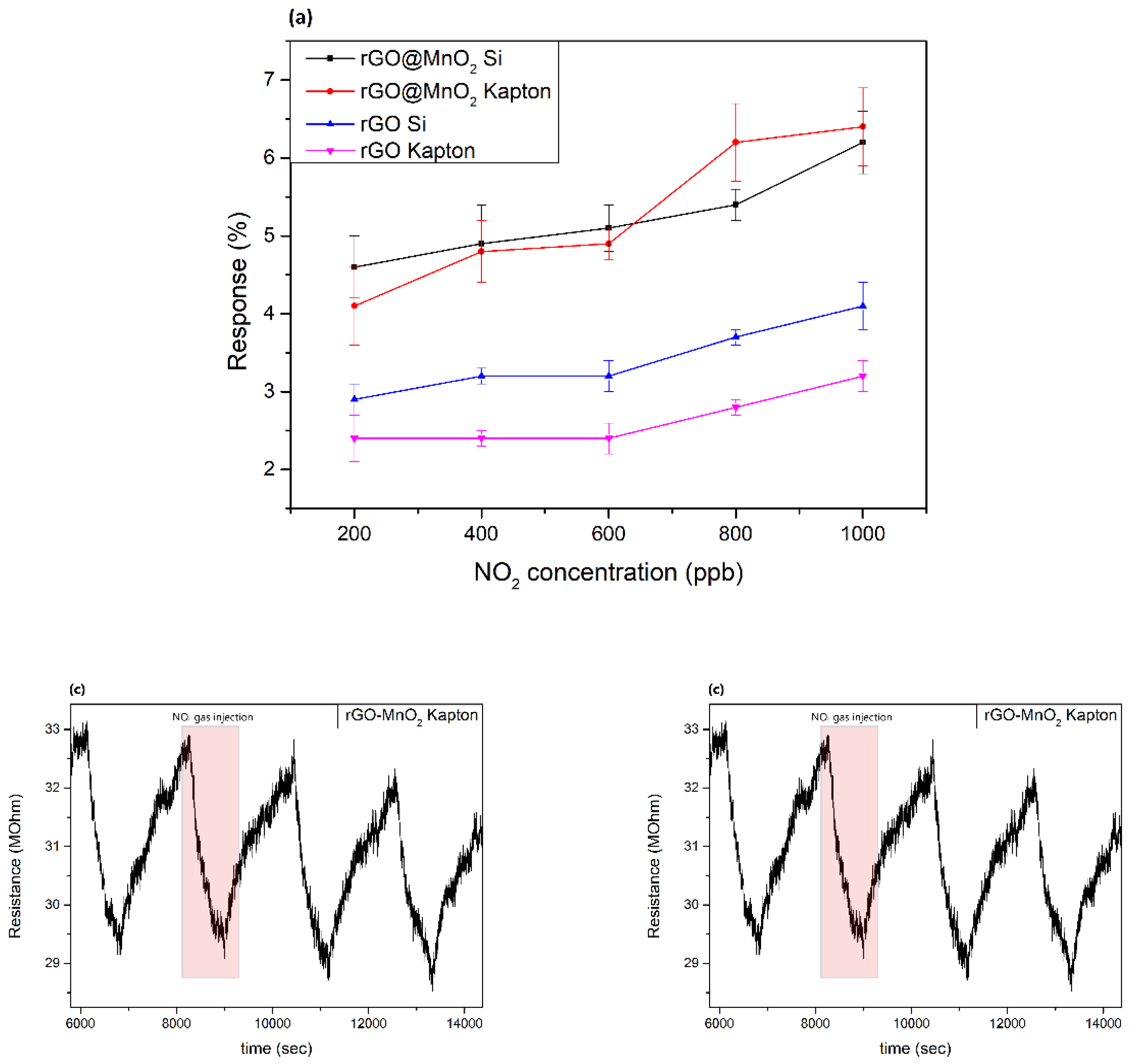
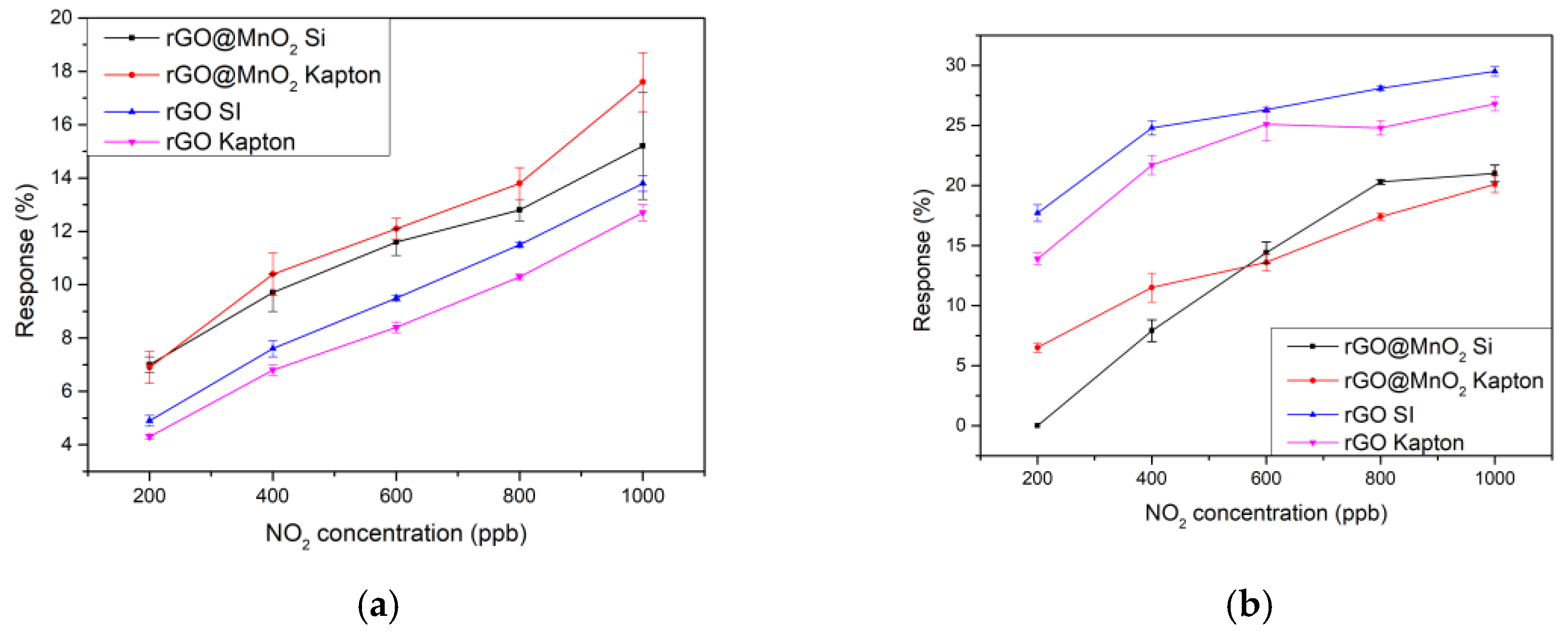
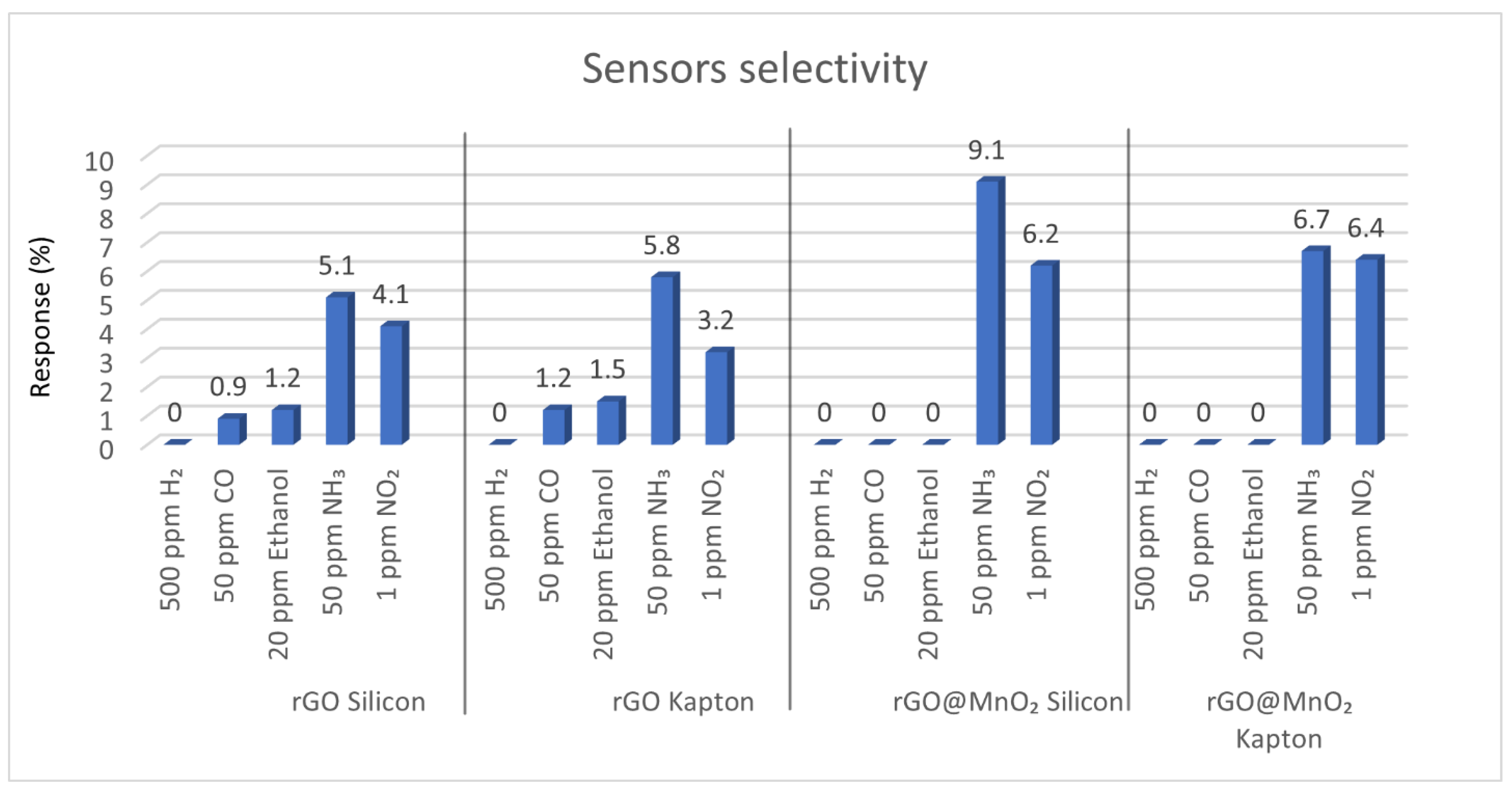
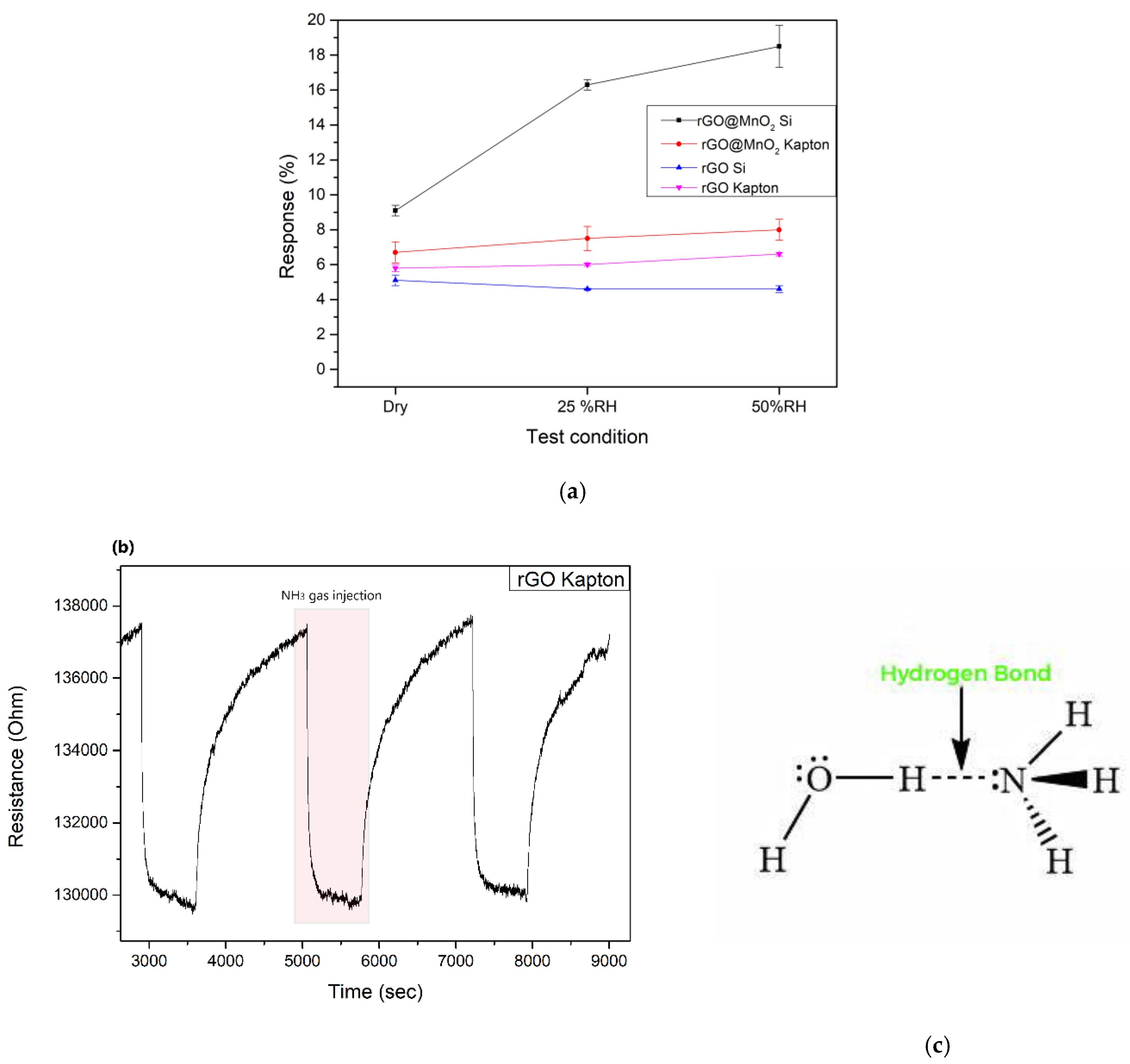
3.2. Gas Sensing Results
3.3. Sensing Mechanism
4. Conclusions
5. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chao Zhang, Yifan Luo, Jiaqiang Xu, Marc Debliquy, Room temperature conductive type metal oxide semiconductor gas sensors for NO2 detection, Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, Volume 289, 2019, Pages 118-133, ISSN 0924-4247. [CrossRef]
- Qili Chen, Shan Wang, Shuaishuai Bai, Lihua Shen, Jiaming Peng, Yufeng Zhang, Xiaoni Cui, Chunxia Yu, Runlan Zhang, Yuangang Li, Zhifang Liu, Sub-ppt NH3 detection by MoS2@sulfur nanosheets, Journal of Alloys and Compounds, Volume 985, 2024, 174070, ISSN 0925-8388. [CrossRef]
- Nisa Naseem, Farwa Tariq, Yumna Malik, Waqar Ali Zahid, Ahmed Abd El-Fattah, Khurshid Ayub, Javed Iqbal, Sensing ability of carbon nitride (C6N8) for the detection of carbon monoxide (CO) and carbon dioxide (CO2), Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, Volume 366, 2024, 114947, ISSN 0924-4247. [CrossRef]
- H. Namduri, S. Nasrazadani, Quantitative analysis of iron oxides using Fourier transform infrared spectrophotometry, Corrosion Science, Volume 50, Issue 9, 2008, Pages 2493-2497, ISSN 0010-938X. [CrossRef]
- Jingyang Shi, Yadong Jiang, Zaihua Duan, Juan Li, Zhen Yuan, Huiling Tai, Designing an optical gas chamber with stepped structure for non-dispersive infrared methane gas sensor, Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, Volume 367, 2024, 115052, ISSN 0924-4247. [CrossRef]
- Elvis D. Okoffo, Kevin V. Thomas, Quantitative analysis of nanoplastics in environmental and potable waters by pyrolysis-gas chromatography–mass spectrometry, Journal of Hazardous Materials, Volume 464, 2024, 133013, ISSN 0304-3894. [CrossRef]
- Gaiardo, A.; Novel, D.; Scattolo, E.; Crivellari, M.; Picciotto, A.; Ficorella, F.; Iacob, E.; Bucciarelli, A.; Petti, L.; Lugli, P.; et al. Optimization of a Low-Power Chemoresistive Gas Sensor: Predictive Thermal Modelling and Mechanical Failure Analysis. Sensors 2021, 21, 783. [CrossRef]
- Kai Sun, Guanghui Zhan, Lin Zhang, Zilin Wang, Shiwei Lin, Highly sensitive NO2 gas sensor based on ZnO nanoarray modulated by oxygen vacancy with Ce doping, Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, Volume 379, 2023, 133294, ISSN 0925-4005. [CrossRef]
- Yulin Kong, Yuxiu Li, Xiuxiu Cui, Linfeng Su, Dian Ma, Tingrun Lai, Lijia Yao, Xuechun Xiao, Yude Wang, SnO2 nanostructured materials used as gas sensors for the detection of hazardous and flammable gases: A review, Nano Materials Science, Volume 4, Issue 4, 2022, Pages 339-350, ISSN 2589-9651. [CrossRef]
- Anna Staerz, Simona Somacescu, Mauro Epifani, Tetsuya Kida, Udo Weimar, and Nicolae Barsan, WO3-Based Gas Sensors: Identifying Inherent Qualities and Understanding the Sensing Mechanism, ACS Sensors 2020 5 (6), 1624-1633. [CrossRef]
- S.Roy Morrison, Semiconductor gas sensors, Sensors and Actuators, Volume 2, 1981, Pages 329-341, ISSN 0250-6874. [CrossRef]
- Schedin, F., Geim, A., Morozov, S. et al. Detection of individual gas molecules adsorbed on graphene. Nature Mater 6, 652–655 (2007). [CrossRef]
- Novoselov KS, Geim AK, Morozov SV, Jiang D, Zhang Y, Dubonos SV, Grigorieva IV, Firsov AA. Electric field effect in atomically thin carbon films. Science. 2004 Oct 22;306(5696):666-9. [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Lu, J.; Zhang, X.; Jin, D.; Jin, H. Engineering of ZnO/rGO towards NO2 Gas Detection: Ratio Modulated Sensing Type and Heterojunction Determined Response. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 917. [CrossRef]
- Anna Thomas, B.G. Jeyaprakash, Selective detection of ammonia by rGO decorated nanostructured ZnO for poultry and farm field applications, Synthetic Metals, Volume 290, 2022, 117140, ISSN 0379-6779. [CrossRef]
- Fan-Li Meng, Zheng Guo, Xing-Jiu Huang, Graphene-based hybrids for chemiresistive gas sensors, TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, Volume 68, 2015, Pages 37-47, ISSN 0165-9936. [CrossRef]
- Majhi, S.M.; Mirzaei, A.; Kim, H.W.; Kim, S.S. Reduced Graphene Oxide (rGO)-Loaded Metal-Oxide Nanofiber Gas Sensors: An Overview. Sensors 2021, 21, 1352. [CrossRef]
- Divya Tripathi et al 2024 Nanotechnology 35 065503. [CrossRef]
- Milad Daneshnazar, Babak Jaleh, Mahtab Eslamipanah, Rajender S. Varma, Optical and gas sensing properties of TiO2/RGO for methanol, ethanol and acetone vapors, Inorganic Chemistry Communications, Volume 145, 2022, 110014, ISSN 1387-7003. [CrossRef]
- Z. U. Abideen, H. W. Kim and S. S. Kim, Chem. Commun., 2015. [CrossRef]
- Jae-Hyoung Lee, Akash Katoch, Sun-Woo Choi, Jae-Hun Kim, Hyoun Woo Kim, and Sang Sub Kim, ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces 2015 7 (5), 3101-3109. [CrossRef]
- Gajanan M. Hingangavkar, Sujit A. Kadam, Yuan-Ron Ma, Sushilkumar S. Bandgar, Ramesh N. Mulik, Vikas B. Patil, Tailored formation of WO3-rGO nanohybrids for dependable low temperature NO2 sensing, Ceramics International, Volume 49, Issue 23, Part B, 2023, Pages 38866-38876, ISSN 0272-8842. [CrossRef]
- Zhang QZ, Zhang D, Miao ZC, Zhang XL, Chou SL. Research Progress in MnO-Carbon Based Supercapacitor Electrode Materials. Small. 2018 Jun;14(24) e1702883. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muyu, Wu & Hou, Pingfu & Dong, Lina & Cai, Lulu & Chen, Zhudian & Zhao, Mingming & Li, Jingjing. (2019). Manganese dioxide nanosheets: from preparation to biomedical applications. International Journal of Nanomedicine. Volume 14. 4781-4800. [CrossRef]
- Malook, K., Khan, H., Shah, M. and Haque, I.-U. (2019), Highly selective and sensitive response of Polypyrrole–MnO2 based composites towards ammonia gas. Polym. Compos., 40: 1676-1683. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Hui & Ou, Kangtai & Guan, Ruihua & Cao, Yang & Sun, Youyi & Li, Xiao. (2022). A Highly Sensitive Room-Temperature NO 2 Gas Sensor based on Porous MnO 2 /rGO Hybrid Composites. Current Nanoscience. 18. [CrossRef]
- Zöpfl, Alexander & Lemberger, Michael-Maximilian & König, Matthias & Ruhl, Guenther & Matysik, Frank-Michael & Hirsch, Thomas. (2014). Reduced graphene oxide and graphene composite materials for improved gas sensing at low temperature. Faraday discussions. 173. 403-14. [CrossRef]
- S. Ghosal and P. Bhattacharyya, "Fabrication, Characterization, and Gas Sensing Performance of Pd, RGO, and MnO2 Nanoflowers-Based Ternary Junction Device," in IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, vol. 66, no. 9, pp. 3982-3987, Sept. 2019. [CrossRef]
- Ahmad Umar, Sheikh Akbar, Rajesh Kumar, Faheem Ahmed, Sajid Ali Ansari, Ahmed A. Ibrahim, Mohsen A. Alhamami, Noura Almehbad, Hassan Algadi, Tubia Almas, Wen Zeng, Unveiling the potential of PANI@MnO2@rGO ternary nanocomposite in energy storage and gas sensing, Chemosphere, Volume349, 2024, 140657, ISSN 0045-6535. [CrossRef]
- Fenping Yin, Shang Wu, Yanbin Wang, Lan Wu, Peilin Yuan, Xia Wang, Self-assembly of mildly reduced graphene oxide monolayer for enhanced Raman scattering, Journal of Solid-State Chemistry, Volume 237, 2016, Pages 57-63, ISSN 0022-4596. [CrossRef]
- R. Britto Hurtado, M. Cortez-Valadez, J.R. Aragon-Guajardo, J.J. Cruz-Rivera, F. Martínez-Suárez, M. Flores-Acosta, One-step synthesis of reduced graphene oxide/gold nanoparticles under ambient conditions, Arabian Journal of Chemistry, Volume 13, Issue 1, 2020, Pages 1633-1640, ISSN 1878-5352. [CrossRef]
- S. Yavuz and P. R. Bandaru, "Ag nanowire coated reduced graphene oxide/n-silicon Schottky junction based solar cell," 2016 IEEE Conference on Technologies for Sustainability (SusTech), Phoenix, AZ, USA, 2016, pp. 265-269. [CrossRef]
- Md Said, Nur Hidayah & Liu, Wei Wen & Lai, Chin wei & Zulkepli, Nik Noriman & Khe, Cheng-Seong & Hashim, U. & Lee, H Cheun. (2017). Comparison on graphite, graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide: Synthesis and characterization. AIP Conference Proceedings. 1892. 150002. [CrossRef]
- Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2019,21, 10125-10134. [CrossRef]
- Meenu Sharma, Sonam Rani, Devesh K. Pathak, Ravi Bhatia, Rajesh Kumar, I.Sameera, Temperature dependent Raman modes of reduced graphene oxide: Effect of anharmonicity, crystallite size and defects, Carbon, Volume 184, 2021, Pages 437-444, ISSN 0008-6223. [CrossRef]
- Girish Murlidhar Rajguru, Rakesh Kumar Mishra, Prashant B. Kharat, Pankaj P. Khirade, Structural, microstructural and optical characteristics of rGO-ZnO nanocomposites via hydrothermal approach, Optical Materials, Volume 154, 2024, 115720, ISSN 0925-3467. [CrossRef]
- Yaseen Muhammad, Mutabar Shah, Muhammad Asim Safi, Sana Gul Khattak, Aqib Aziz, Hoor Hassan, highly selective and sensitive humidity sensor using reduced graphene oxide based iron oxide nanocomposites, Materials Science and Engineering: B, Volume 303, 2024, 117324, ISSN 0921-5107. [CrossRef]
- Z. Li, D.W.W. Gardner, Y. Xia, S. Zhao, A. Pan, N. Goel, S. Bart, C. Liu, J. Yi, C. Carraro, R. Maboudian, Ordered porous RGO/SnO2 thin films for ultrasensitive humidity detection, J. Mater. Chem. C Mater. 11 (2023) 9586–9592. [CrossRef]
- Alaa Fahmy, Ahmed M. Saeed, Usama Dawood, Hassan Abdelbary, Korinna Altmann, Andreas Schönhals, Nano-MnO2/xanthan gum composite films for NO2 gas sensing, Materials Chemistry and Physics, Volume 296, 2023, 127277, ISSN 0254-0584. [CrossRef]
- Pedowitz, M. D., Kim, S., Lewis, D. I., Uppalapati, B., Khan, D., Bayram, F., … Daniels, K. M. (2020). Fast Selective Sensing of Nitrogen-Based Gases Utilizing δ -MnO₂-Epitaxial Graphene-Silicon Carbide Heterostructures for Room Temperature Gas Sensing. Journal of Microelectromechanical Systems, 1–7. [CrossRef]
- Lu, J., Li, D., Chen, X. et al. ZnO/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite with synergic enhanced gas sensing performance for the effective detection of NO2 at room temperature. J Nanopart Res 24, 265 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Kacem, K., Ameur, S., Casanova-Chafer, J. et al. Bio-reduction of graphene oxide using pomegranate peels for NO2 sensing and photocatalysis applications. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 33, 16099–16112 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Bashir E. Hasanov, Juan Casanova-Chafer, Geetanjali Deokar, José D. Gouveia, Saidkhodzha Nematulloev, José R.B. Gomes, Eduard Llobet, Pedro M.F.J. Costa, Amplified sensing of nitrogen dioxide with a phosphate-doped reduced graphene oxide powder, Carbon, Volume 226, 2024, 119207, ISSN 0008-6223. [CrossRef]
- Liang, J., Wu, W., Lou, Q. et al. Room temperature NO2 sensing performance enhancement of VO2(B) composited rGO structure. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 33, 15473–15482 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, Divya & Chauhan, Pratima & Rawat, Ravindra. (2023). A synergistic approach to enhance sensitivity and selectivity of room temperature operable ammonia gas sensor with humidity assistance using RGO/WO3 nanocomposite. Nanotechnology. 35. [CrossRef]
- Mohammad Reza Sovizi, Somayeh Mirzakhani, highly sensitive detection of ammonia gas by 3D flower-like ɤ-MnO2 nanostructure chemiresistor, Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, Volume 111, 2020, Pages 293-301, ISSN 1876-1070. [CrossRef]
- Marimuthu Ganesan, Bharathi Ganapathi, Balaji Parasuraman, Pazhanivel Thangavelu, Sensitivity enhancement of ammonia gas sensor based on NiFe2O4/rGO nanocomposite, Chemical Physics Impact, Volume 8, 2024, 100616, ISSN 2667-0224. [CrossRef]
- Jeevitha G, Abhinayaa R, Mangalaraj D, Ponpandian N, Meena P, Mounasamy V, Madanagurusamy S. Porous reduced graphene oxide (rGO)/WO3 nanocomposites for the enhanced detection of NH3 at room temperature. Nanoscale Adv. 2019 Feb 27;1(5):1799-1811. [CrossRef]
- H. Zhang, Y. Li, Z. Yuan, Y. Lei, X. Li and F. Meng, "Enhanced Ammonia Sensing Performance Based on FeCo2O4/WO3/rGO Ternary Nanocomposites," in IEEE Sensors Journal, vol. 23, no. 21, pp. 25698-25707, 1 Nov.1, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Marimuthu Ganesan, Bharathi Ganapathi, Palanisamy Govindasamy, Balaji Parasuraman, Paramasivam Shanmugam, Rajender Boddula, Ramyakrishna Pothu, Pazhanivel Thangavelu, CoFe2O4/rGO nanocomposite: Synthesis and enhanced ammonia gas sensing properties at room temperature, Results in Chemistry, Volume 7, 2024, 101342, ISSN 2211-7156. [CrossRef]
- Alouani, M.A.; Casanova-Cháfer, J.; Güell, F.; Peña-Martín, E.; Ruiz-Martínez-Alcocer, S.; de Bernardi-Martín, S.; García-Gómez, A.; Vilanova, X.; Llobet, E. ZnO-Loaded Graphene for NO2 Gas Sensing. Sensors 2023, 23, 6055. [CrossRef]
- Ahmad Umar, Ahmed A. Ibrahim, R. Kumar, H. Albargi, Wen Zeng, Mohsen Ali M. Alhmami, Mabkhoot A. Alsaiari, S. Baskoutas, Gas sensor device for high-performance ethanol sensing using α-MnO2 nanoparticles, Materials Letters, Volume 286, 2021, 129232, ISSN 0167-577X. [CrossRef]
- Shyamasree Gupta Chatterjee, Somenath Chatterjee, Ajoy K. Ray, Amit K. Chakraborty, Graphene–metal oxide nanohybrids for toxic gas sensor: A review, Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, Volume 221, 2015, Pages 1170-1181, ISSN 0925-4005. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Dongzhi and Liu, Aiming and Chang, Hongyan and Xia, Bokai, Room-temperature high-performance acetone gas sensor based on hydrothermal synthesized SnO2-reduced graphene oxide hybrid composite, RSC Adv., 2015 Volume 5, issue 4, 3016-3022. [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Xue & Jin, Wei & Tang, Cao & Qi, Xin & Li, Rui & Zhang, Yi & Zhang, Wusheng & Yu, Xue & Zhu, Xiaodong & Ma, Yanqing & Ma, Lei. (2023). Thermal reduced graphene oxide-based gas sensor for rapid detection of ammonia at room temperature. Journal of Materials Science. 58. 1-13. [CrossRef]
- Lv, C.; Hu, C.; Luo, J.; Liu, S.; Qiao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Song, J.; Shi, Y.; Cai, J.; Watanabe, A. Recent Advances in Graphene-Based Humidity Sensors. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 422. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Casanova-Cháfer, J.; Navarrete, E.; Noirfalise, X.; Umek, P.; Bittencourt, C.; Llobet, E. Gas Sensing with Iridium Oxide Nanoparticle Decorated Carbon Nanotubes. Sensors 2019, 19, 113. [CrossRef]


| Sensitivity (% ppm-1) | rGO-MnO2 Silicon | rGO-MnO2 Kapton | rGO Silicon | rGO Kapton | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RH (%) | |||||
| 25 | 9.8 | 12.4 | 10.9 | 10.2 | |
| 70 | 27.2 | 16.6 | 13.5 | 14.5 | |
| Material | NO2 concentration (ppm) | Response (%) | Condition | Sensitivity (%ppm-1) | T (°C) | ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nano-MnO2/xanthan | 7 | 1.21 | Dry | 0.17 | RT | [39] |
| δ-MnO2-Epitaxial Graphene-Silicon Carbide Heterostructures | 5 | 0.27 | 55% RH | 0.14 | RT | [40] |
| Porous MnO2 /rGO | 50 | 5.9 | Dry | 0.118 | RT | [26] |
| ZnO/rGO | 10 | 5.1 | Dry | 0.51 | RT | [41] |
| rGO pomegranate peels | 1 | 3.04 | Dry | 2.94 | 100 | [42] |
| Phosphate doped rGO | 1 | 4.5 | Dry | 4.5 | RT | [43] |
| VO2/rGO | 5 | 1.63 | Dry | 0.326 | RT | [44] |
| MnO2 doped rGO | 1 | 6.2 | Dry | 9.8 | RT | This work |
| MnO2 doped rGO | 1 | 21 | 70% RH | 27.2 | RT | This work |
| Material | NH3 concentration (ppm) | Response (%) | Condition | T (°C) | ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PANI@MnO2@rGO | 50 | 15.5 | Dry | 100 | [29] |
| NiFe2O4/rGO | 50 | 1.17 | Dry | 0 | [47] |
| rGO/WO3 | 40 | 8.03 | 55 % RH | 35 | [48] |
| FeCo2O4/WO3/rGO | 100 | 19.8 | Dry | 200 | [49] |
| CoFe2O4/rGO | 25 | 1.06 | Dry | RT | [50] |
| rGO@MnO2 | 50 | 18.6 | 50% RH | RT | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





