1. Introduction
For a long time in the past, AI has been hailed as an important part of the industrial revolution, and continues to penetrate other industries, such as education, business, finance, manufacturing, as well as social media platforms and healthcare. With the continuous improvement of the data age and the emergence of advanced computer algorithms, people have a better opportunity to build new artificial intelligence models, and use it to achieve faster computing methods, so as to get more convenience. However, especially in healthcare, the centralization of a lot of data and AI faces multiple potential challenges in terms of privacy and regulation.
Hypothetically, if we can find a more efficient way to integrate AI. of data into one and be able to break through the existing challenges while optimizing these risks, this will be a whole new area of research. [
1] Federal Learning (FL) is the solution. Medical data is often scattered across different systems, and security and privacy concerns complicate its effective use. However, advances in AI have brought opportunities for integration and collaboration to this fragmented data. However, data is often scattered across siloed systems, and security and privacy concerns complicate its effective use.
Federated Learning (FL) is therefore the ideal solution to this problem. It allows data to remain local while fostering collaboration between agencies to build more robust AI models together without sacrificing data privacy and security. Through this approach, organizations can share information while protecting sensitive medical data, creating more possibilities for data utilization in drug development and driving innovation in medicine with privacy protection.
2. Related Work
To truly address these issues, we need to innovate traditional approaches and find more effective ways to decentralize data collection through data management tools and policies, while maintaining data security and privacy. In this process, it is not only necessary to continuously enrich AI technology [
2], but also to continuously design how to translate data into more meaningful decision-making processes that drive progress across the industry. This concept is particularly relevant in drug development.
2.1. Drug Development and Federal Learning
Drug development often relies on large amounts of patient data for research, with large amounts of medical data analyzed and validated at every step, from early drug discovery and preclinical trials to eventual clinical trials. However, due to the highly sensitive nature of patient data, how to share and utilize this data while ensuring privacy protection has been a challenge in the industry[
3]. Traditional centralized data processing methods may not only lead to privacy leakage, but also face the problem of data silos, which hinders the effectiveness of cross-institutional cooperation and data sharing.
To sum up, federal learning effectively promotes the sharing and utilization of medical data on the premise of protecting patient privacy, especially in drug development. [
5] This innovative approach not only breaks down data silos and optimizes the research process, but also provides more reliable and efficient data support for decision making in drug development, thereby driving innovation and progress across the healthcare industry.
2.2. Key Features of Federated Learning Include
Data privacy protection: All sensitive data remains local to the data owner and does not leave its original location.
Distributed computing: Each participant independently trains the model using their local data and shares only the parameter updates or gradients of the model, not the original data.
Model collaborative optimization: Build a globally optimized model by aggregating model updates from different participants
This offers good prospects for the development of various AI models, especially where data can be easily accessed centrally to train these models [
6]. However, in some fields, notably medicine, the centralization of data is often made difficult or even impossible by privacy, regulatory, competitive, and budgetary constraints.
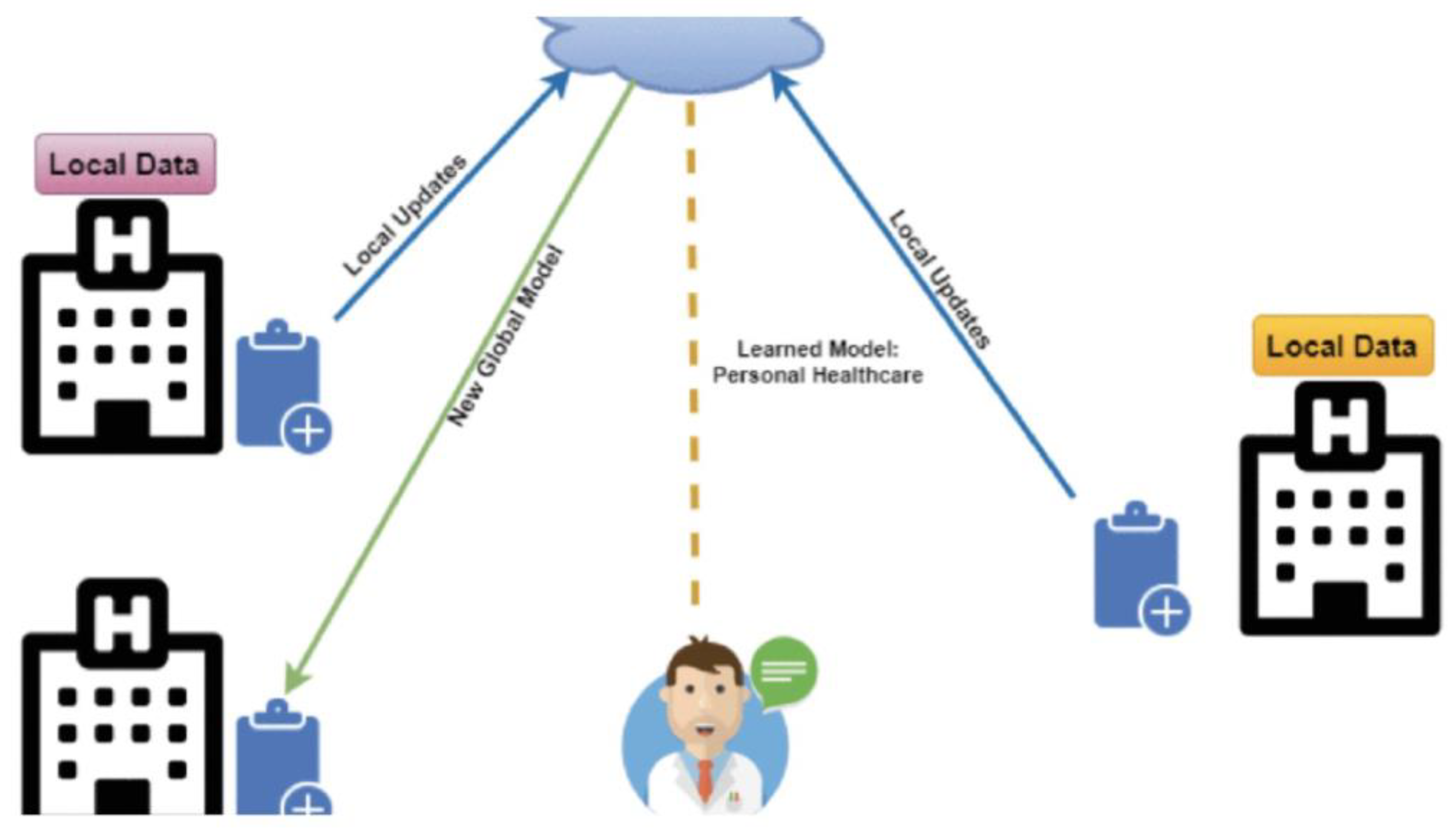
Figure 1 shows the architecture of a federated learning system as a means of distributed learning that can effectively mitigate the data deficiency challenge required to train AI models. By keeping data local and enabling collaboration across institutions, patient types, and countries, Federated Learning (FL) provides a solution for building robust AI models. At the same time, information management - getting the right information to the right people in a timely manner to support effective decision-making - is a pervasive problem.
Data is often scattered in isolated, noninteroperable silos making it difficult to find and access. A mixture of structured and unstructured data, including text, audio, video, and imagery, with disparate formats and standards, is common. Meaningful information is embedded in massive amounts of irrelevant noise. Complicating matters are security and privacy concerns, cybersecurity threats, bandwidth limitations, platform challenges, and constrained budgets[
7]. Once accessed, there must be a means to harness data; analyze, transform, and visualize it; and leverage it to execute automated processes and facilitate decision-making.
Adding to the challenge, there is no universal solution for every need and application. Even if there were, not every platform could simultaneously implement it due to cost and integration complexity. A steady state would never be reached due to ongoing modernization cycles that stretch over decades.
2.3. Federal Learning Integration for Patient Data Privacy
One solution to this problem set is to integrate federated learning in the development of advanced models such as Large Language Model (LLM) [
8]or other GenAI capability, infused with data analysis, automation, and decision support tools. Being federated, it accesses distributed non-standard data sources and integrates their data into a whole for processing and analysis. This is done without consolidation that stresses bandwidth and could compromise security and privacy. The federated learning system has been proven in finance for evaluating risk and detecting fraud, in transportation for route optimization and smart city design, and in healthcare to process patients’ data and provide diagnosis analysis.
Figure 2.
Federated Learning Framework for Healthcare.
Figure 2.
Federated Learning Framework for Healthcare.
In healthcare, federated learning combined with the application of generative AI models (GenAI) is changing the way data is used and analyzed. Federated learning allows access to large-scale structured and unstructured data, such as medical textbooks, journal articles, research reports, electronic health records (EHRs), medical specialty exam questions and answers, audio, video, genomic data, and medical images, which are often distributed across multiple different data sources. Through the power of the GenAI[
9] model, this fragmented data can be integrated and turned into actionable insights to help improve diagnostic accuracy, treatment outcomes, and patient health outcomes. This is all based on strict information security compliance requirements, ensuring that the data remains highly private and secure during use.
In drug development, the introduction of federal learning models is particularly important, especially for sharing medical data while protecting patient privacy. Drug development often requires multi-agency collaboration and large-scale data analysis, but traditional centralized data processing faces privacy breaches and legal and regulatory barriers. With federated learning, drug discovery teams can collaborate to train models on a global scale without transferring raw data, leveraging distributed data from different hospitals and research institutions.
Generative AI models can extract effective information from these diverse medical data and provide accurate drug response prediction and personalized treatment plans. This approach will not only significantly accelerate the development of new drugs, but also ensure that patient data privacy is protected, making drug development more efficient, secure, and compliant with global data privacy and security regulations. In addition, the technology and process are highly transferable and can be applied to almost any industry and scenario, enabling innovation and development in other areas.
2.4. How Federated Learning (FL) Works in Healthcare
Federated Learning (FL) revolutionizes the traditional approach to machine learning by enabling decentralized data processing. Instead of aggregating all data in a central location, FL allows each client to train models locally using its own data, preserving data privacy and security[
10,
11]. This mechanism not only reduces the risk of sensitive data exposure but also ensures compliance with data protection regulations, as the data remains within the client’s infrastructure.
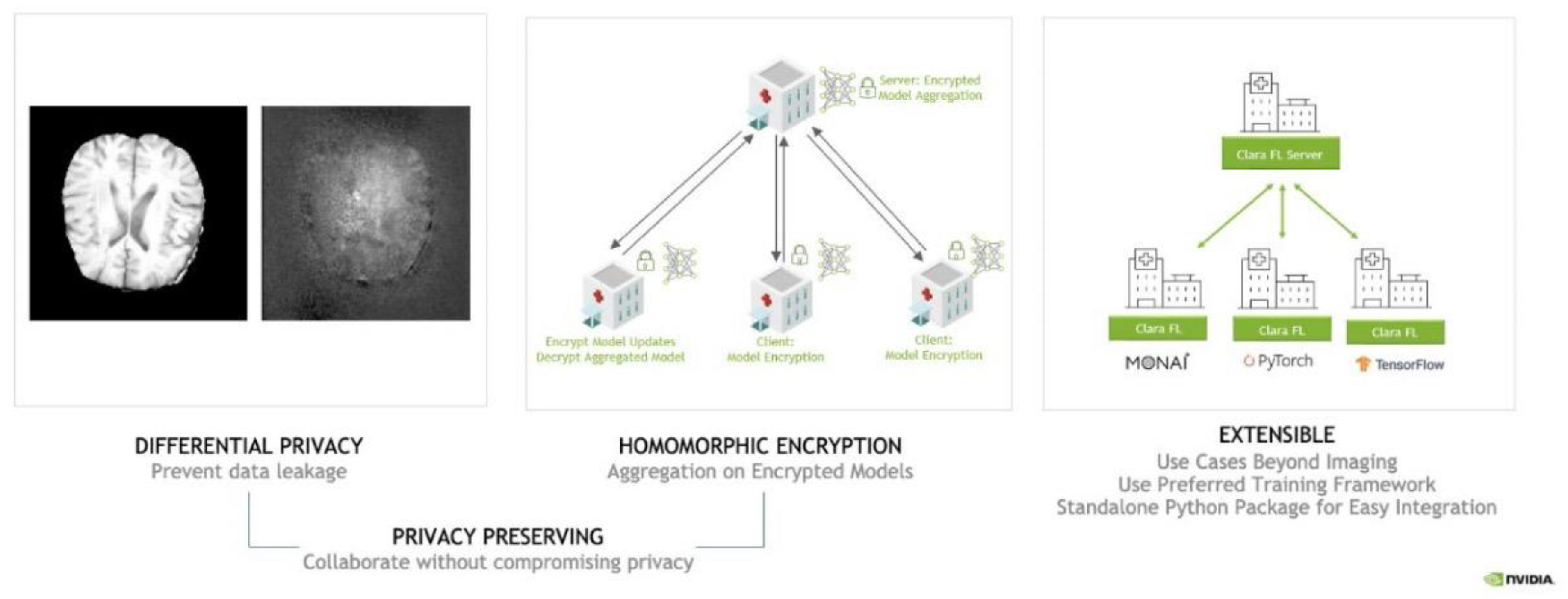
Figure 3.
Preserving & Extensible Collaborative Learning.
Figure 3.
Preserving & Extensible Collaborative Learning.
This Federated Learning approach utilizes a hub-and-spoke communication model consisting of a Federated Learning server as the hub and client-sites as spokes. The Federated Learning server hosts the initial model and then sends its weights to each of the client-sites. The client-sites train the model on their own data at their location, and at the conclusion of this local training, they send back the updated model weights to the Federated Learning Server. The Federated Learning server waits for a certain number of the models to finish local training, and to receive the updated weights from these client-sites, before it aggregates these weights. The newly aggregated weights are then sent back to each of the clients to be used in a new round of local training. These steps are repeated for a predetermined number of rounds [
12]. The resultant Federated Learning model is then automatically validated at each of the client-sites to assess it for generalizability.
To initialize communication in a Federated Learning study, the client submits a request to participate to the server. The server validates the client certificate and, if valid, authorizes the client and responds with a unique token used to identify the client contributions through the Federated Learning study. Once secure communication has been established between clients and server, the remaining network consideration is the bandwidth required to distribute the global model and aggregate client contributions during the rounds of Federated Learning training.
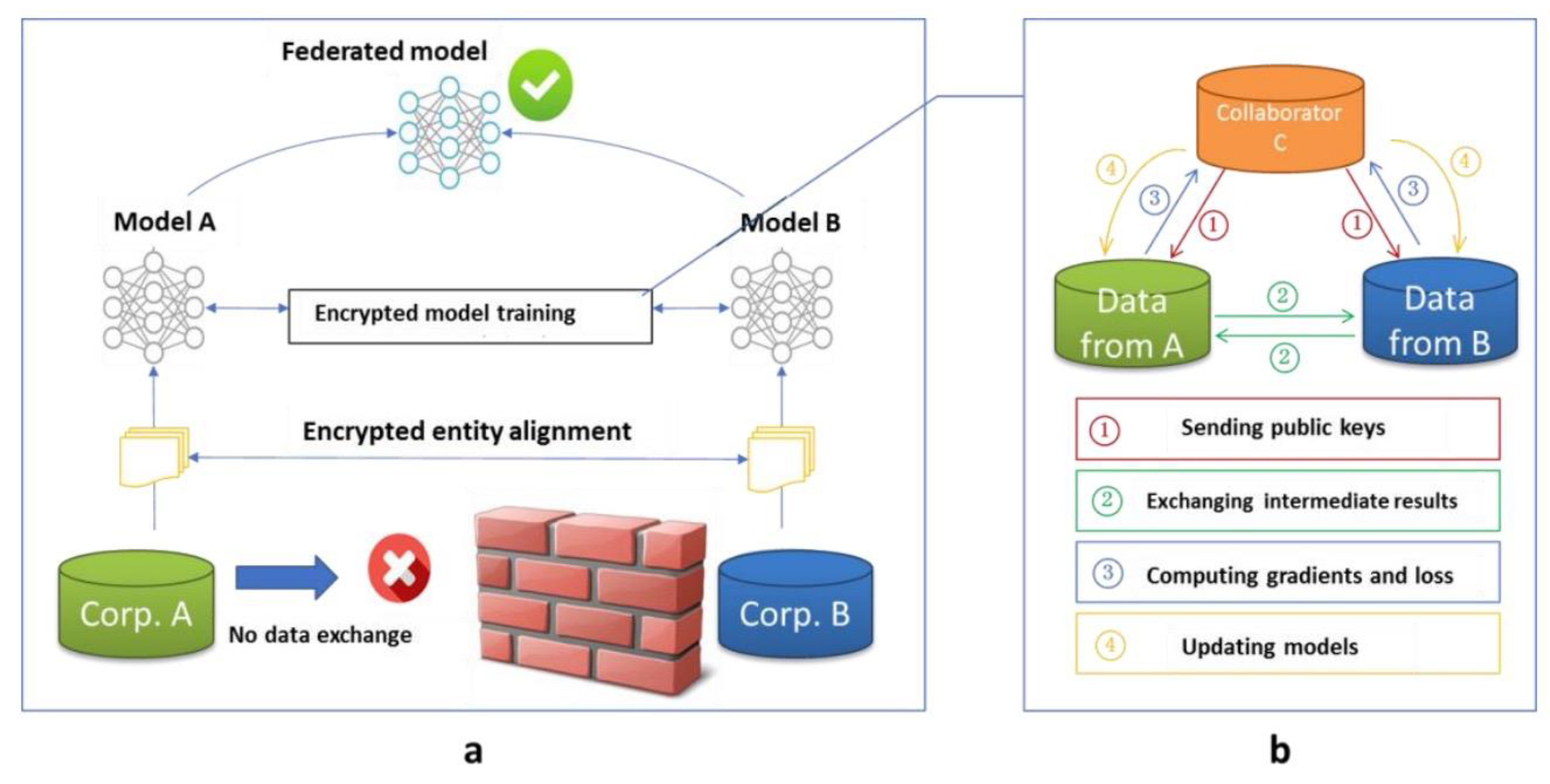
The core principle of FL lies in collaborative model training, where clients share model updates rather than raw data. Each client's local model is trained independently, and only the aggregated model weights or gradients are sent to the central server. This decentralized approach minimizes the likelihood of sensitive information leakage, making FL particularly advantageous for sectors like healthcare, where data privacy is paramount.
In addition, differential privacy and homomorphic encryption are one of the important technologies that can improve data security in the process of federal learning privacy and protection. Differential privacy ensures the protection of the model as well as the personal data homomorphic encryption technology enables efficient computation of sensitive data. Together, these methods enable efficient model training in the customer's physical data, utilizing collaborative intelligence to make final predictions without compromising data privacy in federated learning.
As can be seen from several success stories above, building an enterprise's data consortium, coupled with incentives and possibly blockchain technology, can further simplify the process. These alliances will foster collaboration, ensure contributions are recognized and all participants benefit equitably, ultimately resulting in a more connected and efficient AI ecosystem. Webank's practice provides a model for other industries, demonstrating the practical potential of joint learning for data privacy protection.
3. Methodology
While Federated learning (FL) can provide a high level of security in terms of privacy protection, there are still some risks, such as reconstructing a single training model through model backward inference. One response is to inject noise and distort updates during the training of each node to hide the contribution of individual model nodes and limit the granularity of information shared between training nodes. However, existing research on privacy protection has focused on common machine learning benchmark datasets (such as MNIST) and stochastic gradient descent algorithms.
In this study, we implemented and evaluated a federal learning system for drug development data sharing. By experimenting with clinical trial data, we demonstrate the feasibility of medical data privacy protection technology in drug development.
Our key contributions include: (1) To our knowledge, the implementation and evaluation of the first privacy-protected federal learning system for drug development data analysis; (2) The use of joint average algorithm to deal with momentum optimization and unbalanced training nodes is compared; (3) The sparse vector technique (SVT) is empirically studied to obtain a strong differential privacy guarantee.
3.1. Federated Learning Framework
This paper uses the joint average algorithm to investigate a federated learning system based on a client-server architecture (shown on the left in
Figure 5), where a central server maintains a global DNN model and coordinates local random gradient descent (SGD) updates on the client. This section describes the training process of the client model, the aggregation process of the server model, and the deployment of the privacy protection module on the client side.
3.2. Patient Data Model Training Process
We assume that each institution participating in federated learning has a fixed local data set and sufficient computing resources to conduct small-batch SGD updates. Clients share the same DNN structure and loss function. In round t of joint training, the local model is initialized by reading the global model parameter w(t) from the server and updated to w(l,t) through multiple SGD iterations. After a fixed number of local iterations, the model differences Δw(t) are shared with the aggregation server.
In drug development, clinical trial data is often optimized using momentum-based SGD. The momentum gradient introduces the SGD calculations from the previous step to help speed up training and reduce fluctuations. We explore design options for dealing with these steps in Federated Learning. We recommend restarting the momentum gradient at each round of joint training (algorithm 1, when using the ADAM optimizer) so that local states do not interfere with the global update of the model.
3.3. Patient Data Privacy Protection Model
The client has full control over the shared data and the local training data does not leave the client. Nevertheless, a model regression attack may extract patient privacy information from the updated Δw(t) or global model w(t). We employ selective parameter updating and sparse vector technology (SVT) to provide strong indirect data leakage protection.
Selective parameter updating: At the end of client training, the complete model may overfit and remember local training data, and sharing such a model may lead to data leakage. Therefore, the selective parameter sharing method limits the amount of information shared by clients. Clients upload only a portion of Δw(t) k, which is shared only if the parameter _ i _ _ is greater than the threshold τ(t) k. In addition, data privacy is further protected by clipping its values into a fixed range. The combination of clip gradient and selective parameter sharing can further enhance differential privacy through SVT.
3.4. Server Data Model Aggregation
The server distributes the global model in each round of federated learning and receives simultaneous updates from all clients (Algorithm 3). Due to the different number of local iterations of different clients, the Δw(t) k generated by the client may have different update rates. Therefore, the contribution of each client should be weighed during the aggregation process, especially when dealing with uneven data in drug development. The sparse characteristics shared by some models can also effectively reduce the communication overhead.
3.5. Experimental Data
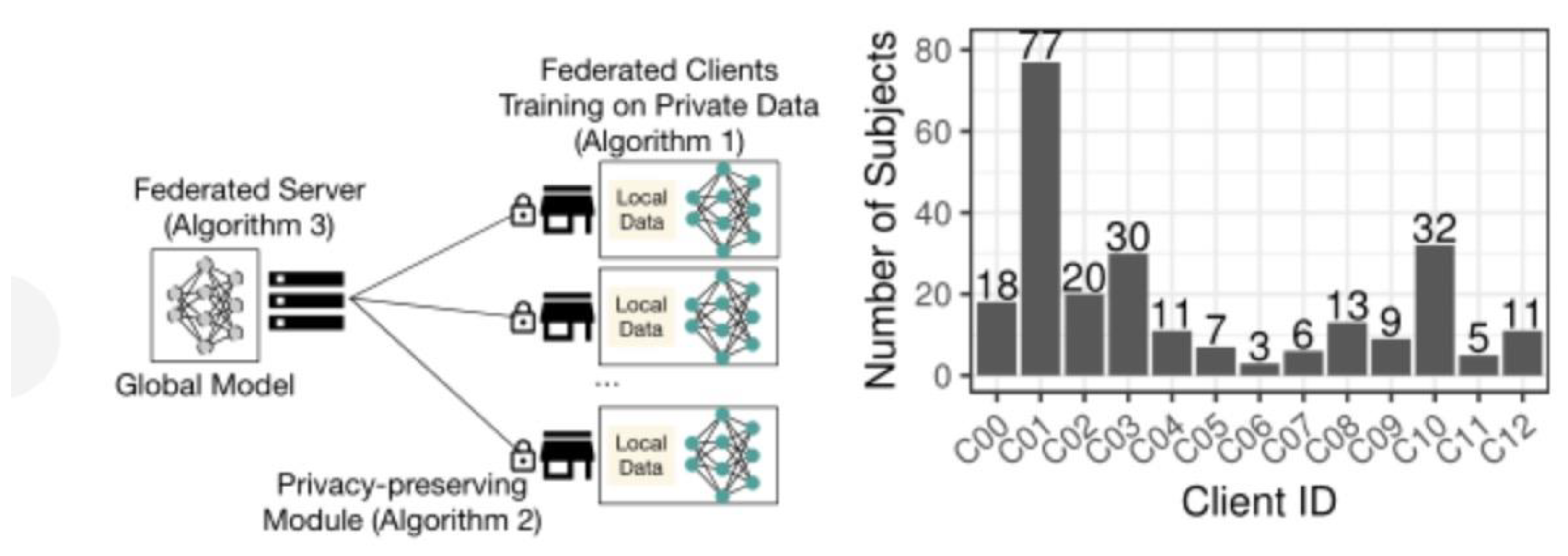
To evaluate the practical application of the federated learning system, we selected a multimodal drug clinical trial dataset containing patient trial data from different institutions. These data are unevenly distributed, and different institutions use different test equipment and protocols, which makes the distribution of data characteristics different. We divided the data set into a 242-patient training set and a 43-patient validation test set. To make joint training more realistic, we further divided the training set into 13 non-overlapping subsets, assigned to each client.
3.6. Experimental Result
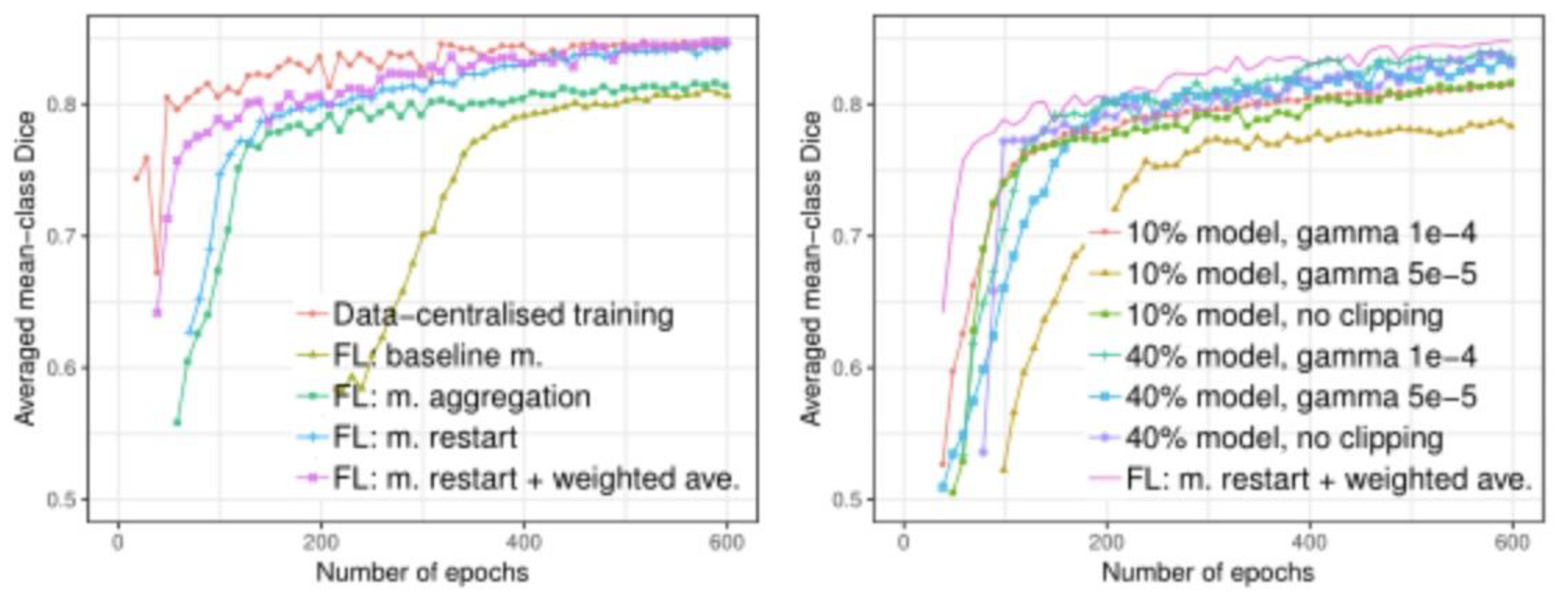
Compared with centralized data set training, federated learning systems can also achieve better model performance without sharing customer data. In the drug development scenario, FL model training, despite a longer convergence time (about 600 rounds), still guarantees similar performance to a centralized dataset model. In addition, in the experiment, FL training time depends on the computing speed of the slowest client.
Figure 6.
Comparison of segmentation performance on the test set with (left): FIvs. non-F'L training, and(right): partial model sharing.
Figure 6.
Comparison of segmentation performance on the test set with (left): FIvs. non-F'L training, and(right): partial model sharing.
4. Conclusions and Discussion
Through this study, we demonstrate the great potential of Federated learning (FL) in privacy-protected medical data sharing, especially in the field of drug development. Our experimental results show that despite significant differences in the data characteristics of different clients, the federated learning system is able to effectively train the model across multiple independent institutions without centralized sharing of sensitive patient data.
Momentum restart and weighted average: From the experimental results, the restart strategy for momentum variables significantly improves the convergence rate of the model, proving the necessity of restarting momentum in each round. This strategy avoids the interference of momentum variables between clients, thus ensuring the stability of the global model. Compared to simple model averaging, weighted averaging of momentum variables further improves the performance of the global model, especially when dealing with unbalanced training iterations between clients. The weighted average is better able to accommodate the different data sizes and training resources of different institutions, which is a major advantage in drug development, as pharmaceutical companies and research institutions often differ in the amount of data and computational resources.
Local model sharing and differential privacy: In our experiments, the local model sharing strategy demonstrated good performance, especially when the client shared 40% of the model parameters, the performance was almost identical to that of centralized training. This means that high model accuracy can be maintained by selectively sharing local model parameters, even when privacy is protected. In addition, experiments show that the differential privacy (DP) parameters have an important effect on the performance of the model. By controlling for the share of parameters protected by DP, we found that sharing fewer model parameters performed better at the same privacy cost. This provides key implications for privacy protection in drug development - by optimizing the proportion of parameters shared, the best balance between privacy protection and model performance can be achieved.
Implications for drug development: Data security and privacy are important considerations in the drug development process, especially in the clinical trial phase. Federal learning technologies allow different pharmaceutical companies and research institutions to share clinical trial data without compromising patient privacy, accelerating the drug discovery and development process. For example, pharmaceutical companies can jointly develop more accurate drug response models while maintaining data localization, improving the efficiency of new drugs to market. In addition, federated learning can effectively address the challenge of unbalanced data in drug development, which is especially important for achieving equitable model training across different research institutions.
Future challenges and directions for Improvement: Although this study demonstrates the feasibility and effectiveness of federated learning in drug development, several challenges remain. First, communication overhead is an important issue, especially when multiple clients are involved. Although we have reduced some of the communication burden through sparse vector technology in the experiment, we still need to develop more efficient communication protocols in the future to further reduce the bandwidth requirements of federated learning. Secondly, model heterogeneity among clients may affect the performance of the global model. Future research can explore adaptive model aggregation strategies to update personalized models according to the specific characteristics of clients, so as to improve the performance of global models. In addition, the further optimization of differential privacy technology is also an important direction for future research, especially in large-scale drug development data, how to achieve stronger privacy protection without significantly affecting the model performance.
This study demonstrates the great potential of federal learning in the field of drug development. Through techniques such as momentum restart, local model sharing, and differential privacy, we successfully demonstrated how to achieve efficient model training while protecting data privacy. Future research could further optimize communication efficiency, model aggregation strategies, and privacy protection techniques to advance the application of federated learning in real-world drug development.
References
- Bakas, S. , et al.: Identifying the best machine learning algorithms for brain tumor segmentation, progression assessment, and overall survival prediction in the BRATS challenge. arXiv:1811.02629 (2018).
- Hitaj, B. , Ateniese, G., Perez-Cruz, F.: Deep models under the GAN: information leakage from collaborative deep learning. In: SIGSAC. pp. 603–618. ACM (2017).
- Kingma, D.P. , Ba, J.: Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv:1412.6980.
- Li, L. , Fan, Y. , Tse, M., & Lin, K. Y. A review of applications in federated learning. Computers & Industrial Engineering 2020, 149, 106854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geyer, R.C. , Klein, T., Nabi, M.: Differentially private federated learning: A client level perspective. arXiv:1712.07557 (2017).
- Truex, S.; , Baracaldo, N.; Anwar, A.; Steinke, T.; Ludwig, H.; Zhang, R.; Zhou, Y. A hybrid approach to privacy-preserving federated learning. In Proceedings of the 12th ACM workshop on artificial intelligence and security, November 2019; pp. 1–11.
- Xu, K. , Zhou, H., Zheng, H., Zhu, M., & Xin, Q. (2024). Intelligent Classification and Personalized Recommendation of E-commerce Products Based on Machine Learning. arXiv:2403.19345.
- Xu, K. , Zheng, H., Zhan, X., Zhou, S., & Niu, K. (2024). Evaluation and Optimization of Intelligent Recommendation System Performance with Cloud Resource Automation Compatibility. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H. , Xu, K. , Zhou, H., Wang, Y., & Su, G. Medication Recommendation System Based on Natural Language Processing for Patient Emotion Analysis. Academic Journal of Science and Technology 2024, 10, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Wu, J.; Song, R.; Guo, L.; Xu, Z. Predicting Financial Enterprise Stocks and Economic Data Trends Using Machine Learning Time Series Analysis. Applied and Computational Engineering 2024, 87, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Ouadrhiri, A. , & Abdelhadi, A. Differential privacy for deep and federated learning: A survey. IEEE access 2022, 10, 22359–22380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R. , Baracaldo, N. , Zhou, Y., Anwar, A., & Ludwig, H. Hybridalpha: An efficient approach for privacy-preserving federated learning. In Proceedings of the 12th ACM workshop on artificial intelligence and security (pp. 13-23)., November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J. , Wang, Y. , Xu, C., Liu, S., Dai, J., & Lan, K. Bioplastic derived from corn stover: Life cycle assessment and artificial intelligence-based analysis of uncertainty and variability. Science of The Total Environment 2024, 946, 174349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J. , Wang, J. , Bao, W., Deng, T., & Bi, S. Application progress of natural language processing technology in financial research. Financial Engineering and Risk Management 2024, 7, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, N. , Sun, K. , Wang, S., Guitton, F., & Guo, Y. Privacy preservation in federated learning: An insightful survey from the GDPR perspective. Computers & Security 2021, 110, 102402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, F., Haddadi, H, Katevas; K., Marin, E., Perino, D., & Kourtellis, June). PPFL: Privacy-preserving federated learning with trusted execution environments. In Proceedings of the 19th annual international conference on mobile systems, applications, and services, June 2021; pp. 94–108.
- Xu, K. , Zhou, H., Zheng, H., Zhu, M., & Xin, Q. (2024). Intelligent Classification and Personalized Recommendation of E-commerce Products Based on Machine Learning. arXiv:2403.19345.
- Xu, K. , Zheng, H., Zhan, X., Zhou, S., & Niu, K. (2024). Evaluation and Optimization of Intelligent Recommendation System Performance with Cloud Resource Automation Compatibility. Appl. Comput. Eng. 2024, 87, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H. , Xu, K. , Zhou, H., Wang, Y., & Su, G. Medication Recommendation System Based on Natural Language Processing for Patient Emotion Analysis. Academic Journal of Science and Technology 2024, 10, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Wu, J.; Song, R.; Guo, L.; Xu, Z. Predicting Financial Enterprise Stocks and Economic Data Trends Using Machine Learning Time Series Analysis. Applied and Computational Engineering 2024, 87, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, P. , Song, B. , Zhan, X., Chen, Z., & Yuan, J. Automating the training and deployment of models in MLOps by integrating systems with machine learning. Applied and Computational Engineering 2024, 67, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B. , Gong, Y. , Zheng, H., Zhang, Y., Huang, J., & Xu, J. Enterprise cloud resource optimization and management based on cloud operations. Applied and Computational Engineering 2024, 67, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B. , & Zhang, Y. Implementation of seamless assistance with Google Assistant leveraging cloud computing. Journal of Cloud Computing 2023, 12, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M. , Yuan, B. , Li, H., & Xu, K. LLM-Cloud Complete: Leveraging Cloud Computing for Efficient Large Language Model-based Code Completion. Journal of Artificial Intelligence General science (JAIGS) ISSN: 3006-4023 2024, 5, 295–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P., Hua, Y., Cao, Q., Zhang, M. Improving the Restore Performance via Physical-Locality Middleware for Backup Systems. In Proceedings of the 21st International Middleware Conference, December 2020; pp. 341–355.
- Zhou, S. , Yuan, B., Xu, K., Zhang, M., & Zheng, W. THE IMPACT OF PRICING SCHEMES ON CLOUD COMPUTING AND DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS. Journal of Knowledge Learning and Science Technology ISSN: 2959-6386 (online) 2024, 3, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnan, M. , Kalra, S. , Cresswell, J. C., Taylor, G. W., & Tizhoosh, H. R. Federated learning and differential privacy for medical image analysis. Scientific reports 2022, 12, 1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, Chengru, and Yida Zhu. "Reinforcement Learning Based Model for Enterprise Financial Asset Risk Assessment and Intelligent Decision Making." (2024).
- Yu, Keke, et al. "Loan Approval Prediction Improved by XGBoost Model Based on Four-Vector Optimization Algorithm." (2024).
- Zhou, S. , Sun, J., & Xu, K. (2024). AI-Driven Data Processing and Decision Optimization in IoT through Edge Computing and Cloud Architecture. Zhou, S.; Sun, J.; Xu, K. AI-Driven Data Processing and Decision Optimization in IoT through Edge Computing and Cloud Architecture. Preprints 2024, 2024100736. [CrossRef]
- Sun, J. , Zhou, S., Zhan, X., & Wu, J. (2024). Enhancing Supply Chain Efficiency with Time Series Analysis and Deep Learning Techniques. Preprints 2024, 2024090983. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H. , Xu, K. , Zhang, M., Tan, H., & Li, H. Efficient resource allocation in cloud computing environments using AI-driven predictive analytics. Applied and Computational Engineering 2024, 82, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).