Submitted:
21 October 2024
Posted:
22 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Theory and Calculation
3. Material and Methods
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Comparison of Results
4.2. Explainability
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Murphy, K.P. Machine Learning: A Probabilistic Perspective; The MIT Press: 2012.
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hornik, K.; Stinchcombe, M.; White, H. Multilayer feedforward networks are universal approximators. Neural networks 1989, 2, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhaskar, H.; Liao, Q.; Poggio, T. When and why are deep networks better than shallow ones? In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, 2017.
- Rumelhart, D.E.; Hinton, G.E.; Williams, R.J. Learning internal representations by error propagation, parallel distributed processing, explorations in the microstructure of cognition, ed. de rumelhart and j. mcclelland. vol. 1. 1986. Biometrika 1986, 71, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A. Attention is all you need. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, Z.R.; Venkatesh, K.; Sulam, J.; Yi, P.H. Visual transformers and convolutional neural networks for disease classification on radiographs: a comparison of performance, sample efficiency, and hidden stratification. Radiology: Artificial Intelligence 2022, 4, e220012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamshirband, S.; Fathi, M.; Dehzangi, A.; Chronopoulos, A.T.; Alinejad-Rokny, H. A review on deep learning approaches in healthcare systems: Taxonomies, challenges, and open issues. J Biomed Inform 2021, 113, 103627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, H.; Yap, P.T.; Bozoki, A.; Liu, M. Federated learning for medical image analysis: A survey. Pattern Recognit 2024, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.S.I.; Rahman, A.; Debnath, T.; Karim, M.R.; Nasir, M.K.; Band, S.S.; Mosavi, A.; Dehzangi, I. Accurate brain tumor detection using deep convolutional neural network. Comput Struct Biotechnol J 2022, 20, 4733–4745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2015; pp. 3431-3440.
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention–MICCAI 2015: 18th international conference, Munich, Germany, October 5-9, 2015, proceedings, part III 18, 2015; pp. 234-241.
- Ibrahim, R.; Shafiq, M.O. Explainable Convolutional Neural Networks: A Taxonomy, Review, and Future Directions. ACM Computing Surveys 2023, 55, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrieta, A.B.; Díaz-Rodríguez, N.; Del Ser, J.; Bennetot, A.; Tabik, S.; Barbado, A.; García, S.; Gil-López, S.; Molina, D.; Benjamins, R. Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI): Concepts, taxonomies, opportunities and challenges toward responsible AI. Information fusion 2020, 58, 82–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- S Band, S.; Yarahmadi, A.; Hsu, C.-C.; Biyari, M.; Sookhak, M.; Ameri, R.; Dehzangi, I.; Chronopoulos, A.T.; Liang, H.-W. Application of explainable artificial intelligence in medical health: A systematic review of interpretability methods. Informatics in Medicine Unlocked 2023, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Velden, B.H.; Kuijf, H.J.; Gilhuijs, K.G.; Viergever, M.A. Explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) in deep learning-based medical image analysis. Medical Image Analysis 2022, 79, 102470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otsu, N. A threshold selection method from gray-level histograms. Automatica 1975, 11, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauvola, J.; Pietikäinen, M. Adaptive document image binarization. Pattern recognition 2000, 33, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholkopf, B.; Smola, A.J. Learning with Kernels: Support Vector Machines, Regularization, Optimization, and Beyond; MIT Press: 2001.
- Zhang, J.; Marszałek, M.; Lazebnik, S.; Schmid, C. Local Features and Kernels for Classification of Texture and Object Categories: A Comprehensive Study. International Journal of Computer Vision 2006, 73, 213–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2016; pp. 770-778.
- Araujo, A.; eacute; Norris, W. ; Sim, J. Computing Receptive Fields of Convolutional Neural Networks. Distill 2019, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Li, Y.; Urtasun, R.; Zemel, R. Understanding the effective receptive field in deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Barcelona, Spain, 2016; pp. 4905–4913.
- Retina Blood Vessel. Available online: https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/abdallahwagih/retina-blood-vessel (accessed on July 1).
- Cervantes, J.; Cervantes, J.; García-Lamont, F.; Yee-Rendon, A.; Cabrera, J.E.; Jalili, L.D. A comprehensive survey on segmentation techniques for retinal vessel segmentation. Neurocomputing 2023, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques dos Santos, J.D.; Marques dos Santos, J.P. Towards XAI: Interpretable Shallow Neural Network Used to Model HCP’s fMRI Motor Paradigm Data. Cham, 2022; pp. 260-274.
- Fisher, A.; Rudin, C.; Dominici, F. All models are wrong, but many are useful: Learning a variable's importance by studying an entire class of prediction models simultaneously. Journal of Machine Learning Research 2019, 20, 1–81. [Google Scholar]
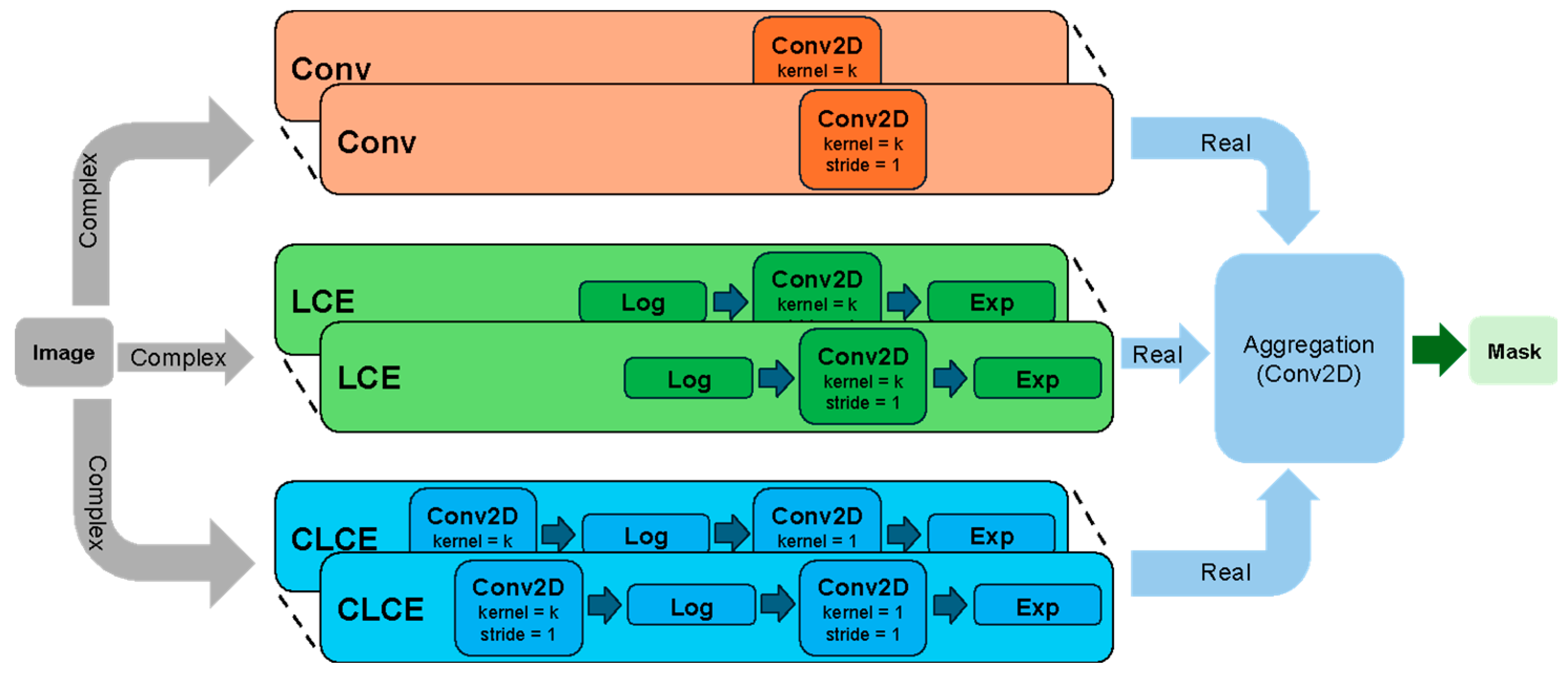
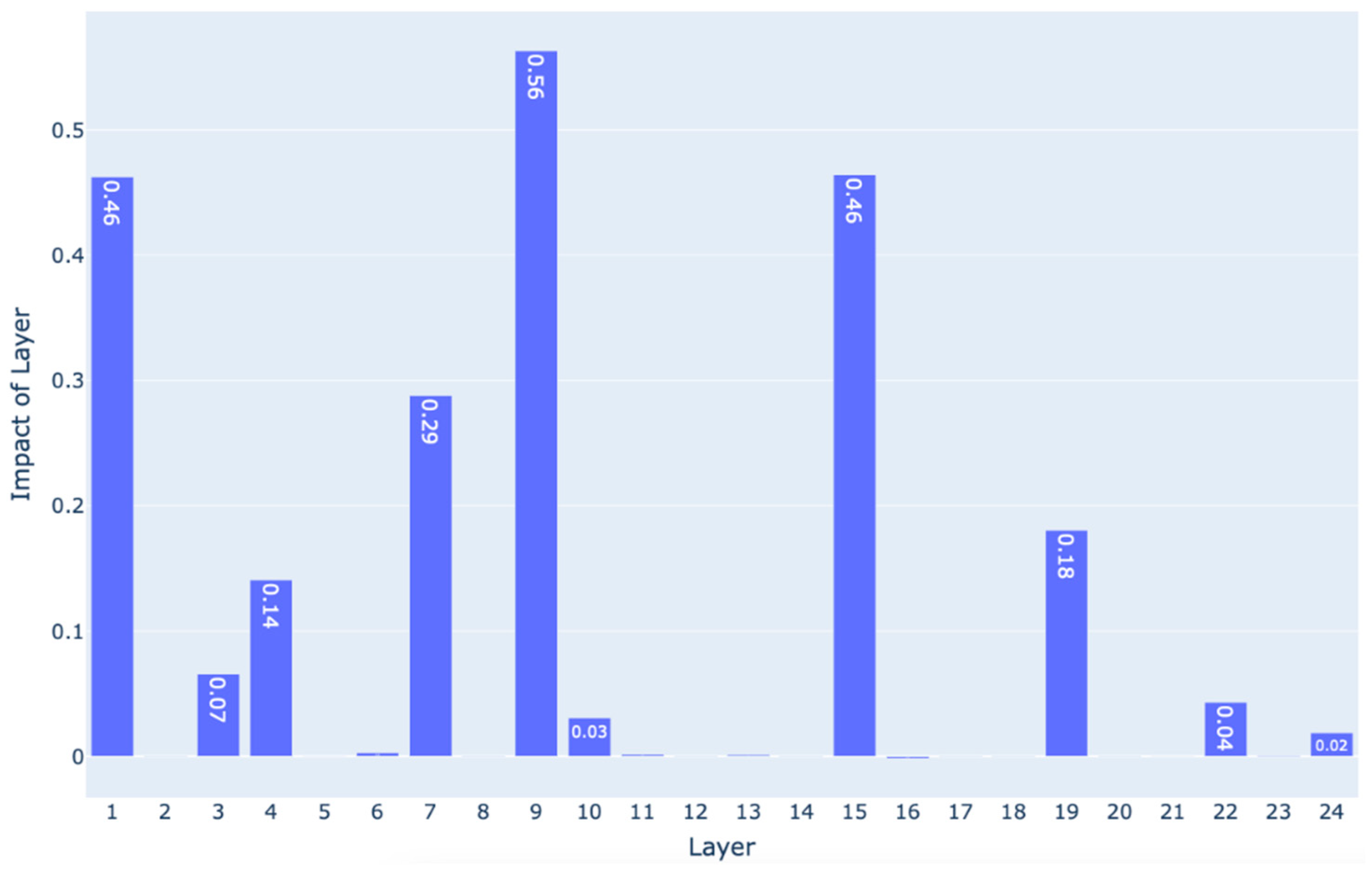
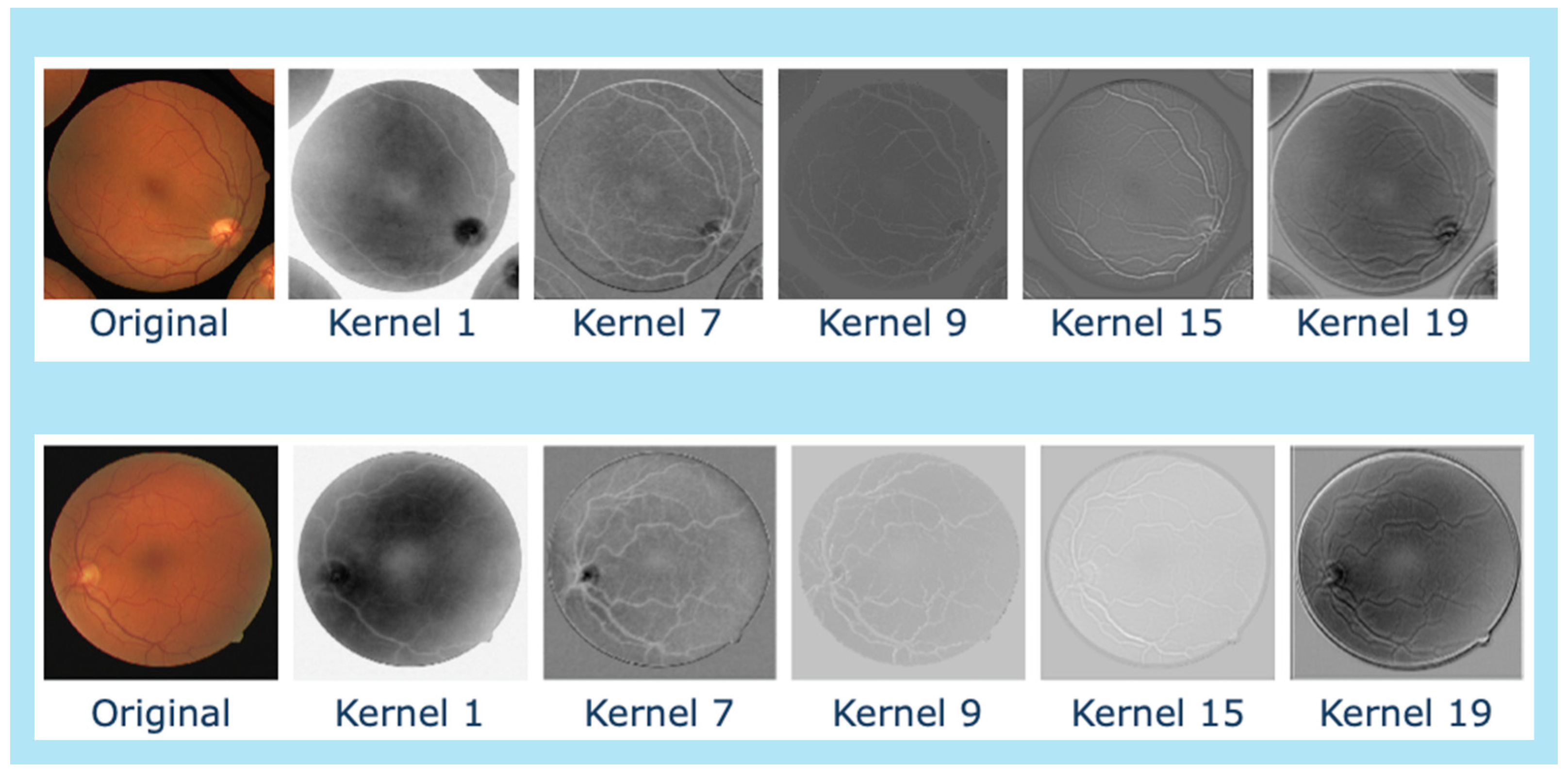
| Kernel Name | Equation |
|---|---|
| Linear | |
| Cosine | |
| Polynomial | |
| Sigmoid | |
| Radial Basis Function (RBF) | |
| Laplacian | |
| Chi-Squared |
| Weighted Operation | Induction | Implementation |
|---|---|---|
| Summation/Subtraction | ||
| Multiplication | ||
| Division | ||
| Power |
| Model | Scores on the training dataset | Scores on the testing dataset | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jaccard (%) | DICE (%) | F1 | Jaccard (%) | DICE (%) | F1 | |
| Fully CNN | 63.3 | 77.6 | 0.78 | 56.8 | 72.4 | 0.72 |
| U-Net | 63.5 | 77.7 | 0.78 | 65.9 | 79.0 | 0.79 |
| Shallow CNN | 56.2 | 72.0 | 0.72 | 58.3 | 73.6 | 0.73 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




