1. Introduction
More than 800 million people worldwide are chronically hungry, and 2 billion are micronutrient-deficient [
1]. Food insecurity and low dietary quality cause huge public health problems. Malnutrition is responsible for physical and mental development impairments, various infectious diseases, and unacceptably high numbers of premature deaths [
2]. Reducing these problems and achieving Sustainable Development Goal 2, “zero hunger and improved nutrition,” requires major transformations in global food systems. Isolated fixes cannot solve the complex issues [
3].
Allium cepa commonly known as Onion, also known as the bulb onion, is a vegetable that is the most widely cultivated species of the genus
Allium. It has been valued as a food and a medicinal plant since ancient times. It is widely cultivated, second only to tomato, and is a vegetable bulb crop known to most cultures and consumed worldwide [
3]. It is a short duration horticultural crop [
4] grown at low latitudes. It is commonly known as “Queen of the kitchen,” due to its highly valued flavor, aroma, and unique taste, and the medicinal properties of its flavor compounds [
5]. Onion is used throughout the year, for example in curries, in the form of spices, in salads, as a condiment, or cooked with other vegetables, such as boiled or baked. It is also used in different forms of processed food, e.g. pickles, powder, paste, and flakes, and it is known for its medicinal values. Vegetables are full of essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that provide many important health benefits to body. The world’s annual production of onions now amounts to 85 million tons. The main producers are China, India and the United States [
6].
Plant biotechnology is changing the agriculture industry [
7]. Advances have produced crops that are resistant to certain diseases that result in higher yields than before, that can grow in extreme soil conditions, such as in arid and salty environments, and that are even infused with nutrients [
8,
9]. Biotechnology innovation has the potential to increase agricultural productivity and quality, ultimately raising incomes for farmers across the world. Colchicine is a toxic chemical that is often used to induce polyploidy in plants [
10]. Basically, the colchicine prevents the microtubule formation during cell division, thus the chromosomes do not pull apart like they normally do [
11,
12]. The end result is a cell that now has double the number of chromosomes that it would normally have.
This study focuses on the induction of polyploidy in the onion seedlings which will provide an improved variety of onion seedlings that show superiority in morphology, antioxidant activity and amount of dissolved sugars through colchicine application in different concentrations.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Induction of Polyploidy
Stock of colchicine solution of 0.2% (w/v) concentration was obtained followed by subsequent serial dilutions to obtain 0.1%w/v and 0.05%w/v concentrations of colchicine solutions respectively. The seeds were socked separately in the concentrations mentioned above (i.e. 0.05%, 0.1% and 0.2%) for the period of 24 hours. After the exposure in the colchicine solutions, the seeds were rinsed thoroughly using tap water to remove the traces of colchicine. Cocopeat was used to make the seedbeds in which the germinated seedlings were raised for the period of four (4) months, data was collected according to the number of shoots and the height of the seedlings in the time interval of two weeks which were formulated into means and standard deviations. Survival rate was also calculated for each treatment during this period.
2.2. Chromosome Visualization
Carmine solution was formed by dissolving 5g in 45ml of 70% Ethanol. Root tips of the treated and control were put in labelled vials (0.05%, 0.1%, 0.2% and control) containing cold water and were placed immediately in the refrigerator and stored at 8℃ for 24 hours. After that, the roots were separately put in 1N HCl for 20 minutes for fixation in order to make the roots softer for squashing. Furthermore, the roots were also rinsed thoroughly in distilled water to remove the traces of 1N HCl, then the roots were cut from the top to remove the root caps leaving only apical meristem then followed by symmetrical dissection of the roots using sterilized razor blade. The dissected roots were put in the carmine solution for the period of 10 minutes to absorb the stain. The roots were placed on the slide and warmed over spirit lamp for few seconds then covered with coverslip, then placed on flat surface and squashed gently using glass rod followed by vertical pressing using blotting paper to remove bubbles and obtain a gentle squash. Observations were conducted using a microscope to examine the chromosomes of each treatment and the control under 100x magnification (oil immersion). Pictures were taken and used for karyotyping analysis.
2.3. Extraction (Maceration)
Samples from the bulbs and shoots of the treated onion seedlings (0.05%, 0.1% and 0.2%) and control were dried separately under a shade and blended to obtain powdery form of each sample using electric blender. From each sample, 10g was weighed using digital weighing balance and put inside a flask, then 150ml of 70% ethanol was poured in every flask followed by thorough mixing and shaking. The mouths of the flasks were closed using foil paper and stored in a dark container for 24 hours. After the period of 24 hours, the mixtures were filtered using Whatman filter paper to obtain the extracts from each sample. The extracts were put in 50ml capacity Eppendorf vials and labeled then stored in a refrigerator for subsequent uses.
2.4. Antioxidant Capacity Determination
The extracts from the samples (both bulbs and shoots of the treated and control) were subjected to free radical scavenging protocol using DPPH (2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl). Stock of DPPH solution was made by weighing 8mg and dissolved in 200ml of 70% ethanol. From the stock, 3ml was measured using a pipette and poured in a vial, 150µl of distilled water was added then followed by storage in a dark container for 30 minutes. After the period of storage, absorbance at the wavelength of 517nm was recorded using spectrophotometer. A stock solution of ascorbic acid was formed by dissolving 1.69mg of it in 100ml distilled water (i.e. making 1mM ascorbic acid) which served as a standard. Furthermore, a serial dilution of four different concentrations was made by adding 2ml of distilled water to the remaining three vials followed by taking 2ml from the stock and mixed serially along the vials (i.e. from 1Mm to 0.125Mm). After that, absorbance was recorded for each concentration of the ascorbic acid at the wavelength of 517nm using spectrophotometer. For each sample, 150µm of the sample was put in a vial and was added with 3ml of DPPH solution and mixed thoroughly and kept in the dark container for 30 minutes. After that, absorbance was recorded for the samples at the wavelength of 517nm using spectrophotometer. The solvent (ethanol) was designated as a blank and absorbance was also recorded. While taking the readings, three replications were made for all the samples and standard. Radical scavenging activities were recorded based on the percentage of DPPH scavenged.
2.5. Dissolved Sugars
The amount of dissolved sugars (glucose, fructose and sucrose) was measured using Abbe refractometer. The device was calibrated by using distilled water to set the scale at ground zero which recorded 0.000 refractive index. For each sample from the treated and control (i.e. bulbs and shoots), the extracts were shaken thoroughly to obtain an even distribution of sugars, then a dropper was used to mount the sample on the cleaned glass of the refractometer and closed, then the knob was adjusted until the dark area is at crosshairs. The extracts from each sample and control were subjected to the determination of their respective refractive indexes. The refractive indexes for all the samples and the control were determined at the wavelength of 589nm and the temperature of 20℃.
2.6. Data Analysis
Completely randomized design was used in this experiment in which every treatment contained three replications. The results were expressed as Mean values ± Standard deviations (SD). Analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used in comparing the means at the probability confidence of p < 0.05 which was performed on Microsoft Excel® 2019 (Microsoft Corporation, Washington USA) and graphs were plotted by the same software while karyotyping was performed using KaryoMeasure software (version 1.7.5.0).
3. Results
3.1. Survival Rate
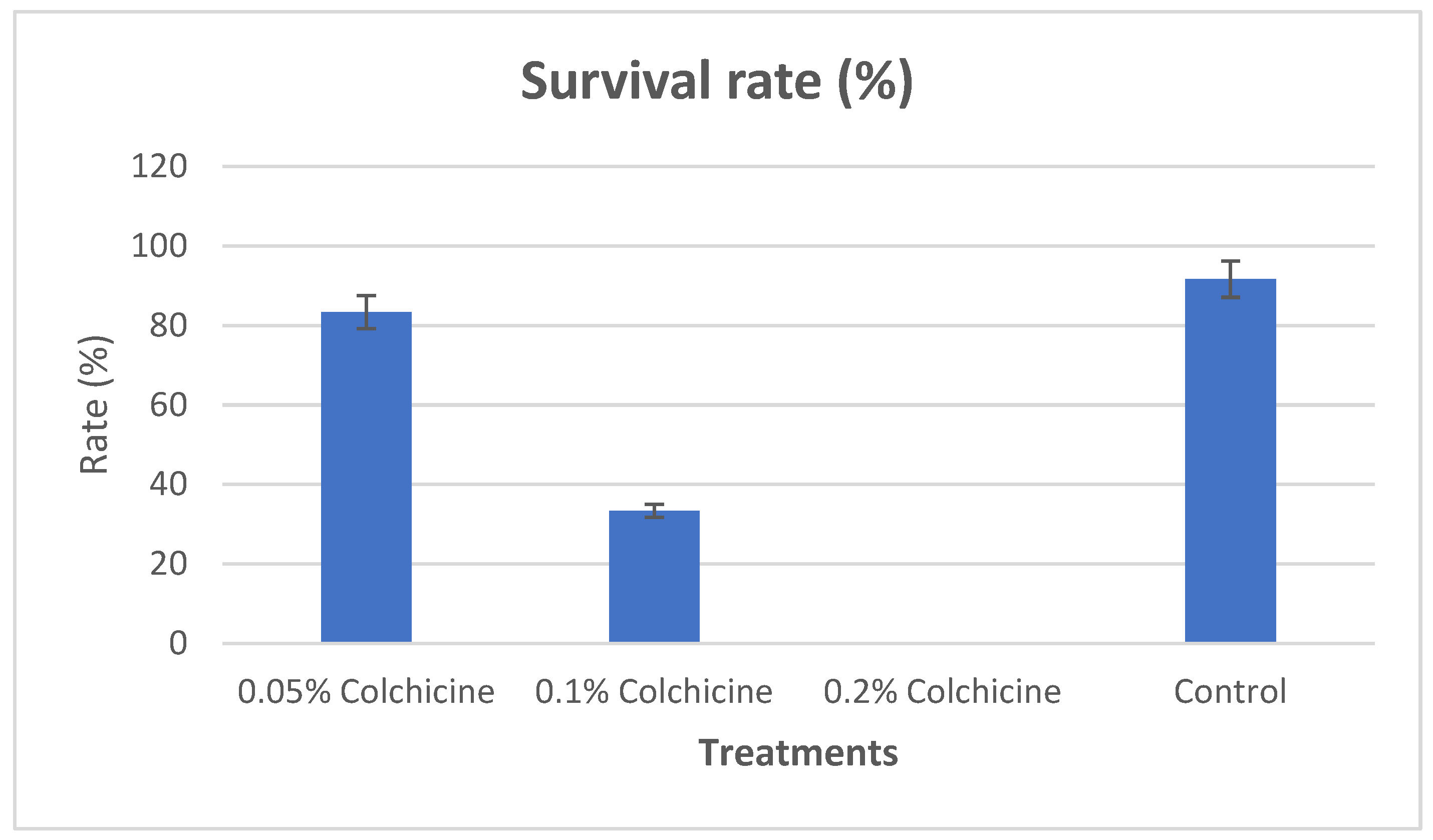
The germination took place after the fifth day, the survival rate was recorded across the treatments and control. The survival rates recorded were 83.33%, 33.33%, 0.00% and 91.67% for 0.05%, 0.1%, 0.2% concentrations of colchicine and control respectively. Seeds that were treated with 0.2% concentration of colchicine recorded no germination during the whole period, as such no data was derived from that treatment (0.2% concentration of colchicine). Henceforth, all the remaining analysis in this work were derived from the seedlings treated with 0.05%, 0.1% and control respectively.
Figure 1.
Showing the survival rate between the treatments and control (the bars represent the percentages of the means) and significant difference at p < 0.05 confidence was achieved using LSD.
Figure 1.
Showing the survival rate between the treatments and control (the bars represent the percentages of the means) and significant difference at p < 0.05 confidence was achieved using LSD.
3.2. Height and number of shoots
After germination, parameters of shoots’ heights and numbers were recorded across the treated and control which was commenced a week after the germination and continued for the period of 14 weeks (3.5 months). A significant difference was observed at p < 0.05 probability from the seedlings treated with 0.05% colchicine compared to the other treatment and control.
Table 1.
Represents the analysis of variance between the treatments and the control at p < 0.05.
Table 1.
Represents the analysis of variance between the treatments and the control at p < 0.05.
| ANOVA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Source of Variation |
SS |
df |
MS |
F |
P-value |
F crit. |
| Between Groups |
2487.609 |
2 |
1243.805 |
5.239149 |
0.009653 |
3.238096 |
| Within Groups |
9258.827 |
39 |
237.4058 |
|
|
|
| Total |
11746.44 |
41 |
|
|
|
|
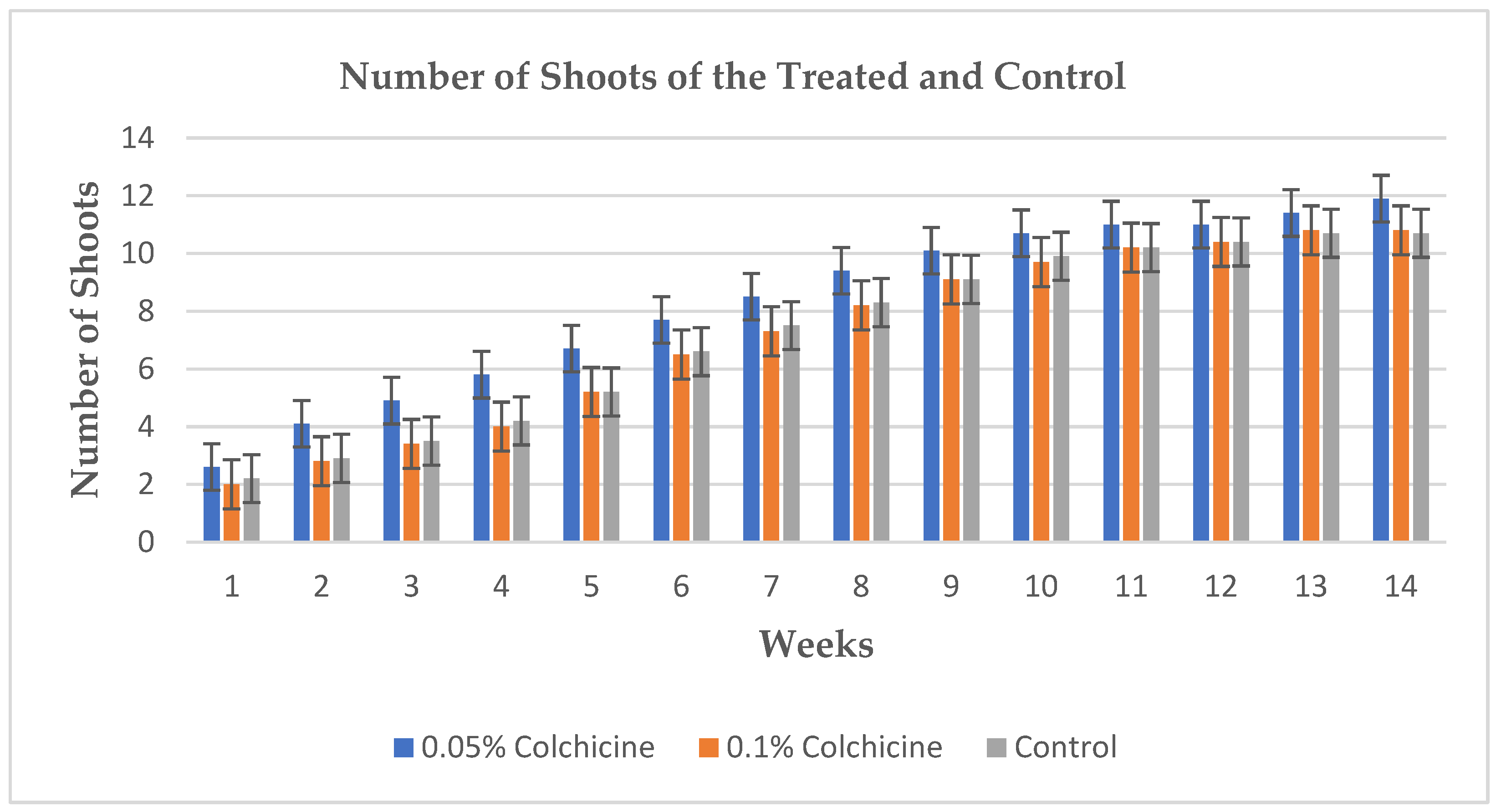
Figure 2. Showing the significant difference based on heights between the treatments and control. Significant difference was not recorded based on the number of shoots between the treatments and control.
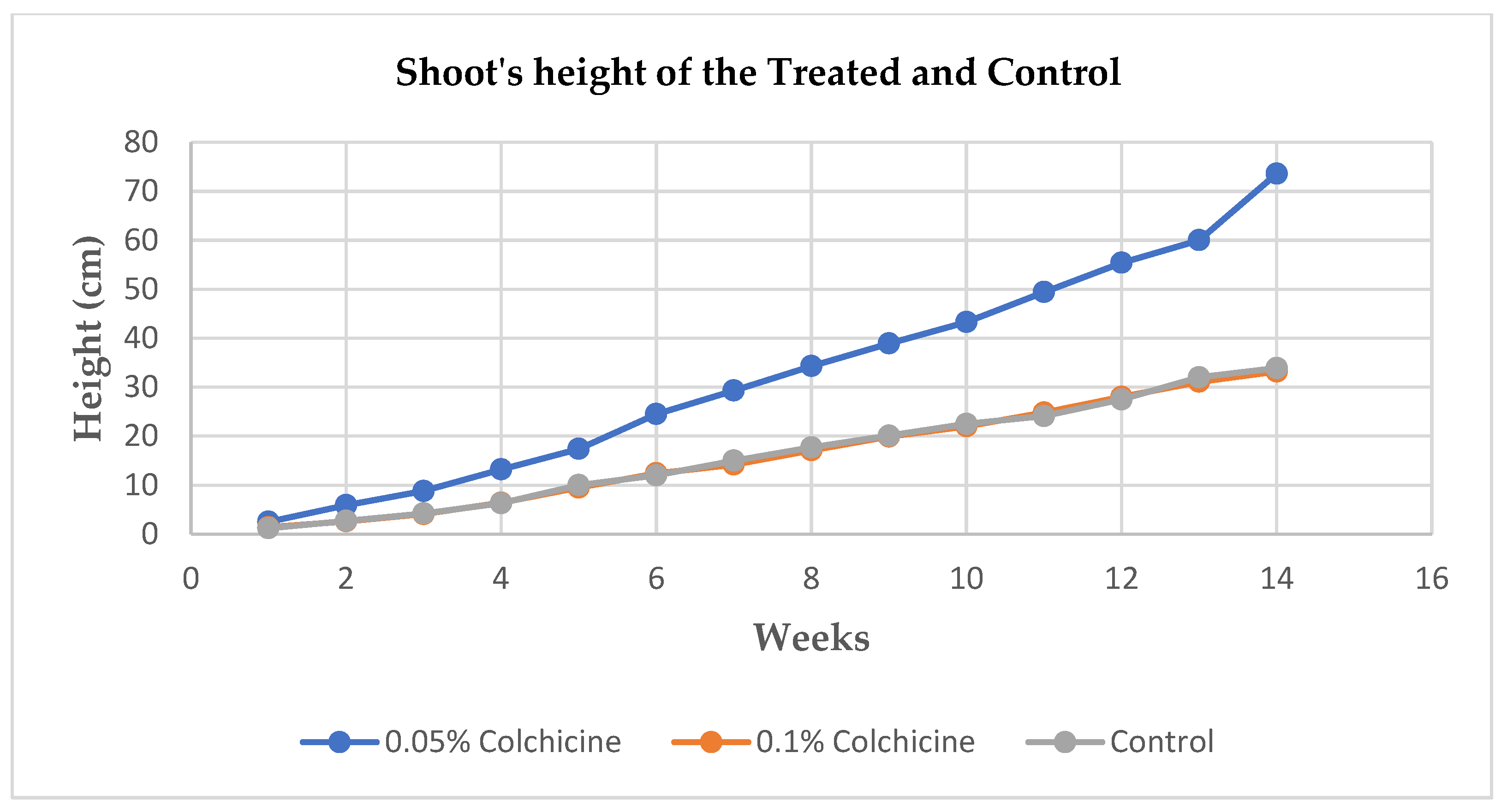
Figure 3. Shows bar chart that represents the number of shoots recorded from the seedlings within the period of fourteen weeks.
3.3. Karyotyping
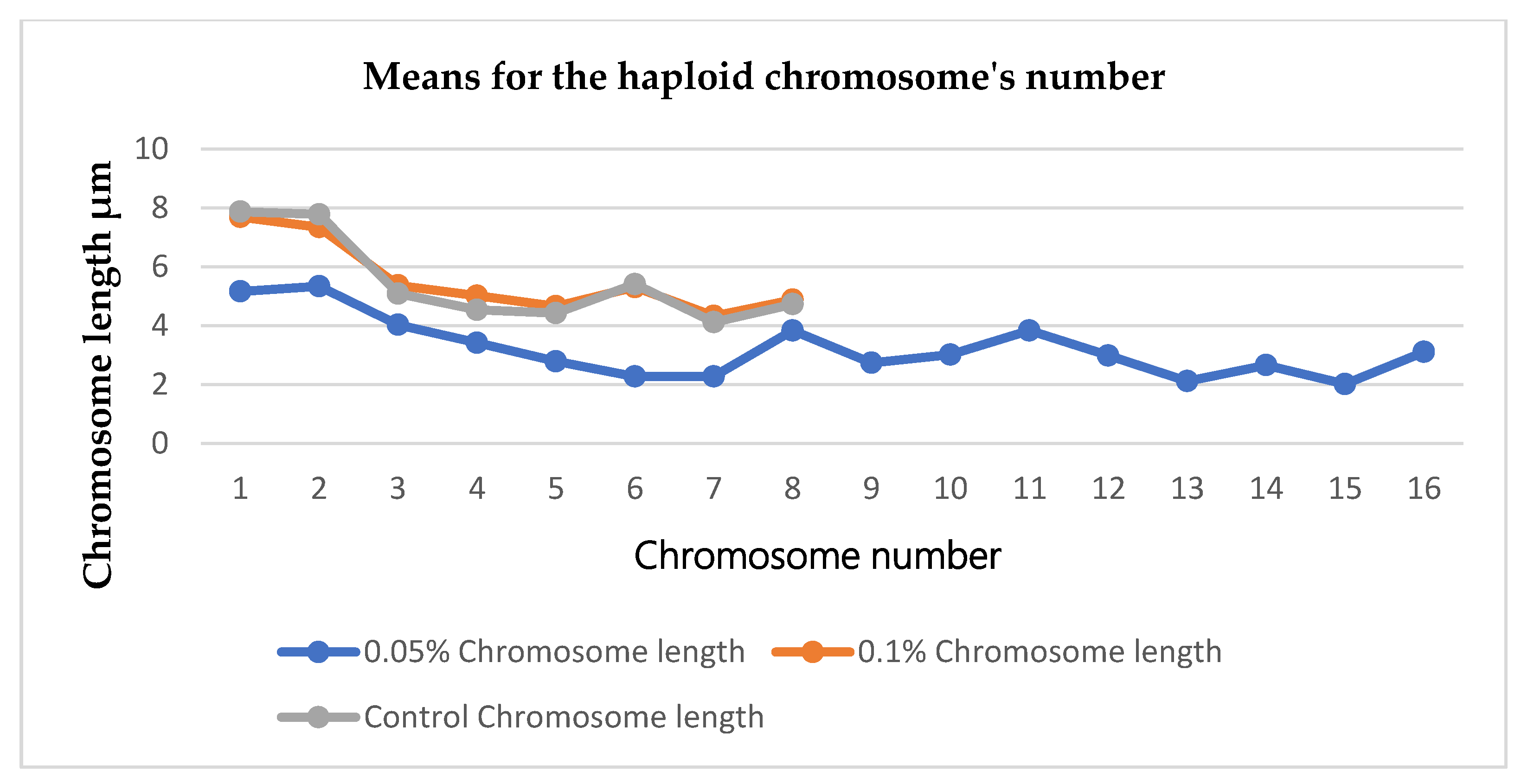
After performing the karyotyping using the tip rots from the 0.05%, 0.1% and control respectively. Mean values were recorded from the haploid chromosome numbers of the seedlings. It was clear that seedlings that were treated with 0.05% concentration of colchicine showed twice the number of chromosomes (2 x 2n = 4n) compared to the 0.1% concentration and control which were (2n). During the karyotyping the software (KaryoMeasure) was calibrated at 10µm in order to have an accurate reading of the chromosomes’ parameters. Chromosomes pictures were represented using idiogram to give a clear picture of the chromosomes from treated seedlings and control. Pictures from 0.05% concentration of colchicine showed sixteen haploid chromosome number (n = 16) during the karyotyping while 0.1% colchicine concentration and control showed eight haploid number of chromosomes (n = 8)
Figure 4 Shows representation of the haploid number of chromosomes between the treatments and control.
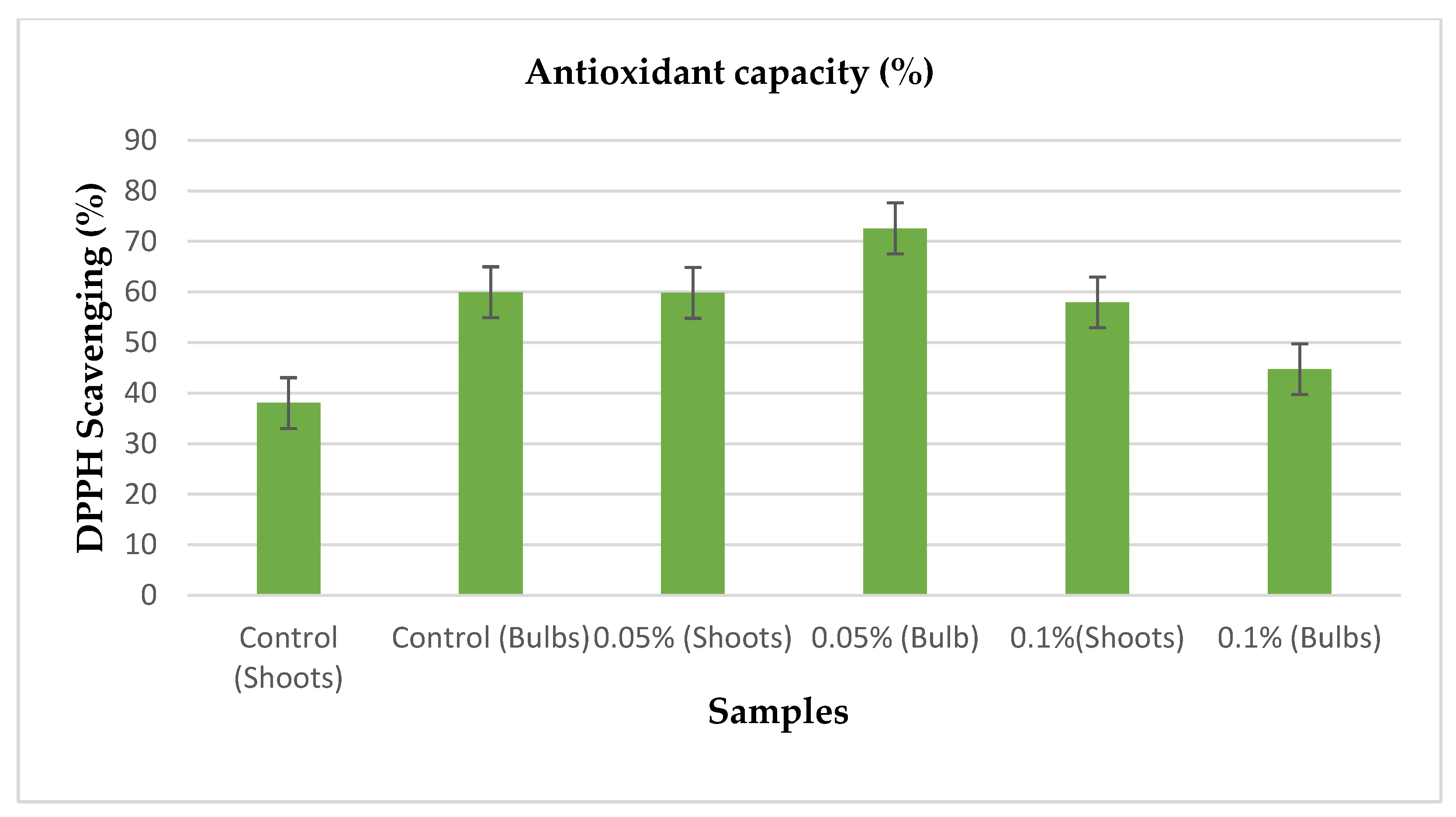
3.4. Antioxidant Capacity Determination
After extractions were made from the dried bulbs and shoots of the treated and control. The extracts were subjected to DPPH scavenging assay by following the protocols provided for the assay, in which the activities of the extracts were recorded in comparison to ascorbic acid which was used as a standard. From the standard (ascorbic acid), the curve was achieved at r2 = 0.9929 in which 1mM from the ascorbic acid showed high antioxidant activity while 0.125mM showed the lowest antioxidant activity.
Table 2.
Shows the table which represents the antioxidant activities from the treated seedlings and control.
Table 2.
Shows the table which represents the antioxidant activities from the treated seedlings and control.
| Samples |
Antioxidant capacity (%) |
Control (Shoots)
Control (Bulbs)
0.05% (Shoots)
0.05% (Bulbs)
0.01% (Shoots)
0.01% (Bulbs) |
0.396595143 ± 38.04692079d
0.659009184 ± 59.97187629b
0.657345703 ± 59.83289084b
0.809970034 ± 72.58480632a
0.634888717 ± 57.9565872bc
0.476858075 ± 44.75296899c |
From the above table, the bulbs from the seedlings treated with 0.05% concentration of colchicine showed highest antioxidant activity then the bulbs from the control followed by the shoots of the seedlings treated with 0.05% concentration of colchicine followed by the shoots of seedlings treated with 0.1% concentration of colchicine. Lowest antioxidant activities were recorded from the bulbs of seedlings treated with 0.1% then followed by the shoots of the control.
Figure 5. Shows the distribution of the antioxidant activities by the seedlings treated with colchicine and control.
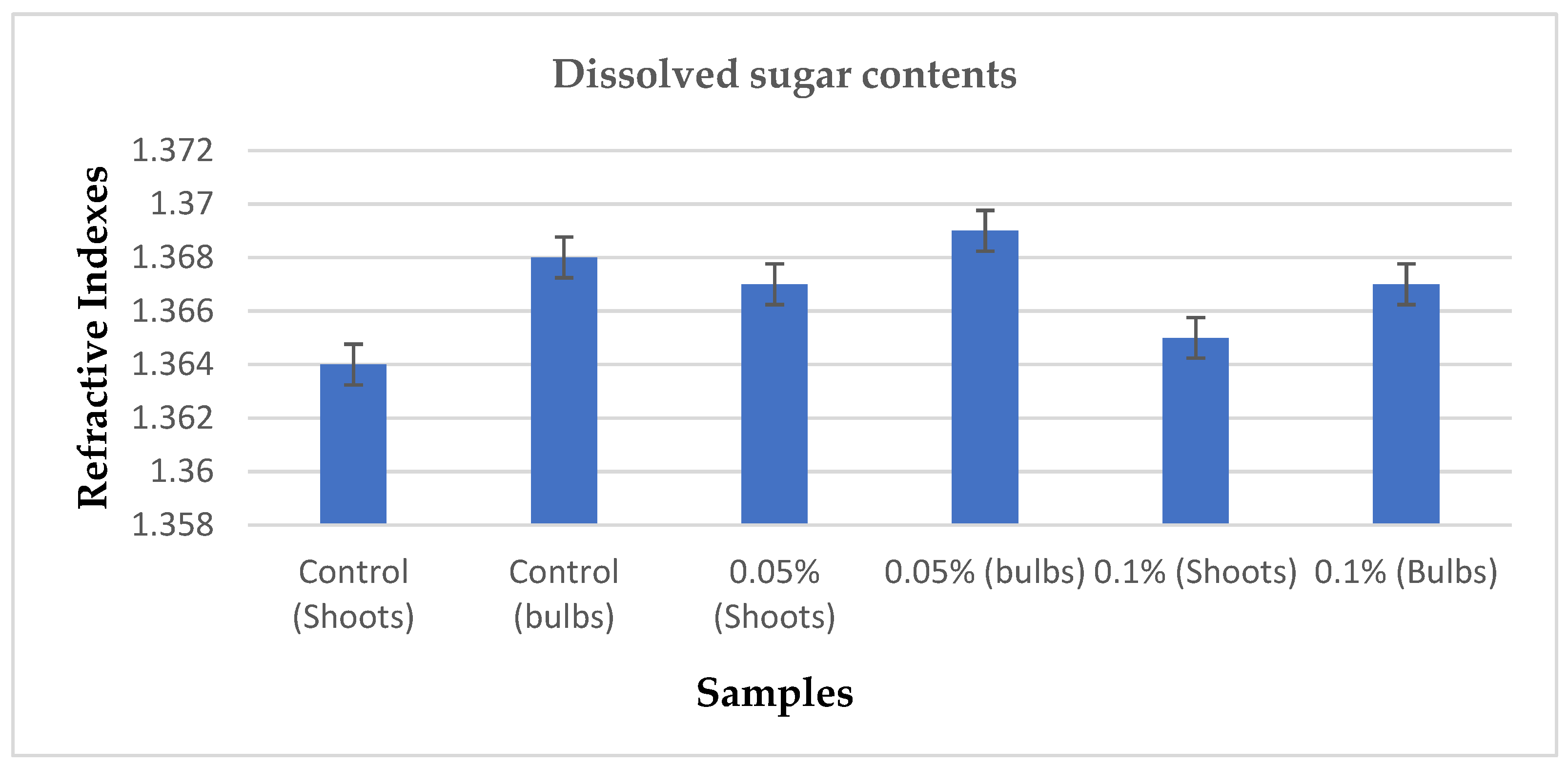
3.5. Dissolved Sugars Determination
From the extracts of the samples, they were subjected to refractometric analysis to measure the amount of dissolved sugar contents from each sample. The refractometer was used to measure the refractive index of each sample at 20℃, the following results were recorded in which the bulbs of the seedlings treated with 0.05% concentration of colchicine showed promising result of 1.369 refractive index followed by other concentrations and control. Generally, the standard refractive indexes of dissolved sugar contents ranges from 1.3357 to 1.4117. The sample which recorded the least refractive index was from the shoots of control. Means were recorded from each sample and were compared in which significant difference was shown from the seedlings treated with 0.05% concentration of colchicine.
Figure 6. Shows the significant difference at the probability confidence of p < 0.05 between the means of the samples.
4. Discussion
The application of colchicine in different concentrations to the seeds of Allium cepa showed effectiveness which led to the induction of polyploidy resulting in the formation tetraploids. The polyploidy was achieved by the application of 0.05% concentration of colchicine. The seedlings that were treated with 0.05% concentration of colchicine showed superiority in terms of seedlings’ heights as they reached the average height of up to 73.6 cm after fourteen weeks, they also showed superiority in terms of the size (diameter) of the bulbs in contrast to other treatment and control. There were significant differences in the above-mentioned parameters in terms of their morphology at p ≤ 0.05 probability, only the number of the shoots showed no significant difference among all the treatments and the control as they averaged almost the same number of shoots throughout the period of fourteen weeks.
The chromosomal analysis served as an indicator for checking the polyploidy induction in this work. The chromosomes counting gave the clear distinction between the treatments as it verified the number of chromosomes between the treatments and control. The chromosomal analysis via karyotyping showed that tetraploids were formed as the seedlings recorded 32 number of chromosomes compared to the diploids which recorded 16 number of chromosomes. Seedlings treated with 0.05% concentration of colchicine appeared to be having 32 number of chromosomes (i.e. they became tetraploid, 4n = 32) while seedlings that were treated with 0.1% and control appeared to have 16 number of chromosomes (i.e. they are diploids, 2n = 16). The statistical analysis showed that there was a significant difference at p ≤ 0.05 probability between the treatments and the control regarding the number of chromosomes. Hence there was a formation of tetraploids from the seedlings that were treated with 0.05% colchicine.
As extracts were made from the shoots and bulbs of the treated and control via maceration, the extract from the bulbs of seedlings treated with 0.05% colchicine showed promising antioxidant activity performance as they recorded the highest DPPH scavenging percentage (approximately 72.58%) compared to other samples. The second-best performing sample was from the bulbs of control (approximately 59.97%) followed by the least performing sample (approximately 38.04%) from the bulb of the samples that were treated with 0.1% colchicine. It can be said that the bulbs of the Allium cepa showed more antioxidant activities than the shoots of the plant.
Dissolved sugars were determined from the treatments and control by subjecting their extracts to refractometry. As expected, the sample from the seedlings that were treated with 0.05% colchicine recorded the highest refractive index which was within the range of conventional refractive indexes of dissolved sugars, the second performing sample in respect to dissolved sugars was the sample from the control. The sample that recorded the least refractive index which was a little lower than the conventional refractive indexes of dissolved sugars was from the seedlings that were treated with the 0.1% colchicine; therefore, it was clear that there was a significant difference between the treatments and control at the probability of p ≤ 0.05.
5. Conclusions
Chromosomal analysis proved the induction of polyploidy in the seedlings treated with 0.05% concentration of colchicine which led to the duplication of chromosomes number of the seedlings leading to the formation of tetraploid plants (4n = 32) in contrast to their diploid intact plants (2n = 16). Induction of polyploidy was achieved by the application 0.05% concentration of colchicine for 24 hours which showed significant differences at the probability confidence of p ≤ 0.05 in the morphology, antioxidant activities and dissolved sugars. High concentration of colchicine may lead to the destruction of seeds due to its high toxicity, it can be concluded that the more the concentration of colchicine, the less chance for polyploidy to be induced.
Author Contributions
.Conceptualization, M.A.A., K.E.M., and N.E.G.; methodology, M.A.A., K.E.M., and N.E.G; software, M.A.A., K.E.M., and N.E.G; validation, M.A.A., K.E.M., N.E.G., and S.O.M.; formal analysis, M.A.A., K.E.M., N.E.G., and S.O.M..; investigation, M.A.A., K.E.M., and N.E.G.; resources, K.E.M., and N.E.G.; data curation, M.A.A.; writing—original draft preparation, M.A.A.; writing—review and editing, M.A.A; visualization, M.A.A., K.E.M., N.E.G., and S.O.M.; supervision, K.E.M.; project administration, N.E.G.; funding acquisition, S.O.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was carried out with the financial support of the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation within the framework of the implementation of a complex project for the creation of high-tech production provided by the Decree of the Russian Federation Government dated 9 April 2010 No. 218. The project “Development of industrial technology and organization in the Far Eastern Federal District of the high-tech production of feed Vitamin A of increased stability and bioavailability”, agreement No. 075-11-2021-065 dated 25 June 2021.
Data Availability Statement
All the experimental works executed in this study are mentioned in the article. Further information can be granted by the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank the Department of Food Engineering and Technology, Advanced Engineering School “Institute of Biotechnology, Bioengineering and Food System”, Far Eastern Federal University (FEFU), Vladivostok, Russia. Our gratitude also goes to the Department of Plant Biology, Faculty of Life Science, Federal University Dutse, Jigawa State, Nigeria.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- FAO 2019a. The State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World. Rome: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations.
- Development Initiative, progress report 2018.
- FAO (2004). The State of Food and Agriculture 2003-2004. Agricultural Biotechnology: Meeting the Needs of the Poor? Rome: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. www.fao.org/3/Y5160E/ y5160e00.htm#TopOfPage.
- Selvaraj S. 1976. Onion: queen of the kitchen. Kisan World, 3 (12): 32–34.
- Price KR, Rhodes MJC. 1997. Analysis of the major flavonol glycosides present in four varieties of onion (Allium cepa) and changes in composition resulting from autolysis. J Sci Food Agric, 74(3):331–339. [CrossRef]
- FAO 2012. World onion production. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. http://faostat.fao.org, accessed February 27, 2017.
- Griesbach, R. J., & Bhat, R. N. (1990). Horticultural Science, 25, 1284–1286. [CrossRef]
- Nakano,M. T., Nomizu, K., Mizunashi,M., Suzuki, S.,Mori, S., Kuwayama,M., et al. (2006). Horticultural Science, 110, 366–371.Author 1, A.B.; Author 2, C. Title of Unpublished Work. Abbreviated Journal Name year, phrase indicating stage of publication (submitted; accepted; in press).
- Chakraborti, S. P., Vijayan, K., Roy, B. N., & Qadri, S. M. (1998). Plant Cell Reports, 17, 799–803.
- Author 1, A.B.; Author 2, C.D.; Author 3, E.F. Title of Presentation. In Proceedings of the Name of the Conference, Location of Conference, Country, Date of Conference (Day Month Year).
- Blakeslee, A.F.; Avery, A.G. Methods of inducing doubling of chromosomes in plants: By treatment with colchicine. J. Hered. 1937, 28, 393–411. [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y., Hahn, E., Murthy, H.N., & Paek, K. (2004). Effect of polyploidy induction on biomass and ginsenoside accumulations in adventitious roots of ginseng. Journal of Plant Biology. 47(4), 356-360. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).