1. Introduction
Recently, surgical procedures in the oncology and cardiology fields have reached a very high diffusion in the general population; in fact, it is estimated that, to date, approximately 1.5 million cardiac surgery interventions and 9 million oncological surgeries are conducted every year in the world, with values constantly increasing [
1,
2]. Since cardiac and oncology surgery often involves invasive procedures, a multitude of negative outcomes can frequently be observed, both in the short and long term. In particular, invasive surgical interventions often lead to the onset of depressive states [
3,
4], pain and reduction of musculoskeletal functionality in patients [
5,
6,
7]. At the musculoskeletal level, this translates into the onset of muscle and joint pain, as well as the appearance of significant postural alterations [
8]. Since posture can be defined as the spinal cord reflex manifestation of convergences and facilitation, secondary to cortical expressiveness [
9], such changes in the postural alignment of patients may be due to information that are aberrant with respect to that which are naturally at the basis of the construction of the posture. This aberrant information may depend on many factors intrinsic to surgical techniques, which can lead to inevitable iatrogenic lesions of muscle-tendon portions [
10], as well as to reconstructive techniques involving the musculoskeletal system and soft tissues [
11].
Given the spread of these post-surgical complications, it is essential in the clinical setting to identify strategies to contain the various symptoms that may be encountered.
Among the post-surgical rehabilitation strategies most frequently found in the literature are, for example, physical exercise, breathing exercises or manual therapy, although the efficacy of these treatments is still unclear and is often based on personal experiences and anecdotes [
12,
13,
14].
A new approach that could prove useful in the delicate area of post-surgical management could be represented by non-invasive instrumental therapies, such as Focused Mechano-Acoustic Vibrations (FMAVs). This therapeutic approach is based on the use of focused vibrations determined by variations in air pressure, produced by a turbine, inside plastic cups appropriately positioned on the patient's muscles receiving stimulation [
15]. The technique is completely non-invasive and allows, by varying the frequency of the administered vibration, to obtain modulatory effects on basal tone of the stimulated muscles [
15,
16]. The therapeutic effects of this approach have been observed in many fields, such as geriatrics [
17], orthopedics [
18], neurology [
19], sports medicine [
20], urology [
21], regenerative medicine [
22] and aesthetic medicine [
23].
Therefore, in light of the considerations made, in this study we observed the effects possibly induced by treatment with FMAVs in a post-surgical rehabilitation context of cardiac and oncological patients.
2. Materials and Methods
This research is a pilot retrospective analytical observational study carried out at the Gemelli Molise Hospital (Campobasso, Italy), in cooperation with the Ce.Fi.R.R. (Center for Physiotherapy, Rehabilitation and Re-Education) staff from January to June 2023.
All the procedures applied comply with the national safety regulations and the protocol is accessible to anyone who does not highlight specific contraindications during the initial clinical evaluation necessary for all patients who access the hospital. The main major contraindications to access the protocol are pregnancy, epilepsy, electrical implants, infections and tuberculosis. The protocol is not an experimental practice, since it applies the same procedures used at the study facility for all patients who do not present the above-mentioned contraindications. This study was conducted in accordance with the ethical principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Written informed consent was obtained at enrolment from participants who were willing and able. Furthermore, the Ce.Fi.R.R., as the institution in charge for carrying out the study through part of its staff, owns the ISO 9001:2015 certification for the realization of "Clinical observational studies in the rehabilitation field" (Certificate from the Italian Accreditation Body "Accredia" n. IT15/0304). Due to these considerations and the lack of incontrovertible national legislation regarding the need for the submission of retrospective and/or non-pharmacological observational studies to an ethics committee [
24], normal ethics committee clearance was not required [
25].
A total of 20 patients (12 women and 8 men; Caucasian ethnicity; average age of 48 years) were observed within the Gemelli Molise Hospital (Campobasso, Italy).
All patients observed had a history of surgery for cardiac or tumor pathology and underwent surgery no more than two months before the start of the treatment protocol. The therapeutic protocol was prescribed by specialist doctors after careful evaluations of the patient's general health status and the possibility and convenience of intervening on his/her post-surgical pain and postural alteration in a minimally invasive way through a complementary approach.
To assess the musculoskeletal health status of patients before (T0) and after (T1) the therapeutic protocol, a routine evaluation of the patients was carried out using 2 diagnostic tools:
- -
Numeric Pain Rating Scale (NPRS): it is one of the most common tools for measuring the pain subjectively perceived by patients. It is a derivate of the Visual-Analogue Scale (VAS) divided into ten levels, usually distributed equidistant on a 10 cm long strip, which correspond to the level of pain perceived by the patient at the time of the evaluation, where 0 is the total absence of pain and 10 is the maximum level of pain imaginable and/or ever experienced by the patient [
26]. This scale is reliable, effective and easy to apply even in the presence of dysfunctions of the general musculoskeletal system [
26]. In the case of the present study, patients were asked to express a value from 0 to 10 corresponding to the maximum level of pain perceived at the site of the body which was more painful for them following the surgery;
- -
Postural Biometric Index (PBI): this is an index calculated by the proprietary software of the Milletrix 3.0 platform (Diasu Health Technologies, Rome, Italy) on the basis of a stabilometric evaluation carried out using the same device [
9]. This index takes into account the parameters of Center of Pressure, Symmetry of Bipodalic Load, Symmetry of Retro-Forefoot Load, Angle of Centers of Pressure, Podalic Angle, Location of Maximum Pressure Point, Symmetry of Support Surface and Center of Gravity Deviation - Center of Pressure [
9]. These parameters are then correlated to obtain an index that quantifies the postural state of the patient [
9]. The PBI value is considered healthy from 0 to 10 and dysfunctional if >10.
The observed patients were subjected to a protocol consisting of the application of FMAVs 2 times a week for 4 weeks, for a total of 8 sessions lasting approximately 20 minutes each, performed on an outpatient basis. FMAVs therapy was administered using the Vibration Sound System (ViSS) (Vissman Europe S.r.l., Rome, Italy), through a vibrating handpiece guided by the therapist. The handpiece was positioned on multiple body areas in which palpable Myofascial Trigger Points (MTrPs) were located. The presence of MTrPs was assessed by the therapist before each session, through a palpatory examination of the patient's body aimed at identifying the most dysfunctional MTrPs (i.e. more painful to palpation or capable of evoking radiated symptoms). When a potential MTrP was manually detected, the therapist performed a functional evaluation of the range of motion of the district where the MTrP was located; if the range of motion of the suspect district resulted reduced compared to the contralateral one, the palpated MTrP was considered in need of stimulation. Each dysfunctional point was stimulated for a time variable from 3 to 5 minutes until the total 20 minutes of treatment per session were reached. The stimulation frequency was set at 120 Hz.
Given the relatively small size of the observed group of patients, the data collected at time T0 and T1 were processed through the application of a non-parametric Wilcoxon signed-rank test. Data analysis was performed through the Statistics Kingdom open online calculator software (
https://www.statskingdom.com, Melbourne, Australia). The observed changes were considered significant for
p values < 0.05.
3. Results
At the end of the therapeutic protocol, it was observed that both the NPRS and PBI values have varied in response to the FMAVs treatment.
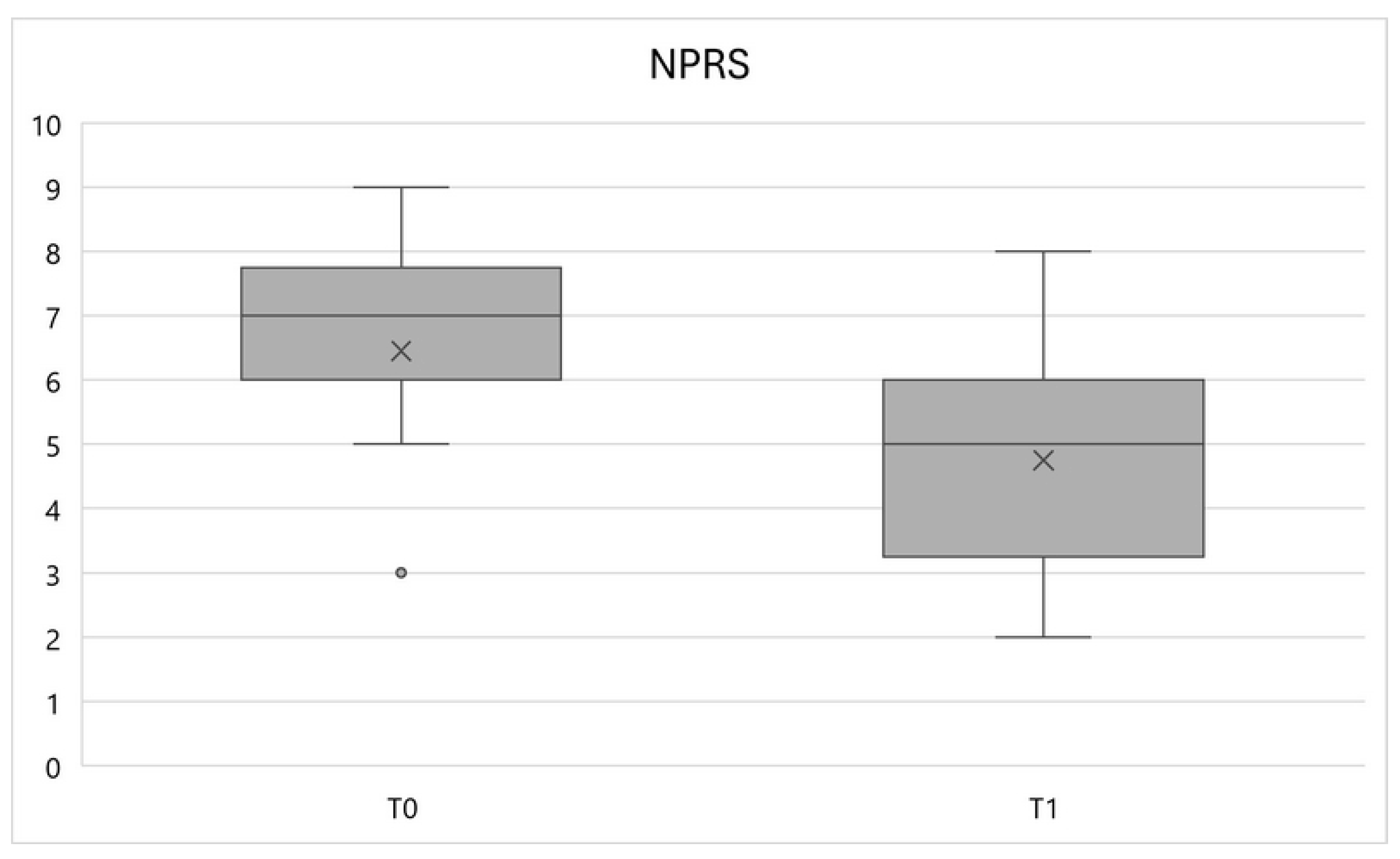
In particular, the NPRS variable showed a significant reduction (
p < 0.01) between times T0 and T1, equal to an average percentage variation of -26.4%, going from a mean value of 6.5 ± 1.6 to 4.7 ± 1.7 (
Figure 1).
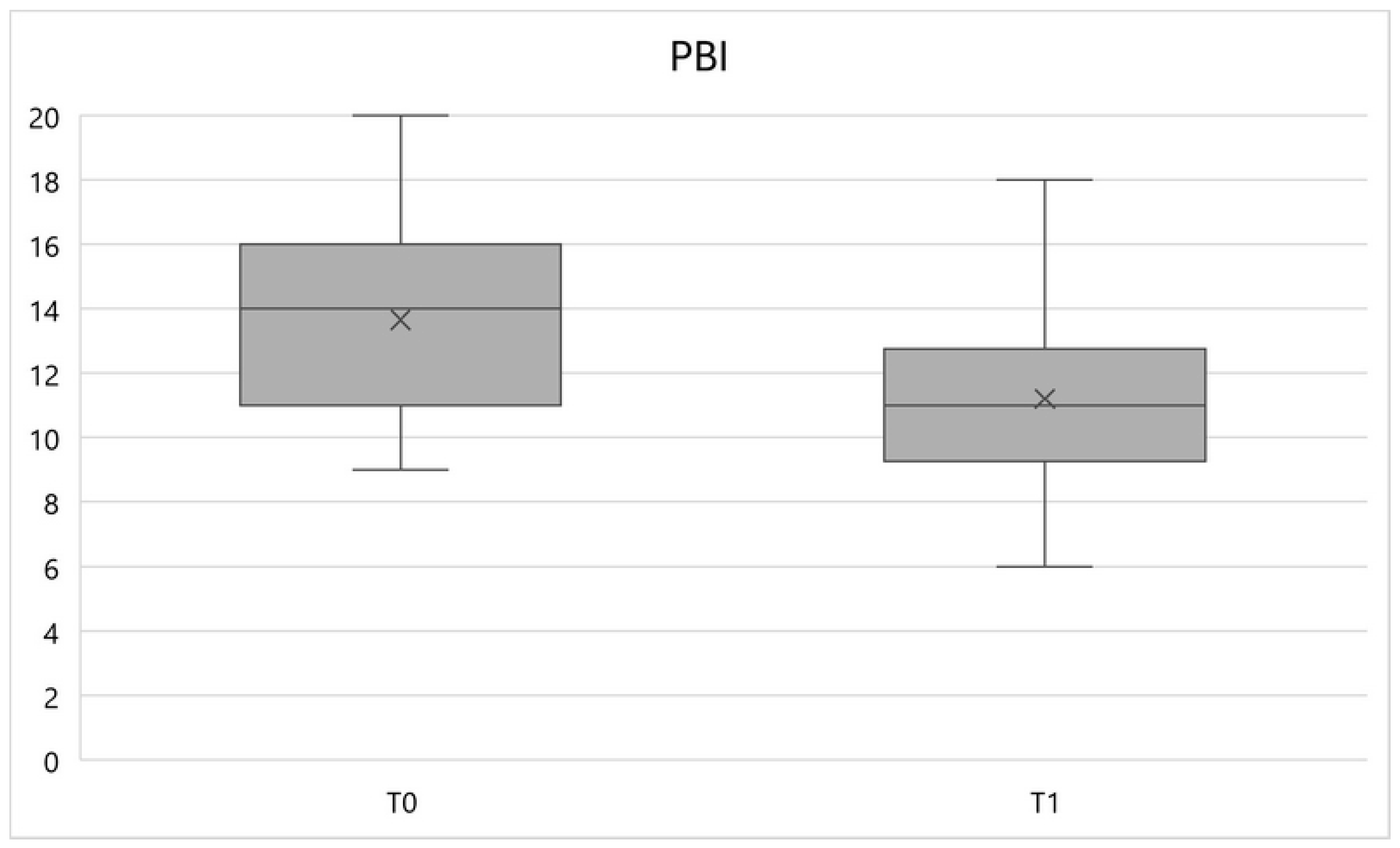
Similarly, the PBI variable underwent a significant reduction (
p < 0.01) between times T0 and T1, equal to a percentage variation of -17.9%, going from an average value of 13.7 ± 3.1 to 11.2 ± 3 (
Figure 2).
4. Discussion
The present pilot analytical retrospective observational study has highlighted how the application of a protocol of 8 FMAVs sessions for a period of 4 weeks is able to induce a reduction in pain, detected with the NPRS scale, and postural dysfunction, detected with the PBI calculation, in post-surgical cardiac and oncological patients.
These results appear consistent with what has already been observed in the literature regarding the efficacy of FMAVs in multiple clinical areas of rehabilitation interest [
15,
16,
17,
18,
19,
20,
21,
22].
Multiple studies in literature have highlighted how vibration therapies are able to reduce musculoskeletal pain, both when applied to the whole body [
27,
28] and in the case of localized application [
29,
30]. The mechanisms by which this pain reduction occurs are still a matter of debate. It is believed that a major influence on the analgesic capabilities of vibrations is to be attributed to the stimulation of the Pacinian corpuscles, which can determine the reduction or increase in perceived pain depending on the frequency and amplitude of the vibrations applied locally to the painful areas [
31]. It is believed that the pain modulating activity induced by vibrations is primarily attributable to Aβ-fibers activation, as well as to the activation of the limbic system, to the reduced local expression of TRPV1 and calcitonin and to the release of oxytocin [
32]. On the contrary, it would seem that the inflammatory aspect of pain is less influenced by vibrational stimulations, which do not seem to be able to induce significant releases of cortisol or opioid neuropeptides in the stimulated tissues [
32]. In any case, the vibrational frequency appears to be a more influential parameter than the stimulation intensity in determining the analgesic potential of vibrations, which is best expressed in a range between 100 and 250 Hz [
32]. This last consideration appears consistent with what has already been observed regarding the optimal ranges of stimulation using FMAVs, according to which frequencies between 100 and 300 Hz express the greatest potential for modulating pain and muscle tone [
15], with frequencies in the range 100-120 Hz appearing to be the most effective in relaxing muscles in a state of increased tension [
15]. Considering that the application in this study was performed with a frequency of 120 Hz on various MTrPs identified in the patients, it is possible that the stimulation simultaneously reduced local pain and the state of tension of the treated muscles, inducing a combined effect of reduction of perceived musculoskeletal pain.
With regard to the aspect of postural improvement, more and more evidence can be collected in literature regarding the influence of vibrations, especially focal ones, in improving the parameters of postural stability and efficiency of various types of subjects, both in the pathological [
33,
34] and sports fields [
35,
36]. It is assumed that the modulation activity of the muscular properties attributable to the FMAVs can determine the improvement of parameters such as strength, resistance, coordination and stability, with positive effects on the postural attitude of the treated subjects. This also appears consistent with what has been experienced in terms of efficacy of FMAVs in the treatment of musculoskeletal and neuromuscular problems, according to a bio-physico-metric approach aimed at improving the postural quality of patients whose pathologies could be linked to the presence of MTrPs [
14,
37].
Howsoever, it should be highlighted that the average value of postural dysfunction detected through the PBI test at the end of the treatment protocol, although significantly improved, was still slightly higher than the maximum acceptable value of 10 [
9]. Taking into account the positive trend of the PBI value detected in our study, this observation indicates that a FMAVs protocol could probably require more time or more frequent sessions to normalize the posture of post-surgical patients, while inducing a reduction in pain to levels below appreciable algesia more rapidly.
Although the results of this study appear encouraging, some limitations of this research must be highlighted. First of all, the study sample is relatively small and not sufficiently homogeneous. This is due to the observational nature of the study, which did not allow for the implementation of strict sample selection procedures, being able to consider only patients who had a similar, but not identical, clinical history and who had undertaken the same treatment protocol in the post-surgical period. Furthermore, for the same reasons, it was not possible to effectively configure a follow-up period or an adequate control group. Nonetheless, the observational setting of the study allowed for the evaluation of the effects of FMAVs directly in the operational field, in a more real clinical context, configuring this research as a pilot for possible experimental studies on the same topic, which could include a larger sample, a control group and a follow-up period, in order to confirm or deny the positive effects of FMAVs observed in this study.
5. Conclusions
This pilot observational study demonstrates how the application of a 4-week FMAVs protocol in post-surgical patients of the cardiac or oncological type is able to produce a significant improvement in pain and postural dysfunction that occur after the surgery. Since the identification of new therapeutic strategies capable of speeding up the recovery of patients of this type could improve the quality of life of the patients themselves and optimize health resources by making the terms of post-surgical hospitalization more efficient, it could be interesting to investigate more extensively on FMAVs in this therapeutic-rehabilitative context.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.B. and M.P.; methodology, G.B.; software, A.D.I.; validation, R.P.; formal analysis, M.P.; investigation, G.B. and A.M.; resources, M.P.; data curation, A.D.I.; writing—original draft preparation, G.B. and L.P.; writing—review and editing, L.P., G.L.M. and P.E.G.; visualization, C.M.; supervision, G.L.M. and P.E.G.; project administration, G.B.; funding acquisition, M.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval were waived for this study due to the fact that the protocol is not an experimental practice, since it applies the same procedures used for all patients who do not present the aforementioned contraindications. This study was conducted in accordance with the ethical principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Written informed consent was obtained at enrolment from participants who were willing and able. Furthermore, the Ce.Fi.R.R., as the institution in charge for carrying out the study through part of its staff, owns the ISO 9001:2015 certification for the realization of "Clinical observational studies in the rehabilitation field" (Certificate from the Italian Accreditation Body "Accredia" n. IT15/0304). Due to these considerations and the lack of incontrovertible national legislation regarding the need for the submission of retrospective and/or non-pharmacological observational studies to an ethics committee, normal ethics committee clearance was not required.
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent was obtained at enrolment from participants who were willing and able.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study, due to the preservation of the privacy of interested parties, could be made available upon motivated and reasonable private request to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Vervoort, D.; Lee, G.; Ghandour, H.; Guetter, C.R.; Adreak, N.; Till, B.M.; Lin, Y. Global cardiac surgical volume and gaps: trends, targets, and way forward. Annals of Thoracic Surgery Short Reports 2024, 2, 320–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, A.C.; Mutebi, M.; Rao, T.S. A review of the current state of global surgical oncology and the role of surgeons who treat cancer: our profession’s imperative to act upon a worldwide crisis in evolution. Annals of Surgical Oncology 2023, 30, 3197–3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correa-Rodríguez, M.; Abu Ejheisheh, M.; Suleiman-Martos, N.; Membrive-Jiménez, M.J.; Velando-Soriano, A.; Schmidt-RioValle, J.; Gómez-Urquiza, J.L. Prevalence of depression in coronary artery bypass surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of clinical medicine 2020, 9, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antoni, M.H.; Jacobs, J.M.; Bouchard, L.C.; Lechner, S.C.; Jutagir, D.R.; Gudenkauf, L.M.; Blomberg, B.B.; Glück, S.; Carver, C.S. Post-surgical depressive symptoms and long-term survival in non-metastatic breast cancer patients at 11-year follow-up. General hospital psychiatry 2017, 44, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberger, D.C.; Pogatzki-Zahn, E.M. Chronic post-surgical pain–update on incidence, risk factors and preventive treatment options. BJA education 2022, 22, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagundes, C.P.; Shi, Q.; Vaporciyan, A.A.; Rice, D.C.; Popat, K.U.; Cleeland, C.S.; Wang, X.S. Symptom recovery after thoracic surgery: Measuring patient-reported outcomes with the MD Anderson Symptom Inventory. The Journal of thoracic and cardiovascular surgery 2015, 150, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Cohen, J.C.; Devasenapathy, N.; Hong, B.Y.; Kheyson, S.; Lu, D.; Oparin, Y.; Kennedy, S.A.; Romerosa, B.; Arora, N.; Kwon, H.Y. Prevalence and intensity of persistent post-surgical pain following breast cancer surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. British journal of anaesthesia. 2020, 125, 346–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangone, M.; Bernetti, A.; Agostini, F.; Paoloni, M.; De Cicco, F.A.; Capobianco, S.V.; Bai, A.V.; Bonifacino, A.; Santilli, V.; Paolucci, T. Changes in spine alignment and postural balance after breast cancer surgery: a rehabilitative point of view. BioResearch open access 2019, 8, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barassi, G.; Di Simone, E.; Galasso, P.; Cristiani, S.; Supplizi, M.; Kontochristos, L.; Colarusso, S.; Visciano, C.P.; Marano, P.; Di Iulio, A.; Giancola, P. Posture and health: are the biomechanical postural evaluation and the postural evaluation questionnaire comparable to and predictive of the digitized biometrics examination? International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2021, 18, 3507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Park, E.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, J.; Park, H.Y.; Yang, J.D.; Jung, T.D. Alteration in skeletal posture between breast reconstruction with latissimus dorsi flap and mastectomy: a prospective comparison study. Gland surgery 2021, 10, 1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocjan, J.; Gzik-Zroska, B.; Nowakowska-Lipiec, K.; Burkacki, M.; Suchoń, S.; Michnik, R.; Czyżewski, D.; Adamek, M. Thoracic surgery may alter body static balance via diaphragm dysfunction. Plos one 2022, 17, e0273641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stiller, K.; McInnes, M.; Huff, N.; Hall, B. Do exercises prevent musculoskeletal complications after cardiac surgery? Physiotherapy Theory and Practice 1997, 13, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filbay, S.R.; Hayes, K.; Holland, A.E. Physiotherapy for patients following coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery: limited uptake of evidence into practice. Physiotherapy theory and practice 2012, 28, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheville, A.L. , Tchou, J. Barriers to rehabilitation following surgery for primary breast cancer. Journal of surgical oncology 2007, 95, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barassi, G.; Di Stefano, G.; Pellegrino, R.; Di Iulio, A.; Gildone, V.; Pensa, G.; Cipriano, M.; Matarese, M.; d’Alessandro, F.; Sacco, F.; Prosperi, L. Focused Mechano-Acoustic Vibrations: Bio-Physico-Metric Approach in Neuromuscular Diseases. Eur J Musculoskel Dis 2024, 13, 41–45. [Google Scholar]
- Saggini, R.; Carmignano, S.M.; Palermo, T.; Bellomo, R.G. Mechanical vibration in rehabilitation: state of the art. Journal of novel physiotherapies 2016, 6, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrangelo, T.; Mancinelli, R.; Toniolo, L.; Cancellara, L.; Paoli, A.; Puglielli, C.; Iodice, P.; Doria, C.; Bosco, G.; d'Amelio, L.; Di Tano, G. Effects of local vibrations on skeletal muscle trophism in elderly people: mechanical, cellular, and molecular events. International journal of molecular medicine 2009, 24, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iodice, P.; Bellomo, R.G.; Migliorini, M.; Megna, M.; Saggini, R. Flexible flatfoot treatment in children with mechanical sound vibration therapy. International Journal of Immunopathology and Pharmacology 2012, 25(1_suppl), 9-15.
- Costantino, C.; Galuppo, L.; Romiti, D. Efficacy of mechano-acoustic vibration on strength, pain, and function in poststroke rehabilitation: a pilot study. Topics in Stroke Rehabilitation 2014, 21, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casale, R.; Ring, H.; Rainoldi, A. High frequency vibration conditioning stimulation centrally reduces myoelectrical manifestation of fatigue in healthy subjects. Journal of electromyography and Kinesiology 2009, 19, 998–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prosperi, L.; Barassi, G.; Panunzio, M.; Pellegrino, R.; Marinucci, C.; Di Iulio, A.; Colombo, A.; Licameli, M.; Moccia, A.; Melchionna, M. Bio-Physics approach to urinary incontinence disabilities. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2022, 19, 12612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sancilio, S.; Nobilio, S.; Ruggiero, A.G.; Di Filippo, E.S.; Stati, G.; Fulle, S.; Bellomo, R.G.; Saggini, R.; Di Pietro, R. Effects of Focused Vibrations on Human Satellite Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2022, 23, 6026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dessy, L.A.; Monarca, C.; Grasso, F.; Saggini, A.; Buccheri, E.M.; Saggini, R.; Scuderi, N. The use of mechanical acoustic vibrations to improve abdominal contour. Aesthetic Plastic Surgery 2008, 32, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Sanctis, V.; Soliman, A.T.; Daar, S.; Tzoulis, P.; Fiscina, B.; Kattamis, C. Retrospective observational studies: Lights and shadows for medical writers. Acta Bio Medica Atenei Parm. 2022, 93, e2022319. [Google Scholar]
- Winter, E.M.; Maughan, R.J. Requirements for ethics approvals. J. Sports Sci. 2009, 27, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheatham, S.W.; Kolber, M.J.; Mokha, M.; Hanney, W.J. Concurrent validity of pain scales in individuals with myofascial pain and fibromyalgia. Journal of Bodywork and Movement Therapies 2018, 22, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alentorn-Geli, E.; Padilla, J.; Moras, G.; Haro, C.L.; Fernández-Solà, J. Six weeks of whole-body vibration exercise improves pain and fatigue in women with fibromyalgia. The Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine 2008, 14, 975–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Wang, W.; Zheng, J.; Chen, S.; Qiao, J.; Wang, X. Whole body vibration exercise for chronic musculoskeletal pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Archives of physical medicine and rehabilitation 2019, 100, 2167–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz Menek, M.; Dansuk, E.; Tayboga, U.I. Effect of Local Vibration Therapy on Pain, Joint Position Sense, Kinesiophobia, and Disability in Cervical Disc Herniation: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Journal of Clinical Medicine 2024, 13, 4566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, S.; Wang, Q.; Semeah, L.M.; Jia, H.; Lv, T.; Li, X.; Wang, R. Immediate effect of local vibration therapy for sport-induced fatigue based on traditional Chinese medicine’s holistic theory. Journal of Multidisciplinary Healthcare 2020, 13, 1993–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollins, M.; Corsi, C.; Sloan, P. Pacinian signals determine the direction and magnitude of the effect of vibration on pain. Perception 2017, 46, 987–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casale, R.; Hansson, P. The analgesic effect of localized vibration: a systematic review: Part 1: the neurophysiological basis. European Journal of Physical and Rehabilitation Medicine 2022, 58, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alashram, A.R.; Padua, E.; Romagnoli, C.; Raju, M.; Annino, G. Clinical effectiveness of focal muscle vibration on gait and postural stability in individuals with neurological disorders: A systematic review. Physiotherapy Research International 2022, 27, e1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrara, P.E.; Gatto, D.M.; Codazza, S.; Zordan, P.; Stefinlongo, G.; Coraci, D.; Lo Monaco, M.R.; Ricciardi, D.; Ronconi, G. Effects of focal muscle vibration on gait and balance in Parkinson patients: preliminary results. Applied Sciences 2022, 12, 10486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germann, D.; El Bouse, A.; Shnier, J.; Abdelkader, N.; Kazemi, M. Effects of local vibration therapy on various performance parameters: a narrative literature review. The Journal of the Canadian Chiropractic Association 2018, 62, 170. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fattorini, L.; Rodio, A.; Pettorossi, V.E.; Filippi, G.M. Is the focal muscle vibration an effective motor conditioning intervention? A systematic review. Journal of functional morphology and kinesiology 2021, 6, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barassi, G.; Prosperi, L.; Marinucci, C.; Di Iorio, A.; Panunzio, M. Focused Mechano-Acoustic Vibrations in Chronic Pain: Bio-Physico-Metric Approach, Key Trigger Points and Posture. Medical Science Pulse 2024, 18, 30. [Google Scholar]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).