Submitted:
22 October 2024
Posted:
23 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
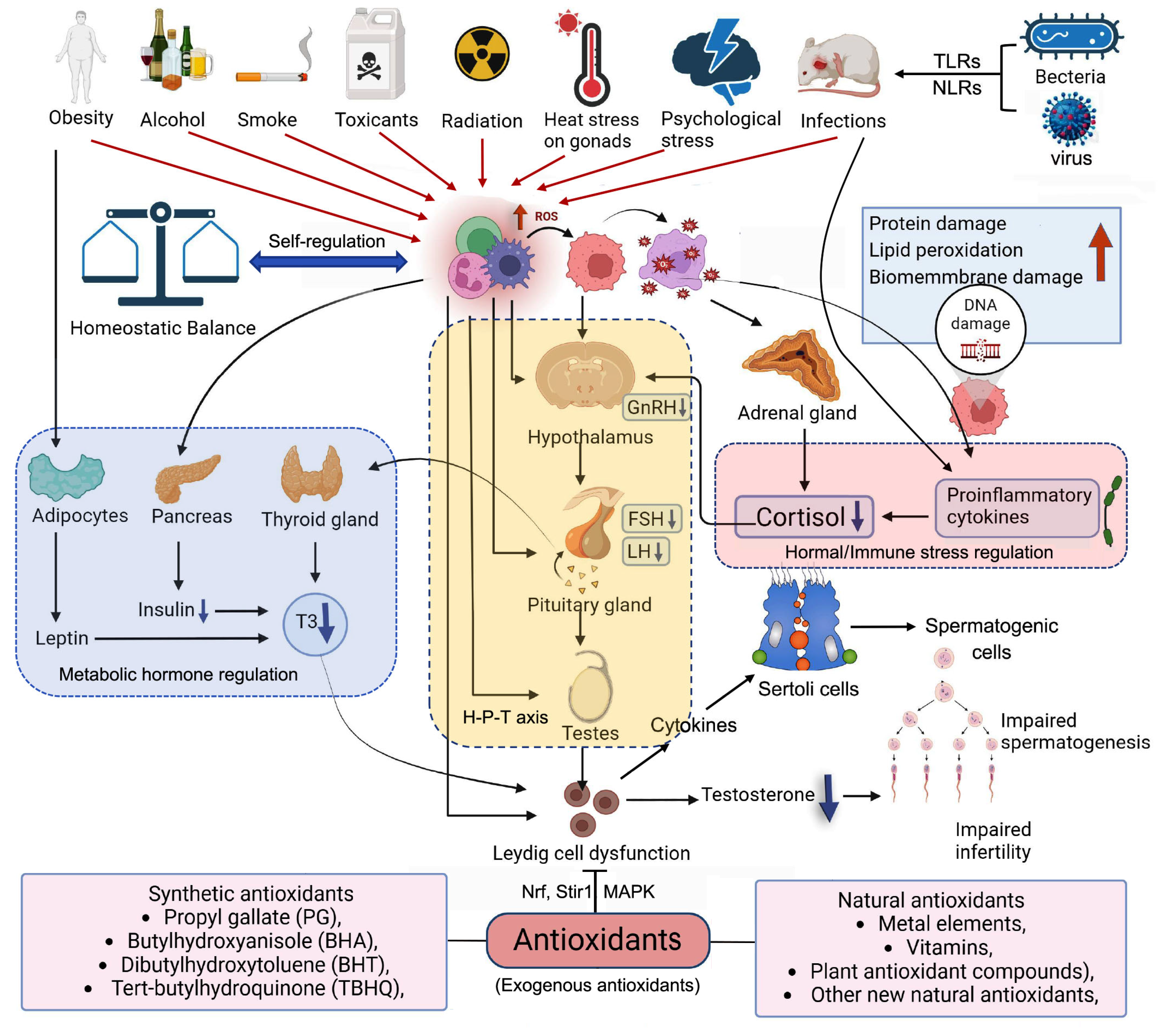
1. Pathways of ROS Production in the Organism and Potential Harm to Male Fertility
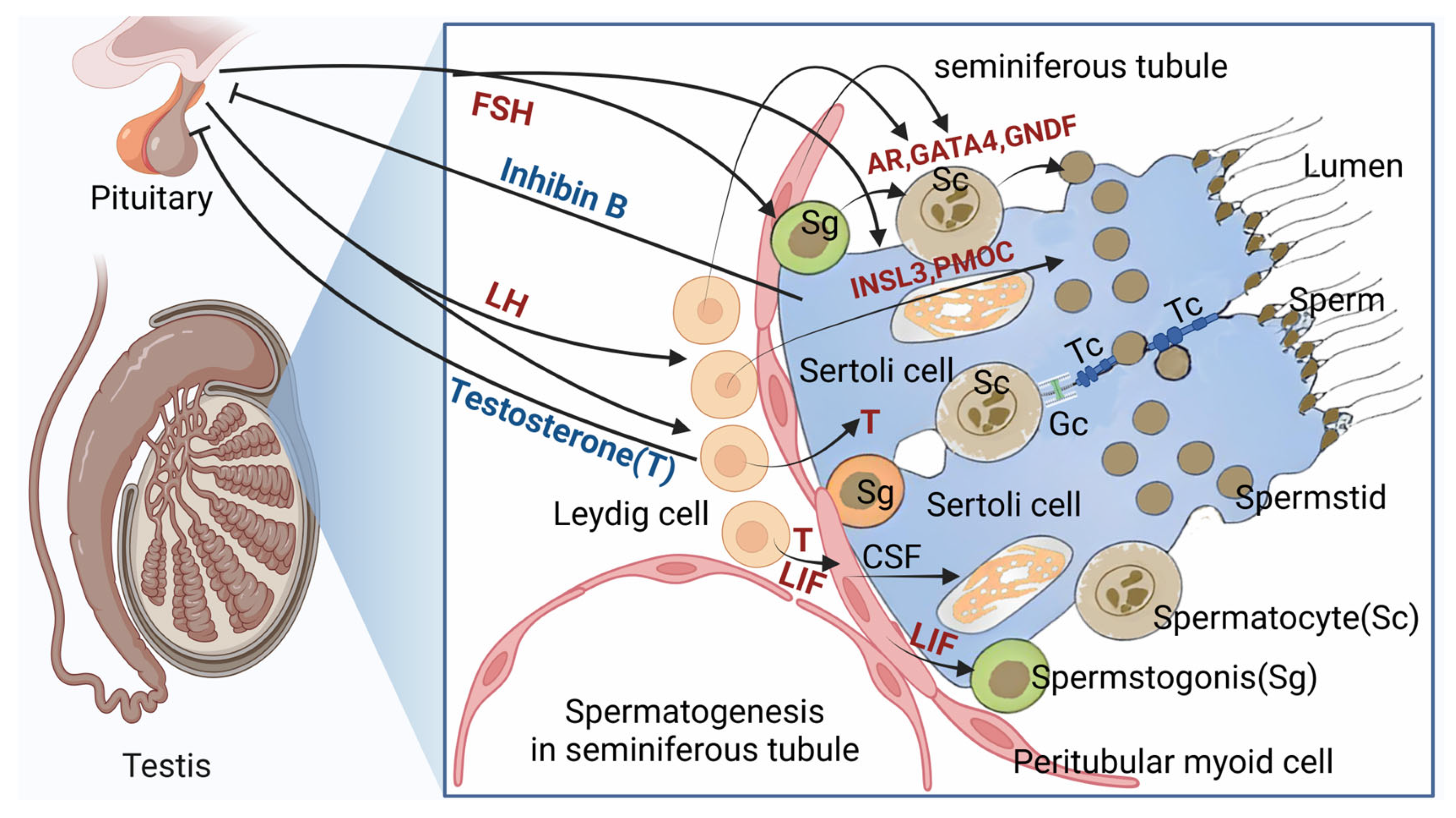
3. Function of Leydig Cells
3.1. Involvement in the Regulation of Spermatogenesis
3.2. Production of Testosterone and Indirect Regulation in Spermatogenesis
3.3. Other Factors Regulating Spermatogenesis via Leydig Cells
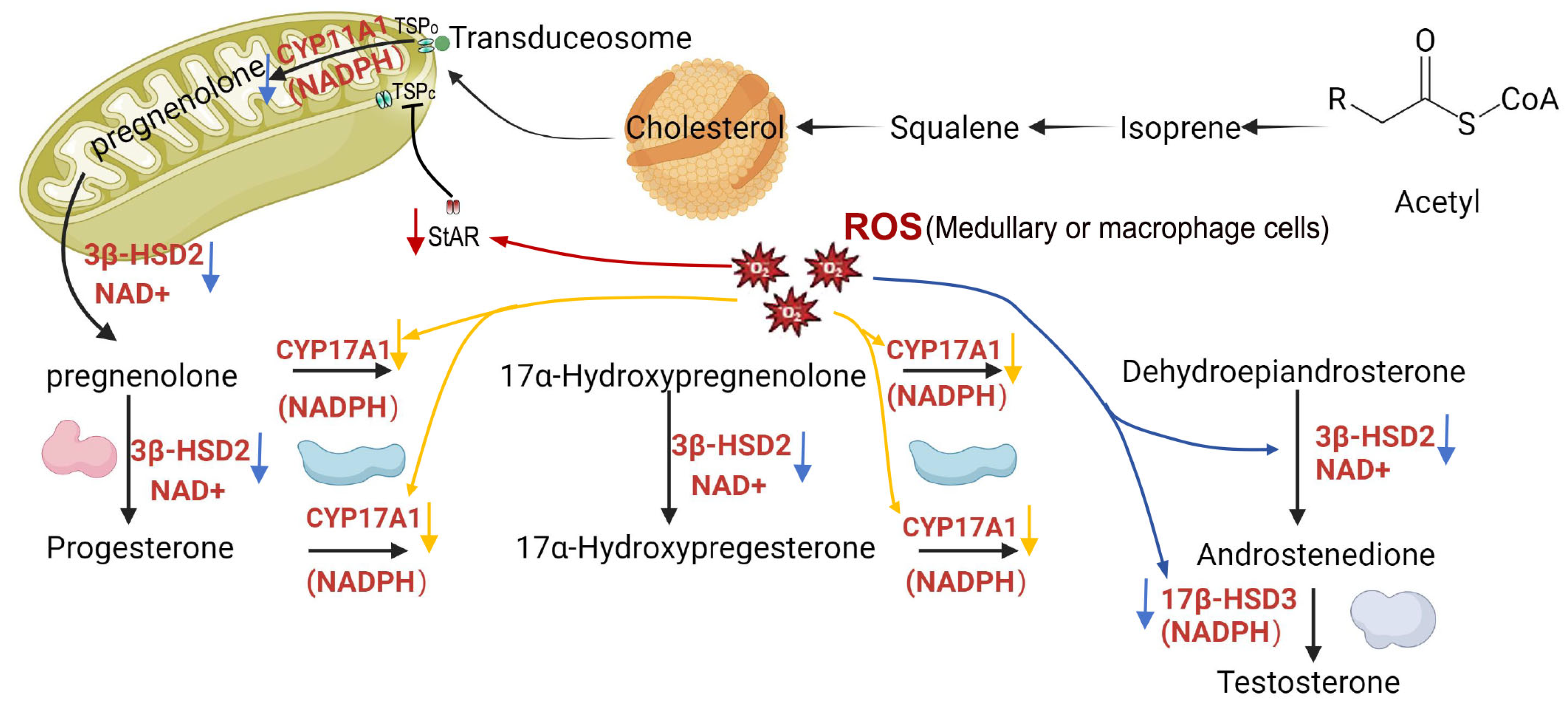
4. The Impairment of Oxidative Stress on Leydig Cell Functions
4.1. Stimulation of Leydig Cell Apoptosis
4.2. Inhibition of Testosterone Production
4.3. Other Harmful Effects
5. Current Status of Research on Antioxidant Stress Substances for Leydig Cells
5.1. Classification of Antioxidant Substances
5.2. Current Research on Antioxidant Substances against Oxidative Stress
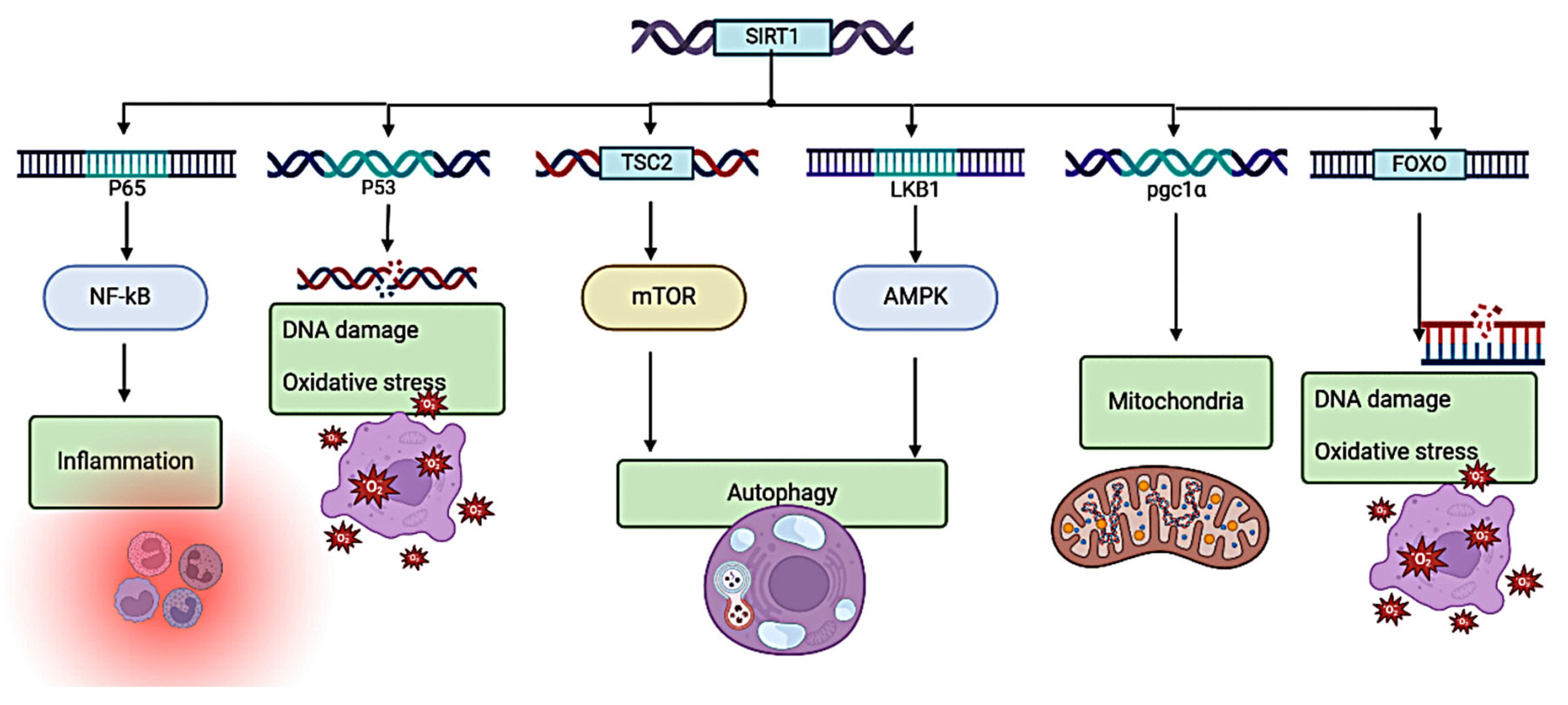
5.3. Typical Pathways against Oxidative Stress in Leydig Cell
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leisegang, K.; Henkel, R.; Agarwal, A. The in vitro modulation of steroidogenesis by inflammatory cytokines and insulin in TM3 Leydig cells. Endocrinology 2018, 16, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riris, A. A. I. D. C.; I'tishom, R.; Khaerunnisa, S.; Juliantina, F.; Qurrota, A.; Mardhiyah, M. S. Role of antioxidant to protect Leydig cells induced by reactive oxygen species, a literature review. 2021, 1.
- Shi, Z.; Feng, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Ding, L.; Dai, J. Perfluorododecanoic acid-induced steroidogenic inhibition is associated with steroidogenic acute regulatory protein and reactive oxygen species in cAMP-stimulated Leydig cells. Toxicol Sci 2010, 114, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yong, L.; Fa, W.; Zhang, R.; Liu, B. T-2 toxin induces apoptosis via the Bax-dependent caspase-3 activation in mouse primary Leydig cells. Journal of Biochemical and Molecular Toxicology.
- Agarwal, A.; Parekh, N.; Selvam, M. K. P.; Henkel, R.; Shah, R.; Kalyan, S.; Punab, M.; Sengupta, P. Male Oxidative Stress Infertility (MOSI), Proposed Terminology and Clinical Practice Guidelines for Management of Idiopathic Male Infertility. World Journal of Men's Health 2019, 37, 296–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aitken, R. J.; Smith, T. B.; Jobling, M. S.; Baker, M. A.; De Iuliis, G. N. Oxidative stress and male reproductive health. Asian Journal of Andrology 2014, 16, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, B. J.; Stocco, D. M.; Tu, H.; Manna, P. R.; Wang, X. J. Cholesterol Transporters of the START Domain Protein Family in Health and Disease. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 2015, 1851, 674–691. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, C. Y.; Wong, E. W. P.; Yan, H. H. N.; Mruk, D. D. Regulation of spermatogenesis in the microenvironment of the seminiferous epithelium, New insights and advances. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology 2010, 315, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrabi, S. S.; Parvez, S.; & Tabassum, H.; & Tabassum, H. Ischemic stroke and mitochondria: Mechanisms and targets. Protoplasma 2020, 257, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharp, J. L.; Ethridge, S. B.; Ballard, S. L.; Adkins, A. E.; Moore, B. L. The effects of chronic estradiol treatment on opioid self-administration in intact female rats. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 2021, 225, 108816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellezza, I.; Giambanco, I.; Minelli, A.; Donato, R. Nrf2-Keap1 signaling in oxidative and reductive stress. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular Cell Research 2018, 1865, 721–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zientara, A.; Dzemali, O.; Odavic, D.; Roukoz, H.; Holzhey, D.; Mohr, F. W. 158-Igiant Aneurysms of Saphenous Vein Grafts, Presentation of Two Uncommon Cases and Surgical Management. Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery 2013, 146, S107–S107. [Google Scholar]
- Cooke, P. S.; Walker, W. H. Male fertility in mice requires classical and nonclassical androgen signaling. Cell Reports 2021, 36, 109557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, X.; Siow, R. C.; Mann, G. E. Impaired redox signaling and antioxidant gene expression in endothelial cells in diabetes: A role for mitochondria and the nuclear factor-E2-related factor 2-Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 defense pathway. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling 2011, 14, 469–487. [Google Scholar]
- Zirkin BR; Papadopoulos V. Leydig cells: formation, function, and regulation. Biol Reprod.
- Manna, P. R.; Cohen-Tannoudji, J.; Counis, R.; Huhtaniemi, I.; Kraemer, F. B.; Stocco, D. M. Mechanisms of action of hormone-sensitive lipase in mouse Leydig cells, its role in the regulation of the steroidogenic acute regulatory protein. Endocrinology 2013, 154, 8505–8518. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, L.; Sun, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, C.; Hu, L.; Xie, Y. Research on the steroidogenesis of proliferated Leydig cells in vitro. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology 2013, 370, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abarikwu, S. O.; Pant, A. B.; Farombi, E. O. Effects of quercetin on mRNA expression of steroidogenesis genes in primary cultures of Leydig cells treated with atrazine. Toxicology in Vitro 2013, 27, 700–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fard, A. H. H.; Kouchesfehani, H. M.; Jalali, H. Investigation of cholestasis-related changes in characteristics of spermatogonial stem cells in testis tissue of male Wistar rats. Cell Journal (Yakhteh) 2020, 22, e13660. [Google Scholar]
- Zirkin, B.R.; Papadopoulos, V. Leydig cells: formation, function, and regulation. Biol Reprod 2018, 99, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leping, Y.; Ye, Z. J.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Xu, B.; Fan, Y.; Li, S.; Liu, C.; Wang, J.; Wang, X. Inhibitors of Testosterone Biosynthetic and Metabolic Activation Enzymes. Steroids 2011, 76, 785–794. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, R.; Wu, J.; Liu, B.; Ma, G.; Zhang, X. The roles and mechanisms of Leydig cells and myoid cells in regulating spermatogenesis. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences 2019, 76, 2681–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shima, Y.; Morohashi, K.I. Leydig progenitor cells in fetal testis. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2017, 445, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanton, P. G.; Sluka, P.; Foo, C. F. H.; Stephens, A. N.; Smith, A. I. Proteomic Changes in Rat Spermatogenesis in Response to In Vivo Androgen Manipulation; Impact on Meiotic Cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miriam, H.; Jenny, S.; Mark, J.; King, N. J. C.; Handelsman, D. J.; Allan, C. M. Sertoli and germ cell development in hypogonadal (hpg) mice expressing transgenic follicle-stimulating hormone alone or in combination with testosterone. Endocrinology 2003, 144, 509–517. [Google Scholar]
- Takada, M.; Fukuhara, D.; Takiura, T.; Nishibori, Y.; Kotani, M.; Kiuchi, Z.; Kudo, A.; Beltcheva, O.; Ito-Nitta, N.; Nitta, K.R. Involvement of GLCCI1 in mouse spermatogenesis. FASEB J 2023, 37, e22680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, W.H. Non-classical actions of testosterone and spermatogenesis. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2010, 365, 1557–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauvigné, F.; Zapater, C.; Gasol, J.M.; Cerdà, J. Germ-line activation of the luteinizing hormone receptor directly drives spermiogenesis in a nonmammalian vertebrate. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2014, 111, 1427–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liza, O. D.; Kyriakos, P.; Andrea, W.; Ulrich, G.; Müller, J.; Gabriele, L.; McLachlan, R. I.; Stanton, P. G. Transcriptional profiling of the hormone-responsive stages of spermatogenesis reveals cell-, stage-, and hormone-specific events. Endocrinology 2009, 150, 5074–5084. [Google Scholar]
- Marettová, E.; Maretta, M.; Legáth, J. Toxic effects of cadmium on testis of birds and mammals: a review. Anim Reprod Sci 2015, 155, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, S.; Wei, X.; Deng, W. Nestin-dependent mitochondria-ER contacts define stem Leydig cell differentiation to attenuate male reproductive ageing. Nat Commun 2022, 13, 4020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svechnikov, K.; Landreh, L.; Weisser, J.; Izzo, G.; Colón, E.; Svechnikov, I.; Söder, O. Origin, development and regulation of human Leydig cells. Hormone Research in Paediatrics 2010, 73, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuichi, S.; Kanako, M.; Shogo, H.; Tatsuhiko, A.; Hiroyuki, O.; Takashi, B.; Sawako, M.; Yurina, S.; Haruhiko, A.; Taro, T. Contribution of Leydig and Sertoli cells to testosterone production in mouse fetal testes. Molecular Endocrinology 2013, 27, 63–73. [Google Scholar]
- De Gendt, K.; Swinnen, J. V.; Saunders, P. T. K.; Atanassova, N.; Sharpe, R. M.; Smith, L. B.; Verhoeven, G. A Sertoli cell-selective knockout of the androgen receptor causes spermatogenic arrest in meiosis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2004, 101, 1327–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willems, A.; Roesl, C.; Mitchell, R. T.; Milne, L.; Jeffery, N.; Smith, S. Sertoli cell androgen receptor signalling in adulthood is essential for post-meiotic germ cell development. Molecular Reproduction & Development 2015, 82, 626–627. [Google Scholar]
- Welsh, M.; Saunders, P. T. K.; Atanassova, N.; Sharpe, R. M.; Smith, L. B. Androgen action via testicular peritubular myoid cells is essential for male fertility. The FASEB Journal 2009, 23, 4218–4230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O'Shaughnessy, P. J.; Verhoeven, G.; De Gendt, K.; Monteiro, A.; Abel, M. H. Direct action through the Sertoli cells is essential for androgen stimulation of spermatogenesis. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 2343–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, T.; Wang, H.; Wang, P.; Geng, L.; Mei, L.; Osakada, T.; Wang, L.; Tang, Y.; Kania, A.; Grinevich, V.; et al. A genetically encoded sensor measures temporal oxytocin release from different neuronal compartments. Nat Biotechnol 2023, 41, 944–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O'Hara, L.; Smith, L. B. Androgen receptor roles in spermatogenesis and infertility. Best Practice & Research Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism 2015, 29, 595–605. [Google Scholar]
- Knobloch, J.; Reichert, J.; Strauch, J.; Linnemann, L.; Schmidt, M.; Marienfeld, R.; Hennies, S.; Merk, H. F.; Hipfel, R.; Broëer, S. Inhibition of the androgen receptor by antisense oligonucleotides regulates the biological activity of androgens in SZ95 sebocytes. Hormone and Metabolic Research 2013, 45, 149–156. [Google Scholar]
- De Gendt, K.; Verhoeven, G.; Swinnen, J. V.; Saunders, P. T. K.; Atanassova, N.; Sharpe, R. M.; Smith, L. B. Tissue- and cell-specific functions of the androgen receptor revealed through conditional knockout models in mice. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology 2012, 352, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, L.; Chen, W.; Cheng, Z.; Wu, S.; He, J.; Han, L.; He, Z.; Qin, W. Novel Gene Regulation in Normal and Abnormal Spermatogenesis. Cells 2021, 10, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Feng, H. L.; Sandlow, J. I.; Cohen, P.; Moul, J. W.; Schiff, J. D. Comparing Expression of Progesterone and Estrogen Receptors in Testicular Tissue From Men With Obstructive and Nonobstructive Azoospermia. Journal of Andrology 2009, 30, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farghaly, L. M.; Mohamed, S. F.; Mostafa, R. M. . Expression of estrogen receptors-α in testicular biopsies from nonobstructive azoospermic patients: a histological and immunohistochemical study. Egyptian Journal of Histology 2012, 35, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, M.C.; McBeath, E. Sertoli Cell-Germ Cell Interactions Within the Niche: Paracrine and Juxtacrine Molecular Communications. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2022, 13, 897062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivell, R.; Hartung, S.; Anand-Ivell, R. Insulin-Like Factor 3, Where Are We Now? Endocrine Reviews 2014, 35, 446–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuyama, H.; Shiraishi, K.; Sano, N.; Shiraishi, K.; Iwamoto, T.; Watanabe, T.; Maruyama, H.; Uchida, K.; Makino, Y.; Okada, H. Gonadotropin actions on spermatogenesis and hormonal therapies for spermatogenic disorders. Endocrine Journal 2017, 64, 123–131. [Google Scholar]
- Herrera-Luna, C. V.; Scarlet, D.; Walter, I.; Aurich, C. Effect of stallion age on the expression of LH and FSH receptors and aromatase P450 in equine male reproductive tissues. Reproduction, Fertility and Development 2016, 28, 2016–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huhtaniemi, I. A short evolutionary history of FSH-stimulated spermatogenesis. Hormones (Athens) 2015, 14, 468–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, S. D.; Curley, C. L.; Han, Z.; Zhu, H.; Wang, R.; McMahon, S. D.; Schauer, D. B. Leukemia Inhibitory Factor-Receptor is Dispensable for Prenatal Testis Development but is Required in Sertoli cells for Normal Spermatogenesis in Mice. Scientific Reports 2018, 8, 11532. [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey, M.S.; Friedman, L.N. Tuberculosis and Biologic Therapies: Anti-Tumor Necrosis Factor-α and Beyond. Clin Chest Med 2019, 40, 721–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, L.; Kowalewski, M.; Reichler, I. M.; Boos, A.; Kowalewski, M. P.; Reichler, I. G.; Gram, A.; Reichler, I. B. Different expression of leptin and IGF1 in the adult and prepubertal testis in dogs. Reproduction in Domestic Animals 2017, 52, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, M. J.; Berger, T.; Roser, J. F. Localization of insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) and IGF-I receptor (IGF-IR) in equine testes. Reproduction in Domestic Animals 2011, 46, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorji, L.; Ohkubo, T.; Miyoshi, K.; Maeda, T.; Fukui, Y. Gene Expression Differences in Oocytes Derived From Adult and Prepubertal Japanese Black Cattle during In Vitro Maturation. Reproduction in Domestic Animals 2011, 46, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Z.; Fan, T.; Xiao, C. TGF-β signaling in health, disease, and therapeutics. Signal Transduct Target Ther 2024, 9, 61. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Weng, B.; Ran, M.; Chen, B.; He, C.; Dong, L.; Peng, F. Genome-wide analysis of long non-coding RNAs and their role in postnatal porcine testis development. Genomics 2017, 109, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lecker, L.S.M.; Berlato, C.; Maniati E; Delaine-Smith R. ; Pearce O.M.T.; Heath O.; Nichols S.J.; Trevisan C.; Novak M.; McDermott J.; Brenton J.D.; Cutillas P.R.; Rajeeve V.; Hennino A.; Drapkin R.; Loessner D.; Balkwill F.R. TGFBI Production by Macrophages Contributes to an Immunosuppressive Microenvironment in Ovarian Cancer. Cancer Res 2021, 81, 5706–5719. [Google Scholar]
- Chauvigné, F. O.; Parhi, J.; Ollé, J.; Peñaranda, D. S.; Weltzien, F. A.; Wong, T. T.; Pérez, L.; Alvarado, M. V. Dual estrogenic regulation of the nuclear progestin receptor and spermatogonial renewal during gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata) spermatogenesis. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part A, Molecular & Integrative Physiology.
- Wang, Y.; Chen, F.; Ye, L.; Xu, Y.; Li, H.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, X. Steroidogenesis in Leydig cells, effects of aging and environmental factors. Reproduction 2017, 154, R111–r122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, B. C.; Okuyama, M. W.; Müller, K.; Ulrich, R.; Rindler, T.; Lux, F.; Eulenburg, V.; Gärtner, U. Steroidogenic enzymes, their products and sex steroid receptors during testis development and spermatogenesis in the domestic cat (Felis catus). Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 2018, 178, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buehr, M.; McLaren, A.; Bartley, A.; Darling, S.; Wylie, C. Proliferation and migration of primordial germ cells in We/We mouse embryos. Cell and Tissue Research 2010, 361, 697–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Ge, R.S.; Zirkin, B.R. Leydig cells: from stem cells to aging. Mol Cell Endocrinol 2009, 306, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beattie, M.; Chen, H.; Fan, J.; Papadopoulos, V.; Miller, P.; Zirkin, B.R. Aging and luteinizing hormone effects on reactive oxygen species production and DNA damage in rat Leydig cells. Biol Reprod 2013, 88, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Y. S.; Song, S. Y.; Sohn, H. E.; Ahn, H. C.; Kim, J. Y.; Choe, Y. S.; Suh, Y. H.; Moon, Y. S.; Kim, J. H.; Song, J. H. Expression of cubilin in mouse testes and Leydig cells. Andrologia 2015, 48, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Wang, X.; Duan, Y.; Li, K.; Ren, Y. Antagonistic effects of selenium on lead-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis of Leydig cells in sheep. Theriogenology 2022, 185, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groeger, G.; Quiney, C.; Cotter, T. G. Hydrogen peroxide as a cell-survival signaling molecule. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling 2009, 11, 2655–2671. [Google Scholar]
- Morielli, T.; O'Flaherty, C. Oxidative stress impairs function and increases redox protein modifications in human spermatozoa. Fertility and Sterility 2015, 103, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jian, Z.; Lingling, Z.; Zheng, L.; Rui, Y.; Xiaoyan, W.; Qiyuan, Y. Leptin level and oxidative stress contribute to obesity-induced low testosterone in murine testicular tissue. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity 2014, 2014, 190945. [Google Scholar]
- Vladimir, E.; Anna, M.; Anatoly, V.; Natalia, V.; Pavel, S. Formation of long-lived reactive species of blood serum proteins induced by low-intensity irradiation of helium-neon laser and their involvement in the generation of reactive oxygen species. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology B, Biology.
- Recknagel, R. O.; Glende, E. A.; Britton, R. S. Free Radical Damage and Lipid Peroxidation. Hepatotoxicology 2020, 2, 165–196. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, T.; Deng, T.; Wang, L.; Jing, W.; Wang, R. Damaged spermatogenic cells induce inflammatory gene expression in mouse Sertoli cells through the activation of Toll-like receptors 2 and 4. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology 2013, 365, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winters, S. J.; Moore, J. P.; Clark, B. J. Leydig cell insufficiency in hypospermatogenesis, a paracrine effect of activin–inhibin signaling? Andrology 2018, 6, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.; Sampath, H. Mitochondrial DNA Integrity, Role in Health and Disease. Cells 2019, 8, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanukoglu, I. Antioxidant Protective Mechanisms against Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Generated by Mitochondrial P450 Systems in Steroidogenic Cells. Drug Metabolism Reviews 2017, 49, 88–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, L.; Latendresse, J. R.; Muskhelishvili, L.; Ton, T. V.; Bishop, J. B.; Delclos, K. B. Effects of acrylamide exposure on serum hormones, gene expression, cell proliferation, and histopathology in male reproductive tissues of Fischer 344 rats. Toxicology Letters 2012, 211, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midzak, A. S.; Akula, N.; Huang, X.; Papadopoulos, V. Mitochondrial regulation of Leydig cell steroid synthesis. Implications for the decline in male testosterone production with advancing age. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology 2009, 300, 89–96. [Google Scholar]
- Monageng, E.; Offor, U.; Takalani, N. B.; Makgotlho, E.; Ngole, E. M.; Shai, L. J.; Aigbe, F. R.; Omoruyi, S. I.; Oladimeji, O.; Obi, P. A. A Review on the Impact of Oxidative Stress and Medicinal Plants on Leydig Cells. Antioxidants (Basel) 2023, 12, 1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, T.; Hu, G.; Dong, B.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, W.; Li, Y.; Yang, F.; Chen, Z. Roscovitine protects murine Leydig cells from lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation. Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine 2017, 13, 2169–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, X.J.; Chen, J.B.; Cao, J.P.; Li, X.; Sun, C.D. Citrus flavonoids and their antioxidant evaluation. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 2022, 62, 3833–3854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Yu, H.; Zhuang, J.; Lu, Y.; Wang, Z. Elemental selenium at nano size possesses lower toxicity without compromising the fundamental effect on selenoenzymes, comparison with selenomethionine in mice. Free Radical Biology and Medicine 2007, 42, 1524–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X. T.; Ding, C.; Zhou, N.; Xu, W.; Li, J.; Luo, Y.; Wu, X. Quercetin protects gastric epithelial cell from oxidative damage in vitro and in vivo. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry 2015, 116, 754–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, N.; Wang, T.; Gan, Q.; Liu, S.; Wang, L.; Jin, B.; Chen, Z.; Hu, H.; Huang, J.; Lu, Z. Plant flavonoids, Classification, distribution, biosynthesis, and antioxidant activity. Food Chemistry 2022, 383, 132531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asensi-Fabado, M. A.; Munne-Bosch, S. Vitamins in plants, occurrence, biosynthesis and antioxidant function. Trends in Plant Science 2010, 15, 582–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmitt, D. J.; Bitencourt, S.; da Silva, G. R.; da Silva, B. S.; Correa, M. C.; Goncalves, W. F.; Cunha, M. E.; Bresciani, T.; Gasperin, B. G.; Dalsenter, P. R. Traditional plants with antioxidant properties in clinical trials-A systematic review. Phytotherapy Research 2021, 35, 5647–5667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, S. A.; Asad, M.; Abdelsalam, K. E. A.; Saeed, M. M.; Majid, S.; Al-Sheikh, Y. A.; Bukhari, S. I.; Siddiq, A.; Alroqi, F. R. Frankincense extract protects against testicular damage through augmentation of antioxidant defense mechanisms and modulation of apoptotic genes expression. Scientific Reports 2022, 12, 12625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, N. K.; Parama, D.; Banik, K.; Bordoloi, D.; Devi, A. K.; Thakur, K. K.; Padmavathi, G.; Venugopal, R.; Fan, L.; Sethi, G. An Update on Pharmacological Potential of Boswellic Acids against Chronic Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2019, 20, 4101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okano, S.; Honda, Y.; Kodama, T.; Yasuda, M.; Masuko, K.; Tanaka, M.; Morimoto, C.; Sakagami, H.; Hatano, T.; Nakano, M. The Effects of Frankincense Essential Oil on Stress in Rats. Journal of Oleo Science 2019, 68, 1003–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M. Y.; Zhu, X. L.; Zhao, B. X.; Wang, H. X.; Cheng, W. J.; Wei, H. Adrenomedullin alleviates the pyroptosis of Leydig cells by promoting autophagy via the ROS-AMPK-mTOR axis. Cell Death & Disease 2019, 10, 489. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, F.; Li, G.; Liu, C.; Gao, L.; Wang, H.; Liu, W.; Ding, Z. Autophagy regulates testosterone synthesis by facilitating cholesterol uptake in Leydig cells. Journal of Cell Biology 2018, 217, 2103–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Song, A.; Hu, W.; Dai, M.; Hou, C.; Jin, Y.; Xia, W.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Z.; Song, X. The Anti-atherosclerotic Effect of Paeonol against Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Proliferation by Up-regulation of Autophagy via the AMPK/mTOR Signaling Pathway. Frontiers in Pharmacology 2017, 8, 948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.; Shi, L.; Li, M. Y.; Zhang, L. N.; Cheng, W. J.; Wei, H. Adrenomedullin protects Leydig cells against lipopolysaccharide-induced oxidative stress and inflammatory reaction via MAPK/NF-κB signalling pathways. Scientific Reports 2017, 7, 16479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Fang, Y.; Tang, D.; Kang, R.; Yao, X.; Meng, X.; Xiao, X. Activation of MT1/MT2 to Protect Testes and Leydig Cells against Cisplatin-Induced Oxidative Stress through the SIRT1/Nrf2 Signaling Pathway. Cells 2022, 11, 1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; He, X.; Zhuang, M.; Niu, R.; Song, Y.; Shen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zou, W. Melatonin Ameliorates Busulfan-Induced Spermatogonial Stem Cell Oxidative Apoptosis in Mouse Testes. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling 2018, 28, 385–400. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, Y.; Li, J.; He, S. Zinc Protects against Heat Stress-Induced Apoptosis via the Inhibition of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in TM3 Leydig Cells. Biological Trace Element Research 2022, 200, 728–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.; Liu, X.; Pan, Z.; Xia, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Zheng, Y.; Yu, Z. Zinc deficiency and cellular oxidative stress, prognostic implications in cardiovascular diseases. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica 2018, 39, 1120–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, H. O.; Teixeira, F. J. Use of medicinal doses of zinc as a safe and efficient coadjutant in the treatment of male hypogonadism. Aging Male 2020, 23, 669–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, M. S.; Wajner, S. M.; Maia, A. L. The role of thyroid hormone in testicular development and function. Journal of Endocrinology 2008, 199, 351–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O'Shaughnessy, P.J.; Monteiro, A.; Verhoeven, G.; De Gendt, K.; Abel, M.H. Effect of FSH on testicular morphology and spermatogenesis in gonadotrophin-deficient hypogonadal mice lacking androgen receptors. Reproduction.
- Gao Y, Lee WM, Cheng CY. Thyroid hormone function in the rat testis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2014, 5, 188. [Google Scholar]
- Manna, P. R.; Kero, J.; Tena-Sempere, M.; Pakarinen, P.; Stocco, D. M.; Huhtaniemi, I. Regulation of the steroidogenic acute regulatory protein, steroidogenesis, and luteinizing hormone receptor function by thyroid hormone in mouse Leydig cells. Endocrinology 2001, 142, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanna, S.; Mitra, S.; Lakhera, P. C.; Sen, P. N-acetylcysteine effectively mitigates cadmium-induced oxidative damage and cell death in Leydig cells in vitro. Drug and Chemical Toxicology 2016, 39, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, S.; Lin, S.; Li, L.; Lu, X.; Chen, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, R.; Wang, H. Melatonin ameliorates diabetic hyperglycaemia-induced impairment of Leydig cell steroidogenic function through activation of SIRT1 pathway. Reproductive Biology and Endocrinology 2022, 20, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balmik, A. A.; Chinnathambi, S. Multi-Faceted Role of Melatonin in Neuroprotection and Amelioration of Tau Aggregates in Alzheimer’s Disease. Journal of Alzheimer's Disease.
- Matos, M. H.; Jenny, S.; Mark, J.; King, N. J. C.; Handelsman, D. J.; Allan, C. M. Melatonin protects against cisplatin-induced ovarian damage in mice via the MT1 receptor and antioxidant activity. Biology of Reproduction 2017, 96, 1244–1255. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, H.; Lee, O. H.; Lee, Y.; Kwon, J. Melatonin prevents cisplatin-induced primordial follicle loss via suppression of PTEN/AKT/FOXO3a pathway activation in the mouse ovary. Journal of Pineal Research 2016, 60, 336–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; He, X.; Zhuang, M.; Niu, R.; Song, Y.; Shen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zou, W. Melatonin Ameliorates Busulfan-Induced Spermatogonial Stem Cell Oxidative Apoptosis in Mouse Testes. Reproductive Sciences 2017, 24, 240–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jambor, T.; Zajickova, T.; Arvay, J.; Kisucka, L.; Ondicova, K.; Lovasova, E.; Capcarova, M. Exceptional Properties of Lepidium sativum L. Extract and Its Impact on Cell Viability, ROS Production, Steroidogenesis, and Intracellular Communication in Mice Leydig Cells In Vitro. Molecules 2022, 27, 5146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, X.; Cao, M.; Song, X.; Zhu, W.; Liu, Y.; Wei, X.; Feng, Z. Resveratrol promotes recovery of immune function of immunosuppressive mice by activating JNK/NF-κB pathway in splenic lymphocytes. Canadian Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology 2017, 95, 763–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donald, E. L.; Stojanovska, L.; Apostolopoulos, V.; Nurgali, K. Resveratrol alleviates oxidative damage in enteric neurons and associated gastrointestinal dysfunction caused by chemotherapeutic agent oxaliplatin. Maturitas 2017, 105, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y. H.; Zhou, L. Y.; Chen, Q. Z.; Yang, Y. J.; Liu, L. Resveratrol inactivates PI3K/Akt signaling through upregulating BMP7 in human colon cancer cells. Oncology Reports 2017, 37, 3572–3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maier-Salamon, A.; Böhmdorfer, M.; Thalhammer, T.; Reznicek, G.; Kunert, O.; Szekeres, T.; Riha, J.; Jaeger, W. Hepatic Glucuronidation of Resveratrol, Interspecies Comparison of Enzyme Kinetic Profiles in Human, Mouse, Rat, and Dog. Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics 2011, 26, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalantari, H.; Das, D. K. Physiological effects of resveratrol. Biofactors 2010, 36, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emilia, J. M.; Eulalia, G. P.; Thais, M.; Manuel, C.; María, M. G.; Mariana, M.; Marta, R. F. trans-Resveratrol, a natural antioxidant from grapes, increases sperm output in healthy rats. Journal of Nutrition 2010, 140, 757–763. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Q.; Xiong, Q.; Zhou, M.; Tian, X.; Yue, K.; Li, Y.; Shu, X.; Ru, Q. Resveratrol attenuates methamphetamine-induced memory impairment via inhibition of oxidative stress and apoptosis in mice. J Food Biochem 2021, 45, e13622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ourique, G. M.; Finamor, I. A.; Saccol, E. M. H.; Schneider, J. A.; Gutierrez, K.; Ferreira, M. R. Resveratrol improves sperm motility, prevents lipid peroxidation and enhances antioxidant defenses in the testes of hyperthyroid rats. Reproductive Toxicology 2013, 37, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucak, M. N.; Tuncer, P. B.; Sariözkan, S.; Ulutas, P. A.; Akcay, E.; Tekin, N.; Buyukleblebici, S.; Tasdemir, U.; Coyan, K. Lycopene and resveratrol improve post-thaw bull sperm parameters, sperm motility, mitochondrial activity and DNA integrity. Andrologia 2014, 46, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Sun, Q.; Li, Z. Resveratrol protects Leydig cells from nicotine-induced oxidative damage through enhanced autophagy. Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology and Physiology 2017, 44, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marti, N.; Bouchoucha, N.; Sauter, K. S.; Flück, C. E. Resveratrol inhibits androgen production of human adrenocortical H295R cells by lowering CYP17 and CYP21 expression and activities. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svechnikov, K.; Spatafora, C.; Svechnikova, I.; Tringali, C.; Söder, O. Effects of resveratrol analogs on steroidogenesis and mitochondrial function in rat Leydig cells in vitro. Journal of Applied Toxicology 2010, 30, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, E. C. B.; Cajueiro, J. F. P.; Silva, S. V.; Soares, P. C.; Guerra, M. M. P. Effect of antioxidants resveratrol and quercetin on in vitro evaluation of frozen ram sperm. Theriogenology 2012, 77, 1722–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y. C.; Nagpal, M. L.; Stocco, D. M.; Lin, T. Effects of genistein, resveratrol, and quercetin on steroidogenesis and proliferation of MA-10 mouse Leydig tumor cells. Journal of Endocrinology 2007, 192, 527–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, M. Z.; Shen, Y.; Tang, R.; Xiao, L.; Zhao, J. Lycopene Prevents DEHP-Induced Leydig Cell Damage with the Nrf2 Antioxidant Signaling Pathway in Mice. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 2020, 68, 2031–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Liu, J.; Luo, L.; Baumbach, G. L.; Shi, R.; Zirkin, B. R. Vitamin E, aging and Leydig cell steroidogenesis. Experimental Gerontology 2005, 40, 728–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omolaoye, T. S.; Cyril, A. C.; Radhakrishnan, R.; Adegoke, E. O.; Otulana, J. O.; Du Plessis, S. S. The Effect of Statins on Male Reproductive Parameters, A Mechanism Involving Dysregulation of Gonadal Hormone Receptors and TRPV1. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2023, 24, 10322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Zhang, A.; Sun, Y.; Wei, X.; Zhu, X.; Jin, Y.; Wang, L. Sirt1 exerts anti-inflammatory effects and promotes steroidogenesis in Leydig cells. Fertility and Sterility 2012, 98, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cormier, M.; Ghouili, F.; Roumaud, P.; Martin, L. J. Influences of flavones on cell viability and cAMP-dependent steroidogenic gene regulation in MA-10 Leydig cells. Cell Biology and Toxicology 2018, 34, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, H.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, H.; Li, B.; Wang, Z.; Li, D.; Jin, Y. Alpha-naphthoflavone attenuates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in oleic acid-treated HepG2 hepatocytes and in high fat diet-fed mice. Biomed Pharmacother 2019, 118, 109287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Receptors/ Cytokines |
Species | Characteristic | cited document |
| AR | Humans, Rats, Dogs | Synergizes with androgens to regulate spermatogenesis | [36,38,39,40,41] |
| ER | Human, Rat | Maintains sperm count and function | [42,43,44] |
| LGRS | Rats | Facilitates the stimulatory effect of INSL3 on cAMP production during spermatogenesis. | [45,46] |
| OTR | Human, monkey | Modulates oxytocin levels within the male reproductive tract. | [38] |
| LHR | Human, rat, flounder | Synergizes with LH to promote testosterone production | [47] |
| FSHR | Human, Rat, Stallion | Mediates the effects of follicle stimulating hormone on spermatogenesis | [47,48,49] |
| LIFR | Rats | Maintenance of germ cell numbers, sperm motility, seminiferous tubule structure and steroid formation | [50] |
| TNFR | Rats | Harmonizes spermatogenesis | [51] |
| IGFR | Rats, Horses, Dogs | Regulates testicular function and germ cell development | [52,53,54] |
| TGF-βR | Human, Rat, Boar | Controls meiosis and early spermatogenesis | [55,56,57] |
| PGR | Humans, cats, sea bream | Regulates the role of progesterone in spermatogenesis | [58,59,60] |
| KIT | Rats | Promotes proliferation, migration and postnatal spermatogenesis of primordial germ cells | [61,62,63] |
| Cubn | Rats | Facilitates endocytosis and nutrient uptake in both germ cells and somatic cells, essential for the sustenance of spermatogenesis. | [64] |
| Source | Species | Characteristic | Reference |
| Synthetic antioxidants | Propyl gallate (PG), Butylhydroxyanisole (BHA), Dibutylhydroxytoluene (BHT), tert-butylhydroquinone (TBHQ), |
Although it has a strong antioxidant capacity, it is capable of producing hydrogen peroxide at physiological pH and temperature. Hydrogen peroxide itself is highly oxidizing and quite toxic to cells. | [80] |
| Natural antioxidants | Metal elements: copper, iron, zinc and manganese | They are cofactors of a series of important antioxidant enzymes, binding with enzymes to make enzymes with strong catalytic activity, by catalyzing superoxide radicals, thus eliminating ROS and preventing their damage to proteins, DNA and lipids. | [81,82] |
| Vitamins: Mainly vitamins A, B, C, E and K. | It not only has strong antioxidant ability, but also has a good protective effect on the structure of biological membranes. | [83,84] | |
| plant antioxidant compounds: mainly polysaccharides, alkaloids, polyphenols, flavonoids and saponins five kinds of compounds. | [85,86,87,88,89,90,91] [92,93] |
||
| Other new natural antioxidants: Astaxanthin and antioxidant peptides | Antioxidant substances capable of traversing the blood-brain barrier can neutralize free radicals within the body, thereby rejuvenating cellular function and promoting overall organism vitality. | [94,95,96] |
| Antioxidant | Oxidative inducer | Animals | Effect | Pathway | Reference | |
| In Vivo Experiments | Adrenomedullin, N-Acetylcysteine |
LPS | Rats | Promoted cellular autophagy and attenuated focal death of LPS-exposed leydig cells | ROS-AMPK -mTOR |
[88,101] |
| Adrenomedullin, N-Acetylcysteine |
LPS | Rats | Reduction of LPS-induced ROS overproduction | MAPK / NF-κB |
[78,79,88,101] | |
| Melatonin | Cis-platinum | Mouse | Through the MT1/MT2 melatonin receptors, melatonin modulates the Sirt1/Nrf2 signaling axis, serving as a pivotal protective agent against cisplatin-induced apoptosis in mouse mesangial cells. | Sirt1 / Nrf2 |
[92,102,103,104,105,106] | |
| Lepidium sativum L | Aluminum oxide | Rats | Significantly reduced levels of ROS production and increased sperm motility and viability in mice | — | [107] | |
| Resveratrol | H2O2 | Mice | Resveratrol safeguards against H2O2-triggered oxidative stress, thereby mitigating the decline in Leydig cell viability and functional proficiency. Lower concentrations of resveratrol had cytoprotective effects on oxidatively stressed leydig cells. | Nrf2- ARE |
[108,109,110,111,112,113,114,115,116,117,118,119,120,121] | |
| Lycopene | Diethylphosphite | Mice | Lycopene is capable of enhancing antioxidant potential by modulating the Nrf2 signaling pathway, subsequently alleviating DEHP-induced damage to Leydig cells. | Nrf2 pathway |
[122] | |
| Cellular experiments | Vitamin E | Environment | Rats | Vitamin E exhibits a notable protective effect against oxidant-mediated lipid peroxidation in cultured Leydig cells, as well as preserving the cells' capacity to produce testosterone in vitro. | — | [123] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





