Submitted:
23 October 2024
Posted:
24 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Definition of Ultra-Central Tumors
3. State of the Art for SBRT for Ultra-Central Tumors
| First Author and year [reference] | Sample size (treatment years) |
Type | Definition of Ultra-Central |
Primary Lung cancer pts | Met pts | Fractions*dose per fraction | Median tumor max D or GTV volume | Median FuP (mo) | SBRT technique |
Main Results and comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Swaminath, 2024 [32] |
23 pts (2014 – 2020) |
Phase III (RCT conventional RT vs SBRT, not stratified for UC tumors) | Tumors abutting PBT or mediastinal organs | 23 (100%) | 0 | 8*7,5 Gy | 25 mm (general population) | 36,1 | 3DCRT, VMAT, IMRT, CK allowed |
3-ys LC 87.6%, EFS 49,1%, OS 63,5% (overall SBRT population). 1 (4,3%) late (12 months) G5 hemoptysis in a tumor abutting proximal bronchus. 4 (17,4%) G≥3 TRAEs. No dosimetry issues according to protocol were found in G5 event. |
| Giuliani, 2024 [31] |
30 pts (2018-2021) |
Phase I | PTV touches or overlaps the central bronchial tree, esophagus, pulmonary vein, or pulmonary artery | 30 (100%) | 0 | 8*7,5 | 26 mm | 36 | 3DCRT, VMAT, CK allowed | 3-ys OS 72.5%, PFS 66.1%, LC 89.6%, RC 96.4%, and DC 85.9%. 6.7% G3-5 TRAEs: 1 G3 dyspnea and 1 G5 pneumonia. PTV Dmax limited to 120%; tumors with endobronchial invasion were excluded. |
| Levy, 2024 [30] |
6/31 pts UC (2015-2017) |
Phase II | GTV ≤1cm from trachea or mainstem bronchi; central: ≤2 cm from PTB or immediately adjacent to pericardial or mediastinal pleura | 6 (100%) | 0 | 8*7,5 | 26 mm | 43 | IMRT, VMAT, Tomotherapy allowed | 3-ys cumulative rate of LP 6,7%. 3-ys PFS and OS 81.5% and 61.1%. 16,1% G≥3 and 3,2% G5 (pneumonitis) early AEs. 58.1% G≥3 and 3.2% G5 (hemoptysis after bronchoscopy) late AEs. |
| Rim, 2024 [41] |
20 (2017-2021) |
Retrospective | Tumor abutting or invading PTB. | 20 (100%); 2 recurrents, 1 SCLC. |
0 | 10*4,5 (5%) 10*5-6 (95%) |
35 mm | 15,8 | IMRT, VMAT | 1-y and 2-ys OS rates were 79.4% and 62.4%, 1-y and 2-ys LC rates were 87.1% and 76.2%. 1 (5%) G≥3 AE = G5 hemoptisis (patient with endobronchial involvement) = 5%. Dmax <110% |
| Bryant, 2024 [42] |
14 (2019-2021) |
Retrospective | GTV ≤1cm from trachea or mainstem bronchi | 9 (64,3%) | 5 (35,7%) |
8*7,5Gy | 17,8 cc | 17,2 | IMRT MRI-guided |
2-ys LC, LFFS, OS, and PFS rates were 92.9%, 85.7%, 92.9%,and 64.3% No acute or late G≥3 AEs. Adaptive plan permitted PBTDmax of 5,7 Gy and GTV D95% at 99,8%. Hotspots ≤120%. |
| Li, 2024 [38] |
154 (2009-2019) |
Retrospective | PTV abutting or overlapping central bronchial tree or esophagus |
32 (20%) treated in curative setting |
122 (80%) | 5*10 most common (42%) 5*6-11 (median 9) |
27 mm | 21,5 | IMRT, VMAT | mOS 44 months, mPFS 8.8 months. 3-ys LC 86%. G3 acute AEs = 3%, 2 esophagitis, 1 atrial fibrillation, 1 pericarditis, 1 pleural effusion. G≥3 late AEs = 4,9%, 3 G3 pneumonitis, 1 G3 chest wall pain, 1 G3 bronchopleural fistula; 1 G4 esophagitis, 1 G4 bronchial obstruction; 1 G5 pneumonitis. Tumor volume overlapping with esophagus correlated with worse LC. Predictors of severe toxicity = PTV size, decreased PTV V95%, lung V5 Gy, and lung V20 Gy. |
| Lee, 2024 [54] |
19 (2019-2022) |
Retrospective | GTV abutting PTB, esophagus or great vessels. GTV ≤2 cm from PTB and mediastinum considered central. | 0 | 19 (100%) | 5*7-12 (median 10) | NR | 19 | IMRT MRI-guided adaptive RT | 1-y and 2-ys LC was 94% and 86%. Median time to distant recurrence 6,6 months. 32% G2 acute toxicities, no other AEs. Plan adapted with isotoxic approach. Re-optimization showed better PTV coverage than original plan. 85% patients had immune and TKI therapy <1 months before SBRT. VEGFRi held >4 weeks before. |
| Ahmadsei, 2023 [52] |
60 (2014-2021) |
Retrospective | PTV overlapping or abutting the PBT, trachea or esophagus | 27 (45%) | 33 (55%) | 8*5-6 Gy 10*4,5-5Gy |
30-70 mm for 66,7% patients. | 26,4 | VMAT | 2-ys OS 65,9% 1-y and 2-ys LC 84,4% and 76,8% 2-ys DC 45% 3% G≥3 Aes: 1 G3 and G4 pneumonitis. 20% cardiovascular events at 2 years: 10% valvopathy, 8,3% atrial fibrillation. Hypothetic association between dose to pulmonary artery and superior cava vein and non-cancer related deaths. No other cardiac substructures dosimetry concerns. |
| Iovoli, 2023 [88] |
49/93 UC pts (2007-2021) | Retrospective | Directly abutting any of proximal airway, mediastinum, great vessels, spinal cord. ≤2 cm categorized as central |
93 (100%) | 0 | 5*10-12 Gy | NR | 32,4 | 3DCRT, VMAT | SAN Dmax and Dmean significantly associated with worse OS with cut-off values of 1309 and 836cGy. |
| Lindberg, 2023 [29] |
230 pts/238 lesions (2010-2018) |
Phase II (65 pts) + retrospective series (165 pts) | UC (groups A,B,D) 1-cm zone around the carina, main bronchi, intermedius bronchus, and lobar bronchi (i.e., the PBT) C (group C): 1-2 cm around the PBT |
196 (77%) | 54 (23%) | 8*7 Gy | 35 mm | 24 (phase II series, nr for overall cohort) | VMAT | 1-y, 3-ys and 5-ys LC rates at were 92%, 84% and 78%. 1-y, 3-ys and 5-ys OS rates were 78%, 40% and 27%. G 3-4 toxicity in 15% pts, and 13% (30pts) had G5 tox (20 hemoptysis, 7 pneumonia, 2 cardiac failures, 1 COPD). Tumor compression of PBT and high maximum dose to the mainstem or intermediate bronchus increased the risk of fatal toxicity. |
| Song, 2023 [46] |
27 pts (2013-2018) |
Retrospective | PTV touching or overlapping the central bronchial tree, esophagus, or pulmonary artery | 27 (100%); 4 recurrent | 0 | 10*6 Gy 7*8 Gy |
37 mm | 41 | IMRT | mOS and mPFS 48 months and 36 months. G≥3 AEs in 5 pts (18,5%): 1 G3 pneumonitis, 2 G3 bronchial obstructions, 1 G5 bronchial obstruction, 1 G5 esophageal perforation. No difference in outcomes, but higher toxicity when compared to analogous central tumors series (G3 =0), with higher Dmax to lungs, bronchus, esophagus and heart. |
| Tonneau, 2023 [33] |
65 lesions (2009-2019) | Retrospective | PTV touching or overlapping the central bronchial tree, esophagus, pulmonary vein, or pulmonary artery. |
65 (100%) | 0 | Mostly 5*10 Gy | NR | 37,6 | VMAT, Cyberkinfe, Tomotherapy | After 37,6 months median follow-up: 10% LR, mOS 37,3 months and mDFS 36,6 months. 2 G5 TRAEs: pneumonitis. Comparison with central and peripheral pts from same center: higher RR e DR with UC lesions (CHR 2.44, 2.15); shorter OS and PFS versus central and peripheral lesions. BED10 <120 correlated with higher LR, RR e DR risks. |
| Tekatli, 2023 [49] |
94 pts (2008-2015) |
Retrospective | GTV ≤1cm from PBT | 94 (100%) | 0 | 8*7,5 Gy 12*5 Gy |
44 mm | 40,5 | VMAT | Considering additional 33 C lesions: mOS 25 months; 3-ys and 5-ys LC 78% and 69%; 3-ys and 5-ys RC 81% and 72%. G≥3 AEs = 20% of which 21% pulmonary, 1% bone fracture. G5 = 12%, all pulmonary, mostly >12 months. Location ≤1 cm from trachea or bronchus and PS 2-3 correlated with pulmonary toxicity. |
| Regnery, 2023 [47] |
16 patients/ 16 lesions 2020-2021 |
Prospective database | PTV overlapping with the PBT or esophagus |
4 (25%) | 12 (75%) | 12*5 Gy 10*5.0-6Gy 8*7,5 Gy 8*5 Gy 6*5 Gy 5*6 Gy |
NR |
24 | IMRT MRI guided adaptive RT | 2-ys OS 67%, 2-ys PFS 37%, 2-ys LC 93%. AEs G≥2 = 56%, 1 G3 bronchial bleeding, 1 G4 bronchial bleeding (further treated with VEGFRi), 1 G3 esophagitis. Lowest BED fractionations used for tumors abutting esophagus. Comparison with C tumors treated with MRI-IMRT: Higher AEs rates but no difference in outcomes. |
| Sandoval, 2023 [37] |
38/47 ultra- central patients (2019-2021) |
Retrospective | GTV ≤1cm from trachea, mainstem bronchi or PBT. C lesions defined as ≤2cm from PBT, mediastinum or pericardium |
22 (46,8%) | 25 (53,2%) | 3*18 (3,5%) 5*10-12 (25,6%) 8*7,5 (47%) 10*5 (6%) 15*4 (17,9%) |
NR | 22,9 | IMRT-MRI guided adaptive RT | 1-y LC 87% (median NR), 1-y OS was 82% (median NR), 1-y PFS was 54%. No acute G≥3 toxicity, 5% late G3 toxicities: esophagitis and pneumonitis. G2 toxicity associated with GTV volume. No statistical outcome differences between UC vs non-UC lesions. |
| Rock 2023 [89] |
50 patients (2009-2020) | Retrospective | PTV overlap or direct tumor abutment with the major vessels, esophagus, or central airway | 34 (68%) | 16 (32%) | 10*4-7 Gy (median 6,5) | NR | 13 (range 0,3 -102) | 3DCRT; IMRT; VMAT | Primary NSCLC: 1-y LC = 83.8%, 3-ys LC = 65.4%; 1-y PFS = 50.1%, 3-ys PFS = 26.8%; 1-y OS = 93.7%, 3-ys OS = 70.5%. Oligometastatic: 1-y LC = 85.2%; 1-y PFS = 12.5%, 1-y OS = 88.9%, 3-ys OS = 44.4%. G≥2 Aes = 22%: 12% G2 pneumonitis, 2% G3 pneumonitis, 2% G2 airway obstruction, 4% G3 obstruction, 2% G5 hemoptysis. |
| Hiroshima, 2022 [43] |
16 patients (2017-2020) | Retrospective | Within 2cm within the PBT | 16 (100%) | 0 | 10*6Gy 4*13,75Gy |
NR | 14,4 | IMRT or VMAT (1-4 fiducials; 4D CT scan) | No LR. OS, cancer-specific survival and PFS at 2 ys: 54.6%, 85.1%, and 33.7% 1 G3 radiation pneumonitis (no other G≥3 Aes). |
| Ligtenberg, 2022 [44] |
12 patients, (2017-2019) | Retrospective | Proximity to the mediastinum | 12 (100%) | 0 | 8*7,5Gy | NR | NR | IMRT or VMAT | MidP-based treatment yield lower OAR doses compared to ITV-based treatment plans on the MR- linac (Mean lung dose significantly lower, difference: -0.3 Gy; p < 0.042). |
| Farrugia, 2022 [53] |
83 patients, (2010 – 2019) | Retrospective | C: < 2 cm within the proximal airway, mediastinum, great vessels, or spinal cord; UC: directly abutting any of the above structures |
83 (100%) | 0 | 5*10Gy; 5*11Gy. | <20mm 68,7% | 33,4 | 3DCRT/ VMAT |
At log rank test and MVA, D45% right atria constraint (candidate cutoff values of 890cGy) was significantly associated with non-cancer associated survival and overall survival. |
| Salvestrini, 2022 [48] |
122 pts/126 lesions (2006/2020) | Retrospective | PTV touches or overlaps the trachea, mainstem-, intermediate-, upper-, middle- or lower- lobe bronchus or the esophagus |
68 (54%) | 58 (46%) | 7*7-8 Gy 6*8 Gy 5*9-12Gy |
37,5 mm | 23 | Cyberknife | 1-,2-, and 5- ys OS rates were 75%, 58%, and 23% 1-, 2- and 5-ys PFS rates at were 63%, 41%, and 15% 1-, 2-, and 5-ys LC rates were 86%, 78%, and 61%. Acute G2 dysphagia, cough, and dyspnea were 11%, 5%, 3%. Acute G3 dyspnea was 0,8%. Late G3 AEs rate = 4%. Tumor size and location close to the trachea rather than PBT correlated with better OS. |
| Wang, 2022 [90] |
58 pts (2010-2018) |
Retrospective | PTV touching or overlapping the PBT, trachea, esophagus, heart, pulmonary vein, or pulmonary artery within 2 cm around the bronchial tree in all directions | 58 (100%) | 0 | 7*8 Gy, 8*7Gy, 6*9,3Gy |
NR | 57 |
Cyberknife | 1-, 2- and 5-ys OS rates were 94.7%, 75.0%, and 45.0%. 1-, 2- and 5-ys LC rates were 91.5%, 78.0%, and 58.6%. G≥3 Aes = 3.5%. Pts with PTV <53.0 cc = better OS. |
| Guillaume, 2021 [56] |
74 pts/ 74 lesions (2012-2018) |
Retrospective | PTV overlapped one of the following OARs: the trachea, right and left main bronchi, intermediate bronchus, lobe bronchi, oesophagus, heart. |
37 (50%) | 37 (50%) | 5-10* (4.5-10 Gy) | 18,3 cc | 25 | CyberKnife, VMAT |
1-y LC rate 96.7%, 2-ys LC rate 87.6% mPFS 12 months. mOS 31 months. G3 AEs = 2.7%. No G4-5 AEs. The type of OAR overlapping with PTV didn’t relate to AE risk. LR more common with GTV receiving Dmin BED10 ≤50 Gy (p = 0.002). |
| Farrugia, 2021 [50] |
43 pts (2010-2019) |
Retrospective | GTV abutting the proximal bronchial tree, trachea, mediastinum, aorta, or spinal cord. | 43 (100%) | 0 | 5* (10-11Gy) | 12,4 cc | 29 | 3DCRT/ VMAT |
UC location was associated with worse non-cancer associated survival and OS, supposedly due to excessive D4cc (of 18Gy) dose to the proximal airways. |
| Breen, 2021 [59] |
110 pts (2008-2019) |
Retrospective | GTV directly touching the PBT or trachea. 2) PTV overlapping the trachea or mainstem bronchi.GTV within 1 cm of the PBT. |
110 (100%) | 0 | 4-8* (7.5-12Gy) (no 7 fractions) |
17.7cc | 30 | 3DCRT, VMAT | OS at 1, 2, and 5 ys was 78%, 57%, and 32% Local progression at 1, 2, and 5 ys was 4%, 16%, and 21%. Acute and late grade 2 + toxicity was seen in 18% and 27%. Four patients (4%) had fatal toxicity. |
| Lodeweges, 2021 [51] |
72 pts (2012-2020) |
Retrospective | PTV abutting or overlapping the main bronchi, trachea and/or esophagus | 72 (100%) | 0 | 12* 5Gy | NR | 19 | VMAT | 3-ys and 2-ys LC rates were 98% and 85%. OS rates at 1- and 2-ys were 77% and 52%. G ≥ 3 was observed in 21%, of which 10 patients (14%) with G≥5 bronchopulmonary hemorrhage. grade >3 toxicity found correlated with Dmean to the main bronchus (p = 0.003), with cutoff value of BED3 = 91 Gy. |
| Mihai, 2021 [57] |
57 pts (2008-2016) |
Retrospective | (GTV) abutting or involving trachea, main or lobar bronchi. | 37 (65%) | 20 (35%) | 4-10* (5-12Gy) (no 7 fractions) |
NR | 26.5 | IMRT | mOS was 34.3. Freedom from local progression at 2 and 4 years was 92 and 79.8%. Fatal hemoptysis 8.7%. |
| Regnery, 2021 [35] |
51 pts (2012-2019) |
Retrospective | Overlap of the PTV with the PBT | 37 (72.5%) | 14 (27.5%) |
10*5Gy | NR | NR | 3D, helical Tomotherapy, or VMAT | 2-ys local failure rate UC = 26.9%; C = 14.6%. 2-ys OS C = 55.4%; UC = 54.9%. 2-ys AE G≥3 15.3% for UC and 7.3% for C lesions. No grade 4 toxicity and only 1 potential grade 5 tox in UC cohort. |
| Cooke, 2020 [66] |
27 pts | Retrospective | NR | 0 | 22 (81%) | 6* 10Gy (no 7 fractions) | 6.6 cc | 11.6 | IMRT, VMAT | 1-year OS 82.7 2-year OS 69.5 1-year IFC 95.2% 2-year IFC 85.7% No AEs G>3 |
| Loi, 2020 [39] |
109 pts (NR) | Retrospective | PTV overlapping with central bronchial tree, esophagus, pulmonary vein, or pulmonary artery |
0 | 109 (100%) | 5-10*(6-10) Gy | 60 cc | 17 | VMAT | 2-ys LC 87%. Improved LC was correlated to PTV V95% > 85% and to GTV< 90cc. Overall and G≥3 toxicity incidence was 20% and 5%, respectively. |
| Shahi, 2020 [60] |
52 pts (84 mets) (2014-2019) | Retrospective | NR | 0 | 52 (100%) | 5* (6-10) Gy | 20 mm | 20 | VMAT | 2-ys Local failure was 9.0%. Median PFS was 4.0 months, and median OS was 31.7 months. AEs G>3 in 6 (11.5%) pts, 71% transient. There was a single (1.9%) G 5 toxicity (radiation pneumonitis). |
| Wang, 2020 [23] |
88 pts (2008-2017) |
Retrospective | GTV abutting the proximal bronchial tree or PTV overlapping esophagus | 53 (60%) | 35 (40%) | 5 * 9-10Gy 8 * 7,5 Gy 15 * 4 Gy |
NR | 19,5 | IMRT, VMAT | 1 and 2-ys rates of local failure were 12.2 % and 19.0 %. 1, 2 and 3-ys OS rates for pts with primary NSCLC were 78.6 %, 64.5 % and 53.1 %. AEs G≥3 22%, including 6 (7%) G≥3 radiation pneumonitis and 4 (4%) G≥3 esophageal injury. TRAEs G5 in ten pts (11.4 %) = hemoptysis, radiation pneumonitis, respiratory failure. BED10 ≥ 100 didn’t correlate with local control (UVA); lung V20 correlated with G≥2 pneumonitis, not dose to PBT; Dmax, D2.5cc, D5cc to esophagus correlated with G≥3 esophageal AE. |
| Zhao, 2020 [40] |
98 (2013-2017) |
Retrospective | PTV overlapping with PBT, esophagus, pulmonary vein or pulmonary artery | 76 (77.6%) | 22 (22.4%) | 8*7,5Gy | NR | 22.9 | 3DCRT, IMRT or VMAT | 2-ys and 3-ys LC, 97.8 and 84.5%. AEs G3 = 3 in the C group (2 dyspnea, 1 pneumonitis) and 2 in the UC group (1 dyspnea, 1 hemoptysis). No G>3 toxicities. ITV predictor for LC (p = 0.001). |
| Yang, 2020 [45] |
21 patients, 2012 – 2018 | Retrospective | UC: PTV abutting or overlapping central structures (including PBT, heart, and great vessels but not the esophagus) | 21 (100%) | 0 | 8*7,5Gy | NR | 15 | VMAT | The 1- and 2-ys OS rates were 87.5% and 76.6%. The 1- and 2-ys PFS rates were 71.1% and 64.0%. The 1- and 2-ys LC rates were 92.9% and 92.9%. AEs G2 19.1%. No G ≥ 3. |
| Duijm, 2019 [58] |
188 patients, 2012 – 2016 | Retrospective | UC: GTV ≤ 2 cm of the esophagus, trachea, mainstem, intermediate, upper, middle or lower lobe bronchus | 154 (82%) | 34 (18%) | 8*7,5Gy; 12*5Gy |
36 mm | NR | VMAT | Acute AEs: G1 (n = 19) and G2 (n = 10) only. Late AEs: 2 possible treatment-related deaths and 2 G3. DVH significantly correlated to acute and late AEs. |
| Meng, 2019 [34] |
80 patients, 2006 – 2015 | Retrospective | C: GTV < 2 cm of, but not abutting, the PBT UC: GTV abutting the PBT |
80 patients (100%) | 0 | 10*6Gy (C); 7*8Gy (UC) |
NR | 44,5 | CK | UC tumors showed worse OS, PFS, and LC compared to C lesions. On MVA, UC and PTV were poor prognostic factors. Toxicity profile similar in the two groups (UC vs C). |
| Cong, 2019 [91] |
51 patients, 2014 – 2017 | Retrospective | UC: GTV abutting or over- lapping the trachea or PBT | 51 patients (100%) | 0 | 5*7Gy | 68 mm | 17 | CK | Median LC was 17 months for stage III pts and 11 months for stage IV or recurrent pts. G3 radiation pneumonitis was recorded in 3 pts (5.9%) and possible treatment-related death in 2 pts (3.9%). |
| Bezjak, 2019 [18] |
120 patients (100 pts PP analysis, 17 UC), (2009 – 2013) |
Prospective, phase I/II study | C: GTV< 2 cm around the PBT or immediately adjacent to the mediastinal or pericardial pleura | 120 (100%) (100 pts PP analysis) | 0 | q 2 day fractionation X 5 fractions over 1.5-2 weeks: Dose Level 1: 5*8Gy 2: 5*8,5GY 3: 5*9GY 4: 5*9,5GY 5: 5*10Gy 6: 5*10,5GY 7: 5*11GY 8: 5*11,5Gy 9: 5*12Gy Protocol treatment begins at Level 5. Levels 1-4 employed if DLT is seen with the Level 5 |
11,2 cc |
37,2 | 3DCRT; VMAT; IMRT | MTD was 12.0 Gy/fx, with a probability of a DLT of 7.2%. 2-year LC rate in this cohort was 87.9%. 2-year PFS in this arm was 54.5%. 2-year OS was 72.7%. Four pts (12.1%) experienced G3 AE during the first year; 1 pts (3%) reported G5 toxicity >1year. |
| Nguyen, 2019 [36] |
68 patients, (2009 – 2017) | Retrospective | C: PTV <2 cm of the PBT UC: PTV overlapped the PBT or esophagus |
53 (78%) | 15 (22%) | 8*5Gy 5*8Gy; 5*10Gy; 4*12,5Gy; 5*11Gy; 8*7Gy; 8*7,5Gy; 5*12Gy. |
NR | 19,7 | IMRT; VMAT | The 2-year estimates of LC (89% and 85%; p 0.72) and OS (76% and 73%; p 0.75) for UC and C tumors were similar. UC tumors increased risk of G2 tox (57.6% vs 14.2%; p 0.007) at 2 years. One patient with an UC tumor developed G5 respiratory failure. |
3.1. Survival Outcomes and Toxicity with SBRT for Ultra-Central Tumors: Prospective Data
3.2. Survival Outcomes and Toxicity with SBRT for Ultra-Central Tumors: Retrospective Data
4. A Proposal for Practical Workflow for Treatment of Ultra-Central Tumors
4.1. Patient Eligibility
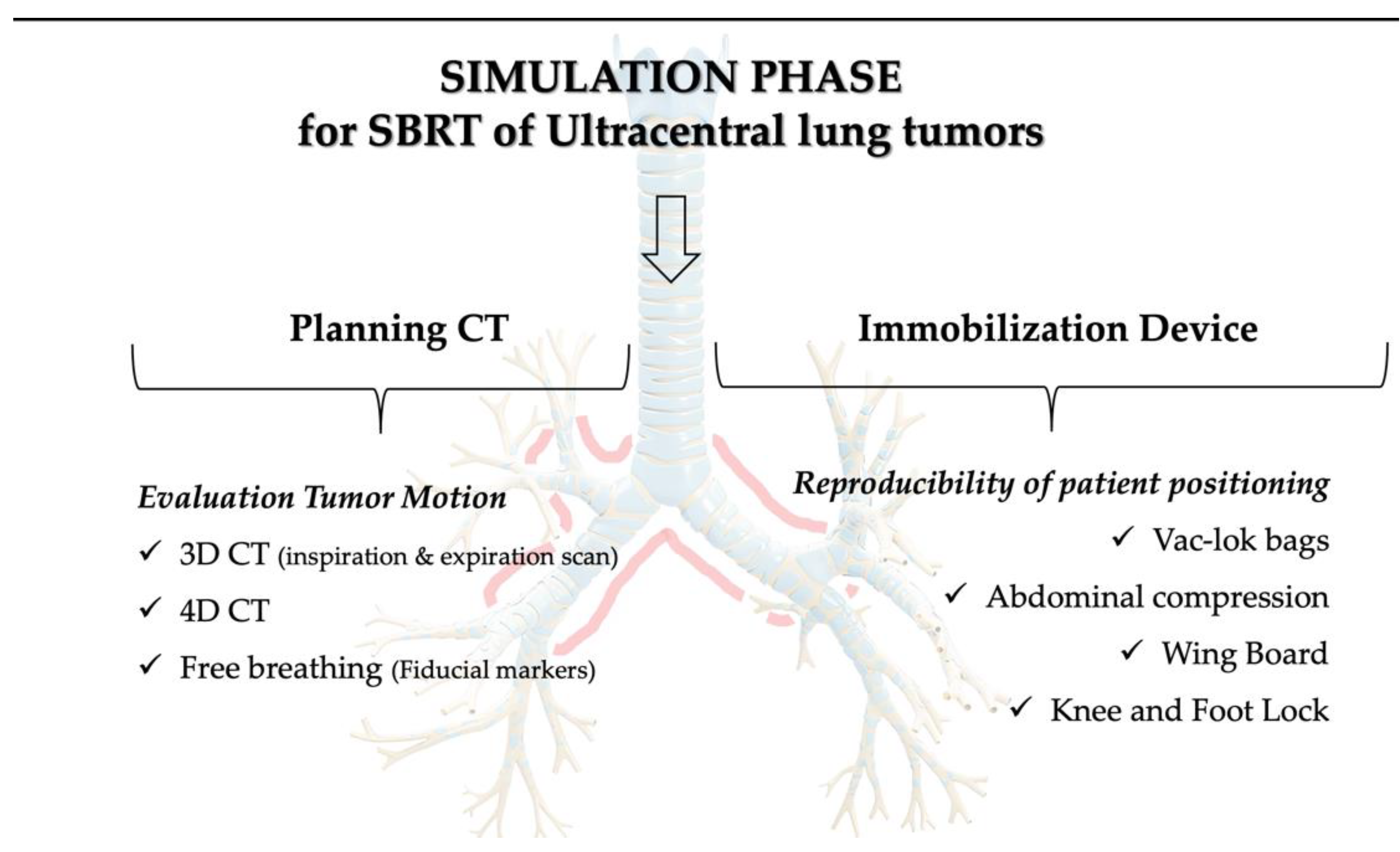
4.2. Simulation Phase and Immobilization Devices
4.3. Treatment Volume
4.4. Treatment Dose and Fractionation
4.5. Setup and Motion Management Systems
4.6. Follow-Up
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- >Lagerwaard, F. J.; Haasbeek, C. J.; Smit, E. F.; Slotman, B. J.; Senan, S. Outcomes of risk-adapted fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for stage I non-small-cell lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2008, 70 (3), 685-692. [CrossRef]
- Timmerman, R.; Paulus, R.; Galvin, J.; Michalski, J.; Straube, W.; Bradley, J.; Fakiris, A.; Bezjak, A.; Videtic, G.; Johnstone, D.; et al. Stereotactic body radiation therapy for inoperable early stage lung cancer. JAMA 2010, 303 (11), 1070-1076. [CrossRef]
- Chang, J. Y.; Liu, H.; Balter, P.; Komaki, R.; Liao, Z.; Welsh, J.; Mehran, R. J.; Roth, J. A.; Swisher, S. G. Clinical outcome and predictors of survival and pneumonitis after stereotactic ablative radiotherapy for stage I non-small cell lung cancer. Radiat Oncol 2012, 7, 152. [CrossRef]
- Taremi, M.; Hope, A.; Dahele, M.; Pearson, S.; Fung, S.; Purdie, T.; Brade, A.; Cho, J.; Sun, A.; Bissonnette, J. P.; et al. Stereotactic body radiotherapy for medically inoperable lung cancer: prospective, single-center study of 108 consecutive patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2012, 82 (2), 967-973. [CrossRef]
- Videtic, G. M. M.; Donington, J.; Giuliani, M.; Heinzerling, J.; Karas, T. Z.; Kelsey, C. R.; Lally, B. E.; Latzka, K.; Lo, S. S.; Moghanaki, D.; et al. Stereotactic body radiation therapy for early-stage non-small cell lung cancer: Executive Summary of an ASTRO Evidence-Based Guideline. Pract Radiat Oncol 2017, 7 (5), 295-301. [CrossRef]
- Guckenberger, M.; Andratschke, N.; Dieckmann, K.; Hoogeman, M. S.; Hoyer, M.; Hurkmans, C.; Tanadini-Lang, S.; Lartigau, E.; Méndez Romero, A.; Senan, S.; et al. ESTRO ACROP consensus guideline on implementation and practice of stereotactic body radiotherapy for peripherally located early stage non-small cell lung cancer. Radiother Oncol 2017, 124 (1), 11-17. [CrossRef]
- Shirvani, S. M.; Jiang, J.; Chang, J. Y.; Welsh, J. W.; Gomez, D. R.; Swisher, S.; Buchholz, T. A.; Smith, B. D. Comparative effectiveness of 5 treatment strategies for early-stage non-small cell lung cancer in the elderly. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2012, 84 (5), 1060-1070. [CrossRef]
- Rusthoven, K. E.; Kavanagh, B. D.; Burri, S. H.; Chen, C.; Cardenes, H.; Chidel, M. A.; Pugh, T. J.; Kane, M.; Gaspar, L. E.; Schefter, T. E. Multi-institutional phase I/II trial of stereotactic body radiation therapy for lung metastases. J Clin Oncol 2009, 27 (10), 1579-1584. [CrossRef]
- Chang, H. J.; Ko, H. L.; Lee, C. Y.; Wu, R. H.; Yeh, Y. W.; Jiang, J. S.; Kao, S. J.; Chi, K. H. Hypofractionated radiotherapy for primary or secondary oligometastatic lung cancer using Tomotherapy. Radiat Oncol 2012, 7, 222. [CrossRef]
- Tateishi, Y.; Takeda, A.; Horita, N.; Tsurugai, Y.; Eriguchi, T.; Kibe, Y.; Sanuki, N.; Kaneko, T. Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy With a High Maximum Dose Improves Local Control, Cancer-Specific Death, and Overall Survival in Peripheral Early-Stage Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2021, 111 (1), 143-151. [CrossRef]
- Timmerman, R.; McGarry, R.; Yiannoutsos, C.; Papiez, L.; Tudor, K.; DeLuca, J.; Ewing, M.; Abdulrahman, R.; DesRosiers, C.; Williams, M.; et al. Excessive toxicity when treating central tumors in a phase II study of stereotactic body radiation therapy for medically inoperable early-stage lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 2006, 24 (30), 4833-4839. [CrossRef]
- Milano, M. T.; Chen, Y.; Katz, A. W.; Philip, A.; Schell, M. C.; Okunieff, P. Central thoracic lesions treated with hypofractionated stereotactic body radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol 2009, 91 (3), 301-306. [CrossRef]
- Chang, J. Y.; Balter, P. A.; Dong, L.; Yang, Q.; Liao, Z.; Jeter, M.; Bucci, M. K.; McAleer, M. F.; Mehran, R. J.; Roth, J. A.; et al. Stereotactic body radiation therapy in centrally and superiorly located stage I or isolated recurrent non-small-cell lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2008, 72 (4), 967-971. [CrossRef]
- Haasbeek, C. J.; Lagerwaard, F. J.; Slotman, B. J.; Senan, S. Outcomes of stereotactic ablative radiotherapy for centrally located early-stage lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 2011, 6 (12), 2036-2043. [CrossRef]
- Rowe, B. P.; Boffa, D. J.; Wilson, L. D.; Kim, A. W.; Detterbeck, F. C.; Decker, R. H. Stereotactic body radiotherapy for central lung tumors. J Thorac Oncol 2012, 7 (9), 1394-1399. [CrossRef]
- Nuyttens, J. J.; van der Voort van Zyp, N. C.; Praag, J.; Aluwini, S.; van Klaveren, R. J.; Verhoef, C.; Pattynama, P. M.; Hoogeman, M. S. Outcome of four-dimensional stereotactic radiotherapy for centrally located lung tumors. Radiother Oncol 2012, 102 (3), 383-387. [CrossRef]
- Corradetti, M. N.; Haas, A. R.; Rengan, R. Central-airway necrosis after stereotactic body-radiation therapy. N Engl J Med 2012, 366 (24), 2327-2329. [CrossRef]
- Bezjak, A.; Paulus, R.; Gaspar, L. E.; Timmerman, R. D.; Straube, W. L.; Ryan, W. F.; Garces, Y. I.; Pu, A. T.; Singh, A. K.; Videtic, G. M.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of a Five-Fraction Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy Schedule for Centrally Located Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: NRG Oncology/RTOG 0813 Trial. J Clin Oncol 2019, 37 (15), 1316-1325. [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Louie, A. V.; Kotecha, R.; Ashfaq Ahmed, M.; Zhang, Z.; Guckenberger, M.; Kim, M. S.; Lo, S. S.; Scorsetti, M.; Tree, A. C.; et al. Stereotactic body radiotherapy for Ultra-Central lung Tumors: A systematic review and Meta-Analysis and International Stereotactic Radiosurgery Society practice guidelines. Lung Cancer 2023, 182, 107281. [CrossRef]
- Tekatli, H.; Haasbeek, N.; Dahele, M.; De Haan, P.; Verbakel, W.; Bongers, E.; Hashemi, S.; Nossent, E.; Spoelstra, F.; de Langen, A. J.; et al. Outcomes of Hypofractionated High-Dose Radiotherapy in Poor-Risk Patients with "Ultracentral" Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. J Thorac Oncol 2016, 11 (7), 1081-1089. [CrossRef]
- Song, S. Y.; Choi, W.; Shin, S. S.; Lee, S. W.; Ahn, S. D.; Kim, J. H.; Je, H. U.; Park, C. I.; Lee, J. S.; Choi, E. K. Fractionated stereotactic body radiation therapy for medically inoperable stage I lung cancer adjacent to central large bronchus. Lung Cancer 2009, 66 (1), 89-93. [CrossRef]
- Haseltine, J. M.; Rimner, A.; Gelblum, D. Y.; Modh, A.; Rosenzweig, K. E.; Jackson, A.; Yorke, E. D.; Wu, A. J. Fatal complications after stereotactic body radiation therapy for central lung tumors abutting the proximal bronchial tree. Pract Radiat Oncol 2016, 6 (2), e27-33. [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Rimner, A.; Gelblum, D. Y.; Dick-Godfrey, R.; McKnight, D.; Torres, D.; Flynn, J.; Zhang, Z.; Sidiqi, B.; Jackson, A.; et al. Analysis of pneumonitis and esophageal injury after stereotactic body radiation therapy for ultra-central lung tumors. Lung Cancer 2020, 147, 45-48. [CrossRef]
- Chaudhuri, A. A.; Tang, C.; Binkley, M. S.; Jin, M.; Wynne, J. F.; von Eyben, R.; Hara, W. Y.; Trakul, N.; Loo, B. W.; Diehn, M. Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy (SABR) for treatment of central and ultra-central lung tumors. Lung Cancer 2015, 89 (1), 50-56. [CrossRef]
- Daly, M.; Novak, J.; Monjazeb, A. P2.05-056 Safety of Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for Central, Ultracentral, and Paramediastinal Lung Tumors. Journal of Thoracic Oncology 2017, 12, S1066. [CrossRef]
- Raman, S.; Yau, V.; Pineda, S.; Le, L. W.; Lau, A.; Bezjak, A.; Cho, B. C. J.; Sun, A.; Hope, A. J.; Giuliani, M. Ultracentral Tumors Treated With Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy: Single-Institution Experience. Clin Lung Cancer 2018, 19 (5), e803-e810. [CrossRef]
- Lindberg, K.; Grozman, V.; Karlsson, K.; Lindberg, S.; Lax, I.; Wersäll, P.; Persson, G. F.; Josipovic, M.; Khalil, A. A.; Moeller, D. S.; et al. The HILUS-Trial-a Prospective Nordic Multicenter Phase 2 Study of Ultracentral Lung Tumors Treated With Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy. J Thorac Oncol 2021, 16 (7), 1200-1210. [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Laba, J. M.; Zayed, S.; Boldt, R. G.; Palma, D. A.; Louie, A. V. Safety and Effectiveness of Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy for Ultra-Central Lung Lesions: A Systematic Review. J Thorac Oncol 2019, 14 (8), 1332-1342. [CrossRef]
- Lindberg, S.; Grozman, V.; Karlsson, K.; Onjukka, E.; Lindbäck, E.; Jirf, K. A.; Lax, I.; Wersäll, P.; Persson, G. F.; Josipovic, M.; et al. Expanded HILUS Trial: A Pooled Analysis of Risk Factors for Toxicity From Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy of Central and Ultracentral Lung Tumors. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2023, 117 (5), 1222-1231. [CrossRef]
- Levy, A.; Adebahr, S.; Hurkmans, C.; Ahmed, M.; Ahmad, S.; Guckenberger, M.; Geets, X.; Lievens, Y.; Lambrecht, M.; Pourel, N.; et al. Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for Centrally Located Inoperable Early-Stage NSCLC: EORTC 22113-08113 LungTech Phase II Trial Results. J Thorac Oncol 2024, 19 (9), 1297-1309. [CrossRef]
- Giuliani, M. E.; Filion, E.; Faria, S.; Kundapur, V.; Toni Vu, T. T. T.; Lok, B. H.; Raman, S.; Bahig, H.; Laba, J. M.; Lang, P.; et al. Stereotactic Radiation for Ultra-Central Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Safety and Efficacy Trial (SUNSET). Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2024, 120 (3), 669-677. [CrossRef]
- Swaminath, A.; Parpia, S.; Wierzbicki, M.; Kundapur, V.; Faria, S.; Okawara, G. S.; Tsakiridis, T. K.; Ahmed, N.; Bujold, A.; Hirmiz, K.; et al. Stereotactic vs Hypofractionated Radiotherapy for Inoperable Stage I Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: The LUSTRE Phase 3 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol 2024. [CrossRef]
- Tonneau, M.; Richard, C.; Routy, B.; Campeau, M. P.; Vu, T.; Filion, E.; Roberge, D.; Mathieu, D.; Doucet, R.; Beliveau-Nadeau, D.; et al. A competing risk analysis of the patterns and risk factors of recurrence in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer treated with stereotactic ablative radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol 2023, 185, 109697. [CrossRef]
- Meng, M. B.; Wang, H. H.; Zaorsky, N. G.; Sun, B. S.; Zhu, L.; Song, Y. C.; Li, F. T.; Dong, Y.; Wang, J. S.; Chen, H. M.; et al. Risk-adapted stereotactic body radiation therapy for central and ultra-central early-stage inoperable non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Sci 2019, 110 (11), 3553-3564. [CrossRef]
- Regnery, S.; Eichkorn, T.; Weykamp, F.; Held, T.; Weusthof, K.; Dinges, L. A.; El-Shafie, R. A.; Winter, H.; Thomas, M.; Debus, J.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy in Ultracentral Lung Tumors Using a Risk-optimized Fractionation Scheme. Clin Lung Cancer 2021, 22 (4), 332-340.e333. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, K. N. B.; Hause, D. J.; Novak, J.; Monjazeb, A. M.; Daly, M. E. Tumor Control and Toxicity after SBRT for Ultracentral, Central, and Paramediastinal Lung Tumors. Pract Radiat Oncol 2019, 9 (2), e196-e202. [CrossRef]
- Sandoval, M. L.; Sim, A. J.; Bryant, J. M.; Bhandari, M.; Wuthrick, E. J.; Perez, B. A.; Dilling, T. J.; Redler, G.; Andreozzi, J.; Nardella, L.; et al. Magnetic Resonance-Guided Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy/Hypofractionated Radiation therapy for Metastatic and Primary Central and Ultracentral Lung Lesions. JTO Clin Res Rep 2023, 4 (5), 100488. [CrossRef]
- Li, G. J.; Tan, H.; Nusrat, H.; Chang, J.; Chen, H.; Poon, I.; Shahi, J.; Tsao, M.; Ung, Y.; Cheung, P.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Ultra-central Thoracic Tumors: A Single Center Retrospective Review. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2024, 120 (2), 359-369. [CrossRef]
- Loi, M.; Franceschini, D.; Dominici, L.; Franzese, C.; Chiola, I.; Comito, T.; Marzo, M.; Reggiori, G.; Mancosu, P.; Tomatis, S.; et al. Stereotactic Radiotherapy for Ultra-Central Lung Oligometastases in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers (Basel) 2020, 12 (4). [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Khawandanh, E.; Thomas, S.; Zhang, S.; Dunne, E. M.; Liu, M.; Schellenberg, D. Outcomes of stereotactic body radiotherapy 60 Gy in 8 fractions when prioritizing organs at risk for central and ultracentral lung tumors. Radiat Oncol 2020, 15 (1), 61. [CrossRef]
- Rim, C. H.; Yoon, W. S.; Park, S. Safety and Efficacy of Moderate-Intensity Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Ultra-Central Lung Tumor. Medicina (Kaunas) 2024, 60 (4). [CrossRef]
- Bryant, J. M.; Cruz-Chamorro, R. J.; Gan, A.; Liveringhouse, C.; Weygand, J.; Nguyen, A.; Keit, E.; Sandoval, M. L.; Sim, A. J.; Perez, B. A.; et al. Structure-specific rigid dose accumulation dosimetric analysis of ablative stereotactic MRI-guided adaptive radiation therapy in ultracentral lung lesions. Commun Med (Lond) 2024, 4 (1), 96. [CrossRef]
- Hiroshima, Y.; Tamaki, Y.; Sawada, T.; Ishida, T.; Yasue, K.; Shinoda, K.; Saito, T.; Kaburagi, T.; Kiyoshima, M.; Okumura, T.; et al. Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for Stage I Lung Cancer With a New Real-time Tumor Tracking System. Anticancer Res 2022, 42 (6), 2989-2995. [CrossRef]
- Ligtenberg, H.; Hackett, S. L.; Merckel, L. G.; Snoeren, L.; Kontaxis, C.; Zachiu, C.; Bol, G. H.; Verhoeff, J. J. C.; Fast, M. F. Towards mid-position based Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy using online magnetic resonance imaging guidance for central lung tumours. Phys Imaging Radiat Oncol 2022, 23, 24-31. [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Cui, J.; Zhao, J.; You, J.; Yu, R.; Yu, H.; Jiang, L.; Li, D.; Xu, B.; Shi, A. Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy of 60 Gy in eight fractions is safe for ultracentral non-small cell lung cancer. Thorac Cancer 2020, 11 (3), 754-761. [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Zhao, L.; Jiang, N.; Ding, N.; Zong, D.; Zhang, N.; Wang, D.; Wen, J.; He, X.; Kong, C.; et al. Long-term outcomes in patients with central and ultracentral non-small cell lung cancer treated with stereotactic body radiotherapy: single-institution experience. Curr Probl Cancer 2023, 47 (3), 100956. [CrossRef]
- Regnery, S.; Katsigiannopulos, E.; Hoegen, P.; Weykamp, F.; Sandrini, E.; Held, T.; Deng, M.; Eichkorn, T.; Buchele, C.; Rippke, C.; et al. To fly or not to fly: Stereotactic MR-guided adaptive radiotherapy effectively treats ultracentral lung tumors with favorable long-term outcomes. Lung Cancer 2023, 179, 107175. [CrossRef]
- Salvestrini, V.; Duijm, M.; Loi, M.; Nuyttens, J. J. Survival and Prognostic Factors of Ultra-Central Tumors Treated with Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy. Cancers (Basel) 2022, 14 (23). [CrossRef]
- Tekatli, H.; Giraud, N.; van Eekelen, R.; Lagerwaard, F. J.; Senan, S. Ten years outcomes after SABR in central and ultracentral primary lung tumors. Radiother Oncol 2023, 188, 109848. [CrossRef]
- Farrugia, M.; Ma, S. J.; Hennon, M.; Nwogu, C.; Dexter, E.; Picone, A.; Demmy, T.; Yendamuri, S.; Yu, H.; Fung-Kee-Fung, S.; et al. Exceeding Radiation Dose to Volume Parameters for the Proximal Airways with Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy Is More Likely for Ultracentral Lung Tumors and Associated with Worse Outcome. Cancers (Basel) 2021, 13 (14). [CrossRef]
- Lodeweges, J. E.; van Rossum, P. S. N.; Bartels, M. M. T. J.; van Lindert, A. S. R.; Pomp, J.; Peters, M.; Verhoeff, J. J. C. Ultra-central lung tumors: safety and efficacy of protracted stereotactic body radiotherapy. Acta Oncol 2021, 60 (8), 1061-1068. [CrossRef]
- Ahmadsei, M.; Thaler, K.; Gasser, E.; Pouymayou, B.; Dal Bello, R.; Christ, S. M.; Willmann, J.; Kovacs, B.; Balermpas, P.; Tanadini-Lang, S.; et al. Dosimetric analysis of 17 cardiac Sub-structures, Toxicity, and survival in ultra central lung tumor patients treated with SBRT. Clin Transl Radiat Oncol 2023, 43, 100675. [CrossRef]
- Farrugia, M.; Yu, H.; Ma, S. J.; Iovoli, A. J.; Pokharel, S.; Sharma, U. C.; Fung-Kee-Fung, S.; Malik, N.; Singh, A. K.; Malhotra, H. Right Atrial Dose Is Associated with Worse Outcome in Patients Undergoing Definitive Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Central Lung Tumors. Cancers (Basel) 2022, 14 (6). [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.; Han, Z.; Huynh, E.; Tjong, M. C.; Cagney, D. N.; Huynh, M. A.; Kann, B. H.; Kozono, D.; Leeman, J. E.; Singer, L.; et al. Widening the therapeutic window for central and ultra-central thoracic oligometastatic disease with stereotactic MR-guided adaptive radiation therapy (SMART). Radiother Oncol 2024, 190, 110034. [CrossRef]
- Ricco, A.; Davis, J.; Rate, W.; Yang, J.; Perry, D.; Pablo, J.; D'Ambrosio, D.; Sharma, S.; Sundararaman, S.; Kolker, J.; et al. Lung metastases treated with stereotactic body radiotherapy: the RSSearch® patient Registry's experience. Radiat Oncol 2017, 12 (1), 35. [CrossRef]
- Guillaume, E.; Tanguy, R.; Ayadi, M.; Claude, L.; Sotton, S.; Moncharmont, C.; Magné, N.; Martel-Lafay, I. Toxicity and efficacy of stereotactic body radiotherapy for ultra-central lung tumours: a single institution real life experience. Br J Radiol 2022, 95 (1129), 20210533. [CrossRef]
- Mihai, A. M.; Armstrong, P. J.; Hickey, D.; Milano, M. T.; Dunne, M.; Healy, K.; Thirion, P.; Heron, D. E.; ElBeltagi, N.; Armstrong, J. G. Late Toxicity and Long-Term Local Control in Patients With Ultra-Central Lung Tumours Treated by Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy-Based Stereotactic Ablative Body Radiotherapy With Homogenous Dose Prescription. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol) 2021, 33 (10), 627-637. [CrossRef]
- Duijm, M.; van der Voort van Zyp, N. C.; van de Vaart, P.; Oomen-de Hoop, E.; Mast, M. E.; Hoogeman, M. S.; Nuyttens, J. J. Predicting High-Grade Esophagus Toxicity After Treating Central Lung Tumors With Stereotactic Radiation Therapy Using a Normal Tissue Complication Probability Model. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2020, 106 (1), 73-81. [CrossRef]
- Breen, W. G.; Jeans, E. B.; Gergelis, K. R.; Garces, Y. I.; Park, S. S.; Merrell, K. W.; Peikert, T. D.; Mansfield, A. S.; Wigle, D. A.; Harmsen, W. S.; et al. Ablative radiotherapy for ultracentral lung cancers: Dosimetric, geometric, and volumetric predictors of outcomes and toxicity. Radiother Oncol 2021, 158, 246-252. [CrossRef]
- Shahi, J.; Poon, I.; Ung, Y. C.; Tsao, M.; Bjarnason, G. A.; Malik, N. H.; Zhang, L.; Louie, A. V.; Cheung, P. Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Mediastinal and Hilar Lymph Node Metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2021, 109 (3), 764-774. [CrossRef]
- Wegner, R. E.; Abel, S.; Hasan, S.; Schumacher, L. Y.; Colonias, A. Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy (SBRT) for Oligometastatic Lung Nodules: A Single Institution Series. Front Oncol 2019, 9, 334. [CrossRef]
- Postmus, P. E.; Kerr, K. M.; Oudkerk, M.; Senan, S.; Waller, D. A.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Escriu, C.; Peters, S.; Committee, E. G. Early and locally advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC): ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol 2017, 28 (suppl_4), iv1-iv21. [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, E.; Sánchez, I.; Díaz, O.; Valles, A.; Balderrama, R.; Fuentes, J.; Lara, B.; Olimón, C.; Ruiz, V.; Rodríguez, J.; et al. Current Evidence for Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy in Lung Metastases. Curr Oncol 2021, 28 (4), 2560-2578. [CrossRef]
- Koba, A.; Hayashi, K.; Suzuki, O.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Ogawa, K.; Chatani, M. Stereotactic body radiotherapy feasibility for patients with peripheral stage I lung cancer and poor pulmonary function. Oncol Lett 2020, 19 (3), 2515-2521. [CrossRef]
- Dahele, M.; Pearson, S.; Purdie, T.; Bissonnette, J. P.; Franks, K.; Brade, A.; Cho, J.; Sun, A.; Hope, A.; Marshall, A.; et al. Practical considerations arising from the implementation of lung stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) at a comprehensive cancer center. J Thorac Oncol 2008, 3 (11), 1332-1341. [CrossRef]
- Cooke, R.; Camilleri, P.; Chu, K. Y.; O'Cathail, S. M.; Robinson, M.; Van Den Heuvel, F.; Hawkins, M. A. Stereotactic body radiotherapy for moderately central and ultra-central oligometastatic disease: Initial outcomes. Tech Innov Patient Support Radiat Oncol 2020, 13, 24-30. [CrossRef]
- Kirkbride, P.; Cooper, T. Stereotactic body radiotherapy. Guidelines for commissioners, providers and clinicians: a national report. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol) 2011, 23 (3), 163-164. [CrossRef]
- Solberg, T. D.; Balter, J. M.; Benedict, S. H.; Fraass, B. A.; Kavanagh, B.; Miyamoto, C.; Pawlicki, T.; Potters, L.; Yamada, Y. Quality and safety considerations in stereotactic radiosurgery and stereotactic body radiation therapy: Executive summary. Pract Radiat Oncol 2012, 2 (1), 2-9. [CrossRef]
- Caillet, V.; Booth, J. T.; Keall, P. IGRT and motion management during lung SBRT delivery. Phys Med 2017, 44, 113-122. [CrossRef]
- Slotman, B. J.; Lagerwaard, F. J.; Senan, S. 4D imaging for target definition in stereotactic radiotherapy for lung cancer. Acta Oncol 2006, 45 (7), 966-972. [CrossRef]
- Grills, I. S.; Hugo, G.; Kestin, L. L.; Galerani, A. P.; Chao, K. K.; Wloch, J.; Yan, D. Image-guided radiotherapy via daily online cone-beam CT substantially reduces margin requirements for stereotactic lung radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2008, 70 (4), 1045-1056. [CrossRef]
- Keall, P. J.; Mageras, G. S.; Balter, J. M.; Emery, R. S.; Forster, K. M.; Jiang, S. B.; Kapatoes, J. M.; Low, D. A.; Murphy, M. J.; Murray, B. R.; et al. The management of respiratory motion in radiation oncology report of AAPM Task Group 76. Med Phys 2006, 33 (10), 3874-3900. [CrossRef]
- Loi, M.; Franceschini, D.; Dominici, L.; Chiola, I.; Franzese, C.; D'Agostino, G. R.; Navarria, P.; Marzo, M.; Paganini, L.; Comito, T.; et al. Dose coverage impacts local control in ultra-central lung oligometastases treated with stereotactic radiotherapy. Strahlenther Onkol 2021, 197 (5), 396-404. [CrossRef]
- Bujold, A.; Craig, T.; Jaffray, D.; Dawson, L. A. Image-guided radiotherapy: has it influenced patient outcomes? Semin Radiat Oncol 2012, 22 (1), 50-61. [CrossRef]
- Jaffray, D. A.; Drake, D. G.; Moreau, M.; Martinez, A. A.; Wong, J. W. A radiographic and tomographic imaging system integrated into a medical linear accelerator for localization of bone and soft-tissue targets. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 1999, 45 (3), 773-789. [CrossRef]
- Shah, C.; Grills, I. S.; Kestin, L. L.; McGrath, S.; Ye, H.; Martin, S. K.; Yan, D. Intrafraction variation of mean tumor position during image-guided hypofractionated stereotactic body radiotherapy for lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2012, 82 (5), 1636-1641. [CrossRef]
- Schulze, R.; Heil, U.; Gross, D.; Bruellmann, D. D.; Dranischnikow, E.; Schwanecke, U.; Schoemer, E. Artefacts in CBCT: a review. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 2011, 40 (5), 265-273. [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, R. A.; Seubert, B.; Stark, S.; Homann, V.; Müller, G.; Flentje, M.; Guckenberger, M. Accuracy and inter-observer variability of 3D versus 4D cone-beam CT based image-guidance in SBRT for lung tumors. Radiat Oncol 2012, 7, 81. [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Ma, C.; Shang, D.; Qiu, Q.; Meng, H.; Duan, J.; Yin, Y. Geometric accuracy evaluation of a six-degree-of-freedom (6-DoF) couch with cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) using a phantom and correlation study of the position errors in pelvic tumor radiotherapy. Transl Cancer Res 2020, 9 (10), 6005-6012. [CrossRef]
- Guo, H. L.; Wu, W. W.; Huan, Y.; Zhang, H. W. SGRT-based stereotactic body radiotherapy for lung cancer setup accuracy and margin of the PTV. J Appl Clin Med Phys 2024, 25 (3), e14195. [CrossRef]
- Sarudis, S.; Karlsson, A.; Bäck, A. Surface guided frameless positioning for lung stereotactic body radiation therapy. J Appl Clin Med Phys 2021, 22 (9), 215-226. [CrossRef]
- Heinzerling, J. H.; Hampton, C. J.; Robinson, M.; Bright, M.; Moeller, B. J.; Ruiz, J.; Prabhu, R.; Burri, S. H.; Foster, R. D. Use of surface-guided radiation therapy in combination with IGRT for setup and intrafraction motion monitoring during stereotactic body radiation therapy treatments of the lung and abdomen. J Appl Clin Med Phys 2020, 21 (5), 48-55. [CrossRef]
- Foster, R. D.; Moeller, B. J.; Robinson, M.; Bright, M.; Ruiz, J. L.; Hampton, C. J.; Heinzerling, J. H. Dosimetric Analysis of Intra-Fraction Motion Detected by Surface-Guided Radiation Therapy During Linac Stereotactic Radiosurgery. Adv Radiat Oncol 2023, 8 (3), 101151. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.; Reinoso, R.; Farah, J.; Yossi, S.; Lorchel, F.; Passerat, V.; Louet, E.; Pouchard, I.; Khodri, M.; Barbet, N. Reproducibility of surface-based deep inspiration breath-hold technique for lung stereotactic body radiotherapy on a closed-bore gantry linac. Phys Imaging Radiat Oncol 2023, 26, 100448. [CrossRef]
- van der Voort van Zyp, N. C.; Prévost, J. B.; Hoogeman, M. S.; Praag, J.; van der Holt, B.; Levendag, P. C.; van Klaveren, R. J.; Pattynama, P.; Nuyttens, J. J. Stereotactic radiotherapy with real-time tumor tracking for non-small cell lung cancer: clinical outcome. Radiother Oncol 2009, 91 (3), 296-300. [CrossRef]
- Nuyttens, J. J.; Prévost, J. B.; Praag, J.; Hoogeman, M.; Van Klaveren, R. J.; Levendag, P. C.; Pattynama, P. M. Lung tumor tracking during stereotactic radiotherapy treatment with the CyberKnife: Marker placement and early results. Acta Oncol 2006, 45 (7), 961-965. [CrossRef]
- Prévost, J. B.; Nuyttens, J. J.; Hoogeman, M. S.; Pöll, J. J.; van Dijk, L. C.; Pattynama, P. M. Endovascular coils as lung tumour markers in real-time tumour tracking stereotactic radiotherapy: preliminary results. Eur Radiol 2008, 18 (8), 1569-1576. [CrossRef]
- Iovoli, A. J.; Yu, H.; Advani, P. G.; Turecki, L.; Malhotra, H. K.; Malik, N. K.; Fung-Kee-Fung, S.; Singh, A. K.; Farrugia, M. K. Sinoatrial Node Dose Is Associated With Worse Survival in Patients Undergoing Definitive Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Central Lung Cancers. Pract Radiat Oncol 2024, 14 (1), e40-e47. [CrossRef]
- Rock, C.; Sood, S.; Cao, Y.; Shelton, S.; Chen, R. C.; Wang, F. Ten fraction hypofractionated stereotactic body radiotherapy for the management of ultracentral lung tumors: a retrospective analysis of dosimetry, outcomes, and toxicity. Radiat Oncol 2023, 18 (1), 128. [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Dong, Y.; Yu, X.; Li, F.; Wang, J.; Chen, H.; Niu, Z.; Song, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Tao, Z. Safety and Efficacy of Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy for Ultra-Central Lung Cancer. Front Oncol 2022, 12, 868844. [CrossRef]
- Cong, Y.; Sun, B.; Wang, J.; Meng, X.; Xuan, L.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Shen, G.; Wu, S. Outcomes and toxicity of stereotactic body radiation therapy for advanced stage ultra-central non-small cell lung cancer. Thorac Cancer 2019, 10 (7), 1567-1575. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





