Submitted:
24 October 2024
Posted:
25 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Background
3. Evaluation of Greenhouse Gas Reduction
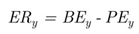 |
(1) |
| ERy | is amount of greenhouse gas emission reduction from project implementation in year y (tCO2eq per year). |
| BEy | is emission of baseline in year y (tCO2eq per year). |
| PEy | is emission of project in year y (tCO2eq per year). |
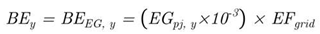 |
(2) |
| BEEG,y | is amount of greenhouse gas emissions from electricity generation of grid in year y (tCO2eq per year). |
| EGPJ,y | is amount of electricity produced from the photovoltaic system in year y (kWh per year). |
| EFgrid | is greenhouse gas emissions from electricity generation of grid (tCO2eq per MWh). |
4. Thailand Policy
4.1. Thailand National Economic and Social Development Plan
4.2. Thailand Integrated Energy Blueprint
4.3. Net Zero Emission, and Carbon Neutrality
5. Economic Analysis Index
5.1. Net Present Value
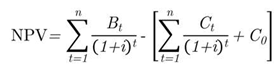 |
(3) |
| Bt | is return/year. |
| Ct | is cost/year. |
| C0 | is first year cost. |
| i | is rate of discount. |
5.2. Internal Rate of Return
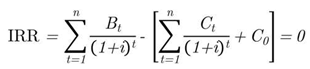 |
(4) |
| r | is IRR. |
5.3. Benefit Cost Ratio
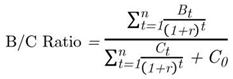 |
(5) |
5.4. Payback Period
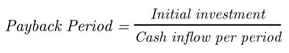 |
(6) |
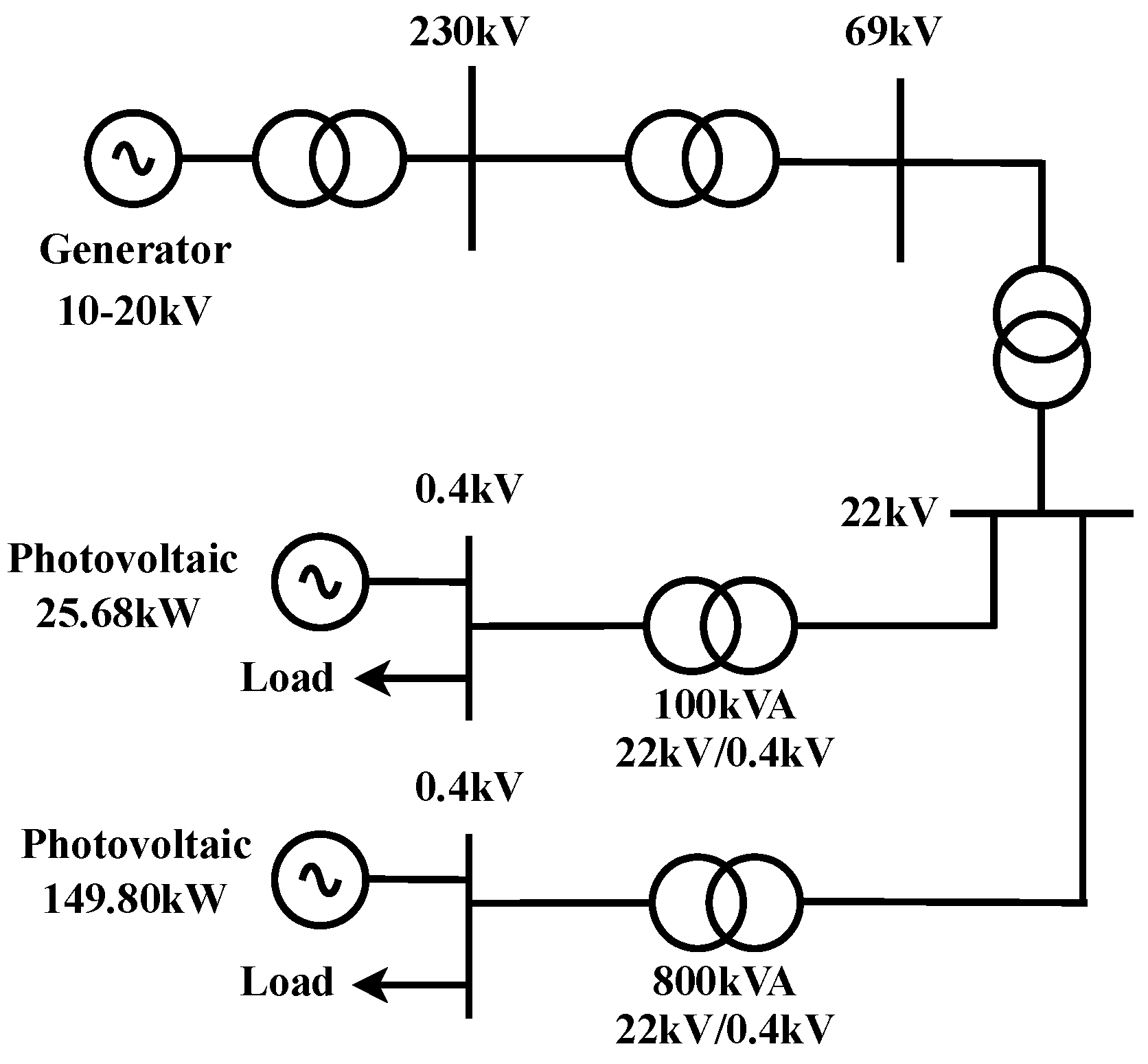
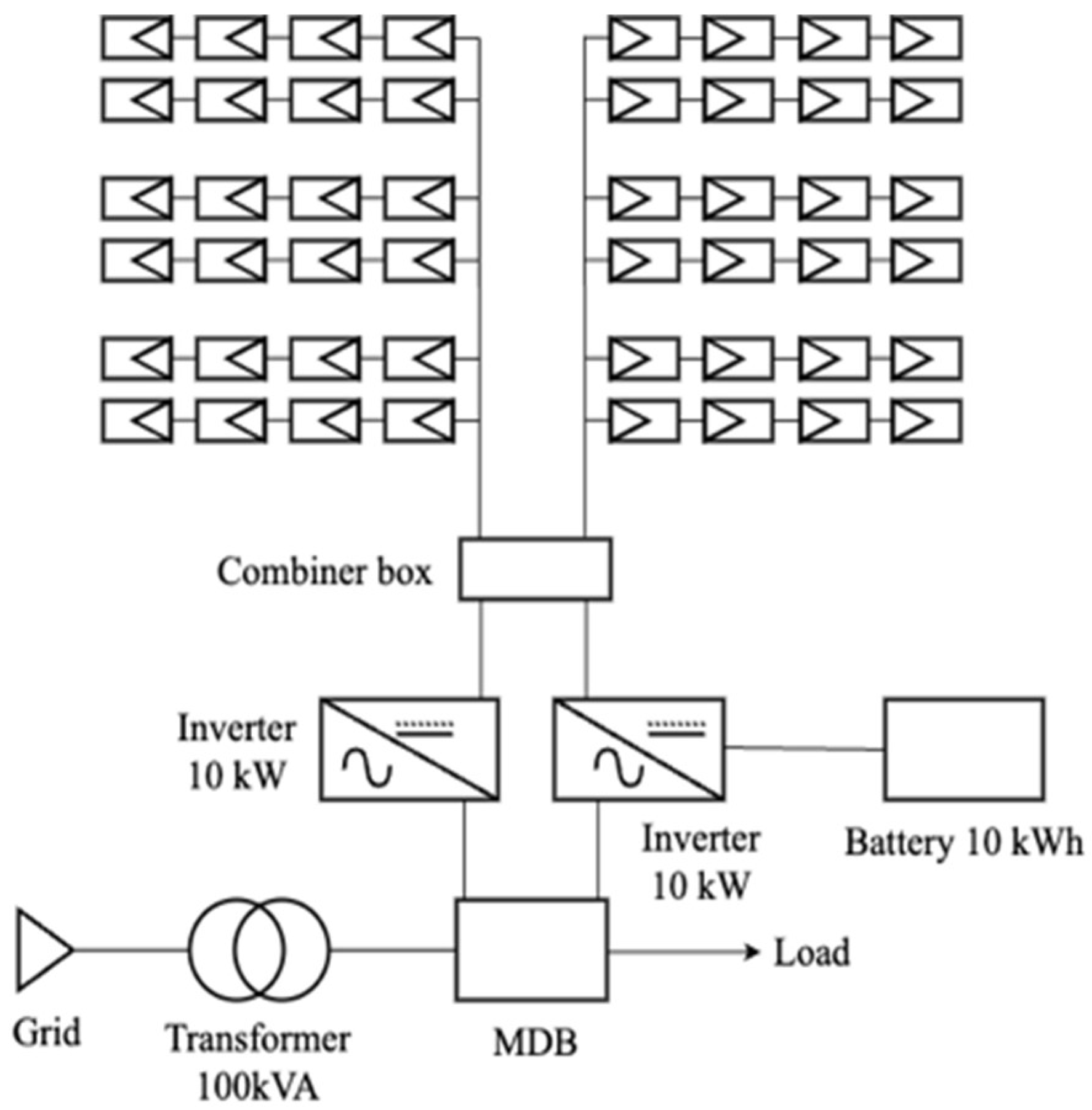
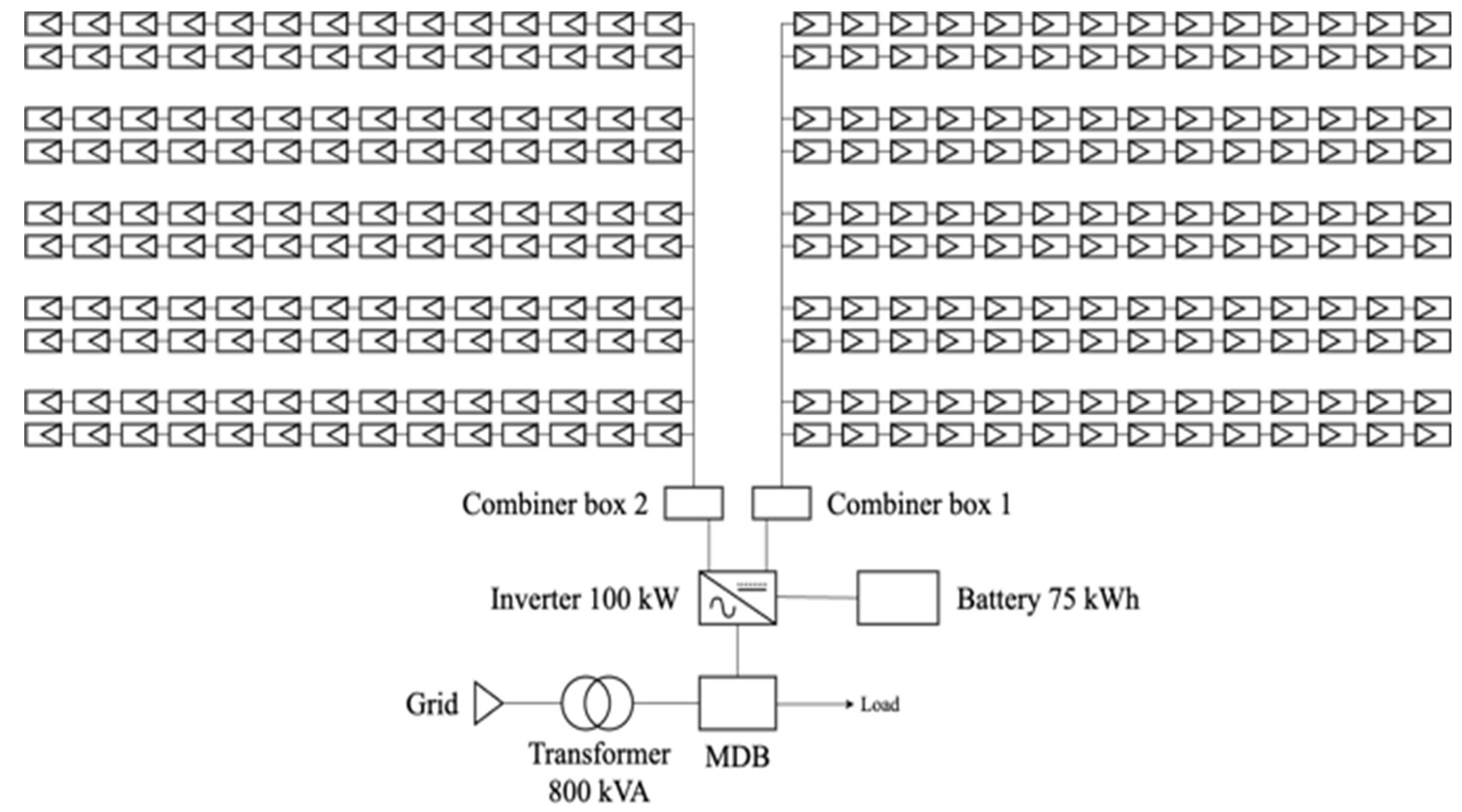
6. Case Study
6.1. Evaluation of Quantity and Value of Carbon Credits
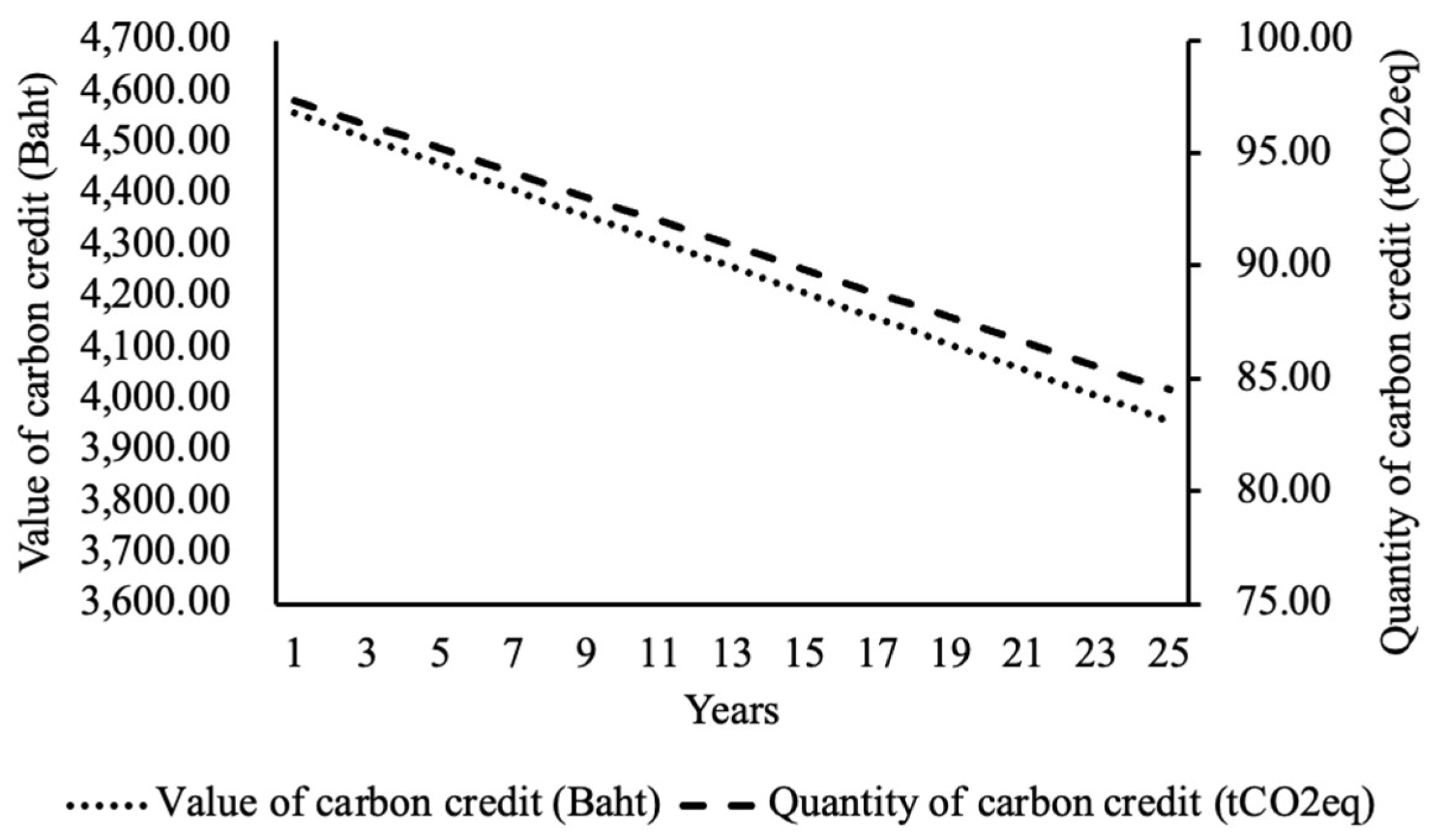

6.2. The Economic Analysis
| Year | Cost | Benefit | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Investment (Baht) |
O&M (Baht) |
Benefit (Baht) |
Cost of Carbon Credit (Baht) | |
| 0 | 5,827,220 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 1 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 735,693.31 | 4,557.66 |
| 2 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 731,646.99 | 4,532.60 |
| 3 | 0.00 | 44,940.00 | 727,600.68 | 4,507.53 |
| 4 | 0.00 | 44,940.00 | 723,554.37 | 4,482.46 |
| 5 | 0.00 | 44,940.00 | 719,508.05 | 4,457.40 |
| 6 | 0.00 | 44,940.00 | 715,461.74 | 4,432.33 |
| 7 | 0.00 | 44,940.00 | 711,415.43 | 4,407.26 |
| 8 | 0.00 | 44,940.00 | 707,369.11 | 4,382.19 |
| 9 | 0.00 | 44,940.00 | 703,322.80 | 4,357.13 |
| 10 | 0.00 | 44,940.00 | 699,276.49 | 4,332.06 |
| 11 | 0.00 | 44,940.00 | 695,230.17 | 4,306.99 |
| 12 | 0.00 | 44,940.00 | 691,183.86 | 4,281.93 |
| 13 | 0.00 | 44,940.00 | 687,137.55 | 4,256.86 |
| 14 | 0.00 | 44,940.00 | 683,091.24 | 4,231.79 |
| 15 | 0.00 | 44,940.00 | 679,044.92 | 4,206.72 |
| 16 | 0.00 | 44,940.00 | 674,998.61 | 4,181.66 |
| 17 | 0.00 | 44,940.00 | 670,952.30 | 4,156.59 |
| 18 | 0.00 | 44,940.00 | 666,905.98 | 4,131.52 |
| 19 | 0.00 | 44,940.00 | 662,859.67 | 4,106.46 |
| 20 | 0.00 | 44,940.00 | 658,813.36 | 4,081.39 |
| 21 | 0.00 | 44,940.00 | 654,767.04 | 4,056.32 |
| 22 | 0.00 | 44,940.00 | 650,720.73 | 4,031.25 |
| 23 | 0.00 | 44,940.00 | 646,674.42 | 4,006.19 |
| 24 | 0.00 | 44,940.00 | 642,628.10 | 3,981.12 |
| 25 | 0.00 | 44,940.00 | 638,581.79 | 3,956.05 |
| Total | 5,827,220 | 1,033,620 | 17,178,438.71 | 106,421.45 |
6.3. The Analysis Benefit Same Area
7. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chilukuri, Y.; Usman, A.; Rajpurohit, B.S. Assessing the Impact of Renewable Energy Sources to Achieve Net Zero Emissions. In Proceedings of 2023 IEEE Conference on Technologies for Sustainability (SusTech), Portland, OR, USA, 19-22 April 2023.
- Tavassoli, M.; Pirzaman, A.K. Comparison of effective greenhouse gases and global warming. In Proceedings of 2023 8th International Conference on Technology and Energy Management (ICTEM), Mazandaran, Babol, Iran, Islamic Republic of, 08-09 February 2023.
- Albuquerque, F.D.B.; Maraqa, M.A.; Chowdhury, R.; Mauga, T.; Alzard, M. Greenhouse gas emissions associated with road transport projects: current status, benchmarking, and assessment tools. Transportation Research Procedia 2020, 48, 2018–2030.
- Iwata, H.; Okada, K. Greenhouse gas emissions and the role of the Kyoto Protocol. Environmental Economics and Policy Studies 2012, 16, 325–342.
- Moiceanu, G.; Dinca, M.N. Climate Change-Greenhouse Gas Emissions Analysis and Forecast in Romania. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12186.
- Sanglimsuwan, K. Carbon Markets: the Simple Fact. Panyapiwat Journal 2011, 3, 123–133.
- Nelson, J.; Gambhir, A.; Daukes, N.E. Solar power for CO2 mitigation. Grantham Institute for Climate Change Imperial College London 2014, Briefing Paper No 11, 1 – 15.
- Naskar, R.; Ghosh, S.; Mandal, R. Analysis on Carbon Credit of a 5KWP Solar Photovoltaic Power Plant at JIS College of Engineering, Kalyani. Imperial Journal of Interdisciplinary Research (IJIR) 2016, 2, 1,506–1,511.
- Ruangsap, N.; Nedphokaew, S.; Rugthaicharoencheep, N. Planning and Operation Enhanced Voltage Profile by Using Distributed Generators Installation in Distribution System with Feeder Reconfiguration. In Proceedings of 2022 International Conference on Power, Energy and Innovations (ICPEI), Pattaya Chonburi, Thailand, 19-21 October 2022.
- Ngamprasert, P.; Wannakarn, P.; Rugthaicharoencheep, N. Enhance Power Loss in Distribution System Synergy Photovoltaic Power Plant. In Proceedings of 2020 International Conference on Power, Energy and Innovations (ICPEI), Chiangmai, Thailand, 14-16 October 2020.
- Drennen, T.E.; Erickson, J.D.; Chapman, D. Solar power and climate change policy in developing countries. Energy Policy 1996, 24, 9–16.
- Naskar, R.; Ghosh, S.; Mandal, R. Estimation & Analysis of a 5KWP Solar Photovoltaic Power Plant at JIS College of Engineering, Kalyani. International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) 2017, 223–230.
- Kale, D.; Kokil, P. A Study of the Performance and Carbon Credit Analysis of a 6 KWP Rooftop Solar Photovoltaic Power Plant at Sanjay Group Aurangabad, India, Innovative Energy & Research 2019, 8, 1–4.
- Bhadke, H.M.; Prajapati, A.B.; Gulhane, M.L. A case study of Government College of Engineering Amravati for its design and assessment of solar PV plant and Carbon credit earned. Journal of Emerging Technologies and Innovative Research 2022, 9, 1–9.
- Charlangsut, N.; Ruangsap, N.; Rugthaicharoencheep, N. An Assessment of a Return from Carbon Credit of a Hybrid Solar Rooftop System. In Proceedings of 2023 International Conference on Power, Energy and Innovations (ICPEI), Phrachuap Khirikhan, Thailand, 18-20 October 2023.
- Boonthienthong, M.; Ruangsap, N.; Charlangsut, N.; Rugthaicharoencheep, N. The Economic Analysis Consider Carbon Credit from Hybrid Solar Rooftop System. In Proceedings of 2023 IEEE PES 15th Asia-Pacific Power and Energy Engineering Conference (APPEEC), Chiang Mai, Thailand, 06-09 December 2023.
- Tantisattayakul, T.; Rassameethammachote, P.; Auisakul, M. Energy, Environmental and Economic Assessment of Solar Rooftop Systems on Buildings of Thammasat University, Rangsit Centre. Thai Science and Technology Journal 2017, 25, 1,083–1,099.
- United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change, ACM0002: Grid-connected electricity generation from renewable sources --- Version 22.0. Available online: https://cdm.unfccc.int/methodologies/DB/XB1TX7TAZ6SLWM9B7BC67THHVD16JV (accessed on 20 October 2024).
- Carbon Credit Certification Office Thailand Greenhouse Gas Management Organization (Public Organization), Emission Factor from Electricity Generation/Consumption for Greenhouse Gas Mitigation Projects and Activities. Available online: https://ghgreduction.tgo.or.th/en/download/120-tver-gwp-emission-factor/3377-emission-factor-30-2565.html (accessed on 20 October 2024).
- Office of the National Economic and Social Development Council Office of the Prime Minister Bangkok, Thailand, The Thirteenth National Economic and Social Development Plan (2023-2027). Available online: https://www.nesdc.go.th/nesdb_en/main.php?filename=develop_issue (accessed on 20 October 2024).
- Traivivatana, S.; Wangjiraniran, W.; Junlakarn, S.; Wansophark, N. Thailand Energy Outlook for the Thailand Integrated Energy Blueprint (TIEB). Energy Procedia 2017, 138, 399–404.
- Office of Natural Resources and Environmental Policy and Planning Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment, Thailand Long-Term Low Greenhouse Gas Emission Development Strategy (Revised Version). Available online: https://unfccc.int/documents/622276?gad_source=1&gclid=CjwKCAjw1NK4BhAwEiwAVUHPUHS-FvBRfsFg2tq6c-V_OMdi6-FW3l0OHTlLEd7hom-OEKXeAY9b4xoC-TYQAvD_BwE (accessed on 20 October 2024).
- Rajbhandari, S.; Winyuchakrit, P.; Pradhan, B.B.; Chaichaloempreecha, A.; Pita, P.; Limmeechokchai, B. Thailand’s net-zero emissions by 2050: analysis of economy-wide impacts. Sustainability Science 2023, 19, 189–202.
- Prechaveerakul, J.; Inwai, C.C. Engineering economic analysis between high power LED and hydrargyrum medium-arc iodide luminaries in studio lighting application. In Proceedings of 2015 18th International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Pattaya, Thailand, 25-28 October 2016.
- Acharya, P.; Regmi, P.P.; Gauchan, D.; Dilli, KC.B.; Gopa, KC. B. Benefit Cost Analysis of Adoption of Small Farm Machineries for Rice Cultivation in Nepal. International Journal of Applied Sciences and Biotechnology (IJASBT) 2020, 8, 448–453.
- Santoso, N.B.; Bahaweres, R.B.; Alaydrus, M. Cost-benefits, NPV, IRR and QoS analysis of the dynamic telecytology system in Indonesia, In Proceedings of 2016 1st International Conference on Biomedical Engineering (IBIOMED), Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 05-06 October 2016.
| Energy plan | Objective |
|---|---|
| AEDP | In 2036 increase renewable energy usage to 20%. |
| EEDP | In 2036 decrease 30% of energy intensity compared to 2010. |
| PDP | To enhance capacity of electricity generation to be sufficient with consumption in future. |
| Gas Plan | Management and provision of natural gas usage to adequately meet future demand. |
| Oil Plan | Management of the optimal level of petroleum consumption and reserves. |
| Year | Electrical energy produced (kW) |
Quantity of Carbon Credits (tCO2eq) |
Value of Carbon Credits (Baht) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 200,378.00 | 97.32 | 4,557.66 |
| 2 | 199,275.92 | 96.79 | 4,532.60 |
| 3 | 198,173.84 | 96.25 | 4,507.53 |
| 4 | 197,071.76 | 95.72 | 4,482.46 |
| 5 | 195,969.68 | 95.18 | 4,457.40 |
| 6 | 194,867.61 | 94.65 | 4,432.33 |
| 7 | 193,765.53 | 94.11 | 4,407.26 |
| 8 | 192,663.45 | 93.58 | 4,382.19 |
| 9 | 191,561.37 | 93.04 | 4,357.13 |
| 10 | 190,459.29 | 92.51 | 4,332.06 |
| 11 | 189,357.21 | 91.97 | 4,306.99 |
| 12 | 188,255.13 | 91.44 | 4,281.93 |
| 13 | 187,153.05 | 90.90 | 4,256.86 |
| 14 | 186,050.97 | 90.36 | 4,231.79 |
| 15 | 184,948.89 | 89.83 | 4,206.72 |
| 16 | 183,846.82 | 89.29 | 4,181.66 |
| 17 | 182,744.74 | 88.76 | 4,156.59 |
| 18 | 181,642.66 | 88.22 | 4,131.52 |
| 19 | 180,540.58 | 87.69 | 4,106.46 |
| 20 | 179,438.50 | 87.15 | 4,081.39 |
| 21 | 178,336.42 | 86.62 | 4,056.32 |
| 22 | 177,234.34 | 86.08 | 4,031.25 |
| 23 | 176,132.26 | 85.55 | 4,006.19 |
| 24 | 175,030.18 | 85.01 | 3,981.12 |
| 25 | 173,928.10 | 84.48 | 3,956.05 |
| Total | 4,678,826.30 | 2,175.18 | 106,421.45 |
| Year | Electrical energy produced (kW) |
Quantity of Carbon Credits (tCO2eq) |
Value of Carbon Credits (Baht) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 35,047.00 | 17.02 | 797.16 |
| 2 | 34,854.24 | 16.93 | 792.77 |
| 3 | 34,661.48 | 16.84 | 788.39 |
| 4 | 34,468.72 | 16.74 | 784.00 |
| 5 | 34,275.97 | 16.65 | 779.62 |
| 6 | 34,083.21 | 16.55 | 775.23 |
| 7 | 33,890.45 | 16.46 | 770.85 |
| 8 | 33,697.69 | 16.37 | 766.47 |
| 9 | 33,504.93 | 16.27 | 762.08 |
| 10 | 33,312.17 | 16.18 | 757.70 |
| 11 | 33,119.42 | 16.09 | 753.31 |
| 12 | 32,926.66 | 15.99 | 748.93 |
| 13 | 32,733.90 | 15.90 | 744.54 |
| 14 | 32,541.14 | 15.81 | 740.16 |
| 15 | 32,348.38 | 15.71 | 735.77 |
| 16 | 32,155.62 | 15.62 | 731.39 |
| 17 | 31,962.86 | 15.52 | 727.01 |
| 18 | 31,770.11 | 15.43 | 722.62 |
| 19 | 31,577.35 | 15.34 | 718.24 |
| 20 | 31,384.59 | 15.24 | 713.85 |
| 21 | 31,191.83 | 15.15 | 709.47 |
| 22 | 30,999.07 | 15.06 | 705.08 |
| 23 | 30,806.31 | 14.96 | 700.70 |
| 24 | 30,613.55 | 14.87 | 696.32 |
| 25 | 30,420.80 | 14.78 | 691.93 |
| Total | 818,347.45 | 397.47 | 18,613.58 |
| Case | NPV (Baht) | IRR (%) | B/C Ratio | Payback Period (Year) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 246,849.61 (FNPV) | 10.57 (FIRR) | 2.771 | 8.493 |
| 2 | 268,718.29 (ENPV) | 10.62 (EIRR) | 2.776 | 8.445 |
| 3 | 279,502.01 (ENPV) | 10.65 (EIRR) | 2.781 | 8.436 |
| 4 | 286,522.75 (ENPV) | 10.66 (EIRR) | 2.789 | 8.436 |
| Year | Cost | Benefit | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Investment (Baht) |
O&M (Baht) |
Benefit (Baht) |
Cost of Carbon Credit (Baht) | |
| 0 | 1,766,336 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 1 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 128,676.02 | 797.16 |
| 2 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 127,968.30 | 792.77 |
| 3 | 0.00 | 11,280.00 | 127,260.58 | 788.39 |
| 4 | 0.00 | 11,280.00 | 126,552.86 | 784.00 |
| 5 | 0.00 | 11,280.00 | 125,845.15 | 779.62 |
| 6 | 0.00 | 11,280.00 | 125,137.43 | 775.23 |
| 7 | 0.00 | 11,280.00 | 124,429.71 | 770.85 |
| 8 | 0.00 | 11,280.00 | 123,721.99 | 766.47 |
| 9 | 0.00 | 11,280.00 | 123,014.27 | 762.08 |
| 10 | 0.00 | 11,280.00 | 122,306.56 | 757.70 |
| 11 | 0.00 | 11,280.00 | 121,598.84 | 753.31 |
| 12 | 0.00 | 11,280.00 | 120,891.12 | 748.93 |
| 13 | 0.00 | 11,280.00 | 120,183.40 | 744.54 |
| 14 | 0.00 | 11,280.00 | 119,475.68 | 740.16 |
| 15 | 0.00 | 11,280.00 | 118,767.97 | 735.77 |
| 16 | 0.00 | 11,280.00 | 118,060.25 | 731.39 |
| 17 | 0.00 | 11,280.00 | 117,352.53 | 727.01 |
| 18 | 0.00 | 11,280.00 | 116,644.81 | 722.62 |
| 19 | 0.00 | 11,280.00 | 115,937.09 | 718.24 |
| 20 | 0.00 | 11,280.00 | 115,229.37 | 713.85 |
| 21 | 0.00 | 11,280.00 | 114,521.66 | 709.47 |
| 22 | 0.00 | 11,280.00 | 113,813.94 | 705.08 |
| 23 | 0.00 | 11,280.00 | 113,106.22 | 700.70 |
| 24 | 0.00 | 11,280.00 | 112,398.50 | 696.32 |
| 25 | 0.00 | 11,280.00 | 111,690.78 | 691.93 |
| Total | 1,766,336 | 259,440.00 | 3,004,585.04 | 18,613.58 |
| Case | NPV (Baht) | IRR (%) | B/C Ratio | Payback Period (Year) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | -729,060.75 (FNPV) | 3.88 (FIRR) | 1.554 | 15.535 |
| 2 | -725,235.82 (ENPV) | 3.91 (EIRR) | 1.557 | 15.484 |
| 3 | -723,349.70 (ENPV) | 3.92 (EIRR) | 1.560 | 15.434 |
| 4 | -722,121.74 (ENPV) | 3.95 (EIRR) | 1.565 | 15.425 |
| Case | Payback Period of 25.68 kWp System (Year) |
Payback period of 25.68 kWp system, when combined profit of 149.80 kWp System (Year) |
Comparison payback period of 25.68 kWp system, when combined profit of 149.80 kWp System (Year) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 15.535 | 10.495 | 5.040 |
| 2 | 15.484 | 10.447 | 5.037 |
| 3 | 15.434 | 10.431 | 5.003 |
| 4 | 15.425 | 10.431 | 4.994 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





