Submitted:
25 October 2024
Posted:
28 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Chikungunya is mosquito born disease that is spread across continents. This research provides valuable insights into the potential functional significance of the hydrophobic tail and cysteine-rich regions in E2 proteins. These findings lay the groundwork for future investigations into the specific roles of the C-terminal domain and post-translational modifications, which could ultimately lead to a better understanding of viral mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets.
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
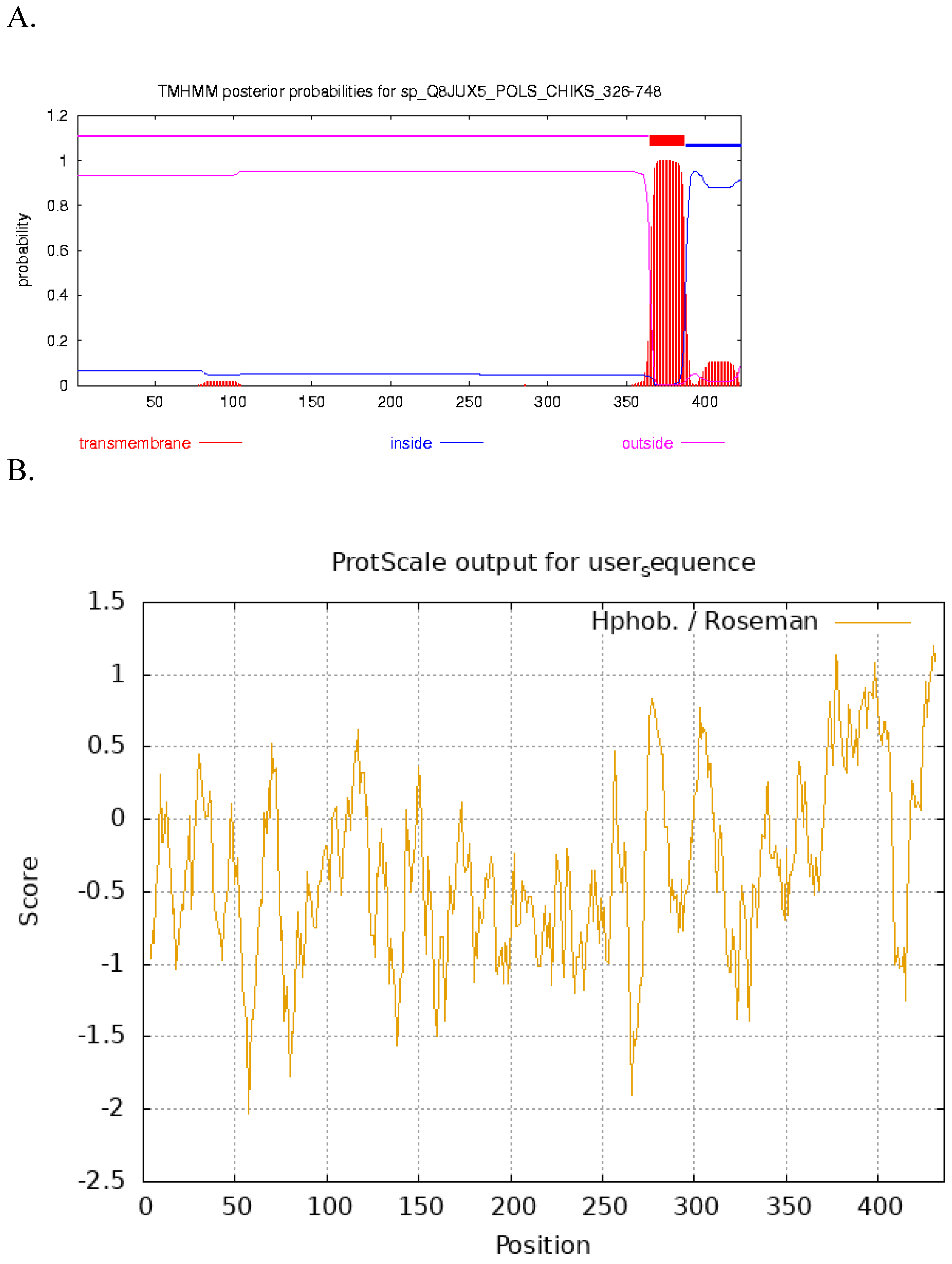
Prediction of Transmembrane Domain
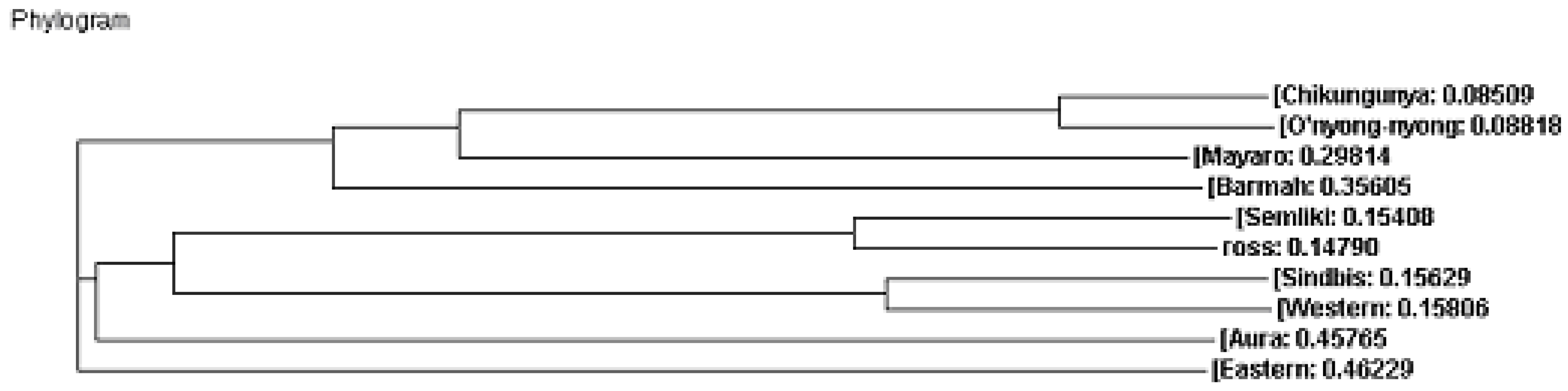
Phylogenetic Analysis
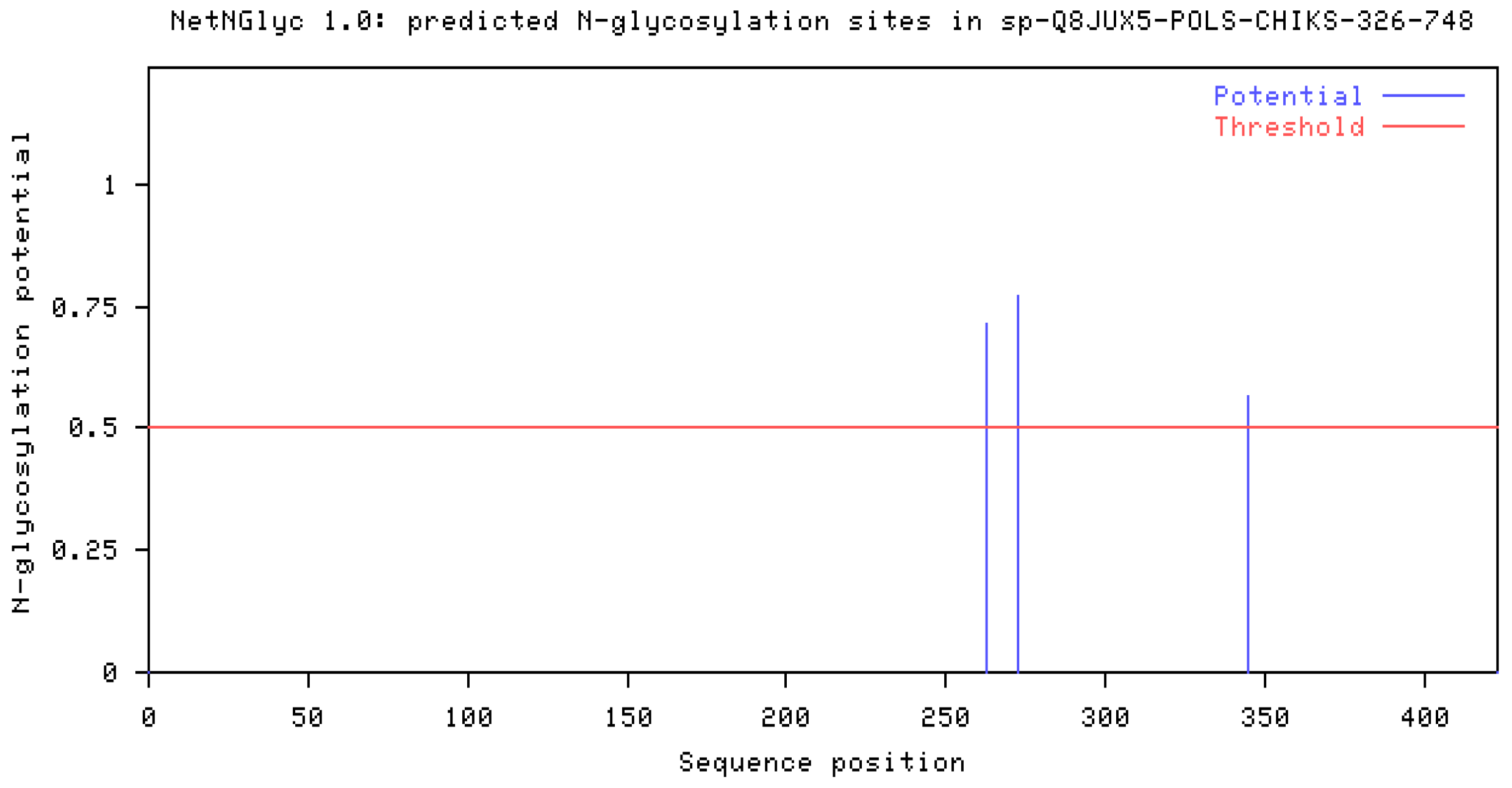
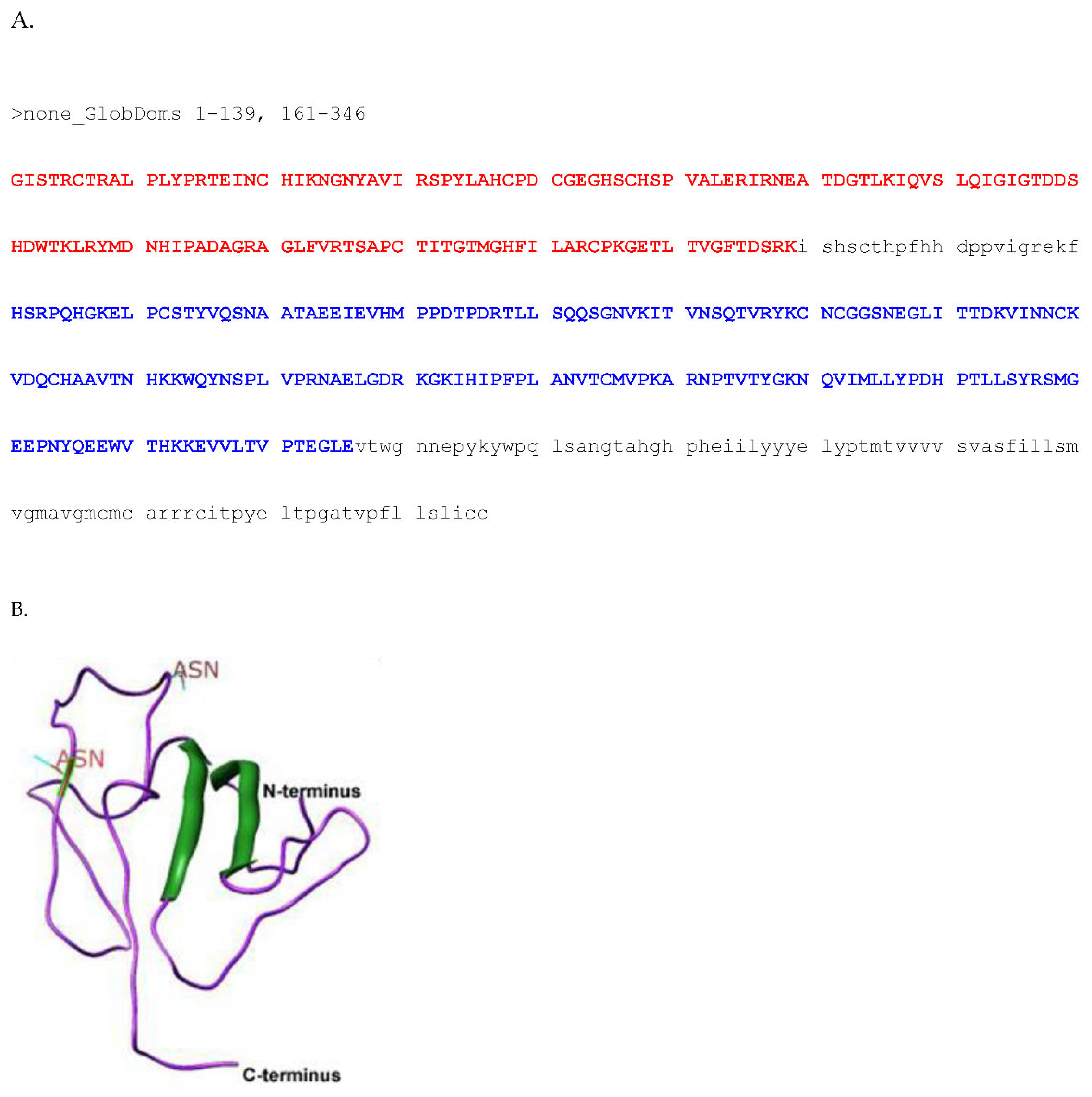
Post-Transnational Modification
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bogunia, M., & Makowski, M. (2020). Influence of Ionic Strength on Hydrophobic Interactions in Water: Dependence on Solute Size and Shape. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 124(46), 10326–10336. [CrossRef]
- Deoshatwar, A., Salve, D., Gopalkrishna, V., Kumar, A., Barve, U., Joshi, M., Katendra, S., Dhembre, V., Maheshwari, S., & Viswanathan, R. (2021). Evidence-Based Health Behavior Interventions for Cholera: Lessons from an Outbreak Investigation in India. The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, 106(1), 229–232. [CrossRef]
- Dobhal, S., Chauhan, K., Kumar, S., Shikha, S., Jogi, M., Kumar, D., Kumar, A., Jaiswal, V., & Kumar, P. (2024). In silico Identification of MHC Displayed Tumor Associated Peptides in Ovarian Cancer for Multi-Epitope Vaccine Construct. Endocrine, Metabolic & Immune Disorders Drug Targets, 24. [CrossRef]
- Duvaud, S., Gabella, C., Lisacek, F., Stockinger, H., Ioannidis, V., & Durinx, C. (2021). Expasy, the Swiss Bioinformatics Resource Portal, as designed by its users. Nucleic Acids Research, 49(W1). [CrossRef]
- Garg, K., Kumar, A., Kizhakkethil, V., Kumar, P., & Singh, S. (2023). Overlap in oncogenic and pro-inflammatory pathways associated with areca nut and nicotine exposure. Cancer Pathogenesis and Therapy. [CrossRef]
- Gill, J., Kumar, A., & Sharma, A. (2022). Structural comparisons reveal diverse binding modes between nucleosome assembly proteins and histones. Epigenetics & Chromatin, 15(1), 20. [CrossRef]
- Gill, J., Kumar, A., Yogavel, M., Belrhali, H., Jain, S. K., Rug, M., Brown, M., Maier, A. G., & Sharma, A. (2010). Structure, localization and histone binding properties of nuclear-associated nucleosome assembly protein from Plasmodium falciparum. Malaria Journal, 9(1), 90. [CrossRef]
- Gill, J., Yogavel, M., Kumar, A., Belrhali, H., Jain, S. K., Rug, M., Brown, M., Maier, A. G., & Sharma, A. (2009). Crystal structure of malaria parasite nucleosome assembly protein: Distinct modes of protein localization and histone recognition. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 284(15), 10076–10087. [CrossRef]
- Gopalkrishna, V., Joshi, M., Viswanathan, R., Malu, G., Ganorkar, N., Chavan, N., Shinde, M., Kumar, A., & Dhurandhare, S. (2019). Cholera outbreak in Aurangabad, Maharashtra, western India. Indian Journal of Medical Research, 150(6), 640. [CrossRef]
- Kaur, R., Kumar, P., & Kumar, A. (2023). Insights on the nuclear shuttling of H2A-H2B histone chaperones. Nucleosides, Nucleotides & Nucleic Acids, 1–13. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A., Barve, U., Gopalkrishna, V., Tandale, B. V, Katendra, S., Joshi, M. S., Salve, D., & Viswanathan, R. (2022). Outbreak of cholera in a remote village in western India. The Indian Journal of Medical Research, 156(3), 442–448. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A., Kashyap, M., Bhavesh, N. S., Yogavel, M., & Sharma, A. (2012). Structural delineation of histone post-translation modifications in histone-nucleosome assembly protein complex. Journal of Structural Biology, 180(1), 1–9. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A., Sharma, D., Aggarwal, M. L., Chacko, K. M., & Bhatt, T. K. (2016). Cancer/testis antigens as molecular drug targets using network pharmacology. Tumor Biology, 37(12), 15697–15705. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P., Dhingra, A., Sharma, D., Kumar, A., & Singh, S. (2022). Microbiome and Development of Ovarian Cancer. Endocrine, Metabolic & Immune Disorders Drug Targets. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P., Rani, A., Singh, S., & Kumar, A. (2022). Recent advances on DNA and omics-based technology in Food testing and authentication: A review. Journal of Food Safety, 42(4). [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P. C., Kumar, A., & Sharma, A. (2009). Analysis of small nucleolar RNAs reveals unique genetic features in malaria parasites. BMC Genomics, 10(1), 68. [CrossRef]
- Roesch, C., Popovici, J., Bin, S., Run, V., Kim, S., Ramboarina, S., Rakotomalala, E., Rakotoarison, R. L., Rasoloharimanana, T., Andriamanantena, Z., Kumar, A., Guillotte-Blisnick, M., Huon, C., Serre, D., Chitnis, C. E., Vigan-Womas, I., & Menard, D. (2018). Genetic diversity in two Plasmodium vivax protein ligands for reticulocyte invasion. PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases, 12(10), e0006555. [CrossRef]
- Sajid, M., Srivastava, S., Kumar, A., Kumar, A., Singh, H., & Bharadwaj, M. (2021). Bacteriome of Moist Smokeless Tobacco Products Consumed in India With Emphasis on the Predictive Functional Potential. Frontiers in Microbiology, 12, 784841. [CrossRef]
- Shahid, M., Srivastava, S., Shukla, P., Yadav, R., Sajid, M., Kumar, A., Singh, S., & Bharadwaj, M. (2023). Characterization of physiochemical parameters & their effect on microbial content of smokeless tobacco products marketed in north India. The Indian Journal of Medical Research, 158(5 & 6), 542–551. [CrossRef]
- Shikha, S., Jogi, M. K., Jha, R., Kumar, R. A., Sah, T., Singh, P., Sagar, R., Kumar, A., Marwal, R., Ponnusamy, K., Agarwal, S. M., Kumar, R. S., Arif, N., Bharadwaj, M., Singh, S., & Kumar, P. (2023). Genome sequencing of SARS-CoV-2 omicron variants in Delhi reveals alterations in immunogenic regions in spike glycoprotein. Frontiers in Immunology, 14, 1209513. [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. (2015). WHO Chikungunya Fact Sheet. World Health Organization Media Centre.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




