Submitted:
25 October 2024
Posted:
28 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
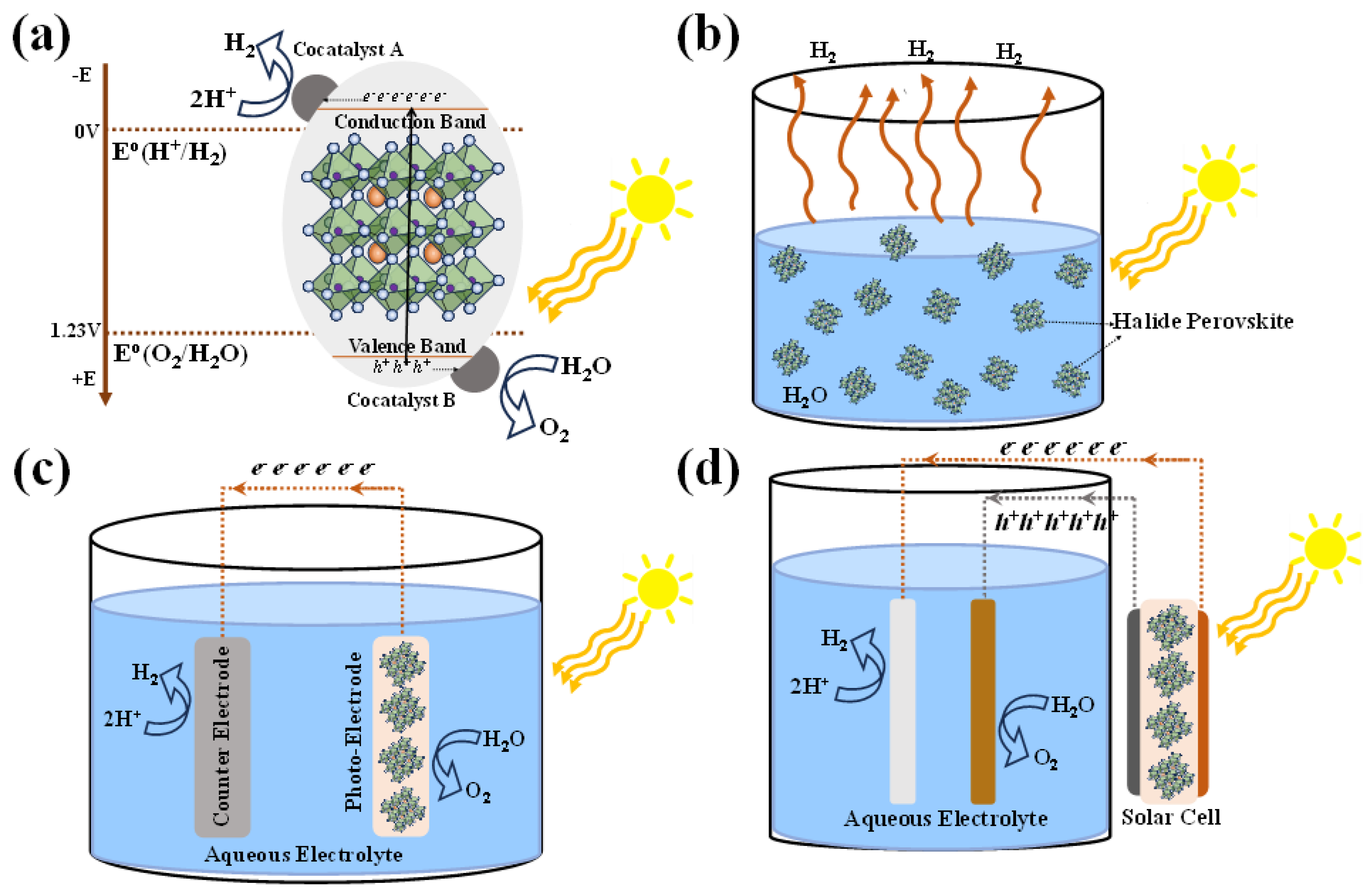
2. Solar-Driven Hydrogen Generation Systems
3. Lead-Halide Perovskites for Hydrogen Generation
4. Issues with Lead HPs for Water Splitting
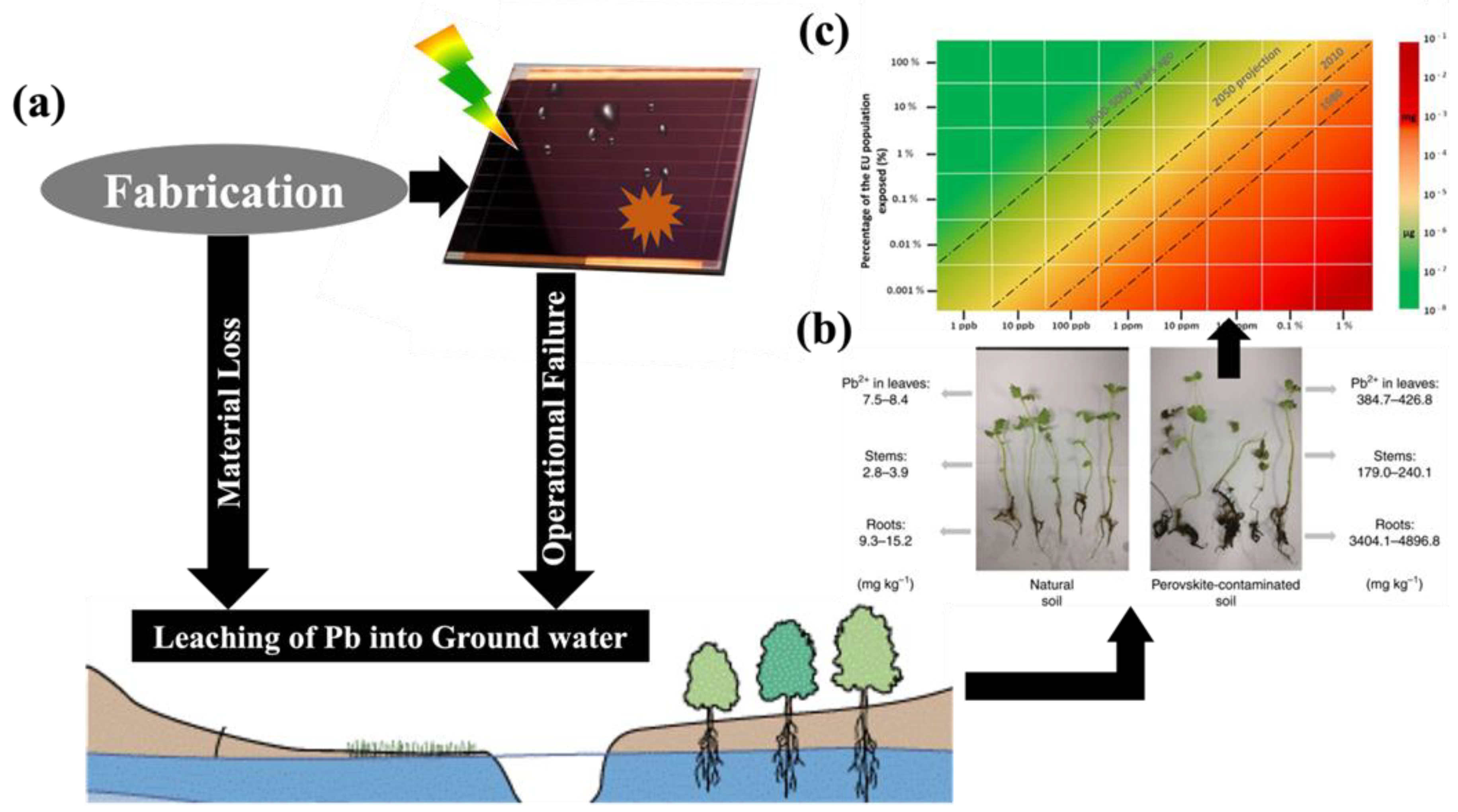
4.1. Toxicity
4.2. Stability
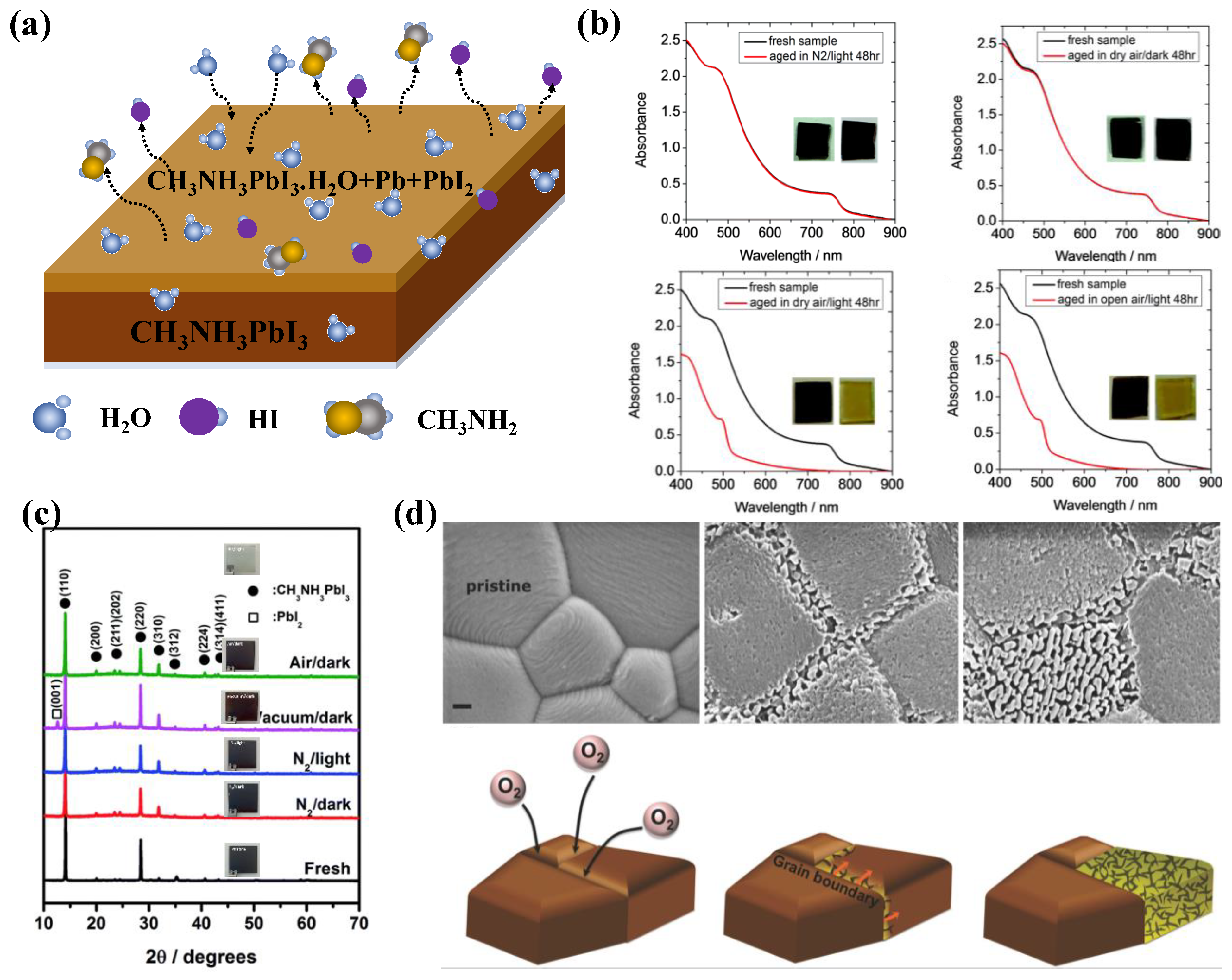
4.2.1. Moisture induced Degradation
4.2.2. Oxygen and Photo- Induced Degradation
4.3. Band Gap of Pb-HPs and Need of Pb-Free HPs in PECs
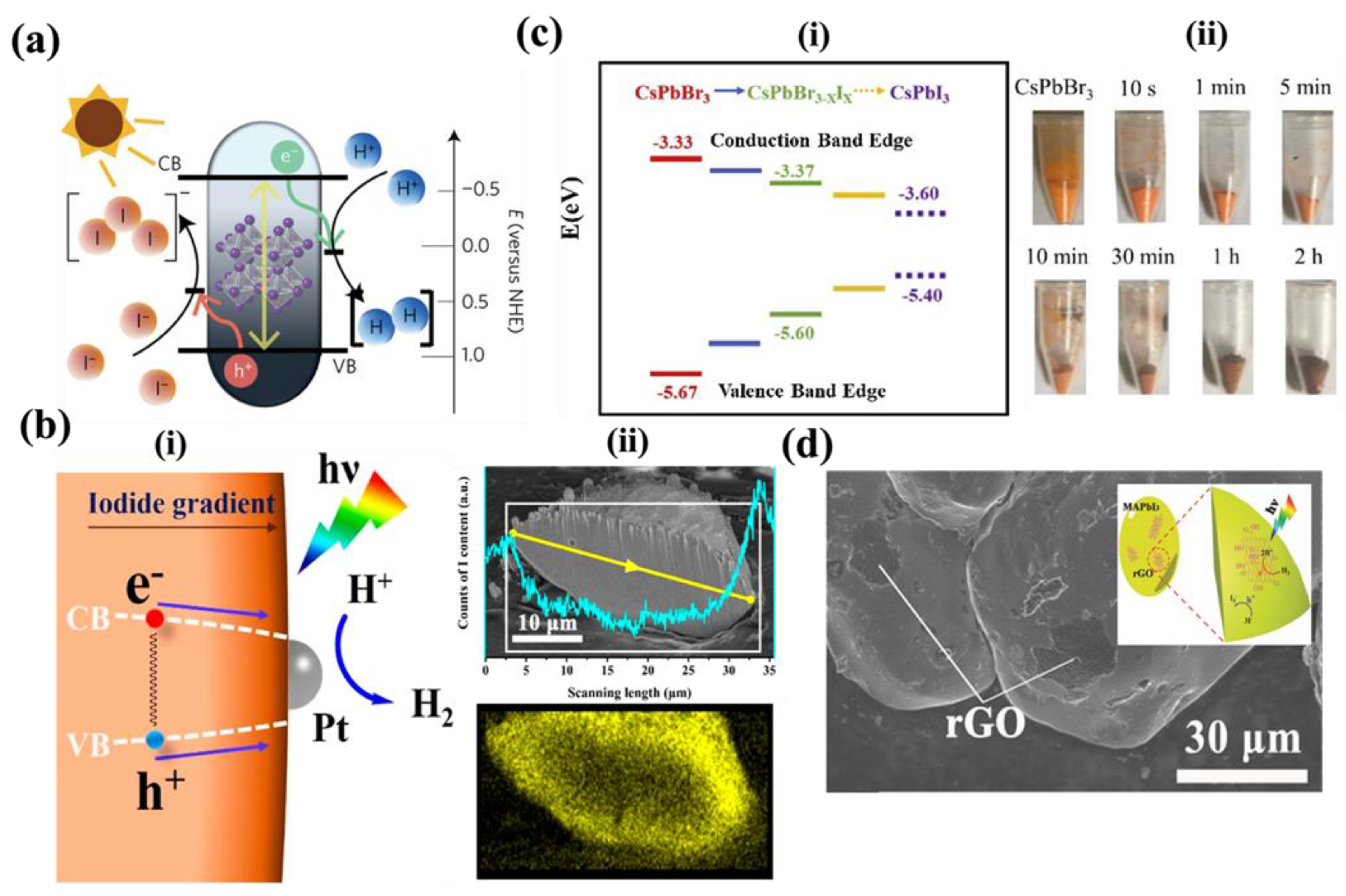
5. Lead-Free Perovskites in Water Splitting/Hydrogen Generation
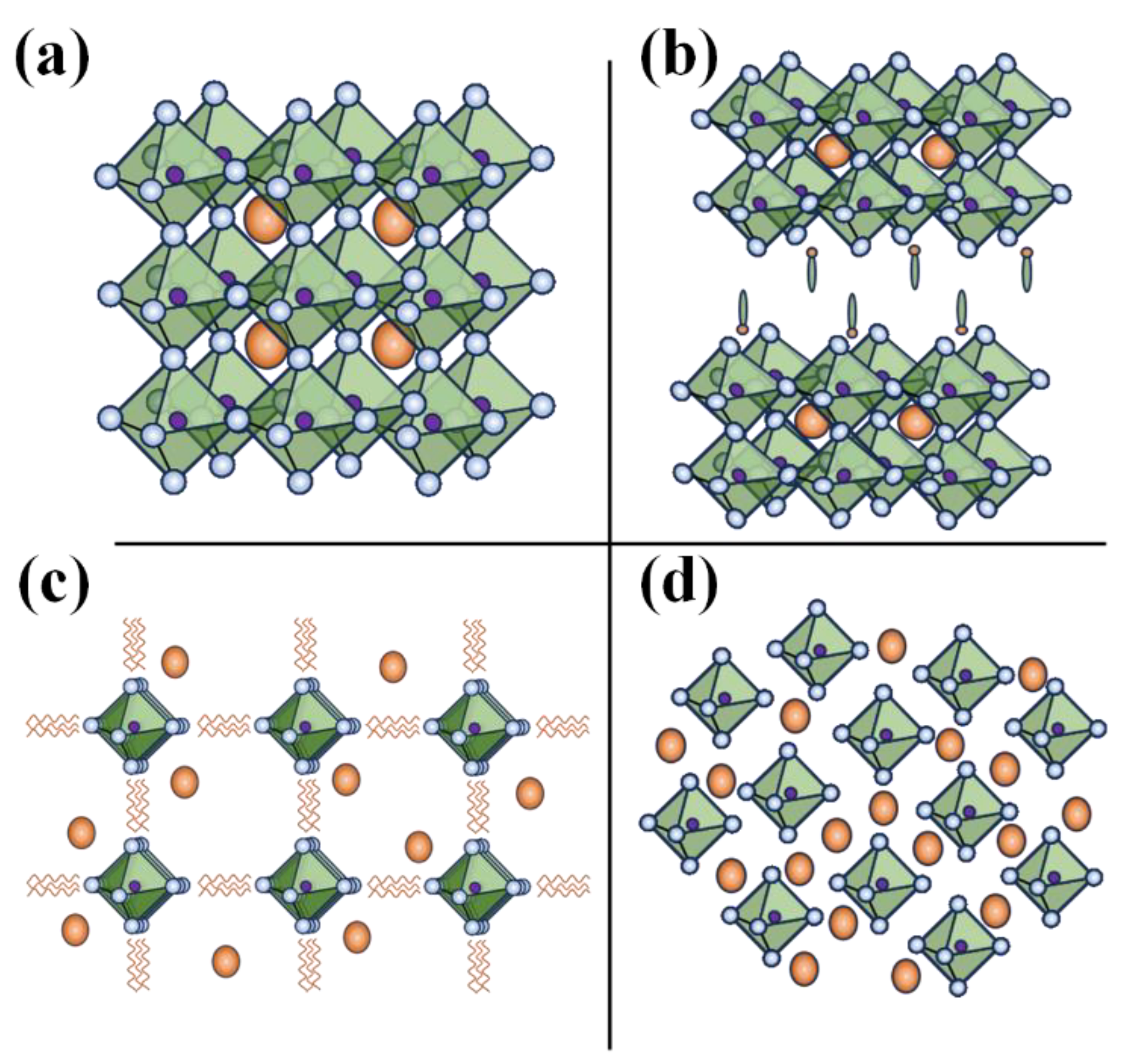
5.1. Classification of HP Perovskites (Based on Their Structure)
5.2. Structure and Bandgap in (Lead-Free) Perovskite
5.3. Photocatalytic Water Splitting Using Pb-Free Halide Perovskites
5.3.1. Bismuth and Antimony HPs
| No | Material | Reaction Medium | Illumination | HER/ Photocurrent | Stability | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | MA3Bi2I9/ Pt | Aqueous HI/H3PO2 | 300 W Xe-lamp with a 400 nm cutoff filter | 169.21 µmol g−1 h−1 | 10 hrs of 7 cycles | 59 |
| 2 | Cs3Bi2I9 | Aqueous HI/H3PO2 | Visible Light | 22.5 μmol h-1 11.7 H2 molecules per second |
5 hrs of 3 cycles | 60 |
| 3 | Cs3Bi2I9 | HI in n ethyl acetate | 100 mW cm-2 | 1504.5 μmol h-1 g-1 | 2 hrs of 4 cycles | 61 |
| 4 | Cs3Bi2I9/Pt | Aqueous HI/H3PO2 Aqueous Me.OH |
100 mW cm-2 (λ > 420 nm) | 2304 μmol g-1 35.5 μmol g-1 |
4 hrs | 62 |
| 5 | MA3Sb2I9/ Pt | Aqueous HI/H3PO2 | 100 mW cm-2 (λ > 400 nm) | 883 | 3 hrs of 4 cycles | 63 |
| 6 | Cs3Sb2I9/ Pt | Aqueous HI/H3PO2 | 100 mW cm-2 (λ ≥ 400 nm) | 804.54 μmol g−1 | 50 h | 64 |
| 7 | 2-AMPSbI5-1 | Sodium sulfate: H2O | 150 W xenon lamp | 106.7 | 4 cycles | 65 |
| 8 | 2-AMPSbI5-2 | Sodium sulfate: H2O | 150 W xenon lamp | 96.3 | 4 cycles | 65 |
| 9 | PtSA/Cs2SnI6 | Aqueous HI | 100 mW cm−2 (λ ≥ 420 nm, | 430 μmol h−1 g−1 | 180 h | 66 |
5.3.2. Tin and Germanium HPs
5.3.2. Vacancy-Order HPs
5.3. Pb-Free HPs for Water Splitting via PEC Systems
6. Enhancing Photocatalytic Performance of Pb-Free HPs
6.1. Band Gap Tuning by Compositional Engineering
6.2. Pb-Free HP Heterojunctions
6.2.1. Semiconductor/Pb-Free Heterojunctions
6.2.2. g-C3N4/Pb-Free HP Heterojunction
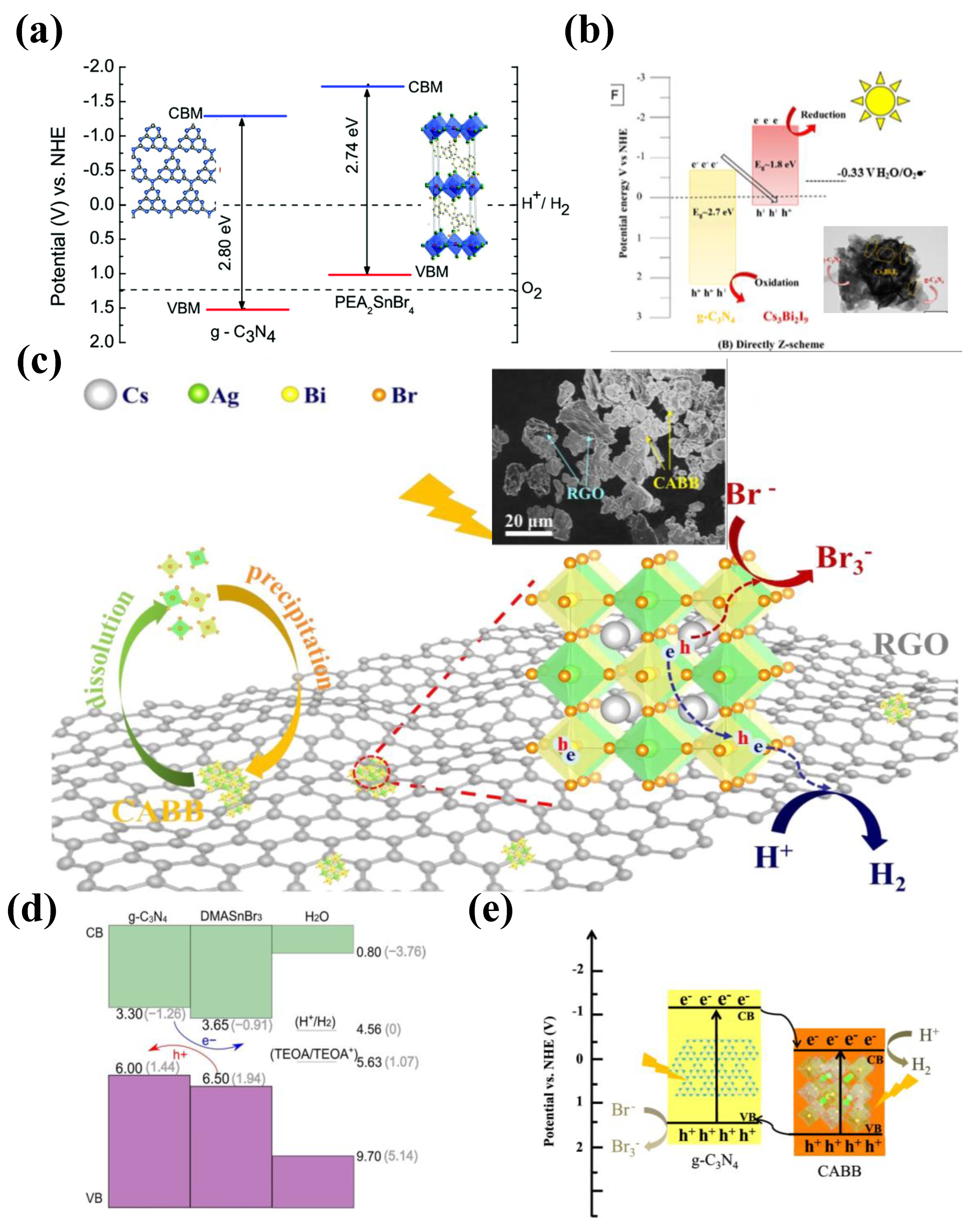
7. Prospectives and Conclusions
- (1).
- Dimensionality and bandgap: In general, most of the non-lead metals (excluding Sn and Ge) tend to crystallize in lower-dimensional perovskite structures. These 0-D and 2-D perovskites inherently exhibit higher band gaps, making them suitable for water splitting applications.
- (2).
- Stability: Unlike conventional lead perovskite with MA cation, lead-free perovskites with Cs cation are structurally stable and allow crystallization of materials into its low dimensional perovskite phases. All inorganic 0-D Bi (/Sb) perovskite and vacancy order Sn, Ag-Bi etc.., exhibited excellent stability in water medium for several hours, proving their potential application in photocatalytic systems. Alternatively, polymer encapsulation, hydrophobic ligand assisted nanoparticle stabilization and core-shell perovskites also enhance stability and can be exploited for photocatalytic water splitting.
- (3).
- Co-catalysts: Loading Pt co-catalyst to improve the HER has become trivial, however this modification in the system improved hydrogen evolution drastically. Considering the total system cost, it is essential to explore alternatives to Pt. While halide-perovskite/Pt based photocatalytic systems are extensively studied, serval other metal (Ni, Cu, Mn) and oxide (-perovskite) co-catalysts in conjunction with lead-free perovskites can be explored.
- (4).
- Lead-free perovskites are usually employed in photocatalytic systems rather than in photoelectrochemical water splitting. Most possible reason would be the challenges in formation of the uniform thin films for the fabrication of photoanode due to their low dimensionality.
- (5).
- Owing to their wide gap, several lead-free perovskite compositions can be excellent choices for coupling with Si cells to develop tandem photoanodes for photoelectrochemical water splitting.
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of interest
References
- Møller, C.K. Crystal structure and photoconductivity of caesium plumbohalides. Nature 1958, 182, 1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, A.; Teshima, K.; Shirai, Y.; Miyasaka, T. Organometal halide perovskites as visible-light sensitizers for photovoltaic cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2009, 131, 6050–6051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Chang, W.J.; Lee, C.W.; Park, S.; Ahn, H.-Y.; Nam, K.T. Photocatalytic hydrogen generation from hydriodic acid using methylammonium lead iodide in dynamic equilibrium with aqueous solution. Nat Energy 2016, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, P.; Guan, Z.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Jin, S.; Dai, Y.; Whangbo, M.-H.; Huang, B. Enhancing the Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution Activity of Mixed-Halide Perovskite CH3NH3PbBr3–xIx Achieved by Bandgap Funneling of Charge Carriers. ACS Catal 2018, 8, 10349–10357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Z.; Wu, Y.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Liu, Y.; Dai, Y.; Whangbo, M.-H.; Huang, B. Perovskite photocatalyst CsPbBr3-xIx with a bandgap funnel structure for H2 evolution under visible light. Appl Catal B 2019, 245, 522–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, P.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zou, G.; Dai, Y.; Whangbo, M.; Huang, B. Composite of CH3NH3PbI3 with Reduced Graphene Oxide as a Highly Efficient and Stable Visible-Light Photocatalyst for Hydrogen Evolution in Aqueous HI Solution. Advanced Materials 2018, 30, 1704342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, H.; Yu, W.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zong, X.; Li, C. Dynamic Interaction between Methylammonium Lead Iodide and TiO2 Nanocrystals Leads to Enhanced Photocatalytic H2 Evolution from HI Splitting. ACS Energy Lett 2018, 3, 1159–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sharma, A.; Duong, T.; Arandiyan, H.; Zhao, T.; Zhang, D.; Su, Z.; Garbrecht, M.; Beck, F.J.; Karuturi, S. Direct solar hydrogen generation at 20% efficiency using low-cost materials. Adv Energy Mater 2021, 11, 2101053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, K.; Branco, B.; Zhao, Y.; Zardetto, V.; Phung, N.; Bracesco, A.; Mazzarella, L.; Wienk, M.M.; Creatore, M.; Isabella, O. Efficient Continuous Light-Driven Electrochemical Water Splitting Enabled by Monolithic Perovskite-Silicon Tandem Photovoltaics. Adv Mater Technol 2023, 8, 2201131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehr, A.M.K.; Agrawal, A.; Mandani, F.; Conrad, C.L.; Jiang, Q.; Park, S.Y.; Alley, O.; Li, B.; Sidhik, S.; Metcalf, I. Integrated halide perovskite photoelectrochemical cells with solar-driven water-splitting efficiency of 20.8%. Nat Commun 2023, 14, 3797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Cao, H.-L.; Jiao, W.-B.; Wang, Q.; Wei, M.; Cantone, I.; Lü, J.; Abate, A. Biological impact of lead from halide perovskites reveals the risk of introducing a safe threshold. Nat Commun 2020, 11, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponti, C.; Nasti, G.; Di Girolamo, D.; Cantone, I.; Alharthi, F.A.; Abate, A. Environmental lead exposure from halide perovskites in solar cells. Trends Ecol Evol 2022, 37, 281–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nain, P.; Kumar, A. Theoretical evaluation of metal release potential of emerging third generation solar photovoltaics. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells 2021, 227, 111120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hailegnaw, B.; Kirmayer, S.; Edri, E.; Hodes, G.; Cahen, D. Rain on methylammonium lead iodide based perovskites: possible environmental effects of perovskite solar cells. J Phys Chem Lett 2015, 6, 1543–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leguy, A.M.A.; Hu, Y.; Campoy-Quiles, M.; Alonso, M.I.; Weber, O.J.; Azarhoosh, P.; van Schilfgaarde, M.; Weller, M.T.; Bein, T.; Nelson, J.; Docampo, P.; Barnes, P.R.F. Reversible Hydration of CH3NH3PbI3 in Films, Single Crystals, and Solar Cells. Chemistry of Materials 2015, 27, 3397–3407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Cao, H.-L.; Jiao, W.-B.; Wang, Q.; Wei, M.; Cantone, I.; Lü, J.; Abate, A. Biological impact of lead from halide perovskites reveals the risk of introducing a safe threshold. Nat Commun 2020, 11, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conings, B.; Drijkoningen, J.; Gauquelin, N.; Babayigit, A.; D’Haen, J.; D’Olieslaeger, L.; Ethirajan, A.; Verbeeck, J.; Manca, J.; Mosconi, E. Intrinsic thermal instability of methylammonium lead trihalide perovskite. Adv Energy Mater 2015, 5, 1500477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Guo, D.; Li, M.; Wang, C.; Zhou, Z.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, F.; Ao, Z.; Nie, Z. Temperature-dependent thermal decomposition pathway of organic–inorganic halide perovskite materials. Chemistry of Materials 2019, 31, 8515–8522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masi, S.; Gualdrón-Reyes, A.F.; Mora-Sero, I. Stabilization of Black Perovskite Phase in FAPbI3 and CsPbI3. ACS Energy Lett 2020, 5, 1974–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, J.M.; Butler, K.T.; Brivio, F.; Hendon, C.H.; van Schilfgaarde, M.; Walsh, A. Atomistic origins of high-performance in hybrid halide perovskite solar cells. Nano Lett 2014, 14, 2584–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, D.; Aristidou, N.; Pont, S.; Sanchez-Molina, I.; Chotchunangatchaval, T.; Wheeler, S.; Durrant, J.R.; Haque, S.A. Light and oxygen induced degradation limits the operational stability of methylammonium lead triiodide perovskite solar cells. Energy Environ Sci 2016, 9, 1655–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Brandl, M.; May, B.; Levchuk, I.; Hou, Y.; Richter, M.; Chen, H.; Chen, S.; Kahmann, S.; Osvet, A. Photoinduced degradation of methylammonium lead triiodide perovskite semiconductors. J Mater Chem A Mater 2016, 4, 15896–15903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Fassl, P.; Becker-Koch, D.; Bausch, A.; Rivkin, B.; Bai, S.; Hopkinson, P.E.; Snaith, H.J.; Vaynzof, Y. Role of microstructure in oxygen induced photodegradation of methylammonium lead triiodide perovskite films. Adv Energy Mater 2017, 7, 1700977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, G.; Li, W.; Meng, F.; Wang, L.; Dong, H.; Qiu, Y. Study on the stability of CH3NH3PbI3 films and the effect of post-modification by aluminum oxide in all-solid-state hybrid solar cells. J Mater Chem A Mater 2014, 2, 705–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habisreutinger, S.N.; Leijtens, T.; Eperon, G.E.; Stranks, S.D.; Nicholas, R.J.; Snaith, H.J. Carbon nanotube/polymer composites as a highly stable hole collection layer in perovskite solar cells. Nano Lett 2014, 14, 5561–5568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Siempelkamp, B.D.; Liu, D.; Kelly, T.L. Investigation of CH3NH3PbI3 Degradation Rates and Mechanisms in Controlled Humidity Environments Using in Situ Techniques. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 1955–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aristidou, N.; Sanchez-Molina, I.; Chotchuangchutchaval, T.; Brown, M.; Martinez, L.; Rath, T.; Haque, S.A. The role of oxygen in the degradation of methylammonium lead trihalide perovskite photoactive layers. Angewandte Chemie 2015, 127, 8326–8330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Liu, Y.; Ding, Y.; Li, F.; Wang, L.; Cai, B.; Zhang, F.; Liu, T.; Boschloo, G.; Johansson, E.M.J. Monolithic FAPbBr3 photoanode for photoelectrochemical water oxidation with low onset-potential and enhanced stability. Nat Commun 2023, 14, 5486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Z.; Chong, W.K.; Ng, A.Y.R.; Li, M.; Ganguly, R.; Sum, T.C.; Soo, H.S. Hydrophobic Metal Halide Perovskites for Visible-Light Photoredox C−C Bond Cleavage and Dehydrogenation Catalysis. Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2019, 58, 3456–3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kore, B.P.; Gardner, J.M. Water-resistant 2D lead (ii) iodide perovskites: correlation between optical properties and phase transitions. Mater Adv 2020, 1, 2395–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalf, I.; Sidhik, S.; Zhang, H.; Agrawal, A.; Persaud, J.; Hou, J.; Even, J.; Mohite, A.D. Synergy of 3D and 2D perovskites for durable, efficient solar cells and beyond. Chem Rev 2023, 123, 9565–9652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Zhou, C.; Tian, Y.; Siegrist, T.; Ma, B. Low-dimensional organometal halide perovskites. ACS Energy Lett 2018, 3, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Eaton, S.W.; Yu, Y.; Dou, L.; Yang, P. Solution-phase synthesis of cesium lead halide perovskite nanowires. J Am Chem Soc 2015, 137, 9230–9233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hintermayr, V.A.; Richter, A.F.; Ehrat, F.; Döblinger, M.; Vanderlinden, W.; Sichert, J.A.; Tong, Y.; Polavarapu, L.; Feldmann, J.; Urban, A.S. Tuning the optical properties of perovskite nanoplatelets through composition and thickness by ligand-assisted exfoliation. Advanced Materials 2016, 28, 9478–9485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadhanala, A.; Ahmad, S.; Zhao, B.; Giesbrecht, N.; Pearce, P.M.; Deschler, F.; Hoye, R.L.Z.; Gödel, K.C.; Bein, T.; Docampo, P.; Dutton, S.E.; De Volder, M.F.L.; Friend, R.H. Blue-green color tunable solution processable organolead chloride–bromide mixed halide perovskites for optoelectronic applications. Nano Lett 2015, 15, 6095–6101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Tian, Y.; Wang, M.; Rose, A.; Besara, T.; Doyle, N.K.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, J.C.; Clark, R.; Hu, Y.; Siegrist, T.; Lin, S.; Ma, B. Low-dimensional organic tin bromide perovskites and their photoinduced structural transformation. Angewandte Chemie 2017, 129, 9146–9150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Cao, B.; Yuan, S.; Chen, X.; Qiu, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Ye, Q.; Wang, H.; Zeng, H.; Liu, J.; Kanatzidis, M.G. From unstable CsSnI3 to air-stable Cs2SnI6: A lead-free perovskite solar cell light absorber with bandgap of 1.48 eV and high absorption coefficient. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells 2017, 159, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasanna, R.; Gold-Parker, A.; Leijtens, T.; Conings, B.; Babayigit, A.; Boyen, H.G.; Toney, M.F.; McGehee, M.D. Band gap tuning via lattice contraction and octahedral tilting in perovskite materials for photovoltaics. J Am Chem Soc 2017, 139, 11117–11124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchenko, E.I.; Korolev, V.V.; Fateev, S.A.; Mitrofanov, A.; Eremin, N.N.; Goodilin, E.A.; Tarasov, A.B. Relationships between distortions of inorganic framework and band gap of layered hybrid halide perovskites. Chemistry of Materials 2021, 33, 7518–7526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pious, J.K.; Muthu, C.; Dani, S.; Saeki, A.; Nair, V.C. Bismuth-based zero-dimensional perovskite-like materials: effect of benzylammonium on dielectric confinement and photoconductivity. Chemistry of Materials 2020, 32, 2647–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Lin, H.; He, Q.; Xu, L.; Worku, M.; Chaaban, M.; Lee, S.; Shi, X.; Du, M.-H.; Ma, B. Low dimensional metal halide perovskites and hybrids. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2018, 137, 38–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.T.; Seifert, S.; Sardar, R. Colloidal Synthesis of Single-Layer Quasi-Ruddlesden–Popper Phase Bismuth-Based Two-Dimensional Perovskite Nanosheets with Controllable Optoelectronic Properties. Chemistry of Materials 2021, 33, 5917–5925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Lambrecht, W.R.L. in APS March Meeting Abstracts 2013, vol. 2013, pp. U23–008.
- Chung, I.; Lee, B.; He, J.; Chang, R.P.H.; Kanatzidis, M.G. All-solid-state dye-sensitized solar cells with high efficiency. Nature 2012, 485, 486–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, T.; Di Liberto, G.; Pacchioni, G. Density functional theory estimate of halide perovskite band gap: When spin orbit coupling helps. Journal of Physical Chemistry C 2022, 126, 2184–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasanna, R.; Gold-Parker, A.; Leijtens, T.; Conings, B.; Babayigit, A.; Boyen, H.-G.; Toney, M.F.; McGehee, M.D. Band gap tuning via lattice contraction and octahedral tilting in perovskite materials for photovoltaics. J Am Chem Soc 2017, 139, 11117–11124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, C.; Patrini, M.; Pisanu, A.; Quadrelli, P.; Milanese, C.; Tealdi, C.; Malavasi, L. Wide band-gap tuning in Sn-based hybrid perovskites through cation replacement: the FA 1− x MA x SnBr 3 mixed system. J Mater Chem A Mater 2017, 5, 9391–9395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisanu, A.; Speltini, A.; Quadrelli, P.; Drera, G.; Sangaletti, L.; Malavasi, L. Enhanced air-stability of Sn-based hybrid perovskites induced by dimethylammonium (DMA): synthesis, characterization, aging and hydrogen photogeneration of the MA1−xDMAxSnBr3 system. J Mater Chem C Mater 2019, 7, 7020–7026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Kavanagh, S.R.; Napari, M.; Palgrave, R.G.; Abdi-Jalebi, M.; Andaji-Garmaroudi, Z.; Davies, D.W.; Laitinen, M.; Julin, J.; Isaacs, M.A. Bandgap lowering in mixed alloys of Cs 2 Ag (Sb x Bi 1− x) Br 6 double perovskite thin films. J Mater Chem A Mater 2020, 8, 21780–21788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebhardt, J.; Elsässer, C. The Electronic Structure of Cs2AgBiBr6 at Room Temperature. Phys. Status Solidi (B) 2022, 259, 2200124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Xian, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, W.; Wen, X.; Rahman, N.U.; Long, Y.; Jia, B.; Fan, J.; Li, W. An Emerging Lead-Free Double-Perovskite Cs2AgFeCl6:In Single Crystal. Adv Funct Mater 2020, 30, 2002225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.-G.; Yang, J.-H.; Fu, Y.; Yang, D.; Xu, Q.; Yu, L.; Wei, S.-H.; Zhang, L. Design of lead-free inorganic halide perovskites for solar cells via cation-transmutation. J Am Chem Soc 2017, 139, 2630–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Z.; Wei, F.; Sun, S.; Kieslich, G.; Cheetham, A.K.; Bristowe, P.D. Exploring the properties of lead-free hybrid double perovskites using a combined computational-experimental approach. J Mater Chem A Mater 2016, 4, 12025–12029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitzi, D.B.; Feild, C.A.; Harrison, W.T.A.; Guloy, A.M. Conducting tin halides with a layered organic-based perovskite structure. Nature 1994, 369, 467–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Liu, J.; Portale, G.; Fang, H.; Blake, G.R.; Brink, G.H.T.; Koster, L.J.A.; Loi, M.A. Highly reproducible Sn-based hybrid perovskite solar cells with 9% efficiency. Adv Energy Mater 2018, 8, 1702019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Xu, Z.; Zuo, S.; Feng, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, J.; Liu, H.; Priya, S. Vapor-fumigation for record efficiency two-dimensional perovskite solar cells with superior stability. Energy Environ Sci 2018, 11, 3349–3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, X.; Ishihara, T.; Nurmikko, A.V. Dielectric confinement effect on excitons in PbI4-based layered semiconductors. Phys Rev B 1992, 45, 6961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.; Khan, B.A.; Sarkar, P. 2D lead free Ruddlesden-Popper phase perovskites as efficient photovoltaic materials: A first-principles investigation. Comput Mater Sci 2022, 211, 111545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Liu, G.; Li, Z.; Lou, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhao, Y. Stable Lead-Free (CH3NH3)3Bi2I9 Perovskite for Photocatalytic Hydrogen Generation. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 2019, 7, 15080–15085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, S.P.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Hazra, V.; Shyamal, S.; Pradhan, N.; Bhattacharyya, S. Cs3Bi2I9 nanodiscs with phase and Bi (iii) state stability under reductive potential or illumination for H 2 generation from diluted aqueous HI. Nanoscale 2022, 14, 4281–4291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Xu, S.; Wu, L.; Tang, H.; Zhou, B.; Xu, J.; Yang, Q.; Zhou, T.; Qiu, Y.; Chen, G.; Waterhouse, G.I.N.; Yan, K. Perovskite Cs3Bi2I9 Hexagonal Prisms with Ordered Geometry for Enhanced Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution. ACS Energy Lett 2022, 7, 3370–3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miodyńska, M.; Klimczuk, T.; Lisowski, W.; Zaleska-Medynska, A. Bi-based halide perovskites: Stability and opportunities in the photocatalytic approach for hydrogen evolution. Catal Commun 2023, 177, 106656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, K.; Niyitanga, T.; Chaudhary, A.; Raza, W.; Khan, R.A.; Kim, H. Hydrothermal Synthesis of MA3Sb2I9 for Hydrogen Production Applications. ChemPhotoChem 2023, 7, e202300104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, K.; Raza, W.; Alsulmi, A.; Kim, H. Improved hydrogen production using lead-free and air stable perovskite-like Cs3Sb2I9. Mater Chem Phys 2023, 307, 128159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokesh, K.; Sakar, M.; Do, T.O. 2-(Aminomethyl pyridine) SbI5: An emerging visible-light driven organic–inorganic hybrid perovskite for photoelectrochemical and photocatalytic applications. Mater Lett 2019, 242, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Chen, H.; Chao, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Lv, F.; Gu, L.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, N.; Wang, J.; Guo, S. Single-atom Pt-I3 sites on all-inorganic Cs2SnI6 perovskite for efficient photocatalytic hydrogen production. Nat Commun 2021, 12, 4412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricciarelli, D.; Kaiser, W.; Mosconi, E.; Wiktor, J.; Ashraf, M.W.; Malavasi, L.; Ambrosio, F.; De Angelis, F. Reaction mechanism of photocatalytic hydrogen production at water/tin halide perovskite interfaces. ACS Energy Lett 2022, 7, 1308–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romani, L.; Speltini, A.; Ambrosio, F.; Mosconi, E.; Profumo, A.; Marelli, M.; Margadonna, S.; Milella, A.; Fracassi, F.; Listorti, A.; De Angelis, F.; Malavasi, L. Water-Stable DMASnBr3 Lead-Free Perovskite for Effective Solar-Driven Photocatalysis. Angewandte Chemie - International Edition 2021, 60, 3611–3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romani, L.; Bala, A.; Kumar, V.; Speltini, A.; Milella, A.; Fracassi, F.; Listorti, A.; Profumo, A.; Malavasi, L. PEA2SnBr4: a water-stable lead-free two-dimensional perovskite and demonstration of its use as a co-catalyst in hydrogen photogeneration and organic-dye degradation. J Mater Chem C Mater 2020, 8, 9189–9194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romani, L.; Speltini, A.; Chiara, R.; Morana, M.; Coccia, C.; Tedesco, C.; Armenise, V.; Colella, S.; Milella, A.; Listorti, A. Air-and water-stable and photocatalytically active germanium-based 2D perovskites by organic spacer engineering. Cell Rep Phys Sci 2023, 4, 101214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdan, M.; Chandiran, A.K. Cs2PtI6 Halide Perovskite is Stable to Air, Moisture, and Extreme pH: Application to Photoelectrochemical Solar Water Oxidation. Angewandte Chemie - International Edition 2020, 59, 16033–16038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Grandhi, G.K.; Al-Anesi, B.; Ali-Löytty, H.; Lahtonen, K.; Grisorio, R.; Vivo, P. Water-resistant perovskite-inspired copper/silver pnictohalide nanocrystals for photoelectrochemical water splitting. Electrochim Acta 2023, 462, 142734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandigana, P.; Pari, S.; Sujatha, D.; Shidhin, M.; Jeyabharathi, C.; Panda, S.K. Lead-Free Bismuth-Based Halide Perovskites with Excellent Stability for Visible-light-Driven Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting. ChemistrySelect 2023, 8, e202204731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikarwar, P.; Koneri, I.T.; Appadurai, T.; Chandiran, A.K. Highly Efficient Photoelectrochemical Water Oxidation Using Cs2AgMCl6(M = In,Bi,Sb) Halide Double Perovskites. Phys Rev Appl 2023, 19, 044083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, N.V.P.; Hamdan, M.; Chandiran, A.K. Stable Cs 2 ReX 6 (X–Cl, Br) vacancy-ordered perovskites for solar water splitting. Sustain Energy Fuels 2023, 7, 949–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, P.; Guan, Z.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Jin, S.; Dai, Y.; Whangbo, M.H.; Huang, B. Enhancing the Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution Activity of Mixed-Halide Perovskite CH3NH3PbBr3–xIx Achieved by Bandgap Funneling of Charge Carriers. ACS Catal 2018, 8, 10349–10357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knezevic, M.; Quach, V.D.; Lampre, I.; Erard, M.; Pernot, P.; Berardan, D.; Colbeau-Justin, C.; Ghazzal, M.N. Adjusting the band gap of CsPbBr3−yXy (X= Cl, I) for optimal interfacial charge transfer and enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen generation. J Mater Chem A Mater 2023, 11, 6226–6236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Mak, C.H.; Wang, C.; Fu, Y.; Li, F.; Jia, G.; Hsieh, C.; Shen, H.; Colmenares, J.C.; Song, H. Bandgap Funneling in Bismuth-Based Hybrid Perovskite Photocatalyst with Efficient Visible-Light-Driven Hydrogen Evolution. Small Methods 2022, 6, 2200326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Wang, P.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, Q.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Liu, Y.; Dai, Y.; Huang, B. Lead-free halide perovskite Cs3Bi2xSb2–2xI9 (x≈ 0.3) possessing the photocatalytic activity for hydrogen evolution comparable to that of (CH3NH3) PbI3. Advanced Materials 2020, 32, 2001344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
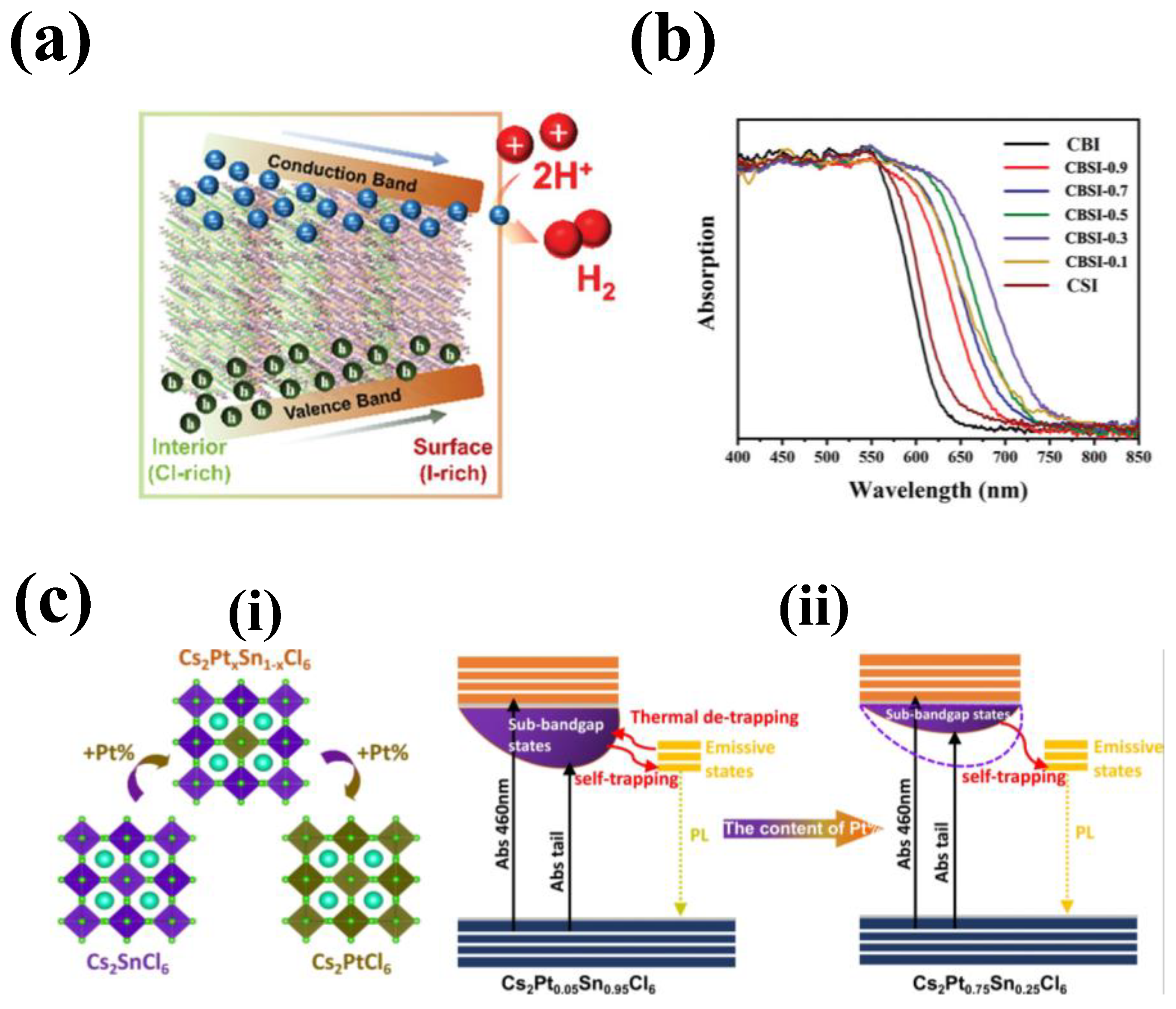
- Yin, H.; Chen, J.; Guan, P.; Zheng, D.; Kong, Q.; Yang, S.; Zhou, P.; Yang, B.; Pullerits, T.; Han, K. Controlling Photoluminescence and Photocatalysis Activities in Lead-Free Cs2PtxSn1−xCl6 Perovskites via Ion Substitution. Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2021, 60, 22693–22699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Chu, Y.; Xu, J. Embedding CsPbBr3 perovskite quantum dots into mesoporous TiO2 beads as an S-scheme heterojunction for CO2 photoreduction. Chemical Engineering Journal 2022, 433, 133762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Liang, X.; Ma, L.; Jing, X.; Chen, D.-L.; Li, Z. ZnSe Nanorods–CsSnCl3 Perovskite Heterojunction Composite for Photocatalytic CO2 Reduction. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 3332–3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, M.; Chi, Z.; Li, W.; Yu, H.; Yang, N.; Yu, H. Internal electric field engineering step-scheme–based heterojunction using lead-free Cs3Bi2Br9 perovskite–modified In4SnS8 for selective photocatalytic CO2 reduction to CO. Appl Catal B 2022, 313, 121426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.-L.; Liu, R.-R.; Mu, Y.-F.; Feng, Y.-X.; Dong, G.-X.; Zhang, M.; Lu, T.-B. In Situ Construction of Lead-Free Perovskite Direct Z-Scheme Heterojunction Cs3Bi2I9/Bi2WO6 for Efficient Photocatalysis of CO2 Reduction. Solar RRL 2021, 5, 2000691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.-J.; Mao, Y.; Wang, B.-H.; Chen, L.; Tian, S.; Hu, B.; Li, Y.-J.; Au, C.-T.; Yin, S.-F. Tuning photocatalytic performance of Cs3Bi2Br9 perovskite by gC3N4 for C(sp3)—H bond activation. Nano Res 2023, 16, 6104–6112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, T.; Das, D.; Das, B.K.; Sarkar, S.; Maiti, S.; Chattopadhyay, K.K. CsPbBrCl2/g-C3N4 type II heterojunction as efficient visible range photocatalyst. J Hazard Mater 2019, 380, 120855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Low, J.; Yu, J.; Jaroniec, M.; Wageh, S.; Al-Ghamdi, A.A. Heterojunction photocatalysts. Advanced Materials 2017, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
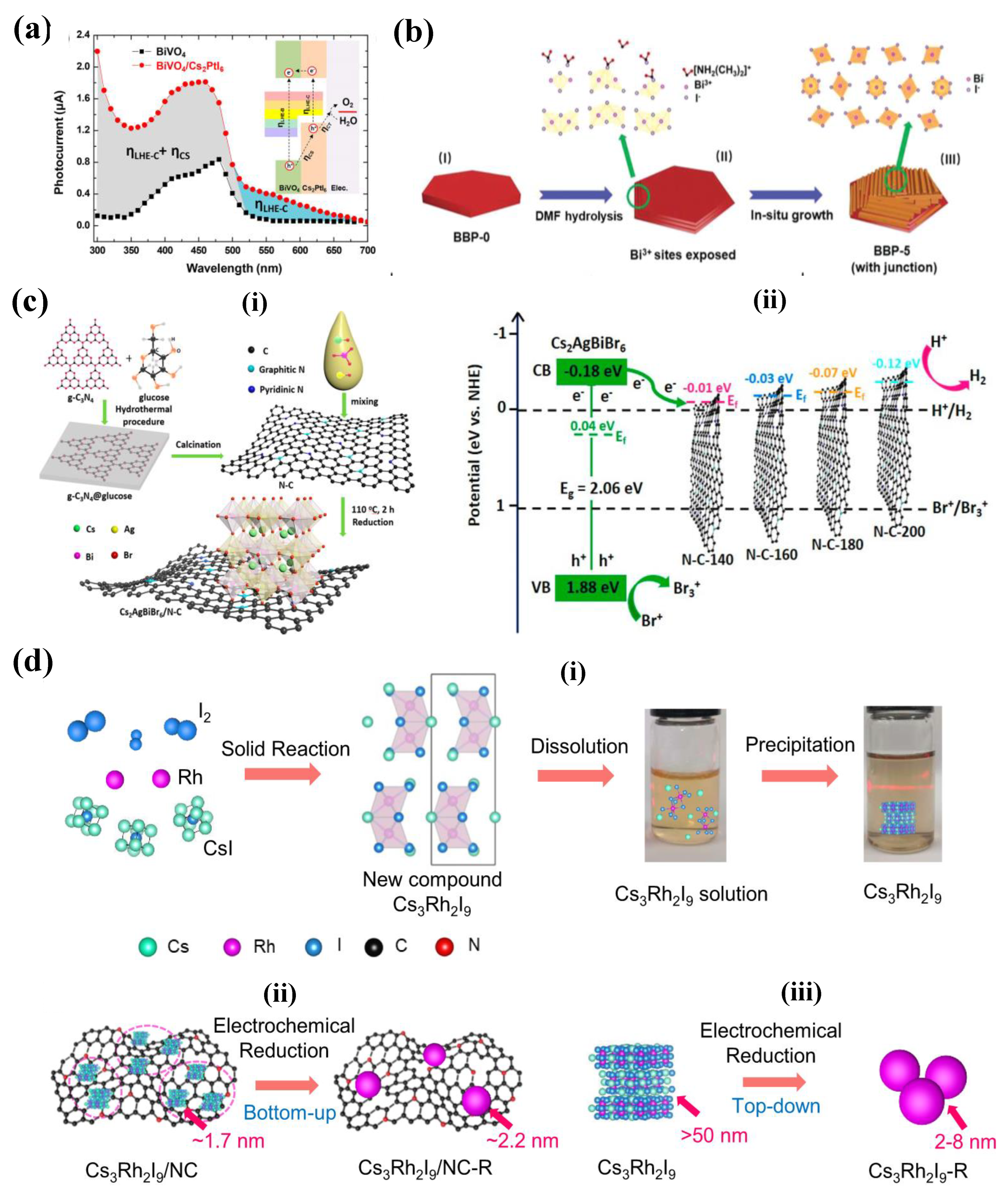
- Jayaraman, J.P.; Hamdan, M.; Velpula, M.; Kaisare, N.S.; Chandiran, A.K. BiVO4/Cs2PtI6 Vacancy-Ordered Halide Perovskite Heterojunction for Panchromatic Light Harvesting and Enhanced Charge Separation in Photoelectrochemical Water Oxidation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2021, 13, 16267–16278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Mak, C.H.; Liu, R.; Wang, Z.; Ji, L.; Song, H.; Tan, C.; Barrière, F.; Hsu, H. In situ formation of bismuth-based perovskite heterostructures for high-performance cocatalyst-free photocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Adv Funct Mater 2020, 30, 2006919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Li, K.; Wu, X.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, K.; Wang, Y.; Loh, K.P.; Shi, Y.; Xu, Q.H. In Situ Synthesis of Lead-Free Halide Perovskite Cs2AgBiBr6 Supported on Nitrogen-Doped Carbon for Efficient Hydrogen Evolution in Aqueous HBr Solution. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2021, 13, 10037–10046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Zhang, Z.; Ju, Q.; Wu, T.; Segre, C.U.; Chen, W.; Peng, H.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Z. Bottom-up evolution of perovskite clusters into high-activity rhodium nanoparticles toward alkaline hydrogen evolution. Nat Commun 2023, 14, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bresolin, B.-M.; Sgarbossa, P.; Bahnemann, D.W.; Sillanpää, M. Cs3Bi2I9/g-C3N4 as a new binary photocatalyst for efficient visible-light photocatalytic processes. Sep Purif Technol 2020, 251, 117320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Yue, D.; Li, X.; Zhao, Y. Lead-free double perovskite Cs2AgBiBr6/RGO composite for efficient visible light photocatalytic H2 evolution. Appl Catal B 2020, 268, 118399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Llamas, M.; Speltini, A.; Profumo, A.; Panzarea, F.; Milella, A.; Fracassi, F.; Listorti, A.; Malavasi, L. Preparation of Heterojunctions Based on Cs3Bi2Br9 Nanocrystals and gC3N4 Nanosheets for Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, K.; Gou, J.; Yang, L.; Zeng, C. Environmentally Stable Mesoporous gC3N4 Modified Lead-Free Double Perovskite Cs2AgBiBr6 for Highly Efficient Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution. Catal Letters 2023, 153, 534–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| No. | Material | Photoanode Area | Electrolyte/ Illumination | Photocurrent | Stability | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Cs2PtI6 | pH -11 1 sun (AM 1.5 G, 100 mW cm–2) |
0.8 mAcm@2 at 1.23 V | 12 h | 71 | |
| 2 | Cu1.4Ag0.6BiI5 | 0.785 cm2 | 1 sun (AM 1.5 G, 100 mW cm–2) | 4.62 mA cm–2 at 1.23 VRHE | ~5 h | 72 |
| 3 | Cs2AgBiCl6 | 1 cm2 | 1 M KOH 1 Sun |
3.85 mA @ 1.0 V (Vs Ag/AgCl) | 10 h | 73 |
| 4 | Cs3Bi2Cl9 | 1 cm2 | 1 M KOH 1 Sun |
3.85 mA @ 1.0 V (Vs Ag/AgCl) | 10 h | 73 |
| 5 | Cs2AgInCl6 | - | water and acetonitrile |
0.75 mA cm−2 @ 600 mV (Vs RHE) | 2 h | 74 |
| 6 | Cs2ReBr6 | 25 mm2 | 1.5 mM KOH solution 1 Sun |
0.20 mA cm−2 0.4 V vs. Ag/AgCl | 75 | |
| 7 | Cs2ReI6 | 25 mm2 | 1.5 mM KOH solution 1 Sun |
0.14 mA cm−2 0.4 V vs. Ag/AgCl | 75 |
| Heterojunction | Reaction Solution | Light Source | HER (µmol g-1 h-1) | Stability | Photocurrent | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BiVO4/Cs2PtI6 | H2O:KOH | 500 Wm-2 , AM 1.5G filter | - | 2 mA cm−2 at 1.23 V (vs RHE) | 88 | |
| Cs2AgInCl6/ IrOx | CH3CN:H2O | 1 Sun | 2 h | 155.8 mA @ 600mV (vs RHE) | 74 | |
| MA3Bi2I9/DMA3BiI6 | H2O:HBr | 100 mW cm−2 (λ ≥ 420 nm) | 198.2 | 10 h / 10 cycles | 89 | |
| 2-AMPSbI5/ GO | sodium sulfate:H2O | 150 W xenon lamp | 185.8 | 4 cycles | 65 | |
| Cs2AgBiBr6/N-C | H2O:HBr | λ ≥ 420 nm | 380 | 3 h / 6 cycles | 90 | |
| Cs3Rh2I9/NC-R | H2O:KOH | 50h | mass activity of 772.1 mA mg−1 (10mA cm−2 at 1.23 V (vs RHE) |
91 |
| Material | Reaction Solution | Light Source | Hydrogen Evolution Rate (µmol g-1 h-1) | Stability | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEA2SnBr4 | H2O/ 10 % TEOA | 500 Wm-2 , AM 1.5G filter | 1613 | - | 69 |
| PhBz2GeI4 | H2O/ 10 % TEOA | 500 Wm-2 , AM 1.5G filter | 1200 | 6h / 4 cycles | 70 |
| Cs3Bi2I9 | H2O/ 10 % Me.OH | 450 W Xe lamp | 920.76 | 6 h | 92 |
| Cs2AgBiBr6 -rGO |
H2O/HBr | >420 nm | 48.9 | 10h / 12 cycles | 93 |
| DMASnX3 | H2O/10 % TEOA | 500 Wm-2 , 300-800 nm | 1730 | 4 h | 68 |
| Cs3Bi2Br9 | H2O/10 % TEOA | 500 Wm-2 , 300-800 nm | 4 593 | - | 94 |
| Cs2AgBiBr6 | HBr/ 20% H3PO2 | 300 W (λ ≥ 420 nm) | 60 | 3h/ 14 cycles | 95 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





