1. Introduction
Radio frequency (RF)-based wireless energy transfer (WET) is a key enabling technology for developing intelligent and self-sustaining Internet of Everything (IoE) networks in the 6G era [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5,
6,
7]. It enables the continuous supply of power to wireless devices over the air, such as wearable electronic devices, extended reality devices, and robotics, without the need for frequent battery replacements or wired power lines. Moreover, compared to traditional power systems, RF-based WET can significantly enhance the quality of service for powering devices by adapting to different physical conditions and service requirements while also improving throughput and robustness [
1,
2,
3].
In recent years, unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) have gained significant attention in various scenarios due to their deployment flexibility, mobility, and cost-effectiveness, leading to widespread adoption across various applications, including military operations, cargo delivery, disaster management, and communication platforms [
8,
9,
10,
11,
12,
13,
14,
15]. They provide greater flexibility in system design and operation within wireless networks by allowing adjustments to the deployment position and path of UAVs, yielding significant advantages such as coverage enhancements [
8,
9,
10,
11,
12,
13,
14,
15].
Thanks to its potential advantages, UAV-enabled wireless energy transfer (WET) has received great attention for providing ground devices with more efficient and stable power compared to conventional WET systems, which use fixed-location energy transmitters [
15,
16,
17,
18,
19,
20,
21,
22,
23,
24]. In particular, UAVs are able to move flexibly in three-dimensional (3D) space, utilizing favorable line-of-sight (LoS) channels with ground devices. As such, UAVs can serve as a new type of aerial energy transmitter, reducing the transmission distances for powering devices while avoiding obstacles and shadow fading, even in remote areas where conventional fixed-location energy transmitters are not available. Accordingly, UAV-enabled WET is able to overcome energy bottlenecks as well as meet urgent energy demands, thereby extending the operational lifespan of energy-constrained devices, especially in dynamic or hard-to-reach environments such as smart cities, wireless sensor networks, and maritime networks, among others [
15,
16,
17,
18]. However, effective UAV trajectory design is required to reap potential gains from UAV-enabled WET.
In practical UAV-enabled WET scenarios, a UAV may move closer to a device in order to reduce the transmission distance for improved power efficiency. This may result in the UAV moving farther away from another device, thereby decreasing the overall energy transfer efficiency. To address this challenge, UAV trajectory design has been extensively studied to improve the energy transfer performance for multiple devices [
15,
16,
17,
18,
19,
20,
21]. Specifically, in a single UAV-enabled WET system, an optimal one-dimensional (1D) trajectory design at a fixed altitude was proposed to maximize the minimum received energy among all devices during a given charging period [
16]. For a more general context, the design of a two-dimensional (2D) UAV trajectory at a fixed altitude was studied to optimize the energy transferred to all devices during a given charging period [
17], with further investigations in a more practical scenario [
18]. Moreover, the design of a 3D UAV trajectory within a specified altitude range was explored to maximize the total received energy across all devices for a given charging period [
19]. The joint design of 2D UAV trajectory and orientation of 1D directional antenna array at the UAV with a fixed altitude was also studied [
20] and further extended to a structure that includes a 3D directional antenna array at the UAV [
21]. Moreover, a multi-UAV-enabled WET system capable of covering a large area was proposed, and effective trajectory designs for multiple UAVs were studied to enhance energy transfer performance across various scenarios [
15,
22,
23,
24].
Meanwhile, energy beamforming has been recognized as a promising technology for significantly increasing the energy transfer efficiency of RF-based WET systems, particularly compared to single-antenna omni-directional transmission [
2,
3,
4]. An energy transmitter with multiple antennas can simultaneously focus energy beams toward devices in the desired directions, thereby overcoming high propagation path loss without increasing transmit power or bandwidth. In this regard, various energy beamforming techniques have been proposed for use in terrestrial wireless networks with perfect channel state information (CSI) as well as with imperfect CSI [
3,
4,
5,
6,
7]. Moreover, due to the advantage of having LoS channels, beamforming techniques combined with resource allocation and optimization have been widely considered to enhance power transfer performance in various UAV-enabled systems [
25]. Beamforming combined with optimization of placement and resource allocation has been studied to maximize energy efficiency in wireless-powered UAV communication systems with non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) [
26]. Additionally, hybrid beamforming with resource allocation has been explored in UAV-enabled wireless-powered mobile edge computing networks [
27]. Furthermore, the joint optimization of beamforming, transmit power, power-splitting ratio, and UAV trajectory was proposed to enhance communication performance in UAV-enabled relay networks with wireless power transfer [
28]. For UAV-enabled wireless-powered communication networks (WPCNs), beamforming techniques have also been explored using a backscattering scheme [
29] and reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RIS) [
30], by jointly optimizing time allocation. Various beamforming techniques for UAV-enabled systems have been proposed in conjunction with resource allocation and optimization. However, existing studies have primarily focused on wireless-powered communication systems (WPCNs) or simultaneous wireless information and power transfer (SWIPT) systems, with an emphasis on optimizing communication performance. To the best of our knowledge, despite its significant utility, an energy beamforming technique that focuses solely on increasing energy transfer efficiency to simultaneously charge multiple devices, rather than on communication performance, has not been fully studied to realize its potential gains in UAV-enabled WET systems.
Motivated by the aforementioned observations, we focus on energy beamforming design to optimize energy transfer efficiency for UAV-enabled WET systems. In practical WET networks, multiple devices have different energy requirements, and their charging times vary based on the amount of energy needed. Therefore, UAV altitude and energy beamforming must be optimized accordingly. To this end, this paper investigates a joint design of UAV altitude and energy beamforming to minimize the overall charging time required for all energy-harvesting devices (EHDs) to meet their energy requirements. Thus, a large number of EHDs are efficiently served simultaneously while avoiding unnecessary energy transfer from the UAV. Our main contributions are summarized as follows:
We propose the joint design of UAV altitude- and channel statistics-based energy beamforming, where the EHDs’ energy demands are considered in efficiently and simultaneously serving the EHDs while reducing the additional resources and costs associated with obtaining perfect channel state information. In contrast to existing works on UAV-enabled WET, which consider only the LoS dominant channel without small-scale fading, we adopt the more general air-to-ground (A2G) Rician fading channel while also taking into account the characteristic nature of the aerial channel in practical UAV scenarios, where the channel statistics depend on the altitude of the UAV.
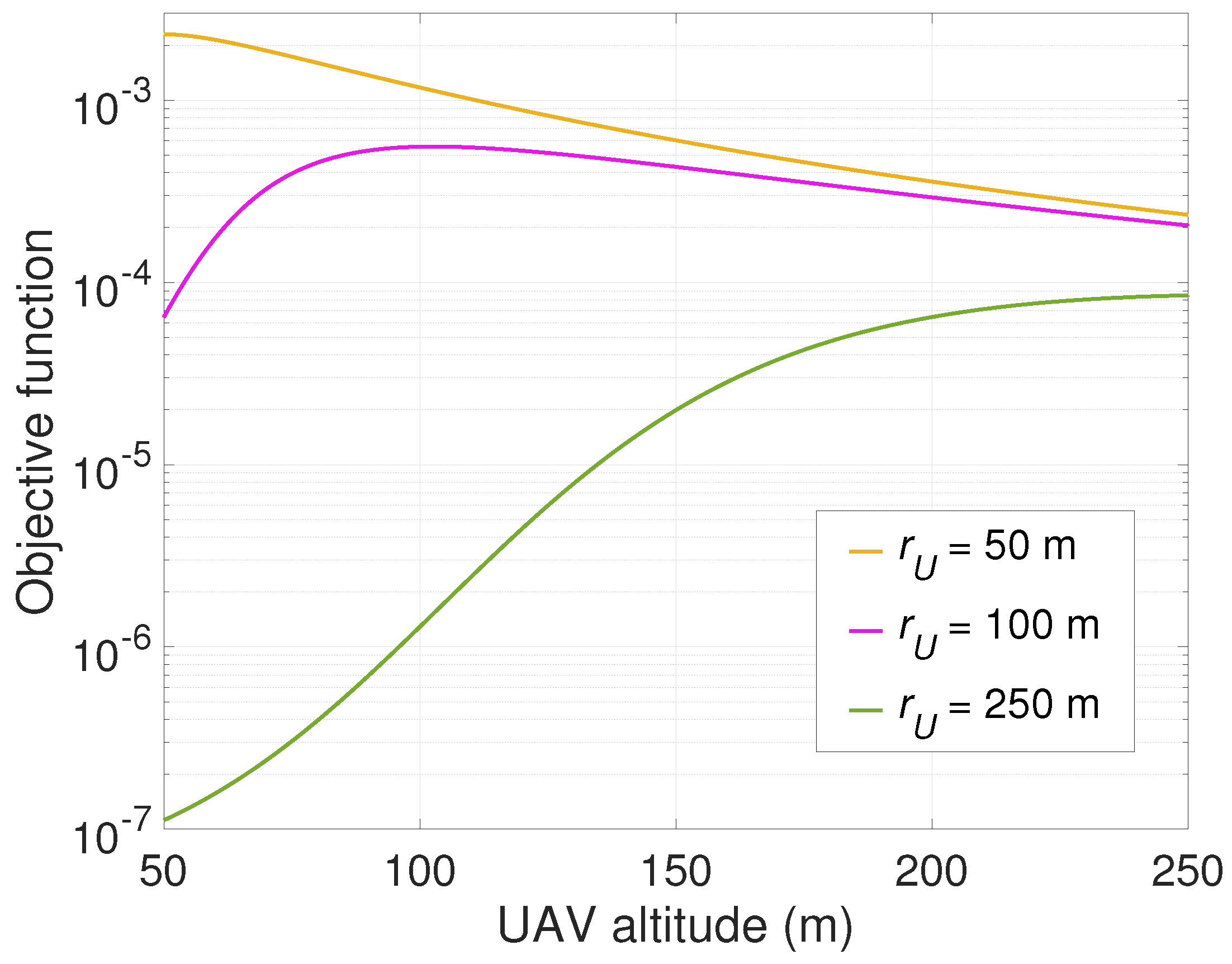
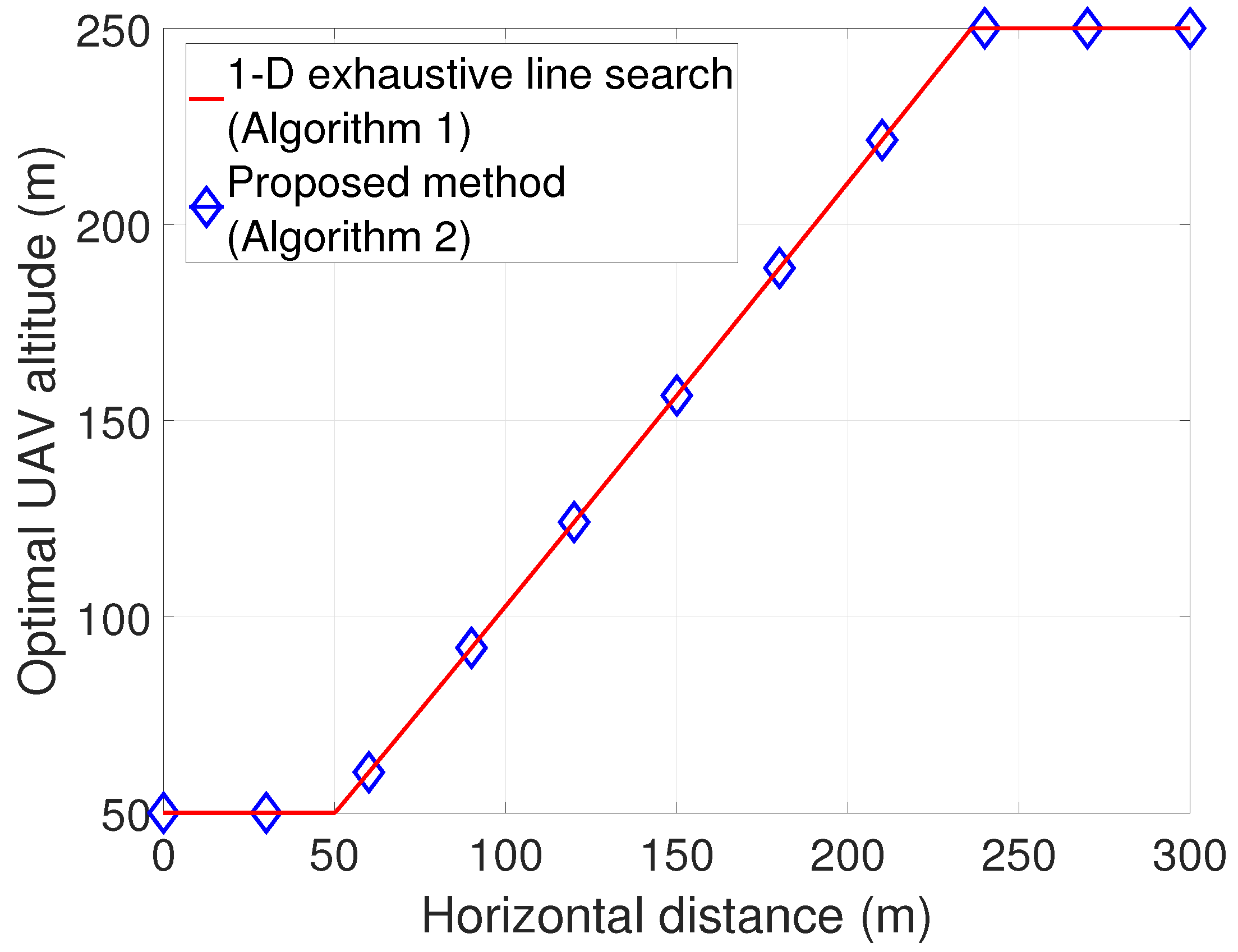
Due to the highly non-convex and non-linear nature of our design problem, we first jointly optimize UAV altitude and energy beamforming in a single-EHD scenario to draw insights. We derive a solution for optimal energy beamforming in closed form, thereby developing an efficient algorithm with low complexity in obtaining the optimal solution.
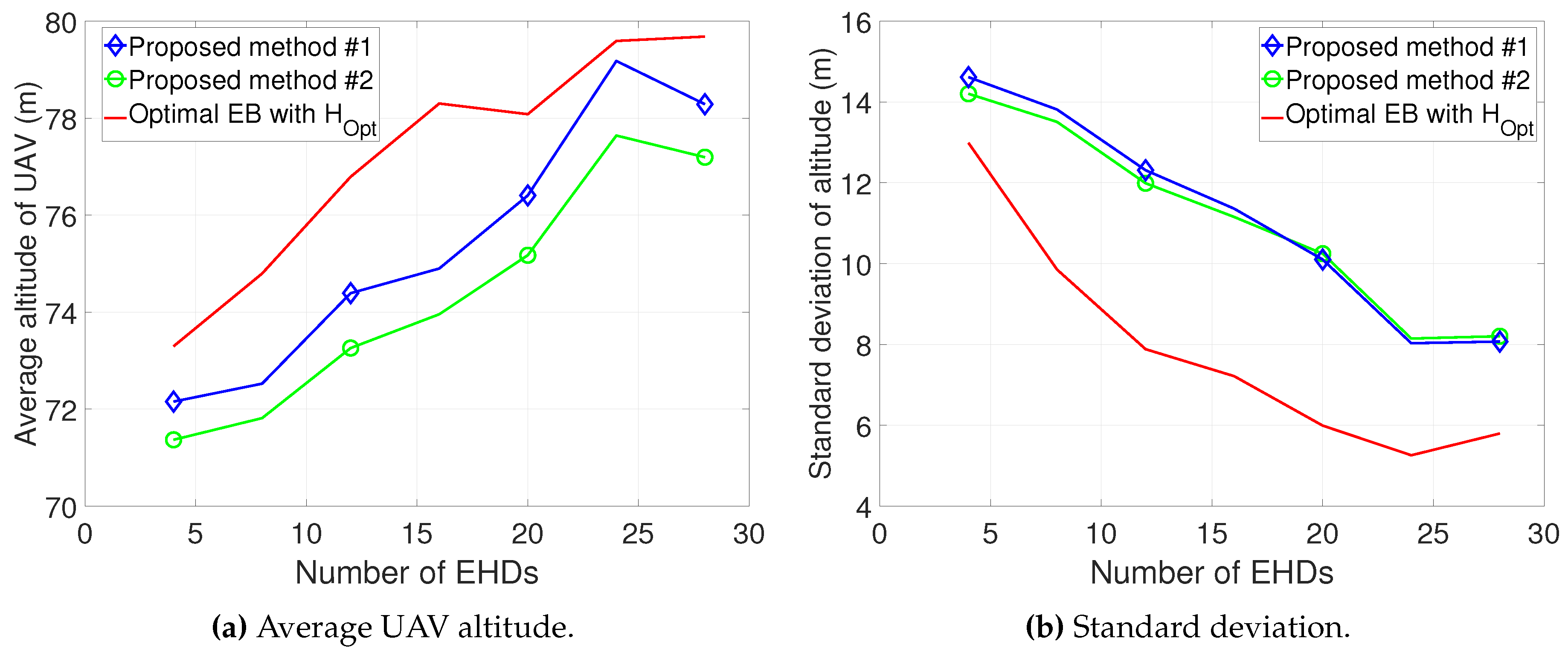
We devise an efficient algorithm to jointly optimize the UAV altitude and energy beamforming in a scenario with multiple EHDs by investigating the optimal conditions as well as the dual problem. Motivated by insights from the design for a single-EHD scenario, we also develop an efficient low-complexity method for determining near-optimal altitude and energy beamforming. Moreover, we explore a sub-optimal design by leveraging weighted-sum energy beamforming in closed form with considerably reduced computational complexity.
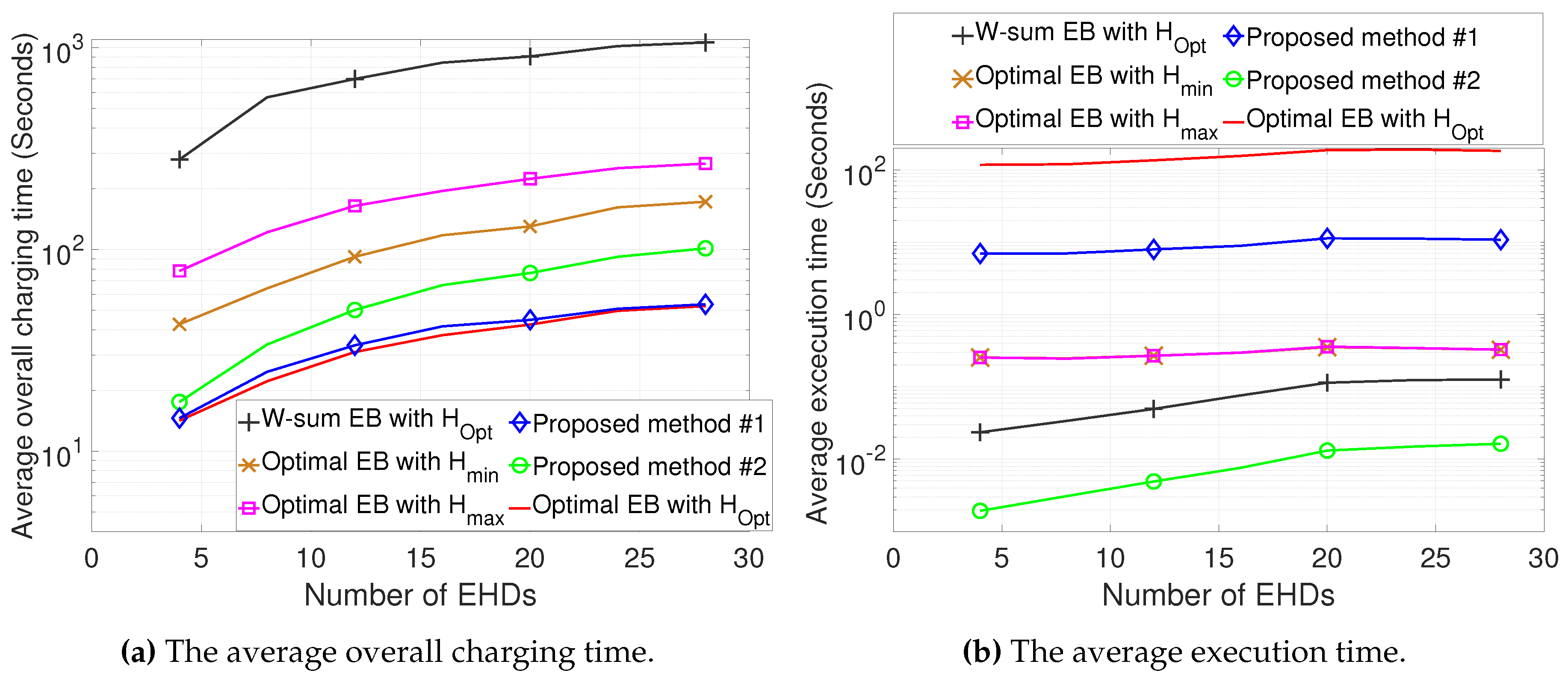
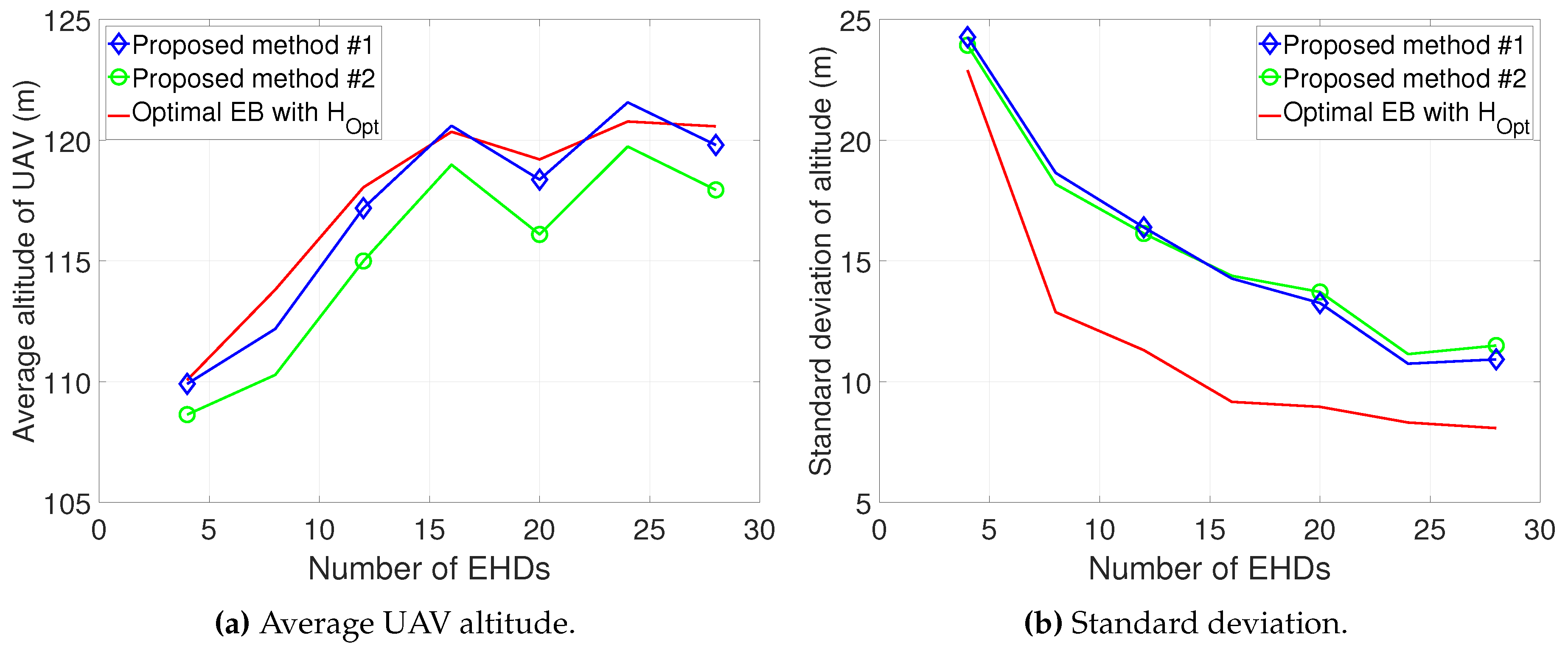
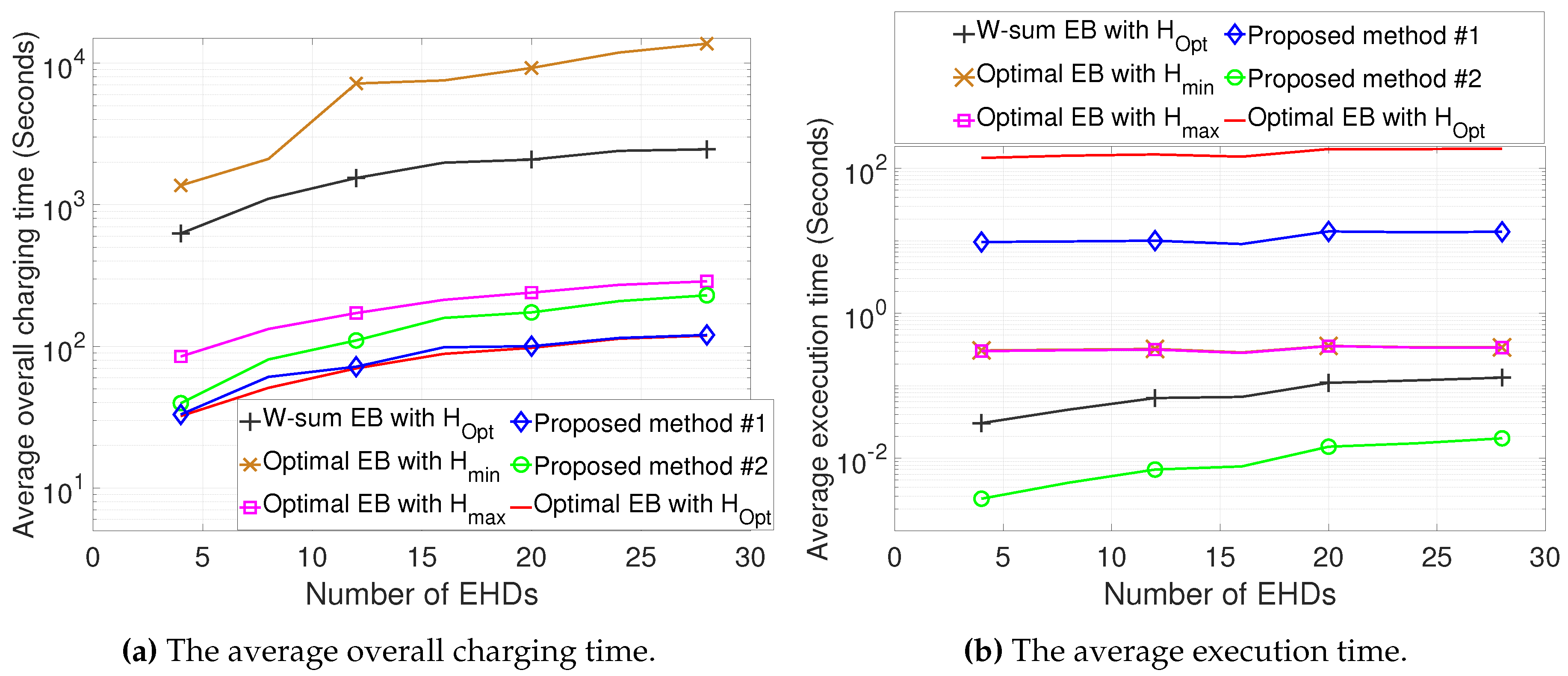
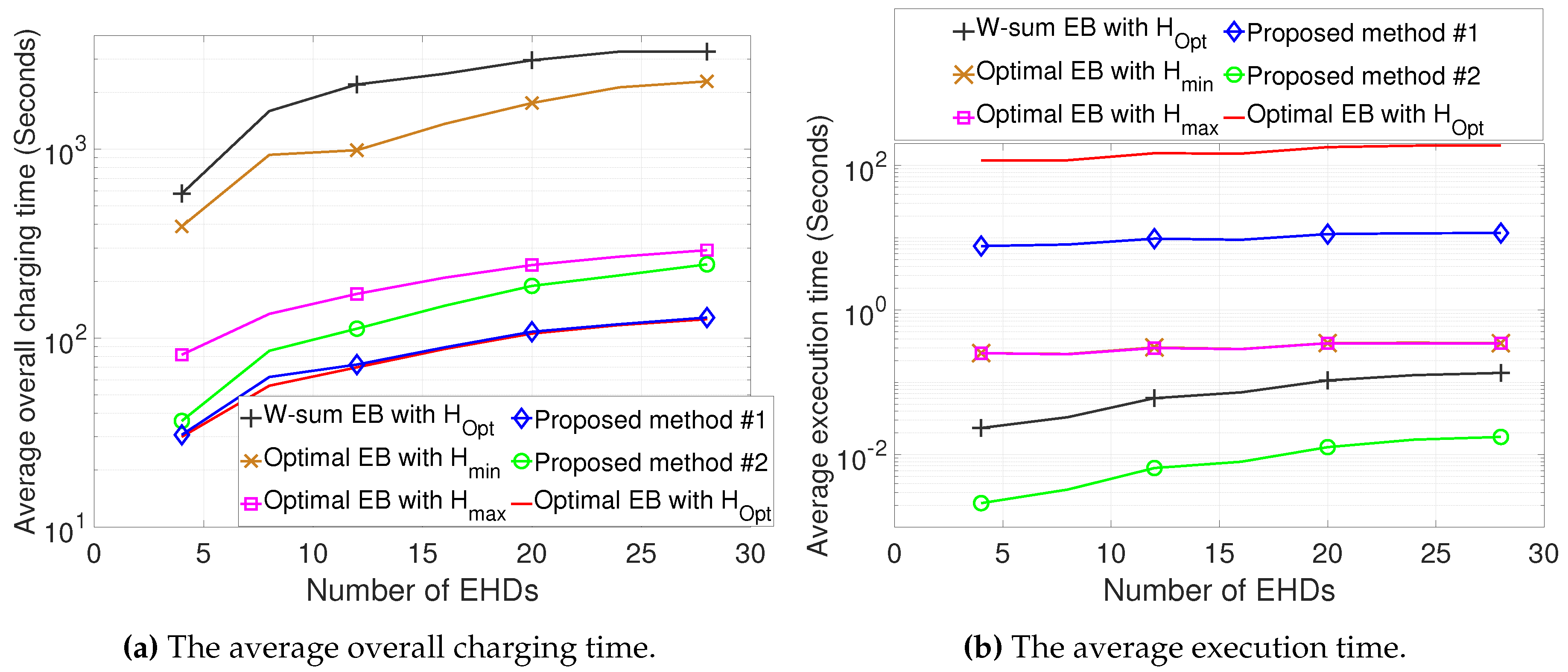
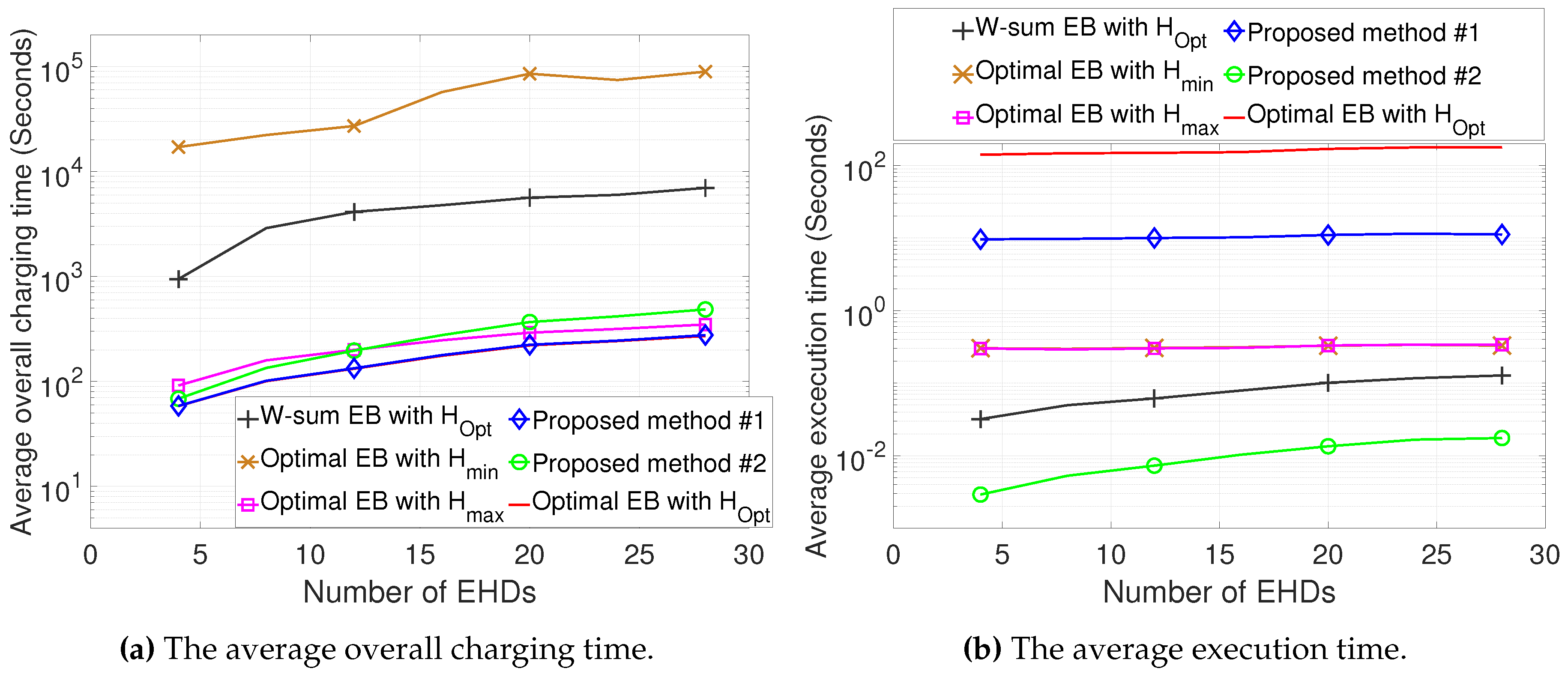
The numerical results demonstrate that compared to conventional methods, the proposed methods can significantly reduce the overall charging time while also decreasing the computational complexity.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows. In
Section 2, we introduce the system model and formulate our design problem. In
Section 3, we jointly optimize UAV altitude and energy beamforming for a single-EHD scenario. In
Section 4, we propose the methods for jointly optimizing UAV altitude and energy beamforming in a multiple-EHD scenario. We evaluate our proposed methods in
Section 5 and conclude our paper in
Section 6.
6. Conclusion
In this paper, we propose the joint design of UAV altitude- and channel statistics-based energy beamforming in order to minimize the overall charging time required for all EHDs by considering the A2G Rician fading channel. To solve the formulated problem, which is highly non-convex and non-linear, we first optimized our design for a single EHD by deriving optimal energy beamforming in closed form, thereby developing the low-complexity algorithm to obtain the optimal altitude. Then, considering multiple EHDs, we developed efficient algorithms for the joint design of altitude and energy beamforming based on the dual problem. We further explored two efficient methods with low complexity, yielding a near-optimal solution driven by insights from the design for a single-EHD scenario, as well as a sub-optimal solution by leveraging closed-form weighted-sum energy beamforming. The numerical results demonstrate that compared to conventional methods, the proposed joint design can be used to substantially reduce both the overall charging time as well as the computational complexity. While the overall charging time increases in the Dense Urban environment compared to the Urban environment due to a lower LoS probability, the average execution time remains similar, highlighting the robustness of the proposed methods in terms of complexity reduction.
Although the proposed methods are based on long-term channel statistics, they can be extended to scenarios with perfect CSI by replacing the long-term channel statistics with instantaneous CSI. In addition, the proposed method can be adapted to different channel models, such as Nakagami fading, by redefining statistical expectations and modifying the algorithm with necessary mathematical derivations to incorporate new fading characteristics. Extending the proposed methods to provide a comprehensive analysis of scalability, especially when dealing with large numbers of EHDs in diverse environmental conditions, remains one of our ongoing research topics. Additionally, the joint design of altitude and energy beamforming, taking into account practical factors such as the UAV’s energy consumption, is also part of our ongoing work for future research. Moreover, future work will focus on enhancing the proposed model to adapt to dynamic environmental changes that may impact the UAV’s ability to maintain optimal altitude, ensuring robustness in real-world scenarios