Submitted:
25 October 2024
Posted:
28 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Hypofunction of the glutamate system in the brain is one of the pathophysiological hypotheses for schizophrenia. Accumulating animal and clinical studies show that sarcosine (N-methylglycine), a glycine transporter-1 inhibitor, is effective for ameliorating the negative and cognitive symptoms of schizophrenia. The aims of the present study were to observe the effects of sarcosine on neuronal activity in the dorsal CA1 (dCA1) hippocampal neurons within an NMDA receptor hypofunction model induced by MK801. We applied in vivo calcium imaging to observe the dynamics of fluorescence from the dCA1 hippocampal neurons when the mice were exploring in an open field. Using this tool, we directly measured and compared neuronal properties between sarcosine-treated and untreated mice. At the same time, the physiological function of the neurons was also quantified by measuring their place fields. Our data demonstrated that MK-801 (0.2 mg/kg) diminished the fluorescence intensity of dCA1 neurons that had been genetically modified with a calcium indicator. MK-801 also significantly increased the correlation coefficient between the fluorescence dynamics of pairs of cells, a feature that may be linked to the symptom of disorganization in human patients with schizophrenia. The spatial correlations of place fields in the mice were impaired by MK-801 as well. Injected sarcosine (500 mg or 1000 mg/kg) significantly alleviated the abovementioned abnormalities. Our data provide evidence to support the use of sarcosine to alleviate symptoms of schizophrenia, especially hippocampus-related functions.
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Substances and Animals
2.2. Surgery and Viral Injection
2.3. Experimental Procedures
2.4. Data Analysis
2.4.1. Processing of the Ca2+ Imaging Videos
2.4.2. Comparisons of Grouped Fluorescence Intensity
2.4.3. Correlation Matrix
2.4.4. Spatial Correlation
2.5. Statistics
3. Results
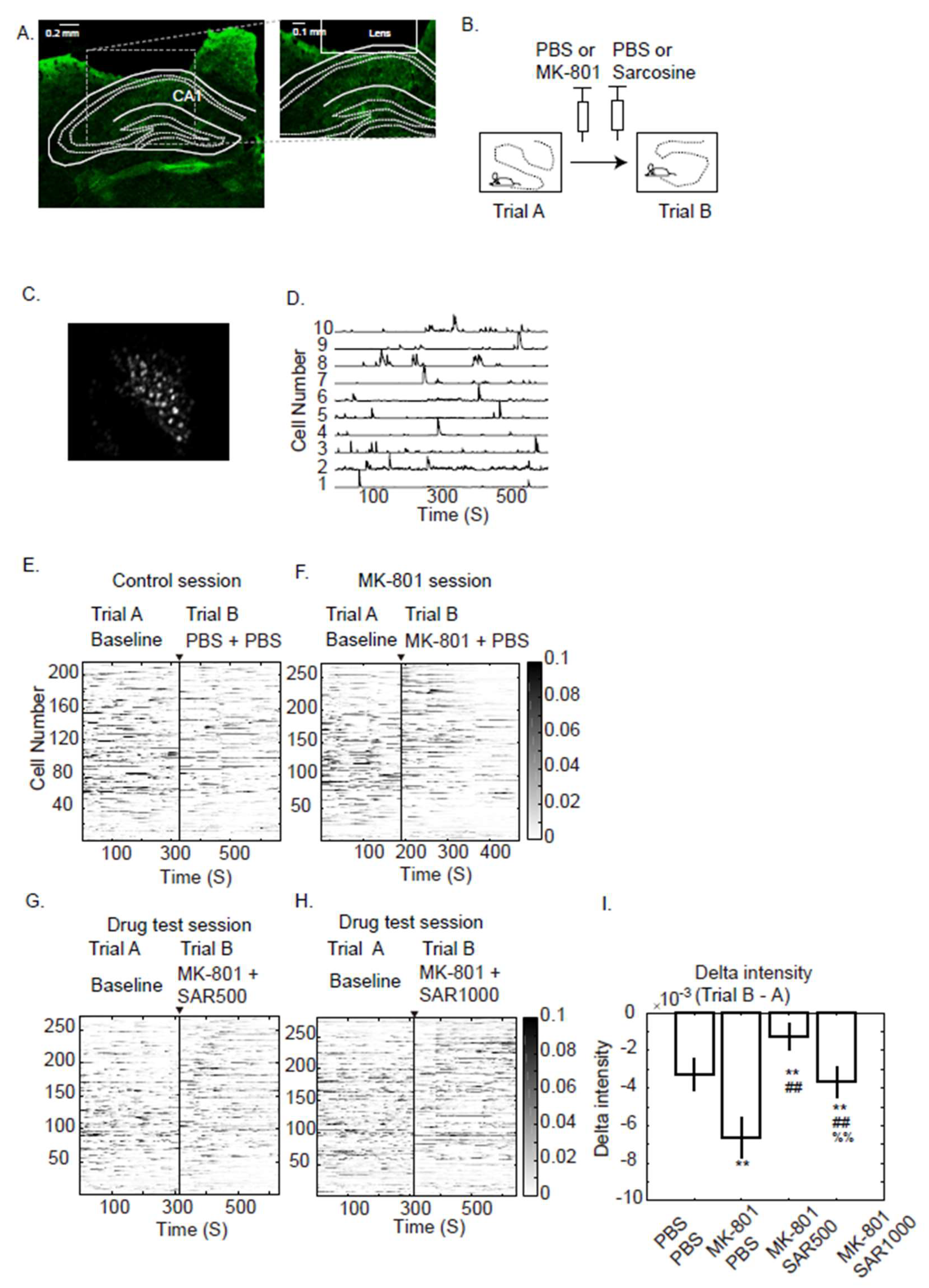
3.1. Single Neuron Fluorescence Intensity
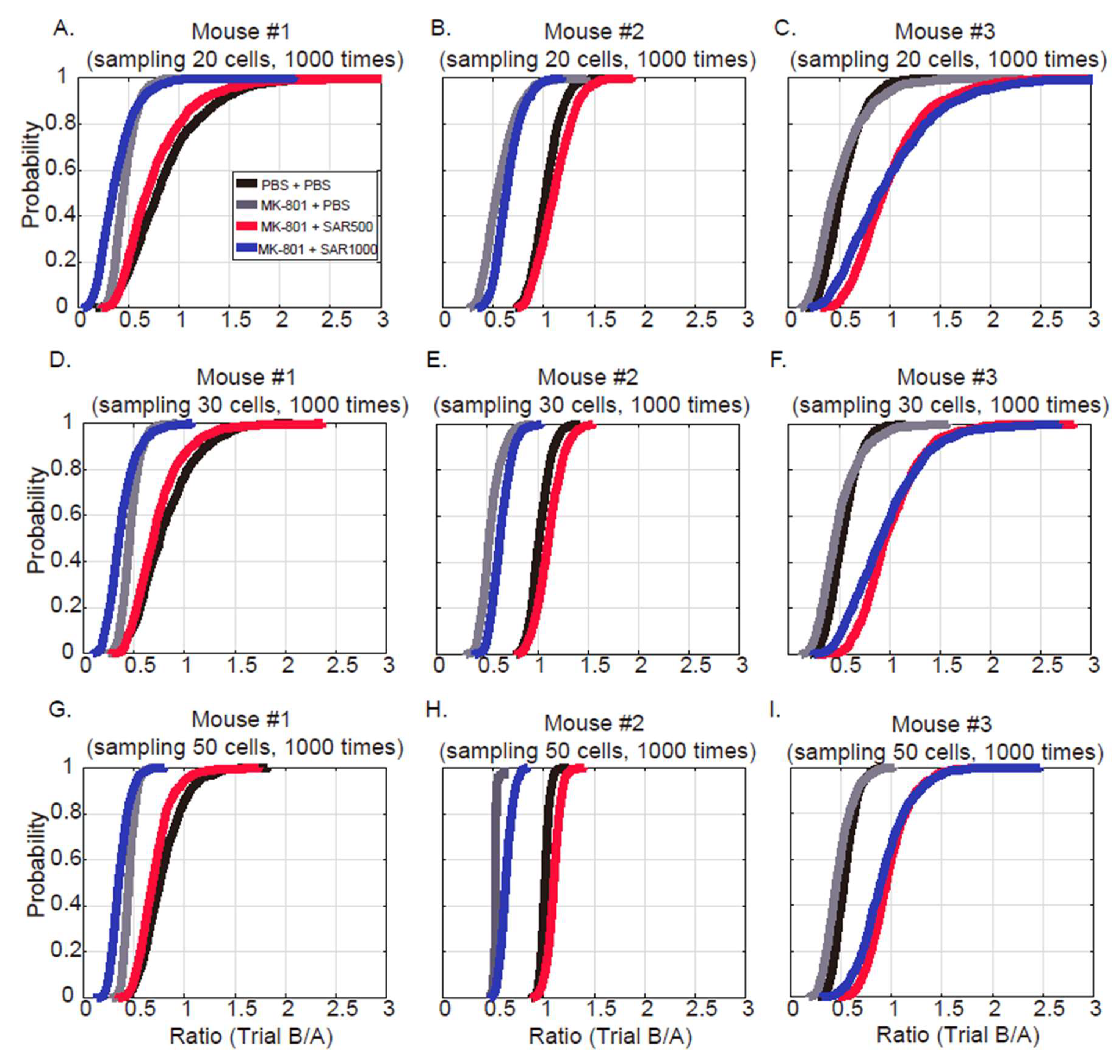
3.2. Grouped Fluorescence Intensity
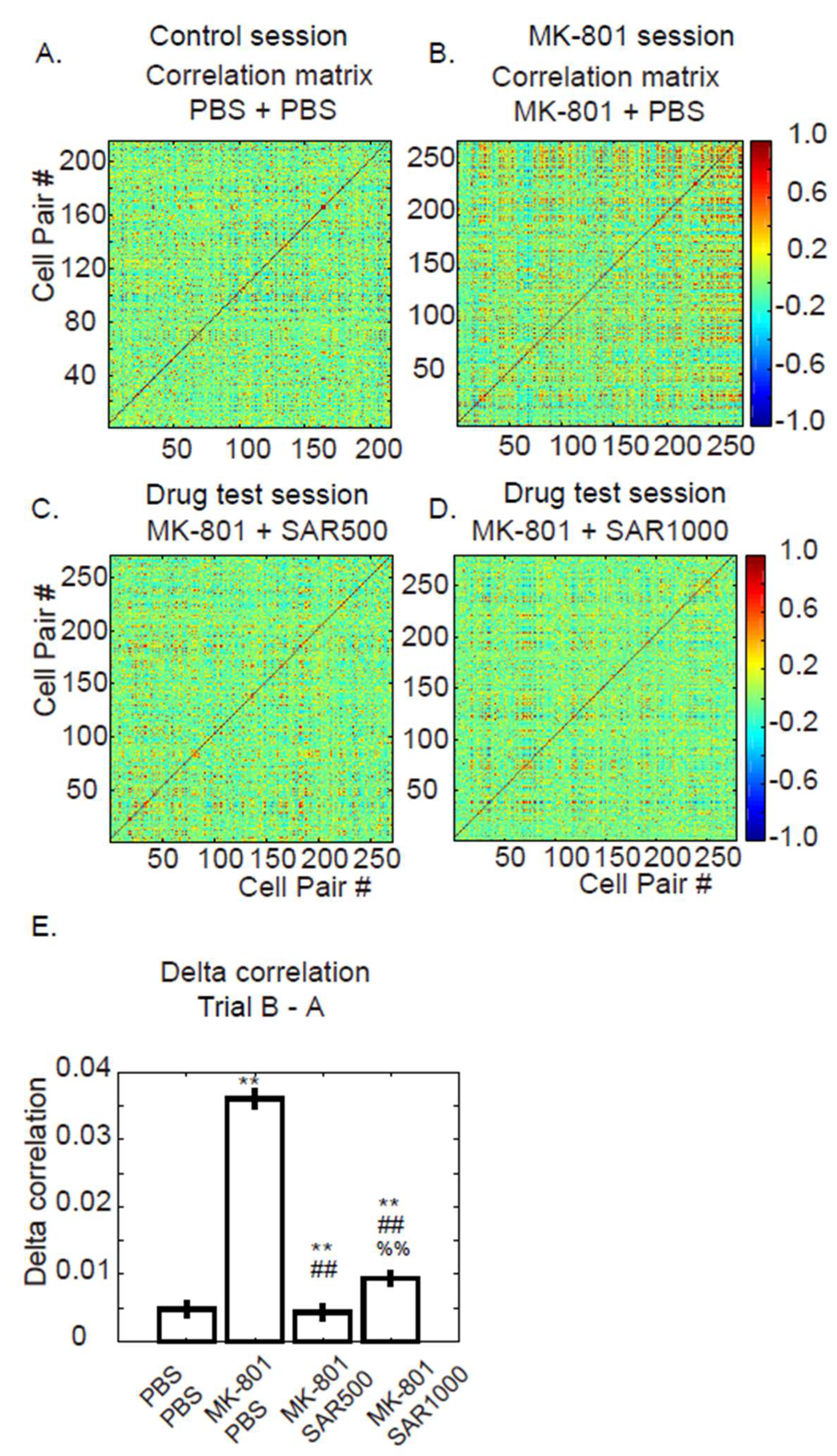
3.3. Pairwise Fluorescence Correlation
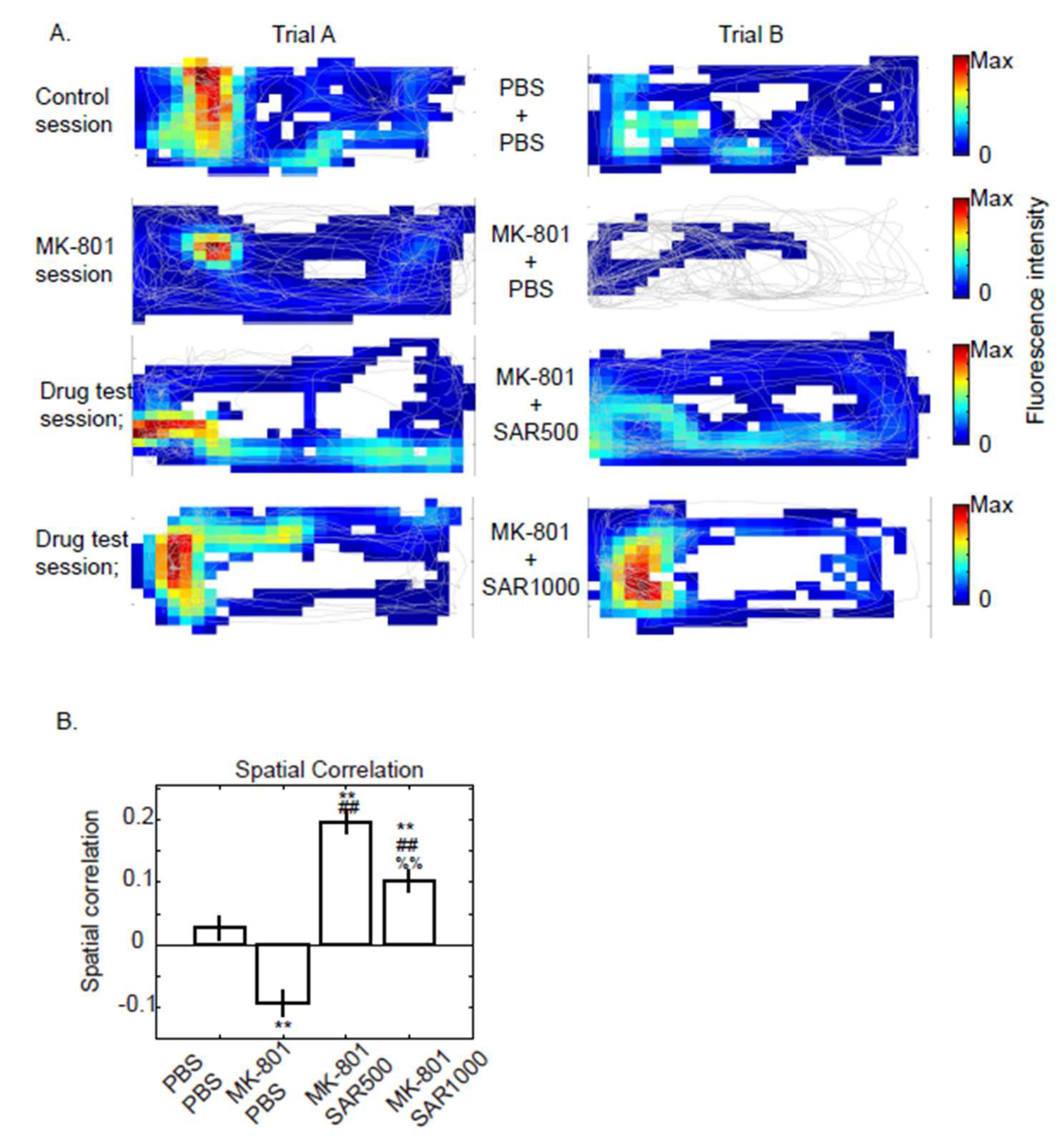
3.4. Spatial Correlation of Fluorescence Map
4. Discussion
4.1. Fluorescence Intensity
4.2. Measure the Grouped and Paired Cells
4.3. Physiological Function of dCA1 Neurons
4.4. Sarcosine Treatment
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data accessibility
Acknowledgments
Competing interests
Ethics approval and informed consent
Abbreviations
| dCA1 | dorsal hippocampal cornu ammonis area 1 |
| GRIN | Gradient index |
| IP | Intraperitoneal |
| K-S | Kolmogorov-Smirnov |
| MC | Movement correction |
| NMDA | N-methyl-D-aspartate |
| PBS | Phosphate buffered saline |
| SAR500 | Sarcosine 500 mg/kg |
| SAR1000 | Sarcosine 1000 mg/kg |
References
- Howes, O.; McCutcheon, R.; Stone, J. Glutamate and dopamine in schizophrenia: an update for the 21st century. J Psychopharmacol 2015, 29, 97–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javitt, D.C. Glutamate and schizophrenia: phencyclidine, N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors, and dopamine-glutamate interactions. Int Rev Neurobiol 2007, 78, 69–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moghaddam, B.; Javitt, D. From revolution to evolution: the glutamate hypothesis of schizophrenia and its implication for treatment. Neuropsychopharmacology 2012, 37, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olney, J.W.; Newcomer, J.W.; Farber, N.B. NMDA receptor hypofunction model of schizophrenia. J Psychiatr Res 1999, 33, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.C. Schizophrenia and Madness; George Allen & Unwin: 1982.
- Balu, D.T. The NMDA receptor and schizophrenia: From pathophysiology to treatment. Adv Pharmacol 2016, 76, 351–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javitt, D.C.; Balla, A.; Burch, S.; Suckow, R.; Xie, S.; Sershen, H. Reversal of phencyclidine-induced dopaminergic dysregulation by N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor/glycine-site agonists. Neuropsychopharmacology 2004, 29, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesh, T.A.; Niendam, T.A.; Minzenberg, M.J.; Carter, C.S. Cognitive control deficits in schizophrenia: mechanisms and meaning. Neuropsychopharmacology 2011, 36, 316–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipina, T.; Labrie, V.; Weiner, I.; Roder, J. Modulators of the glycine site on NMDA receptors, D-serine and ALX 5407, display similar beneficial effects to clozapine in mouse models of schizophrenia. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2005, 179, 54–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javitt, D.C. Glycine transport inhibitors and the treatment of schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 2008, 63, 6–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Snyder, G.L.; Vanover, K.E. Dopamine targeting drugs for the treatment of schizophrenia: past, present and future. Curr Top Med Chem 2016, 16, 3385–3403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, R.A. The blood-brain barrier and glutamate. Am J Clin Nutr 2009, 90, 867S–874S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javitt, D.C.; Silipo, G.; Cienfuegos, A.; Shelley, A.M.; Bark, N.; Park, M.; Lindenmayer, J.P.; Suckow, R.; Zukin, S.R. Adjunctive high-dose glycine in the treatment of schizophrenia. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 2001, 4, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heresco-Levy, U.; Javitt, D.C.; Ermilov, M.; Mordel, C.; Silipo, G.; Lichtenstein, M. Efficacy of high-dose glycine in the treatment of enduring negative symptoms of schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 1999, 56, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lane, H.Y.; Liu, Y.C.; Huang, C.L.; Chang, Y.C.; Liau, C.H.; Perng, C.H.; Tsai, G.E. Sarcosine (N-methylglycine) treatment for acute schizophrenia: a randomized, double-blind study. Biol Psychiatry 2008, 63, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lane, H.Y.; Chang, Y.C.; Liu, Y.C.; Chiu, C.C.; Tsai, G.E. Sarcosine or D-serine add-on treatment for acute exacerbation of schizophrenia: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2005, 62, 1196–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, G.; Lane, H.Y.; Yang, P.; Chong, M.Y.; Lange, N. Glycine transporter I inhibitor, N-methylglycine (sarcosine), added to antipsychotics for the treatment of schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 2004, 55, 452–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, H.Y.; Lin, C.H.; Huang, Y.J.; Liao, C.H.; Chang, Y.C.; Tsai, G.E. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled comparison study of sarcosine (N-methylglycine) and D-serine add-on treatment for schizophrenia. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 2010, 13, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergeron, R.; Meyer, T.M.; Coyle, J.T.; Greene, R.W. Modulation of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor function by glycine transport. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1998, 95, 15730–15734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, J.C.; Hung, W.L.; Lin, B.X.; Shih, M.H.; Lu, L.Y.; Luo, D.Z.; Tai, H.C.; Studer, V.; Min, M.Y.; Lai, W.S. Therapeutic potential and underlying mechanism of sarcosine (N-methylglycine) in N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor hypofunction models of schizophrenia. J Psychopharmacol 2019, 33, 1288–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svoboda, J.; Stankova, A.; Entlerova, M.; Stuchlik, A. Acute administration of MK-801 in an animal model of psychosis in rats interferes with cognitively demanding forms of behavioral flexibility on a rotating arena. Front Behav Neurosci 2015, 9, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csernansky, J.G.; Martin, M.; Shah, R.; Bertchume, A.; Colvin, J.; Dong, H. Cholinesterase inhibitors ameliorate behavioral deficits induced by MK-801 in mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 2005, 30, 2135–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resendez, S.L.; Jennings, J.H.; Ung, R.L.; Namboodiri, V.M.; Zhou, Z.C.; Otis, J.M.; Nomura, H.; McHenry, J.A.; Kosyk, O.; Stuber, G.D. Visualization of cortical, subcortical and deep brain neural circuit dynamics during naturalistic mammalian behavior with head-mounted microscopes and chronically implanted lenses. Nat Protoc 2016, 11, 566–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O'Keefe, J.; Dostrovsky, J. The hippocampus as a spatial map. Preliminary evidence from unit activity in the freely-moving rat. Brain Res 1971, 34, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Li, C.; Singh-Alvarado, J.; Zhou, Z.C.; Frohlich, F.; Mooney, R.; Wang, F. MIN1PIPE: A miniscope 1-photon-based calcium imaging signal extraction pipeline. Cell Rep 2018, 23, 3673–3684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghandour, K.; Ohkawa, N.; Fung, C.C.A.; Asai, H.; Saitoh, Y.; Takekawa, T.; Okubo-Suzuki, R.; Soya, S.; Nishizono, H.; Matsuo, M.; et al. Orchestrated ensemble activities constitute a hippocampal memory engram. Nat Commun 2019, 10, 2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, M.; Kobayashi, K.; Ohkura, M.; Nakai, J.; Matsuzaki, M. Two-photon calcium imaging of the medial prefrontal cortex and hippocampus without cortical invasion. Elife 2017, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, J.C.; Su, K.; Goldberg, A.R.; Luna, V.M.; Biane, J.S.; Ordek, G.; Zhou, P.; Ong, S.K.; Wright, M.A.; Zweifel, L.; et al. Anxiety Cells in a Hippocampal-Hypothalamic Circuit. Neuron 2018, 97, 670–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mau, W.; Sullivan, D.W.; Kinsky, N.R.; Hasselmo, M.E.; Howard, M.W.; Eichenbaum, H. The same hippocampal CA1 population simultaneously codes temporal information over multiple timescales. Curr Biol 2018, 28, 1499–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaremba, J.D.; Diamantopoulou, A.; Danielson, N.B.; Grosmark, A.D.; Kaifosh, P.W.; Bowler, J.C.; Liao, Z.; Sparks, F.T.; Gogos, J.A.; Losonczy, A. Impaired hippocampal place cell dynamics in a mouse model of the 22q11.2 deletion. Nat Neurosci 2017, 20, 1612–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieri, K.W.; Bobbitt, K.N.; Colgin, L.L. Slow and fast gamma rhythms coordinate different spatial coding modes in hippocampal place cells. Neuron 2014, 82, 670–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, Y.T.; Zheng, C.; Colgin, L.L. Slow gamma rhythms in CA3 are entrained by slow gamma activity in the dentate gyrus. J Neurophysiol 2016, 116, 2594–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nahum-Levy, R.; Lipinski, D.; Shavit, S.; Benveniste, M. Desensitization of NMDA receptor channels is modulated by glutamate agonists. Biophys J 2001, 80, 2152–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebb, D.O. The organization of behavior; a neuropsychological theory; Wiley: Oxford, England, 1949; pp. xix, 335-xix, 335.
- Hakami, T.; Jones, N.C.; Tolmacheva, E.A.; Gaudias, J.; Chaumont, J.; Salzberg, M.; O'Brien, T.J.; Pinault, D. NMDA receptor hypofunction leads to generalized and persistent aberrant gamma oscillations independent of hyperlocomotion and the state of consciousness. PLoS One 2009, 4, e6755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olypher, A.V.; Klement, D.; Fenton, A.A. Cognitive disorganization in hippocampus: a physiological model of the disorganization in psychosis. J Neurosci 2006, 26, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liddle, P.F.; Morris, D.L. Schizophrenic syndromes and frontal lobe performance. Br J Psychiatry 1991, 158, 340–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dana, H.; Sun, Y.; Mohar, B.; Hulse, B.K.; Kerlin, A.M.; Hasseman, J.P.; Tsegaye, G.; Tsang, A.; Wong, A.; Patel, R.; et al. High-performance calcium sensors for imaging activity in neuronal populations and microcompartments. Nat Methods 2019, 16, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenton, A.A.; Kao, H.Y.; Neymotin, S.A.; Olypher, A.; Vayntrub, Y.; Lytton, W.W.; Ludvig, N. Unmasking the CA1 ensemble place code by exposures to small and large environments: more place cells and multiple, irregularly arranged, and expanded place fields in the larger space. J Neurosci 2008, 28, 11250–11262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balu, D.T.; Coyle, J.T. The NMDA receptor 'glycine modulatory site' in schizophrenia: D-serine, glycine, and beyond. Curr Opin Pharmacol 2015, 20, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiaz, R.; Kent, I.; Rubinstein, K.; Sela, B.A.; Javitt, D.; Weiser, M. Safety, tolerability and pharmacokinetics of open label sarcosine added on to anti-psychotic treatment in schizophrenia - preliminary study. Isr J Psychiatry Relat Sci 2015, 52, 12–15. [Google Scholar]
| PBS+PBS | MK801+PBS | MK801+SAR500 | MK801+SAR1000 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mouse 10 | 199 | 101 | 150 | 161 |
| Mouse 11 | 59 | 51 | 69 | 90 |
| Mouse 12 | 215 | 271 | 270 | 279 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





