1. Introduction
In critically ill patients, inadequate oxygen supply to tissues results in anaerobic glycolysis and consequently increased lactate production [
1,
2]. Hyperlactatemia with or without acidosis, is considered a sign of organ hypoperfusion and/or tissue hypoxia, signifies the acute circulatory failure and it is closely related to the severity of the underlying condition and the clinical outcome [
1,
2,
3]. Apart from anaerobic production, impaired lactate metabolism can result from factors other than tissue hypoxia [
4,
5]. In patients with sepsis, hyperlactatemia can be associated with an alteration in oxygen extraction that has been attributed to microcirculatory dysfunction and to impaired cellular oxygen utilization, as well as to changes in lactate clearance [
6,
7]. Increased lactate levels are used worldwide for early diagnosis, management, and in risk stratification of patients with sepsis and/or septic shock [
8].
In addition to lactate, hypoalbuminemia upon hospital admission is common in critical illness. Among other factors, such as malnutrition, a decreased serum albumin level is mainly attributable to the inflammation, resulting in increased vascular permeability, leading thus, to a greater capillary leakage of albumin to the interstitial space [
9,
10]. Accordingly, hypoalbuminemia is considered an indicator of the severity of inflammation state, and it has been associated with poor outcomes [
11].
It has been shown that the ratio between lactate and albumin could provide further information as an early prognostic marker for critically ill sepsis patients [
12,
13,
14,
15,
16,
17], as well as in patients with sepsis in the emergency department [
18,
19], having better prognostic performance than lactate alone, in most of the studies. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by the severe acute respiratory syn drome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) could justify the possibility of similar response, as a cause of viral sepsis [
20]. Indeed, in the context of severe COVID-19, rapid albumin loss has been described in critically ill patients during the early phase [
21,
22]. Although the majority of COVID-19 patients have normal lactate levels on admission to the intensive care unit (ICU), a significant percentage of patients has elevated levels; these patients exhibit a significantly higher ICU mortality risk [
23,
24,
25].
In critically ill patients with COVID-19 the ratio between lactate and albumin has not been studied. Therefore, we evaluated the prognostic performance of the lactate/albumin ratio on ICU mortality in a large cohort of critically ill patients admitted to our ICU during the pandemic. We hypothesized that lactate/albumin ratio is better prognostic marker than lactate alone in prediction of mortality among critically ill patients admitted to the ICU due to COVID-19.
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design
This is a single-center retrospective cohort study of prospectively collected data derived from the COVID-19 dataset (formed in March 2020) [
26] for all critically ill patients admitted to the university ICU at "Evangelismos" Hospital, a tertiary care center in Athens, Greece, between March 2020 and April 2022. All patients suffered from severe SARS-CoV-2 infection, confirmed by a real-time reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction assay of nasopharyngeal swab specimens. Patients who died within 24 hours post ICU admission as well as patients who received albumin infusion before admission to the ICU were excluded.
2.2. Data Collection
The collected data encompassed demographics, laboratory tests, illness severity upon ICU admission, comorbidities, need for mechanical ventilation, vasoactive agents use, vaccination status, remdesivir and/or dexamethasone treatment, require ment for continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT), length of ICU stay and ICU clinical outcome. Routine laboratory tests included red blood cell (RBC) and white blood cell (WBC) counts, neutrophil and lymphocyte counts, hemoglobin, hematocrit, platelet count, C-reactive protein (CRP), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), creatinine, highly sensitive cardiac troponin I (Hs-cTnI), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), bilirubin, sodium, glucose, d-dimers, fibrinogen, lactate, albumin and PaO2/FiO2 ratio.
The illness severity was evaluated by the Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation (APACHE) II [
27] and the Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) [
28] scoring systems, calculated on the first day of ICU admission. Comorbidities included hypertension, diabetes mellitus, obesity, cardiovascular disease, chronic pulmonary disease, chronic kidney disease and active malignancy. To account for comorbidities, the Charlson Comorbidity Index was calculated [
29]. Shock was defined as hypotension (systolic blood pressure < 90mm Hg and/or mean arterial pressure < 65mm Hg), persisting despite adequate volume resuscitation, requiring administration of vasoactive agents [
30].
The lactate /albumin ratio was calculated by dividing the arterial lactate level by the serum albumin value. In addition, the neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR) was calculated by dividing the absolute neutrophil count by the absolute lymphocyte count. Variables not routinely measured, such as ferritin or cytokines, were not included in the analysis. All variables mentioned above were collected within 24 hours of patients’ ICU admission. If the patient had multiple measurements within this time period, data from the initial measurement were used. The collection of anonymized data for the study was approved by the Hospital Ethics Committee (Protocol Number 116/2021).
2.3. Statistical Analysis
Continuous variables were expressed as median and interquartile range (IQR), while categorical variables were presented as proportions. Continuous variables were analyzed using the Mann-Whitney U test or Kruskal-Wallis test. To handle missing data, we employed multiple imputations, implemented through the 'mice' package in R software. All variables used in the analyses had less than 5% of missing values, except for d-dimers with 19%.
Correlations between variables were estimated by Spearman’s Rho coefficient. Cox proportional hazards models were used to calculate the hazard ratio (HR) and the 95% confidence interval (CI) of the lactate/albumin ratio for ICU all-cause mortality, with adjustments made for multiple variables. The multivariate analysis included the following variables: age, sex, NLR, Hb, PLT count, sodium, creatinine, AST, ALT, LDH, hs-cTnI, CRP, fibrinogen, d-dimers, PaO2/FiO2 ratio, presence of shock, vaccination status, CRRT, remdesivir, dexamethasone, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, obesity, cardiovascular disease, chronic pulmonary disease, chronic kidney disease and active malignancy. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis was used to estimate the ICU mortality based on the lactate/albumin ratio quartiles. Additionally, we analyzed the nonlinear association between the lactate/albumin ratio and ICU all-cause mortality using a restricted cubic spline regression model with four knots. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were used to determine the cutoff value of the lactate/albumin ratio and to evaluate the predictive power of lactate/albumin ratio, lactate, albumin, and APACHE II score for ICU all-cause mortality. An optimal cut-off was calculated by means of Youden's index. Further stratified analyses were conducted based on age (< 65 and ≥ 65 years), sex, hypertension, and coronary heart disease to assess the consistency of the prognostic value of the lactate/albumin ratio for outcome. Interactions between the lactate/albumin ratio and stratification variables were examined using likelihood ratio tests. All analyses were performed using R software (version 4.3.3), and a two-tailed p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
A total of 805 patients were included in the final analysis. Of them, 548 (68%) were males, and their median (IQR) age was 67 (57-76) years. APACHE II score was 14 (11-19) and SOFA score was 7 (4-9). The most frequent comorbidities were hypertension (41%), diabetes (25%), and cardiovascular disease (25%). All-cause ICU mortality in the entire population was 48%, and CRRT was required by 30% of patients; 61 (7.6%) patients were fully vaccinated, 637 (79%) received dexamethasone and 391 (49%) received remdesivir. Median lactate/albumin ratio was 0.53 (0.39-0.79),
Table 1. Lactate/albumin ratio, lactate, albumin, hs-cTnI, d-dimers, fibrinogen, age, APACHE II and SOFA scores, Charlson comorbidity index, as well as the presence of cardiovascular disease, were significantly higher in survivors as compared to non-survivors,
Table 1. Baseline characteristics of the cohort according to lactate/albumin ratio quartiles are shown in
Table 2. ICU mortality, CRRT need, mechanical ventilation on admission, age, APACHE II score, SOFA score and Charlson comorbidity index, as well as the presence of cardiovascular disease, were significantly different across the lactate/albumin ratio quartiles.
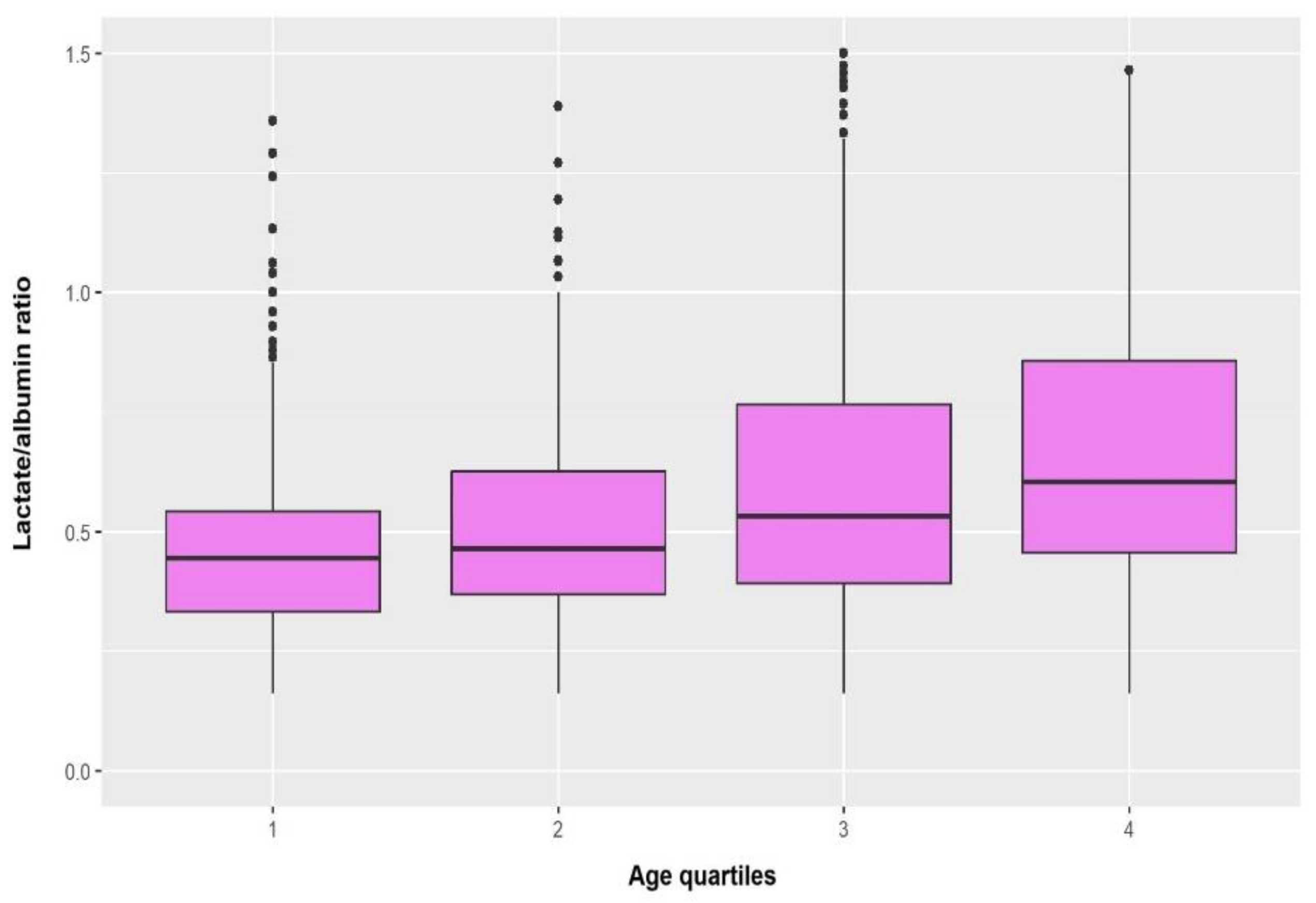
Figure 1 depicts the boxplots of lactate/albumin ratio according to age quartiles. Lactate/albumin ratio was significantly increased in the fourth quartile compared with the lower age quartiles (4 vs 1, p<0.001; 4 vs 2, p=0.007).
3.2. Correlations of Lactate/Albumin Ratio with Other Variables
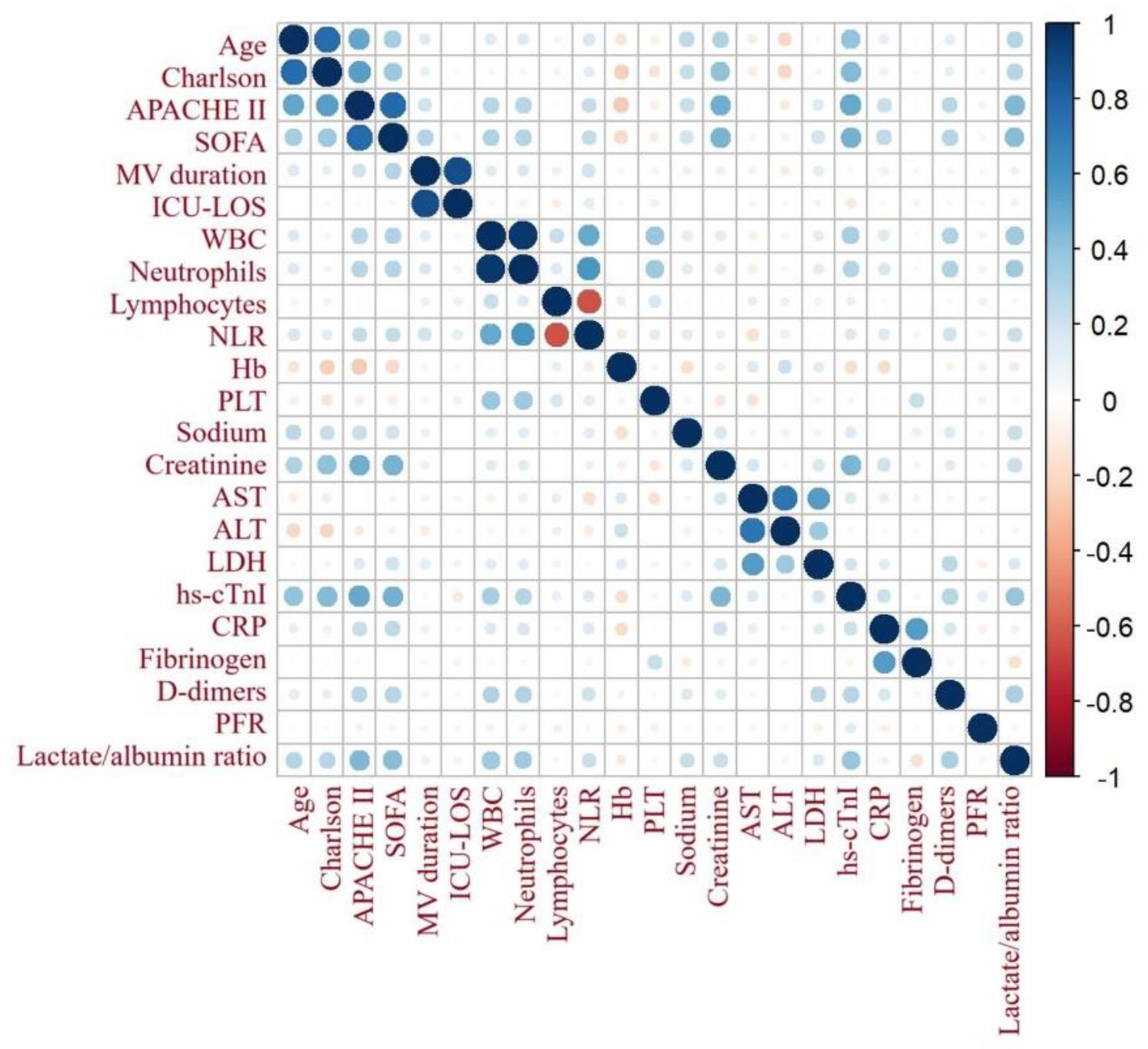
Figure 2 demonstrates the correlation matrix of lactate/albumin ratio with other variables. Lactate/albumin ratio was significantly correlated with age (r=0.16, p<0.001), Charlson comorbidity index (r=0.22, p<0.001), APACHE II (r=0.46, p<0.001) and SOFA (r=0.42, p<0.001) scores, NLR (r=0.11, p=0.002), PLT count (r=-0.15, p<0.001), creatinine (r=0.11, p=0.001), LDH (r=0.41, p<0.001), Hs-cTnI (r=0.24, p<0.001), CRP (r=0.08, p<0.02), fibrinogen (r=-0.2, p<0.001) and d-dimers (r=0.14, p<0.001).
3.3. Survival Analysis
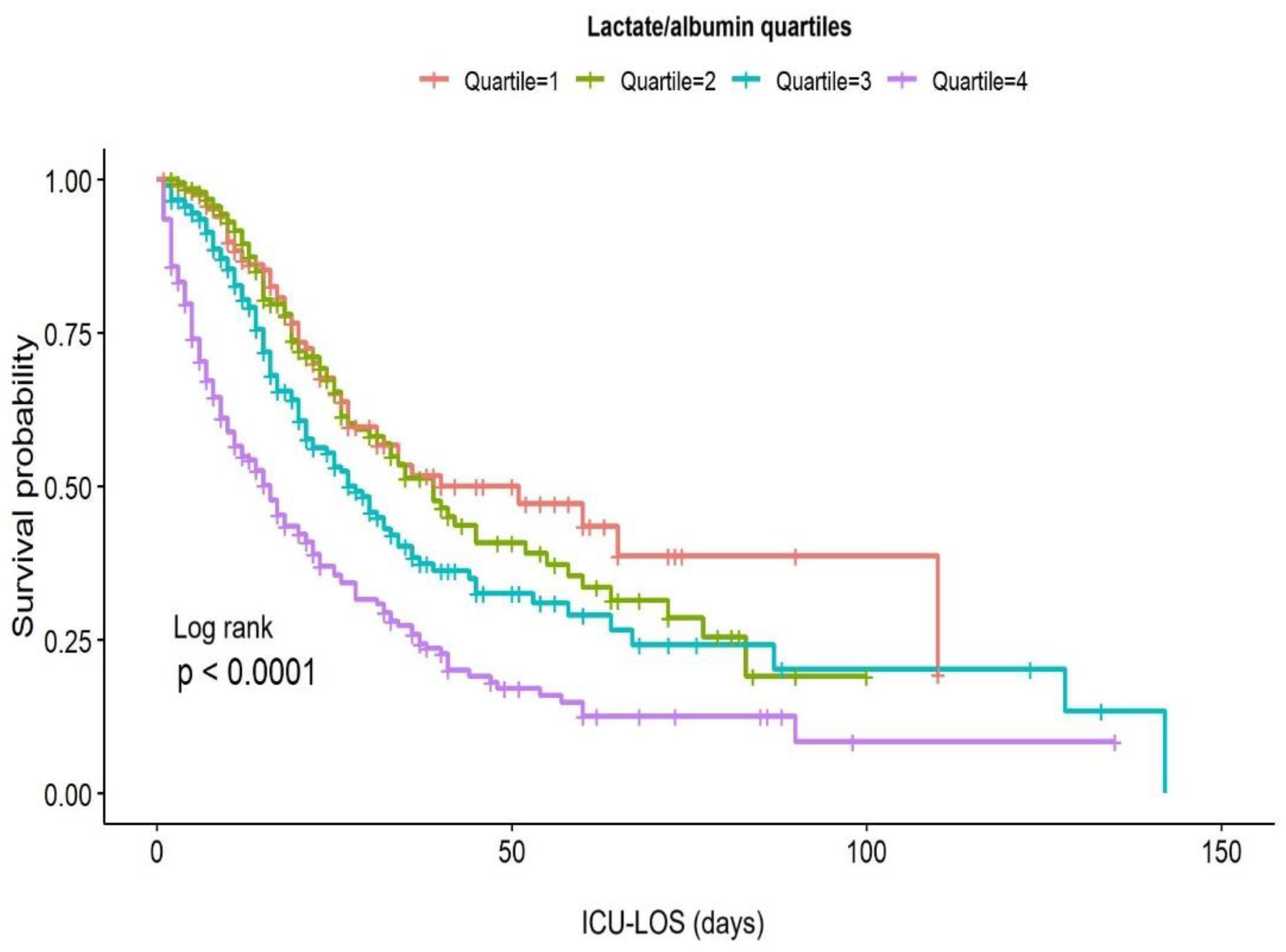
Figure 3 illustrates Kaplan-Meier survival curves for the lactate/albumin ratio quartiles. Log-rank test revealed significantly lower survival probability for the higher lactate/albumin ratio quartiles (p<0.001). In univariable Cox proportional hazards analysis, lactate/albumin ratio was significantly associated with ICU mortality (HR=1.6, CI: 1.4-1.7). Furthermore, a multivariable model adjusted for multiple parameters revealed lactate/albumin ratio as an independent risk factor for ICU mortality (HR=1.39, CI: 1.27-1.52),
Table 3.
Figure 4 illustrates a restricted cubic spline regression model, revealing a non-linear relationship between the lactate/albumin ratio level and the ICU all-cause mortality in the aforementioned multivariable model (p for nonlinear=0.025).
3.4. ROC Curves Analysis
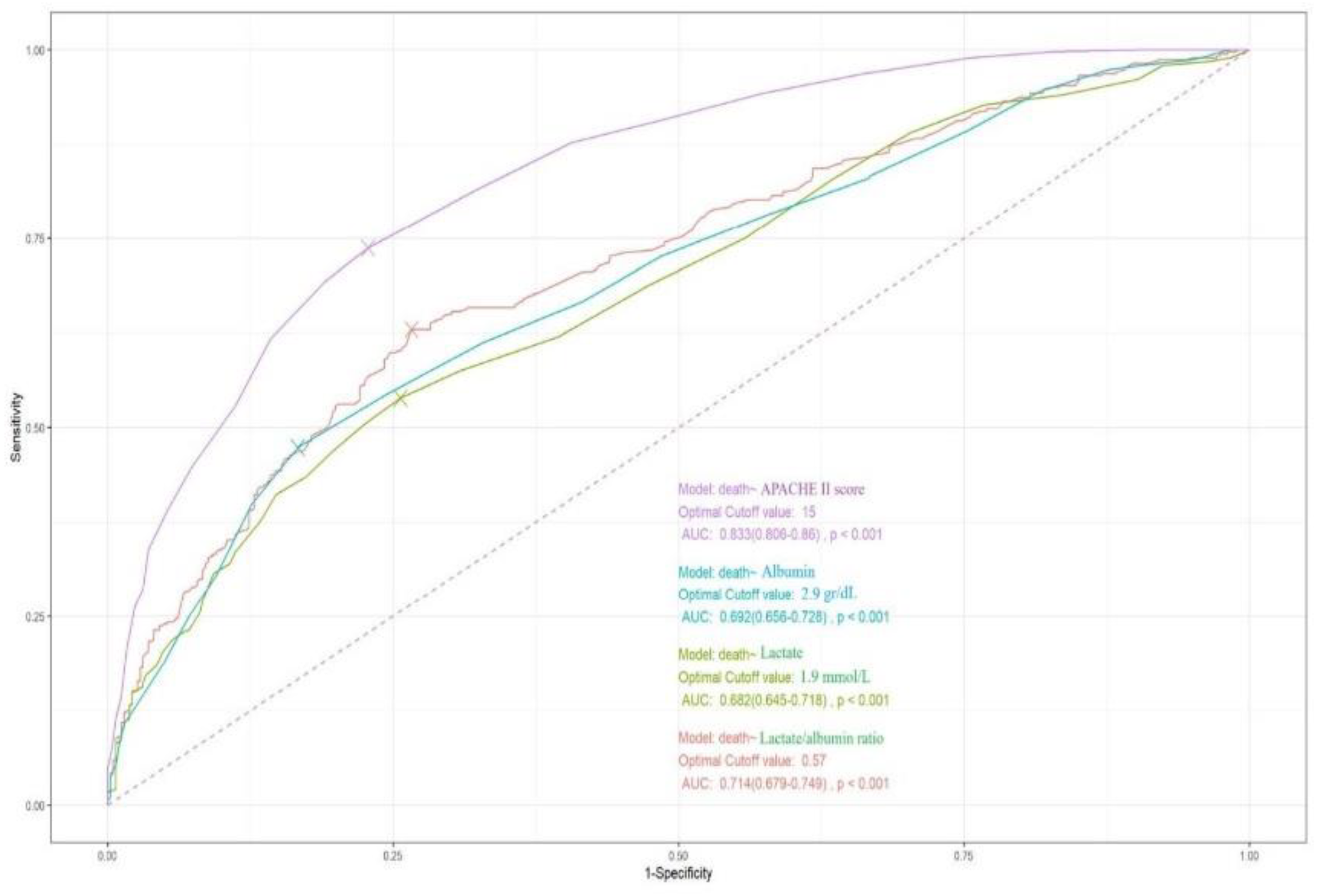
Figure 5 depicts the ROC curves of APACHE II score, lactate/albumin ratio, lactate and albumin for ICU mortality prediction, with AUCs of 0.83 (95% CI: 0.80-0.86), 0.71(0.68-0.75), 0.68 (0.64-0.72), and 0.69 (0.65-0.73), respectively. DeLong test demonstrated that the AUC of lactate/albumin ratio was significantly higher than that of lactate (p<0.001). An optimal cut-off value of lactate/albumin ratio of 0.57 had a sensitivity of 63% and a specificity of 73% for ICU mortality prediction.
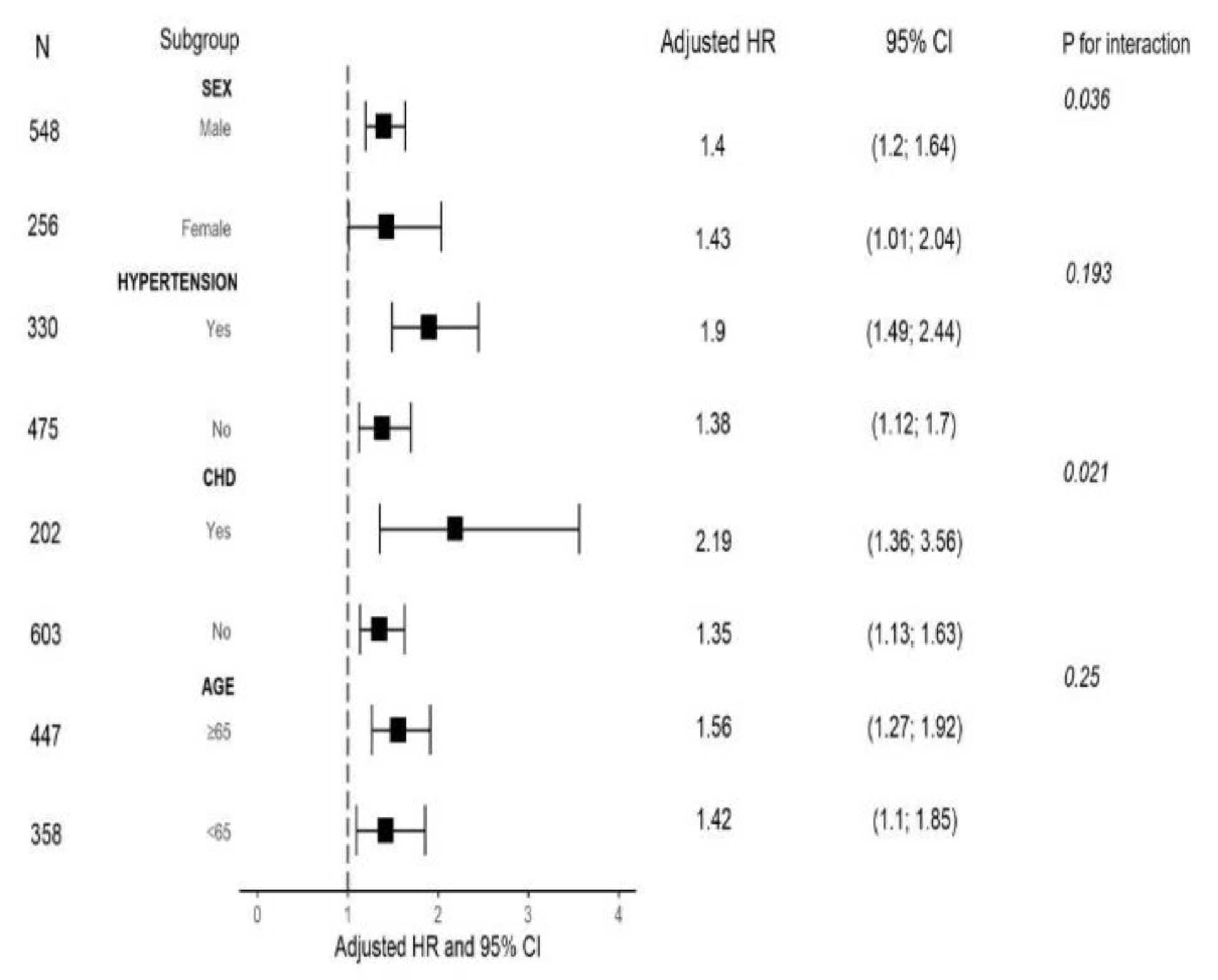
3.5. Subgroup Analyses
We also performed a risk stratification analysis of the lactate/albumin ratio for the primary endpoint across multiple subgroups, such as age, sex, hypertension and cardiovascular disease. Lactate/albumin ratio was significantly associated with increased ICU all-cause mortality in subgroups defined by age < 65 years, age ≥ 65 years, female and male sex, presence and absence of hypertension, as well as presence and absence of cardiovascular disease. Significant interactions were found between lactate/albumin ratio and sex, as well as between lactate/albumin ratio and cardiovascular disease in subgroup analyses (all p for interaction < 0.05).
Figure 6 shows the forest plot of subgroup analyses for the association of lactate/albumin ratio with ICU mortality.
4. Discussion
In this study, we evaluated the effectiveness of lactate/albumin ratio for mortality prediction in a large cohort of patients with severe COVID-19, admitted to the ICU. The main findings are the following: (i) patients with high lactate/albumin ratio on the first day of ICU admission had significantly lower survival rates, (ii) lactate/albumin ratio was an independent risk factor for ICU mortality, (iii) ROC curve analysis showed that lactate/albumin ratio was superior in outcome prediction than lactate alone. These results underscore the superiority of lactate/albumin ratio as a predictive marker for ICU outcome in COVID-19 critically ill patients.
The prognostic significance of lactate/albumin ratio in septic patients has been investigated in several studies [
12,
13,
14,
15,
16,
17,
18,
19]. Wang B. and colleagues [
12] were the first to demonstrate the lactate/albumin ratio as an independent predictor of mortality in patients with severe sepsis and septic shock. Since then, the majority of the next studies confirmed the better prognostic performance of lactate/albumin ratio compared to a single lactate measurement in predicting ICU mortality [
13,
14,
15,
16,
17,
18], whereas elsewhere the performance of lactate/albumin ratio was equivalent to lactate alone in predicting mortality in a large cohort of ICU patients [
19].
However, even though the aforementioned recent studies have focused on the use of lactate/albumin ratio to predict mortality in critically ill patients with sepsis, this index has not been studied in patients with COVID-19, which represents a type of viral sepsis [
20]. To the best of our knowledge, the present study is the first to examine the prognostic performance of lactate/albumin ratio in patients admitted to the ICU due to COVID-19. We showed that at admission to the ICU, both lactate and albumin as well as their ratio exhibited an acceptable performance; however, the lactate/albumin ratio appeared to be superior for predicting mortality in these patients, as reflected by a higher AUC, compared to that of lactate alone. These findings are in accordance with those of the previous studies in non-COVID population, mentioned above [
12,
13,
14,
15,
16,
17,
18].
In addition, our study examined the utility of lactate/albumin ratio in various subgroups inside the cohort of the COVID-19 critically ill patients, defined by age, sex and history of hypertension and cardiovascular disease. These analyses revealed that the prognostic value of lactate/albumin ratio was consistent across these subgroups, after adjusting for all covariates, with notable interactions between lactate/albumin ratio and sex, as well as history of cardiovascular coronary heart disease.
The role of lactate/albumin ratio as a prognostic marker is further supported by comparing its performance with other biomarkers. Jeong et al. [
31] compared lactate/albumin ratio with the red cell distribution width/albumin ratio and found lactate/albumin ratio to be equally effective in predicting 28-day mortality in critically ill patients with pneumonia requiring mechanical ventilation. On the contrary, a nonlinear relationship between lactate/albumin ratio and in-hospital mortality in ICU patients with acute respiratory failure of various etiologies has been reported [
32].
In a very recent work by Wang HX and colleagues [
33], the lactate/ albumin ratio was an independent predictive factor for 28-day overall mortality in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Interestingly, the AUC of lactate/albumin ratio was the same with that of our study (71%), and provided significantly higher discrimination compared with lactate or albumin alone, similar to our findings. Since almost all patients of our cohort presented COVID-19-related ARDS, the consistency in the results of both studies is not surprising.
Furthermore, it should be noted that lactate/albumin ratio has also shown promise in specific subgroups of critically ill patients, such as those with heart failure [
34], acute kidney injury undergoing renal replacement therapy [
35] or burn patients [
36], suggesting that lactate/albumin ratio is not only a general marker of critical illness severity but also has condition-specific utility.
Certain limitations include the retrospective nature of this single-center study, factors that may limit the ability to draw definitive conclusions about causality as well as the lack of information on the trajectory of lactate/albumin ratio and its association with outcome. Thus, the impact of dynamic changes of the ratio on prognosis has not been assessed. In addition, albumin levels can be influenced by factors beyond critical illness, such as nutritional status, liver function, and fluid balance. This variability can introduce confounding into lactate/albumin ratio measurements and affect its reliability as a prognostic tool. However, the large size of our sample, including all patients admitted to our ICU due to COVID-19 over the pandemic, minimizes potential sources of confounding.
In conclusion, the lactate/albumin ratio at ICU admission, easily obtained from routine laboratory tests, performs better than lactate alone and it could serve as a reliable indicator for the prognosis of critically ill COVID-19 patients. Further research should focus on refining lactate/albumin ratio risk models and exploring its role in guiding therapeutic interventions. The integration of lactate/albumin ratio into established clinical scoring systems may further enhance its utility in predicting outcomes and improving patient care.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.K.; Data curation, A.G., D.E.K., S.K., D.T., E.M., Formal analysis, S.K., Investigation, S.K., F.K., G.D., E.T., I.D., C.R.; Methodology, S.K, A.K., C.R., ; Writing - original draft, S.K. and C.R.; Writing - review and editing, S.K., A.G., I.D. and C.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study was approved by the ethical committee of ‘Evangelismos’ Hospital, Athens, Greece. Consent for publication: Not applicable; Availability of data and materials: The datasets used/or analyzed in the present study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
- Rashkin, M.; Boxkin, C.; Baughman, R. Oxygen delivery in critically ill patients: relationship to blood lactate and survival. Chest 1985, 87, 580-84. [CrossRef]
- Bakker, J.; Vincent J-L. The oxygen-supply dependency phenomenon is associated with increased blood lactate levels. J Crit Care 1991, 6, 152-159. [CrossRef]
- Kraut, JA.; Madias, NE. Lactic Acidosis. N Engl J Med 2014, 371, 2309-2319. [CrossRef]
- Gibot, S. On the origins of lactate during sepsis. Critical Care 2012, 16, 151. [CrossRef]
- Routsi, C.; Bardouniotou, E.; Delivoria-loannidou, V.; Kazi, D.; Roussos, C.; Zakynthinos, S. Pulmonary lactate release in patients with acute lung injury is not attributable to lung tissue hypoxia. Crit Care Med 1999, 27, 2469-2473. [CrossRef]
- Michaeli, B.; Martinez, A.; Revelly, JP.; Cayeux, MC.; Chioléro, RL.; Tappy, L.; Berger, MM. Effects of endotoxin on lactate metabolism in humans. Critical Care 2012, 16:R139. [CrossRef]
- Bakker, J.; Coffernil, M.; Leon, M.; Gris, P.; Vincent, JL. Blood Lactate Levels Are Superior to Oxygen-Derived Variables in Predicting Outcome in Human Septic Shock. Chest 1991, 99, 956-62. [CrossRef]
- Bakker, J.; Nijsten, MW.; Jansen, TC. Clinical use of lactate monitoring in critically ill patients. Ann Intensive Care 2013, 3, 12. [CrossRef]
- Fleck, A.; Raines, G.; Hawker, F.; Trotter, J.; Wallace, PI.; Lendingham, IM.; Calman, KC. Increased vascular permeability: A major cause of hypoalbuminaemia in disease and injury. Lancet 1985, 1, 781–784. [CrossRef]
- Soeters, PB.; Wolfe, RR.; Shenkin, A. Hypoalbuminemia: Pathogenesis and clinical significance. J Parenter Enteral Nutr 2019, 43, 181–193. [CrossRef]
- Arnau-Barres, I.; Guerri-Fernandez, R.; Luque, S.; Sorli, L.; Vázquez O.; Miralles R. Serum albumin is a strong predictor of sepsis outcome in elderly patients. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 2019, 38, 743–746. [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Chen, G.; Cao, Y.; Xue, J.; Li, J.; Wu, Y. Correlation of lactate/albumin ratio level to organ failure and mortality in severe sepsis and septic shock. J Crit Care 2015, 30, 271-5. [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; Hwang, SY.; Jo, IJ.; Kim, WY.; Ryoo, SM.; Kang, GH.; Kim, K.; Jo, YH.; Chung, SP.; Joo, YS. et al. Prognostic value of the lactate/albumin ratio for predicting 28-day mortality in critically ill sepsis patients. Shock 2018, 50, 545-550. [CrossRef]
- Cakir, E.; Turan, O. Lactate/albumin ratio is more effective than lactate or albumin alone in predicting clinical outcomes in intensive care patients with sepsis. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 2021, 81, 225-229. [CrossRef]
- Lichtenauer, M.; Wernly, B.; Ohnewein, B.; Franz, M.; Kabisch, B.; Muessig, J.;IMasyuk, M.; Lauten, A.; Schulze, PC.; Hoppe, UC.; et al. The Lactate/Albumin Ratio: A Valuable Tool for Risk Stratification in Septic Patients Admitted to ICU. Int J Mol Sci 2017, 18, 1893. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zhan, H.; Chen, J.; Mo, J.; Huang, S. Predictive value of lactate/albumin ratio for death and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome in patients with sepsis. J Med Biochem 2024, 43, 617-625. [CrossRef]
- Shadvar, K.; Nader-Djalal, N.; Vahed, N.; Sanaie, S.; Iranpour, A.; Mahmoodpoor, A.; Vahedian-Azimi, A.; Samim, A.; Rahimi-Bashar, F. Comparison of lactate/albumin ratio to lactate and lactate clearance for predicting outcomes in patients with septic shock admitted to intensive care unit: an observational study. Sci Rep 2022, 12, 1304. [CrossRef]
- Bou Chebl, R.; Jamali, S.; Sabra, M.; Safa, R.; Berbari, I.; Shami, A.; Makki, M.; Tamim, H.; Abou Dagher, G. Lactate/Albumin Ratio as a Predictor of In-Hospital Mortality in Septic Patients Presenting to the Emergency Department. Front Med (Lausanne) 2020, 7, 550182. [CrossRef]
- Gharipour, A.; Razavi, R.; Gharipour, M.; Mukasa, D. Lactate/albumin ratio: An early prognostic marker in critically ill patients. Am J Emerg Med 2020, 38, 2088-2095. [CrossRef]
- Karakike, E.; Giamarellos-Bourboulis, EJ.; Kyprianou, M.; Fleischmann-Struzek, C.; Pletz, MW.; Netea, MG.; Reinhart, K.; Kyriazopoulou, E. Coronavirus disease 2019 as cause of viral sepsis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit. Care Med 2021, 49, 2042-2057. [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Hoffman, KL.; Xu, Z.; Sanchez, E.; Siempos, II.; Harrington, JS.; Racanelli, AC.; Plataki, M.; Wang, F.; Schenck, EJ. Evaluation of Albumin Kinetics in Critically Ill Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 Compared to Those With Sepsis-Induced Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Crit Care Explor 2021, 3, e0589. [CrossRef]
- Kokkoris, S.; Kanavou, A.; Katsaros, D.; Karageorgiou, S.; Kremmydas, P.; Gkoufa, A.; Ntaidou, T.; Giannopoulos, C.; Kardamitsi, MA.; Dimopoulou, G.; et al. Temporal trends in laboratory parameters in survivors and non-survivors of critical COVID-19 illness and the effect of dexamethasone treatment. Biomed Rep 2023, 20, 12. [CrossRef]
- Carpenè, G.; Onorato, D.; Nocini, R.; Fortunato, G.; Rizk, JG.; Henry, BM.; Lippi G. Blood lactate concentration in COVID-19: a systematic literature review. Clin Chem Lab Med 2021, 60, 332-337. [CrossRef]
- Vassiliou, AG.; Tsipilis, S.; Keskinidou, C.; Vrettou, CS.; Jahaj, E.; Gallos, P.; Routsi, C.; Orfanos, SE.; Kotanidou, A.; Dimopoulou, I. Lactate and Lactate-to-Pyruvate Ratio in Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients: A Pilot Study. J Pers Med 2022, 12, 171. [CrossRef]
- Iepsen, UW.; Plovsing, RR.; Tjelle, K.; Foss, NB.; Meyhoff, CS.; Ryrsø, CK.; Berg, RMG.; Secher, NH. The role of lactate in sepsis and COVID-19: Perspective from contracting skeletal muscle metabolism. Exp Physiol 2022, 107, 665-673. [CrossRef]
- Routsi, C.; Magira, E.; Kokkoris, S.; Siempos, I.; Vrettou, C.; Zervakis, D.; Ischaki, E.; Malahias, S.; Sigala, I.; Asimakos, A.; et al. Hospital resources may be an important aspect of mortality rate among critically ill patients with CO VID-19: the paradigm of Greece. J Clin Med 2020, 9, 3730. [CrossRef]
- Knaus, WA.; Draper, EA.; Wagner, DP.; Zimmerman, JE. APACHE II: a severity of disease classification system. Crit Care Med 1985, 13, 818–29.
- Vincent, JL.; Moreno, R.; Takala, J.; Willatts, S.; De Mendonça, A.; Bruining, H.; Reinhart, CK.; Suter, PM.; Thijs, LG. The SOFA (Sepsis-related Organ Failure Assessment) score to describe organ dysfunction/failure. On behalf of the Working Group on Sepsis-Related Problems of the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine. Intensive Care Med 1996, 22, 707-10. [CrossRef]
- Charlson, ME.; Pompei, P.; Ales, KL.; MacKenzie, CR. A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longi tudinal studies: development and validation. J Chronic Dis 1987, 40, 373–83. [CrossRef]
- Cecconi, M.; De Backer, D.; Antonelli, M.; Beale, R.; Bakker, J.; Hofer, C.; Jaeschke, R.; Mebazaa, A.; Pinsky, MR.; Teboul, JL.; et al. Consensus on circulatory shock and hemodynamic monitoring. Task force of the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine. Intensive Care Med 2014, 40, 1795–1815. [CrossRef]
- Jeong, JH.; Heo, M.; Lee, SJ.; Jeong, YY.; Lee, JD.; Yoo, JW. Clinical Usefulness of Red Cell Distribution Width/Albumin Ratio to Discriminate 28-Day Mortality in Critically Ill Patients with Pneumonia Receiving Invasive Mechanical Ventilation, Compared with Lacate/Albumin Ratio: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Diagnostics (Basel) 2021, 11, 2344. [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Kang, Q.; Wang, F.; Yu, W. Association of lactate/albumin ratio with in-hospital mortality in ICU patients with acute respiratory failure: A retrospective analysis based on MIMIC-IV database. Medicine (Baltimore) 2023, 102, e35410. [CrossRef]
- Wang, HX.; Huang, XH.; Ma, LQ.; Yang, ZJ.; Wang, HL.; Xu, B.; Luo, MQ. Association between lactate-to-albumin ratio and short-time mortality in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome. J Clin Anesth 2024, 99, 111632. [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Zhao, L.; Zhao, H.; Zeng, F.; Peng, C.; Guo, W.; Yan, H. The value of lactate/albumin ratio for predicting the clinical outcomes of critically ill patients with heart failure. Ann Transl Med 2021, 9, 118. [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Min, J.; Lu, J.; Zhong, L.; Luo, H. Association between lactate/albumin ratio and prognosis in critically ill patients with acute kidney injury undergoing continuous renal replacement therapy. Ren Fail 2024, 46, 2374451. [CrossRef]
- Dudoignon, E.; Quennesson, T.; De Tymowski, C.; Moreno, N.; Coutrot, M.; Chaussard, M.; Guillemet, L.; Abid, S.; Fratani, A.; Ressaire, Q.; et al. Usefulness of lactate albumin ratio at admission to predict 28-day mortality in critically ill severely burned patients: A retrospective cohort study. Burns 2022, 48, 1836-1844. [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Boxplots of lactate/albumin ratio according to age quartiles.
Figure 1.
Boxplots of lactate/albumin ratio according to age quartiles.
Figure 2.
Correlation matrix of lactate/albumin ratio with other variables. Lactate/albumin ratio was significantly correlated with all other variables, except for lymphocytes, hemoglobin and PFR. Abbreviations: APACHE, acute physiology and chronic health evaluation; SOFA, sequential organ failure assessment ; MV, mechanical ventilation; ICU-LOS, intensive care unit-length of stay; WBC, white blood cell; NLR, neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio; Hb, hemoglobin; PLT, platelets; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; hs-cTnI, high sensitivity cardiac troponin I; CRP, C-reactive protein; PFR, PaO2/FiO2 ratio.
Figure 2.
Correlation matrix of lactate/albumin ratio with other variables. Lactate/albumin ratio was significantly correlated with all other variables, except for lymphocytes, hemoglobin and PFR. Abbreviations: APACHE, acute physiology and chronic health evaluation; SOFA, sequential organ failure assessment ; MV, mechanical ventilation; ICU-LOS, intensive care unit-length of stay; WBC, white blood cell; NLR, neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio; Hb, hemoglobin; PLT, platelets; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; hs-cTnI, high sensitivity cardiac troponin I; CRP, C-reactive protein; PFR, PaO2/FiO2 ratio.
Figure 3.
Kaplan-Meier survival curves according to lactate/albumin ratio quartiles. Abbreviations: ICU-LOS, intensive care unit-length of stay. .
Figure 3.
Kaplan-Meier survival curves according to lactate/albumin ratio quartiles. Abbreviations: ICU-LOS, intensive care unit-length of stay. .
Figure 4.
Restricted cubic spline regression analysis of lactate/albumin ratio with ICU mortality. The heavy central lines represent the estimated adjusted HR, with shaded ribbons indicating the corresponding 95% CI. The histogram illustrates the distribution of patients. There was a non-linear association between lactate/albumin ratio and HR. The model was adjusted for age, sex, NLR, Hb, PLT count, sodium, creatinine, AST, ALT, LDH, hs-cTnI, CRP, fibrinogen, d-dimers, PFR, presence of shock, vaccination status, CRRT, remdesivir, dexamethasone, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, obesity, coronary heart disease, chronic pulmonary disease, chronic kidney disease and active malignancy. Abbreviations: ICU, intensive care unit; HR, hazard ratio; CI, confidence interval; NLR, neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio; Hb, hemoglobin; PLT, platelets; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; hs-cTnI, high sensitivity cardiac troponin I; CRP, C-reactive protein; PFR, PaO2/FiO2 ratio; CRRT, continuous renal replacement therapy.
Figure 4.
Restricted cubic spline regression analysis of lactate/albumin ratio with ICU mortality. The heavy central lines represent the estimated adjusted HR, with shaded ribbons indicating the corresponding 95% CI. The histogram illustrates the distribution of patients. There was a non-linear association between lactate/albumin ratio and HR. The model was adjusted for age, sex, NLR, Hb, PLT count, sodium, creatinine, AST, ALT, LDH, hs-cTnI, CRP, fibrinogen, d-dimers, PFR, presence of shock, vaccination status, CRRT, remdesivir, dexamethasone, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, obesity, coronary heart disease, chronic pulmonary disease, chronic kidney disease and active malignancy. Abbreviations: ICU, intensive care unit; HR, hazard ratio; CI, confidence interval; NLR, neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio; Hb, hemoglobin; PLT, platelets; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; hs-cTnI, high sensitivity cardiac troponin I; CRP, C-reactive protein; PFR, PaO2/FiO2 ratio; CRRT, continuous renal replacement therapy.
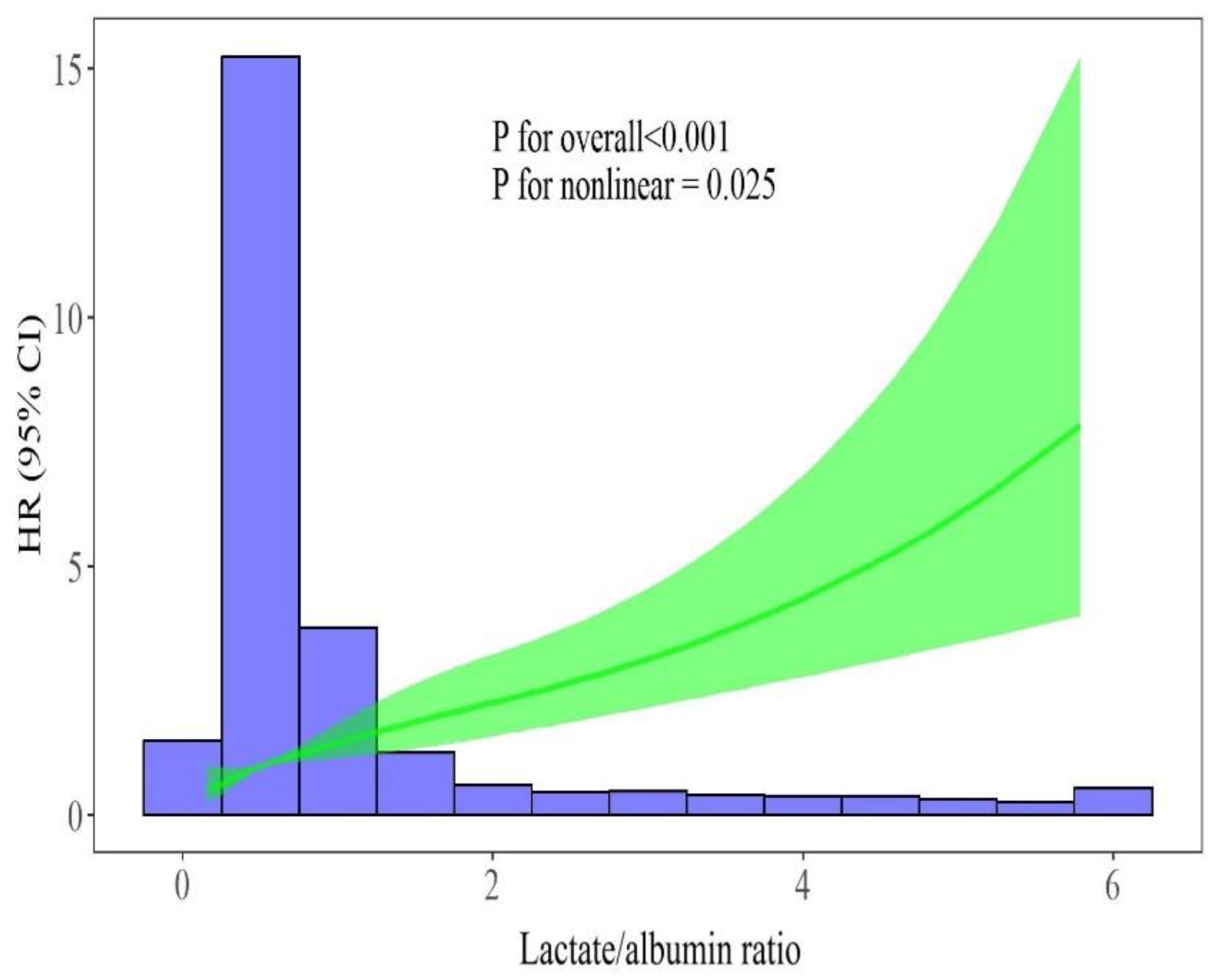
Figure 5.
ROC curves for lactate/albumin ratio, lactate, albumin, and APACHE II score in predicting ICU mortality. Abbreviations: ROC, receiver-operating characteristics; APACHE, acute physiology and chronic health evaluation; ICU, intensive care unit.
Figure 5.
ROC curves for lactate/albumin ratio, lactate, albumin, and APACHE II score in predicting ICU mortality. Abbreviations: ROC, receiver-operating characteristics; APACHE, acute physiology and chronic health evaluation; ICU, intensive care unit.
Figure 6.
Forest plot of subgroup analyses for the association of lactate/albumin ratio with ICU mortality. Abbreviations: ICU, intensive care unit; HR: hazard ratio; CI: confidence interval; CHD, cardiovascular disease.
Figure 6.
Forest plot of subgroup analyses for the association of lactate/albumin ratio with ICU mortality. Abbreviations: ICU, intensive care unit; HR: hazard ratio; CI: confidence interval; CHD, cardiovascular disease.
Table 1.
Baseline characteristics of the patient cohort grouped by outcome.
Table 1.
Baseline characteristics of the patient cohort grouped by outcome.
| Characteristic |
Overall
N = 805 |
Survival
N = 421 |
Non-survival
N = 384 |
P-value |
| Demographics |
|
|
|
|
| Sex, male, n (%) |
548 (68%) |
285 (68%) |
263 (68%) |
0.8 |
| Age, years |
67 (57, 76) |
61 (52, 70) |
73 (65, 79) |
<0.001 |
| Age quartiles |
|
|
|
<0.001 |
| 1 |
201 (25%) |
158 (38%) |
43 (11%) |
|
| 2 |
192 (24%) |
127 (30%) |
65 (17%) |
|
| 3 |
210 (26%) |
86 (20%) |
124 (32%) |
|
| 4 |
202 (25%) |
50 (12%) |
152 (40%) |
|
| Severity scores |
|
|
|
|
| Charlson comorbidity index |
3 (2, 5) |
2 (1, 4) |
4 (3, 6) |
<0.001 |
| APACHE II score |
14 (11, 19) |
11 (9, 14) |
18.0 (14, 23) |
<0.001 |
| SOFA score |
7 (4, 9) |
6 (2, 7) |
8 (7, 10) |
<0.001 |
| Outcomes |
|
|
|
|
| CRRT, n (%) |
238 (30%) |
51 (12%) |
187 (49%) |
<0.001 |
| MV duration, days |
11 (4, 24) |
8 (0, 23) |
14 (7, 25) |
<0.001 |
| ICU-LOS, days |
15 (8, 29) |
15 (8, 33) |
15 (8, 26) |
0.056 |
| Laboratory tests |
|
|
|
|
| WBC count, x 109/L |
10 (7, 15) |
9 (7, 13) |
11 (8, 16) |
<0.001 |
| Neutrophil count, x 109/L |
8.7 (5.7, 12.9) |
8.0 (5.4, 11.9) |
9.7 (6.6, 14.4) |
<0.001 |
| Lymphocyte count, x 109/L |
0.76 (0.51, 1.10) |
0.80 (0.55, 1.11) |
0.73 (0.47, 1.10) |
0.015 |
| NLR |
12 (7, 20) |
10 (6, 17) |
14 (8, 23) |
<0.001 |
| Hb, g/dL |
12.4 (10.8, 13.7) |
12.7 (11.4, 13.8) |
11.9 (10.1, 13.5) |
<0.001 |
| PLT count, x 109/L |
241 (182, 309) |
254 (199, 321) |
226 (164, 296) |
<0.001 |
| Albumin, g/dL |
3.2 (2.8, 3.6) |
3.4 (3.1, 3.6) |
3.0 (2.6, 3.4) |
<0.001 |
| Sodium, mEq/L |
140 (137, 143) |
139 (136, 142) |
141 (138, 145) |
<0.001 |
| Creatinine, mg/dL |
0.9 (0.7, 1.3) |
0.8 (0.7, 1.0) |
1.1 (0.8, 1.6) |
<0.001 |
| AST, IU/L |
38 (25, 66) |
37 (25, 60) |
39 (25, 72) |
0.2 |
| ALT, IU/L |
32 (19, 54) |
34 (21, 54) |
28 (17, 58) |
0.020 |
| LDH, IU/L |
456 (347, 624) |
437 (312, 573) |
488 (370, 669) |
<0.001 |
| hs-cTnI, ng/L |
24 (10, 77) |
15 (7, 41) |
42 (17, 123) |
<0.001 |
| CRP, mg/dL |
11 (5, 18) |
10 (4, 17) |
12 (7, 20) |
<0.001 |
| Fibrinogen, mg/dL |
579 (474, 701) |
575 (485, 686) |
583 (459, 708) |
>0.9 |
| D-dimers, mg/L |
1.6 (0.9, 3.9) |
1.2 (0.7, 2.7) |
2.2 (1.1, 5.0) |
<0.001 |
| PaO2/FiO2 ratio |
126 (88, 187) |
136 (93, 206) |
118 (83, 173) |
<0.001 |
| Lactate, mmol/L |
1.70 (1.30, 2.30) |
1.50 (1.20, 1.90) |
2.00 (1.45, 2.90) |
<0.001 |
| Lactate/albumin ratio |
0.53 (0.39, 0.79) |
0.46 (0.35, 0.58) |
0.64 (0.46, 1.02) |
<0.001 |
| Lactate/albumin ratio quartiles |
|
|
|
<0.001 |
| 1 |
206 (26%) |
150 (36%) |
56 (15%) |
|
| 2 |
198 (25%) |
123 (29%) |
75 (20%) |
|
| 3 |
203 (25%) |
96 (23%) |
107 (28%) |
|
| 4 |
198 (25%) |
52 (12%) |
146 (38%) |
|
| Treatment |
|
|
|
|
| Full vaccination, n (%) |
0 (0%) |
26 (6.2%) |
35 (9.1%) |
0.12 |
| Remdesivir, n (%) |
391 (49%) |
221 (52%) |
170 (44%) |
0.020 |
| Dexamethasone, n (%) |
637 (79%) |
328 (78%) |
309 (80%) |
0.4 |
| Tocilizumab, n (%) |
36 (4.5%) |
28 (6.7%) |
8 (2.1%) |
0.002 |
| MV on admission, n (%) |
588 (73%) |
252 (60%) |
336 (88%) |
<0.001 |
| HFNC on admission, n (%) |
158 (20%) |
116 (28%) |
42 (11%) |
<0.001 |
| Shock on admission, n (%) |
304 (38%) |
172 (41%) |
132 (34%) |
0.058 |
| Comorbidities |
|
|
|
|
| Hypertension, n (%) |
330 (41%) |
159 (38%) |
171 (45%) |
0.051 |
| Diabetes mellitus, n (%) |
204 (25%) |
99 (24%) |
105 (27%) |
0.2 |
| Obesity, n (%) |
104 (13%) |
63 (15%) |
41 (11%) |
0.070 |
| Cardiovascular disease, n (%) |
202 (25%) |
81 (19%) |
121 (32%) |
<0.001 |
| Chronic pulmonary disease, n (%) |
106 (13%) |
40 (9.5%) |
66 (17%) |
0.001 |
| Malignancy, n (%) |
85 (11%) |
24 (5.7%) |
61 (16%) |
<0.001 |
| Chronic kidney disease, n (%) |
65 (8.1%) |
15 (3.6%) |
50 (13%) |
<0.001 |
Data are expressed as median (IQR), unless otherwise denoted.
Abbreviations: IQR, interquartile range; APACHE, acute physiology and chronic health evaluation; SOFA, sequential organ failure assessment ; MV, mechanical ventilation; ICU-LOS, intensive care unit-length of stay; WBC, white blood cell; NLR, neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio; Hb, hemoglobin; PLT, platelets; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; hs-cTnI, high sensitivity cardiac troponin I; CRP, C-reactive protein; CRRT, continuous renal replacement therapy; HFNC, high flow nasal cannula. |
Table 2.
Baseline characteristics according to lactate/albumin ratio quartiles.
Table 2.
Baseline characteristics according to lactate/albumin ratio quartiles.
| Characteristic |
Quartile 1
N = 206 |
Quartile 2
N = 198 |
Quartile 3
N = 203 |
Quartile 4
N = 198 |
P-value |
| Demographics |
|
|
|
|
|
| Sex, male, n (%) |
134 (65%) |
141 (71%) |
139 (68%) |
134 (68%) |
0.6 |
| Age, years |
61 (52, 70) |
64 (54, 73) |
70 (61, 77) |
72 (63, 80) |
<0.001 |
| Severity scores |
|
|
|
|
|
| Charlson comorbidity index |
3 (1, 4) |
3 (1, 4) |
4 (2, 5) |
4 (3, 6) |
<0.001 |
| APACHE II score |
11 (8, 16) |
13 (9, 16) |
14 (12, 18) |
19 (15, 24) |
<0.001 |
| SOFA score |
6 (2, 7) |
6 (3, 8) |
7 (6, 8) |
8 (7, 11) |
<0.001 |
| Outcomes |
|
|
|
|
|
| ICU outcome, death, n (%) |
56 (27%) |
75 (38%) |
107 (53%) |
146 (74%) |
<0.001 |
| CRRT, n (%) |
49 (24%) |
44 (22%) |
65 (32%) |
80 (40%) |
<0.001 |
| MV duration, days |
9 (0, 20) |
13 (5, 26) |
14 (6, 26) |
10 (4, 23) |
<0.001 |
| ICU-LOS, days |
14 (8, 25) |
17 (9, 33) |
17 (10, 31) |
12 (5, 28) |
<0.001 |
| Laboratory tests |
|
|
|
|
|
| WBC count, x 109/L |
8 (6, 11) |
9 (7, 13) |
11 (8, 15) |
14 (10, 20) |
<0.001 |
| Neutrophil count, x 109/L |
6.5 (4.6, 9.5) |
8.2 (5.4, 11.9) |
9.3 (7.1, 13.7) |
12.4 (8.0, 17.4) |
<0.001 |
| Lymphocyte count, x 109/L |
0.70 (0.49, 1.07) |
0.80 (0.54, 1.11) |
0.66 (0.48, 0.99) |
0.84 (0.54, 1.24) |
0.022 |
| NLR |
9 (5, 16) |
10 (6, 16) |
14 (8, 22) |
16 (8, 24) |
<0.001 |
| Hb, g/dL |
12 (11, 14) |
13 (11, 14) |
12 (11, 14) |
12 (9, 13) |
<0.001 |
| PLT count, x 109/L |
231 (180, 295) |
263 (203, 325) |
251 (194, 326) |
222 (159, 303) |
<0.001 |
| Albumin, g/dL |
3.6 (3.3, 3.8) |
3.3 (3.1, 3.6) |
3.0 (2.8, 3.4) |
2.8 (2.4, 3.1) |
<0.001 |
| Sodium, mEq/L |
139 (137, 141) |
140 (136, 142) |
140 (137, 143) |
143 (138, 147) |
<0.001 |
| Creatinine, mg/dL |
0.8 (0.7, 1.1) |
0.8 (0.7, 1.0) |
0.9 (0.7, 1.3) |
1.2 (0.8, 1.9) |
<0.001 |
| AST, IU/L |
41 (26, 64) |
38 (26, 65) |
36 (22, 59) |
38 (24, 95) |
0.12 |
| ALT, IU/L |
34 (21, 54) |
33 (21, 55) |
30 (19, 51) |
29 (15, 67) |
0.2 |
| LDH, IU/L |
430 (298, 550) |
455 (352, 591) |
469 (350, 634) |
478 (358, 842) |
0.001 |
| hs-cTnI, ng/L |
13 (7, 38) |
16 (8, 47) |
23 (12, 62) |
74 (27, 223) |
<0.001 |
| CRP, mg/dL |
11 (4, 18) |
11 (5, 17) |
11 (5, 18) |
13 (6, 21) |
0.085 |
| Fibrinogen, mg/dL |
595 (513, 726) |
588 (506, 679) |
593 (485, 721) |
510 (375, 669) |
<0.001 |
| D-dimers, mg/L |
1.1 (0.7, 2.2) |
1.3 (0.7, 2.7) |
2.2 (1.1, 4.3) |
2.5 (1.3, 10.0) |
<0.001 |
| PaO2/FiO2 ratio |
121 (90, 183) |
121 (87, 180) |
132 (86, 192) |
140 (94, 200) |
0.3 |
| Lactate, mmol/L |
1.1 (0.9, 1.3) |
1.5 (1.4, 1.6) |
1.9 (1.7, 2.2) |
3.3 (2.7, 5.4) |
<0.001 |
| Shock on admission, n (%) |
74 (36%) |
92 (46%) |
94 (46%) |
44 (22%) |
<0.001 |
| Treatment |
|
|
|
|
|
| Full vaccination, n (%) |
15 (7.3%) |
12 (6.1%) |
14 (6.9%) |
20 (10%) |
0.5 |
| Remdesivir, n (%) |
100 (49%) |
109 (55%) |
102 (50%) |
80 (40%) |
0.031 |
| Dexamethasone, n (%) |
150 (73%) |
166 (84%) |
182 (90%) |
139 (70%) |
<0.001 |
| Tocilizumab, n (%) |
5 (2.4%) |
11 (5.6%) |
13 (6.4%) |
7 (3.5%) |
0.2 |
| MV on admission, n (%) |
104 (50%) |
139 (70%) |
169 (83%) |
176 (89%) |
<0.001 |
| HFNC on admission, n (%) |
71 (34%) |
46 (23%) |
28 (14%) |
13 (6.6%) |
<0.001 |
| Comorbidities |
|
|
|
|
|
| Hypertension, n (%) |
84 (41%) |
77 (39%) |
85 (42%) |
84 (42%) |
0.9 |
| Diabetes, n (%) |
59 (29%) |
51 (26%) |
47 (23%) |
47 (24%) |
0.6 |
| Obesity, n (%) |
37 (18%) |
27 (14%) |
29 (14%) |
11 (5.6%) |
0.002 |
| Cardiovascular disease, n (%) |
40 (19%) |
42 (21%) |
54 (27%) |
66 (33%) |
0.006 |
| Chronic pulmonary disease, n (%) |
25 (12%) |
22 (11%) |
30 (15%) |
29 (15%) |
0.6 |
| Malignancy, n (%) |
23 (11%) |
19 (9.6%) |
18 (8.9%) |
25 (13%) |
0.6 |
| Chronic kidney disease, n (%) |
16 (7.8%) |
10 (5.1%) |
15 (7.4%) |
24 (12%) |
0.073 |
Data are expressed as median (IQR), unless otherwise denoted.
Abbreviations: IQR, interquartile range; APACHE, acute physiology and chronic health evaluation; SOFA, sequential organ failure assessment; MV, mechanical ventilation; ICU-LOS, intensive care unit-length of stay; WBC, white blood cell; NLR, neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio; Hb, hemoglobin; PLT, platelets; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; hs-cTnI, high sensitivity cardiac troponin I; CRP, C-reactive protein; CRRT, continuous renal replacement therapy; HFNC, high flow nasal cannula. |
Table 3.
Cox regression analysis of lactate/albumin ratio and ICU mortality.
Table 3.
Cox regression analysis of lactate/albumin ratio and ICU mortality.
| |
Univariate model |
*Multivariate model
|
| Variable |
HR (95%CI) |
P-value |
HR (95%CI) |
P-value |
| Lactate/albumin ratio |
1.60 (1.40-1.70) |
<0.001 |
1.39 (1.27-1.52) |
<0.001 |
*The model was adjusted for age, sex, NLR, Hb, PLT count, sodium, creatinine, AST, ALT, LDH, hs-cTnI, CRP, fibrinogen, d-dimers, PaO2/FiO2 ratio, presence of shock, vaccination status, CRRT, remdesivir, dexamethasone, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, obesity, coronary heart disease, chronic pulmonary disease, chronic kidney disease and active malignancy.
Abbreviations: HR, hazard ratio; CI, confidence interval; NLR, neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio; Hb, hemoglobin; PLT, platelets; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; hs-cTnI, high sensitivity cardiac troponin I; CRP, C-reactive protein; CRRT, continuous renal replacement therapy. |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).