1. Introduction
One of the main defenses against infections and the systemic propagation of the local microbiota is the mucosal surfaces of the host. The gastrointestinal (GI) tract, respiratory system, and female upper reproductive systems are examples of type I mucosal surfaces in humans. Based on their unique features, type II mucosal surfaces are found in the mouth, alimentary tract, and the female lower reproductive systems. Together, these two types of mucosal surfaces account for more than 400 m² surfaces in humans [
1]. Fundamentally, type I mucosal surfaces have: simple columnar epithelium covering them, major secretory antibodies represented by the immunoglobulins A (sIgA), and polymeric immunoglobulin receptor (pIgR). The type II mucosal layers have stratified squamous (non-keratinized) epithelium, the dominant isotype represented by IgG rather than IgA, and pIgR is absent [
1]. The gastrointestinal tract and gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT) represent a unique system which constantly confronted with discordant signals. The organism comes into contact with more antigens in this area than in any other region. Along with its properties associated with food intake, digestion, nutrients absorption from food, swap of water and electrolytes, and hormone synthesis, it must quickly recognize between invasive pathogens and healthy food antigens, as well as the commensal bacteria from the gut microbiota [
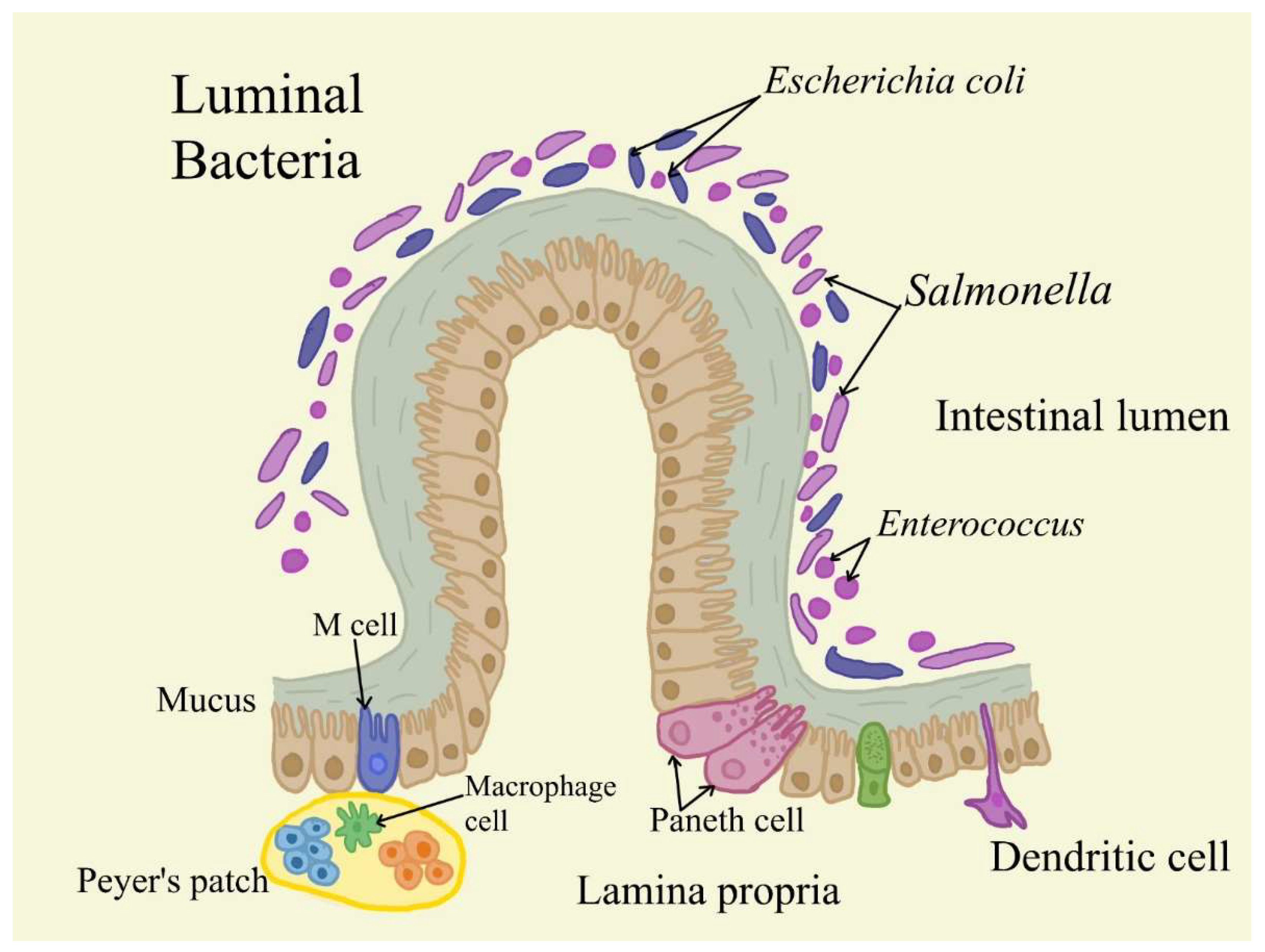
2]. The majority of the intestinal mucosal immune system is found in the lamina propria, which is placed underneath the intestinal epithelial layer [
3]. Dendritic cells, macrophages, innate lymphoid cells (ILCs), CD4+ T cells (Th1, Th17, Treg cells), CD8+ T cells, isolated lymphoid follicules (ILFs) and IgA-secreting plasma cells belong to the different types of innate and adaptive immune cells present here. Together, these cells sustain the intestinal mucosal barrier and supply protection against pathogen invasion (
Figure 1).
Consequently, lamina propria T cells exhibit the capacity to promptly respond to stimuli from the luminal microenvironment and start both pro- and anti-inflammatory reactions [
4]. The primary causes of persistent intestinal inflammation and tissue damage in people with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) are uncontrolled inflammatory reactions to dietary antigens or commensal microorganisms [
5]. The mucosal immune system is tightly controlled to stay in a healthy state. For the maintenance of colon homeostasis, local Tregs are essential [
6]. Numerous bacterial metabolites, including tryptophan metabolites, some secondary bile acid conjugates, and short chain fatty acids (SCFAs), are responsible for the triggering of colonic Tregs [
7,
8,
9,
10,
11]. The immune system and commensal microorganisms interact and change over time. Food affects this interaction by giving gut bacteria substrates, and certain foods can directly affect immune cells. Therefore, this paper aims to investigate the link between LP and cancer in humans.
2. The Methodology Used in This Review
For this review, different phrases and keywords were utilized to methodically evaluate research articles and reviews that were collected from several global databases. Lamina propria, GALT, gastrointestinal tract, and colorectal were among the keywords used. The data included in this review was issued between 2010 and the present. To achieve the aims of this study, several topics were examined, including the relationship between lamina propria, microbiota, and inflammation, the effects of inflammation states on lamina propria functionality, the intricate association of specific lamina propria components and colorectal cancer (CRC) and the impact of different microbial metabolites on lamina propria in terms of inflammation and tumorigenesis development.
Immune reactions can occur in ordinary lymphoid organs (such as lymph nodes or the spleen) and in special structures called tertiary lymphoid tissue. These structures form abnormally (ectopically) on affected areas by infection or inflammation. There, immune system cells gather and organize similarly to secondary lymphoid organs, forming germinal centers of B cells (responsible for producing antibodies) and specific areas for T cells (which coordinate the immune response). This occurs when the body must fight a localized infection or inflammation, even outside the normal sites of immune activity [
12].
The innate immunity cell's role, including macrophages, neutrophils, and myeloid-derived suppressor cells in promoting cancer progression is recognized in a wide variety of tumor types. Lately, also B cells are crucial in establishing the chronic inflammation associated with
de novo carcinogenesis. The mechanism is likely to be antibody-dependent, with the accumulation of IgG immune complexes, activation of innate immune cells, including tumor-associated macrophages (TAM), through the Fc gamma Receptor (FcR), and polarization to an immunosuppressive phenotype [
13].
In colorectal cancer (CRC), a group of immune and inflammatory cells is seen infiltrating the affected tissue, consisting of lymphocytes (essential immune cells), neutrophils (cells responsible for rapid response to infections), and macrophages (cells that engulf and destroy pathogens). These cells after their entrance can accumulate at the edge where the tumor interacts with the surrounding healthy tissue, an area essential for cancer progression or control. Infiltrating T lymphocytes have a protective role in this tumor, being significantly associated with better clinical results [
14].
It was found that tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes are not only scattered throughout the stroma and interspersed between tumor cells. They also group in aggregates resembling tertiary lymphoid tissue [
15].
3. Lamina Propria Dendritic Cells in Healthy State
The body's reaction to a given antigen can either be pro- or anti-inflammatory, and this is mostly determined by lamina propria dendritic cells (LPDCs) (
Table 1). For local proliferation, DCs that are repopulating tissues from monocyte precursors depend on a granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF). Conventional DCs (cDCs), which originate from the CDP, live in secondary lymphoid tissues and show high levels of CD11c along with variable levels of CD8α and CD11b [
16].
The CDP is also the source of plasmacytoid DCs (pDCs), that are specialized for generating type I interferons. The developed state of DCs has significant effects on immunity in addition to functional subsets of DCs. Highly specialized for antigen presentation are mature DCs that have previously been in contact with inflammatory stimuli and microbial products. As a result, mature DCs tend to live in secondary lymphoid organs where they are well-positioned to prime antigen-specific T lymphocytes and express high quantities of co-stimulatory molecules [
17]. Peripheral tolerance to gastrointestinal luminal antigens and self is constantly and directly maintained by LPDCs. LPDCs exhibit a variety of functionally unique characteristics, similar to LP macrophages.
LPDCs require chemokine receptor 1 (CX3CR1) to extend their processes beyond the epithelial cell layer to collect luminal antigens [
18]. There are two major categories of LPDCs to take into account: CD103⁺ and CD103−. By generating retinoic acid and converting growth factor-β together, the CD103⁺ LPDCS stimulate the development of Foxp3+ regulatory T cells [
19,
20]. However, CD103− LPDCs promote the growth of inflammation and upregulate the production of inflammatory mediators after stimulation with TLR ligands, including IL-6 and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) [
21]. The lack of CD103⁺ CX3CR1− LPDCs increases epithelial damage during colitis, hence their presence is especially crucial in reducing unneeded inflammation [
22].
4. Innate Lymphoid Cells in Healthy State
Another cellular group present in the lamina propria includes innate lymphoid cells (ILCs). ILCs have a physical similarity to lymphocytes [
23], but they lack antigen receptors that trigger recombination. ILCs are especially abundant in mucous membranes such as the gastrointestinal tract, airways, and skin, where they sensor and integrate environment signals to rapidly activate the innate immune response, releasing effector molecules that engage mucosal immune defense and tissue homeostasis [
24]. ILCs are the innate equivalent of the T cells that have an important role in developing and maintaining the sub-epithelial lymphoid tissue of the intestines. They share a common progenitor with lymphocytes but are distinct from them because they lack T-cell receptors and they are constantly producing their cytokines unlike T cells’ activation-required production. Three major categories can be used to categorize them (
Table 1). Group 1 ILCs, which include natural killer cells, are distinguished by their ability to produce interferon gamma (IFN-γ). Areas of mucosal inflammation are home to a large number of transcription factor (T-bet+) group 1 ILCs [
25,
26]. Group 2 ILCs are found in both lymphoid and non-lymphoid tissues and are usually a mark of inflammation, secreting IL-5 and IL-13. However, Transcription factors GATA3 and RAR-related orphan receptor alpha (RORα) are necessary for the generation of group 2 ILCs, and IL-5 and IL-13 are this group's distinctive cytokines [
25]. Group 3, ILC3s are found in the greatest abundance at the mucosal barrier surfaces and exhibit receptor related orphan receptors (ROR). The so-called lymphoid tissue inducer (LTi) cells represent an ILC3 subtype [
27].
With a better understanding of the mechanisms of development and the molecules involved in the functions of the T cell and ILC subset, a new classification of ILC was proposed in 2018: cytotoxic NK cell, non-cytotoxic helper ILC1, ILC2, ILC3, and LTi cell [
24]. Given that ILCs and T cells share similar transcription factors and cytokine production capacities, they are also assumed to be their innate functional counterparts, with NK cells, ILC1, ILC2, and ILC3 representing cytotoxic CD8+ T cells, CD4+ T helper (Th) cells 1, Th2, and Th17/Th22, respectively [
28,
29].
ILC3s are the predominant subpopulation in ILCs identified in the intestines of rodents and humans (
Table 1). They are primarily responsible for producing IL-17 and IL-22 when local signaling molecules like IL-23 and IL-1b are activated. This helps to coordinate the innate immune response to both intra- and extracellular pathogens and preserve tissue homeostasis [
30].
According to the expression of C-C chemokine receptor type 6 (CCR6), ILC3 can be classified into CCR6+ILC3s and CCR6-ILC3s. The lamina propria contains the majority of CCR6-ILC3 cells, which are further subdivided into NCR+ILC3 and NCR-ILC3 cells. Although NCR-ILC3 makes up only 15% of intestinal ILC3, it expresses mostly IL-17 and less IL-22. In contrast, NCR+ILC3 makes up around 70% of intestinal ILC3 and expresses primarily IL-22 and less IL-17 [
31].
ILC3 is required to maintain the intestinal epithelial barrier and immune homeostasis. ILC3 plays a key part in this crucial function by secreting cytokines like IL-22 and IL-17. By activating STAT3 in epithelial cells, IL-22 promotes the expression of mucins involved in the composition of the mucus layer to recover mucus-producing goblet cells, alleviate colonic inflammation, and regulate intestinal mucosal wound healing [
32]. IL-22 initiates DNA damage response in epithelial stem cells
via aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) sensing of genotoxic phytochemicals, preventing malignant transformation and cancer development (
Table 1). Inducing the production of cytokines and chemokines to attract neutrophils to the infection site, IL-17 is primarily generated by NCR-ILC3 and has a role in immune-inflammatory and anti-infective responses [
33].
It is important to mention that the healthy gut contains ILC1s, ILC3s, and ILC3/NKs, but no ILC2s. ILC1-like and ILC2 subsets unique to tumors were also found in CRC patients. The role of helper-like ILCs in tumorigenesis and cancer immunity is less clear and appears to depend on the tumor microenvironment. ILC1s produce large amounts of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as IFN-γ and TNF-a, which favor tumorigenesis. However, IFN-g can also limit tumor growth in certain tumor microenvironments [
34]. ILC2s are mostly detrimental in various tumor settings [
35].
Intestinal malignancies have been connected to dysregulated ILC responses. Low levels of ILC2s are found in a variety of human disease disorders [
36,
37]. In contrast, CRC patients have large numbers of ILC1s in the intestines and abnormally low levels of ILC3s, which normally densely populate the colon at a steady state. The severity of CRC has indeed been linked to reductions in the ILC3/ILC1 ratio. The baseline helper-like ILC landscape, in terms of the composition, diversity, and functional status of these cells in the human gut, remains incompletely explored under tumor conditions [
38,
39] (
Table 1).
It was discovered that helper-like ILCs from CRC patients contained two additional subsets: an ILC2 (ctILC2) subset and an ILC1-like subset exclusive to CRC tissue. Higher frequencies of SLAMF1-expressing helper-like ILCs were detected in the blood of CRC patients. SLAMF1 (signaling lymphocytic activation molecule family member 1, CD150) was discovered to be exclusively expressed on ctILCs [
39].
5. Isolated Lymphoid Follicles in Healthy State
Isolated lymphoid follicles (ILFs) can be classified as mucosal ILFs (M-ILFs) which are located in the lamina propria only, and submucosal ILFs (SM-ILFs), which protrude in the lamina but are also present in the submucosa. M-ILFs are usually located in the ileum and the distal colon while the SM-ILFs are mostly found in the colon [
40]. Approximately 90% of the cells in ILFs are lymphocytes, with a slightly higher proportion of T cells than B cells while the GALT-free lamina propria contains cytokine-producing T-cell subsets. It also includes many dendritic cells, which migrate through the lymph to mesenteric lymph nodes, and present antigens to T cells [
41].
Contrary to the small intestine, most lymphocytes in the lamina propria of the large intestine are B cells [
42]. The polymeric immunoglobulin receptor induces the lamina propria B cells to produce dimeric IgA, which is then transcytosed by epithelial cells and enters the intestinal lumen [
43]. Although gastrointestinal infections can produce antigen-specific IgA, gastrointestinal IgA production also performs a crucial role at baseline by preventing commensal microbes from passing past the epithelium and improving the absorption of luminal bacteria by M cells [
44] (
Table 1).
It has also been observed that in colonic inflammation there is a tight connection between the degree of epithelial damage and the number, diameter, and cellular compounds of sub-epithelial lymphoid follicles [
45]. The more severe the epithelial destruction that develops, the higher the number of ILFs that can be found in adjacent mucosa.
Several reports have investigated the association between lymphoid aggregates and colonic tumors in rodents [
46,
47]. The results indicate that colonic crypts overlying ILFs show a significantly higher proliferative activity, which may also influence genetically defected epithelial cells. Hence, the risk of carcinoma is increased in the colonic mucosa of ILFs compared to mucosa without ILFs.
In various inflammation models, tissue-derived dendritic cells have been shown to migrate from the inflammatory site
via lymphatics vessels to secondary lymphoid organs where they interact with lymphocytes [
48]. Based on their dual phenotype, follicular dendritic cells may represent a transformation switch point among immigrating bone marrow-derived stem cells in ILFs and the surrounding subepithelial myofibroblasts. This suggests a potential mechanism of change and adaptation in the context of inflammation and tumor development.
Sub-epithelial myofibroblasts (SEMFs) exist as a syncytium that extends throughout the colonic lamina propria, merging with the pericytes surrounding the blood vessels [
49]. SEMFs are involved in two epithelial repair processes [
50] (
Table 1). The first process, called restitution [
51], is responsible for the healing of superficial, minor or moderate injuries, and allows rapid restoration of the epithelial layer. The second one comes into play when the injury is more severe and deep, requiring complete repair of the tissues beneath the epithelium as well as the basement membrane, which supports the epithelial structure [
52].
SEMFs appear early in the cancer’s development. The mutual interaction (through direct cell-cell contacts and paracrine signals) between cancer cells and SEMFs is essential for invasive growth and is translated into a poor clinical prognosis [
45].
In ILFs, TLRs (Toll-like receptors) are expressed on the cells of the monocyte/macrophage system, on some kinds of T cells, as well as on intestinal epithelial, endothelial, and stromal cells. TLRs can also bind endogenous ligands including necrotic cells, heat shock proteins, and extracellular matrix components [
45].
TLR4 was also shown to be expressed in human colon carcinoma cells and functionally active. It may play an important role in promoting the immune escape of human colon carcinoma cells by inducing immunosuppressive factors and apoptosis resistance, and it may also promote the proliferation and migration of cancer cells [
53].
Experimental studies have shown that intestinal lymphoid follicles (ILF) could contribute to the development of adenocarcinomas in colon cancer. However, in humans, the presence of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes is associated with better prognosis in CRC, as well as high DNA microsatellite instability, a characteristic of certain cancers [
54]. These results indicate that ILFs in the early stages of colorectal cancer have a defensive rather than a tumor-promoting role (
Table 1).
In addition, Gutfeld et al [
55] found that cells in ILFs, as well as other inflammatory and endothelial cells in the colon, express a protein called serum amyloid A, which increases in the presence of trauma, infection, or cancer. This expression of serum amyloid A suggests a role in the development of CRC.
6. T Cell Trafficking to the GALT and Gut
In the case of intestinal infections, naïve T cells from the blood must arrive at special sites in the gut where they prepare to respond to antigens. These so-called GALT sites include Peyer's patches PPs, and mesenteric lymph nodes MLNs. Here, they encounter antigens from the digestive tract presented by dendritic cells, which are immune cells that carry antigens from the gut to these ganglia. This process triggers the activation of T cells and transforms them into effector cells Th1 and/or Th17, ready to attack pathogens [
56] (
Table 2).
According to different research, antigen-carrying dendritic cells (DCs) from the intestinal mucosa and Peyer's patches are carried to the MLNs by the associated lymphatic vessels. These nodes may be the primary site where naïve T cells first encounter specific antigens in the gut, triggering their activation. After activation, T cells become effector cells, that is, cells capable of causing an immune response, including in cases of disease or infection [
56].
The migration of these T cells from the blood to special lymphoid areas, such as lymph nodes, is accomplished
via high endothelial venules (HEVs). These are specialized blood vessels that help attract and transport immune cells to tissues where they can perform their infection-fighting functions [
57] (
Table 2).
The HEVs (high endothelial venules) that are associated with Peyer's patches contain a molecule called MAdCAM-1, which helps attach lymphocytes to these blood vessels. In contrast, HEVs in mesenteric lymph nodes express both MAdCAM-1 and PNAd, another adhesion molecule. L-selectin, a protein on the surface of T cells, binds to these molecules to help lymphocytes anchor to HEVs, thereby initiating a process called "rolling," which is crucial for T cell migration.
In mesenteric nodes, naïve T cells can use another molecule, α4β7, to attach to MAdCAM-1 (
Table 2). This interaction contributes to the firm adhesion and arrest of lymphocytes, which allows them to enter the MLNs and Peyer's patches [
58,
59,
60]. Once naïve CD4+ T cells reach these areas, they encounter specific enteric antigens presented by dendritic cells, which collaborate with the major histocompatibility complex II (MHC II) complex.
During the initial activation process, T cells proliferate, lose L-selectin, and increase the expression of adhesion molecules that help them home to the gut. These molecules, such as α4β7 and CCR9, interact with MAdCAM-1 and CCL25 in the postcapillary venules, thereby facilitating the migration of T cells to the small intestine. This process is essential for T cells to reach the site of infection or inflammation, where they can respond to antigens [
61].
After the effector T cells enter the intestinal tissues, they re-encounter the specific antigens they recognize. This time, antigens are presented by a greater variety of specialized antigen-presenting cells (APCs), such as macrophages and B cells, in addition to dendritic cells (DCs). This second encounter with the antigen causes a much faster and more intense reaction from the effector T cells. This process leads to a significant increase in the production of cytokines such as IFN-γ (interferon-gamma), IL-17, TNF-α (tumor necrosis factor alpha), lymphotoxin-α and IL-2, molecules that play an important role in the immune and inflammatory response [
62] (
Table 2).
This accelerated response helps to more effectively defend against infection and coordinate inflammatory reactions, thereby helping to eliminate pathogens from the gut.
7. Dismicrobism
In healthy people, stomach acidity plays a crucial role in preventing bacteria from colonizing the gut. The acidic environment in the stomach acts as a natural barrier, killing or inhibiting the growth of bacteria before they reach the intestine. This process ensures that the intestinal bacterial flora remains balanced, preventing overpopulation with potentially harmful bacteria. Gastric acidity is thus an important defense mechanism against infections and intestinal microbiota imbalances. The microbiota exerts diverse physiological functions including growth inhibition of pathogenic microorganisms, synthesis of compounds useful for the tropism of colonic mucosa, regulation of intestinal lymphoid tissue, and synthesis of amino acids [
63] (
Table 3).
Dismicrobism leads to the imbalance of the normal bacterial flora in the gut. When this balance is disrupted, it can affect how the immune system responds to pathogens. In particular, this imbalance can activate GALT. GALT activation triggers immune reactions in the gut that can lead to inflammation or other immune disorders if not properly regulated. Specifically, the microbiological imbalance (dysbiosis) causes a modification of intercellular tight junctions leading to an effective penetration of antigens responsible for the activation of GALT with consequent tissue damage [
64] (
Table 3).
Changed dietary patterns had a significant (57%) on the composition of the gut microbiome, explaining more than half of the observed variation, while genetic factors play a much smaller role, contributing only a small proportion (12%). The Western diet, characterized by high consumption of sugar and fat, can cause dysbiosis, that is, an imbalance of intestinal bacteria. This imbalance negatively affects both gastrointestinal metabolism, i.e. the way the body processes and uses nutrients, and the balance of the immune system [
65]. Over time, this type of eating can contribute to digestive disorders and immune problems [
66]. Vegetarianism, which is high in fibbers, results in increased short-chain fatty acid production by microbes leading to a decrease in intestinal pH and consequently preventing the growth of potentially pathogenic bacteria such as
E.coli and members of
the Enterobacteriaceae [
67] (
Table 3).
7.1. Mucosal-Associated Lymphoid Tissue (MALT) Lymphomas
It is believed that mucosal-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) lymphomas develop in the marginal zone and are closely linked to
Helicobacter. Approximately 90% of MALT lymphomas are associated with
Helicobacter infection [
68]
.
H. helmanii, found in both humans and mice, also leads to MALT lymphoma which is preceded by inflammation and high endothelial venules-like vesicles, which are associated with lymphocyte recruitment and present in other chronic inflammatory conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, and colitis
. Several animal studies have shown that either a mixture of bacteria or a single species may significantly affect immune cell population and activity [
69]. For example, inoculation with segmented filamentous bacteria caused a change in T cell activity eliciting a range of responses including increases in IL-10, IL-17, and IFN-γ. Inoculation of
Sphingomonas yanoikuyae caused a systemic change in immune cell populations.
Bacterioides fragilis can induce a Th17 response in mice which was then shown to be required for tumorigenesis [
70]. Bacteria can also directly alter inflammation-related pathways. Inoculation with common human commensal bacterium
B. thetaiotaomicron, B. longum, or both increased TNF-α- and IFN-γ-associated pathways [
70].
7.2. Dismicrobism in CRC
There is a study that showed enrichment in the luminal compartment of CRC patients compared to controls of bacteria belonging to Enterococcus, Escherichia, Shigella, Klebsiella, Streptococcus, and Peptostreptococcus, and a depletion of bacteria belonging to Lachnospiraceae family (butyrate-producing bacteria).
Studies of microbiota in intermediate stages of CRC revealed an increased abundance of
Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes, and
Proteobacteria at the intestinal mucosal surface in patients with adenoma compared with non-adenoma subjects [
64].
About 1%-2% of CRC patients have a pathological background of intestinal mucosa inflammation [
71]. This “inflammatory background” of colonic mucosa can evolve into a less (low-grade) or more severe (high-grade) dysplasia, which through neoplastic transformation gives rise to carcinoma “in situ” and finally “invasive” carcinoma.
Mice colonized with enterotoxigenic B. Fragilis exhibit colonic Th17 inflammatory infiltrates involved in the induction of colon tumors, as indicated by inhibition of colon tumor formation following treatment with anti-IL-17 antibody.
The commensal microbiota, play an important role in regulating the immune system. These bacteria can influence the expression of heat shock proteins (Hsps), which are proteins produced by cells in response to stress, such as infection or inflammation. In particular, Hsp60 and Hsp70, both constitute a group of autoantigens able to trigger immune-regulatory pathways.
Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), particularly butyrate, formed from the bacterial fermentation of indigestible carbohydrates, are nutrients and growth signals for the intestinal epithelium and may play a role in CRC prevention [
72]. In normal colonocytes, butyrate prevents apoptosis and subsequent mucosal atrophy [
73].
Fortunately, butyrate plays a protective role in colon cancer cells. It helps prevent the development of cancer through several mechanisms: it promotes cell differentiation (the process by which cells become specialized), reduces the uncontrolled proliferation of cancer cells, induces apoptosis (programmed cell death) and inhibits angiogenesis (the formation of new blood vessels that feed tumors).
Intestinal microbiota also metabolizes certain foods, such as cruciferous vegetables (broccoli, cabbage, cauliflower) or garlic, generating compounds with anticancer properties, such as sulforaphane, butyrate, N-acetyl-cysteine, and ally1 mercaptan. These compounds protect gut microbiome and reduce the risk of cancer. Thus, microbe-derived metabolites can counteract the carcinogenetic process by triggering cell cycle arrest and apoptosis of tumoral cells through interference with HDAC activity.
Experimental data show that consumption of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids can decrease the incidence of sporadic CRC. Eicosapentaenoic free fatty acid reduces polyps formation and growth in models of familial adenomatous polyposis [
74].
8. CRC Carcinogenesis
The second most common cause of cancer-related fatalities worldwide is colorectal cancer. Tumor-infiltrating T-cells correspond to Chron ’s-like lymphoid reaction (CLR), a perituoral lymphoid aggregate at the tumor’s edge. Those CLRs are unique tertiary lymphoid organs linked to a more favorable prognosis and a lower chance of metastasis.
ILF characteristics can predetermine the immuno-phenotype of CLR in metastatic and non-metastatic CRC. CD20+ B cells within ILFs are associated with improved prognosis of CRC in liver metastasis patients [
75].
ILC3s infiltrate tumors and their activation and cytokine production have pro-tumorigenic effects. IL-23 expression is higher in CRC tissues, and the activation of IL-22 production
via ILC3-activating IL-1 has been associated with CRC, alongside IL-17A [
75].
Increasing reports have revealed the role of ILC3s in a range of cancers, including CRC by infiltrating the tumors and affecting the tumoral microenvironment [
76]. ILC3s use inflammatory molecules including IL-17 and IL-22 to promote the growth of tumors. The gut microbiota may control this route by causing macrophages to release IL-23 and IL-7. This pathway may be regulated by intestinal flora activating macrophages to secrete IL-23 and IL-7. In addition, the loss of MHC II in ILC3 will lead to dysregulation between Th17 cells and immune competence, thereby promoting tumor progression [
24]. ILC3 can also differentiate into ILCregs and secrete IL-10 to promote tumors. However, by regulating the microbial and immunological environments and promoting the formation of lymphoid tissue, ILC3 may prevent the growth of tumors. ILC3 releases CXCL10, which attracts CD4T and CD8T cells to enter tumor cells and release granzyme, perforin, and IFN-γ to suppress tumor cells. IFN-γ production is enhanced by ILC3's flexibility between ILC1 and ex-ILC3. The recently discovered ability of ILC3 to differentiate into NK cells may also be an anti-tumor pathway [
77] (
Table 4).
In both adaptive and innate immune cells, intestinal injuries trigger the production of CPEB4, which is necessary to translate cytokine mRNAs, including the one encoding interleukin-22. Accordingly, CPEB4 is necessary to develop GALTs and maintain intestinal immune homeostasis, mediating repair, and remodeling after acute inflammatory tissue damage and promoting the resolution of intestinal inflammation. In patients with IBD and colorectal cancer, inflammatory cells consistently overexpress CPEB4, which promotes the growth of tumors [
78].
To better understand how the CPEB4 protein influences the functioning of the intestinal barrier, the researchers used a genetically modified mouse model in which the CPEB4 gene was completely disabled (total knockout). GALT in CPEB4KO mice was altered, with a reduction in the number and size of Peyer’s patches and cryptopatches, which maintain the intestinal immune barrier [
78]. Peyer’s patches of CPEB4KOmice exhibited an aberrant composition of T and B lymphocytes, with decreased frequency of total CD3+ T lymphocytes due to reduced T-helper CD4+ and cytotoxic CD8+ T cells and increased frequency of CD19+ B lymphocytes. In the colonic lamina propria, we also found a significant reduction in the frequency of CD3+ T-lymphocytes in CPEB4KO mice, accompanied by increased CD19+ B lymphocyte frequency [
79] (
Table 5).
CPEB4 regulates certain cytokines (signaling proteins) in intestinal immune cells, such as IL-17a, IL-17f and IL-22, which are essential for a healthy immune response. At moderate and well-controlled levels, these cytokines help maintain the balance of the immune system and protect against infection. But if they are either over- or under-expressed, immune responses become unbalanced, leading to chronic inflammation and disruption of lymphoid tissue.
In chronic intestinal inflammation, such as ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease, CPEB4 levels have been observed to increase significantly, accumulating in inflammatory cells. This accumulation is associated with excessive activation of the Th17 immune response, which contributes to the chronic inflammation in these diseases [
80].
Inflammation frequently promotes the various stages of carcinogenesis and predisposes people to develop cancer. Thus, patients suffering from longstanding IBD have an increased risk of developing CRC. Although CPEB4 knockdown animals show more persistent inflammation and difficulties repairing damaged intestinal epithelia, they also have a lower incidence of colorectal cancer. CPEB4 is overexpressed in samples from whole (including tumoral niche) CRC and is associated with poor prognosis. Similar to inflammation, the CPEB4 depletion phenotype in CAC is linked with poor IL-22 translation. Thus, Th17 cells and Th17 cytokines, such as IL-17A, IL-21, and IL-22, have been described to mainly be pro-tumorigenic in the context of CRC [
81] (
Table 5).
9. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
This review tried to highlight the role of the lamina propria through its components in maintaining health, and the changes occurring as a result of inflammation and ultimately colorectal cancer. Unfortunately, the lamina propria from GALT is not as intensively studied as the other components of this lymphoid tissue. All of the lamina propria cells are important in improving inflammation and preventing cancer. Moreover, different cells such as T cells can respond quickly and specifically to the gut microenvironment stimuli, and initiate anti- and pro-inflammatory actions.
1. Therefore, the intestinal LP has many different kinds of DCs. Additionally, through generating beneficial mediators, inhibiting pro-inflammatory reactions, and actively inducing adaptive immunological tolerance, LPDCs regulate the intestinal environment and luminal contents to sustain homeostasis. Although certain LPDCs tend to strengthen adaptive inflammatory reactions to foreign antigens, others actively promote tolerance. Thus, an imbalance throughout all of these physiological systems, however, can swing the balance in favor of IBD and chronic intestinal inflammation.
2. Moreover, there is evidence linking dysregulated ILC responses to intestinal cancers. ILC2s are found in trace amounts in different human clinical situations [
36,
37]. In contrast, ILC3s, which typically densely populate the colon at a steady state, are abnormally low in CRC patients, while ILC1s are disproportionately abundant in the intestines. ILC3/ILC1 ratio decreases have been connected to the severity of colorectal cancer.
3. Regarding other cells from the lamina, experimental results show that ILFs in the early stages of colorectal cancer have a defensive rather than a tumor-promoting role.
4. Lamina propria T cells, after their activation become effector cells, in the sense to have the ability to initiate an immune response, including in cases of disease or infection [
54].
For the mucosal immune system to remain healthy, it must be strictly regulated. The presence of local Tregs is essential in colon homeostasis [
6]. SCFAs and tryptophan metabolites are among the several bacterial metabolites that trigger colonic Tregs [
7,
8,
9,
10,
11]. The body's defense system is significantly regulated by the commensal microbiome. These bacteria can regulate the expression of heat shock proteins (Hsps), which are proteins that cells produce in reaction to stressors like inflammation or infection.
In addition, the intestinal microbiota metabolizes aliments like garlic and cruciferous vegetables to produce anticancer compounds including ally1 mercaptan, butyrate, sulforaphane, and N-acetyl-cysteine. These compounds lower the risk of cancer and sustain the gut microbiota.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.M.; E.R. and A.O.S; methodology, A.I.; C.R. software, C.R.; validation, E.R., A.O.S. and A.I.; formal analysis, A.I.; investigation, C.M.; resources, E.R.; data curation, C.R.; writing—original draft preparation, C.M.; E.R. and A.O.S; writing—review and editing, A.I. and C.M; visualization, C.R.; supervision, A.O.S.; project administration, A.O.S; funding acquisition, C.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Kim, S.-H.; Lee, K.-Y.; Jang, Y.-S. Mucosal Immune System and M Cell-targeting Strategies for Oral Mucosal Vaccination. Immune Netw. 2012, 12, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sansonetti, P.J. War and peace at mucosal surfaces. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 4, 953–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelaseyed, T.; Bergström, J.H.; Gustafsson, J.K.; Ermund, A.; Birchenough, G.M.H.; Schütte, A.; van der Post, S.; Svensson, F.; Rodríguez-Piñeiro, A.M.; Nyström, E.E.L.; et al. The mucus and mucins of the goblet cells and enterocytes provide the first defense line of the gastrointestinal tract and interact with the immune system. Immunol. Rev. 2014, 260, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDermott, A.J.; Huffnagle, G.B. The microbiome and regulation of mucosal immunity. Immunology 2014, 142, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, E.R.; Zisman, T.L.; Suskind, D.L. The microbiota in inflammatory bowel disease: current and therapeutic insights. J. Inflamm. Res. 2017, ume 10, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanoue, T.; Atarashi, K.; Honda, K. Development and maintenance of intestinal regulatory T cells. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.M.; Howitt, M.R.; Panikov, N.; Michaud, M.; Gallini, C.A.; Bohlooly-Y, M.; Glickman, J.N.; Garrett, W.S. The Microbial Metabolites, Short-Chain Fatty Acids, Regulate Colonic Treg Cell Homeostasis. Science 2013, 341, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, C.; McKenney, P.T.; Konstantinovsky, D.; Isaeva, O.I.; Schizas, M.; Verter, J.; Mai, C.; Jin, W.-B.; Guo, C.-J.; Violante, S.; et al. Bacterial metabolism of bile acids promotes generation of peripheral regulatory T cells. Nature 2020, 581, 475–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furusawa, Y.; Obata, Y.; Fukuda, S.; Endo, T.A.; Nakato, G.; Takahashi, D.; Nakanishi, Y.; Uetake, C.; Kato, K.; Kato, T.; et al. Commensal microbe-derived butyrate induces the differentiation of colonic regulatory T cells. Nature 2013, 504, 446–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Sun, X.; Oh, S.F.; Wu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, W.; Geva-Zatorsky, N.; Jupp, R.; Mathis, D.; Benoist, C.; et al. Microbial bile acid metabolites modulate gut RORγ+ regulatory T cell homeostasis. Nature 2020, 577, 410–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamas, B.; Richard, M.L.; Leducq, V.; Pham, H.-P.; Michel, M.-L.; Da Costa, G.; Bridonneau, C.; Jegou, S.; Hoffmann, T.W.; Natividad, J.M.; et al. CARD9 impacts colitis by altering gut microbiota metabolism of tryptophan into aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligands. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carragher, D.M.; Rangel-Moreno, J.; Randall, T.D. Ectopic lymphoid tissues and local immunity. Semin. Immunol. 2008, 20, 26–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.; Liu, Y.; Ali, N.M.; Zhang, B.; Cui, X. The role of innate immune cells in the tumor microenvironment and research progress in anti-tumor therapy. Front. Immunol. 2023, 13, 1039260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergomas, F.; Grizzi, F.; Doni, A.; Pesce, S.; Laghi, L.; Allavena, P.; Mantovani, A.; Marchesi, F. Tertiary Intratumor Lymphoid Tissue in Colo-Rectal Cancer. Cancers 2011, 4, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, R.; Oshi, M.; Asaoka, M.; Yan, L.; Benesch, M.G.; Khoury, T.; Nagahashi, M.; Miyoshi, Y.; Endo, I.; Ishikawa, T.; et al. Intratumoral Tumor Infiltrating Lymphocytes (TILs) are Associated With Cell Proliferation and Better Survival But Not Always With Chemotherapy Response in Breast Cancer. Ann. Surg. 2023, 278, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutella, S.; Bonanno, G.; Pierelli, L.; Mariotti, A.; Capoluongo, E.; Contemi, A.M.; Ameglio, F.; Curti, A.; de Ritis, D.G.; Voso, M.T.; et al. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor promotes the generation of regulatory DC through induction of IL-10 and IFN-α. Eur. J. Immunol. 2004, 34, 1291–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rescigno, M.; Di Sabatino, A. Dendritic cells in intestinal homeostasis and disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 2441–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niess, J.H.; Brand, S.; Gu, X.; Landsman, L.; Jung, S.; McCormick, B.A.; Vyas, J.M.; Boes, M.; Ploegh, H.L.; Fox, J.G.; et al. CX 3 CR1-Mediated Dendritic Cell Access to the Intestinal Lumen and Bacterial Clearance. Science 2005, 307, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Rio, M.; Bernhardt, G.; Rodriguez-Barbosa, J.; Förster, R. Development and functional specialization of CD103+ dendritic cells. Immunol. Rev. 2010, 234, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.-M.; Hall, J.A.; Blank, R.B.; Bouladoux, N.; Oukka, M.; Mora, J.R.; Belkaid, Y. Small intestine lamina propria dendritic cells promote de novo generation of Foxp3 T reg cells via retinoic acid. J. Exp. Med. 2007, 204, 1775–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Rio, M.-L.; Rodriguez-Barbosa, J.-I.; Bölter, J.; Ballmaier, M.; Dittrich-Breiholz, O.; Kracht, M.; Jung, S.; Förster, R. CX3CR1+c-kit+ Bone Marrow Cells Give Rise to CD103+ and CD103− Dendritic Cells with Distinct Functional Properties. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 6178–6188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varol, C.; Vallon-Eberhard, A.; Elinav, E.; Aychek, T.; Shapira, Y.; Luche, H.; Fehling, H.J.; Hardt, W.-D.; Shakhar, G.; Jung, S. Intestinal Lamina Propria Dendritic Cell Subsets Have Different Origin and Functions. Immunity 2009, 31, 502–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buonocore, S.; Ahern, P.P.; Uhlig, H.H.; Ivanov, I.I.; Littman, D.R.; Maloy, K.J.; Powrie, F. Innate lymphoid cells drive interleukin-23-dependent innate intestinal pathology. Nature 2010, 464, 1371–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, W.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, J. The role of group 3 innate lymphoid cell in intestinal disease. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spits, H.; Artis, D.; Colonna, M.; Diefenbach, A.; Di Santo, J.P.; Eberl, G.; Koyasu, S.; Locksley, R.M.; McKenzie, A.N.J.; Mebius, R.E.; et al. Innate lymphoid cells — A proposal for uniform nomenclature. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernink, J.H.; Peters, C.P.; Munneke, M.; te Velde, A.A.; Meijer, S.L.; Weijer, K.; Hreggvidsdottir, H.S.; Heinsbroek, S.E.; Legrand, N.; Buskens, C.J.; et al. Human type 1 innate lymphoid cells accumulate in inflamed mucosal tissues. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, P.B.; Eriksen, L.L.; Fenton, T.M.; Bailey, M.; Agace, W.W.; Mörbe, U.M. The porcine large intestine contains developmentally distinct submucosal lymphoid clusters and mucosal isolated lymphoid follicles. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2022, 131, 104375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherrier, D.E.; Serafini, N.; Di Santo, J.P. Innate Lymphoid Cell Development: A T Cell Perspective. Immunity 2018, 48, 1091–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivier, E.; Artis, D.; Colonna, M.; Diefenbach, A.; Di Santo, J.P.; Eberl, G.; Koyasu, S.; Locksley, R.M.; McKenzie, A.N.J.; Mebius, R.E.; et al. Innate Lymphoid Cells: 10 Years On. Cell 2018, 174, 1054–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korchagina, A.A.; Shein, S.A.; Koroleva, E.; Tumanov, A.V. Transcriptional control of ILC identity. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1146077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valle-Noguera, A.; Ochoa-Ramos, A.; Gomez-Sánchez, M.J.; Cruz-Adalia, A. Type 3 Innate Lymphoid Cells as Regulators of the Host-Pathogen Interaction. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, H.; Wang, A.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Han, J.; Chen, W.; Wang, S.; Wu, Y.; Lu, Y. Innate Lymphoid Cells: Regulators of Gut Barrier Function and Immune Homeostasis. J. Immunol. Res. 2019, 2019, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffith, B.D.; Frankel, T.L. The Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor: Impact on the Tumor Immune Microenvironment and Modulation as a Potential Therapy. Cancers 2024, 16, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, F.; Cardoso, A.P.; Gonçalves, R.M.; Serre, K.; Oliveira, M.J. Interferon-Gamma at the Crossroads of Tumor Immune Surveillance or Evasion. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bie, Q.; Zhang, P.; Su, Z.; Zheng, D.; Ying, X.; Wu, Y.; Yang, H.; Chen, D.; Wang, S.; Xu, H. Polarization of ILC2s in Peripheral Blood Might Contribute to Immunosuppressive Microenvironment in Patients with Gastric Cancer. J. Immunol. Res. 2014, 2014, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, A.; Vermi, W.; Lee, J.S.; Lonardi, S.; Gilfillan, S.; Newberry, R.D.; Cella, M.; Colonna, M. Intraepithelial Type 1 Innate Lymphoid Cells Are a Unique Subset of IL-12- and IL-15-Responsive IFN-γ-Producing Cells. Immunity 2013, 38, 769–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoni, Y.; Fehlings, M.; Kløverpris, H.N.; McGovern, N.; Koo, S.-L.; Loh, C.Y.; Lim, S.; Kurioka, A.; Fergusson, J.R.; Tang, C.-L.; et al. Human Innate Lymphoid Cell Subsets Possess Tissue-Type Based Heterogeneity in Phenotype and Frequency. Immunity 2017, 46, 148–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrega, P.; Orecchia, P.; Quatrini, L.; Tumino, N.; Venè, R.; Benelli, R.; Poggi, A.; Scabini, S.; Mingari, M.C.; Moretta, L.; et al. Characterisation of innate lymphoid cell subsets infiltrating colorectal carcinoma. Gut 2020, 69, 2261–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, A.; Ogino, T.; Kayama, H.; Okuzaki, D.; Nishimura, J.; Fujino, S.; Miyoshi, N.; Takahashi, H.; Uemura, M.; Matsuda, C.; et al. Human NKp44+ Group 3 Innate Lymphoid Cells Associate with Tumor-Associated Tertiary Lymphoid Structures in Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2020, 8, 724–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, R.G.; Newberry, R.D. Isolated Lymphoid Follicles Can Function as Sites for Induction of Mucosal Immune Responses. Ann. New York Acad. Sci. 2004, 1029, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenton, T.M.; Jørgensen, P.B.; Niss, K.; Rubin, S.J.; Mörbe, U.M.; Riis, L.B.; Da Silva, C.; Plumb, A.; Vandamme, J.; Jakobsen, H.L.; et al. Immune Profiling of Human Gut-Associated Lymphoid Tissue Identifies a Role for Isolated Lymphoid Follicles in Priming of Region-Specific Immunity. Immunity 2020, 52, 557–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reséndiz-Albor, A.A.; Esquivel, R.; López-Revilla, R.; Verdín, L.; Moreno-Fierros, L. Striking phenotypic and functional differences in lamina propria lymphocytes from the large and small intestine of mice. Life Sci. 2005, 76, 2783–2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerutti, A. Location, location, location: B-cell differentiation in the gut lamina propria. Mucosal Immunol. 2008, 1, 8–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankel, G.; Phillips, A.D.; Novakova, M.; Field, H.; Candy, D.C.; Schauer, D.B.; Douce, G.; Dougan, G. Intimin from enteropathogenic Escherichia coli restores murine virulence to a Citrobacter rodentium eaeA mutant: induction of an immunoglobulin A response to intimin and EspB. Infect. Immun. 1996, 64, 5315–5325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipos, F. Isolated lymphoid follicles in colon: Switch points between inflammation and colorectal cancer? World J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 17, 1666–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardman, W.; Cameron, I.L. Colonic crypts located over lymphoid nodules of 1,2-dimethylhydrazine-treated rats are hyperplastic and at high risk of forming adenocarcinomas. Carcinog. 1994, 15, 2353–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauss, K.M.; Locniskar, M.; Pavlina, T.; Newberne, P.M. Morphology and Distribution of 1,2-Dimethylhydrazine Dihydrochloride-Induced Colon Tumors and Their Relationship to Gut-Associated Lymphoid Tissue in the Rat2. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1984, 73, 915–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakubzick, C.; Bogunovic, M.; Bonito, A.J.; Kuan, E.L.; Merad, M.; Randolph, G.J. Lymph-migrating, tissue-derived dendritic cells are minor constituents within steady-state lymph nodes. J. Exp. Med. 2008, 205, 2839–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, N.C.; Haire, M.F.; Palade, G.E. Morphologic and biochemical evidence for a contractile cell network within the rat intestinal mucosa. Gastroenterology 1987, 92, 68–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andoh, A.; Bamba, S.; Fujiyama, Y.; Brittan, M.; Wright, N.A. Colonic subepithelial myofibroblasts in mucosal inflammation and repair: contribution of bone marrow-derived stem cells to the gut regenerative response. J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 40, 1089–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podolsky, D.K. Healing the epithelium: Solving the problem from two sides. J. Gastroenterol. 1997, 32, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, J.L.; Granger, D.N. The cellular and molecular basis of gastric mucosal defense. FASEB J. 1996, 10, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.-Y.; Wang, H.; Zhu, Y.-Q.; Wei, B. Expression and Functional Research of TLR4 in Human Colon Carcinoma. Am. J. Med Sci. 2010, 339, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael-Robinson, J.M.; Biemer-Hüttmann, A.-E.; Purdie, D.M.; Walsh, M.D.; Simms, L.A.; Biden, K.G.; Young, J.P.; Leggett, B.A.; Jass, J.R.; Radford-Smith, G.L. Tumour infiltrating lymphocytes and apoptosis are independent features in colorectal cancer stratified according to microsatellite instability status. Gut 2001, 48, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutfeld, O.; Prus, D.; Ackerman, Z.; Dishon, S.; Linke, R.P.; Levin, M.; Urieli-Shoval, S. Expression of serum amyloid A, in normal, dysplastic, and neoplastic human colonic mucosa: Implication for a role in colonic tumorigenesis. J. Histochem. Cytochem. Off. J. Histochem. Soc. 2006, 54, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koboziev, I.; Karlsson, F.; Grisham, M.B. Gut-associated lymphoid tissue, T cell trafficking, and chronic intestinal inflammation. Ann. New York Acad. Sci. 2010, 1207, E86–E93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, L.; Girard, J.-P. High endothelial venules (HEVs) in immunity, inflammation and cancer. Angiogenesis 2021, 24, 719–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luster, A.D.; Alon, R.; von Andrian, U.H. Immune cell migration in inflammation: present and future therapeutic targets. Nat. Immunol. 2005, 6, 1182–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, R.J. Homing imprinting and immunomodulation in the gut: Role of dendritic cells and retinoids. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2008, 14, 275–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Andrian, U.H.; Mempel, T.R. Homing and cellular traffic in lymph nodes. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 3, 867–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Ward, E.J.; Marelli-Berg, F.M. Mechanisms of T cell organotropism. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 3009–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rastogi, I.; Jeon, D.; Moseman, J.E.; Muralidhar, A.; Potluri, H.K.; McNeel, D.G. Role of B cells as antigen presenting cells. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 954936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickard, J.M.; Zeng, M.Y.; Caruso, R.; Núñez, G. Gut microbiota: Role in pathogen colonization, immune responses, and inflammatory disease. Immunol. Rev. 2017, 279, 70–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomasello, G.; Tralongo, P.; Damiani, P.; Sinagra, E.; Di Trapani, B.; Zeenny, M.N.; Hussein, I.H.; Jurjus, A.; Leone, A. Dismicrobism in inflammatory bowel disease and colorectal cancer: Changes in response of colocytes. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 18121–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemente-Suárez, V.J.; Beltrán-Velasco, A.I.; Redondo-Flórez, L.; Martín-Rodríguez, A.; Tornero-Aguilera, J.F. Global Impacts of Western Diet and Its Effects on Metabolism and Health: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducluzeau, R.; Guy-Grand, D.; Muller, M.C. Increase in the Population of Duodenal Immunoglobulin A Plasmocytes in Axenic Mice Associated with Different Living or Dead Bacterial Strains of Intestinal Origin. Infect. Immun. 1978, 21, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmer, J.; Lange, B.; Frick, J.-S.; Sauer, H.; Zimmermann, K.; Schwiertz, A.; Rusch, K.; Klosterhalfen, S.; Enck, P. A vegan or vegetarian diet substantially alters the human colonic faecal microbiota. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 66, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, N.; Iijima, K.; Koike, T.; Imatani, A.; Shimosegawa, T. Helicobacter pylori-negative gastric mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphomas: A review. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 8014–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgner, A.; Lehn, N.; Andersen, L.P.; Thiede, C.; Bennedsen, M.; Trebesius, K.; Neubauer, B.; Neubauer, A.; Stolte, M.; Bayerdörffer, E. Helicobacter heilmannii–associated primary gastric low-grade MALT lymphoma: Complete remission after curing the infection. Gastroenterology 2000, 118, 821–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, M.L.; Schiestl, R.H. Intestinal Microbiome and Lymphoma Development. Cancer J. 2014, 20, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, C.D.; Milner, J.A. Gastrointestinal microflora, food components and colon cancer prevention. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2009, 20, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoran, D.L.; Barhoumi, R.; Burghardt, R.C.; Chapkin, R.S.; Lupton, J.R. Diet and carcinogen alter luminal butyrate concentration and intracellular pH in isolated rat colonocytes. Nutr. Cancer 1997, 27, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basson, M.D.; Liu, Y.-W.; Hanly, A.M.; Emenaker, N.J.; Shenoy, S.G.; Rothberg, B.E.G. Identification and comparative analysis of human colonocyte short-chain fatty acid response genes. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2000, 4, 501–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shenderov, B.A. Gut indigenous microbiota and epigenetics. Microb. Ecol. Heal. Dis. 2012, 23, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozek, L.S.; Schmit, S.L.; Greenson, J.K.; Tomsho, L.P.; Rennert, H.S.; Rennert, G.; Gruber, S.B. Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes, Crohn’s-Like Lymphoid Reaction, and Survival From Colorectal Cancer. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2016, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrega, P.; Loiacono, F.; Di Carlo, E.; Scaramuccia, A.; Mora, M.; Conte, R.; Benelli, R.; Spaggiari, G.M.; Cantoni, C.; Campana, S.; et al. NCR+ILC3 concentrate in human lung cancer and associate with intratumoral lymphoid structures. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo-González, R.; Valle-Noguera, A.; Gomez-Sánchez, M.J.; Xia, P.; Cruz-Adalia, A. Innate lymphoid cells type 3 in cancer. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1033252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibilio, A.; Suñer, C.; Fernández-Alfara, M.; Martín, J.; Berenguer, A.; Calon, A.; Chanes, V.; Millanes-Romero, A.; Fernández-Miranda, G.; Batlle, E.; et al. Immune translational control by CPEB4 regulates intestinal inflammation resolution and colorectal cancer development. iScience 2022, 25, 103790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasparakis, M.; Alexopoulou, L.; Grell, M.; Pfizenmaier, K.; Bluethmann, H.; Kollias, G. Peyer’s patch organogenesis is intact yet formation of B lymphocyte follicles is defective in peripheral lymphoid organs of mice deficient for tumor necrosis factor and its 55-kDa receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1997, 94, 6319–6323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Lu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Shi, Z.; Hu, L.; Zeng, Z.; Tu, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Xu, Q. Th17 Cells in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Cytokines, Plasticity, and Therapies. J. Immunol. Res. 2021, 2021, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Xiao, Y.; Chen, C.; Wei, X.; Hu, C.; Ling, X.; Liu, X. MicroRNA-203-mediated posttranscriptional deregulation of CPEB4 contributes to colorectal cancer progression. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 466, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).