Submitted:
28 October 2024
Posted:
29 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
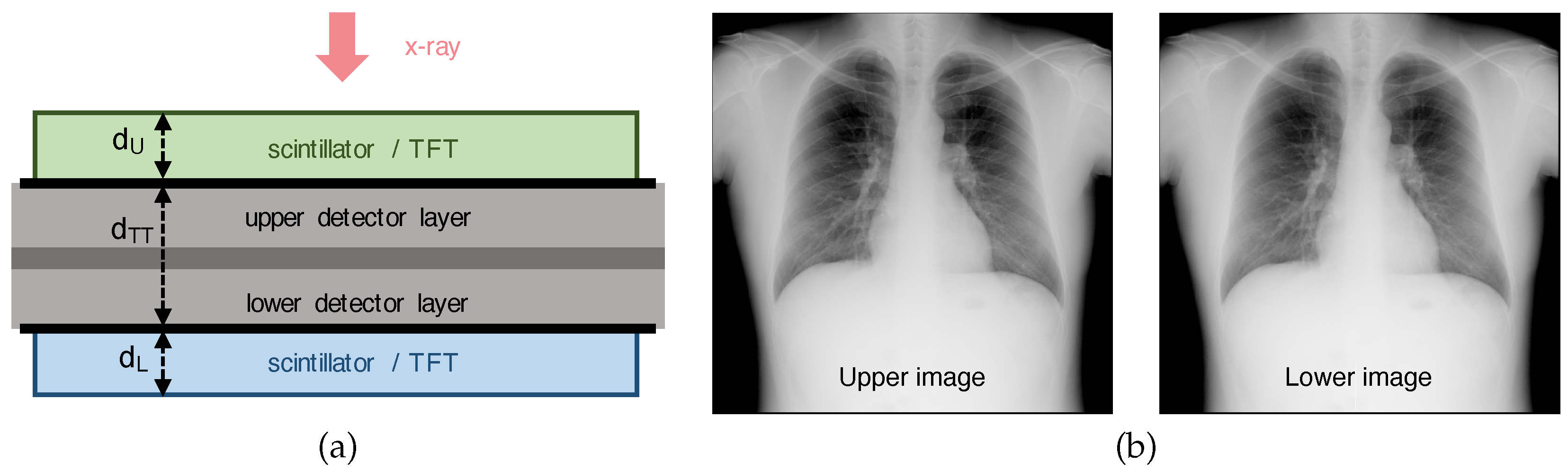
1. Introduction
- Spatial translation while stacking the layers
- Scale due to the x-ray projection
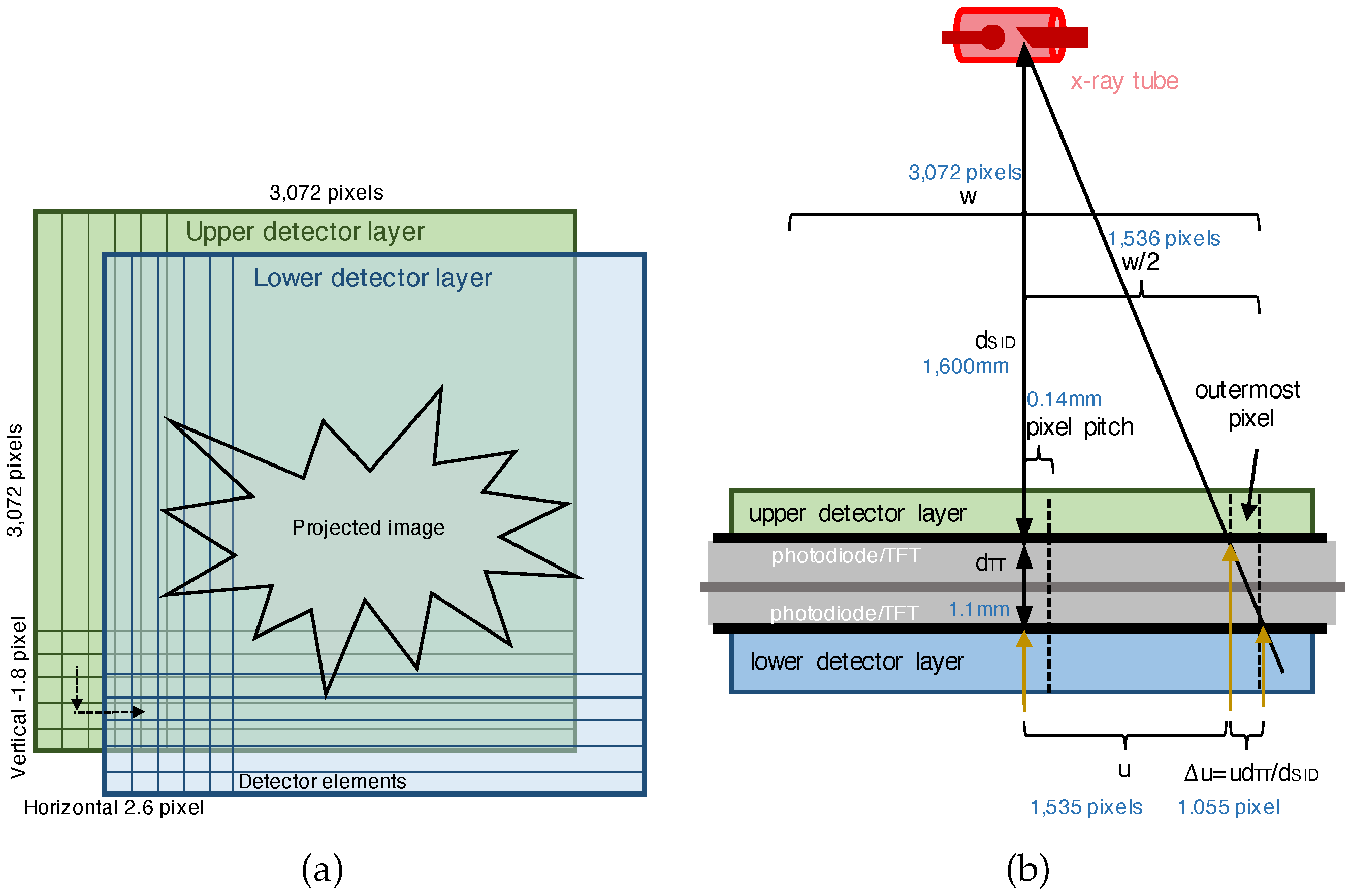
2. Two-Step Registration for the Dual-Layer Flat-Panel Detector
- 0)
- Find the translation of the lower image based on a subpixel registration; calculate the scale factor for a given SID.
- 1)
- Translate the lower image using the translation estimate based on the Fourier shift theorem.
- 2)
- Transform the lower image using the scale factor based on a cubic interpolation.
3. Theoretical Analysis of the Registration Method
3.1. Modulation Transfer Function of the Convex Combination Image
3.2. Noise Power Spectrum and the Detective Quantum Efficiency
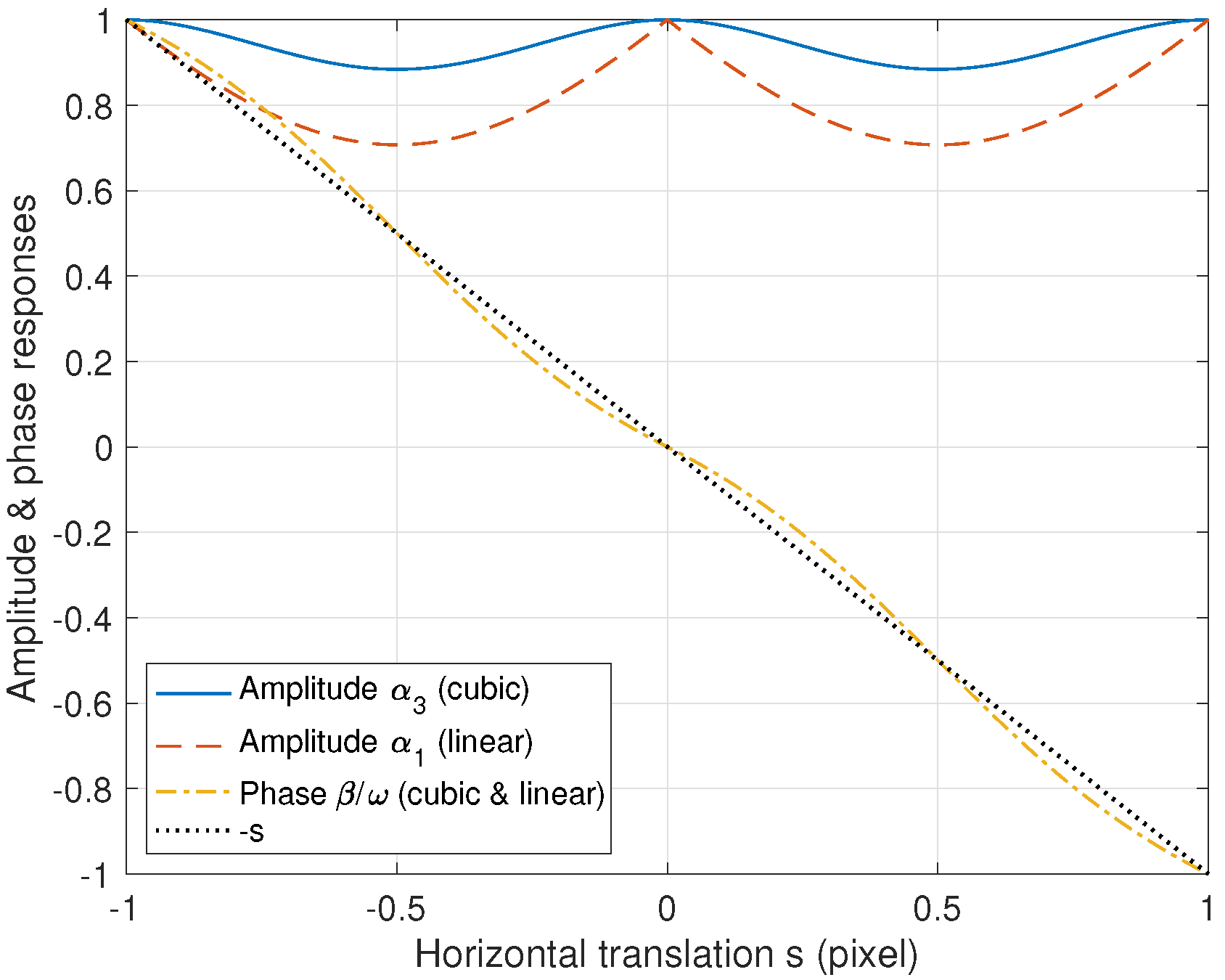
3.3. Projection and a Scale Translation with Interpolation
4. Numerical Results
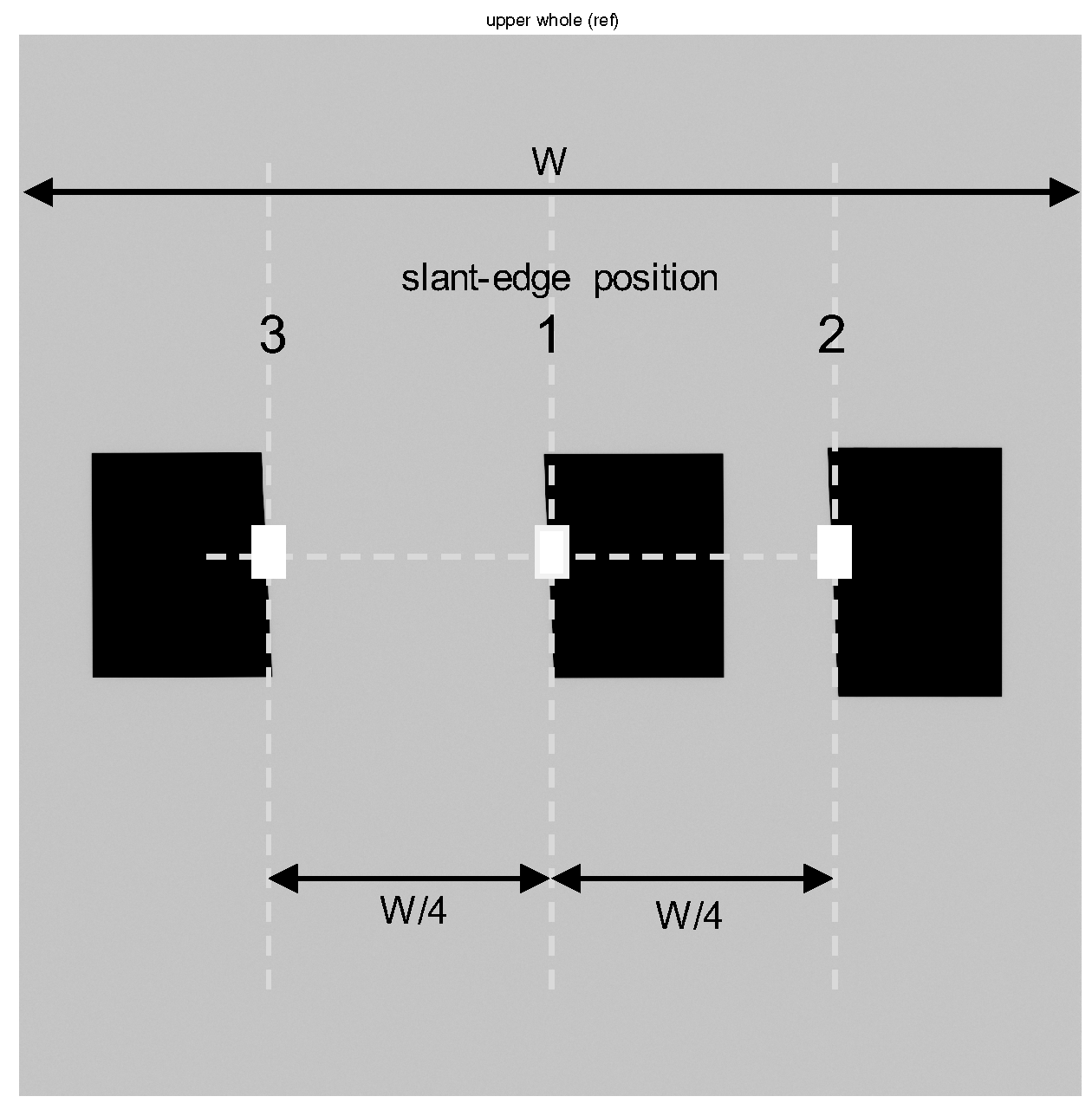
4.1. Numerical Performance Observation
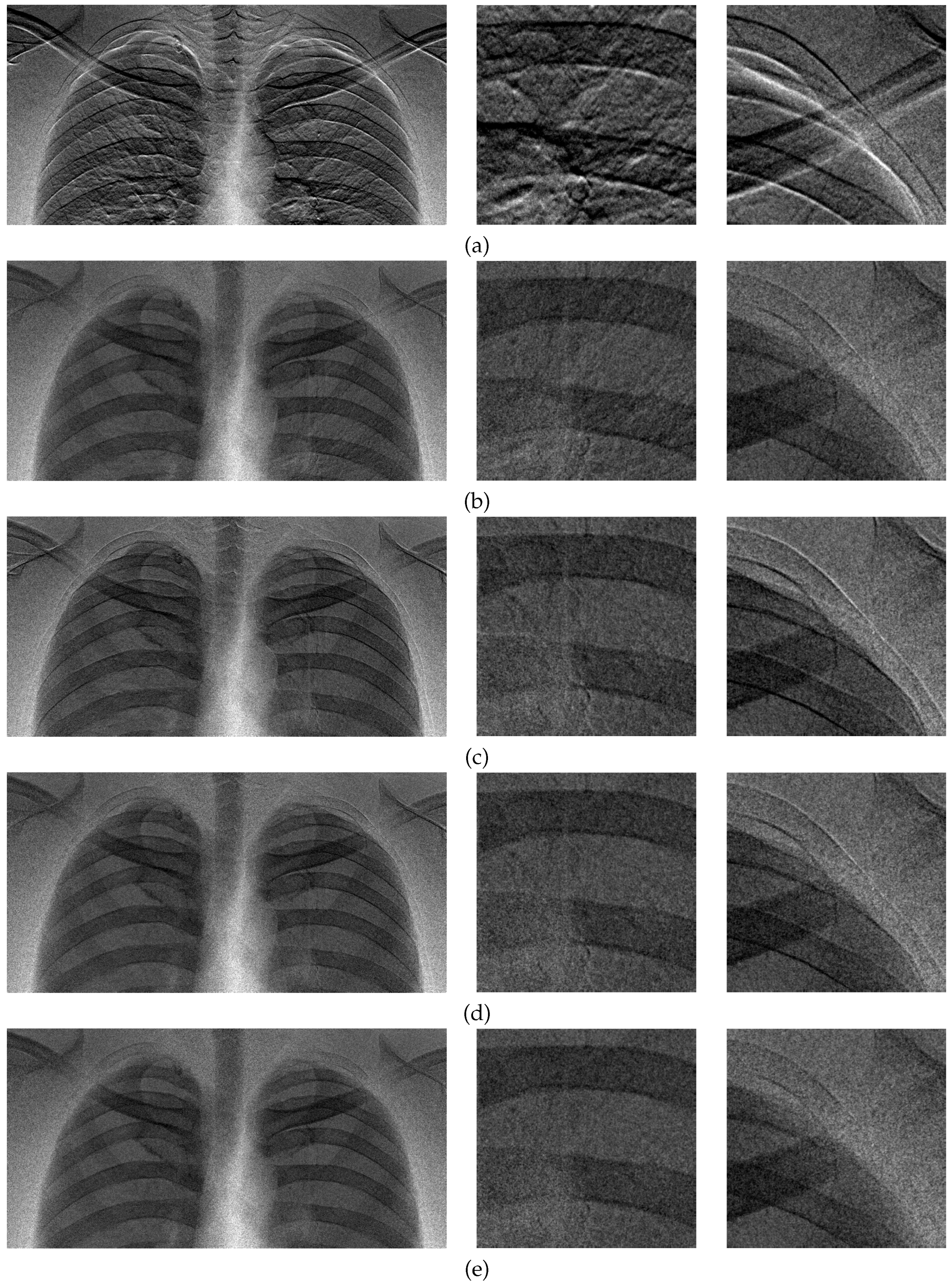
4.2. Registration Example of the Chest X-Ray Images
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DFD | Dual-layer flat-panel detector |
| DQE | Detective quantum efficiency |
| MTF | Modulation transfer function |
| NNPS | Normalized noise power spectrum |
| NPS | Noise power spectrum |
| TFT | Thin-film-transistor |
| SID | Source-to-image distance |
References
- Ishigaki, T.; Sakuma, S.; Horikawa, Y.; Ikeda, M.; Yamaguchi, H. One-shot dual-energy subtraction imaging. Radiology 1986, 161, 271–273. [CrossRef]
- McCollough, C.H.; Leng, S.; Yu, L.; Fletcher, J.G. Dual- and multi-energy CT: principles, technical approaches, and clinical applications. Radiology 2015, 276, 637–653. [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Lu, M.; Bennett, N.R.; Shapiro, E.; Zhang, J.; Colbeth, R.; Star-Lack, J.; Wang, A.S. Characterization and potential applications of a dual-layer flat-panel detector. Med. Phys. 2020, 47, 3332–3343. [CrossRef]
- van Hamersvelt, R.; Schilham, A.; Engelke K, den Harder, A.; de Keizer, B.; Verhaar, H.; Leiner, T.; de Jong, P.; Willemink, M. Accuracy of bone mineral density quantification using dual-layer spectral detector CT: a phantom study. Eur Radiol. 2017, 27, 4351–4359. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhou, H.; Gu, S.; Xia, Y.; Liao, H.; Deng, Y.; Gao, H. Dual-energy head cone-beam CT using a dual-layer flat-panel detector: Hybrid material decomposition and a feasibility study. Medical Physics 2023, 50, 6762–6778. [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Wang, A.; Shapiro, E.; Shiroma, A.; Zhang, J.; Steiger, J.; Star-Lack, J. Dual energy imaging with a dual-layer flat panel detector. In Proceedings of the Med. Imag.: Phys. Med. Imag. SPIE, 2019, Vol. 10948, pp. 269 – 278. [CrossRef]
- Engel, K.J.; Menser, B.; Rohr, P.; Ruetten, W.; Simon, M.; Thran, A. Dual layer x-ray detector simulation. In Proceedings of the Med. Imag.: Phys. Med. Imag. SPIE, 2020, Vol. 11312, pp. 398 – 409. [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.S. Convex combination of images from dual-layer detectors for high detective quantum efficiencies. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2023, 70, 1804–1814. [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.S. Measurements of the noise power spectrum for digital x-ray imaging devices. Phys. Med. Biol. 2024, 69, 03TR01. [CrossRef]
- Su, T.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, X.; Tan, Y.; Cui, H.; Zeng, D.; Guo, J.; Zheng, H.; Ma, J.; Liang, D.; et al. Super resolution dual-energy cone-beam CT imaging with dual-layer flat-panel detector. IEEE Trans. Med. Imag. 2024, 43, 734–744. [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Kim, D.S. High-precision alignments for dual-layer detectors based on a slant-edge phantom. In Proceedings of the IEEE Int. Symp. Biomed. Imag. (ISBI), 2024, pp. 1–5. [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Kim, D.S. Subpixel registration for dual-layer detectors based on the amplitude response. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 153019–153029. [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, R.E.; Seibert, J.A.; Thompson, S.K. Comparison of dual energy detector system performance. Med. Phys. 2004, 31, 556–565. [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, R.C.; Woods, R.E. Digital Image Processing, 3rd. ed.; Prentice Hall: NY, 2008.
- Maintz, J.; Viergever, M.A. A survey of medical image registration. Med. Image Anal. 1998, 2, 1–36. [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.; Goyal, A. Classification based survey of image registration methods. In Proceedings of the 2013 Fourth International Conference on Computing, Communications and Networking Technologies (ICCCNT), 2013, pp. 1–7. [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Gao, S.; Jiang, W.; Kudchadker, R.J. Independent evaluation of the effectiveness of IsoCal in improving image center accuracy on Varian TrueBeam and Clinac machines. Journal of Applied Clinical Medical Physics 2018, 19, 483–490. [CrossRef]
- Zitová, B.; Flusser, J. Image registration methods: a survey. Image, Vis., Comput. 2003, 21, 977–1000. [CrossRef]
- Tian, Q.; Huhns, M.N. Algorithms for subpixel registration. Comput. Vis., Graph., Image Process. 1986, 35, 220–233. [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Su, W. Subpixel accuracy image registration by spectrum cancellation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Int. Conf. Acoustics, Speech, Signal Process., 1993, Vol. 5, pp. 153–156 vol.5. [CrossRef]
- Efrat, A.; Gotsman, C. Subpixel image registration using circular fiducials. In Proceedings of the 2nd Israel Symp. Theory Comput. Syst., 1993, pp. 49–58. [CrossRef]
- Shekarforoush, H.; Berthod, M.; Zerubia, J. Subpixel image registration by estimating the polyphase decomposition of cross power spectrum. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conf. Comput. Vision, Patt. Recog., 1996, pp. 532–537. [CrossRef]
- Foroosh, H.; Zerubia, J.; Berthod, M. Extension of phase correlation to subpixel registration. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2002, 11, 188–200. [CrossRef]
- Argyriou, V.; Vlachos, T. Sub-pixel motion estimation using gradient cross-correlation. In Proceedings of the 7th Int. Symp. Signal Process., Its Appls, 2003. Proceedings., 2003, Vol. 2, pp. 215–218. [CrossRef]
- Guizar-Sicairos, M.; Thurman, S.T.; Fienup, J.R. Efficient subpixel image registration algorithms. Opt. Lett. 2008, 33, 156–158. [CrossRef]
- Rohde, G.K.; Aldroubi, A.; Healy, D.M. Interpolation artifacts in sub-pixel image registration. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2009, 18, 333–345. [CrossRef]
- Tzimiropoulos, G.; Argyriou, V.; Stathaki, T. Subpixel registration with gradient correlation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2011, 20, 1761–1767. [CrossRef]
- HajiRassouliha, A.; Taberner, A.J.; Nash, M.P.; Nielsen, P.M. Subpixel phase-based image registration using Savitzky–Golay differentiators in gradient-correlation. Comp. Vision, Image Understanding 2018, 170, 28–39. [CrossRef]
- International Electrotechnical Commission. Medical Electrical Equipment Characteristics of Digital X-ray Imaging Devices-Part1-1: Determination of the Detective Quantum Efficiency Detectors used in Radiographic Imaging; IEC 62220-1-1: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015.
- Fujita, H.; Tsai, D.Y.; Itoh, T.; Doi, K.; Morishita, J.; Ueda, K.; Ohtsuka, A. A simple method for determining the modulation transfer function in digital radiography. IEEE Trans. Med. Imag. 1992, 11, 34–39. [CrossRef]
- Unser, M. Splines: a perfect fit for signal and image processing. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 1999, 16, 22–38. [CrossRef]
- Catmull, E.E.; Rom, R. A class of local interpolating splines. Computer Aided Geometric Design 1974, pp. 317–326. [CrossRef]
- Lucas, B.; Kanade, T. An iterative image registration technique with an application to stereo vision. In Proceedings of the Imaging Understanding Workshop, 1981, pp. 121–130.
- Viola, P.; Wells, W. Alignment by maximization of mutual information. In Proceedings of the IEEE Int. Conf. Comput. Vision, 1995, pp. 16–23. [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.S.; Lee, K. Block-coordinate Gauss-Newton optimization and constrained monotone regression for image registration in the presence of outlier objects. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2008, 17, 798–810. [CrossRef]
- Harris, C.G.; Stephens, M.J. A combined corner and edge detector. In Proceedings of the Alvey Vision Conference, 1988.
- Alcantarilla, P.F.; Bartoli, A.; Davison, A.J. KAZE features. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision – ECCV 2012; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2012; pp. 214–227.
- Kim, D.S. Noise power spectrum measurements in digital imaging with gain nonuniformilty correction. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2016, 25, 3712–3722. [CrossRef]
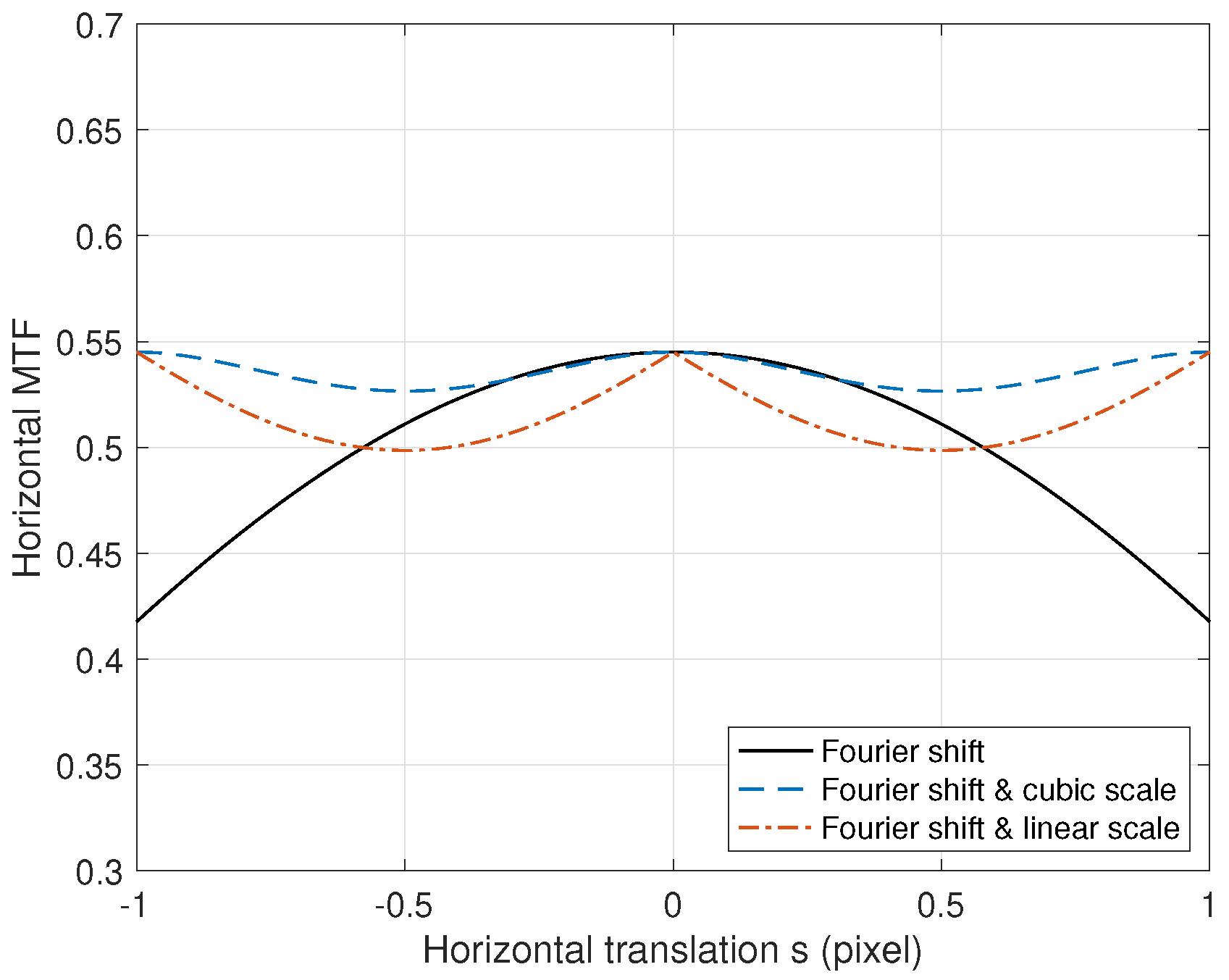
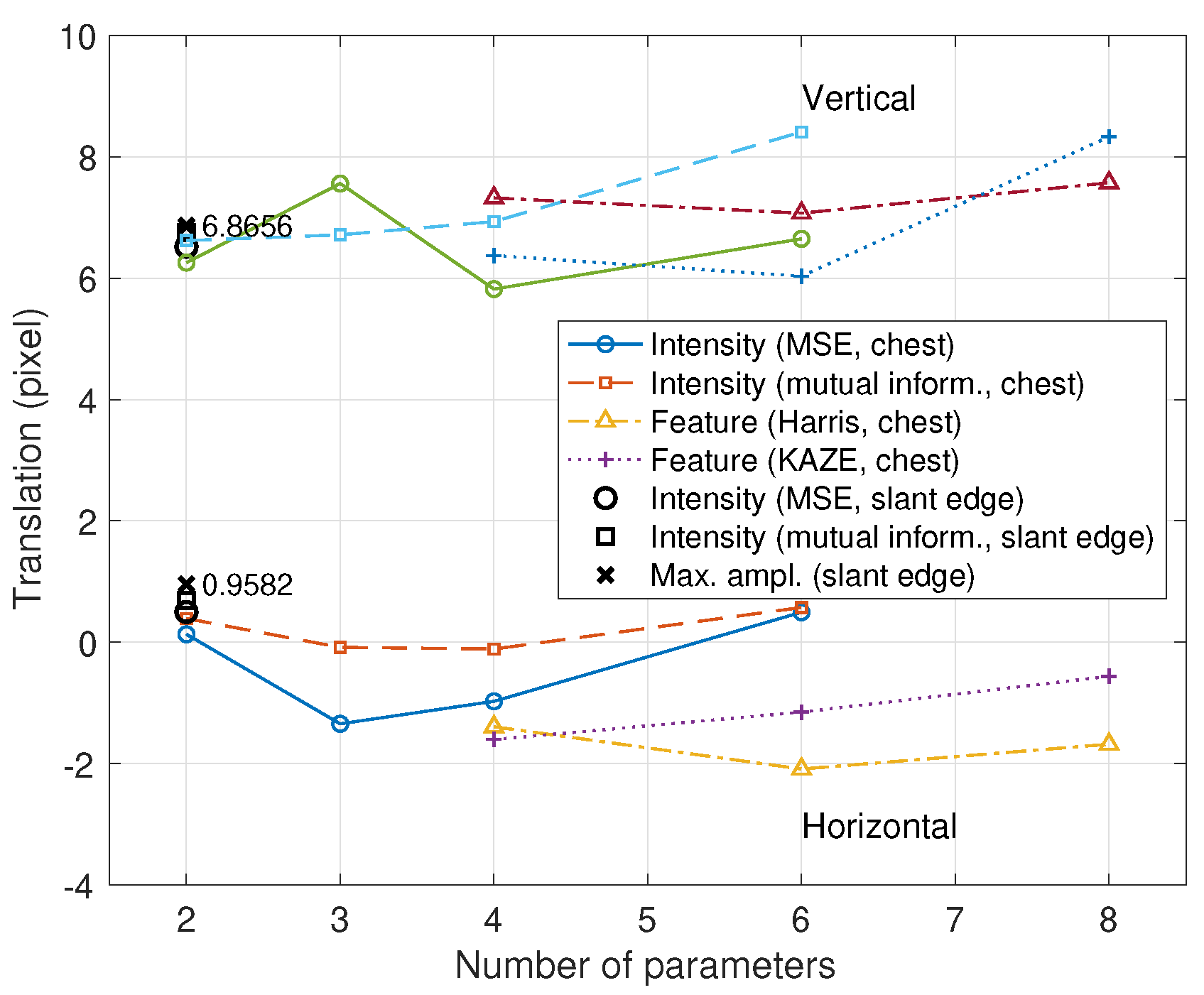
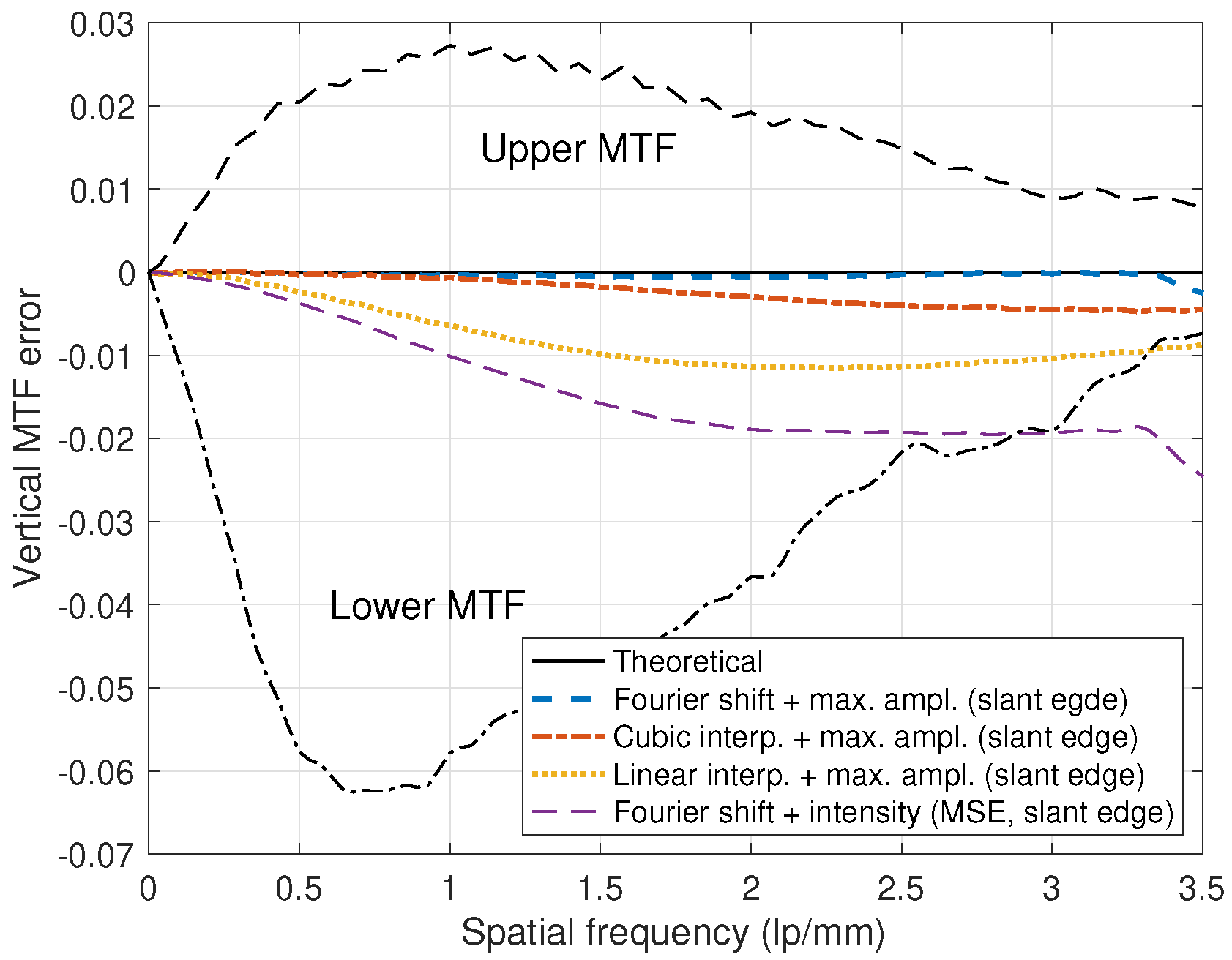
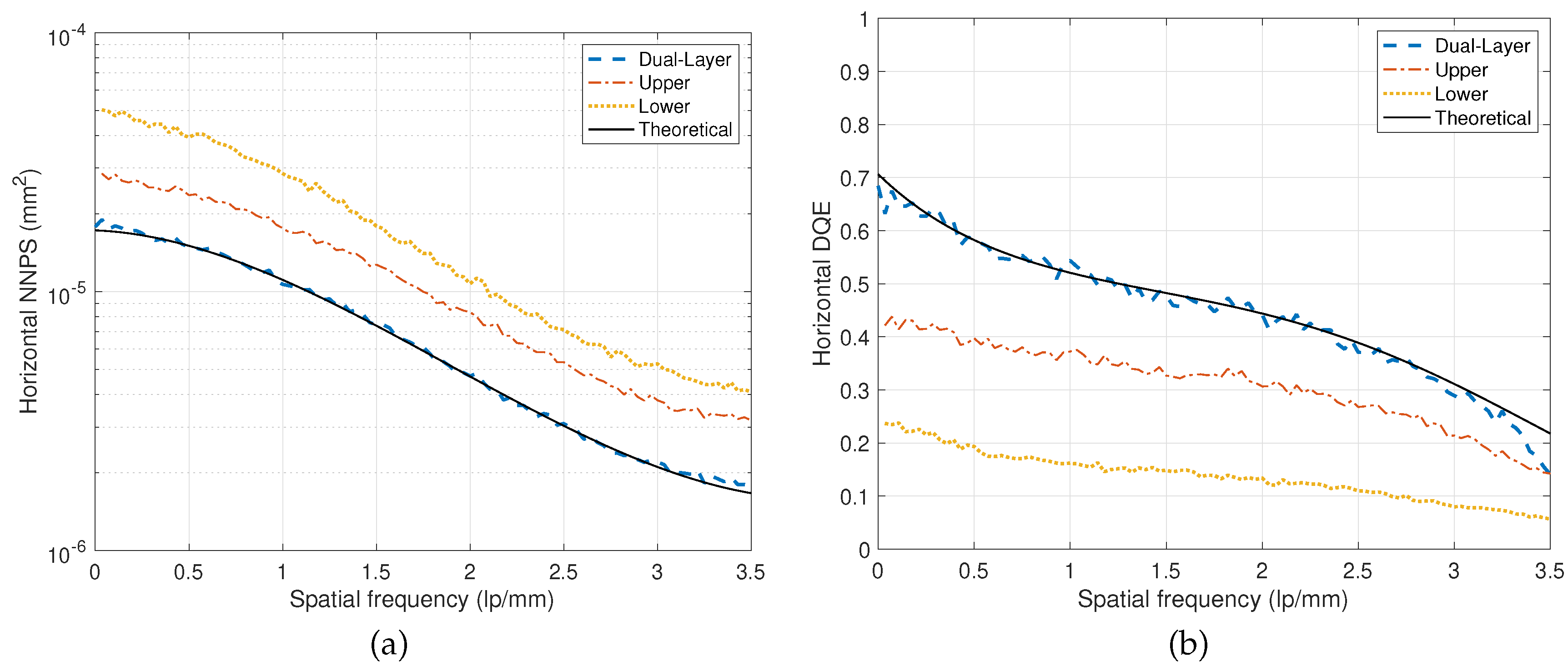
| Distance | CsI(Tl) scintillator | Intermediate | TFT | ||||
| Detector | filter | Photodiode | Stacking | Company | |||
| Lu et al. [6], 2019 | 2.5 | 0.2 | 0.55 | 1 Cu | a-Si | Normal | Varex,USA |
| Shi et al. [3], 2020 | 2.5 | 0.2 | 0.55 | 1 Cu | a-Si | Normal | Varex,USA |
| Kim [8], 2023 | 1.3-2.2 | 0.5 | 0.5 | No filter,0.5 Cu | a-Si/IGZO | Normal,inverted upper/lower | DRTECH,Korea |
| Wang et al. [5], 2023 | - | 0.2-0.55 | 0.55 | No filter,1 Cu | a-Si | Normal | Varex,USA |
| Su et al. [10], 2024 | 6.6 | 0.26 | 0.55 | 1 Cu | a-Si | Normal | CareRay,China |
| Lee & Kim [11,12], 2024 | 1.1 | 0.35-0.5 | 0.5 | No filter | a-IGZO | Inverted lower | DRTECH,Korea |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





