1. Introduction
Electricity markets worldwide have adopted various pricing schemes, which are primarily categorized into three types: nodal, zonal, and uniform pricing. Nodal pricing determines the individual electricity prices for all nodes in the transmission network and provides the most granular and accurate price signals. Zonal pricing is an intermediate approach that divides the electricity market into several bidding zones by setting a single price in each zone. Finally, uniform pricing, the simplest method, establishes one price for the entire electricity market [
1,
2,
3]. Each pricing scheme offers unique advantages and disadvantages. Nodal pricing is the most effective in terms of maximizing social welfare and managing congestion; however, it involves high computational complexity. Uniform pricing, although simple, is limited in terms of providing accurate price signals. Whereas, zonal pricing offers a compromise between these two approaches [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5,
6].
Recently, the global shift in energy policy from fossil-based sources to zero-carbon systems has facilitated a rapid increase in renewable energy sources. This has posed new challenges for power system operations. In the short-term, the intermittent nature of renewable energy sources has increased system-balancing needs and the associated redispatch costs. Whereas, in the long-term, this transition intensifies the geographical separation between the load centers and generation sources, thereby exacerbating grid congestion problems [
4,
7,
8,
9,
10,
11,
12]. To address these issues, several electricity markets are transitioning to more granular pricing schemes such as zonal and nodal pricing. These schemes reflect the locational system conditions more accurately. Consequently, they can improve economic price signals to guide investment decisions to appropriate locations, enhance congestion management, and ultimately maximize social welfare. For instance, Italy, Australia, and Japan are currently pursuing a transition from zonal to nodal pricing, whereas South Korea, the UK, and Germany, which currently employ uniform pricing, are considering introducing zonal pricing [
13,
14,
15,
16,
17,
18,
19].
However, transitioning between these pricing schemes involves complex issues. In particular, the financial impact on market participants is the most significant obstacle to the transition process. Regardless of the theoretical validity of a pricing scheme, if it imposes excessive financial burdens on existing market participants, its implementation in the actual electricity market becomes challenging. Moreover, it may also cause social problems owing to substantial stranded costs [
20]. Furthermore, unforeseen challenges may arise during the pricing-scheme transition, such as the potential for abuse of market power [
21]. For instance, in markets wherein a single entity plays multiple roles (e.g., as both a transmission company and a retailer), the transition to more granular pricing could result in conflicts of interest and market inefficiencies. Considering these complexities, a comprehensive quantitative analysis of pricing-scheme transitions is crucial. Such research can identify the financial impacts on market participants and the potential social risks that may occur during the transition process. This proactive approach is essential for formulating an appropriate pricing transition pathway that balances improved market efficiency with stability, thereby contributing to more sustainable electricity markets.
Previous studies have recognized the importance of this issue and attempted to analyze the effects of transitioning pricing schemes from various perspectives [
2,
4,
13,
15,
16,
20,
22,
23,
24]. These studies consistently concluded that the transition to more granular pricing schemes induces significant improvements in terms of maximizing social welfare and congestion management. Despite the significant contributions of these studies, several important challenges remain.
First, although pricing schemes encompass both pricing mechanisms
1 and market-clearing models, most previous studies have not comprehensively considered these two elements. For example, within a specific pricing scheme, various pricing mechanisms such as system marginal price (SMP), zonal marginal price (ZMP), locational marginal price (LMP), and extended locational marginal price (ELMP) are applicable [
16]. Moreover, when implementing zonal pricing, different market-clearing models can be formulated, such as available transfer capacity (ATC), which facilitates power transactions between bidding zones based on predefined maximum transmission capacities, and flow-based market coupling (FBMC), which optimizes power transactions between bidding zones based on the physical characteristics of the network [
6,
25,
26]. However, previous studies have focused on the analysis of the changes in either the pricing mechanism or market-clearing model individually. Consequently, they have not comprehensively analyzed pricing schemes that reflect various combinations of these two elements. In addition, prior research has primarily focused on analyzing the impact of transitioning to nodal pricing. This has resulted in a relative lack of comparative studies on the transition from uniform to zonal pricing.
The objective of this study was to comprehensively evaluate the impact of zonal and nodal pricing schemes on large power systems by considering various combinations of pricing mechanisms and market-clearing models. By analyzing diverse schemes, this study proposed an appropriate pricing transition pathway. The study sought to strike a balance between implementing more granular price signals, which theoretically enhance social welfare, and minimizing potential market disruptions, relative to the currently adopted scheme. Using this balanced approach, this study aimed to formulate policy implications that maximize efficiency gains while ensuring market stability throughout the transition process.
This study focused on the South Korean electricity market as a case study. South Korea's electricity market, which currently employs uniform pricing based on SMP, is plagued by significant challenges in managing the geographical separation between load centers and generation sources, as well as congestion management owing to the absence of locational price signals. These limitations have become increasingly pronounced with the growing share of renewable energy, thereby rendering transitioning to zonal or nodal pricing an urgent task. However, a detailed analysis of this transition is lacking. Thus, this facilitates a suitable environment for analyzing the effects of transitioning to zonal and nodal pricing. Furthermore, South Korea's unique market structure, wherein a single transmission company (Transco) functions as a monopoly retailer, offers a distinctive opportunity to examine the effect of a transition in pricing schemes on potential conflicts of interest for the Transco.
To achieve the research objectives, this study adopted a stepwise approach as follows:
First, we utilized PLEXOS, an advanced software tool for power system modeling and simulation [
27], to model the power system at various levels of granularity, yielding a detailed 4,579-node representation. This comprehensive modeling approach facilitated a nuanced analysis of complex interactions within a power system.
Second, we constructed a comprehensive set of zonal and nodal pricing schemes that reflected the changes in pricing mechanisms and market-clearing models. These schemes represented various potential pricing schemes that could be introduced into the Korean electricity market in the long-term.
Uniform pricing based on SMP (currently adopted pricing scheme)
Zonal pricing with two bidding zones based on SMP
Zonal pricing with two bidding zones based on ZMP
Zonal pricing using ATC with five bidding zones based on ZMP
Zonal pricing using FBMC with five bidding zones based on ZMP
Nodal pricing based on LMP
Nodal pricing based on ELMP
Third, we conducted quantitative assessments through simulations for each of the aforementioned pricing schemes, covering the entire year 2023. These assessments focused on evaluating important metrics such as market prices, power flow in the system, power purchase costs for retailer, generation costs, revenue, and profits for power producers.
This study made the following key contributions:
We quantified the impact of various pricing schemes on the electricity market, incorporating simultaneous changes in both the pricing mechanisms and market-clearing models, an aspect not fully explored in previous studies.
We identified the potential conflicts of interest for Transco in case of the transition to zonal and nodal pricing within a unique market structure wherein Transco functions as a monopoly retailer.
We evaluated quantifiable metrics, such as financial impacts on market participants and potential social risks associated with various pricing schemes. This can sever to guide policymakers towards an appropriate pricing transition pathway and policy implications, while offering crucial information for stakeholders to adapt to potential changes.
We contributed valuable insights applicable to electricity markets worldwide, considering the transition to zonal and nodal pricing, based on a comprehensive analysis of the Korean case study.
The remainder of this paper is structured as follows.
Section 2 describes the pricing schemes (uniform, zonal, and nodal), preceded by explanations of the market-clearing models and pricing mechanisms that form the basis for these pricing schemes.
Section 3 introduces a comprehensive set of zonal and nodal pricing schemes for the simulations, provides a brief overview of the Korean electricity market, and details the data used in these simulations.
Section 4 presents and discusses the results. Finally,
Section 5 concludes with key findings, policy implications, and suggestions for future research.
2. Fundamentals of Pricing Schemes: Uniform, Zonal, and Nodal Pricing
This section provides an essential background for understanding market-clearing models and pricing mechanisms in electricity markets, which form the basis for uniform, zonal, and nodal pricing schemes.
Electricity markets typically follow a two-step process: the market-clearing model, followed by the application of pricing mechanisms, as shown in
Table 1 [
28]. Market-clearing models are generally solved by employing an optimization process called unit commitment and economic dispatch (UCED). This process considers various constraints, including power balance and transmission flow constraints such as ATC, FBMC, and DC optimal power flow (DC-OPF) [
6,
25,
26]. Upon the completion of the market-clearing model, different pricing mechanisms can be applied to determine the market prices. These mechanisms include the SMP, LMP, ZMP, and ELMP. The combination of the market-clearing model and chosen pricing mechanism yields different outcomes, even within the same general scheme (uniform, zonal, or nodal).
2.1. Market-Clearing Models
In general, wholesale electricity markets employ objective functions and constraints [
29], as listed in
Table 1. The objective function usually aims to minimize the total system cost or maximize social welfare subject to several technical and economic constraints. These constraints typically include generator output limits, ramp rate constraints, minimum up and down time requirements, power balance constraints, transmission flow constraints, and other relevant system operational constraints (e.g., reserve requirements). Although these models are largely similar across different electricity markets, there exhibit notable differences in terms of the implementation of power balance and transmission flow constraints in various electricity markets.
2.1.1. Power Balance Constraints
The power balance constraint, a fundamental principle in electricity markets, ensures that the supply satisfies the demand at all times. At the node level, this constraint can be formulated mathematically as shown in Equation (1); where, the index
represents the individual nodes. This formulation adapts to different market aggregation levels: at the zone level,
represents the zones; at the national level, it is simplified to a single entity representing the entire electricity market
where
indicates the generation from generator
at time
,
is the net power flow on branch
at time
, and
is the demand at bus
at time
. The set
includes all generators at bus
, and
includes all branches connected to bus
.
The level at which this constraint is implemented—national, zonal, or nodal—is intrinsically linked to the choice of the pricing scheme. The national-level balance corresponds closely to uniform pricing, whereas the zone-level balance aligns with zonal pricing. Finally, the node-level balance is fundamental to nodal pricing. Each of these implementation levels reflects a different approach to managing power balance and pricing in electricity markets.
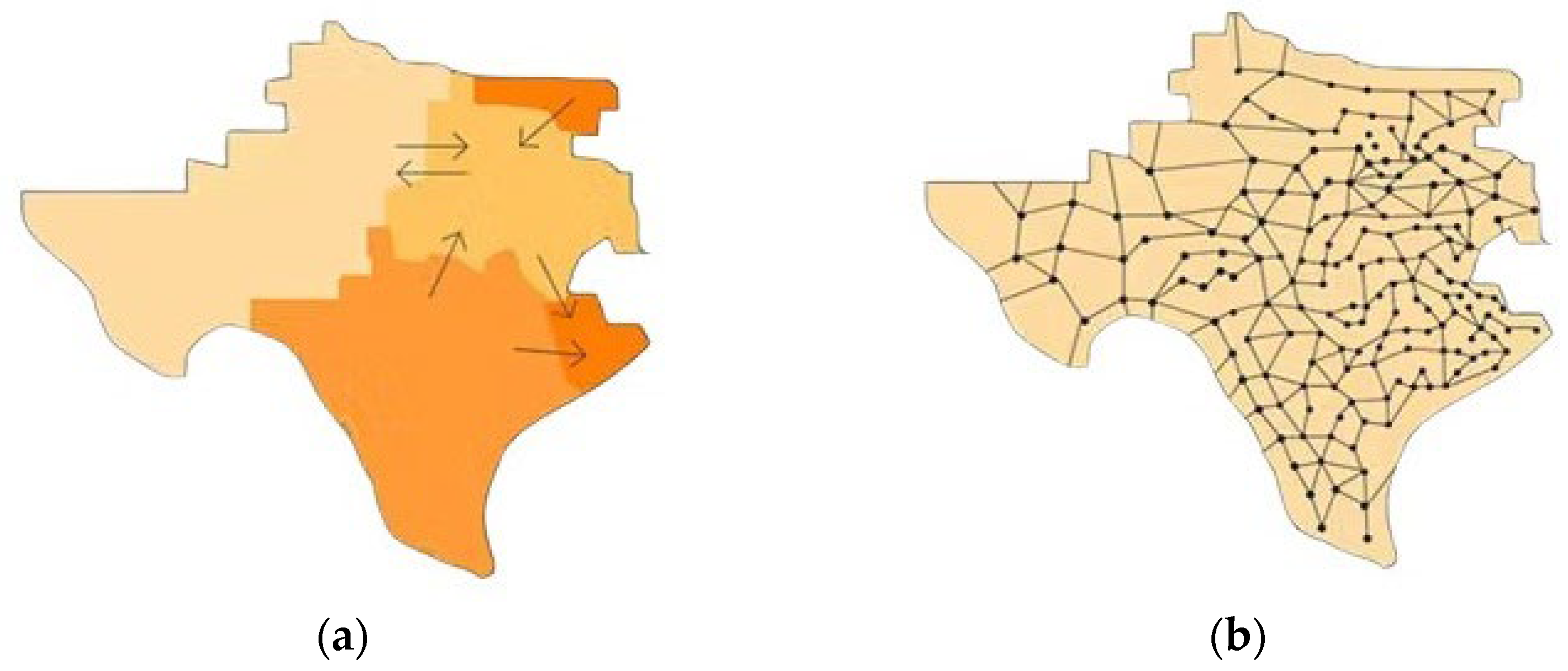
Figure 1 illustrates this concept using Electric Reliability Council of Texas (ERCOT) as an example, showing both zone- and node-level representations.
2.1.2. Transmission Flow Constraints
The key differentiating factor among electricity markets is the treatment of transmission flow constraints. These constraints are modeled using various approaches, ranging from simplified representations to more complex methods. In zonal pricing, ATC and FBMC are commonly used. ATC is simpler but less reflective of network interconnectivity, whereas FBMC offers higher efficiency, albeit with greater complexity [
6,
25,
26]. In nodal pricing, the DC-OPF approximation of the AC optimal power flow (AC-OPF) is typically applied due to computational limitations in case of practical market operations [
26]. These variations in constraint modeling can significantly affect the market outcomes, including dispatch decisions and pricing.
where is the predefined transfer limits for branch .
FBMC: This approach considers the impact of power flows on multiple lines simultaneously using power transfer distribution factors (PTDFs). The zonal PTDF matrix is applied only to calculate flows on critical branches (CBs), facilitating a focused consideration of key network constraints while preserving the zonal market structure. The FBMC approach is characterized by Equations (3) and (4).
where
is the zonal PTDF matrix for branch
and zone
, and
is the net exchange in zone
. The parameter
indicates the thermal limit of branch
, and the set
refers to all the CBs within the network. Generally,
is calculated based on node-level PTDF matrix; further details can be found in [
25,
26].
where is the node-level PTDF matrix for line and node , and is the net injection at node .
2.2. Pricing Mechanisms
Based on the market-clearing model described earlier, various pricing mechanisms are employed to determine market prices. These mechanisms are based on the primal and dual variables from the market-clearing model. The resulting market prices serve as the foundation for the settlement calculations in the electricity market.
2.2.1. Locational Marginal Price (LMP) and Zonal Marginal Price (ZMP)
LMP is a widely adopted pricing mechanism in most existing electricity markets. This mechanism reflects the cost of satisfying an incremental unit of demand at each node by incorporating the cost of energy and its delivery (including losses and congestion). LMP provides the highest granularity and calculates the price for each node in the system [
31]. This is calculated using Equation (7):
where
is the marginal cost of the reference node.
is the marginal loss factor at node
, and
is the Lagrangian multiplier related to the
th transmission constraint.
Theoretically, ZMP is similar to LMP; however, it simplifies the approach by aggregating nodes into zones [
3]. Whereas the LMP calculates the prices for each node, the ZMP determines a single price for each zone.
Notably, although these market prices are determined by marginal costs, generators may incur financial losses owing to quasi-fixed costs, such as no-load and start-up costs. As a result, make-whole payments (MWPs) are necessary to compensate generators for these losses.
2.2.2. Extended Locational Marginal Price (ELMP)
Electricity markets, formulated using mixed integer linear programming (MILP), face challenges owing to their nonconvexity. As previously discussed, traditional marginal cost pricing may not allow some generators to recover their full production costs, leading to MWPs. These payments can distort price signals and reduce market transparency [
32,
33].
ELMP has been developed as a practical alternative to address these issues, approximating convex hull pricing, while balancing accuracy with computational feasibility. This method allows fast-start resources (FSRs) to set prices and reduce side payments by adding their quasi-fixed costs to their production costs and allowing partial commitment [
28].
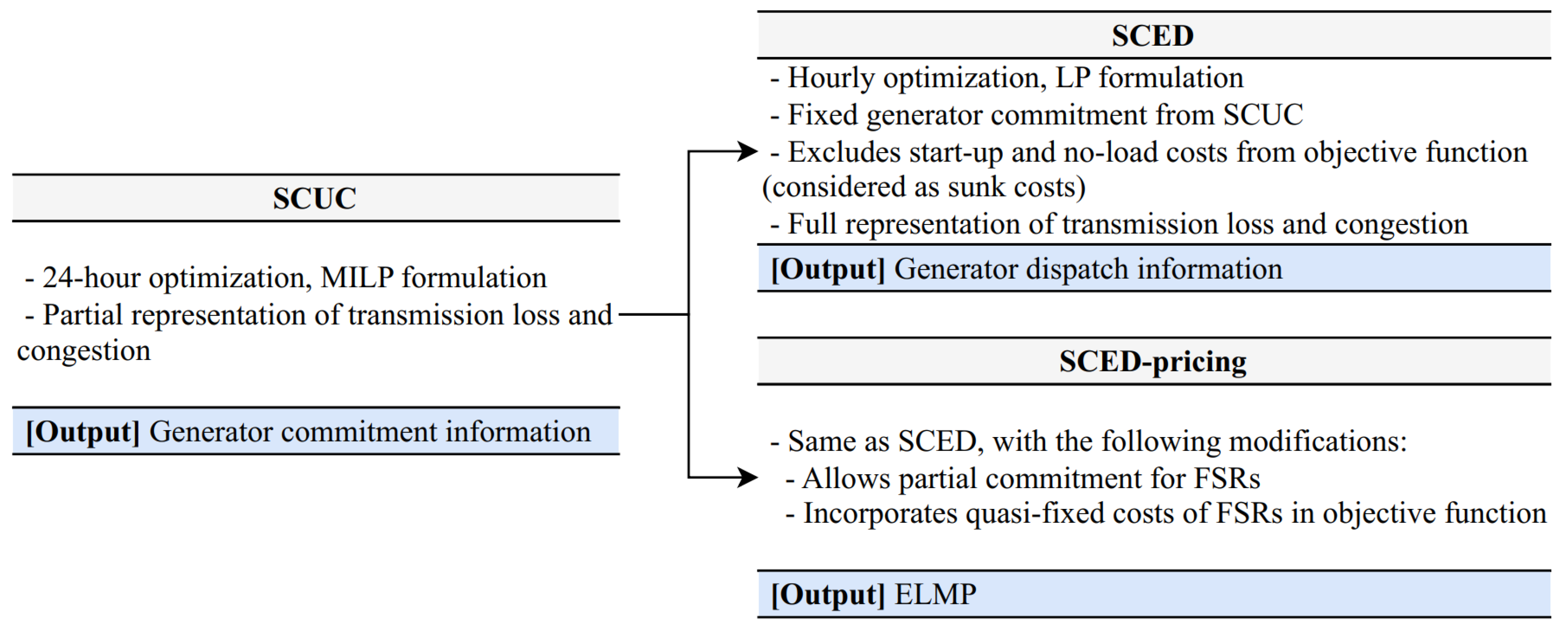
Figure 2 illustrates the ELMP adopted by the Midcontinent Independent System Operator (MISO), which is a representative electricity market using this price mechanism [
34]. Owing to the computational complexity of node-level UCED, the process is structured into two primary parts: security-constrained unit commitment (SCUC), followed by security-constrained economic dispatch (SCED) and SCED-pricing.
The SCUC is formulated as an MILP problem and optimized over a 24 hours horizon. It incorporates transmission losses exogenously and only checks the transmission flow constraints for the watchlist transmission set wherein binding or violations are anticipated. Consequently, the resulting hourly generator commitment information is passed on to the SCED and SCED-pricing.
The SCED is formulated as an hourly linear programming (LP) problem that determines the optimal dispatch based on fixed generator commitments from the SCUC. Unlike SCUC, SCED conducts a more extensive evaluation of transmission flow constraints, encompassing a broader set of transmission lines beyond the predefined watchlist. The objective function excludes start-up and no-load costs as sunk costs, whereas the transmission losses are determined endogenously through marginal loss factors. The SCED outputs the generator dispatch information used in the system operations.
SCED-pricing, executed independently of the SCED, is also modeled as an hourly LP problem. It shares fundamental characteristics with SCED. The key distinction is that SCED-pricing facilitates partial commitment for committed FSRs by relaxing their binary variables to 0–1. This approach facilitates these resources in setting the market prices and incorporate certain no-load and start-up costs. The market prices derived from the SCED-pricing, calculated using the LMP formulation in Equation (7), are defined as ELMP. In MISO, FSR-qualified generators are defined as units that can start up within 1 hour or less, with a minimum run time of 1 hour or less.
2.2.3. System Marginal Price (SMP)
Another approach to addressing quasi-fixed costs in electricity markets involves incorporating them directly into market prices, as exemplified by the Korean electricity market. The SMP adopted in the Korean electricity market is determined by the marginal cost of the most expensive unit dispatched to satisfy the demand, including no-load and start-up costs as a form of average cost [
20]. This is calculated using Equation (8).
where
,
, and
denote the coefficients of the quadratic cost function, and
refers to the start-up costs of generator
. Further,
and
are the binary status of the generator, where
indicates the operating status and
refers to the start-up status. In addition,
and
denote the start and end times of a contiguous commitment period, respectively, and
is a subset of the generators eligible to set the market price.
The determination of is crucial for replicating the effects of marginal cost pricing based on Lagrangian multipliers. In marginal cost pricing based on Lagrangian multipliers, the binding constraints naturally prevent certain generators from setting the prices. To replicate this effect in the SMP mechanism, which does not inherently have this feature, the Korean market applies the following rules to exclude certain generators from the price settings:
Generators with binding ramp rate constraints
Generators operating at their minimum output level
Generators with binding transmission or generation constraints
Additionally, when transmission lines between adjacent zones are congested, the SMP for each zone is calculated using only the
within that specific zone. This allows the SMP mechanism to emulate Lagrangian multiplier-based pricing by separating market prices under these congestion conditions. Although this mechanism offers a straightforward method for including start-up and no-load costs in market prices, it is plagued by certain challenges, particularly in terms of the price regressivity problem and potential distortion of price signals [
20].
2.3. Pricing Schemes in the Electricity Market
The combination of market-clearing models and pricing mechanisms has facilitated various pricing schemes for electricity markets. Although power balance constraints naturally align with uniform, zonal, and nodal pricing schemes, the primary focus of this study was the combination of transmission flow constraints and pricing mechanisms. This interplay forms the basis for the different pricing schemes observed in electricity markets. For instance, zonal pricing can utilize either ATC or FBMC with ZMP, while nodal pricing usually implements DC-OPF with LMP or ELMP [
26]. The various pricing schemes resulting from these combinations, which will be analyzed in this study, are presented in detail in
Section 3.
3. Methodology and Simulation Framework
This study explored various potential pricing schemes that could be implemented in the Korean electricity market in the long-term and investigated appropriate pricing transition pathways through simulation and quantitative analysis. This section proposes a comprehensive set of zonal and nodal pricing schemes for the simulation, provides a brief overview of the Korean electricity market, and outlines the simulation design and data used in the analysis. These elements establish the foundation for the subsequent analysis and discussion of the results.
3.1. Proposed Pricing Schemes and Korean Electricity Market Overview
As explained in
Section 2, pricing schemes encompass both the market-clearing model (specifically, the transmission flow model) and pricing mechanisms. Therefore, we proposed and constructed seven comprehensive pricing schemes, including currently adopted schemes, by combining these two factors, as presented in
Table 2.
For nodal pricing, the DC-OPF with marginal loss factors is commonly used as the transmission flow model to account for both transmission losses and congestion while ensuring computational efficiency. Adhering to this common practice, this study applied the DC-OPF to model nodal pricing schemes. In addition, LMP and ELMP were considered as pricing mechanisms, categorizing nodal pricing into two schemes: Nodal (LMP) and Nodal (ELMP).
Zonal pricing can be implemented using various bidding zone configurations. Although the determination of optimal bidding zone configurations is an important research area [
3,
6,
12,
22], this study did not focus on this aspect. Instead, this study adopted two specific bidding zone configurations for the Korean electricity market, as illustrated in
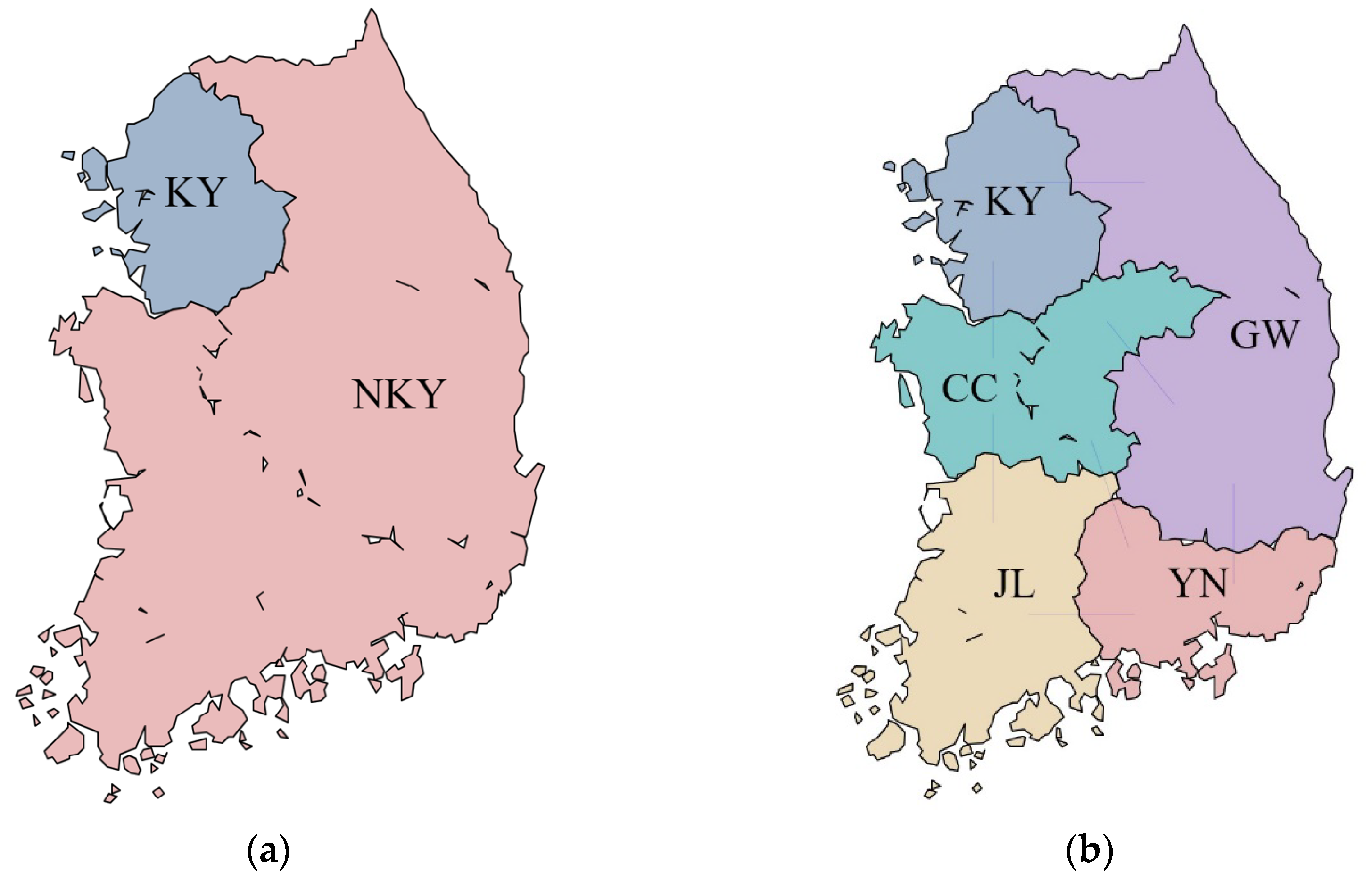
Figure 3. These configurations represent the most prominent options currently under discussion in Korea. They were selected for their relevance to ongoing policy debates and their potential for practical implementation.
The first configuration, shown in (a), divides South Korea into two bidding zones: the capital region (KY) and non-capital region (NKY)
2. The second configuration, illustrated in (b), delineates five bidding zones based on administrative districts, with certain modifications to consider the power system characteristics: the capital region (KY), Chungcheong (CC), Yeungnam (YN), Gangwon (GW), and Jeolla (JL)
3.
For 5-zonal pricing, both FBMC and ATC were considered as transmission flow models, with ZMP applied as the pricing mechanism. For 2-zonal pricing, only the ATC was considered because the benefits of the FBMC are limited owing to the single transmission line connecting the two bidding zones. Both the ZMP and SMP can be applied as pricing mechanisms for 2-zonal pricing. The reasons why the SMP cannot be applied to 5-zonal pricing are elucidated in
Section 4. Consequently, this study configured zonal pricing into four pricing schemes: 5-Zonal (FBMC and ZMP), 5-Zonal (ATC and ZMP), 2-Zonal (ZMP), and 2-Zonal (SMP).
Finally, although uniform pricing can be implemented in various forms, this study focused on evaluating the transition from the current pricing scheme to zonal and nodal pricing. Therefore, we considered only the Uniform (SMP) scheme currently adopted in the Korean electricity market as the "As-Is" scenario. This reflected the unique characteristics of the Korean electricity market.
In contrast to typical uniform pricing, the Korean market incorporates a transmission flow model by using ATC for the capital (KY) and non-capital (NKY) regions.
Due to the cost-based pool system, SMP mechanisms are applied to compensate the generators for no-load and start-up costs.
The market has a unique structure wherein a single company Transco functions as a monopolistic retailer.
These proposed pricing schemes facilitated the assessment of the effects of transitioning from existing to more granular pricing schemes. In
Section 4, we present the quantitative results of the transition to zonal and nodal pricing schemes and examine their impact on potential conflicts of interest for Transco, considering the unique aspects of the Korean electricity market.
3.2. Simulation Design and Input Data
This study applied the seven pricing schemes proposed in
Section 3.1 to the Korean electricity market. The simulation results were analyzed based on actual power system data for the entire year 2023. To ensure consistency and minimize distortions, we used a common dataset and topology across all simulations, capturing only the effects caused by changes in pricing schemes.
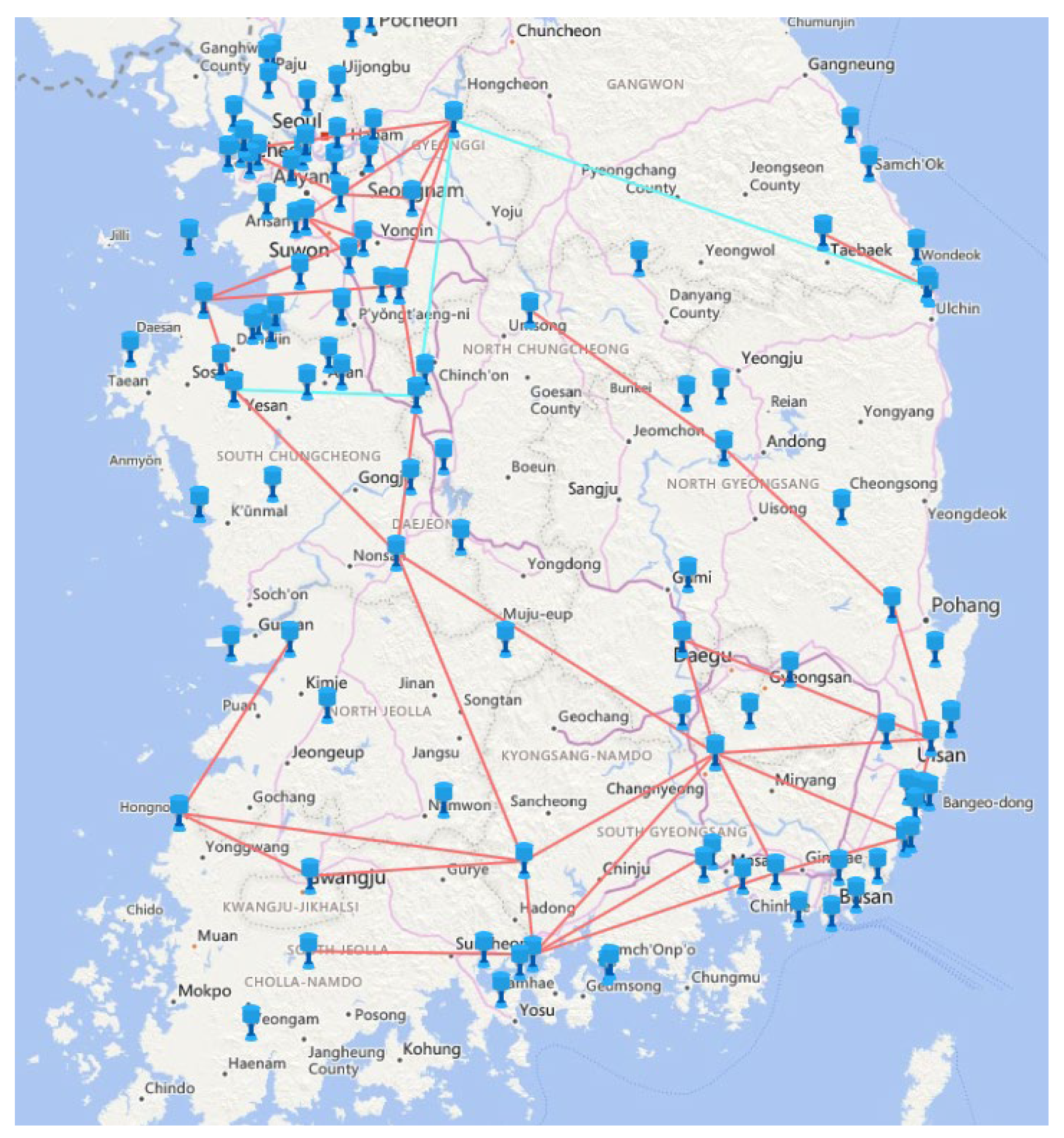
The power system was modeled at various levels of granularity, yielding detailed 4,579-node representation, as illustrated in
Figure 4. The topology included 3,322 transformers (considering 3-winding transformers), 3,056 transmission lines, 4,579 buses (including auxiliary buses for 3-winding transformers), and 1,597 generators (including distributed energy resources). To enhance the reliability of our modeling approach, we utilized PLEXOS, an advanced software tool for power-system modeling and simulation. The UCED problem and pricing processes were implemented using the CPLEX solver, which is a typical MILP and LP solver available in PLEXOS. The mixed integer programming (MIP) gap tolerance was set to 0.0001%. Our simulation methodology performed 24 hours optimizations with hourly time steps. Each day's results informed the subsequent day’s initial conditions, creating a continuous chain of linked optimizations throughout the simulation period.
The simulation model incorporated comprehensive input data and detailed modeling techniques to accurately reflect the Korean power system. Hourly demand data for 2023 were included, with a peak demand of 94,529 MW and an annual consumption of 566,160 GWh [
35,
36]. The load distribution was modeled at a detailed nodal level, with the demand allocated to individual nodes based on node-specific load participation factors relative to the total system demand.
The generator data, including the installed capacities (totaling 150.4 GW), average generation costs, and average annual maintenance days for the various types of power plants are summarized in
Table 3 [
35,
36]. Conventional power sources were modeled with detailed technical characteristics, including output ranges, ramp rates, minimum up and down times, cost functions, and start-up costs. For renewable energy sources, hourly time-series data were employed to capture generation profiles, with annual average capacity factors of 14.4% and 19.7% for solar and wind power, respectively.
The transmission network model incorporated transmission line and transformer parameters, such as thermal limits, reactance, and resistance, thereby enabling an accurate representation of network topology. In this study, the ATC model employed relatively slack transfer capacities, with predefined limits set to the thermal limits of the transmission lines. For the FBMC model, all transmission lines connecting bidding zones were considered as CBs. The model implemented a co-optimization of energy and 4.5 GW of operating reserves, as practiced in the Korean electricity market. In addition, following the same market practices, it incorporated 25 key generation and transmission constraints for transient stability, voltage stability, and other operational requirements, as listed in
Table 4. Although specific data values are subject to confidentiality requirements, our approach aimed to provide a reliable representation of the Korean power system by using comprehensive input data and detailed modeling techniques. Additional information about our modeling is available upon reasonable request and is subject to data protection agreements.
The proposed modeling approach accommodated seven proposed pricing schemes while maintaining a consistent underlying system representation. In nodal pricing, the system representation remained unchanged, thereby preserving the detailed node-level granularity. For zonal and uniform pricing, the generators and loads were aggregated according to their respective zones, and the transmission capacity connecting different bidding zones was represented by the sum of the thermal limits of all transmission lines crossing from one zone to the other [
29]. Because of this zonal aggregation, only interzonal power flows were considered, whereas intrazonal power flows were omitted from the model [
38]. In addition to these general modeling approaches, each pricing scheme had specific assumptions and modeling considerations, as follows.
- 8.
Nodal (LMP) and Nodal (ELMP): As explained in Section 2, Nodal (LMP) and Nodal (ELMP) refer to the results of the SCED and SCED-pricing, respectively, following SCUC execution. In our study, for the SCUC, all transmission lines were considered watchlist transmission sets. The MIP gap tolerance for SCUC was set at 0.1% as per the MISO market rules [34], compared to the typical 0.0001%. The DC-OPF for nodal pricing employed a distributed slack bus model.
- 9.
Nodal (ELMP): While MISO considers generators capable of starting within 1 hour or less with a minimum run time of 1 hour or less as FSRs, such resources are scarce in the Korean electricity market. Therefore, this study expanded the FSR qualification to resources with a minimum runtime of 4 hours or less for a Nodal (ELMP) scheme simulation.
- 10.
5-Zonal (FBMC, ZMP): For the 5-Zonal (FBMC, ZMP), the characteristics of the transmission lines connecting different zones were estimated. Specifically their resistance and reactance were calculated using PSS/E-based system reduction techniques.
- 11.
Bidding strategy: The current Korean electricity market operates on a cost-based pool system, wherein generators are required for bidding based on marginal costs. However, under pricing mechanisms, such as ZMP, LMP, and ELMP, generators generally submit price bids that are at least sufficient to recover the opportunity costs associated with invested capital, such as the time value of money during the production period. In this study, for schemes adopting ZMP, LMP, and ELMP mechanisms, we assumed a weighted average cost of capital (WACC) of 5.5% and a 3-month capital recovery period, thereby applying a mark-up on short-run marginal costs in the price bidding process.
- 12.
Pricing process implementation: PLEXOS provides built-in pricing processes for the ZMP, LMP, and ELMP. However, the SMP, which follows Korea-specific rules, was not built into the PLEXOS. To address this, we implemented Equation (8) from
Section 2 and the Korean market rules in a separate Python-based script. This script utilized the generator commitment, dispatch, and other relevant data from PLEXOS to calculate the SMP according to Korean market rules.
- 13.
Transmission losses: To consider transmission losses, we adopted a sequential linear programming (SLP) method to update marginal loss factors [
39]. This process iteratively refines the marginal loss factors for each node, reducing the gap between the actual (quadratic model) and modeled losses to 0.001% tolerance. For schemes using the ATC model, which does not incorporate the transmission line resistance, it is not feasible to endogenously calculate losses based on the marginal loss factors. Instead, to minimize distortions in scheme comparisons owing to transmission losses, we added the losses observed in the nodal pricing scheme to the system demand.
4. Simulation Results
Our analysis conducted simulations for each pricing scheme, evaluating metrics such as market prices, power flow, power purchase costs for retailer, and generation costs, revenue, and profits for power producers throughout 2023.
The subsequent subsections are structured as follows. First, to establish the reliability of our model, we compare the actual 2023 Korean electricity market prices with the Uniform (SMP) market prices simulated using our model in
Section 4.1. The Uniform (SMP) scheme in our model was designed to simulate the pricing scheme currently adopted in the Korean electricity market. Subsequently, we analyze the results of the seven proposed pricing schemes and divide our examination into the following sections: market price in
Section 4.2, financial impacts on power producers and retailer in
Section 4.3, and power flow in
Section 4.4. Finally, through a sensitivity analysis of
Table 4 in
Section 4.5, we examine how transitioning to zonal and nodal pricing schemes affects the potential conflicts of interest for Transco in a market structure wherein a single Transco also acts as a monopoly retailer.
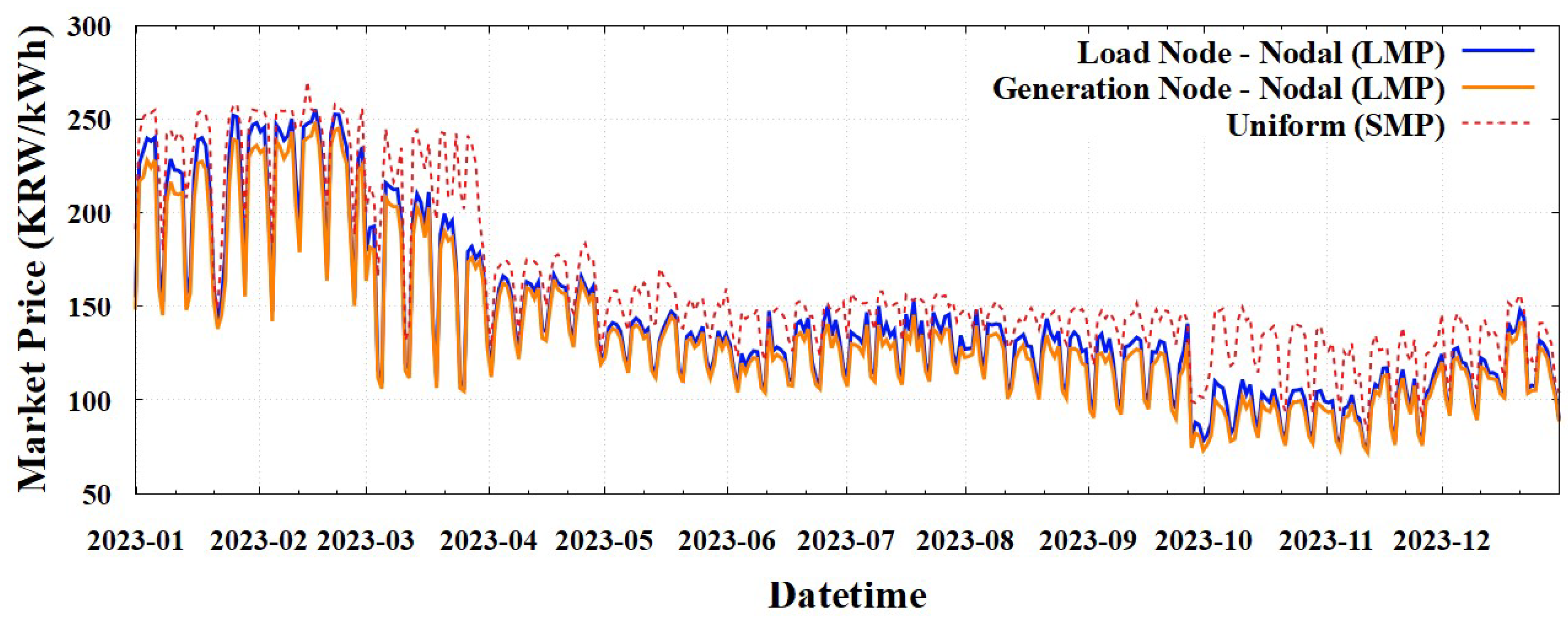
4.1. Model Validation: Comparison of Simulated Uniform (SMP) and Actual Market Prices
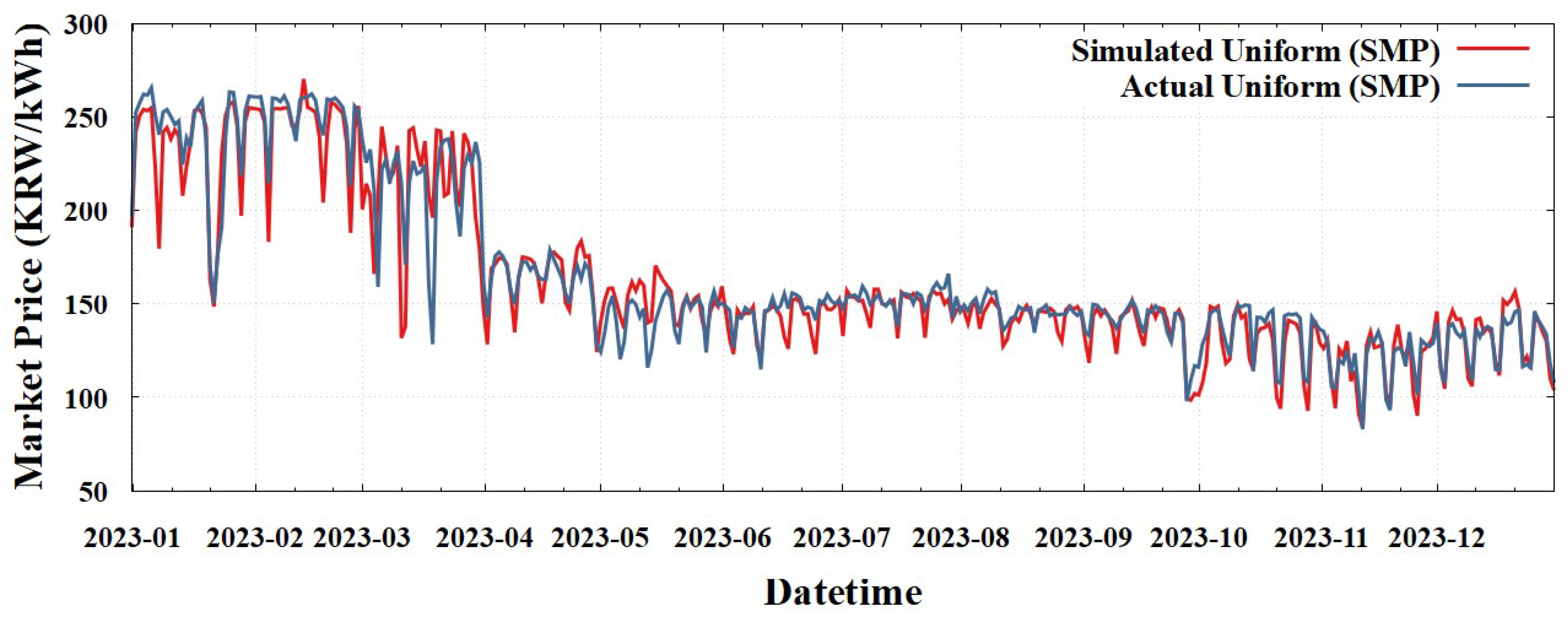
To validate the reliability of the simulation model, we compared the simulated market prices from our Uniform (SMP) scheme with the actual market prices for 2023. The annual load-weighted average price derived from our model was 164.75 KRW/kWh, closely aligning with the actual market price of 167.00 KRW/kWh [
40], thus indicating a deviation of only 1.35%.
Although perfect alignment is challenging owing to limitations in accessing precise maintenance schedules, heat demand for combined heat and power (CHP) sources, and other factors, this level of accuracy substantiates the reliability of the simulation model.
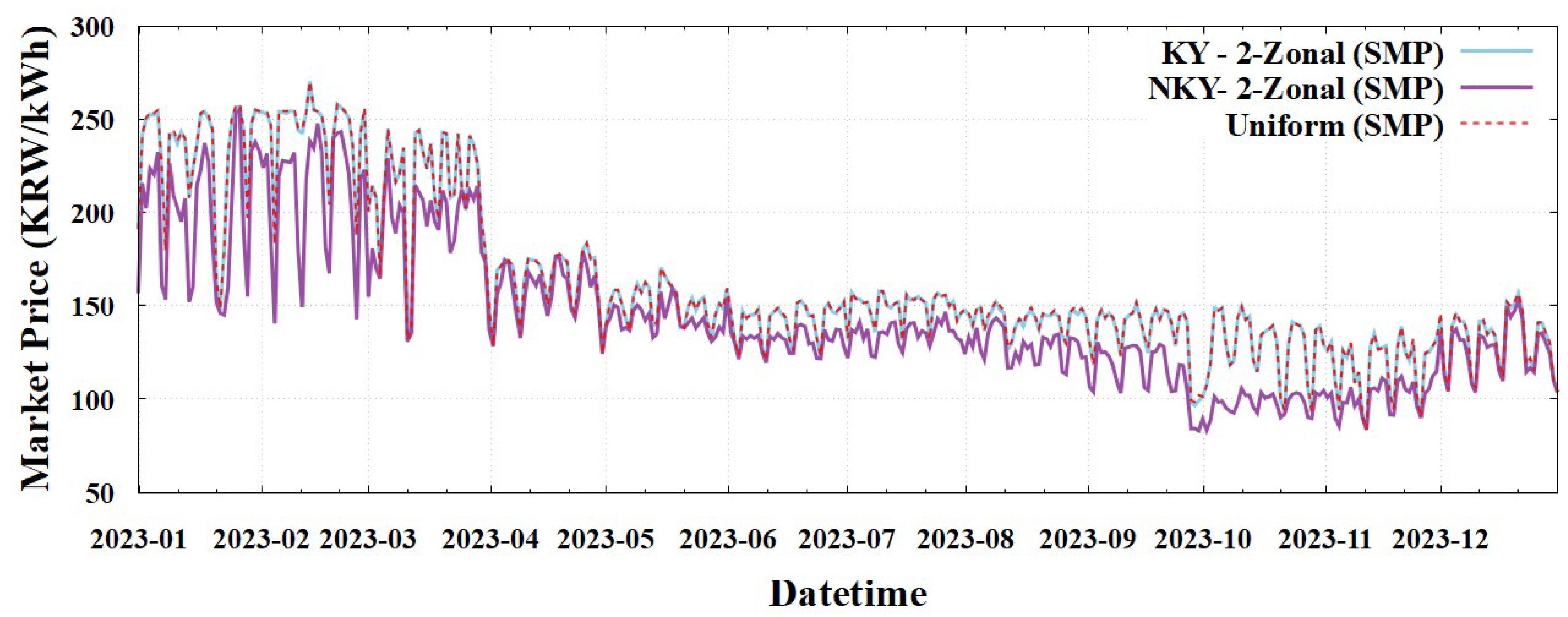
Figure 5 illustrates a daily comparison between the simulated and actual market prices. As evident, our model effectively captured both overall trends and short-term fluctuations throughout the year. This comprehensive validation, encompassing both annual averages and daily dynamics, provides a robust foundation for subsequent analyses of the zonal and nodal pricing schemes.
4.2. Market Price
In this section, we analyze and compare the market prices resulting from the different pricing schemes: current uniform, 2-zonal, 5-zonal, and nodal pricing. Our analysis begins by examining the differences between the currently adopted Uniform (SMP) and the 2-zonal pricing schemes, which include both 2-Zonal (SMP) and 2-Zonal (ZMP) schemes, as illustrated in
Table 5.
When analyzing the 2-Zonal (SMP), we observed that the KY zone maintains a price level nearly identical to the current Uniform (SMP). However, the NKY zone exhibited a significant market price decrease of 11.4%. In contrast, the 2-Zonal (ZMP) facilitated an average price reduction of approximately 8.2% for both the KY and NKY compared to the 2-Zonal (SMP). This price reduction is attributed to the fundamental difference between the SMP and ZMP mechanisms in their treatment of the no-load and start-up costs. The SMP compensates for these costs; however, the ZMP does not.
The dramatic price divergence between the KY and NKY zones under the 2-Zonal (SMP) scheme may raise questions. This phenomenon is rooted in the imbalance between the electricity demand and supply in the Korean power system.
Table 6 summarizes the demand and generation for the capital (KY) and non-capital (NKY) regions for 2023. As illustrated in
Table 6, although the KY zone accounted for approximately 40% of the total demand, it contributed to only approximately 20% of the total generation. This imbalance resulted in a significant power flow from NKY to KY. Moreover, the distribution of generation sources was exacerbated the price divergence. Low-cost generation and renewable energy sources, particularly solar PV, were predominantly located in the NKY zone, whereas high-cost generation sources were concentrated in the KY zone. Consequently, under the current Uniform (SMP), price-setting units were mostly situated in the KY zone.
This distribution explains why the market price of the KY zone under the 2-Zonal (SMP) model remained nearly identical to the Uniform (SMP) price
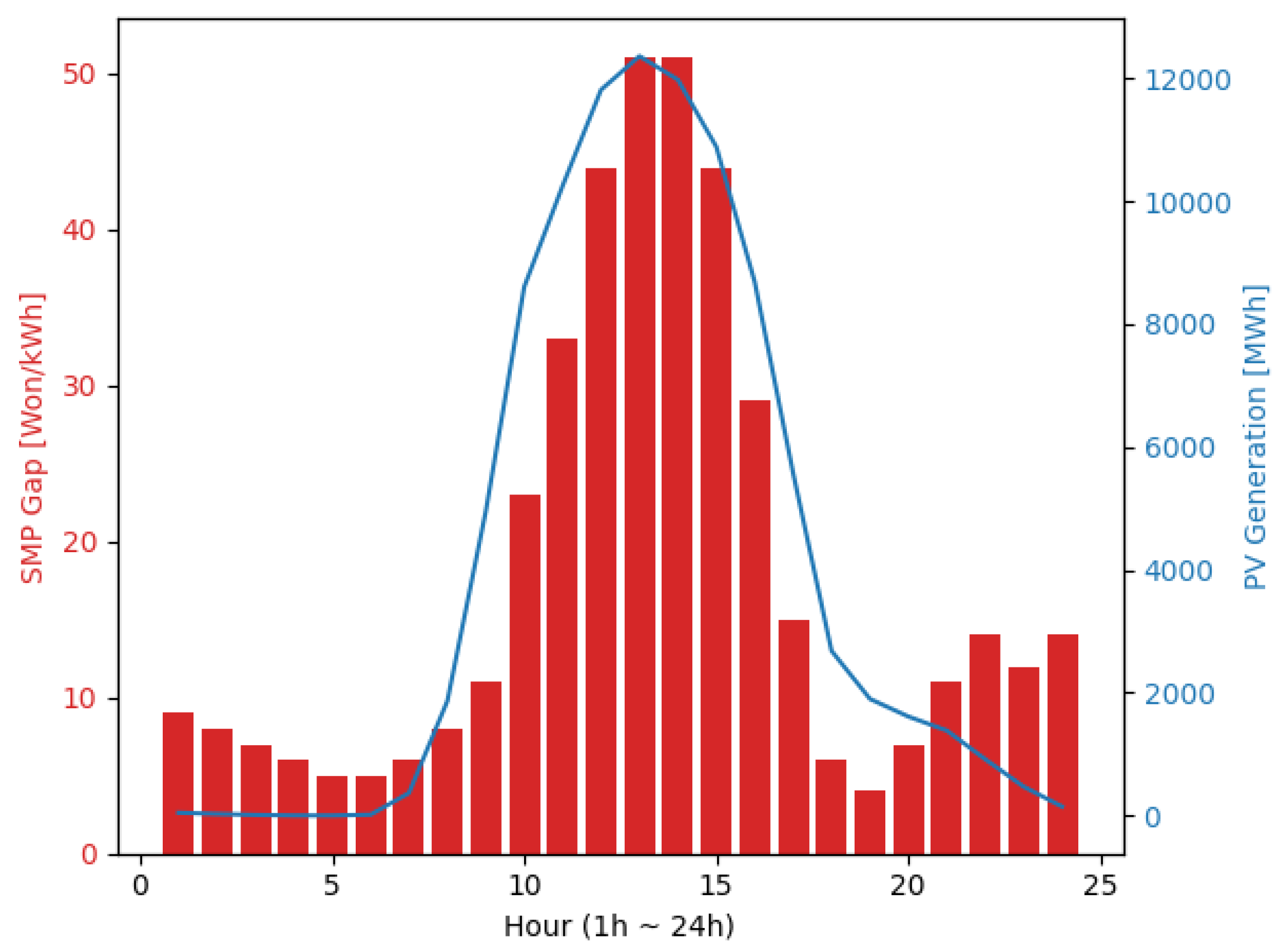
4. Conversely, the significant price decrease in the NKY zone was particularly influenced by the concentration of solar PV generation, with 93.1% of such sources located in this zone [
36]. To illustrate this effect,
Figure 6 depicts the annual hourly average solar PV generation pattern alongside the market price gap between the KY and NKY zones under the 2-Zonal (SMP) throughout the year 2023. This visualization clearly demonstrates the positive correlation between solar power generation in the power system and the price differential between the two zones.
Market price separation occurs when the transmission lines become congested. In the current imbalanced structure, NKY generation flowed to KY, and price separation occurred when transmission lines become congested during high-demand periods. This typically occurred between 10:00 and 17:00, when demand peaked. Coincidentally, this timeframe corresponded to a period of rapidly increasing solar PV generation, which was predominantly concentrated in the NKY zone. This temporal overlap between high demand and peak solar PV generation resulted in a unique dynamic of zonal pricing. During these hours, while KY's market price was set by the LNG plants, and the NKY's marginal unit shifted to coal plants owing to the influx of solar PV generation. This shift in marginal units within each zone explains the significant price disparity observed in the 2-zonal pricing scheme. In 2023, an exceptionally large gap between coal and LNG fuel costs led to a significant price divergence; however, the magnitude of this effect may vary annually based on fuel costs and changes in the merit order.
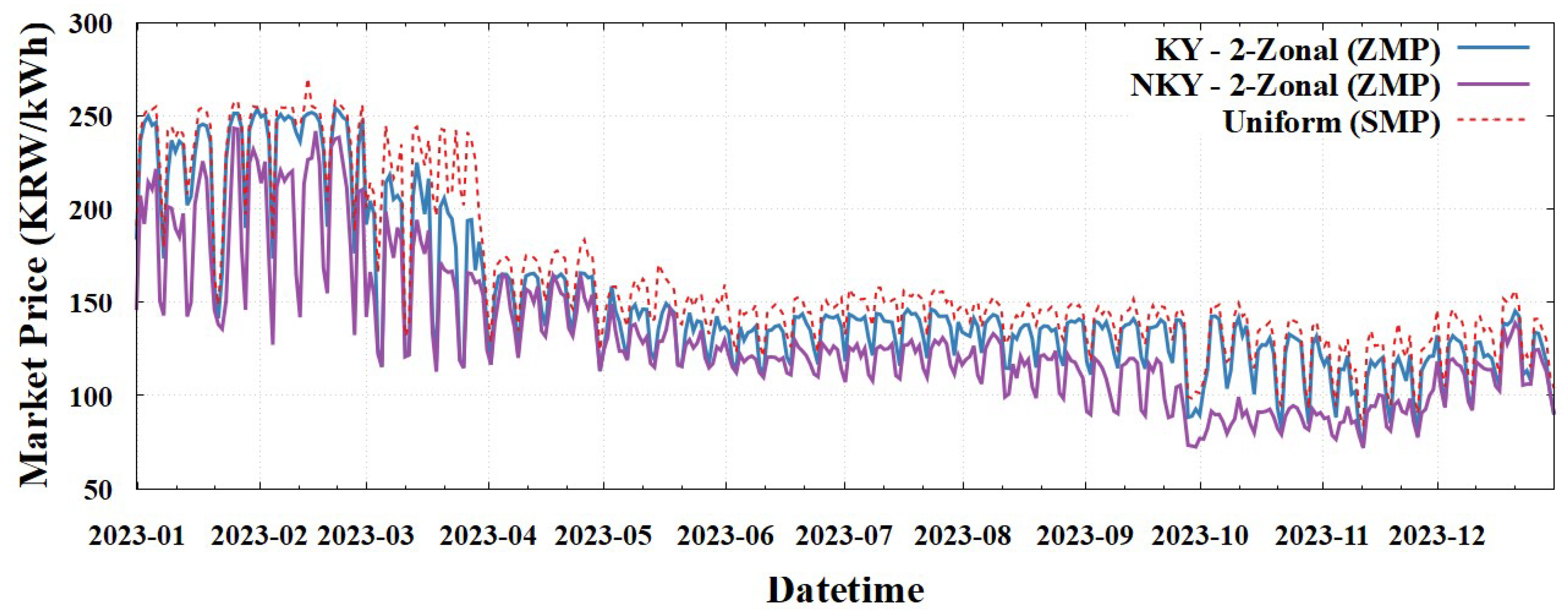
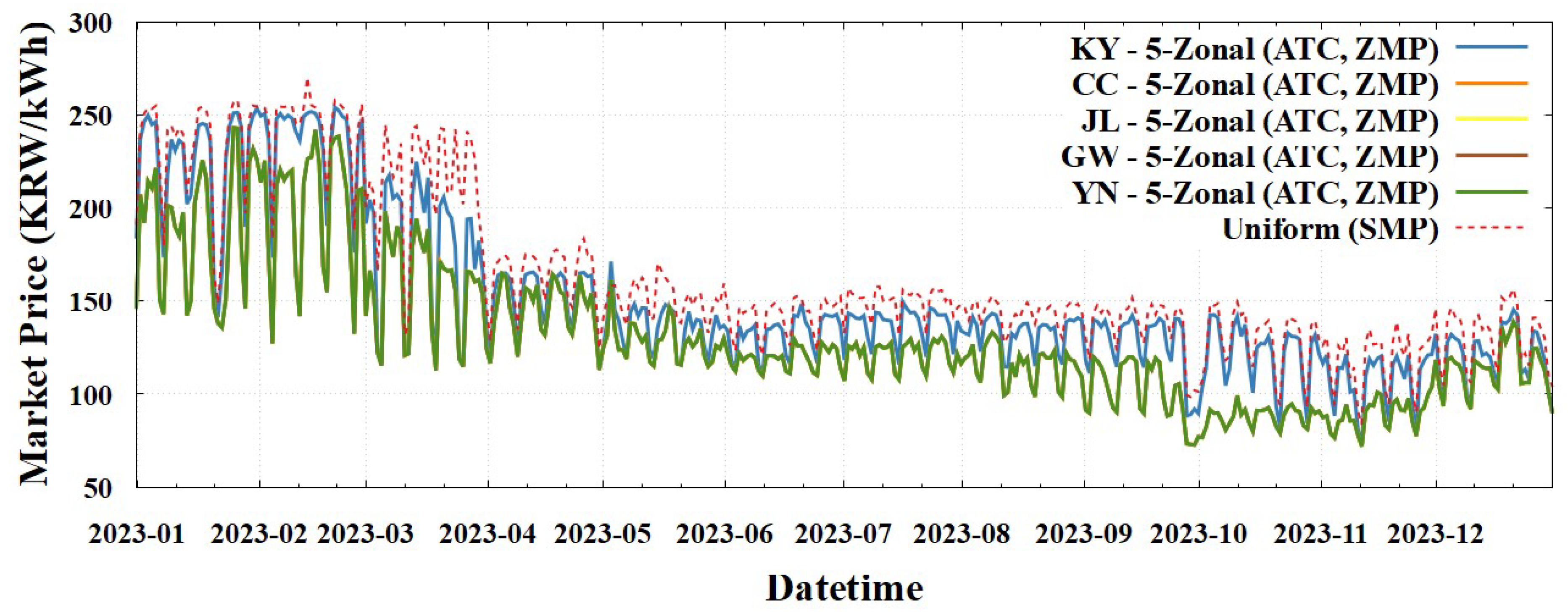
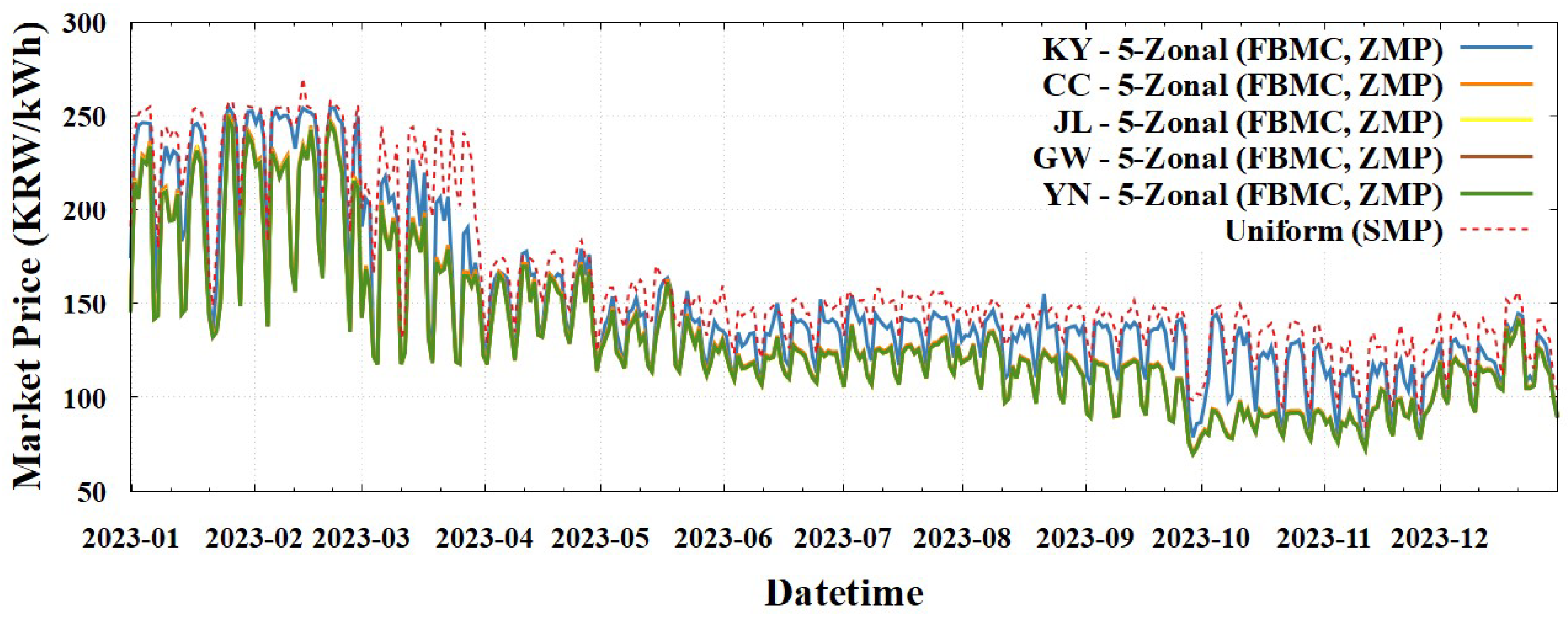
We now examine the market prices resulting from the 5-zonal pricing schemes categorized as 5-Zonal (ATC, ZMP) and 5-Zonal (FBMC, ZMP).
Table 7 presents a comparative analysis of the pricing outcomes across the five designated zones.
Our analysis of the 5-zonal pricing schemes revealed noteworthy insights. As evidenced in
Table 7, the price differentials among the four zones within NKY (CC, JL, KW, YN) were notably small, ranging as 0.81–1.46 KRW/kWh, regardless of application of the 5-Zonal (ATC, ZMP) or 5-Zonal (FBMC, ZMP) scheme. This holds true although the FBMC model, which incorporated the zonal PTDF matrix and marginal loss factors, tended to reflect the network characteristics more accurately than the ATC model. The consistently small price differences across both the schemes indicated to the occurrence of minimal congestion between the four zones within NKY, even when considering more precise network modeling.
By extending this analysis, we observed that the 5-zonal pricing schemes effectively replicated the market price levels of the previously discussed 2-Zonal (ZMP) scheme. This similarity in outcomes can be attributed to two key factors: negligible price differentiation within the NKY zone (discussed earlier) and the persistence of the binding transmission flow constraint between the NKY and KY zones. Essentially, the absence of significant congestion within NKY, coupled with the dominant congestion between NKY and KY, resulted in price patterns that closely mirrored those observed in the simpler 2-Zonal (ZMP).
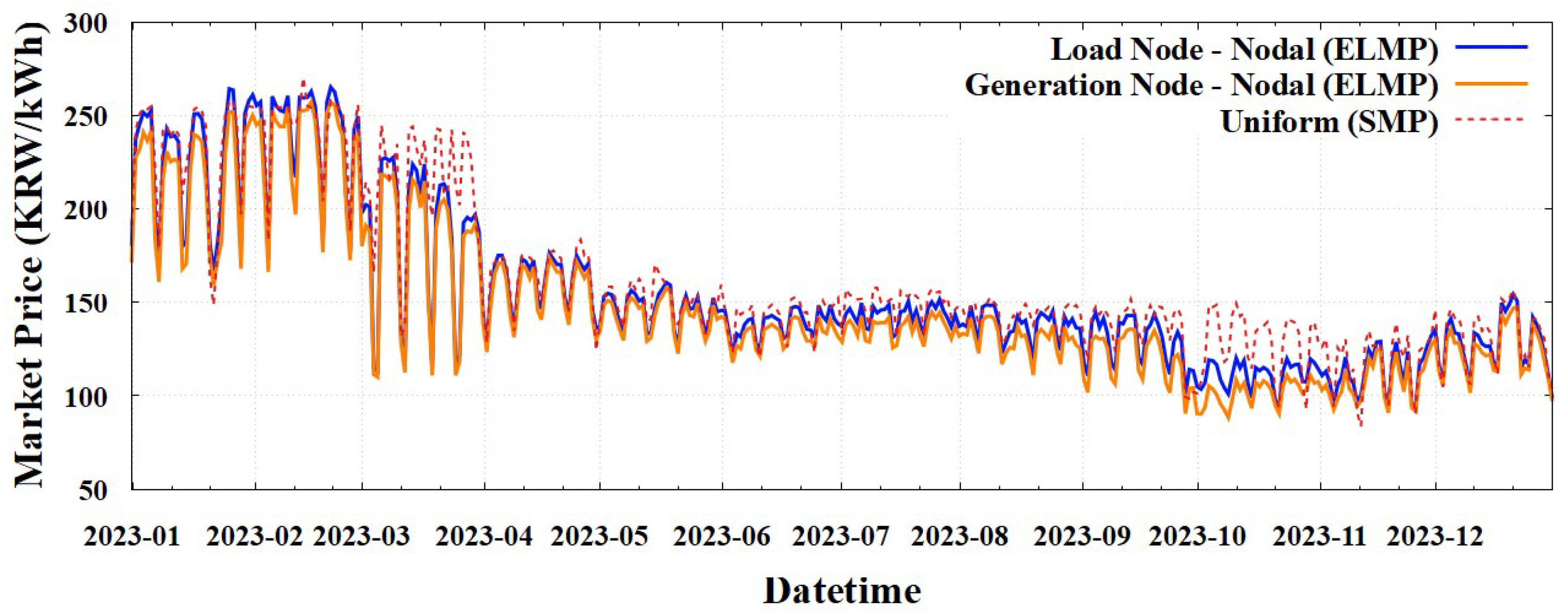
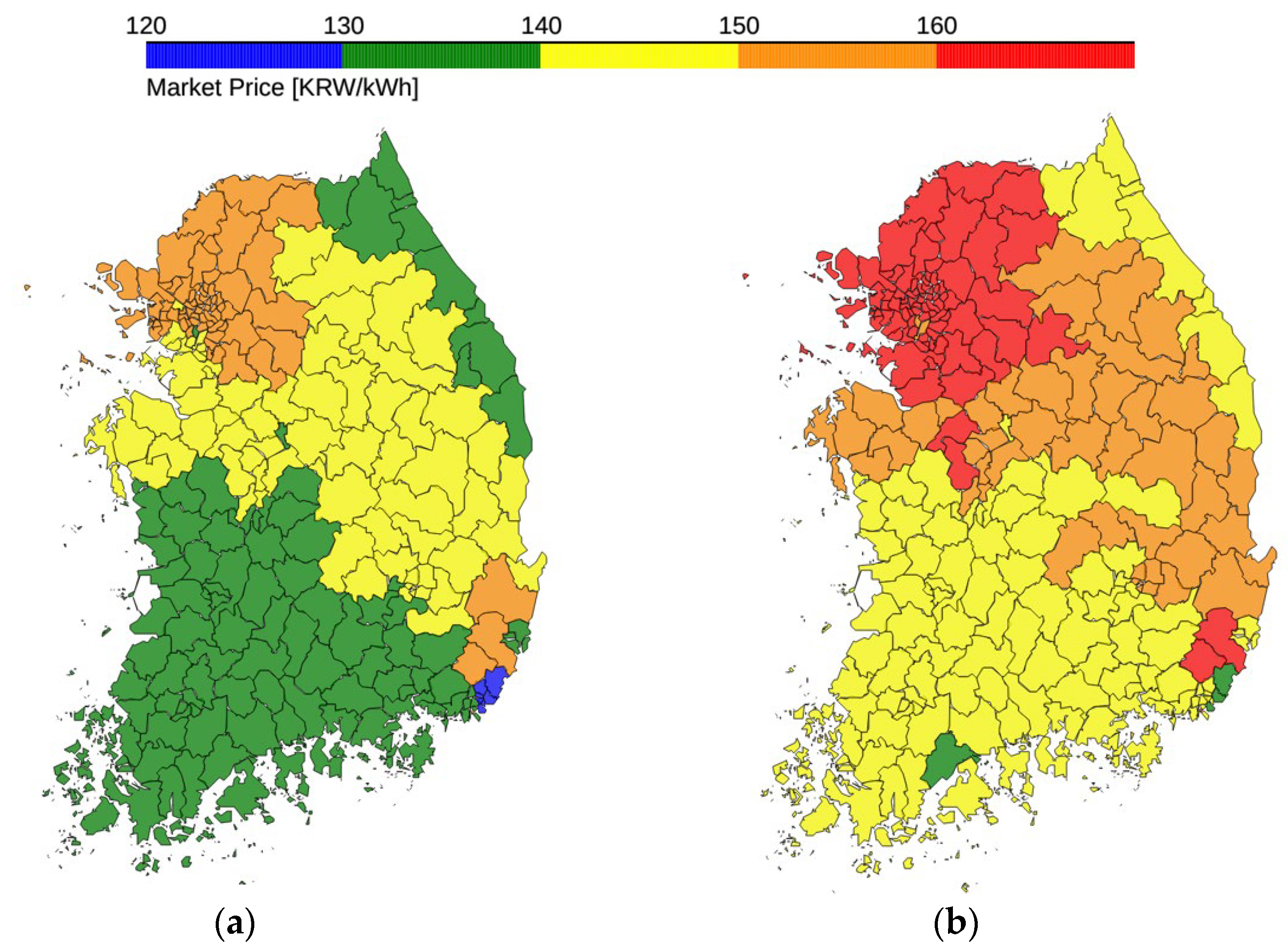
Finally, we present the nodal pricing results, categorized as Nodal (LMP) and Nodal (ELMP), in
Table 8 and
Figure 7.
Table 8 lists the average market prices for the load and generation nodes across the entire Korean power market, calculated as load- and generation-weighted averages, respectively.
Figure 7 offers a visual representation of these weighted average market prices for nodes within each subregional administrative division, providing a detailed geographical perspective on the price distribution under nodal pricing.
Nodal (ELMP) yielded higher prices than Nodal (LMP) because owing to the partial incorporation of the FSR's no-load and start-up costs into market prices based on allowance for their partial commitment. Regardless of the specific nodal pricing scheme, the nodal pricing results maintained the trend observed in zonal pricing, with the KY zone generally exhibiting higher market prices than the NKY zone. Further, the results aligned with the typical expectation that load nodes experienced higher prices than generation nodes owing to transmission losses and network congestion [
41]. Consequently, this detailed nodal pricing reflected the local network constraints and delivery costs across the network, offering precise economic signals for market participants.
Nodal pricing resulted in varied prices across individual nodes, implying that the market prices affecting each generator can vary significantly, in contrast to that in the current uniform pricing system.
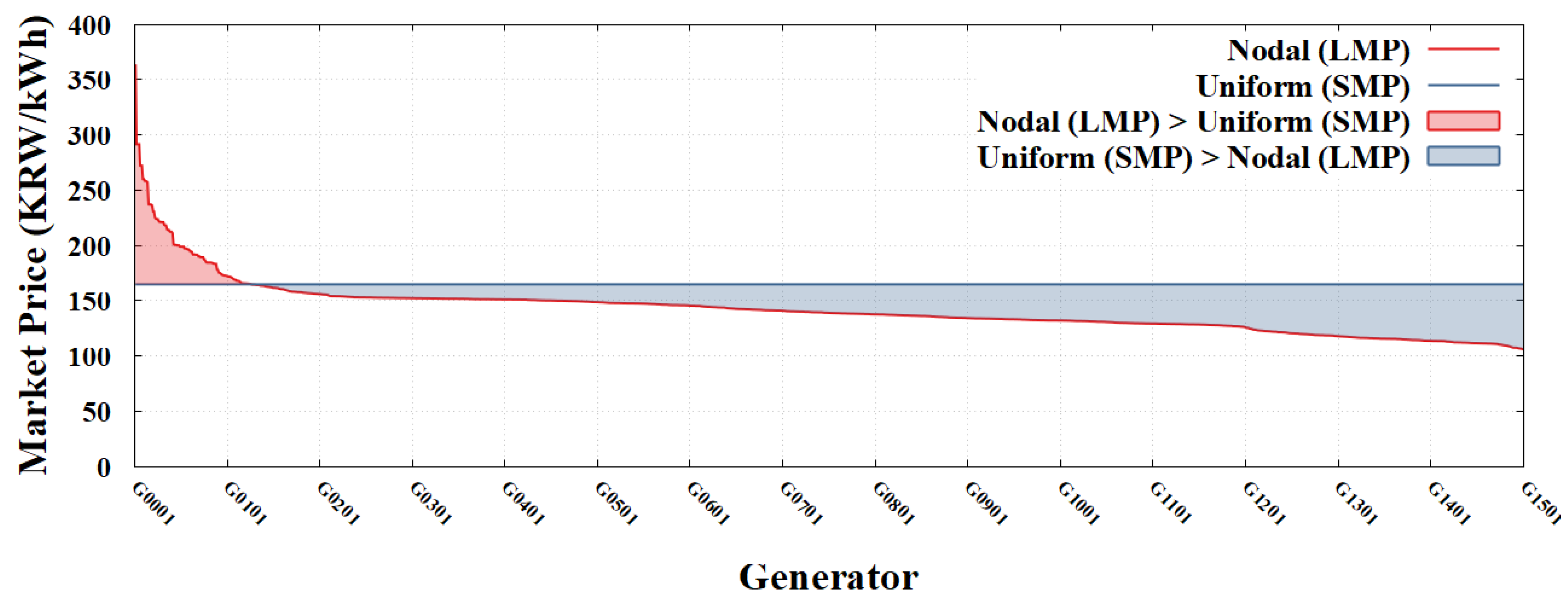
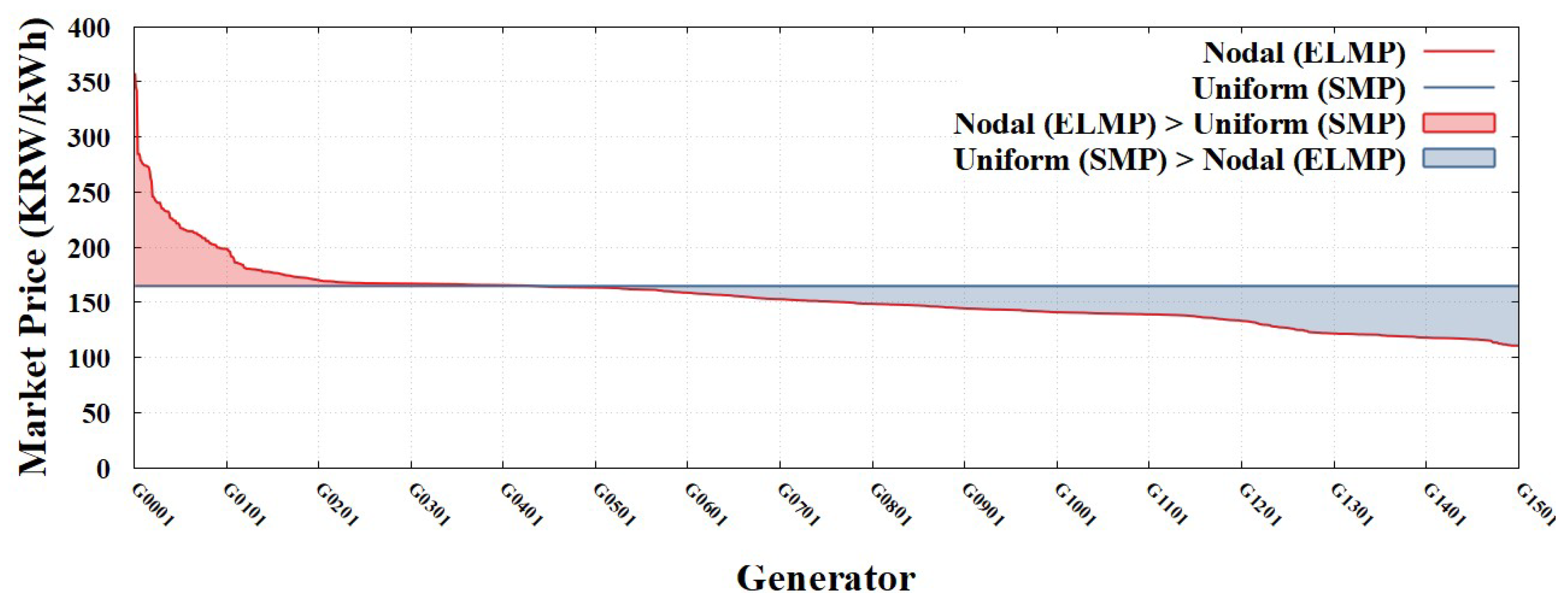
Figure 8 and
Figure 9 compare the market prices that each of the 1,597 generators would receive under the Nodal (LMP) and Nodal (ELMP) pricing schemes, respectively, against the current Uniform (SMP) adopted in the Korean power market. Under Nodal (LMP), 91.7% of the generators exhibited a price drop compared with Uniform (SMP), whereas 71.1% experienced a reduction under Nodal (ELMP). Notably, the Nodal (ELMP) presented here may yield more optimistic outcomes for generators than a standard ELMP implementation, as it assumes a broader range of units qualify as FSRs, leading to higher market prices.
To summarize our findings from the market price analysis:
The market price trend followed the order: Uniform (SMP) > 2-Zonal (SMP) > 2-Zonal (ZMP) ≈ 5-Zonal (ATC, ZMP) ≈ 5-Zonal (FBMC, ZMP).
- 14.
In nodal pricing, which was not directly comparable to uniform and zonal pricing, approximately 71.1–91.7% of the generators faced downside risk under both the Nodal (LMP) and Nodal (ELMP) schemes.
- 15.
On a market-wide level, the average market price was expected to decrease by 4.8–7.0%, even though the 2-Zonal (SMP) and Nodal (ELMP), which compensated for the no-load and start-up costs, exhibited the least price reduction compared to the currently adopted pricing scheme.
- 16.
However, when analyzed at the zonal or granular level, this market price reduction was found to be concentrated among generators in non-capital region.
These results suggest that although the transition to more granular pricing schemes may facilitate overall market price reductions, the impact is likely to be unevenly distributed. The generators in non-capital region are expected to bear a disproportionate share of downside risk. For a more detailed examination of the daily market prices across different pricing schemes, please refer to
Appendix A.
4.3. Financial Impacts for Power Producers and Retailer
Following the calculation of the market prices under each pricing scheme, the power purchase costs, generation costs, revenues, and profits must be quantified to assess the financial impact on power producers and retailer. These quantitative indicators can be calculated using the results of the market-clearing models and the pricing mechanisms described in the previous subsection.
In this study, the single retailer was assumed to purchase electricity at the market price corresponding to its specific area. Accordingly, the retailer’s power purchase cost is defined in Equation (9) as the product of the demand and market price at the respective zone or node, depending on the pricing scheme. The generation costs of the power producers, including fuel and start-up costs, are expressed as Equation (10). Energy revenue is defined in Equation (11) as the product of the market price and generation output determined by the market-clearing model. Furthermore, the MWPs, which compensate for deficits in generation costs, are determined by Equation (12) as the difference between energy revenues and generation costs per hour. Finally, the profit of power producers is expressed in Equation (13) as the sum of the energy revenues and MWPs minus the generation costs. If the generators receive MWPs, their profit during those specific operating hours is zero. The following equations define the calculations:
where
is the market price in area
at time
, and
denotes the market price received by generator
at time
.
Based on these definitions, the comparative financial effects between uniform and zonal pricing and between uniform and nodal pricing, are presented in
Table 9 and
Table 10, respectively. For a more detailed examination of the financial effects across pricing schemes at the zonal level, please refer to
Appendix B.
The results for power purchase costs, energy revenues, and profits followed a trend similar to that of the market prices discussed in the previous section. This trend can be summarized as: Uniform (SMP) > Nodal (ELMP) ≈ 2-Zonal (SMP) > Nodal (LMP) ≈ 5-Zonal (FBMC, ZMP) ≈ 5-Zonal (ATC, ZMP) ≈ 2-Zonal (ZMP). However, the MWP exhibited a trend opposite to that of the market prices. This is because it compensated for deficits in generation costs when energy revenues were insufficient, which resulted in higher MWPs under pricing schemes that yield lower market prices.
An analysis of generation costs revealed that while uniform and zonal pricing exhibited minimal differences, nodal pricing resulted in higher generation costs owing to the additional constraints in more granular representation of the network topology at the node level. However, these results did not consider redispatch costs. If such costs were considered, the opposite trend in the generation costs would likely be observed. In other words, the general consensus is that when the total system costs include both generation costs of the wholesale electricity market and redispatch costs of the balancing market, nodal pricing typically yields the lowest total costs [
1,
2,
25]. The results presented in
Table 9 and
Table 10 differ from this consensus because we excluded the balancing market from our analysis. This limitation of the study is discussed in greater detail in the conclusion section.
4.4. Power Flows
While
Section 4.2 and
Section 4.3 primarily focus on the results dominated by pricing mechanisms, power flow is an aspect strictly related to the market-clearing model. Consequently, the power flows for the Uniform (SMP), 2-Zonal (SMP), and 2-Zonal (ZMP) zones, which shared common market-clearing results, were identical. Within the nodal pricing, Nodal (LMP) and Nodal (ELMP) shared the same market-clearing results. Notably, the power flow resulting from nodal pricing can be considered to align with the actual power flows, that is, power system operations. Only the 5-zonal pricing yielded different market-clearing results depending on whether the ATC or FBMC model was used.
The results for uniform pricing and 2-zonal pricing, which stem from the imbalance between the capital and non-capital regions mentioned in
Table 6, indicated an annual average flow of 11,661 MW from NKY to KY, with transmission congestion occurring for 4,376 hours annually.
Our primary focus was on the 5-zonal pricing.
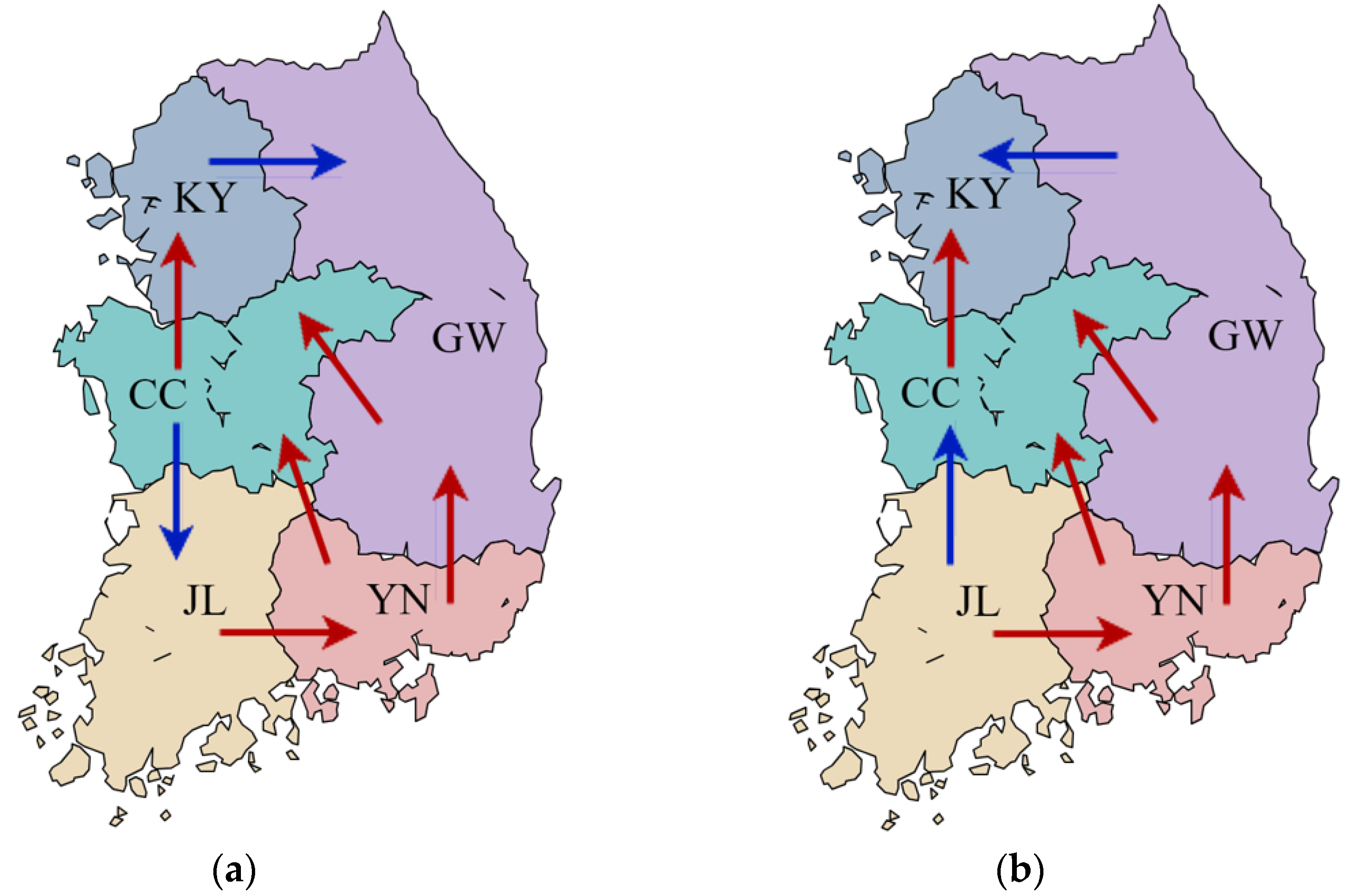
Figure 10 illustrates the power flow between each zone when adopting the ATC and FBMC model in 5-zonal pricing. In
Figure 10, the red lines represent identical flows in the ATC and FBMC models, whereas the blue lines indicate different flows. Specifically, the flows differed in the two transmission lines: KY→GW and CC→JL.
Table 11 presents the annual average power flow and congestion hours between the zones. To compare the results of the 5-zonal pricing with the actual power flows, we must consider that the actual power flows were derived from nodal pricing. Therefore, for a direct comparison with the 5-zonal pricing, we aggregated the power flow results from nodal pricing into the zones defined in the 5-zonal pricing scheme. The aggregated results, reflecting the zonal grouping of power flows from the nodal pricing, are presented in
Table 11 for comparison.
Two significant implications can be drawn from these results. First, the ATC model, which disregards physical laws, produced interzonal flows that deviated from actual power flows. Consequently, if redispatch, which was not considered in this study, were to be considered, it is anticipated that the ATC model would facilitate a substantial increase in side payments. In contrast, the FBMC model demonstrated reasonable interzonal power flows compared to the actual flows. Although the FBMC model necessitates accompanying processes such as system reduction, it is expected to necessitate less redispatch than the ATC model, which is a commonly observed advantage in previous studies [
25].
Second, this analysis elucidated why the SMP mechanisms could not be applied to 5-zonal pricing in the Korean power system. As illustrated in
Figure 10, Korea's power system forms a loop network. The SMP mechanism is based on the rule of separating market prices when transmission lines between adjacent zones are congested. For instance, consider a scenario where the CC-JL line is congested, necessitating different prices between these two zones. Simultaneously, if the CC-YN and YN-JL lines are not congested, the SMP mechanism would imply that prices in these zones should remain uniform. This creates a logical contradiction, as the CC and JL zones would be required to have both different and identical prices at the same time, making it impossible to adopt the SMP mechanism in the loop network. Consequently, although the SMP mechanism can be applied to radial systems, such as Australia or a 2-zonal pricing in the Korean power system, it is not applicable to such loop systems.
4.5. Impact of Zonal and Nodal Pricing on Transco's Conflicts of Interest in a Combined Transmission-Retail Monopoly
In the current Korean electricity market, the Korea Electric Power Corporation (KEPCO) acts simultaneously as both a Transco, which should remain neutral to maximize social welfare, and a retail monopoly, which is motivated to minimize power purchase costs [
42]. This section investigates the effect of the transition to more granular pricing schemes on the potentially conflicting interests of Transco in this unique structure.
In Korea, certain generation and transmission constraints are incorporated into the market-clearing model to address issues such as equipment overload, transient stability, and voltage stability, as listed in
Table 4. Transco bears significant responsibilities for maintaining power system reliability, including expanding transmission lines, increasing energy storage system (ESS) capacity for grid stabilization, reinforcing reactive power compensation equipment, and maintaining transmission facilities [
43]. If these investments and improvements could alleviate the generation and transmission constraints outlined in
Table 4, a reduction in the generation costs would be anticipated. However, this could paradoxically lead to an increase in power purchase costs, creating a potential conflict of interest for Transco.
To explore this dynamic, we conducted a sensitivity analysis across seven pricing schemes, examining the impact of alleviating generation and transmission constraints. It was assumed that this alleviation resulted from Transco’s efforts to enhance power system reliability. Specifically, we compared the change in generation costs (a proxy for social welfare) to the change in power purchase costs. As presented in
Table 4, although the Korean electricity market typically applies 25 generation and transmission constraints, we simplified our sensitivity analysis to manage the computational load. Instead of analyzing each of the 25 constraints individually, we relaxed all constraints applicable to each zone simultaneously. Further, to reduce computational complexity, we set the MIP gap tolerance to 0.1% in the sensitivity analysis.
Table 12 and
Table 13 present the changes in generation and power purchase costs when the generation and transmission constraints were relaxed for each zone under different pricing schemes. For example, the costs listed for the CC zone reflected the results obtained when only the constraints applicable to the CC zone in
Table 4 were relaxed. The base case represents the generation and power purchase costs when all constraints listed in
Table 4 were applied. The numbers in parentheses indicate the rate of change compared with the base case when the constraints for the applicable zone were relaxed.
As presented in
Table 12 and
Table 13, our analysis revealed that, while generation costs invariably decreased with the relaxation of constraints across all cases, power purchase costs may not necessarily exhibit the same trend. In the currently adopted Uniform (SMP), the power purchase costs remain relatively stable despite the relaxation of generation and transmission constraints, owing to the formation of a single price for the entire wholesale electricity market. Conversely, in the zonal and nodal pricing schemes, we observed cases wherein the purchase costs increased when the generation and transmission constraints were relaxed, particularly evident in the KY, JL, and YN zones. For example, when high-cost generators were subject to must-run constraints with minimum output requirements, these generators typically operated at the lower bound of their constraint, precluding them from setting market prices. In this case, lower-cost generators determined the market price. However, upon relaxation of these constraints, previously uncommitted generators with intermediate marginal costs became economically viable for dispatch. This shift in the merit order resulted in these newly committed units setting the market price, potentially leading to higher market prices in the affected zones or nodes, despite the overall reduction in the generation costs.
This finding has significant implications for the transition to zonal or nodal pricing, particularly for firms with monopolistic structures in transmission and retail. Although we did not consider the costs of improvements made by Transco to enhance power system reliability in this analysis, our results suggest that there may be incentives for a combined Transco-retailer to prioritize addressing the generation and transmission constraints that minimize power purchase costs rather than maximize overall social welfare. This conflict of interest could potentially lead to Transco intentionally delaying certain transmission investments or biasing the prioritization of projects.
Considering these potential conflicts, it may be worth considering having an independent entity assume the role of determining the prioritization and execution of projects related to maintaining power system reliability, such as transmission line expansions, increasing the ESS capacity for grid stability, and reinforcing reactive power compensation equipment. This could help ensure that investment decisions are made with true neutrality, thereby prioritizing overall system efficiency and social welfare.
5. Conclusions
This study quantified the impact and policy implications of transitioning to zonal and nodal pricing in the electricity market, considering South Korea as a case study. We modeled the power system at various levels of granularity, yielding a detailed 4,579-node representation and constructed a comprehensive set of seven pricing schemes that reflected the changes in market-clearing models and pricing mechanisms. Our primary objective was to evaluate the impact of these schemes on large power systems, propose an appropriate pricing transition pathway, identify potential conflicts of interest for Transco, and evaluate the financial impact on market participants and the associated social risks.
Our findings suggest the following policy implications:
Our research indicates that, under the current SMP-based uniform pricing, the schemes causing the least market impact were SMP-based zonal pricing with two bidding zones and ELMP, a specific type of nodal pricing. These results are expected to provide critical guidance for the development of an appropriate pricing transition pathway that aims to implement more granular price signals, while minimizing market disruption. However, on a market-wide level, a price reduction of 4.8–7.0% appears inevitable.
We found no evidence to support a significant transition to a 5-zonal pricing system. Owing to the minimal transmission congestion within the non-capital region, the price differences between zones in this region ranged 0.81–1.46 KRW/kWh. Consequently, all the elements were similar to a ZMP-based zonal pricing with two bidding zones. Moreover, the implementation of a 5-zonal pricing system may necessitate system reduction techniques, and risk-producing power flows that are inconsistent with actual system operations.
When transitioning to nodal pricing, 71.1–91.7% of generators were likely to experience a decrease in their received market prices under both LMP and ELMP mechanisms compared to the current pricing scheme. Moreover, across all the proposed zonal and nodal pricing schemes, market price reductions were found to be significantly concentrated among generators in non-capital regions. This finding suggests that the transition to more granular pricing schemes, while potentially leading to overall price reductions, would likely have an unevenly distributed impact. Here, non-capital generators are expected to bear a disproportionate share of the downside risk.
Consequently, to address these policy implications, Korea's electricity market requires mid- to long-term preparation in the following areas:
For a transition to more granular pricing schemes, our research suggests an appropriate pathway that involves first moving from the current uniform pricing to SMP-based zonal pricing with two bidding zones, and then progressing to ELMP as the final stage. However, there is a critical need to analyze the potential market exit of non-capital region generators owing to revenue structure changes and its subsequent impact on any future capacity market and resource adequacy. To address these challenges, the implementation of a capacity market based on the net cost of new entry (Net CONE) [
44], which considers revenue decline, could reduce the power producers' resistance to the transition to zonal and nodal pricing while improving overall market efficiency and enhancing system reliability.
Considering the loop network of Korea's power system, the maintenance of SMP mechanisms beyond SMP-based zonal pricing with two bidding zones will be limited in the future. Therefore, transitioning from a cost-based pool to a price-bidding system should be considered. Furthermore, in the transition to zonal or nodal pricing, it is imperative to initiate discussions on two critical aspects. The first is the mechanisms for settling the congestion surplus that is expected to arise, such as the implementation of financial transmission rights (FTRs) [
5,
45]. The second is the implementation of more granular retail electricity prices to ensure accurate price signals [
46].
To mitigate potential conflicts of interest for Transco in markets with a monopolistic structure in transmission and retail, it may be beneficial to explore the involvement of an independent entity in prioritizing and executing projects related to power system reliability. This could help ensure that investment decisions are made with impartiality, thereby focusing on overall system efficiency and social welfare rather than aligning with the interests of Transco.
This study had several limitations that provide opportunities for future research. Our analysis focused on the wholesale electricity markets and excluded redispatch costs in the balancing market. Future research incorporating these costs could provide a more comprehensive analysis of pricing transitions. In addition, we defined zones based on administrative districts; however, research on optimal zone delineation is crucial for maximizing social welfare in zonal pricing.
The effectiveness of specific pricing schemes can vary depending on factors such as generation mix, fuel costs, and demand profiles. Therefore, each power market should conduct rigorous simulations to determine the most suitable pricing scheme under specific conditions. Nevertheless, our research offered valuable insights for electricity markets worldwide, considering zonal and nodal pricing transitions by providing a comprehensive analysis of various pricing schemes. This detailed examination provided important guidance for policymakers and stakeholders to navigate the complexities of electricity market reform.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.K.; Methodology, K.K.; Software, K.K.; Validation, K.K., W.K., and H.S.; Formal Analysis, H.O.; Investigation, K.K.; Resources, H.Y. (H. Yun); Data Curation, H.Y. (H. Yoon); Writing – Original Draft Preparation, K.K.; Writing – Review & Editing, H.S. and W.K.; Visualization, K.K.; Supervision, W.K.; Project Administration, W.K.; Funding Acquisition, W.K.
Funding
This work was supported by a Korea Institute of Energy Technology Evaluation and Planning (KETEP) grant funded by the Korean government (MOTIE) (20214000000140, Graduate School of Convergence for Clean Energy Integrated Power Generation). The authors also appreciate financial support from the Ministry of Education of the Republic of Korea and the National Research Foundation of Korea (RS-2023-00242047).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated and/or analyzed in the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request, subject to data-sharing restrictions and confidentiality agreements.
Acknowledgments
All support for this study was provided by author contributions or funding sections.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Appendix A
Figure A1.
Daily market prices under 2-Zonal (SMP) for 2023.
Figure A1.
Daily market prices under 2-Zonal (SMP) for 2023.
Figure A2.
Daily market prices under 2-Zonal (ZMP) for 2023.
Figure A2.
Daily market prices under 2-Zonal (ZMP) for 2023.
Figure A3.
Daily market prices under 5-Zonal (ATC, ZMP) for 2023.
Figure A3.
Daily market prices under 5-Zonal (ATC, ZMP) for 2023.
Figure A4.
Daily market prices under 5-Zonal (FBMC, ZMP) for 2023.
Figure A4.
Daily market prices under 5-Zonal (FBMC, ZMP) for 2023.
Figure A5.
Daily market prices under Nodal (LMP) for 2023.
Figure A5.
Daily market prices under Nodal (LMP) for 2023.
Figure A6.
Daily market prices under Nodal (ELMP) for 2023.
Figure A6.
Daily market prices under Nodal (ELMP) for 2023.
Appendix B
Table B1.
Comparative financial impacts based on zone of uniform and 2-zonal pricing.
Table B1.
Comparative financial impacts based on zone of uniform and 2-zonal pricing.
Pricing Scheme
(KRW billion) |
Uniform (SMP) |
2-Zonal (SMP) |
2-Zonal (ZMP) |
| KY |
NKY |
KY |
NKY |
KY |
NKY |
| Retailer |
Power Purchase Cost |
36,334 |
57,476 |
36,237 |
51,042 |
33,665 |
46,296 |
| Power Producers |
Generation Cost |
16,616 |
22,701 |
16,616 |
22,701 |
16,616 |
22,701 |
| Energy Revenues |
20,276 |
73,629 |
20,226 |
65,336 |
18,598 |
59,827 |
| Make-Whole Payments |
1,041 |
551 |
1,052 |
894 |
1,560 |
1,245 |
| Profit |
4,701 |
51,478 |
4,663 |
43,529 |
3,542 |
38,371 |
Table B2.
Comparative financial impacts based on zone of 5-Zonal (ATC, ZMP).
Table B2.
Comparative financial impacts based on zone of 5-Zonal (ATC, ZMP).
Pricing Scheme
(KRW billion) |
5-Zonal (ATC, ZMP) |
| KY |
CC |
JL |
KW |
YN |
| Retailer |
Power Purchase Cost |
33,677 |
12,713 |
8,728 |
11,932 |
12,935 |
| Power Producers |
Generation Cost |
16,617 |
10,875 |
1,938 |
3,801 |
6,087 |
| Energy Revenues |
18,606 |
15,007 |
11,844 |
18,087 |
14,902 |
| Make-Whole Payments |
1,559 |
493 |
203 |
135 |
414 |
| Profit |
3,549 |
4,626 |
10,109 |
14,421 |
9,229 |
Table B3.
Comparative financial impacts based on zone of 5-Zonal (FBMC, ZMP).
Table B3.
Comparative financial impacts based on zone of 5-Zonal (FBMC, ZMP).
Pricing Scheme
(KRW billion) |
5-Zonal (FBMC, ZMP) |
| KY |
CC |
JL |
KW |
YN |
| Retailer |
Power Purchase Cost |
33,371 |
12,986 |
8,820 |
12,063 |
13,072 |
| Power Producers |
Generation Cost |
16,071 |
11,084 |
2,016 |
3,829 |
6,271 |
| Energy Revenues |
17,940 |
15,541 |
12,047 |
18,301 |
15,260 |
| Make-Whole Payments |
1,638 |
466 |
200 |
128 |
420 |
| Profit |
3,507 |
4,923 |
10,231 |
14,600 |
9,409 |
Notes
| 1 |
In this paper, we use the term "pricing schemes" to refer to broad market structures such as uniform, zonal, and nodal pricing. "Pricing mechanisms," in our context, describe specific methods for calculating market prices within these schemes, including system marginal price (SMP), zonal marginal price (ZMP), locational marginal price (LMP), and extended locational marginal price (ELMP). Although these terms may be used differently elsewhere, we maintain this distinction throughout this paper. |
| 2 |
KY, derived from the Korean term “Kyongin,” encompasses Seoul, Incheon, and Gyeonggi province, while NKY represents the rest of the country. |
| 3 |
These abbreviations are derived from Korean province names. Note that the Gangwon (GW) zone slightly differs from the standard administrative district, incorporating parts of Gyeongbuk province to reflect the distribution of nuclear power plants in the zone. |
| 4 |
The slight increase observed in KY prices under the 2-Zonal (SMP) compared to the Uniform (SMP) is owing to numerical effects from the load-weighted average calculation. |
References
- Ding, F.; Fuller, J.D. Nodal, Uniform, or Zonal Pricing: Distribution of Economic Surplus. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems 2005, 20, 875–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weibelzahl, M. Nodal, Zonal, or Uniform Electricity Pricing: How to Deal with Network Congestion. Frontiers in Energy 2017, 11, 210–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.Q.; Chen, Q.X.; Lin, W.M.; Hong, Y.R.; Xia, Q.; Chen, Z.X.; Wu, Y.; Xin, J.B. Zonal Marginal Pricing Approach Based on Sequential Network Partition and Congestion Contribution Identification. International Journal of Electrical Power and Energy Systems 2013, 51, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuhoff, K.; Barquin, J.; Bialek, J.W.; Boyd, R.; Dent, C.J.; Echavarren, F.; Grau, T.; von Hirschhausen, C.; Hobbs, B.F.; Kunz, F.; et al. Renewable Electric Energy Integration: Quantifying the Value of Design of Markets for International Transmission Capacity. Energy Econ 2013, 40, 760–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Srivastava, S.C.; Singh, S.N. Congestion Management in Competitive Power Market: A Bibliographical Survey. Electric Power Systems Research 2005, 76, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, V.; Martin, A.; Weibelzahl, M.; Zöttl, G. On the Long Run Effects of Market Splitting: Why More Price Zones Might Decrease Welfare. Energy Policy 2016, 94, 453–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.W.; Kim, M.K. Multi-Objective Optimization of Voltage-Stability Based on Congestion Management for Integrating Wind Power into the Electricity Market. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Yun, J.; Ding, T.; Liu, F.; Ju, Y.; Yuan, S. Robust Co-Optimization to Energy and Reserve Joint Dispatch Considering Wind Power Generation and Zonal Reserve Constraints in Real-Time Electricity Markets. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhou, H.; Meng, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhou, M. Multi-Stage Coordinated Planning for Transmission and Energy Storage Considering Large-Scale Renewable Energy Integration. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 6486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, P.; Abid, M.; Adun, H.; Kemena Awoh, D.; Cai, D.; Zaini, J.H.; Bamisile, O. Progress in Energy Storage Technologies and Methods for Renewable Energy Systems Application. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 5626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, H.; Wu, B.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, J.; Zhou, Y.; Meng, Z.; Wu, Z. Synergistic Optimization of Coal Power and Renewable Energy Based on Generalized Adequacy. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 7864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosius, M.; Grimm, V.; Kleinert, T.; Liers, F.; Schmidt, M.; Zöttl, G. Endogenous Price Zones and Investment Incentives in Electricity Markets: An Application of Multilevel Optimization with Graph Partitioning. Energy Econ 2020, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonopoulos, G.; Vitiello, S.; Fulli, G.; Masera, M. Nodal Pricing in the European Internal Electricity Market. Publications Office of the European Union, Luxembourg. 2020.
- Birkett, E. Reforming Australia’s Electricity Market. Policy Exchange, UK. 2021.
- Egerer, J.; Weibezahn, J.; Hermann, H. Two Price Zones for the German Electricity Market — Market Implications and Distributional Effects. Energy Econ 2016, 59, 365–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofgem. Assessment of Locational Wholesale Pricing for GB. UK. 2023.
- Simshauser, P. Renewable Energy Zones in Australia’s National Electricity Market. Energy Econ 2021, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suliman, M.S.; Farzaneh, H. Econometric Analysis of Pricing and Energy Policy Regulations in Japan Electric Power Exchange Spot Market. Clean Eng Technol 2022, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Huang, T.; Conti, S.; Bompard, E. Performance Assessment of Electricity Market Zones Reconfiguration: The Italian Case. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 22nd Mediterranean Electrotechnical Conference, IEEE Melecon 2024, Portugal; 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, H.; Kim, T.H.; Kwag, K.; Kim, W. A Comparative Study of Pricing Mechanisms to Reduce Side-Payments in the Electricity Market: A Case Study for South Korea. Energies 2021, 14, 3395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaleta, M. A Generalized Class of Locational Pricing Mechanisms for the Electricity Markets. Energy Econ 2020, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poyrazoglu, G. Determination of Price Zones during Transition from Uniform to Zonal Electricity Market: A Case Study for Turkey. Energies 2021, 14, 1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, R. Nodal Pricing of Electricity: How Much Does It Cost to Get It Wrong? J Regul Econ 2007, 31, 125–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triolo, R.C.; Wolak, F.A. Quantifying the Benefits of a Nodal Market Design in the Texas Electricity Market. Energy Econ 2022, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarfati, M.; Hesamzadeh, M.R.; Holmberg, P. Production Efficiency of Nodal and Zonal Pricing in Imperfectly Competitive Electricity Markets. Energy Strategy Reviews 2019, 24, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjorndal, E.; Bjorndal, M.H.; Cai, H. Flow-Based Market Coupling in the European Electricity Market-A Comparison of Efficiency and Feasibility. NHH Department of Business and Management Science, Norway. 2018.
- PLEXOS Energy Exemplar. Available online: https://www.energyexemplar.com/plexos (accessed on 18 September 2024).
- Schiro, D.A.; Zheng, T.; Zhao, F.; Litvinov, E. Convex Hull Pricing in Electricity Markets: Formulation, Analysis, and Implementation Challenges. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems 2016, 31, 4068–4075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dicorato, M.; L’Abbate, A.; Minoia, A.; Trovato, M. Pricing Criterions in Presence of Intra- and Inter-Zonal Constraints. Electric Power Systems Research 2003, 66, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zonal and Nodal Representations in ERCOT. Available online: https://www.tdworld.com/grid-innovations/article/20963765/texas-transformed (accessed on 18 September 2024).
- Li, F.; Bo, R. DCOPF-Based LMP Simulation: Algorithm, Comparison with ACOPF, and Sensitivity. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems 2007, 22, 1475–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bichler, M.; Knörr, J.; Maldonado, F. Pricing in Nonconvex Markets: How to Price Electricity in the Presence of Demand Response. Information Systems Research 2023, 34, 652–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, R.P.; Sotkiewicz, P.M.; Hobbs, B.F.; Rothkopf, M.H.; Stewart, W.R. Efficient Market-Clearing Prices in Markets with Nonconvexities. Eur J Oper Res 2005, 164, 269–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MISO. Energy and Operating Reserve Markets Business Practices Manual. US. 2022.
- Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy. The 10th Basic Plan for Long-Term Electricity Supply and Demand. South Korea. 2023. (In Korean).
- EPSIS Electric Power Statistics Information System. Available online: https://epsis.kpx.or.kr/epsisnew/ (accessed on 17 September 2024). (In Korean).
- Bank of Korea. Available online: https://www.bok.or.kr/ (accessed on 6 September 2024). (In Korean).
- Sarfati, M.; Holmberg, P. Simulation and Evaluation of Zonal Electricity Market Designs. Electric Power Systems Research 2020, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldridge, B.; O’neill, R.P.; Castillo, A. Marginal Loss Calculations for the DCOPF. FERC Technical Report on Loss Estimation, US. 2017.
- KPX Korea Power Exchange Homepage. Available online: https://www.kpx.or.kr/ (accessed on 6 September 2024). (In Korean).
- Kirschen, D. S.; Strbac, G. Fundamentals of Power System Economics, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, 2018.
- Lee, B.H.; Ahn, H.H. Electricity Industry Restructuring Revisited: The Case of Korea. Energy Policy 2006, 34, 1115–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prandini, A. Good, BETTA, Best? The Role of Industry Structure in Electricity Reform in Scotland. Energy Policy 2007, 35, 1628–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Zheng, T.; Litvinov, E. Constructing Demand Curves in Forward Capacity Market. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems 2017, 33, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunz, F.; Rosellón, J.; Kemfert, C. Introduction of Nodal Pricing into the New Mexican Electricity Market through FTR Allocations. Energy Journal 2017, 38, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borenstein, S.; Bushnell, J. The US Electricity Industry after 20 Years of Restructuring. Annual Reviews of Economics 2015, 7, 437–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Comparison of (
a) zonal and (
b) nodal representations in ERCOT [
30].
Figure 1.
Comparison of (
a) zonal and (
b) nodal representations in ERCOT [
30].
Figure 2.
SCUC, SCED, and SCED-pricing procedure in MISO.
Figure 2.
SCUC, SCED, and SCED-pricing procedure in MISO.
Figure 3.
Proposed bidding zone configurations for zonal pricing in the Korean power system: (a) two bidding zones and (b) five bidding zones.
Figure 3.
Proposed bidding zone configurations for zonal pricing in the Korean power system: (a) two bidding zones and (b) five bidding zones.
Figure 4.
Simplified visualization of the Korean power system (345 kV and above).
Figure 4.
Simplified visualization of the Korean power system (345 kV and above).
Figure 5.
Comparison of daily simulated Uniform (SMP) and actual market prices for 2023.
Figure 5.
Comparison of daily simulated Uniform (SMP) and actual market prices for 2023.
Figure 6.
Annual hourly average solar PV generation and market price gap between KY and NKY zones under the 2-Zonal (SMP).
Figure 6.
Annual hourly average solar PV generation and market price gap between KY and NKY zones under the 2-Zonal (SMP).
Figure 7.
Geographical distribution of nodal prices in the Korean power system: (a) Nodal (LMP) and (b) Nodal (ELMP).
Figure 7.
Geographical distribution of nodal prices in the Korean power system: (a) Nodal (LMP) and (b) Nodal (ELMP).
Figure 8.
Comparison of Nodal (LMP) and Uniform (SMP) prices for individual generators.
Figure 8.
Comparison of Nodal (LMP) and Uniform (SMP) prices for individual generators.
Figure 9.
Comparison of Nodal (ELMP) and Uniform (SMP) prices for individual generators.
Figure 9.
Comparison of Nodal (ELMP) and Uniform (SMP) prices for individual generators.
Figure 10.
Comparison of interzonal power flows of (a) 5-Zonal (ATC, ZMP) and (b) 5-Zonal (FBMC, ZMP).
Figure 10.
Comparison of interzonal power flows of (a) 5-Zonal (ATC, ZMP) and (b) 5-Zonal (FBMC, ZMP).
Table 1.
Overview of electricity market operation.
Table 1.
Overview of electricity market operation.
| Market-Clearing Models |
Pricing Mechanisms |
| Objective Function |
Minimize the total system cost or maximize social welfare |
LMP
ZMP
ELMP
SMP |
| Constraints |
Generator output limits
Generator ramp rate constraints
Generator minimum up and down time requirements
Power balance constraints
Transmission flow constraints
Other system operational constraints |
Table 2.
Overview of proposed pricing schemes.
Table 2.
Overview of proposed pricing schemes.
| Category |
Transmission Flow Models |
Pricing Mechanisms |
Pricing Schemes |
| To-Be |
Nodal Pricing |
DC-OPF |
LMP |
Nodal (LMP) |
| ELMP |
Nodal (ELMP) |
| 5-Zonal Pricing |
FBMC |
ZMP |
5-Zonal (FBMC, ZMP) |
| ATC |
5-Zonal (ATC, ZMP) |
| 2-Zonal Pricing |
ATC |
ZMP |
2-Zonal (ZMP) |
| SMP |
2-Zonal (SMP) |
| As-Is |
Uniform Pricing |
ATC |
SMP |
Uniform (SMP) |
Table 3.
Summary of generator data.
Table 3.
Summary of generator data.
| Category |
Installed Capacity (MW) |
Average Generation Costs (KRW/kWh) |
Average Annual Maintenance Days |
| Nuclear |
25,782 |
6.37 |
70 |
| Coal |
37,934 |
101.11 |
42 |
| LNG |
49,061 |
180.01 |
28 |
| Oil |
112 |
330.18 |
42 |
| Hydropower |
1,484 |
0 |
0 |
| Pumped Storage |
4,700 |
0 |
35 |
| Solar PV |
26,652 |
0 |
0 |
| Wind |
2,214 |
0 |
0 |
| Other Renewables |
2,448 |
0 |
0 |
Table 4.
Summary of generation and transmission constraints.
Table 4.
Summary of generation and transmission constraints.
| Category |
Applicable Zone |
Constraint Type |
| Transmission Constraints |
NKY-KY |
Maintain total power flow below a stricter limit (1) |
| JL-CC |
Maintain total power flow below a stricter limit (1) |
| Generation Constraints |
KY |
Must-run (6)
Must-run with minimum output (1) |
| YD |
Conditional shutdown (1)
Maximum output limit (1) |
| JL |
Must-run (3)
Maximum output limit (1) |
| CC |
Must-run (1)
Maximum output limit (5) |
| YN |
Must-run (2)
Minimum output limit (2) |
Table 5.
Comparison of market prices under Uniform (SMP) and 2-zonal pricing schemes.
Table 5.
Comparison of market prices under Uniform (SMP) and 2-zonal pricing schemes.
| Pricing Scheme |
Uniform (SMP) |
2-Zonal (SMP) |
2-Zonal (ZMP) |
| KY |
NKY |
KY |
NKY |
| Market Price (KRW/kWh) |
164.75 |
164.76 |
146.05 |
153.07 |
132.47 |
Table 6.
Regional distribution of electricity demand and generation.
Table 6.
Regional distribution of electricity demand and generation.
| Category |
Capital (KY) |
Non-Capital (NKY) |
| Demand (TWh) |
219.9 (38.6%) |
349.5 (61.4%) |
| Generation (TWh) |
118.3 (20.1%) |
455.0 (79.9%) |
Table 7.
Comparison of market prices under 5-zonal pricing schemes.
Table 7.
Comparison of market prices under 5-zonal pricing schemes.
| Market Price (KRW/kWh) |
KY |
CC |
JL |
KW |
YN |
| 5-Zonal (ATC, ZMP) |
153.12 |
132.27 |
132.44 |
133.06 |
132.25 |
| 5-Zonal (FBMC, ZMP) |
151.73 |
135.12 |
133.85 |
134.52 |
133.66 |
Table 8.
Comparison of market prices under nodal pricing schemes.
Table 8.
Comparison of market prices under nodal pricing schemes.
| Pricing Scheme |
Nodal (LMP) |
Nodal (ELMP) |
| Node Type |
Load |
Generation |
Load |
Generation |
| Market Price (KRW/kWh) |
144.38 |
138.45 |
156.84 |
149.82 |
Table 9.
Comparative financial impacts of uniform and zonal pricing.
Table 9.
Comparative financial impacts of uniform and zonal pricing.
Pricing Scheme
(KRW billion) |
Uniform (SMP) |
Zonal Pricing |
| 2-Zonal (SMP) |
2-Zonal (ZMP) |
5-Zonal (ATC, ZMP) |
5-Zonal (FBMC, ZMP) |
| Retailer |
Power Purchase Cost |
93,810 |
87,279 |
79,962 |
79,984 |
80,313 |
| Power Producers |
Generation Cost |
39,317 |
39,317 |
39,317 |
39,317 |
39,271 |
| Energy Revenues |
93,905 |
85,562 |
78,425 |
78,446 |
79,088 |
| Make-Whole Payments |
1,592 |
1,947 |
2,805 |
2,805 |
2,853 |
| Profit |
56,179 |
48,191 |
41,913 |
41,934 |
42,670 |
Table 10.
Comparative financial impacts of uniform and nodal pricing.
Table 10.
Comparative financial impacts of uniform and nodal pricing.
Pricing Scheme
(KRW billion) |
Uniform (SMP) |
Nodal Pricing |
| Nodal (LMP) |
Nodal (ELMP) |
| Retailer |
Power Purchase Cost |
93,810 |
81,739 |
88,795 |
| Power Producers |
Generation Cost |
39,317 |
40,863 |
40,863 |
| Energy Revenues |
93,905 |
79,374 |
85,923 |
| Make-Whole Payments |
1,592 |
2,940 |
2,064 |
| Profit |
56,179 |
41,451 |
47,123 |
Table 11.
Comparison of annual average power flows and congestion hours between zones in 5-zonal pricing and aggregated nodal pricing results.
Table 11.
Comparison of annual average power flows and congestion hours between zones in 5-zonal pricing and aggregated nodal pricing results.
| Pricing Scheme |
5-Zonal (ATC, ZMP) |
5-Zonal (FBMC, ZMP) |
Nodal Pricing |
| Average Flow (MW) |
Congestion Hours (h) |
Average Flow (MW) |
Congestion Hours (h) |
Average Flow (MW) |
Congestion Hours (h) |
| KY→GW |
4,423 |
4,374 |
-4,491 |
3,665 |
-5,619 |
1,457 |
| CC→KY |
16,083 |
4,374 |
7,615 |
3,665 |
6,947 |
1,457 |
| GW→CC |
14,996 |
5,275 |
2,347 |
0 |
1,697 |
0 |
| CC→JL |
1,814 |
8,083 |
-2,865 |
431 |
-2,280 |
86 |
| JL→YN |
4,802 |
568 |
166 |
1 |
34 |
0 |
| YN→CC |
875 |
8,612 |
184 |
2 |
174 |
0 |
| YN→GW |
5,065 |
0 |
1,310 |
0 |
1,691 |
0 |
Table 12.
Generation and power purchase cost sensitivity to generation and transmission constraint relaxation in uniform and zonal pricing.
Table 12.
Generation and power purchase cost sensitivity to generation and transmission constraint relaxation in uniform and zonal pricing.
Pricing Scheme
(KRW billion) |
Uniform (SMP) |
2-Zonal (SMP) |
2-Zonal (ZMP) |
5-Zonal (ATC, ZMP) |
5-Zonal (FBMC, ZMP |
| Base Case |
Generation Cost |
39,329 |
39,329 |
39,329 |
39,328 |
39,282 |
| Purchase Cost |
94,033 |
87,512 |
80,593 |
80,539 |
80,727 |
| KY |
Generation Cost |
38,586
(-1.89%) |
38,586
(-1.89%) |
38,586
(-1.89%) |
38,587
(-1.88%) |
38,221
(-2.70%) |
| Purchase Cost |
89,797
(-4.50%) |
89,797
(+2.61%) |
82,412
(+2.26%) |
82,459
(+2.38%) |
75,054
(-7.03%) |
| CC |
Generation Cost |
38,346
(-2.50%) |
38,346
(-2.50%) |
38,346
(-2.50%) |
38,345
(-2.50%) |
39,118
(-0.42%) |
| Purchase Cost |
92,232
(-1.91%) |
82,453
(-5.78%) |
75,148
(-6.76%) |
75,221
(-6.60%) |
81,229
(+0.62%) |
| JL |
Generation Cost |
39,160
(-0.43%) |
39,160
(-0.43%) |
39,160
(-0.43%) |
39,158
(-0.43%) |
38,662
(-1.58%) |
| Purchase Cost |
93,836
(-0.21%) |
87,572
(+0.07%) |
80,843
(+0.31%) |
81,111
(+0.71%) |
82,798
(+2.57%) |
| KW |
Generation Cost |
39,223
(-0.27%) |
39,223
(-0.27%) |
39,223
(-0.27%) |
39,222
(-0.27%) |
39,169
(-0.29%) |
| Purchase Cost |
93,709
(-0.34%) |
86,759
(-0.86%) |
79,823
(-0.96%) |
79,794
(-0.93%) |
79,929
(-0.99%) |
| YN |
Generation Cost |
39,022
(-0.78%) |
39,022
(-0.78%) |
39,022
(-0.78%) |
39,021
(-0.78%) |
38,983
(-0.76%) |
| Purchase Cost |
94,046
(+0.01%) |
88,422
(+1.04%) |
81,522
(+1.15%) |
81,448
(+1.13%) |
81,669
(+1.17%) |
Table 13.
Generation and power purchase cost sensitivity to generation and transmission constraint relaxation in nodal pricing.
Table 13.
Generation and power purchase cost sensitivity to generation and transmission constraint relaxation in nodal pricing.
Pricing Scheme
(KRW billion) |
Nodal (LMP) |
Nodal (ELMP) |
| Base Case |
Generation Cost |
40,863 |
40,863 |
| Purchase Cost |
81,739 |
88,795 |
| KY |
Generation Cost |
40,510
(-0.86%) |
40,510
(-0.86%) |
| Purchase Cost |
83,914
(+2.66%) |
87,799
(-1.12%) |
| CC |
Generation Cost |
39,596
(-3.10%) |
39,596
(-3.10%) |
| Purchase Cost |
75,449
(-7.70%) |
81,976
(-7.68%) |
| JL |
Generation Cost |
40,702
(-0.39%) |
40,702
(-0.39%) |
| Purchase Cost |
81,736
(-0.00%) |
87,527
(-1.43%) |
| KW |
Generation Cost |
40,755
(-0.26%) |
40,755
(-0.26%) |
| Purchase Cost |
81,037
(-0.86%) |
88,560
(-0.26%) |
| YN |
Generation Cost |
40,632
(-0.57%) |
40,632
(-0.57%) |
| Purchase Cost |
82,510
(+0.94%) |
93,886
(+5.73%) |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).