1. Introduction
In today’s digital age, the sharing of data in agri-food supply chains is pivotal for fostering sustainable practices within the agri-food industry. It enables the development of smarter decision-support systems, leading to optimized resource management, increased productivity, and reduced environmental impact [
1]. Furthermore, data sharing fosters transparency and accountability, empowering consumers to make informed choices about agri-food products they purchase. This transparency, along with data-driven decision-making across the sector, is also the key to unlocking the full potential of the agri-food sector in addressing climate change and food security challenges [
2,
3]. Recent rapid technological developments, particularly in artificial intelligence, promise further progress in these areas, provided there is seamless and granular access to high-quality data on operations in agri-food chains [
4].
Despite the growing need for data-driven solutions, data sharing and data use in agri-food chains remain limited [
5]. Efforts to build a data-centric agri-food economy have intensified in recent years; however, farmers have not been meaningfully included in data governance structures, which has led to less participatory and less effective data-sharing ecosystems [
6]. This exclusion extends beyond farmers, as many small agri-food businesses and processing companies also remain at the fringes of data exchange ecosystems. These challenges are primarily driven by barriers such as lack of digital infrastructure, financial constraints, power imbalances in data control, and behavioral factors such as mistrust, data privacy concerns, and reluctance to engage with new technologies [
7,
8]. It is therefore imperative that we gain a deeper understanding of the diverse needs, expectations, motivations of various stakeholders, as well as their concerns, regarding the sharing, exchange, and use of agri-food data. Such an understanding is essential for fostering collaboration and creating more efficient and effective data-sharing mechanisms that enable informed decision-making across the agri-food sector.
The aim of this study is to investigate the perspectives of market actors in the upstream agri-food chain – from farm to transport and packaging – on data sharing for traceability and transparency-oriented digital systems accessible to both government agencies and the wider public. The limited participation of these actors in data-sharing initiatives has hindered progress; yet sharing primary production data from these segments remains crucial for enhancing overall supply chain performance and enabling reliable, comprehensive sustainability reporting [
9,
10]. Based on a national 2-year pilot for digital food passports, a system designed to digitally track food products from production to consumption, this investigation highlights the views and preferences of stakeholders involved in the upstream agri-food supply chains of three Polish markets – beef, pork, and potato – regarding agri-food data sharing. It will explore their perceived benefits and incentives, as well as barriers and concerns that hinder their participation in multi-actor data-sharing initiatives. The study also aims to understand their willingness to cooperate to foster more sustainable practices through information exchange and data disclosure. Our study seeks to address the following research questions:
What are the key motivating factors and barriers influencing farmers and other market actors’ willingness to share production and other data in agri-food chains?
What role does sustainability play in stakeholders’ motivations to share data within the agri-food chains?
Understanding the interplay of motivational drivers and barriers to data sharing is essential for designing initiatives that effectively promote transparency and sustainability. The findings of this work will therefore offer practical insights to guide the development of policies and interventions aimed at fostering data sharing and collaboration in agri-food chains, both in Poland and beyond.
2. Theoretical Background
A diverse set of theoretical frameworks has been used to analyze and explain the complexities of data sharing in supply chains, including transaction cost economics, behavioral economics, contingency theory, resource-based view, resource dependency theory, and relational governance theories such as social networks, social exchange and the theory of planned behaviour [
11,
12,
13,
14,
15]. These theoretical perspectives help to better understand various aspects of information and data sharing, including the motivations behind sharing, building blocks of the data sharing ecosystem, the types of information and data exchanged, and the impact of different factors on data sharing practices. In the context of the agri-food sector, theoretical frameworks centered around socio-technical systems, relational governance and sustainability have been frequently employed to analyze the various factors influencing agri-food data sharing [
9,
16,
17,
18,
19].
Our theoretical approach focuses on a set of factors that influence market actors’ decisions to participate in data sharing initiatives aimed at providing transparency through systems accessible to the public. Unlike prior research that predominantly focused on factors affecting bilateral data-sharing within smart farming systems, we broaden the scope to include the influence of public perception and the strategic presentation of data to external stakeholders such as government bodies and consumers. By doing so, we aim to capture additional motivational factors and barriers that arise when data sharing extends beyond traditional supply chain partnerships or obligatory data reporting in closed ecosystems.
Existing research consistently points to the crucial role of trust as a foundation for successful data exchange in the agri-food sector [
7,
20,
21,
22]. Clear communication, transparency, and leveraging pre-existing trust networks are essential for fostering data-sharing behavior [
23]. Since the digital economy relies on extensive and automated data exchange, trust in the security and proper handling of shared data is indispensable [
15,
24]. Empirical evidence shows however that actual trust levels in the agri-food sector, particularly towards data collectors and technology providers, are still quite low. This low trust is especially pronounced among farmers who perceive the agricultural data economy as a system that primarily benefits other stakeholders, potentially at their own expense [
16,
24]. Farmers’ reluctance stems from concerns that data sharing could compromise their privacy and worsen existing power imbalances within the supply chain, enabling entities with substantial resources to capture a disproportionate share of the value generated by agricultural activities. Furthermore, farmers are wary of losing control over their data and the possibility that technology providers might dominate crucial aspects of agricultural operations [
7,
8,
25]. Similarly, concerns persist that data collection by government agencies and public authorities may intensify regulatory burdens and oversight, potentially leading to heightened scrutiny and enforcement and potential invasions of privacy [
17]. Agri-food processing companies have also expressed numerous concerns, particularly that disclosing too much data could expose sensitive details about their operations and production processes, potentially creating a competitive disadvantage [
24].
Research suggests that a clear value proposition and vision of tangible benefits resulting from data sharing should be communicated effectively to engage stakeholders [
17]. Perceived benefits, such as improved efficiency, smoother operations, access to new markets, and increased sales and profitability, have been found to be crucial in encouraging data sharing. Identifying value streams arising from data sharing with active user involvement has also been recommended to ensure that these benefits align with the actual needs and expectations of stakeholders [
19]. At the system level, increased data sharing and collaboration within agri-food chains can lead to optimized resource management, greater transparency and traceability, waste reduction, and comprehensive emissions tracking, and ultimately, improved sustainability [
26,
27,
28]. Yet, while these benefits are well documented at the aggregate level, they may not be easily recognized at the level of individual producers or farms. In addition, empirical findings indicate that stakeholders may be hesitant to share certain data categories, despite their significant potential to improve sustainability and deliver public goods [
7].
Stakeholders’ decisions to engage in data sharing are strongly influenced by relational factors such as the strength of network ties, structural elements like the data-sharing model, and external considerations including legal frameworks, regulatory incentives, and perceived risks [
23,
29,
30]. In networks where cooperation and shared norms are strong, observing others’ participation can encourage data-sharing behaviors [
31]. Also, when data is shared among select and trusted parties, as e.g. in private data-sharing platforms or industry consortia, concerns over privacy and data misuse may be less pronounced than in open, multi-actor or transparency-oriented systems that make data accessible to a wider audience [
32]. Furthermore, regulatory incentives that link data sharing to sustainability compliance can motivate stakeholders to participate, as adherence to these standards helps in accessing new markets and enhances stakeholders’ competitiveness and resilience [
33]. On the other hand, the fear of reputational damage can fuel selective data disclosure, creating a reluctance to share data that might be perceived negatively by the public, even if it could yield valuable insights when shared and analyzed collectively [
29,
34]. Particularly in consumer-targeted systems, stakeholders may prioritize sharing information that enhances their market reputation, avoiding disclosures that could trigger public overreactions damaging their image [
35].
Due to the complex interplay of socio-economic and behavioral factors influencing data sharing, researchers and sectoral experts emphasize the need for implementing specific governance mechanisms and technical approaches to support and facilitate agri-food data sharing and utilization [
8]. Specifically, ensuring data security, privacy, transparency, and control over data flows – collectively known as data sovereignty – have been found critical for building trust and fostering participation in data exchanges [
23]. In the European Union context, the emphasis on trust and appropriate legal, organizational and technical frameworks has paved the way for the establishment of independent data intermediaries, alongside the concept of data spaces [
34]. This framework now serves as a key tool for efficient data exchange across organizations and sectors, with data sovereignty – the authority and control over data, including decisions on how it is accessed, used, and shared – as its foundational principle. Within the agri-food sector specifically, the literature highlights several key technological enablers for creating such trusted and effective environments for data sharing initiatives. These include semantic web technologies, privacy-preserving frameworks, security-enhanced distributed ledger technologies, blockchain-based approaches, and federated machine learning [
36,
37,
38].
Nevertheless, the willingness and readiness of agri-food stakeholders to adopt digital technologies and participate in data collaboration frameworks are contingent upon addressing a range of organizational and technical challenges [
39]. Unstable contractual relationships and fragmentation within agri-food supply chains discourage investment in shared data platforms. Moreover, merely accessing and utilizing such platforms requires significant upfront technology investments and ongoing maintenance costs, which exceed the financial capabilities of smaller actors [
40]. Additionally, the agri-food sector still lags behind in terms of digital infrastructure and ensuring data interoperability, which not only raises costs but also makes the benefits of data sharing less apparent. The lack of institutionalized information exchange standards and prevailing uncertainties regarding costs and return on investment further complicate collaboration efforts [
26,
41]. Furthermore, limited digital skills among stakeholders often result in the underutilization of available digital solutions and functionalities, as they are perceived as either ill-suited to their needs or overly complex [
42]. In light of these challenges, a number of studies and international reports have advocated for concerted actions by the public and private sectors to develop open data standards, invest in secure and interoperable data infrastructure, and provide financial and technical support to under-resourced actors in the agri-food sector [
6,
26,
43,
44,
45,
46]. Furthermore, studies highlight the importance of capacity building, training and educational programs aimed at both enhancing data management skills among stakeholders and ensuring equitable access to these technologies, as vital components for the success of data sharing initiatives [
7,
8,
21].
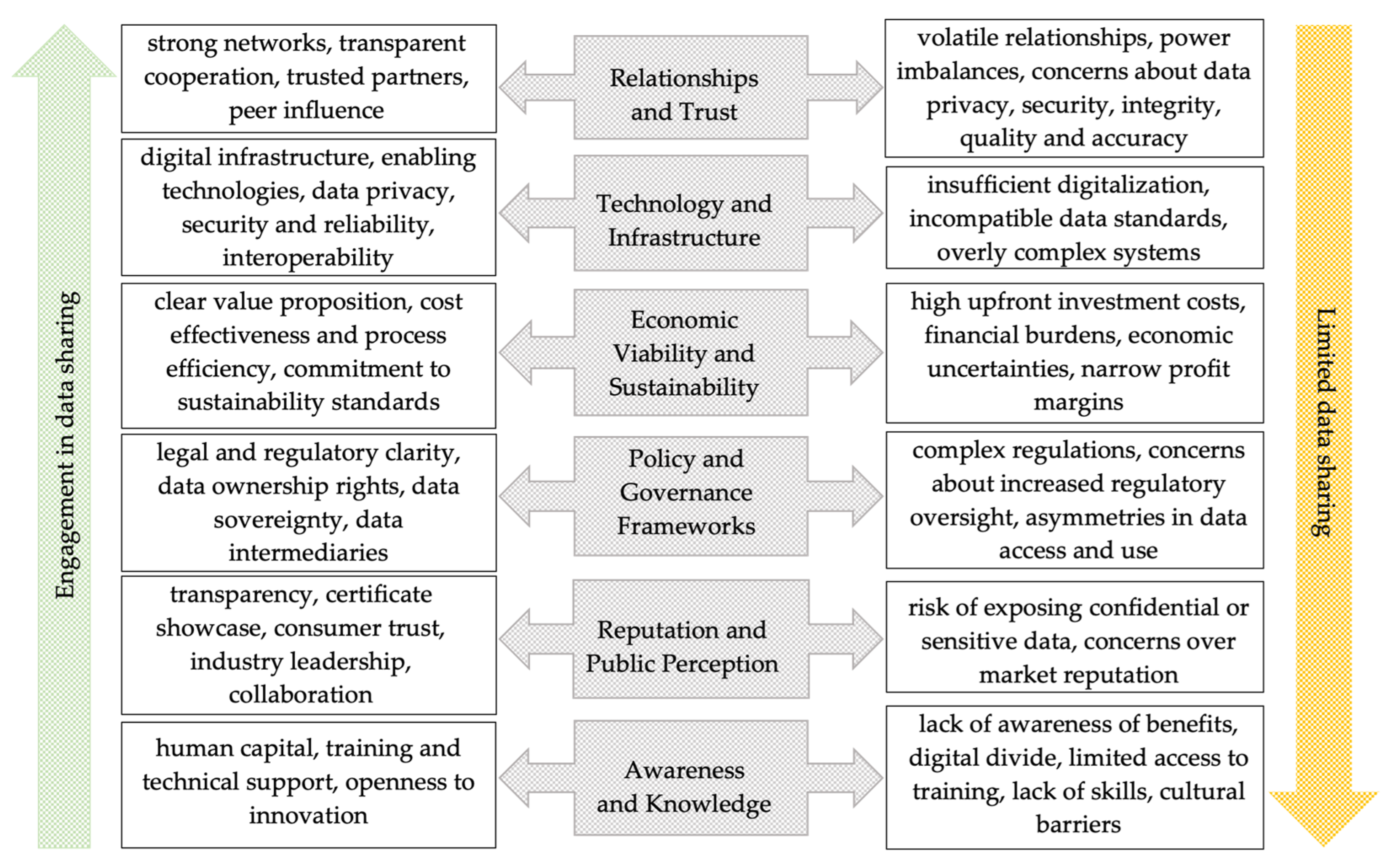
Based on insights from the literature, we employ the identified framework of incentive structures and barriers as a reference point to better understand the perspectives and approaches of Polish agri-food chain stakeholders towards data sharing. Incentives structures encompass elements such as established relationships and trust, technological enablers, economic and value considerations, as well as policy, legal and governance frameworks. Market recognition, reputation, education and capacity building are also key drivers. On the other hand, barriers to data sharing stem from organizational and structural challenges within supply chain cooperation, which often lead to trust deficits. Additional hurdles include technical limitations, financial burdens and economic uncertainties, lack of comprehensive regulations and data governance policies, concerns over reputational risks and limited awareness and knowledge about the benefits of data sharing.
Figure 1 visually illustrates our framework, highlighting the factors that facilitate or hinder data sharing within specific categories which collectively influence the overall level of engagement in data sharing.
The presented framework encompasses multiple dimensions – systemic and structural, technological, socio-economic, sustainability and environmental, as well as human and knowledge-based – which allow for a comprehensive analysis of agri-food stakeholders’ perspectives, preferences and behaviors related to data sharing. It will serve as the primary lens through which the Polish digital passport pilot data will be examined. Furthermore, by leveraging this multifaceted framework, we intend to generate practical insights from the Polish case study that can inform policy and practice of data sharing in agri-food chains.
3. Materials and Methods
To gain an in-depth understanding of the factors influencing agri-food chain stakeholders’ willingness and motivations to share data in transparency-oriented digital systems, we employ a qualitative case study approach. Our focus is on a pilot implementation of the digital food passport system in Poland, which serves as an illustrative example of such a data-sharing arrangement. The pilot, initiated by the National Support Center for Agriculture as a research and development project and conducted by the NASK - National Research Institute between December 2021 and November 2023, was the first attempt in Poland to assess the feasibility of a digital system for tracking food products from farm to shelf, providing reliable and complete information on their origin, journey, and quality. Spanning the beef, pork, and potato markets – selected due to expressed interest from industry-level organizations – the pilot aimed to evaluate the feasibility of such a digital food tracking system. The intention was to test the system with the goal of expanding it to other markets, ultimately aiming to facilitate access to information about Polish food and foster sustainable development in the agri-food sector.
The pilot involved participants from various stages of the supply chain: agricultural producers, processors, and companies handling transport, storage, and packaging. It started with preliminary research among stakeholders in selected markets to explore their willingness to collect, aggregate, and share information within a single data platform for issuing digital passports for food products. Exploratory interviews were conducted with 19 actors representing various stages of the production chain who were interested in and decided to join the pilot. Insights gathered from these interviews informed an analysis of stakeholder needs and expectations concerning the functionalities of the digital food passport system. Subsequently, AS-IS (current state) process interviews were conducted to gather key information at their premises, including types of data required for the system, data flows and potential barriers to data sharing. The second, developmental phase of the pilot involved the TO-BE analyses and deployment of an IT system designed to record production and supply chain events within the selected markets. In total, 70 market actors participated in testing a common system designed to collect, process, and provide access to supply chain data, with the goal of issuing ‘food passports’.
The pilot predominantly attracted participants from the meat market, particularly beef producers who operate within well-organized, dense networks of cooperation, are export-oriented, and focus on achieving higher price premiums for quality. Farmers constituted the most represented group, followed by a smaller number of participants from the agri-food processing sector, as well as transport and packaging. Some participants operated across multiple links in the supply chain (Table 1). Following a period of data sharing, pilot participants were invited to complete a voluntary survey to assess their experiences, perceptions, and satisfaction with the data sharing process and the prototypes of food passports.
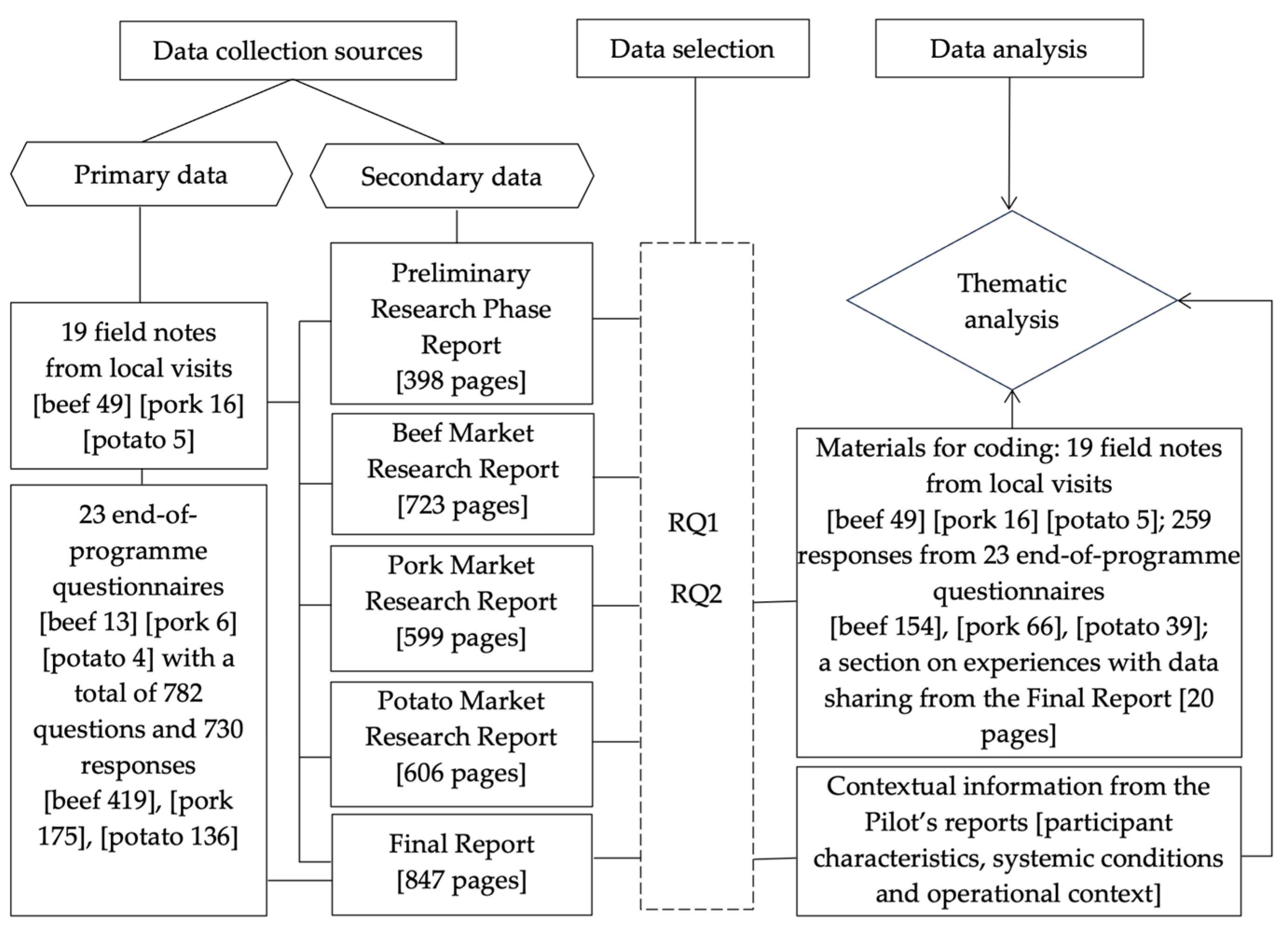
Our examination, grounded in the wealth of information gathered over the course of the pilot, involved a retrospective analysis of the project’s documentation. This allowed us to delve deeper into stakeholder perspectives informed by their interactions and experiences with the data-sharing system. Materials examined included:
- ▪
nineteen field notes compiled during on-site conversations with pilot participants, capturing insights into their operational processes, needs and challenges faced and approaches towards the food passports system; these materials informed the pilot’s reports and approaches towards the food passports system;
- ▪
twenty-three completed end-of-programme questionnaires, which provided quantitative and qualitative data on participant experiences, satisfaction levels and suggestions for future improvements, and contributed to the final project report;
- ▪
five comprehensive reports (totaling approximately 3000 pages) generated during the pilot, encompassing the preliminary research phase, detailed analyses of the three specific market sectors involved, and a final project report that synthesized overall findings and recommendations.
We conducted a thorough review of these data sources, selecting relevant parts that aligned with our research questions on key drivers and barriers to data sharing in agri-food chains, and the role of sustainability in stakeholder motivations (
Figure 2). These selected segments were then subject to thematic analysis [
47,
48]. Given that the field notes and questionnaires collected during the surveys were foundational inputs for the pilot’s reports, we excluded overlapping reports’ content to avoid redundancy. Yet, specific sections of reports associated with technical, organizational, legal and socio-behavioral aspects provided a context for understanding factors affecting data-sharing within the agri-food chains involved. Field notes were included in their entirety for coding. Of the 34 survey questions, 15 were identified as relevant to our research; these encompassed closed questions, multiple-choice questions with comments, and open-ended responses. Additionally, the section of the Final Report specifically referring to data-sharing experiences and cooperation with technology providers was included in the materials subject to coding, as it covered complementary information.
The selected data sources were checked to ensure coverage of perspectives from all three segments of the involved agri-food chains: farmers, agri-food processing, and transport and packaging in beef, pork and potato markets. The coding process was guided by the theoretical insights from the literature review presented in the previous section. These informed the development of codes, the identification of key elements within the data, and the interpretation of emerging themes. The data was coded using QDA Miner Lite software, with two researchers independently coding the data and then comparing their results. The outcomes were discussed, and the common codebook was agreed upon. Subsequently, the entire dataset was re-coded using the agreed-upon coding scheme. Following the coding process, thematic analysis was used to identify the key factors influencing approaches to data-sharing among the different actor groups.
4. Results
Analysis of the data revealed seven key themes reflecting market participants’ perspectives on data sharing for the issuance of digital food passports (
Table 2). Each of the themes encompassed multifaceted aspects that included both factors facilitating and constraining data sharing. The primary incentive for all market participants to adopt the digital passport system was the promise of more effective traceability for food quality assurance. This included improving transparency and integrity in agri-food chains, along with increased economic and financial benefits, leading to higher profitability. The main obstacles were excessive bureaucracy and the slow pace of digitalization both among market participants and public administration handling agricultural issues. Additionally, limited automation and high costs of digital technologies emerged as significant hurdles. Consequently, market participants sought solutions to reduce bureaucracy, accelerate digitalization, and make technology more accessible. Participants also referred to environmental sustainability in production and supply chains as a motivation for data sharing. However, it was mentioned less frequently compared to other themes.
4.1. Collaboration and Transparency for Food Quality and Integrity
The pilot’s participants from all three markets – beef, pork, and potato – shared a common understanding of the necessity of increasing transparency and access to information throughout the supply chain as a key element in improving food quality and integrity. They highlighted the need to adapt to the growing consumer demand for information about product origins – it is important to confirm meat quality through the transparency and openness of information regarding animal breeding, feeding, and treatment (Q5-B). Equally important was the desire to streamline operations within the supply chain by expanding data sharing beyond current practices. However, while all markets and segments recognized the need for improving access to supply chain data, their approaches to sharing this data and their willingness to do so varied. Specifically, beef producers were more willing to invest time and resources in the new data-sharing system, viewing it as a tool to increase trust and validate high-quality claims. Conversely, pork producers, whose products do not enjoy the same premium image, were less convinced of the system’s benefits. Nevertheless, all participants considered easy and fast access to verified data about supply chain partners crucial. For instance, in the beef market, farmers expected easy access to slaughterhouse reports after slaughter (Q1-B). Similarly, slaughterhouses needed better access and integration of animal treatment data from farmers into the meat production supply chain (FN11-B). Collaboration during the pilot enabled the co-development of a prototype of a system that allowed authorized entities to share data sets regarding the product, its quality parameters, the history of events at production stages, information about individual entities involved in these stages, as well as information about tests performed and certificates obtained for the product (FR) (p. 62). Overall, participants viewed data sharing as a practical investment to increase transparency in commercial relationships and in improving product traceability and safety for consumers. They also believed it would lower the risk of purchasing products of inappropriate quality and help them avoid the consequences of actions by non-compliant actors (The system will ensure full traceability in a short time – which is important in case of inspections and recalls, Q6-PK).
4.2. Economic Benefits and Profitability
Direct economic benefits, such as the ability to sell at higher prices and having guaranteed payments (Q1-PT), greater profit by proving the good quality of products (Q2-PK), or a price increase for the finished product (Q5-B), were the strongest common motivator for market actors to engage in data sharing. Participants expressed hopes that food passports would become widely recognized documents, granting them broader market access, facilitating trade and exports, and ultimately increasing their income (Q4-PT). They also expressed a strong interest in integrating the online marketplace into the system. They viewed it as a tool to foster informed decision-making for buyers, attract better offers for sellers, and enhance transaction effectiveness and overall market competitiveness (Q4-B, Q13-B, Q3-PK, FN1-PT, Q4-PT). The potential of the data-sharing system to enhance access to consumer demand data also served as a strong motivator for participants. This was seen as particularly important for smaller farms which bear higher unit costs and face greater challenges in accessing valuable information, such as market data or consumer demand insights, including data on specific locations with high demand for high-quality food (FN1-B). Furthermore, participants saw digital technologies and automation as crucial for enabling data-driven decision-making and increasing efficiency on their farms and in plants. Potato farmers expected data sharing to expand the use of precision agriculture, including the development of recommendation systems for suitable potato varieties based on soil test results (Q3-PT). Meanwhile, meat producers anticipated that greater automation such as using RFID ear tags for automated data collection at gates (Q11-B) and implementing automated feeding systems (Q3-B, Q2-PK) would optimize processes and improve efficiency. However, concerns were also raised about the substantial costs of integrating new technologies, adapting to change, and the potential for increased labor costs due to new data-sharing commitments, especially given the slow pace of automation in the industry. These concerns were especially prevalent in the pig market, where some participants saw no clear path to increased meat prices and thus no compelling benefits to justify the costs of participating in the data-exchange system
4.3. Law, Regulation and Administration
A key concern highlighted by participants during the pilot was the excessive bureaucracy and administrative burden associated with reporting the same or overlapping data multiple times to different government agencies. Unless legislation changes, participants noted, data will continue to be duplicated because all institutions still expect data in their own templates, often resulting in redundant submissions (Q2-B). Emphasizing the need for legislative changes, they advocated for standardized data collection and streamlined reporting processes. Furthermore, they stressed the importance of cooperation with public administration, recognizing its role as a guarantor of the food passport’s credibility (FR). There was also an expectation that government agencies would adapt their data collection processes to utilize the information contained in the food passporting system, thereby eliminating the need for farmers to provide duplicate data or submit them in paper form or via Excel spreadsheets (B5, FN10, Pt1). Producers highlighted that simplifying registration, inspection, and certification processes would incentivize data sharing by reducing the administrative burden associated with compliance (FN3-B, Q8-B, Q4-PK, Q3-PT). A voluntary data-exchange system was largely favored, with participants emphasizing their desire for autonomy in deciding how and when to share their data and advocating for a system based on incentives and motivation rather than obligation (Q4-B). As one participant put it, making participation obligatory would encourage attempts to camouflage activities that do not align with the goals of the passporting system (Q1-PK). At the same time, providing financial support for equipment and software provisioning and specific support measures – such as higher scoring in EU support programs and exemptions from agricultural or property taxes – were put forward as key elements in motivating further data-sharing efforts (Q1-PT, Q3-PT, Q5-PK).
4.4. Access to Technologies and Applications
During the testing of solutions for digital food passports, participants encountered numerous challenges related to the accessibility and functionality of the technologies and applications used. An ongoing issue was the insufficient level of digitalization and automation among market entities and problems related to the range of the Internet on the farm. Participants also highlighted the lack of interoperability between the systems used - another obstacle for farmers is the lack of synchronization between the computer systems embedded in agricultural machinery and their home computer systems or other agricultural machines (Q1-PT). Integration of the passporting system with both agricultural machinery systems, such as GPS systems that record field operations (Q3-PT) and public administration registers (e.g. run by the Agency for Restructuring and Modernization of Agriculture, the Plant Health and Seed Inspection Service, the District Chemical and Agricultural Station) was expected to enable the automatic import and export of data (FR, Q8-B, Q2-PK, Q3-PK). However, this integration was hindered by limited capacity within public sector institutions, which faced challenges such as underdeveloped digital information systems and a lack of APIs for data exchange (FR). Significant advancements in the digitalization of the broader agri-food sector, including farms, businesses, and public institutions, were therefore seen as crucial for fostering further engagement in data-sharing initiatives. Specifically, participants expressed expectations for user-friendly software features, technical support, and training, emphasizing the need to reduce labor-intensive data handling. They called for functionalities such as automatically generating comprehensive animal histories – including events like ear tag losses, disease occurrences, treatments, and weight recordings (Q6-B), an easy way to input data on routinely conducted procedures (Q5-PK), on-demand functions allowing for the upload of additional data categories (Q2-B, Q4-B), as well as improved fluidity in navigating the software (Q1-PK). Potato producers desired mobile applications that assign laborers specific tasks, such as fertilization or treatments, with a breakdown by field sector (Q3-PT) and display all relevant data on a single screen (Q2-PT)
4.5. Knowledge, Awareness, and Promotion
Participants viewed digital food passports as tools for marketing, product promotion, and enhancing brand image, particularly by showcasing information about acquired certifications. To maximize these benefits, they emphasized the need for regular social campaigns to promote both the producers and products participating in the passport system (Q1-B, Q10-B, Q11-B, Q1-PK, Q2-PK, Q2-PT, Q5-PT). This was seen as important not only for raising consumer awareness of the system but also for attracting other agri-food chain actors to achieve the scale benefits of such a system (FR, Q1-B). Furthermore, participants stressed the importance of providing training and knowledge transfer to potential new members, helping them meet the system’s requirements and improve the quality of their products so they could join (e.g. through education on optimal cattle raising periods). Agri-food processing companies, in particular, expected educational programs that would explain and promote relevant quality standards concerning raw agricultural produce to farmers (Q11-B). However, participants also noted that without systemic tools for effective, unified communication with markets, promoting greater engagement and achieving scale effects in data sharing was challenging (FR). During the pilot implementation, a noticeable tension emerged between the desire for greater transparency and concerns over potential reputational damage. Many participants pointed out that the general public and consumers often do not understand the principles of good agricultural and agri-food processing practices. Even farmers using sustainable production methods, along with agri-food processors, transporters, and packaging companies, worried about the potential for their data to be misinterpreted in the market. Concerns arose around various data points, such as information on trade names of plant protections products or animal treatments and medications. As one participant noted, providing information about treatments and medications could be misunderstood by consumers – consumers lack knowledge on this topic (Q9-B). Similarly, sharing information on the time spent in cold storage raised concerns - while the appropriate time improves the quality of the meat, the consumer may think that the meat has been 'sitting for too long' (Q12-B). Therefore, campaigns aimed at increasing both consumer awareness and knowledge about agriculture, production, and processing processes emerged as important factors for market entities that could alleviate these concerns and support further data exchange processes within the food supply chain.
4.6. Trusted and Effective Data Management
Participants in the pilot emphasized the critical importance of robust data management policies, focusing on concerns such as data control, privacy, security, quality, accuracy, and ethical use. This was particularly evident in their reluctance to share breeding and husbandry data, highlighting concerns about its privacy and the subsequent loss of control over how the data might be used or shared by others. Specifically, participants were concerned about who the recipients of the data were (who has access to it) and about control over cloud solutions (FR) (p. 50). For instance, pork market representatives in the transport and agri-food processing sectors were concerned that their data may not be secure and could therefore be used by their competitors to their detriment (Q6-PK). Ensuring the quality and accuracy of data entered into the system was another key concern for participants. They emphasized the importance of appropriate data scope, arguing against the inclusion of excessive details that do not add value to oversight systems or consumer information (Q1-B). Some participants also expressed concerns about whether the data will be correctly entered by the participants of the system (Q13-B, Q3-PT). As participants indicated, intermediaries involved in the purchase of agricultural products change frequently and may not be subject to systemic oversight, which raises doubts about the trustworthiness of their data (FN9-B). The shared conviction about the need for data immutability to guarantee accuracy led to a preference for blockchain or blockchain-like solutions (Q1-B). Ultimately, cooperation and coordination with government agencies were viewed as essential steps toward ensuring the trusted and effective data management required to maintain confidence in the issued food passports (FR).
4.7. Sustainability in Agriculture and Supply Chains
While sustainability was not the most frequently discussed topic in the participants’ direct statements, it remained an important issue for them. Their application to and active participation in the pilot project reflected their awareness of the growing expectations from both consumers and importers for concrete proof that food products are produced within sustainable production systems (FR). Participants demonstrated this commitment through a collective emphasis on animal welfare, biodiversity conservation, efficient resource use, technological advancements, and supply chain optimization as key pathways to enhance sustainability. Specifically, organic producers and others involved in organic food processing and transport emphasized the need to actively promote the high quality of their products to encourage consumers to buy organic foods (Q1-B). The environmental aspect of sustainability was primarily linked to its potential to improve animal and soil health and enhance food product quality and taste: This is family farming, of the ecological type, this means that breeding is not used in the indoor stall-based system but in the open space all year round, the animals are fed exclusively with natural products such as hay, silage, straw, which results in the absence of diseases and improvement of taste qualities (FN1-B). At the same time, in some markets, difficulties associated with the development of organic production – operating in batches with a small number of animals – were emphasized. As one participant from the food processing sector noted: This production caused significant economic losses. Demand was low, and stopping the production line to slaughter such a small number of animals was costly in relation to the revenue from sales (FN4-PK). Other participants aimed to enhance the sustainability of their farms through the use of precision farming techniques. In the meat sector, expanding the use of alert systems for animal health and welfare based on sensors was indicated as required action (FN1-B, FN6-B, FN9-B). Potato producers expected the easy ordering and access to various tests, including soil and yield analysis and monitoring crop health, identifying water deficiencies, and optimizing resource use (Q3-PT). Additionally, the need to support shortening the supply chains was highlighted. As one participant stated: High meat quality is achieved thanks to the breed and through the applied breeding system and feeding method, and ultimately - by shortening the supply chain (FN1-B). Based on their experience with the pilot project, participants also highlighted the value of a food passport system that goes beyond simple traceability by validating high quality and sustainable production methods. They emphasized that access to this system should be granted to select entities who are monitored by appropriate institutions and possess relevant certifications (FN3-B). However, collaboration for sustainability across the entire supply chain has not been widely discussed or explored.
Collectively, these themes reveal that market actors had numerous expectations and hopes, but also faced significant concerns and challenges related to data sharing within agri-food supply chains. The findings illustrate a quite complex picture of efforts to build a sophisticated data-sharing system across three agricultural markets in Poland, all within a socio-economic context characterized by a relatively low level of digital maturity. While these perspectives primarily come from entities more open to collaboration – since they chose to join the pilot – they highlight specific areas that require attention to facilitate broader participation in data sharing initiatives aimed at enhancing transparency and sustainability in agri-food supply chains. Common motivations and concerns were identified across all segments involved in the pilots; however, the significance of certain motivations and barriers differed among stakeholders, reflecting their specific roles in the supply chain. Farmers were primarily motivated by the potential to achieve higher prices for their products and to reduce administrative burdens. For agri-food processors, the main motivation was ensuring the quality and integrity of raw materials and agricultural produce. Processors, as well as transport and packaging companies, were interested in gaining better access to supply chain data to ensure traceability and quality during production processes and operations. These differences naturally reflected their roles in the supply chain, which drove their interest toward specific aspects of agri-food data sharing. Additionally, participants in the pilot in all three markets expressed expectations for continued engagement from public institutions in facilitating data sharing, highlighting the crucial role of the public sector in supporting these initiatives.
5. Discussion
Data exchange systems enabling better resource management and tracking of food product history, quality, safety, authenticity, and ethical and sustainability compliance are essential for a transparent and sustainable food system [
1,
45,
49]. With the European Green Deal and Farm to Fork strategy demanding greater transparency and sustainability in reporting, the need for more extensive data sharing in agri-food chains has become even more pressing [
50,
51,
52]. The pilot project analyzed in this study developed the prototypes of digital food passports across three agricultural markets, confirming the feasibility of establishing and scaling such a system in the three markets studied as well as the potential for rolling it out in other agricultural markets in Poland. However, it also highlighted numerous barriers that still hinder the extensive data sharing required for such systems.
The willingness of farmers and other market actors to share data with supply chain partners and government agencies was influenced by a range of factors, including economic, legal, technical, organizational, and financial considerations. Our findings support existing literature, highlighting the necessity of a clear value proposition for farmers and other actors within the production and distribution chain to invest resources and time in additional data exchange systems [
8,
17]. Stakeholders must be convinced that such a system will not only provide consumers with information that supports more informed purchasing decisions, but will also significantly improve their operations and enhance the marketability of their products, leading to higher profits. For farmers participating in the pilot factors such as reducing burdensome reporting procedures and direct financial incentives played a particularly important role. These needs and preferences are not unique to any single market, but are common among farmers across the European Union, as the issues of low profitability and excessive bureaucracy consistently arise during stakeholder consultations concerning Common Agricultural Policy reforms [
53,
54]. At higher levels of the supply chain, data collaboration was seen as a practical tool to ensure high-quality raw materials and promote premium-priced food with the use of digital passports.
The observed mobilization and interest in data sharing within the beef sector can be attributed to its robust industry-level organization. The Polish Beef Strategy 2022 [
55] unified stakeholders and encouraged for developing a long-term strategy for 2030, with a key focus on expanding data sharing beyond the current system. Prior experience with data collection within the EU’s identification and traceability systems for livestock, along with the voluntary adoption of more advanced methods like DNA testing, fostered trust and raised awareness of the crucial role of data collaboration. Thus, the experiences collected during the pilot reinforce the evidence presented in other studies on the underlying importance of collective goals, collaboration, and trust in establishing successful data-sharing initiatives [
7,
18,
20,
23]. Yet, the two other relatively well-organized agricultural sectors included in the pilot did not exhibit the same level of engagement in data sharing. This suggests that cooperation, trust, and awareness of data collaboration importance alone are not sufficient to motivate data exchange. In these specific cases, price sensitivity and the perception of products as non-premium or having limited potential for margin growth appeared to be key deterrents. The relationship between market prices and the propensity for data exchange within agri-food chains warrants therefore a closer examination in future research.
Findings from the pilot confirmed the importance of appropriate legal, organizational, and technical frameworks in building effective data exchange systems, consistent with existing research [
21,
38]. It became evident that in the agri-food sector, where digitalization and automation levels are still quite low, data-sharing initiatives require particularly careful planning and support mechanisms to facilitate participation and ensure they are not perceived as burdensome by participants. This underscores the need for joint efforts between the private and public sectors in digital transformation across the agri-food sector [
6,
45]. Successful data sharing requires not only active participation from market actors, but also significant commitment from public sector agencies, which, given their inspection and monitoring functions, are integral to traceability and quality confirmation systems in agri-food chains. By developing digital infrastructure and modernizing their own systems and processes, public institutions can facilitate more efficient communication, reduce administrative burdens, and provide centralized access to essential information and services [
43,
44]. In countries that are behind in digital transformation, these enhancements alone could drive greater participation in data exchange systems.
A key subsequent observation from this analysis is that even in socio-economic contexts characterized by low digitalization, farmers and other stakeholders within the agri-food chain may still be highly aware of the potential threats associated with data exchange and usage. Thus, in addition to technological advancements, market actors also expect robust data governance policies that provide clear rules for data access and usage, along with strong privacy protection and greater control over their data [
23]. Confidence in the security, quality and integrity of data is essential for market actors to make informed decisions based on the data shared within sectoral data exchange systems. This need is even more critical in systems built on transparency and public communication with consumers and other market participants. The importance of data governance issues for farmers and agri-food chain stakeholders is already widely recognized [
8,
19]. This recognition has led to the adoption of new data regulations in the EU and the establishment of a common European agricultural data space, aimed at improving the security and trustworthiness of data exchange within the sector [
56].
Understanding the motivations and concerns of agri-food stakeholders regarding their data and its use is essential for developing strategies that enhance sustainability within agri-food chains and the sector as a whole [
9,
51,
57]. The development and testing of digital food passport prototypes in Poland highlighted a tendency among market actors to prioritize sharing data for financial and economic gains. This means that demonstrating how data sharing leads to increased profitability, cost savings, or market advantages should be an integral part of efforts to engage stakeholders in data-sharing initiatives within supply chains. However, this emphasis on financial gains could also lead to an imbalance, as data that could support other dimensions of sustainable development – such as environmental protection and improved working conditions – may not be exchanged to a sufficient degree for their broader utilization. Taken together, the evidence from the Polish pilot reinforces the perspective that digitalization and data are primarily used to enhance economic viability, rather than being leveraged to fully support all dimensions of sustainable development [
58]. Until market actors see direct financial benefits from the additional effort required to exchange environmental and other data, it may be necessary to provide additional public support for initiatives in this area.
An essential approach to achieving a more balanced contribution to agri-food data sharing is through education, raising awareness, and promoting all market actors who adhere to sustainability principles [
58]. As the Polish pilot highlights, market actors may be reluctant to share certain types of data in consumer-facing information systems due to fears that it will be misunderstood or misinterpreted, potentially harming their market position. More broadly, agri-food chain stakeholders shared a common apprehension that consumers and the broader public do not fully understand all aspects of agricultural practices, often adopting overly simplistic interpretations. These concerns about the lack of sufficient knowledge to properly interpret the data were present among different groups of the pilot’s participants, including farmers employing sustainable practices. Dilemmas surrounding the disclosure of data and information in the broader context of social reception – where transparency is increasingly important, but the potential costs of losing reputation or image are high – require careful consideration [
29,
34]. Yet, they have not been thoroughly analyzed in the literature on the development of data-sharing systems in agri-food chains. Further research is therefore needed to determine whether social and educational campaigns raising consumer awareness about agricultural practices could indeed foster data sharing and transparency by addressing producer concerns about public misinterpretation of their data.
While the pilot revealed high expectations for the public’s perception of agriculture and agri-food products, it also highlighted that stakeholders themselves recognize the need for additional sector-wide efforts to build knowledge and skills among all market actors to enhance sustainable development. These needs and expectations of more forward-thinking market actors can be viewed as part of their broader strategy to shape the industry’s image in response to increasing regulatory demands, while also protecting their own interests by proactively mitigating risks posed by non-compliant entities. They also reflect an awareness of the scale of benefits that data exchange among all participants and links in the supply chain can bring.
6. Conclusions
Gaining a deeper understanding of market actors’ motivations and behaviors is essential for enhancing the prospects of achieving sustainability goals in the agri-food sector. Data-sharing systems drive the digital transformation of the food system, enabling data-driven insights that promote sustainability and resilience. Collaboration on data between supply chain participants – alongside parallel investments in the digitization of production processes – not only underpins product tracking systems to identify potential food safety issues but also optimizes the entire supply chain and generates greater added value through improved access to market data and other relevant information.
The pilot project on digital food passports in Poland explored the feasibility of establishing a comprehensive data-sharing system among market actors under the supervisory role of public sector agencies. Materials and data gathered over the two-year duration of the project provide valuable insights into stakeholder approaches to collaboration within agri-food supply chains. The findings underscore the necessity for producers to perceive tangible benefits from their engagement in data sharing such as direct financial gains, higher market prices, expanded export opportunities, or improved efficiency. They also indicate that the motivations to share data for broader environmental and social welfare purposes are noticeably weaker. This is unsurprising in voluntary data-exchange systems designed to provide information beyond what is mandated by law. However, this also highlights the need for strategies that better align individual interests with broader sustainability goals within such voluntary, industry-wide systems.
This study also suggests that incentivizing agri-food data sharing may require more intensive educational and social campaigns directed at both producers and consumers. By addressing stakeholders’ concerns and highlighting the long-term benefits of comprehensive data exchange, such initiatives can enhance participation and contribute to the advancement of all dimensions of sustainability in agri-food chains. Further research is required to explore different aspects of socio-economic frameworks and key collaboration strategies to achieve these goals.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on
Preprints.org. Supplement S1: Overview of documents constituting outputs of the Digital Food Passports pilot in Poland; Table S1a: Reports from the Digital Food Passports pilot in Poland; Table S1b: List of appendices to reports from the Digital Food Passports pilot in Poland; Supplement S2: Coding process; Table S2: Initial codes and final agreed codes for thematic analysis.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.K. and P.M.; methodology, K.K.; data curation, K.K. and P.M.; software and data coding, K.K. and P.M.; formal analysis, K.K. and P.M.; validation, K.K. and P.M.; writing—original draft preparation, K.K.; writing—review and editing, P.M. and K.K.; visualization, K.K.; project administration, K.K. and P.M.; funding acquisition, K.K. and P.M.
Funding
This research was funded by the Institute of Agricultural and Food Economics—National Research Institute, Warsaw, Poland and Łukasiewicz Research Network – Poznan Institute of Technology, Poznan, Poland.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
This research is based on anonymized primary data collected by P.M. during the research phase of the Digital Food Passports pilot in Poland, as well as reports from the pilot, which were provided by the National Support Centre for Agriculture (KOWR) on May 15, 2024, through the public sector information reuse procedure. Due to privacy considerations, only a portion of the data presented in this study is available upon reasonable request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors sincerely thank Jacek Jarząbek for sharing valuable comments and feedback as both a researcher and the lead reporter of the findings from the Digital Food Passports pilot in Poland, during his tenure at NASK – National Research Institute.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations were adopted for the coding materials: Field notes (FN): FN1-B to FN12-B (beef market), FN1-PK to FN5-PK (pork market), FN1-PT to FN2-PT (potato market); Questionnaires (Q): Q1-B to Q13-B (beef market), Q1-PK to Q6-PK (pork market), Q1-PT to Q4-PT (potato market); Final report: FR.
References
- Kamble, S.; Gunasekaran, A.; Gawankar, S. Achieving sustainable performance in a data-driven agriculture supply chain: A review for research and applications. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2020, 244, 179–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rejeb, A.; Rejeb, K.; Zailani, S. Big data for sustainable agri-food supply chains: a review and future research perspectives. Journal of Data, Information and Management. 2021, 3, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbate, S.; Centobelli, P.; Cerchione, R. The digital and sustainable transition of the agri-food sector. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2023, 187, 122222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trabelsi, M.; Casprini, E.; Fiorini, N.; Zanni, L. Unleashing the value of artificial intelligence in the agri-food sector: where are we? Br. Food J. 2023, 125, 482–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaco, L.C.; Brewer, B.E.; Gray, A.W. Data on data: An analysis of data usage and analytics in the agricultural supply chain. Appl. Econ. Perspec. Policy 2023, 45, 1577–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intellecap Advisory Services Private Limited. Unlocking Data Sharing in Agriculture. Available online: https://www.idhsustainabletrade.com/uploaded/2024/01/Unlocking-Data-Sharing-in-Agriculture-January-2024.pdf (accessed on 19.08.2024).
- Wiseman, L.; Sanderson, J.; Zhang, A.; Jakku, E. Farmers and their data: An examination of farmers’ reluctance to share their data through the lens of the laws impacting smart farming. NJAS-Wageningen Journal of Life Sciences 2019, 90-91, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouanjean, M.-A.; Casalinii, F.; Wiseman, L.; Gray, E. Issues around data governance in the digital transformation of agriculture. OECD Food, Agriculture and Fisheries Papers 2020, 146, OECD. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moysiadis, T.; Spanaki, K.; Kassahun, A.; Kläser, S.; Becker, N.; Alexiou, G.; Zotos, N.; Karali, I. AgriFood supply chain traceability: data sharing in a farm-to-fork case. Benchmarking: An International Journal 2023, 30, 3090–3123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenzel, A.; Waichman, I. Supply-chain data sharing for scope 3 emissions. npj Clim. Action 2023, 2, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madlberger, M. What drives firms to engage in interorganizational information sharing in supply chain management? International Journal of e-Collaboration 2009, 5, 18–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kembro, J.; Selviaridis, K.; Näslund, D. Theoretical perspectives on information sharing in supply chains: a systematic literature review and conceptual framework. Supply Chain Management 2014, 19, 609–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghababsheh, M.; Gallear, D. Socially Sustainable Supply Chain Management and Suppliers’ Social Performance: The Role of Social Capital. Journal of Business Ethics 2021, 173, 855–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.T.; Lee, HH.; Hwang, T. Logistics integration in the supply chain: a resource dependence theory perspective. International Journal of Quality Innovation 2020, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leckel, A.; Linnartz, M. Towards the Internet of Production – How To Increase Data Sharing For Successful Supply Chain Collaboration. Journal of Production Systems and Logistics 2023, 3, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakku, E.; Taylor, B.; Fleming, A.; Mason, C.; Fielke, S.; Sounness, C.; Thorburn, P. If they don’t tell us what they do with it, why would we trust them? Trust, transparency and benefit-sharing in Smart Farming. NJAS-Wageningen Journal of Life Sciences 2019, 90-91, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Heath, R.; McRobert, K.; Llewellyn, R.; Sanderson, J.; Wiseman, L.; Rainbow, R. Who will benefit from big data? Farmers’ perspective on willingness to share farm data. J. Rural Stud. 2021, 88, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, H.; Rix, C.; Effertz, A.; Bergau, S.; Maass, W. Data Sharing in the German Food Industry-Empirical Insights. In DataEcoSys – Data EcoSystem in Information Systems, AMCIS 2022 Proceedings 1, Minneapolis, MN USA, 10-14 August 2022, https://aisel.aisnet.org/amcis2022/DataEcoSys/DataEcoSys/1.
- Wolfert, S.; Verdouw, C.; van Wassenaer, L.; Dolfsma, W.; Klerkx, L. Digital innovation ecosystems in agri-food: design principles and organizational framework. Agricultural Systems 2023, 204, 103558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Burg, S.; Wiseman, L.; Krkeljas, J. Trust in farm data sharing: reflections on the EU code of conduct for agricultural data sharing. Ethics Inf. Technol. 2021, 23, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šestak, M.; Copot, D. Towards trusted data sharing and exchange in agro-food supply chains: Design principles for agricultural data spaces. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajdić, D.; Kotzab, H.; Petljak, K. Collaboration, trust and performance in agri-food supply chains: a bibliometric analysis. Br. Food J. 2023, 125, 752–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, C.S.; Gemtou, M.; Anastasiou, E.; Fountas, S. Building Trust: A Systematic Review of the Drivers and Barriers of Agricultural Data Sharing. Smart Agric. Technol. 2024, 8, 100477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krumpholz, A.; Grobler, M.; Gaire, R.; Mason, C.; Burns, S. Raising Trust in the Food Supply Chain. In Workshop on Usable Security and Privacy (USEC), Auckland, New Zealand, 7 May 2021. [CrossRef]
- Bronson, K. Smart farming: including rights holders for responsible agricultural innovation. Technology Innovation Management Review 2018, 8, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonkman, J.; Badraoui, I.; Verduijn, T. Data sharing in food supply chains and the feasibility of cross-chain data platforms for added value. Transportation Research Procedia 2022, 67, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Accorsi, R.; Cholette, S.; Guidani, B.; Manzini, R.; Ronzoni, M. Sustainability assessment of transport operations in local Food Supply Chain networks. Transportation Research Procedia 2022, 67, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corallo, A.; De Giovanni, M.; Latino, M.E.; Menegoli, M. Leveraging on technology and sustainability to innovate the supply chain: a proposal of agri-food value chain model. Supply Chain Management 2024, 29, 661–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susha, I.; Gil-Garcia, J.R. A collaborative governance approach to partnerships addressing public problems with private data. In Proceedings of the 52nd Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Grand Wailea, Hawaii, USA, 8-11 January 2019; pp. 2892–2901. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, C.; Regan, Á.; van der Burg, S. Farming futures: Perspectives of Irish agricultural stakeholders on data sharing and data governance. Agric Human Values 2023, 40, 565–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klievink, B.; Van Der Voort, H.; Veeneman, W. Creating value through data collaboratives. Information Polity 2018, 23, 379–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jussen, I., Schweihoff, J., Möller, F. Tensions in Inter-Organizational Data Sharing: Findings from Literature and Practice, 2023 IEEE 25th Conference on Business Informatics (CBI), Prague, Czech Republic, 21-23 June 2023, pp. 1-10. [CrossRef]
- Myshko, A.; Checchinato, F.; Colapinto, C.; Finotto, V.; Mauracher, Ch. Towards the twin transition in the agri-food sector? Framing the current debate on sustainability and digitalisation, J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 452, 142063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal, J. Private sector trust in data sharing: enablers in the European Union. Data Policy 2024, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minnens, F.; Luijckx, N.; Verbeke, W. Food Supply Chain Stakeholders’ Perspectives on Sharing Information to Detect and Prevent Food Integrity Issues. Foods 2019, 8, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durrant, A.; Markovic, M.; Matthews, D.; May, D.; Leontidis, G.; Enright, J. How might technology rise to the challenge of data sharing in agri-food? Glob. Food Sec. 2021, 28, 100493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durrant, A.; Markovic, M.; Matthews, D.; May, D.; Enright, J.; Leontidis, G. The role of cross-silo federated learning in facilitating data sharing in the agri-food sector. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 193, 106648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewster, C.; Kalatzis, N.; Nouwt, B.; Kruiger, H.; Verhoosel, J. Data Sharing in Agricultural Supply Chains: Using semantics to enable sustainable food systems. Semant. Web 2024, 15, 1207–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vern, P.; Miftah, N.; Panghal, A. Digital Technology: Implementation Challenges and Strategies in Agri-Food Supply Chain. In Agri-Food 4.0: Innovations, Challenges and Strategies; Mor, R.S., Kumar, D. Singh, A., Eds.; Emerald Publishing Limited, Leeds, UK, 2022; Advanced Series in Management, Vol. 27, pp. 17-30. ISBN 978-1-80117-499-2.
- Schroeder, K.; Lampietti, J.; Elabed, G. What's Cooking: Digital Transformation of the Agrifood System. Agriculture and Food Series; World Bank, Washington, DC, USA. 2021; Available online https://hdl.handle.net/10986/35216. (accessed on 4 September 2024).
- Dolfsma, W.; Isakhanyan, G.; Wolfert, S. Information Exchange in Supply Chains: The Case of Agritech. J. Econ. Issues 2021, 55, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masi, M.; De Rosa, M.; Vecchio, Y.; Bartoli, L.; Adinolfi, F. The long way to innovation adoption: insights from precision agriculture. Agric. Food Econ. 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehlers, M.H.; Finger, R.; El Benni, N.; Gocht, A.; Sørensen, C.A.G.; Gusset, M.; Pfeifer, K.; Poppe, K.; Regan, Á.; Rose, D.Ch.; Wolfert, S.; Huber, R. Scenarios for European agricultural policymaking in the era of digitalisation. Agricultural Systems 2022, 196, 103318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukk, M.; Põder, A.; Viira, A.H. The role of public policies in the digitalisation of the agri-food sector. A systematic review. NJAS: Impact in Agricultural and Life Sciences 2022, 94, 217–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unlocking the potential of data for sustainable agriculture. Strategic Research and Innovation Agenda. European Partnership Agriculture of Data 2023. Available online: https://research-and-innovation.ec.europa.eu/system/files/2023-08/AgData%20SRIA%20final_version.pdf (accessed on 6 September 2024).
- Advancing Digital Public Infrastructure for the Agriculture Sector. Briefing Paper. January 2024, World Economic Forum in collaboration with PwC. Available online: https://www3.weforum.org/docs/WEF_Advancing_Digital_Public_Infrastructure_Agriculture_Sector_2024.pdf (accessed on 6 September 2024).
- Braun, V.; Clarke, V. Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qual. Res. Psychol. 2006, 3, 77–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, V.; Clarke, V. Thematic Analysis. In Encyclopedia of Quality of Life and Well-Being Research Maggino, F., Eds.; Springer, Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 1-7, ISBN 978-3-319-69909-7.
- Rozenstein, O.; Cohen, Y.; Alchanatis, V.; Behrendt, K.; Bonfil, D.J.; Eshel, G.; Harari, A.; Harris, W.; Klapp, I.; Laor, I.; et al. Data-driven agriculture and sustainable farming: friends or foes? Precision Agric. 2024, 25, 520–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrzaszcz, W.; Prandecki, K. Agriculture and the European Green Deal. Zagadnienia Ekonomiki Rolnej/Problems of Agricultural Economics, 2020, 365, 156–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczepaniak, I.; Szajner, P. Strategia „Od pola do stołu” w sektorze przetwórstwa spożywczego („Farm to Fork” Strategy in the food processing sector). Fundacja Gospodarki i Administracji Publicznej, Kraków, Poland, 2022; pp. 1-77, ISBN 978-83-67140-08-9.
- Bachmann, N.; Tripathi, S.; Brunner, M.; Jodlbauer, H. The Contribution of Data-Driven Technologies in Achieving the Sustainable Development Goals. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, A. The challenges of the next CAP: doing more with less. Agriregionieuropa 2017, 13. Available online: https://agriregionieuropa.univpm.it/it/content/article/31/50/challenges-next-cap-doing-more-less (accessed on 11 October 2024).
- European Commission, Simplification: first insights into the results of the survey running from 7 March to 8 April 2024, October 2024. Available online: https://agriculture.ec.europa.eu/document/download/e229b590-8cfc-4028-9a77-47a706058e5e_en?filename=presentation-farmers-simplification-survey-results_en.pdf (accessed on 11 October 2024).
- Rada Wołowiny (Beef Council), Strategia rozwoju rynku Polska Wołowina (Polish Beef Market Development Strategy). 24 April 2019, Avaliable online: https://www.radawolowiny.pl/wp-content/uploads/2022/01/Polska-wolowina-strategia-przyjeta-na-posiedzeniu-Porozumienia-Rolniczego-.pdf. (accessed on 11 October 2024).
- Building a European framework for the secure and trusted data space for agriculture, Coordination and Support Action AgriDataSpace funded by Horizon Europe, Policy Brief, September 2024. Available online: https://agridataspace-csa.eu/wp-content/uploads/2024/09/AGRIDATA-SPACE-FINAL-BROCHURE-V5.pdf (accessed on 18 October 2024).
- Brown, C.; Kovács, E.; Herzon, I.; Villamayor-Tomas, S.; Albizua, A.; Galanaki, A.; Grammatikopoulou, I.; McCracken, D.; Olsson, J.A.; Zinngrebe, Y. Simplistic understandings of farmer motivations could undermine the environmental potential of the common agricultural policy. Land Use Policy 2021, 101, 105136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacPherson, J.; Voglhuber-Slavinsky, A.; Olbrisch, M.; Schöbel, P.; Dönitz, E.; Mouratiadou, I.; Helming, K. Future agricultural systems and the role of digitalization for achieving sustainability goals. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2022, 42, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).