Introduction
Infrastructure, which includes essential services like transportation, energy, and telecommunication systems, plays a pivotal role in the socioeconomic growth of any nation (OECD 2019). Such projects require diverse skills, capital sources, and the involvement of a broad range of industries and businesses. However, there is a significant gap between the required infrastructure development and the available human, physical, and fiscal resource, particularly in the Least Developed Countries (LDCs) (Tian et al. 2022).
Currently, the United Nations has classified 47 countries as least developed countries, which are given priority for implementing the sustainable development goals (SDGs) (UNCTAD 2019). The categorization of a country as an LDC is based on three criteria: low income per capita, low index of human capital, and high fragility in economic conditions (Hurley and Voituriez 2016). These nations have struggled to secure financial support for their proposed sustainable development and value creation (UNCTAD 2019; OECD 2020), a challenge further compounded by the COVID-19 crisis (OECD 2020).
Traditionally, LDCs have relied on foreign investments, a form of private financing, to fund most of their infrastructure capital accumulation (UNCTAD 2019). However, the proportion of private capital they attract consistently remains minimal compared to other nations. In 2018, only approximately $3.8 billion was mobilized in LDCs, representing only 7.5% of the total funding. In contrast, high-income countries managed to allocate over $84 billion (41%), and low-to-middle-income nations brought in $68 billion (33%) in the same period (OECD 2020).
Despite the potential availability of private investments, the investment risks and challenges of LDCs impede the private sector's capacity to invest in infrastructure projects in these regions (Kumar et al. 2019). These obstacles may occasionally be attributed to market failure (Gutman et al. 2015). Infrastructure projects in LDCs, which mainly serve local markets and generate income in local currency, are adversely affected by the insufficient exchange rates and tenors available for matching assets and liabilities. These projects are also susceptible to foreign exchange rate fluctuations, negatively affecting profitability (UNCTAD 2019). In addition, the cost of project preparation can escalate in more minor and isolated markets, while inadequate macroeconomic and project-level information makes effective modeling difficult (OECD 2020).
Apart from market-related difficulties, investor-specific challenges also contribute to the problems in LDCs. The lack of project finance knowledge, technical skills, and fund absorption capacity among local investors makes successful project planning and execution difficult (Tian et al. 2020). Additionally, most LDC sponsors lack the financial capacity to offer guarantees, and financing costs typically surpass existing assets, while enforceability of collateral issues intensifies the problem (OECD 2020).
The government bodies of LDCs also poses significant obstacles. SDG-focused initiatives are often carried out in collaboration with governments or depend on legislative conditions allowing for financial and other innovations. However, foreign investors may be less willing to invest in LDCs due to actual or potential doubts about the efficiency or reliability of their institutions (OECD 2020). The inadequacy of national regulatory frameworks often leads to reliance on international regulations and voluntary corporate actions, generally viewed as suboptimal alternatives, negatively impacting private sector growth. The absence of a stable regulatory environment for private sector engagement represents a risk to donors, whose views on ODA-backed private sector instruments may vary in additionality, potentially influencing development outcomes and the worth of financial resources (Carter and Stone 2015).
To address these concerns, donors can create a co-decision platform with recipient countries to discuss methodologies, transparency, funding decisions, and a unified view of private sector participation (UNCTAD 2019). Blockchain technology emerges as a fitting solution, as it represents a decentralized, digital ledger that records all transactions among contracting parties in a transparent, immutable, and auditable manner. It is built on a distributed database shared between the network's participants, thus eliminating the need for a centralized authority or third-party trust (Casino et al. 2019). However, blockchain applications are not limited to this. The idea of a blockchain-based smart contract can be expanded to include Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs). DAOs are a form of community organization and collective decision-making framework where the final decisions can be automated, adhering to the rules and principles defined in the relevant code, with no further human intervention (Diallo et al. 2018).
The purpose of this research is thus to investigate the potential of the DAO blockchain to improve the private funding governance of infrastructure projects in LDCs. This research, in particular, delivers a conceptual framework for leveraging blockchain technology in the financing and governance of these projects. A real-world case study is also conducted to evaluate the framework's potential to improve project performance. This study aims to contribute to ongoing efforts to promote sustainable and equitable economic growth in LDCs through innovative finance and governance tools.
Literature Review
Studies focusing on blockchain technology within the construction sector have increased substantially in recent years (Scott et al. 2021). Most of these studies have centered on construction supply chain management, asset management, payment procedures, energy management, enhanced file-sharing protocols, and building maintenance (Perera et al. 2020; Kiu et al. 2022). Despite this, the application of blockchain technology to infrastructure financing has received relatively little attention.
The existing body of research in infrastructure finance primarily revolves around the process of asset tokenization (Tian et al. 2020). This means creating digital tokens on a blockchain representing a real-world asset, in this case, infrastructure assets (Uzsoki 2019). This process improves liquidity, increases efficiency, and expands accessibility to a broader investor base (Tian et al. 2020). However, managing these tokenized assets, particularly concerning their distribution to stakeholders, is an area that needs more attention. Current distribution platforms such as MakerDAO and Silta operate on a model that distributes tokens equally to all stakeholders (Sun et al. 2022). While this method appears fair, it overlooks the unique complexities of infrastructure projects that often require more nuanced decision-making processes.
Infrastructure projects are typically large-scale undertakings involving various stakeholders with varying degrees of knowledge, skills, and involvement. Equal distribution of tokens might not adequately reflect the value that some stakeholders bring to the project, nor does it incentivize expert participation. A one-size-fits-all approach may not be suitable here. This is where the concepts of Financial Governance and Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) come into play.
Financial governance encompasses various practices, rules, and processes for managing and overseeing financial resources (Khan 2014). Typically, this process breaks down into three primary stages: budget preparation, budget execution paired with internal control, and monitoring and evaluation. Effective financial governance contributes to solid fiscal management, efficient resource allocation, and a foundation for transparency and accountability (Asian Development Bank 2017). LDCs often struggle with this due to challenges like weak institutional capability, insufficient legislative frameworks, and limited access to capital markets (Hurley and Voituriez 2016). Tackling these challenges can help LDCs attract private investment for infrastructure projects and foster long-term sustainable economic growth (African Financial Governance Status Report 2011).
Smart contracts, a significant feature of blockchain, are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into lines of code (Alharby and Moorsel 2017). These computer programs automatically execute transactions when predefined conditions are met, eliminating the need for a third-party intermediary (Singh et al. 2020). The idea of Blockchain-based smart contracts can extend to DAOs. A DAO is a system that uses a collection of computer programs, where smart contracts establish the rules that govern the organization in advance (Wang et al. 2019). Unlike traditional methods, in DAOs, decision-making occurs from interactions among various stakeholders within the DAO forum. The main characteristic of a DAO is its autonomy, which requires automated software to ensure that choices can be executed without the need for further human intervention (El Faqir et al. 2020). When certain conditions of a smart contract are met, the decentralized network will execute the contract automatically. For instance, once a contractor obtains sufficient votes from DAO members, payments will be made to the owner (Diallo et al. 2018).
Smart agencies are the building blocks of DAOs, which are atomic governing entities whose operations are based on the blockchain using smart contracts. Each agency's governance mechanism can take multiple forms; one is the proposal-based governance system, where decisions are made by a majority YES/NO vote. The protocols governing these agencies are steadfast, allowing modifications only under pre-determined conditions (Swan 2015). Depending on their governance system, they may or may not be autonomous. For example, an agency may retain the veto option over its decision-making process for another agency. A DAO is a decentralized and meshed network of agencies that work as one entity without having a single control point. Instead of central management, incentives promote indirect cooperation among agents, a concept known as stigmergy in biology (Jentzsch 2016). Unlike traditional legacy organizations with scalability constraints, a DAO is a super-scalable organization that incorporates the efficiency, agility, and scalability of free markets while maintaining the coherence of a startup and the ability to pursue scalable purposes (Swan 2015).
This study aims to develop a conceptual framework for enhancing private financing for infrastructure projects within LDCs, addressing the existing gap in the literature. Utilizing the potential of blockchain technology, DAO frameworks, and financial governance terms, this study explores two main areas:
- (1)
How blockchain technology, facilitated through a DAO, can act as a driving force to attract necessary resources and skills to LDCs.
- (2)
The potential of blockchain technology, incorporated within DAOs, to address the persistent challenges related to infrastructure financing and governance in LDCs.
The results of this study provide construction management stakeholders in LDCs with practical guidelines and insights, facilitating more effective infrastructure financing in these contexts.
Methodology
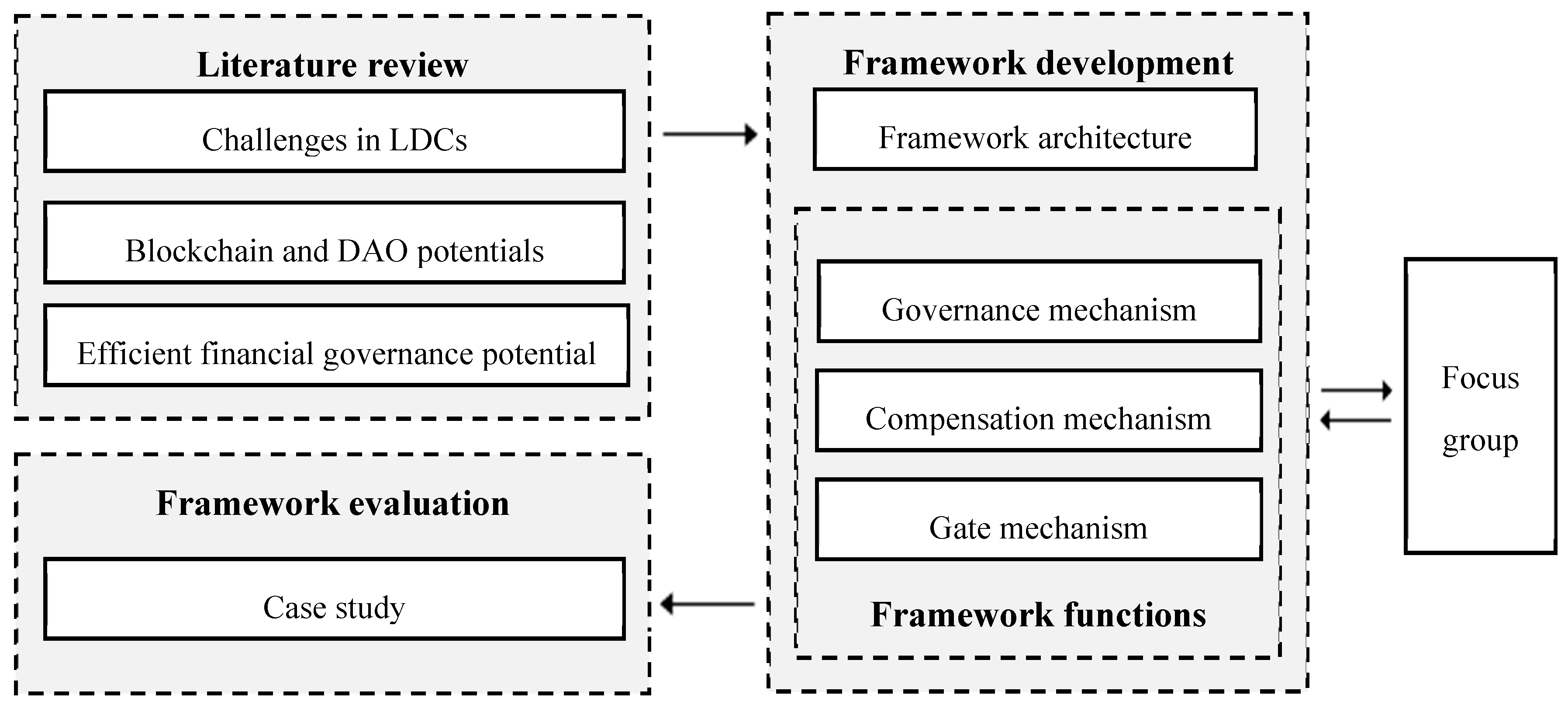
Figure 1 provides a visual representation of the study's methodology, which is explained in detail in the following sections.
In developing the suggested framework, a focus group method was employed, as outlined in Luke and Goodrich (2019). Two experienced professionals were engaged: one with a strong background developing blockchain solutions for enterprises, and another, an infrastructure finance lawyer with two decades of global expertise. This initial draft was emailed to these experts for feedback on refining the framework. Face-to-face interviews were conducted using web-based platforms, and notes were taken during each meeting for inclusion in the focus group proceedings. The authors regularly communicated with the consultants to ensure all suggestions were applied and any issues or inconsistencies were quickly resolved.
The Proposed Framework’s Architecture
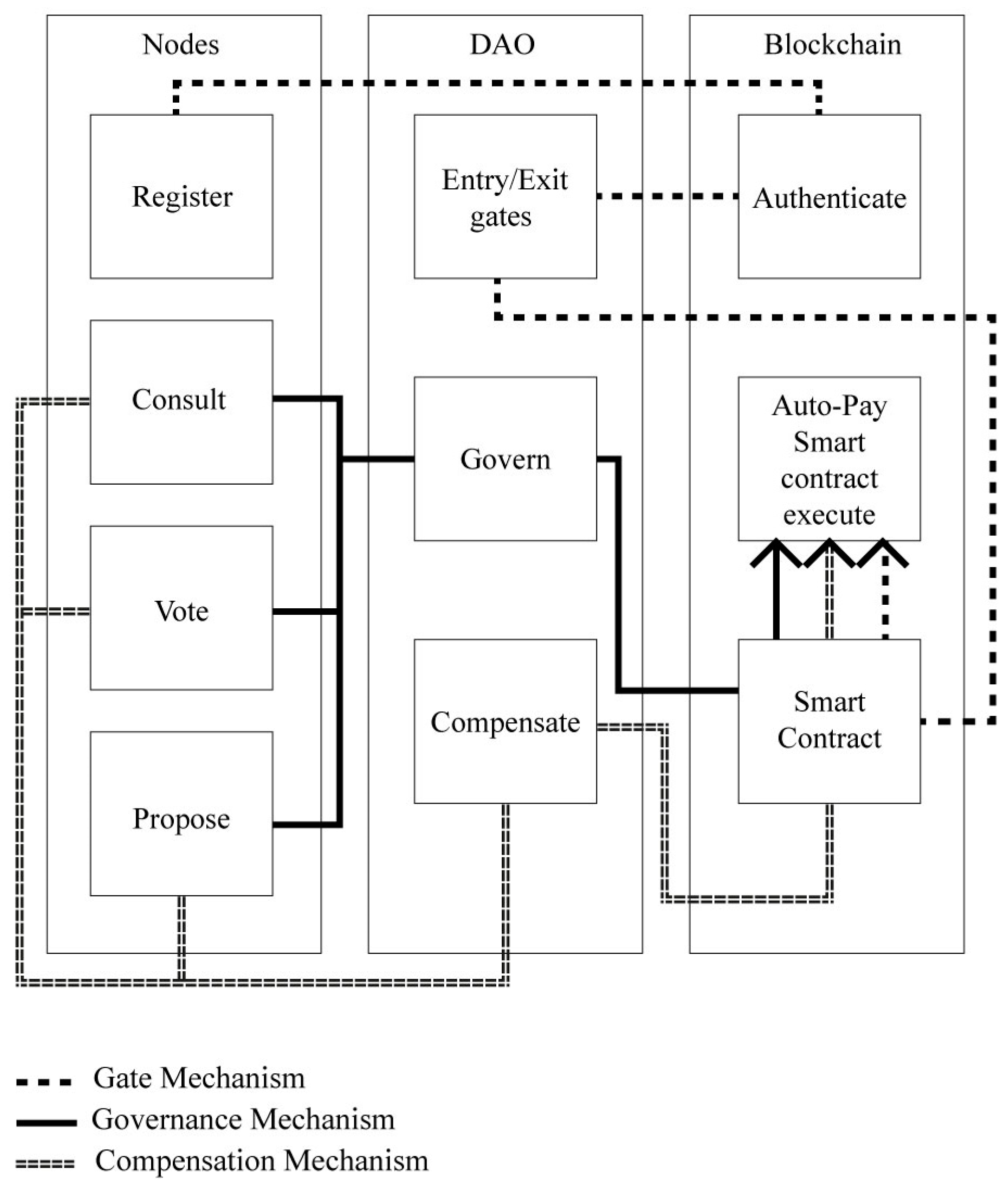
The proposed framework for governing infrastructure financing through blockchain features an integrated process to enhance transparency, efficiency, and accountability. This approach comprises three main components: the first layer of blockchain, the DAO blockchain layer, and the node layer, as shown in
Figure 2.
The proposed framework is built on the first layer of blockchain technology, which acts as a decentralized, unchangeable ledger for all financial activities. It ensures tamper-proof preservation of all financial data, thus securing open and immutable transactions. The second component, the DAO blockchain layer, constitutes the governance aspect of the infrastructure financing framework, which allows for the independent and decentralized allocation of funds. The smart contracts running on the first layer blockchain enforce the rules and guidelines established by the DAO blockchain layer for financing infrastructure. Nodes, which represent users of this framework, can be any entity - individual or organizational - engaged in infrastructure financing activities, such as investors, fund managers, infrastructure developers, and governmental bodies. These nodes can interact with the DAO and primary blockchain layer through a user-friendly interface. The interaction between these three layers is pivotal for successfully operating the infrastructure financing governance framework. Nodes can initiate different actions, such as registering, proposing a project, submitting a funding request, or voting on a project proposal.
The core foundation of this architecture, the DAO layer, presents three essential functions: gatekeeping, decision-making, and governance, as shown in
Figure 2. These roles together contribute to the smooth and effective functioning of the infrastructure finance governance system. The gatekeeping function controls access to the proposed framework. By setting unique criteria for each node to join the platform, this function guarantees that only valid and authorized participants can partake in infrastructure financing activities. Initially, each node must authenticate on the blockchain layer to access the infrastructure financing decision-making system. Once authenticated, the node navigates the entry and exit gates on the DAO layer. If the node meets the established criteria, it can engage in infrastructure financing activities as a valid member of the smart contracts provided on the blockchain layer. This function provides a crucial layer of security and trust by regulating participation in infrastructure financing activities, thereby reducing the risk of fraudulent or unauthorized transactions.
The governance mechanism depends on the active involvement of its nodes to facilitate effective governance. The platform allows qualified nodes to propose various actions for voting by poll voters. These include essential funding and infrastructure project decisions, such as contractor payment requests. Concurrently, voters can vote on these proposals, which are then processed by the DAO layer to ensure a transparent and decentralized decision-making process. Additionally, advisors can contribute significantly by offering expert commentary on proposals and other framework elements. Collectively, these features constitute a decentralized, equitable, and multilevel governance framework that assures efficient management of infrastructure finance projects. After processing all inputs from the qualified nodes, the DAO layer can produce outputs for the smart contracts to be executed on the blockchain layer. This outcome reflects the nodes' collective decision-making and ensures that governance actions are implemented uniformly and transparently.
The compensation function is a pivotal mechanism to foster active participation and knowledge contribution from nodes within the framework by offering incentives. The level of compensation for different nodes varies and depends on the time, effort, and expertise they contribute to the platform. Rewards can be in the form of exchangeable tokens, which can either be cashed out or utilized as currency within the system. This compensation function aids in cultivating a vibrant and dedicated ecosystem of nodes, rewarding active participation and knowledge contribution toward the platform's success. By providing these functions on the DAO level, the infrastructure financing governance framework can develop outputs for smart contract execution and finalize payments. This seamless integration between the DAO and blockchain layers can ensure that decisions made through the governance mechanism are implemented effectively and transparently. Moreover, nodes might receive additional rewards based on their previous decisions, fostering sound decision-making practices and ensuring efficient and effective platform management.
The Decision-Making Structure
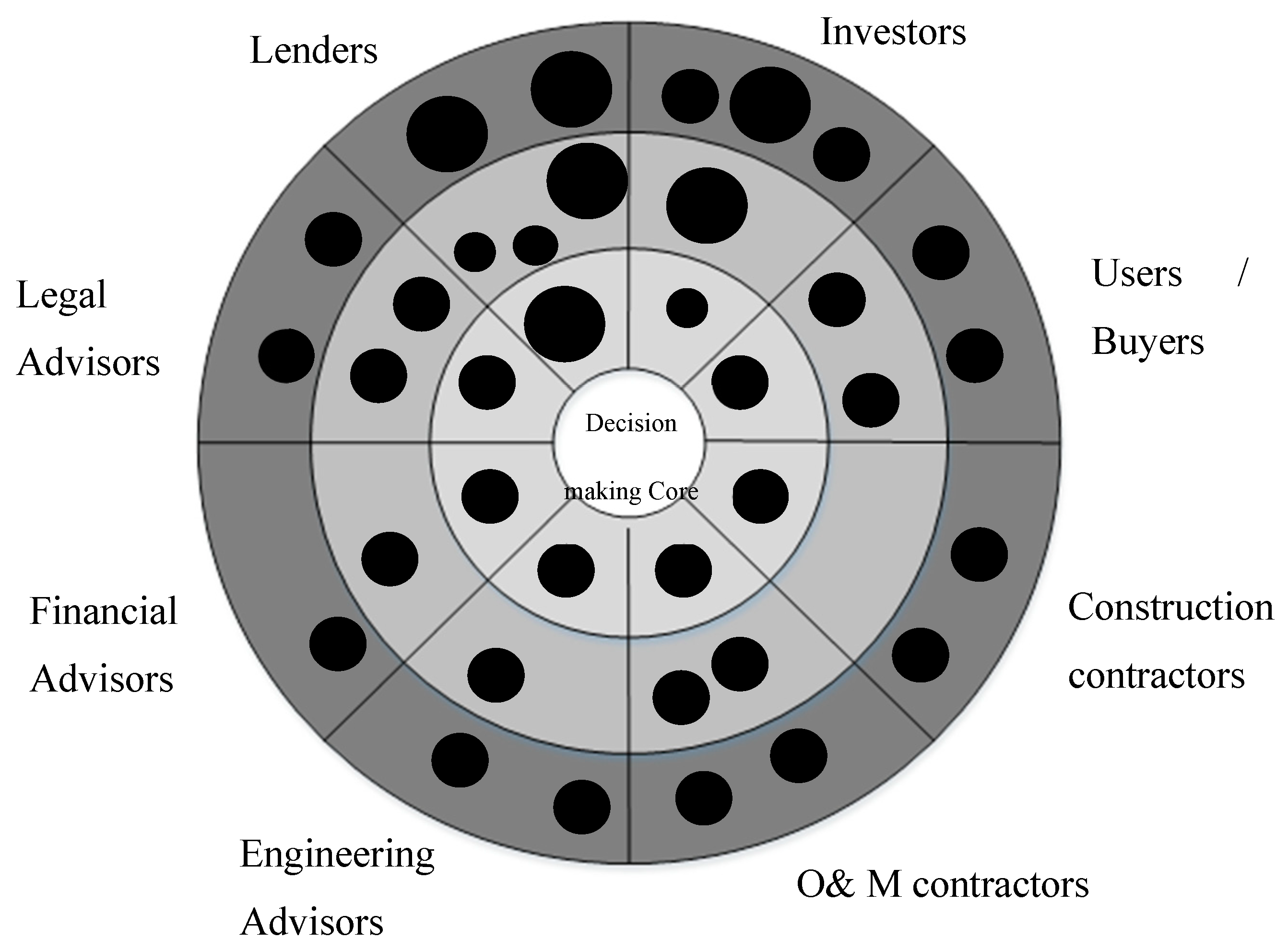
In the absence of a central authority or Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV), this study proposed a decision-making structure and responsibility allocation mechanism, as depicted in
Figure 3. The figure illustrates the voting power distribution among different parties, determined by their roles and reputations. In this structure, the node's proximity to the core represents more significant influence and higher commitments and responsibilities. This arrangement guarantees that parties with superior expertise, reputation, and experience have a more substantial influence on the decision-making processes. Parties within this framework are classified into three categories:
1. Members holding a passive role
This role belongs to ambassadors (Soleimani et al. 2019), which includes investors and lenders who do not possess adequate expertise to participate in the voting mechanism actively. Ambassadors can only observe the project's progress and cash flow transactions. The defining attribute of this group is the size of their financial contribution. All lenders and investors must clear anti-money laundering (AML) and Know Your Client (KYC) checks.
2- Active Voting Members
This group comprises contributors with sufficient knowledge about infrastructure projects within the context of LDCs, allowing them to vote on proposals based on their relative majorities to make decisions.
They must meet specific pre-established eligibility criteria defined by the coordinators, who make up the decision-making core. Following is a formula for calculating the impact of each vote:
where
is the weight of votes,
represents the advisor or normal contributor index,
denotes the reputation score,
stands for the size index (for investors and lenders), and
is the relative majority, which can be either 1 or 0.
The formula aims to evaluate the significance of voters within the groups (contributors and advisors) and distinguish their respective impacts. It is due to the difference in the influence of a vote from an advisor compared to a regular contributor. The 'reputation' here refers to the voter's visibility or credibility within the decision-making structure, with those closest to the core having a more significant influence. The investment size index is determined by the number of tokens dedicated to the project or the size of the wallet. For lenders, the index is based on the amount of money they intend to lend to the project and the desired payback time intervals or preferred repayment terms. The relative majority is a factor that determines a specific member's eligibility to participate in the voting process.
3. Decision-making core unit or coordinators
This group comprises individual and institutional advisors and experts with high reputations and a spectrum of expertise. They can vote on proposals directly related to their areas of expertise. For instance, legal advisors should engage with the project's legal proposals. The following equation is proposed to specify the impact of each vote:
In this formula, indicates the weight of votes, signifies the advisor or normal contributor index, is the reputation, and represents the relative majority, taking a value of either 1 or 0.
This equation only considers the voter's expertise and reputation, as the size of their wallets should not impact the decision-making process. Even if one of the members in the decision-making core is an investor, the impact of their vote will be considered based on their expertise rather than the amount of money they have in their wallets. This power distribution ensures that decisions are made by knowledgeable and experienced individuals, promoting transparency and accountability in the decision-making process.
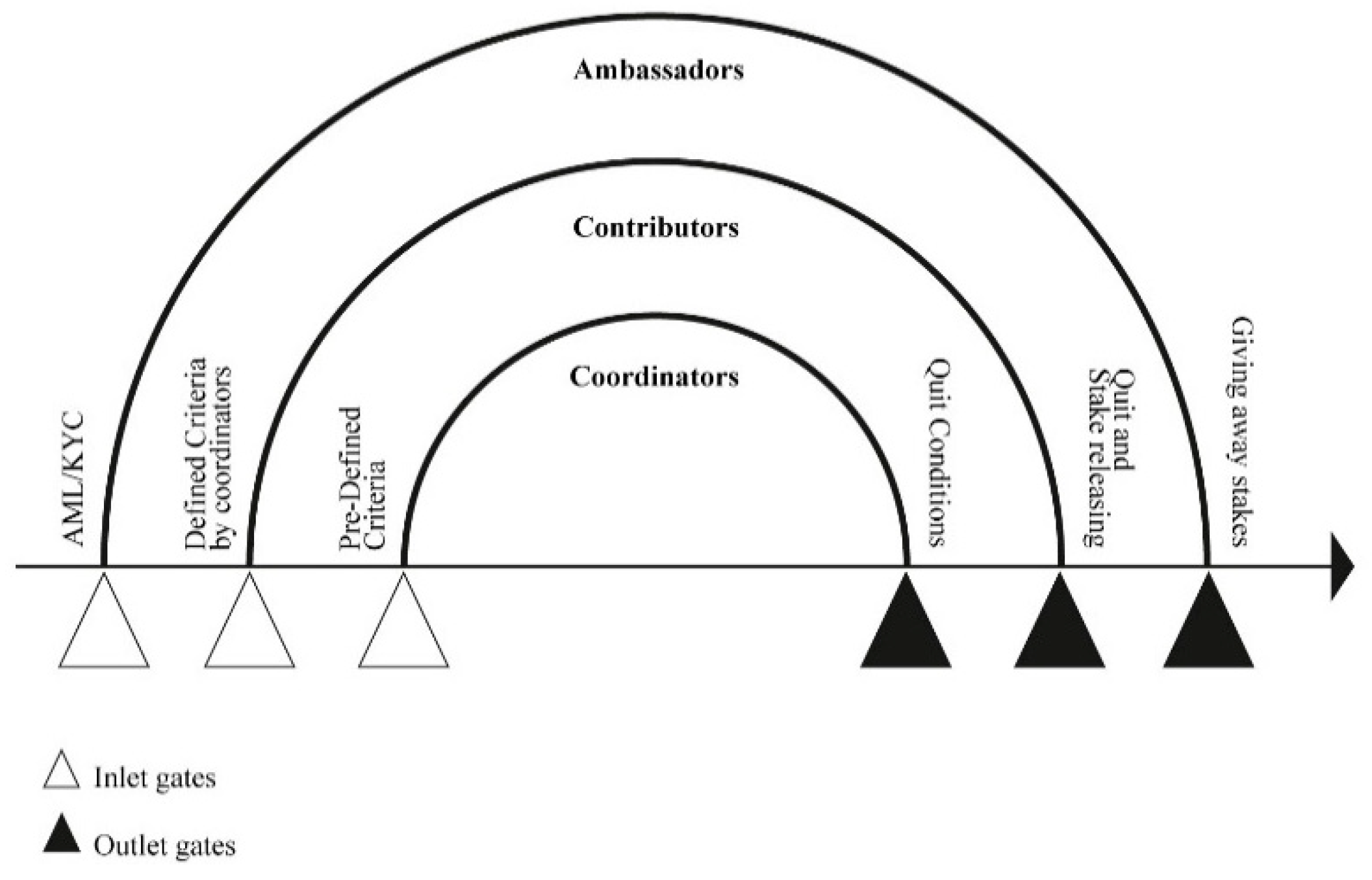
Entry and Exit Gates
Figure 4 demonstrates the requirements for joining and exiting each group in the proposed infrastructure financing governance framework. Ambassadors must pass AML/KYC check-ups to enter the group and release all their tokens to leave. Similarly, Contributors must meet specific criteria set by the coordinators for admission and surrender all their tokens, including governance and utility tokens, when exiting. Additionally, coordinators and contributors must wait until all the proposals they contributed to have been processed in the decision-making process before exiting the group (Soleimani et al. 2019). Implementing these rules within the proposed framework guarantees that only committed and capable individuals can participate in decision-making. The exit regulations further maintain transparency and accountability by preventing participants from leaving the group immediately after the approval of their proposals.
Proposals
Members of the infrastructure financing governance framework may propose one of the following on the network:
- (1)
Proposal for Reputation Assignment: Members may propose assigning reputation to certain contractors or service providers based on past performance. Successful implementation of such a proposal leads to the new member receiving DAO shares, granting them governance rights and a claim to the assets linked to these DAO shares.
- (2)
Proposal for Utility Token Transfer: Members may propose transferring utility tokens as a reward for a service provided by a member, such as contractors who have completed a project. This proposal compensates members for their services.
- (3)
Proposal for Utility Token Awards: Members may propose awarding utility tokens to coordinators and contributors based on their contributions to the network. For instance, advisors and experts may be compensated automatically with these tokens when they contribute value to the network.
By allowing members to propose these actions, the infrastructure financing governance framework promotes decentralized decision-making and incentivizes active participation in the network. These proposals ensure the network is run efficiently and provide a fair compensation mechanism for the contributions of all members.
Compensation and Incentives
The compensation and incentive system is built on the amount of time spent on proposals, regardless of whether a member makes a decision or not. For instance, an advisor may review a proposal without making any decision yet still receive compensation for the time expended. Based on proposals from Prime DAO and MKR, the following incentive system is presented:
In this equation, denotes incentive value, represents the Annual FTE salary in USD, stands for the time of commitment, reflects the reputation, is the common commitment time for an annual FTE, and indicates the minimum qualified node Reputation.
A member's incentive is directly correlated with their reputation compared to their group's minimum level. For example, suppose a minimum of 100 reputation points is required to enter as a contributor, and a member's reputation level is 150 points. In that case, they will be paid 1.5 times the base salary in that category. This reputation-based reward mechanism encourages active participation, ensuring members with more outstanding expertise and reputation are rewarded justly, promoting effective network management.
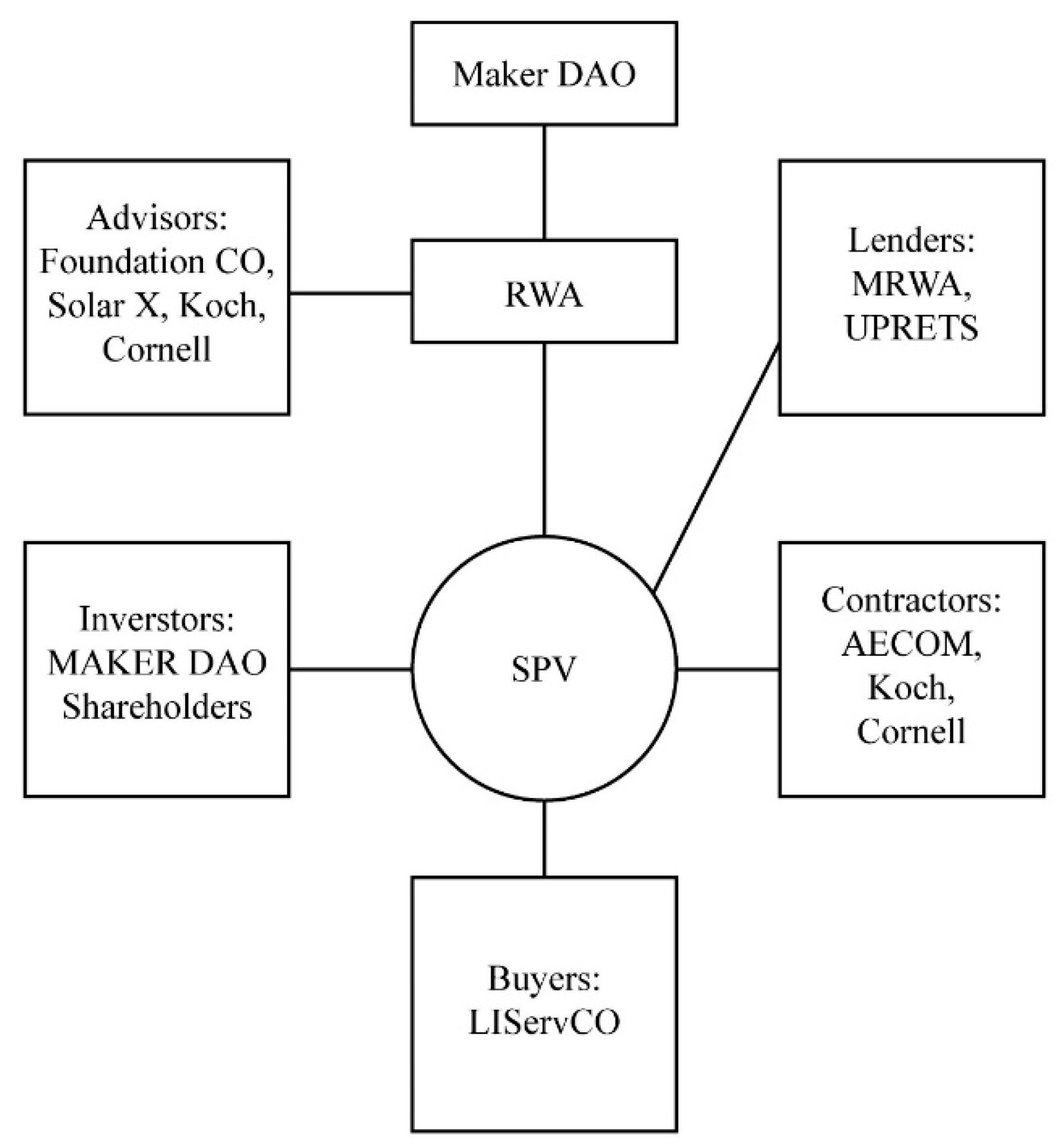
Case Study (Maker DAO Solar X Project)
The Maker DAO Solar X project is an innovative initiative aimed at transforming solar energy financing through a decentralized and transparent financial system. A separate entity, Solar X Group Mattituck, LLC (Project Co), was established to build a solar farm in the area to achieve this goal. As part of the agreement, Solar X Group and third-party sponsors, including high-net-worth individuals and businesses, funded the operation, maintenance, and ownership of the solar farm by Project Co. One of the project's goals was to take advantage of the federal investment tax credit. Solar X Group proposed to build a large solar farm in the hamlet of Mattituck, located in Suffolk County, New York. The first loan disbursement, which amounted to $3,285,000, was disbursed to Project Co and used to purchase land and cover engineering and pre-development costs. The purpose of the direct loan was to raise capital for a single project, thereby facilitating the project's financing.
Mechanism
Maker DAO has established a company called RWA to manage the Solar X project and oversee all its financial aspects. RWA has created a particular purpose vehicle (SPV) to facilitate communication among all the project participants. An SPV is a legal entity created to execute a specific project and is used to isolate the risks and liabilities of that project from those of its parent company (MKR.com). The various actors in the Solar X project are connected to the network through the SPV created by RWA.
Decision-Making Process
The decision-making core of Maker DAO, which includes its various members, cannot directly affect the financial governance of the Solar X project. Only RWA experts in their respective fields can participate in the decision-making processes related to the project. The RWA Foundation is composed of several components and members who work towards achieving the Foundation's goals. The decision-making powers of each Foundation member are different. The Foundation's members and supervisors are responsible for voting, appointing, or removing directors at the general meeting. On the other hand, the directors are responsible for managing the Foundation and have the power to select or remove supervisors. The Secretary of the Foundation is a licensed service provider legally required to be a member, with MakerDAO as the beneficiary if specified. A committee member is a resource to guide directors on specific topics, whereas authorized signers allow directors to delegate some tasks.
Table 1 shows the different powers of the members.
Results and Discussion
In this section, the case study is compared with the proposed framework to determine whether the framework effectively addresses the issues associated with infrastructure financing.
Table 2 presents the summarized findings. The case study elaborates on how the Solar X Group set up a solar farm with third-party investor support. Nevertheless, the framework's intention is broader, addressing general infrastructure finance concerns, such as stakeholder participation, risk distribution, and innovative financing methods.
For a comprehensive comparison, seven pivotal factors were examined: the classification of voting power, defining exit gates, time-based compensation, expertise-based compensation, consultant availability, SPV, and scalability.
MakerDAO SolarX did not clearly define a method for distributing voting power or tokens. This may result in the concentration of decision-making power in the hands of a few, resulting in biased decision-making in favor of one group or failure to leverage the knowledge of all stakeholders. In addition, the lack of a defined voting mechanism might lead to uncertainty and mistrust among the stakeholders, potentially undermining the project's success. In the proposed framework, on the other hand, power is allocated according to both capital investment and expertise. This approach ensures that the decisions are not solely driven by financial capacity but also informed by industry knowledge and practical insights, thus facilitating better decision-making and reducing the likelihood of poor investment decisions and project mismanagement.
The case study defined some gates for investors, primarily focused on AML and KYC regulations. While these measures are essential for regulatory compliance and risk management, they are insufficient for ensuring the quality of decision-making or the stability of the project. The proposed framework addresses these gaps by providing distinct entry and exit gates. In addition to addressing regulatory issues and mitigating fraud risk, these gates enhance the platform's overall structure and decision-making process. A critical feature of these gates is their ability to facilitate expert-based decision-making. By setting strict entry criteria, the framework ensures that only qualified and knowledgeable stakeholders can participate in the project. This approach ensures decisions are not only based on financial considerations but also on technical expertise and industry insights. Furthermore, the exit gates in the proposed framework safeguard the project from abrupt or destabilizing departures. They help maintain project stability and continuity, which is particularly important for long-term, high-cost infrastructure projects. By providing a clear path for exit, stakeholders can better plan their investment strategies, contributing to a more predictable and stable investment environment. These additional features will increase security and stability and promote a more systematic, informed, and expertise-based decision-making process.
One of the most significant features of the proposed framework is incorporating both time- and expertise-based compensation systems. The MakerDAO SolarX model employed a time-based compensation system, an effective strategy for rewarding long-term commitment; however, it can fail to incentivize the contribution of individuals with the required expertise but lack significant time commitment or financial investment. The proposed framework addresses this issue by rewarding not only the duration of involvement but also the depth of involvement based on the expertise of the stakeholder. In this way, long-term investors and skilled professionals can be motivated to participate actively, thereby improving the quality of decision-making and leading to a more balanced, inclusive, and sustainable infrastructure financing environment.
Infrastructure financing is an intricate field that requires the availability of consultants. However, the existing MakerDAO SolarX case study lacked a defined consulting system. This may result in the underutilization of available expertise and ultimately impede the project's progress. Accordingly, the suggested framework emphasizes the inclusion of consultants and the possibility of outsourcing essential services. Participants with specialized expertise, in particular, can fill two distinct roles. They engage in decision-making and act as consultants, offering invaluable perspectives and guidance to fellow investors. It creates a mutually beneficial environment: experts contribute to their maximum potential, and other investors benefit from a more informed decision-making process. Consultant involvement also adds a layer of transparency and accuracy to the project. This can encourage public sector adoption and raise overall awareness about the project. Additionally, by addressing organizational costs, the approach guarantees a more thorough solution for executing the project.
The MakerDAO SolarX case study employs Special-Purpose Vehicles (SPVs) for project financing, a common strategy in infrastructure financing. However, an SPV often introduces an intermediary layer in the process, potentially limiting blockchain technology's advantages, such as transparency and decentralization. The proposed framework eliminates the traditional use of SPVs in infrastructure financing, resulting in a maximum benefit from blockchain technology. This method increases transparency by ensuring that every transaction is recorded and traceable on the blockchain. Moreover, it reinforces the principle of decentralization by ensuring that all participants are directly involved in the decision-making process. In addition to simplifying engagement, fully decentralized governance can also attract a broader range of investors by eliminating intermediary-related barriers.
Scalability is an essential factor determining the effectiveness and potential for widespread adoption of any financing framework. In the MakerDAO SolarX case study, scalability is limited due to its reliance on SPVs. The SPV approach requires setting up a new vehicle for each project, which can be time-consuming, costly, and complex. Such limitations could restrict its broad implementation, particularly for projects of varying sizes or complexity. Conversely, the proposed framework is designed with scalability at its core. It offers a flexible approach that can be easily adapted to fit the needs of any infrastructure project, regardless of its size, scope, or complexity. This scalability is achieved by eliminating the need for an SPV, thereby removing the bottlenecks associated with establishing a new vehicle for each project. Using blockchain technology and focusing on decentralization, the framework can handle multiple projects simultaneously without needing separate governing bodies. Consequently, this approach enhances efficiency, reduces costs, and broadens potential applications across various sectors.
Conclusions
This study aimed to develop a conceptual framework using blockchain technology and DAOs to address the challenges of private financing in infrastructure projects within LDCs. The proposed framework consists of three primary components: the foundational blockchain layer, the DAO blockchain layer, and the node layer. The foundational blockchain layer provides a decentralized ledger, ensuring the integrity and immutability of financial records. The DAO layer introduces governance, facilitated by smart contracts from the base blockchain, and is vital for decentralized fund allocation. Nodes interact with these layers, representing users like investors and governmental entities. The DAO layer includes three functions:
- (1)
Decision-making: The framework outlines a decision-making structure without a central authority, categorizing stakeholders into passive observers (investors and lenders), active voters with a complex weighted system based on expertise and contributions, and a core of high-reputation experts voting on specific domains, ensuring informed, expertise-driven, and transparent decisions.
- (2)
Gatekeeping: There are strict entrance and exit requirements for participants in the governance framework. These rules enhance commitment, ensuring transparency and accountability in decision-making.
- (3)
Governance mechanism: The framework allows members to make proposals regarding reputation, utility token transactions, and rewards. This promotes decentralized operations and active network engagement. Besides that, the proposed reward mechanism compensates members based on their time on proposals and their reputation within the group. This approach motivates active and knowledgeable engagement.
The study utilized a case study, the Maker DAO Solar X project, to assess the proposed infrastructure financing framework's effectiveness. The project focused on decentralized solar energy financing, leading to establishment of a solar farm in Mattituck, New York, managed by a unique company, RWA, with financing mechanisms involving SPVs. It was found that the proposed infrastructure financing framework outperformed the Maker DAO Solar X model in all comparison dimensions. The project's voting power distribution was ambiguous, raising concerns about potential decision-making bias. In contrast, the framework proposed a balanced power distribution based on financial contribution and expertise. While Solar X used a time-based compensation system, the framework rewards both time and expertise, enhancing decision quality. Further, the use of SPVs in the case study presented scalability limitations. However, the proposed framework, leveraging blockchain, would provide greater scalability, increased transparency, and direct stakeholder engagement, offering a more robust solution for infrastructure financing. The study's findings offer clear insights for stakeholders involved in LDC infrastructure projects, especially private investors and government bodies, to enhance the quality and efficiency of infrastructure planning and execution within these countries.
One limitation of this study was the lack of research on the applications of blockchain technology, especially the DAO blockchain, to financing infrastructure projects. A lack of literature posed challenges in developing a solid theoretical basis for the study. Additionally, due to the limited availability of applicable case studies, our evaluation of the proposed framework was constrained to a single case, potentially narrowing our practical understanding. The recognition of these limitations provides avenues for further research.
Integrating AI into the DAO model can significantly enhance its efficiency for future studies ( Moayyed and Agapaki, 2024). Leveraging AI's capabilities in data analytics, predictive modelling, and scenario simulation can enable autonomous resource allocation, timely bottleneck identification, and refined decision-making within the DAO infrastructure.
Disclosure Statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Data Availability Statement
References
- Alharby M, Van Moorsel A. 2017. Blockchain-based smart contracts: A systematic mapping study. arXiv:1710.06372.
- Asian Development Bank. 2017. Meeting Asia’s infrastructure needs. Special Report.
- Carter DB, Stone RW. 2015. Democracy and multilateralism: the case of vote buying in the UN General Assembly. Int Organ. 69(1):1-33. [CrossRef]
- Casino F, Dasaklis TK, Patsakis C. 2019. A systematic literature review of blockchain-based applications: Current status, classification and open issues. Telemat inform. 36:55-81. [CrossRef]
- Diallo N, Shi W, Xu L, Gao Z, Chen L, Lu Y, Shah N, Carranco L, Le TC, Surez AB, Turner G. 2018. eGov-DAO: A better government using blockchain based decentralized autonomous organization. ICEDEG 166-171.
- El Faqir Y, Arroyo J, Hassan S. 2020. An overview of decentralized autonomous organizations on the blockchain. Proc. 16th Int'l Symp Open Collab. 1-8.
- Gutman J, Sy A, Chattopadhyay S. 2015. Financing African infrastructure: Can the world deliver?
- Hurley, G, Voituriez T. 2016. Financing the SDGs in the Least Developed Countries: Diversifying the financing Tool-box and Managing Vulnerability. Diss. AFD; UNDP.
- Jentzsch C. 2016. Decentralized autonomous organization to automate governance. White paper.
- Khan N, Yaqoob I, Hashem IA, Inayat Z, Mahmoud Ali WK, Alam M, Shiraz M, Gani A. 2014. Big data: survey, technologies, opportunities, and challenges. Sci World J.
- Kiu MS, Chia FC, Wong PF. 2022. Exploring the potentials of blockchain application in construction industry: a systematic review. Int J Constr Manag. 22(15):2931-40. [CrossRef]
- Kumar R, Kumar RR, Stauvermann PJ, Chakradhar J. 2019. The effectiveness of fisheries subsidies as a trade policy tool to achieving sustainable development goals at the WTO. Mar Policy. 100:132-40.
- Luke M, Goodrich KM. 2019. Focus group research: An intentional strategy for applied group research? J Spec Group Work. 44(2):77-81.
- OECD. 2019. OECD Skills Outlook 2019: thriving in a Digital World., 252. Paris: Organisation for Economic Co-operation Development.
- Perera S, Nanayakkara S, Rodrigo MN, Senaratne S, Weinand R. 2020. Blockchain technology: Is it hype or real in the construction industry? J Ind Inf Integr. 17:100125.
- Scott DJ, Broyd T, Ma L. 2021. Exploratory literature review of blockchain in the construction industry. Autom constr.132:103914. [CrossRef]
- Singh A, Parizi RM, Zhang Q, Choo KK, Dehghantanha A. 2020. Blockchain smart contracts formalization: Approaches and challenges to address vulnerabilities. Comput Secur. 88:101654. [CrossRef]
- Soleimani S, Bruwer J, Gross MJ, Lee R. 2019. Astro-tourism conceptualisation as special-interest tourism (SIT) field: A phenomonological approach. Curr Issues Tour. 22(18):2299-314. [CrossRef]
- Sun X, Chen X, Stasinakis C, Sermpinis G. 2022. Multiparty Democracy in Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO): Evidence from MakerDAO. arXiv:2210.11203.
- Swan M. 2015. Blockchain thinking: The brain as a decentralized autonomous corporation [commentary]. IEEE Technol Soc Mag. 34(4):41-52. [CrossRef]
- Tian Y, Lu Z, Adriaens P, Minchin RE, Caithness A, Woo J. 2020. Finance infrastructure through blockchain-based tokenization. Front Eng Manag. 7:485-99. [CrossRef]
- Tian Y, Minchin RE, Petersen C, Moayed E, Adriaens P. 2022. Financing Public-Private Partnership Infrastructure Projects through Tokenization-enabled Project Finance on Blockchain. IOP Conf Ser: Mater Sci Eng. (Vol. 1218, No. 1, p. 012027). IOP Publishing. [CrossRef]
- UNCTAD. 2019. The least developed countries report 2019: the present and future of external development finance–old dependence, new challenges. New York: UNCTAD.
- Uzsoki D. 2019. Tokenization of infrastructure: a blockchain-based solution to financing sustainable infrastructure.
- Wang S, Ding W, Li J, Yuan Y, Ouyang L, Wang FY. 2019. Decentralized autonomous organizations: Concept, model, and applications. IEEE Trans Comput Soc Syst. 6(5):870-8. [CrossRef]
- Moayyed, E., & Agapaki, E. (2024). Smart Construction Contract Generation Framework for Improved Decision-Making Processes. In Computing in Civil Engineering 2023 (pp. 332-339).
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).