Submitted:
30 October 2024
Posted:
31 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Background: COVID-19 mainly affects the respiratory system, although its manifestations are multisystemic. Increasingly, complications presented after the acute phase are still being rec-ognized and are associated with impaired functional status and health-related quality of life (HRQoL). The objective was assess the functional status and HRQoL of patients with post-COVID-19. Methods: This was a cross-sectional study involving individuals affected by COVID-19 who had persistent symptoms for one month after the acute phase of the disease. HRQoL was verified through the Short Form Health Survey 36 (SF-36) and, functional status was assessed using the six-minute walk test (6MWT), the Fatigue Severity Scale (FSS), the Med-ical Research Council (MRC) Dyspnea Scale and, the Post-COVID-19 Functional Status Scale (PCFS). Results: Were included 123 patients, 73 (59.35%) were male, with a mean age of 49.17±13.48 years and a body mass index of 31.02±6.56 stratified into three groups, not recov-ered group (NRG=23), ward recovered group (WHG=60), and intensive care unit group (ICUG=40). The main symptoms were muscle weakness (74.17%) and dyspnea (68.33%). In rela-tion to the distance covered in the 6MWT, the GNR group walked 12.83% below the predicted values, GNR 20.21% and the UGCI 28.82%, respectively. The MRC dyspnea scale had a mean value of less than 3 and the FSS scale had a mean value over 4, indicating considerable fatigue. In the PCFS scale, a significant difference was observed (p>0.0005); while in the SF-36, all HRQoL domains were compromised. Conclusion: Post-COVID-19 patients involved in this study showed a significant decline in functional status and an impairment of HRQoL.
Keywords:
1. Introduction
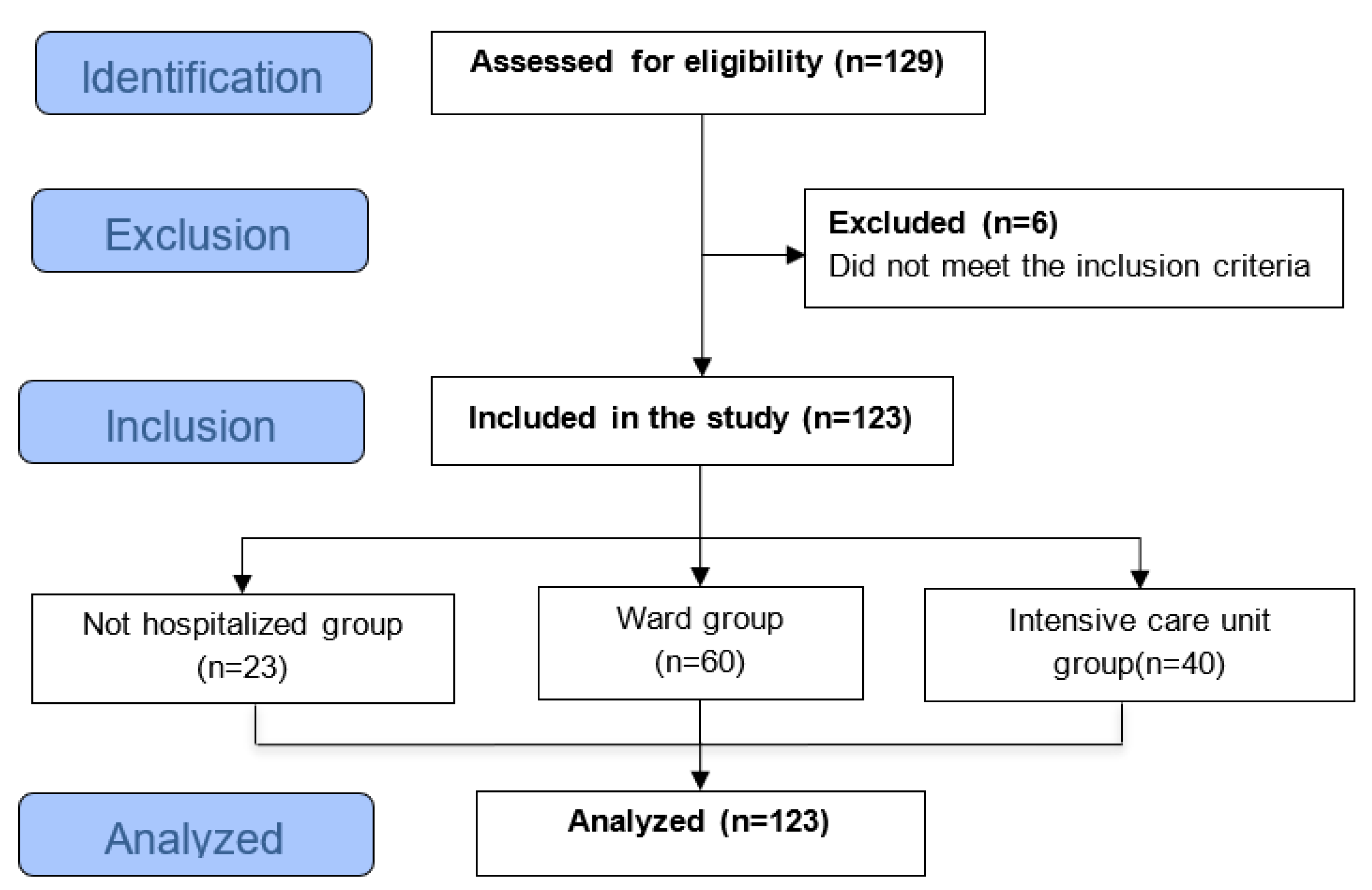
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Ethical Aspects
2.3. Selection of Participants
2.4. Inclusion Criteria
2.5. Exclusion Criteria
2.6. Outcomes and Measurement Instruments
2.6.1. Exercise Capacity: Six-Minute Test
2.6.2. Muscle Fatigue: Fatigue Severity Scale (FSS)
2.6.3. Severity of Dyspnea: Medical Research Council (MRC) Dyspnea Scale
2.6.4. Functional Status: Post-COVID-19 Functional Status Scale (PCFS)
2.6.5. HRQoL: Short Form Health Survey 36 (SF-36)
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Del Rio, C.; Malani P.N. 2019 Novel Coronavirus-Important Information for Clinicians. JAMA. 2020, 323, 1039–1040. [CrossRef]
- Parasher, A. COVID-19: Current understanding of its Pathophysiology, Clinical presentation and Treatment. Postgrad Med J. 2021, 97, 312–320. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Eijk, L.E.; Binkhorst, M.; Bourgonje, A.R., et al. COVID-19: immunopathology, pathophysiological mechanisms, and treatment options. J Pathol. 2021, 254, 307–331. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Z.J.; Shan, J. Review 2019 Novel coronavirus: where we are and what we know. Infection. 2020, 48, 155–163. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakodkar, P.; Kaka. N.; Baig, M.N. A Comprehensive Literature Review on the Clinical Presentation, and Management of the Pandemic Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Cureus. 2020, 12, e7560.
- Grasselli, G.; Zangrillo, A.; Zanella, A., et al. Baseline Characteristics and Outcomes of 1591 Patients Infected With SARS-CoV-2 Admitted to ICUs of the Lombardy Region, Italy. JAMA. 2020,323, 1574–1581.
- Oronsky, B.; Larson, C.; Hammond, T.C., et al. A Review of Persistent Post-COVID Syndrome (PPCS). Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2023, 64, 66–74.
- Yuan, N.; Lv, Z.H.; Sun, C.R., et al. Post-acute COVID-19 symptom risk in hospitalized and non-hospitalized COVID-19 survivors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Public Health. 2023; 11:1112383.
- Nalbandian, A.; Sehgal, K.; Gupta, A., et al. Post-acute COVID-19 syndrome. Nat Med. 2021, 27, 601–615. [CrossRef]
- Chippa V, Aleem A, Anjum F. Post-Acute Coronavirus (COVID-19) Syndrome. 2023 Feb 3. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024.
- Rochmawati, E.; Iskandar, A.C.;, Kamilah, F. Persistent symptoms among post-COVID-19 survivors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Nurs. 2024, 33, 29–39. [CrossRef]
- Carfì, A.; Bernabei, R.; Landi, F. Gemelli Against COVID-19 Post-Acute Care Study Group. Persistent Symptoms in Patients After Acute COVID-19. JAMA. 2020, 324, 603–605.
- Carenzo, L.; Protti, A.; Dalla Corte, F., et al. Short-term health-related quality of life, physical function and psychological consequences of severe COVID-19. Annals of Intensive Care. 2021, 11, 1–8. [CrossRef]
- 14. Gemelli Against COVID-19 Post-Acute Care Study Group. Post-COVID-19 global health strategies: the need for an interdisciplinary approach. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2020, 32, 1613-20.
- Barker-Davies. R.M.; O'Sullivan, O.; Prathima Senaratne, P.K., et al. The Stanford Hall consensus statement for post-COVID-19 rehabilitation. Br J Sports Med 2020, 54, 949–59.
- Von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M., et al. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: guidelines for reporting observational studies. Lancet. 2007, 370, 1453–1457.
- Sciurba, F.C.; Slivka, W.A. Six-minute walk-testing. Semin Resp Crit Care Med 1998, 9, 383–91. [CrossRef]
- ATS Committee on Proficiency Standards for Clinical Pulmonary Function Laboratories. ATS statement: guidelines for the six-minute walk test. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002, 166, 111–117.
- Britto, R.R.; Probst, V.S;, de Andrade, A.F., et al. Reference equations for the six-minute walk distance based on a Brazilian multicenter study. Braz J Phys Ther. 2013, 17, 556–563.
- Krupp, L.B.; LaRocca, N.G.; Muir-Nash, J.; Steinberg, A.D. The fatigue severity scale: application to patients with multiple sclerosis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Archives of neurology. 1989, 46, 1121–1123. [CrossRef]
- Valderramas, S.; Feres, A.C.; Melo, A. Reliability and validity study of a Brazilian-Portuguese version of the fatigue severity scale in Parkinson’s disease patients. Arquivos de neuro-psiquiatria. 2012, 70, 497–500.
- Bestall, J.C; Paul, E.A.; Garrod, R., et al. Usefulness of the Medical Research Council (MRC) dyspnoea scale as a measure of disability in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Thorax. 1999, 54, 581–586.
- Kovelis, D.; Segretti, N.O.; Probst, V.S.; Lareau, S.C.; Brunetto, A.F.; Pitta F. Validation of the Modified Pulmonary Functional Status and Dyspnea Questionnaire and the Medical Research Council scale for use in Brazilian patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Jornal Brasileiro de pneumologia. 2008, 34, 1008–18. [CrossRef]
- Boon, G.J.A.M.; Barco, S.; Bertoletti, L., et al. Measuring functional limitations after venous thromboembolism: optimization of the Post-VTE Functional Status (PVFS) Scale. Thromb Res. 2020, 190, 45–51.
- Klok, F.A.; Boon, G.J.; Barco, S., et al. The Post-COVID-19 Functional Status scale: a tool to measure functional status over time after COVID-19. Eur Respir J. 2020, 56, 2001494. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erber, J.; Wießner, J.R; Zimmermann, G.S., et al. Longitudinal Assessment of Health and Quality of Life of COVID-19 Patients Requiring Intensive Care-An Observational Study. J Clin Med. 2021, 10, 5469.
- Ware Jr, J.E.; Sherbourne, C.D. The MOS 36-item short-form health survey (SF-36): I. Conceptual framework and item selection. Medical care. 1992, 473–483. [CrossRef]
- Ciconelli, R.M.; Ferraz, M.B.; Santos, W.; Meinão, I.; Quaresma, M.R. Tradução para a língua portuguesa e validação do questionário genérico de avaliação de qualidade de vida SF-36 (Brasil SF-36). Rev bras reumatol. 1999, 39, 143–150.
- Li, L.Q.; Huang, T.; Wang, Y.Q., et al. COVID-19 patients' clinical characteristics, discharge rate, and fatality rate of meta-analysis. J Med Virol. 2020, 92, 577–583.
- Luo, D.; Mei, B.; Wang, P., et al. Prevalence and risk factors for persistent symptoms after COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2024, 30, 328–335.
- Taboada, M.; Moreno, E.; Cariñena, A., et al. Quality of life, functional status, and persistent symptoms after intensive care of COVID-19 patients. Br J Anaesth. 2021, 126, e110–e113.
- Demoule, A.; Morawiec, E.; Decavele, M., et al. Health-related quality of life of COVID-19 two and 12 months after intensive care unit admission. Annals of Intensive Care. 2022, 12, 16. [CrossRef]
- Leidy, N.K. Functional status and the forward progress of merry-go-rounds: toward a coherent analytical framework. Nurs Res. 1994, 43, 196–202. [CrossRef]
- Torres-Castro, R.; Núñez-Cortés, R.; Larrateguy, S., et al. Assessment of Exercise Capacity in Post-COVID-19 Patients: How Is the Appropriate Test Chosen? Life 2023, 13, 621. [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, F.; Calabrese, A.; Iovene, B., et al. Residual respiratory impairment after COVID-19 pneumonia. BMC Pulm Med. 2021, 21, 241.
- Cortés-Telles, A.; López-Romero, S.; Figueroa-Hurtado, E., et al. Pulmonary function and functional capacity in COVID-19 survivors with persistent dyspnoea. Respiratory Physiology & Neurobiology. 2021, 288, 103644.
- Magdy, D.M.; Metwally, A.; Tawab, D.A.; Hassan, S.A.; Makboul, M.; Farghaly, S. Long-term COVID-19 effects on pulmonary function, exercise capacity, and health status. Annals of Thoracic Medicine 2022, 17, 28–36. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Betschart, M.; Rezek, S.; Unger, I., et al. One year follow-up of physical performance and quality of life in patients surviving COVID-19: a prospective cohort study. Swiss medical weekly 2021, 151, w30072.
- Wu, X.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Y.. et al. 3-month, 6-month, 9-month, and 12-month respiratory outcomes in patients following COVID-19-related hospitalisation: a prospective study. Lancet Respir Med. 2021, 9, 747–754. [CrossRef]
- Núñez-Cortés, R.; Malhue-Vidal, C., Gath, F., et al. The Impact of Charlson Comorbidity Index on the Functional Capacity of COVID-19 Survivors: A Prospective Cohort Study with One-Year Follow-Up. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2022, 19, 7473.
- Johnsen, S.; Sattler, S.M.; Miskowiak, K.W., et al. Descriptive analysis of long COVID sequelae identified in a multidisciplinary clinic serving hospitalised and non-hospitalised patients. ERJ Open Res. 2021, 7, 00205–02021.
- Betschart, M.; Rezek, S.; Unger, I., et al. One year follow-up of physical performance and quality of life in patients surviving COVID-19: a prospective cohort study. Swiss medical weekly. 2021, 151, w30072.
- Smith, J.M.; Lee, A.C.; Zeleznik, H., et al. Home and community-based physical therapist management of adults with post-intensive care syndrome. Phys Ther. 2020, 100, 1062–1073.
- Giurgi-Oncu, C.; Tudoran, C.; Pop, G.N., et al. Cardiovascular Abnormalities and Mental Health Difficulties Result in a Reduced Quality of Life in the Post-Acute COVID-19 Syndrome. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 1456.
- Grover, S.; Sahoo, S., Mishra, E., et al. Fatigue, perceived stigma, self-reported cognitive deficits and psychological morbidity in patients recovered from COVID-19 infection. Asian J Psychiatr. 2021, 64, 102815. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eleftheriou, A.; Rokou, A.; Arvaniti, A.; Nena, E.; Steiropoulos, P. Sleep Quality and Mental Health of Medical Students in Greece During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Front Public Health. 2021, 9, 775374. [CrossRef]
- AlRasheed, M.M.; Al-Aqeel, S.; Aboheimed, G.I., et al. Quality of Life, Fatigue, and Physical Symptoms Post-COVID-19 Condition: A Cross-Sectional Comparative Study. Healthcare 2023, 11, 1660.
- The World Health Organization Quality of Life assessment (WHOQOL): position paper from the World Health Organization. Soc Sci Med. 1995, 41, 1403–1409. [CrossRef]
- Rubenstein, L.V.; Calkins, D.R.; Greenfield, S., et al. Health status assessment for elderly patients. Report of the Society of General Internal Medicine Task Force on Health Assessment. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1989, 37, 562–569. [CrossRef]
- Beyer, S.; Haufe, S.; Meike, D., et al. Post-COVID-19 syndrome: Physical capacity, fatigue and quality of life. PLoS One. 2023, 18, e0292928. [CrossRef]
- Toh, M.R.; Teo, Y.R.; Poh, L.C.R., et al. Impact of COVID infection on lung function test and quality of life. Sci Rep. 2023, 13, 17275. [CrossRef]
- Magdy, D.M.; Metwally, A.; Tawab, D.A., et al. Long-term COVID-19 effects on pulmonary function, exercise capacity, and health status. Annals of Thoracic Medicine 2022, 17, 28–36. [CrossRef]
- Simonelli, C.; Paneroni, M.; Vitacca, M.; Ambrosino, N. Measures of physical performance in COVID-19 patients: a mapping review. Pulmonology 2021, 27, 518–528. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variables |
not hospitalized (n=23) |
hospitalized | p | |
| Ward (n=60) | ICU (n=40) | |||
| Sex | ns | |||
| Male | 12 (52.17%) | 34 (56.67%) | 27 (67.5%) | |
| Feminine | 11 (47.83%) | 26 (43.33%) | 13 (32.6%) | |
| Ethnicity | ns | |||
| White | 8 (34.78%) | 23 (38.33%) | 13 (32.5%) | |
| Brown | 11 (47.83%) | 28 (46.67%) | 23 (57.5%) | |
| Black | 4 (17.39%) | 9 (15.00%) | 4 (10%) | |
| Age (years) | 45.78 ± 15.25 | 50.32 ± 12.97 | 49.48 ± 13.18 | ns |
| Weight (kg) | 85.61± 24.02 | 85.49 ± 16.7 | 87.1 ± 20.59 | ns |
| BMI | 31.42 ± 8.34 | 30.84 ± 5.9 | 31.06 ± 6.52 | ns |
| SBP (mmHg) | 125.45 ± 16.54 | 121.87 ± 12.31 | 120.5 ± 13.39 | ns |
| DBP (mmHg) | 81.36 ± 15.21 | 81.00 ± 10.69 | 80.25 ± 12.09 | ns |
| Hospitalization time (days) | N/A | 9.48 ± 4.94 | 18.26 ± 9.42 | *** |
| ICU stay (days) | N/A | N/A | 11.97 ± 9.36 | |
| Oxygen therapy | 2 (8.70%) | 60 (100%) | 40 (100%) | ns |
| NIV | N/A | 30 (50%) | 40 (100%) | *** |
| VMI | N/A | N/A | 12 (20%) | |
| Variables |
not hospitalized (n=23) |
hospitalized | p | |
| Ward (n=60) | ICU (n=40) | |||
| Ageusia | 4 (17.39%) | 13 (21.67%) | 9 (22.5%) | ns |
| Anosmia | 5 (21.74%) | 12 (20%) | 8 (20%) | ns |
| Changes in sleep | 15 (65.22%) | 30 (50%) | 19 (47.5%) | ns |
| Visual changes | 4 (17.39%) | 10 (16.67%) | 6 (15%) | ns |
| Arthralgia | 5 (21.74%) | 15 (25%) | 12 (30%) | ns |
| Headache | 14 (60.87%) | 26 (43.33%) | 19 (47.5%) | ns |
| Concentration deficit | 4 (17.39%) | 9 (15%) | 4 (10%) | ns |
| Memory deficit | 13 (65.52%) | 25 (41.67%) | 10 (25%) | ns |
| Balance deficit | 9 (39.13%) | 23 (38.33%) | 19 (47.5%) | ns |
| Dyspnea | 17 (73.91%) | 39 (65%) | 29 (72.5%) | ns |
| Muscle weakness | 14 (60.87%) | 41 (68.33%) | 36 (90%)b, c | * |
| Myalgia | 12 (52.17%) | 25 (41.67%) | 19 (47.5%) | ns |
| Paresthesia | 10 (43.48%) | 16 (26.67%) | 13 (32.5%) | ns |
| Tachycardia | 12 (52.17%) | 29 (48.33%) | 18 (45%) | ns |
| Tremors | 9 (39.13%) | 23 (38.33%) | 14 (35%) | ns |
| Dizziness | 13 (65.52%) | 22 (36.67%) | 13 (32.5%) | ns |
| Cough | 6 (26.09%) | 30 (50%) | 23 (57.5%) | ns |
| Variables |
not hospitalized (n=23) |
hospitalized | p | |
| Ward (n=60) | ICU (n=40) | |||
| Anxiety | 7 (30.43%) | 13 (21.67%) | 14 (35%) | ns |
| Asthma | 1 (4.35%) | 3 (5%) | 0 (0%) | ns |
| Depression | 2 (8.7%) | 6 (10%) | 2 (5%) | ns |
| Dyslipidemia | 4 (17.39%) | 6 (10%) | 4 (10%) | ns |
| Diabetes Mellitus | 1 (4.35%) | 5 (8.33%) | 9 (22.5%)c | ** |
| COPD | 1 (4.35%) | 2 (3.33%) | 0 (0%) | ns |
| Hypothyroidism | 2 (8.0%) | 6 (10%) | 1 (2.5%) | *** |
| Hepatic steatosis | 2 (8.7%) | 2 (3.33%) | 3 (7.5%) | ns |
| SAH | 5 (21.74%) | 17 (28.33%)a | 18 (45%)c | ns |
| Obesity | 2 (8.7%) | 12 (20)a | 10 (25%)c | ** |
| Variables |
not hospitalized (n=23) |
hospitalized | p | |
| Ward (n=60) | ICU (n=40) | |||
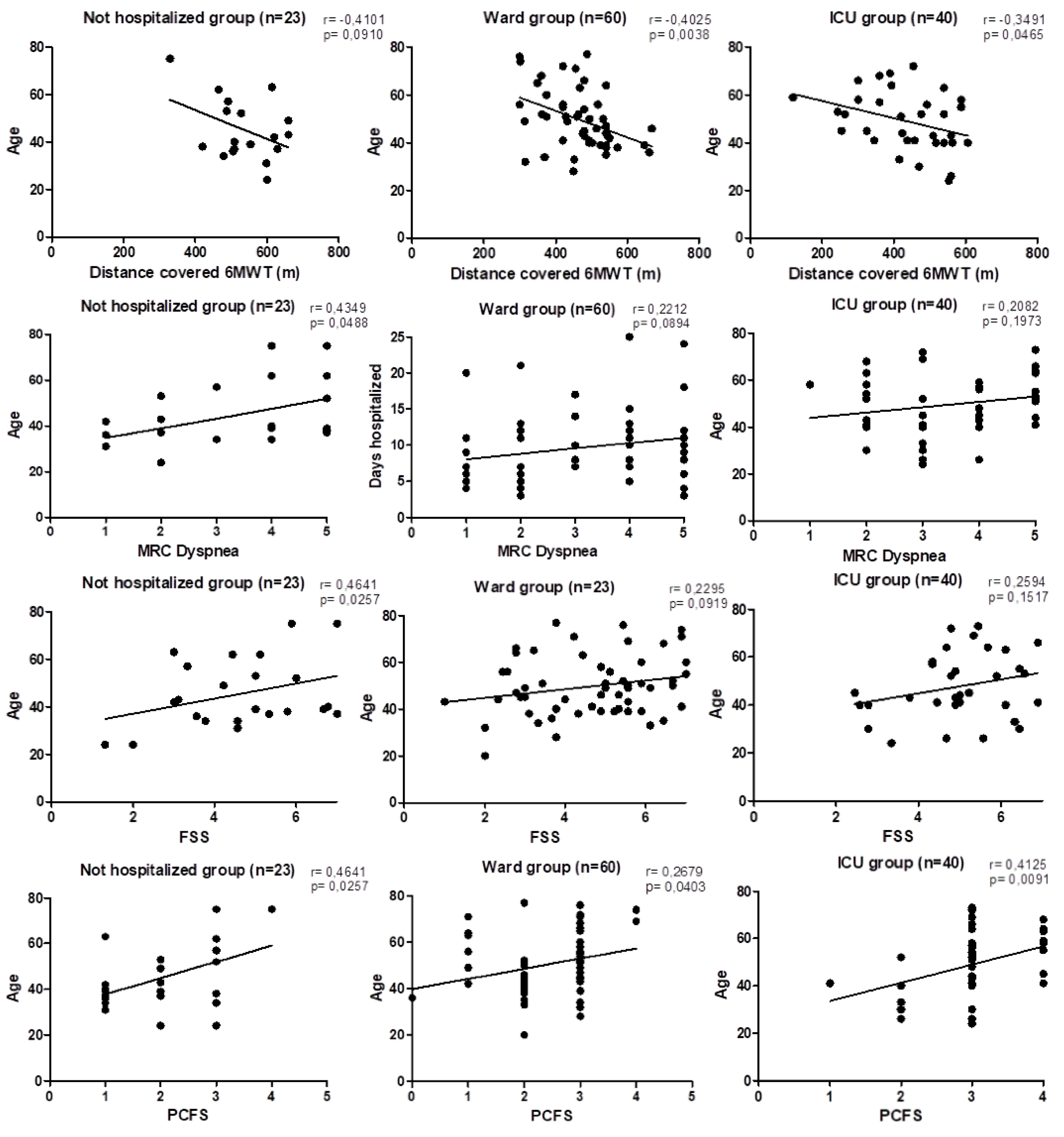
| 6MWD' (m) | 520.42 ± 93.89 | 450.03 ± 96.43a | 420.73 ± 122.78c | ** |
| 6MWD' pred (%) | 87.17 ± 16.00 | 79.79, ± 13.92a | 71.18 ± 18.74c | ** |
| MRC dyspnea | 3.38 ± 1.56 | 3.02 ± 1.46 | 3.44 ± 1.23 | ns |
| Grade 1 | 6 (26.09%) | 11 (18.33%) | 1 (2.5%) | |
| Grade 2 | 3 (13.04%) | 15 (25%) | 10 (25%) | |
| Grade 3 | 2 (8.70%) | 9 (15%) | 10 (25%) | |
| Grade 4 | 5 (21.74%) | 12 (20%) | 8 (20%) | |
| Grade 5 | 7 (30.43%) | 13 (21.67%) | 11 (27.5%) | |
| PCFS | 2.17 ± 1.03 | 2.42 ± 0.7a | 2.98 ± 0.7c | *** |
| Grade 1 | 8 (34.78%) | 6 (10%) | 2 (5%) | |
| Grade 2 | 5 (21.74%) | 22 (36.67%) | 6 (15%) | |
| grade 3 | 8 (34.78%) | 29 (48.33%) | 23 (57%) | |
| Grade 4 | 2 (8.70%) | 2 (3.33%) | 9 (22.5%) | |
| FSS | 4.77 ± 1.55 | 4.24 ± 1.78 | 4.87 ± 1.36 | ns |
| Variables | Not hospitalized (n=23) | hospitalized | p | |
| Ward (n=60) | ICU (n=40) | |||
| SF-36 (0-100) | ||||
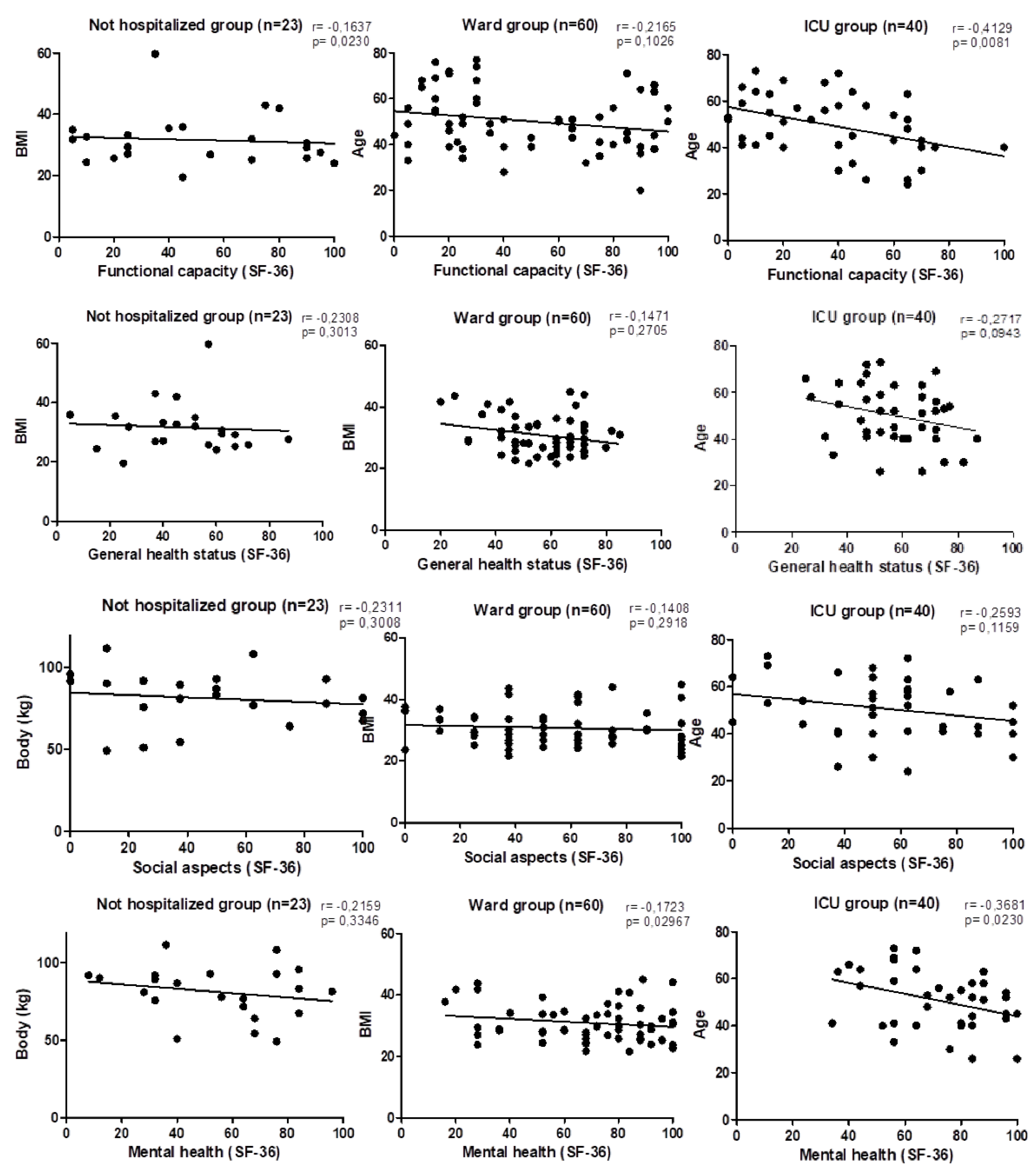
| Functional capacity | 50.23 ± 32.42 | 47.29 ± 31.93 | 37.63 ± 25.7 | ns |
| Limitation by physical aspects | 19.32 ± 35.3 | 27.59 ± 38.81 | 9.38 ± 26.97b, c | * |
| Pain | 53.23 ± 27.21 | 60.98 ± 30.74 | 54.50 ± 29.11 | ns |
| General health status | 46.95 ± 20.12 | 57.53 ± 14.49a | 56.53 ± 15.35c | * |
| Vitality | 45.23 ± 24.08 | 56.29 ± 26.08 | 55.75 ± 20.77 | ns |
| Social aspects | 47.73 ± 32.88 | 55.17 ± 30.17 | 54.44 ± 28.43 | ns |
| Emotional aspects | 43.94 ± 41.64 | 51.72 ± 43.79 | 44.16 ± 42.96 | ns |
| Mental health | 54.36 ± 27.09 | 69.47 ± 23.31a | 70.95 ± 19.48c | * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





